Abstract
In response to the current global challenge due to COVID-19, a dataset in this paper presented survey data of COVID-19 vaccine side effects among hospital staff in a national referral hospital in Indonesia. This survey data included the hospital staff of Dr. M. Djamil Hospital Padang, a national referral hospital in Indonesia, through a survey distributed via an online questionnaire, assessing COVID-19 vaccine side effects from 9th February to 13th February 2021. The items of the side effects included swelling, redness, itching, fever, headache, muscle pain, fatigue, coughing, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, breathlessness, joint pain, fainted, anaphylactic reaction, itch, and swollen lymph nodes. In this survey data, we collected a total of 840 responses. The survey data were analyzed using univariate and bivariate analysis. Data analysis was performed using IBM version 25.0.
Keywords: COVID-19, Hospital, Side effects, Staff, Vaccine, Indonesia
Specifications Table
| Subject | Public health |
| Specific subject area | Health education, health promotion |
| Type of data | Primary data Tables Figure |
| How data were acquired | Data was collected using an online survey platform (Google Forms). The questionnaire is provided as a supplementary file. |
| Data format | Raw Analyzed |
| Parameters for data collection | The hospital staff who have received COVID-19 vaccine were identified through medical records review at Dr. M. Djamil General Hospital Padang, a national referral hospital in Indonesia. A total of 840 hospital staff were included to have survey assessing COVID-19 vaccine side effects, i.e., swelling, redness, itching, fever, headache, muscle pain, fatigue, coughing, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, breathlessness, joint pain, fainted, anaphylactic reaction, itch, and swollen lymph nodes. |
| Description of data collection | The data was collected through an online questionnaire, which was sent to the hospital staff in a national referral hospital in Indonesia through convenience sampling technique. |
| Data source location | Region: Southeast Asia Country: Indonesia |
| Data accessibility | The dataset is provided as a supplementary file. |
Value of the Data
-
•
The data is essential since this is the first survey involving large number of hospital staff in a national referral hospital in Indonesia to assess COVID-19 vaccine side effects, including swelling, redness, itching, fever, headache, muscle pain, fatigue, coughing, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, breathlessness, joint pain, fainted, anaphylactic reaction, itch, and swollen lymph nodes.
-
•
All researchers in communicable disease, epidemiology, and health promotion could benefit from these data since our findings can improve community knowledge and awareness about the COVID-19 vaccine, thus expected to increase public willingness to participate. Therefore, the data is necessary for health promotion and education to control COVID-19 transmission through vaccination and end the pandemic.
-
•
The data is valuable to researchers who would like to compare our results with other studies on COVID-19 vaccine side effects from other countries, as well as to researchers who want to perform a systematic review and meta-analysis study in the future.
-
•
These data may assist the government or health policymaker by providing scientific evidence-based data for developing COVID-19 related guidelines, as well as health policy formulations and implementation on COVID-19 vaccination.
1. Data Description
The dataset provides an insightful information based on survey data of COVID-19 vaccine side effects among hospital staff in a national referral hospital Indonesia, i.e., Dr. M. Djamil General Hospital Padang. The hospital staff who received COVID-19 vaccination were identified through medical records review. The survey data were collected from 840 hospital staffs in this national referral hospital to determine COVID-19 vaccine side effects, i.e., swelling, redness, itching, fever, headache, muscle pain, fatigue, coughing, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, breathlessness, joint pain, fainted, anaphylactic reaction, itch, and swollen lymph nodes [1,2]. The questionnaire is provided as a supplementary file. The participant characteristics are presented in Table 1.
Table 1.
Respondent characteristics (n = 840).
| Characteristics | Category | f (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Sex | Male | 270 (32.1) |
| Female | 570 (67.9) | |
| Age (years) | < 20 | 3 (0.4) |
| 20–25 | 79 (9.4) | |
| 26–30 | 205 (24.4) | |
| 31–35 | 190 (22.6) | |
| 36–40 | 120 (14.3) | |
| 41–45 | 72 (8.6) | |
| 46–50 | 70 (8.3) | |
| 51–55 | 72 (8.6) | |
| 56–60 | 26 (3.1) | |
| > 60 | 3 (0.4) | |
| Professions | Midwife | 29 (3.5) |
| Nurse | 363 (43.2) | |
| Medical doctor | 115 (13.7) | |
| Medical specialist | 49 (5.8) | |
| Non-medical staff | 284 (33.8) | |
| Educational background | Middle school | 2 (0.2) |
| High school | 107 (12.7) | |
| Undergraduate degree | 632 (75.2) | |
| Graduate degree | 99 (11.8) | |
| Living area | Downtown | 594 (70.7) |
| Outskirt | 246 (29.3) | |
| Marriage | 177 (88.5) |
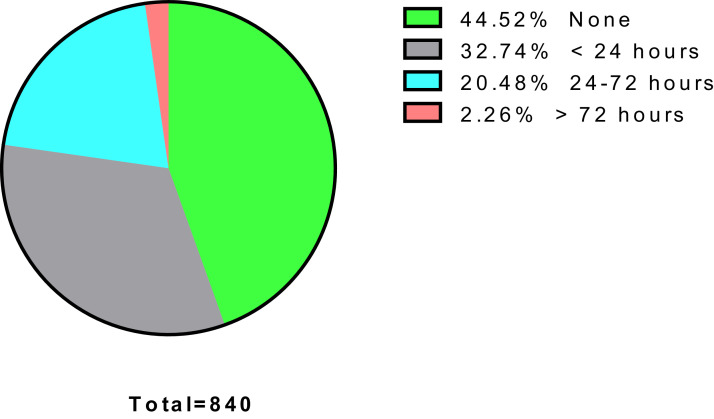
The side effects data of COVID-19 vaccine among the hospital staff is presented in Table 2. The side effects of COVID-19 vaccine based on stratification according to medical staff and non-medical staff are presented in Table 3. The symptom onset of COVID-19 side effects among the hospital staff is presented in Fig. 1. The side effects of COVID-19 vaccine based on symptom onset among the hospital staff are described in Table 4. The association of side effects of COVID-19 vaccine with age of the hospital staff is presented in Table 5.
Table 2.
The side effects of COVID-19 vaccine among hospital staff in a national referral hospital Indonesia.
| Side Effects | Category | f (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Swelling | Yes | 77 (9.2) |
| No | 763 (90.8) | |
| Redness | Yes | 17 (2.0) |
| No | 823 (98.0) | |
| Itching | Yes | 0 |
| No | 840 (100.0) | |
| Fever | Yes | 13 (1.5) |
| No | 827 (98.5) | |
| Headache | Yes | 186 (22.1) |
| No | 654 (77.9) | |
| Muscle pain | Yes | 333 (39.6) |
| No | 507 (60.4) | |
| Tiredness | Yes | 301 (35.8) |
| No | 539 (64.2) | |
| Coughing | Yes | 66 (7.9) |
| No | 774 (92.1) | |
| Diarrhea | Yes | 26 (3.1) |
| No | 814 (96.9) | |
| Nausea and vomiting | Yes | 1.5 |
| No | 98.5 | |
| Breathlessness | Yes | 11 (1.3) |
| No | 829 (98.7) | |
| Joint pain | Yes | 13 (1.5) |
| No | 827 (98.5) | |
| Fainted | Yes | 1 (0.1) |
| No | 839 (99.9) | |
| Anaphylactic reaction | Yes | 3 (0.4) |
| No | 837 (99.6) | |
| Tingling | Yes | 58 (6.9) |
| No | 782 (93.1) | |
| Swollen lymph nodes | Yes | 4 (0.5) |
| No | 836 (99.5) |
Table 3.
The side effects of COVID-19 vaccine based on stratification according to medical staff and non-medical staff in a national referral hospital Indonesia.
| Hospital Staff |
||
|---|---|---|
| Medical Staff (n = 556) | Non-Medical Staff (n = 284) | |
| Side Effects | (f/%) | (f/%) |
| Swelling | 48 (8.6) | 29 (10.2) |
| Redness | 13 (2.3) | 4 (1.4) |
| Itching | 0 | 0 |
| Fever | 10 (1.8) | 3 (1.1) |
| Headache | 133 (23.9) | 53 (18.7) |
| Muscle pain | 233 (41.9) | 100 (35.2) |
| Tiredness | 201 (36.2) | 100 (35.2) |
| Coughing | 47 (8.5) | 19 (6.7) |
| Diarrhea | 20 (3.6) | 6 (2.1) |
| Nausea and vomiting | 11 (2.0) | 2 (0.7) |
| Breathlessness | 6 (1.1) | 5 (1.8) |
| Joint pain | 7 (1.3) | 6 (2.1) |
| Fainted | 0 | 1 (0.4) |
| Anaphylactic reaction | 2 (0.4) | 1 (0.4) |
| Tingling | 37 (6.7) | 21 (7.4) |
| Swollen lymph nodes | 2 (0.4) | 2 (0.7) |
Fig. 1.
The symptoms time of COVID-19 side effects among hospital staff in a national referral hospital Indonesia.
Table 4.
The side effects of COVID-19 vaccine based on symptoms time among hospital staff in a national referral hospital Indonesia.
| Medical Staff (n = 335) |
Non-Medical Staff (n = 131) |
|||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Side Effects | < 24 h (n = 192) (f/%) | ≥ 24 h (n = 143) (f/%) | < 24 h (n = 83) (f/%) | ≥ 24 h (n = 48) (f/%) |
| Swelling | 25 (13.0) | 16 (11.2) | 15 (18.1) | 8 (16.7) |
| Redness | 8 (4.2) | 3 (2.1) | 1 (1.2) | 1 (2.1) |
| Itching | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Fever | 6 (3.1) | 4 (2.8) | 2 (2.4) | 1 (2.1) |
| Headache | 54 (28.1) | 74 (51.7) | 24 (28.9) | 18 (37.5) |
| Muscle pain | 114 (59.4) | 91 (63.6) | 39 (47.0) | 31 (64.6) |
| Tiredness | 81 (42.2) | 94 (65.7) | 48 (57.8) | 28 (58.3) |
| Coughing | 17 (8.9) | 28 (19.6) | 6 (7.2) | 8 (16.7) |
| Diarrhea | 5 (2.6) | 15 (10.5) | 2 (2.4) | 4 (8.3) |
| Nausea and vomiting | 7 (3.6) | 4 (2.8) | 0 | 1 (2.1) |
| Breathlessness | 4 (2.1) | 2 (1.4) | 1 (1.2) | 3 (6.3) |
| Joint pain | 3 (1.6) | 4 (2.8) | 3 (3.6) | 2 (4.2) |
| Fainted | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Anaphylactic reaction | 1 (0.5) | 0 | 0 | 0 |
| Tingling | 15 (7.8) | 21 (14.7) | 9 (10.8) | 8 (16.7) |
| Swollen lymph nodes | 1 (0.5) | 1 (0.7) | 2 (2.4) | 0 |
Table 5.
The association of side effects of COVID-19 vaccine with age among hospital staff in a national referral hospital Indonesia.
| Age (n = 840) |
||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| >50 years (n = 101) | ≤ 50 years (n = 739) | |||
| Side Effects | (f/%) | (f/%) | p-value | OR (95% CI) |
| Swelling | 5 (5.0) | 72 (9.7) | 0.167 | 0.48 (0.19–1.22) |
| Redness | 1 (1.0) | 16 (2.2) | 0.709 | 0.45 (0.05–3.44) |
| Itching | 0 | 0 | N/A | N/A |
| Fever | 2 (2.0) | 11 (1.5) | 0.663 | 1.33 (0.29–6.12) |
| Headache | 19 (18.8) | 167 (22.6) | 0.464 | 0.79 (0.46–1.34) |
| Muscle pain | 33 (32.7) | 300 (40.6) | 0.156 | 0.71 (0.45–1.10) |
| Tiredness | 31 (30.7) | 270 (36.5) | 0.299 | 0.76 (0.49–1.20) |
| Coughing | 7 (6.9) | 59 (8.0) | 0.864 | 0.85 (0.38–1.93) |
| Diarrhea | 5 (5.0) | 21 (2.8) | 0.227 | 1.78 (0.65–4.83) |
| Nausea and vomiting | 1 (1.0) | 12 (1.6) | 1.000 | 0.60 (0.07–4.70) |
| Breathlessness | 3 (3.0) | 8 (1.1) | 0.136 | 2.79 (0.73–10.72) |
| Joint pain | 1 (1.0) | 12 (1.6) | 1.000 | 0.60 (0.07–4.70) |
| Fainted | 0 | 1 (0.1) | 1.000 | N/A |
| Anaphylactic reaction | 0 | 3 (0.4) | 1.000 | N/A |
| Tingling | 5 (5.0) | 53 (7.2) | 0.537 | 0.67 (0.26–1.72) |
| Swollen lymph nodes | 1 (1.0) | 3 (0.4) | 0.402 | 2.45 (0.25–23.81) |
N/A, not account; OR, odd ratio; *, significant at p < 0.05.
2. Experimental Design, Materials and Methods
This survey was performed using a cross-sectional method to determine COVID-19 side effects among hospital staff in a national referral hospital in Indonesia. This dataset was collected as a form of the commencement of the COVID-19 Sinovac vaccine vaccination in Indonesia which began on January 13rd, 2021. The vaccination was conducted in stages, in which the initial stage of vaccination was targeted at groups of hospital staff. Collection of datasets in Dr. M Djamil General Hospital Padang was performed after the vaccine administration to the medical and non-medical staff at Dr. M Djamil General Hospital Padang, gradually from January 18, 2021 to January 31, 2021. The questionnaire assessing the side effects of the COVID-19 vaccine was established based on infection prevention and control principles and procedures for COVID-19 vaccination activities in Indonesia [1]. Furthermore, the survey validation was performed by testing the survey before use. The survey validation showed good internal consistency for all items in the questionnaire with a Cronbach alpha value of 0.815. This dataset demonstrated the side effects of COVID-19 vaccination among medical and non-medical staff in one of the national referral hospitals in Indonesia, in which the majority of staff were at the group of age ≤ 50 years and the rest were at the group of age > 50 years. According to the International Council on Adult Immunization (ICAI), the latter mentioned group are more likely to have underlying comorbidities, and thus there is a greater need to prioritize this group in the vaccine distribution [2].
The dataset included 840 hospital staff in a national referral hospital in Indonesia identified through medical records review at Dr. M. Djamil General Hospital Padang, Indonesia. Written online informed consent was provided. The collection response data was conducted between February 9th and 13th, 2021. We preferred to use WhatsApp Messenger for enrolling potential participants. A questionnaire was presented in Google Forms and the link generated was then shared via WhatsApp Messenger after the contact number of participants was collected by medical records review with legal permission. The sampling technique in this dataset is convenience sampling [3]. The inclusion criteria included hospital staff who received COVID-19 vaccination with no comorbidity [4,5]. The univariate analysis was performed using frequency and percentage, while the bivariate analysis was conducted using the chi-square test. P-value of < 0.05 shows a statistically significant difference between groups. Odds ratios with 95% confidence interval was presented. All data analysis was performed using IBM version 25.0.
Ethics Statement
This survey data passed the ethical review by the ethics commiittee of the Faculty of Medicine, Andalas University, Indonesia (No. 361/ KEP/ FK/ 2021). The survey data was conducted according to the Declaration of Helsinki.
CRediT Author Statement
Dovy Djanas: Conceptualization, Investigation, Data curation, Writing – original draft; Yusirwan: Conceptualization, Methodology; Rose Dinda Martini: Conceptualization, Investigation; Rahmadian: Conceptualization, Investigation; Hendria Putra: Data curation, Investigation; Adriani Zanir: Data curation, Investigation, Methodolology; Syahrial: Investigation, Writing – original draft; Ricvan Dana Nindrea: Conceptualization, Formal analysis, Methodology, Visualization, Writing – original draft, Writing – review & editing.
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships which have, or could be perceived to have, influenced the work reported in this article.
Acknowledgments
The author would like to thanks to participants who were willing to give a response to this survey data.
Footnotes
Supplementary material associated with this article can be found in the online version at doi:10.1016/j.dib.2021.107098.
Appendix. Supplementary materials
References
- 1.Ministry of Health Republic of Indonesia . Ministry of Health Republic of Indonesia; 2021. Decision of the Directorate General Of Disease Prevention and Control number HK.02.02/4/1/2021 Regarding Technical Instructions For the Implementation of Vaccinations in the Context of Preventing the COVID-19 Pandemic. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Privor-Dumm L.A., Poland G.A., Barratt J J., Durrheim D.N., Knoll M.D., Vasudevan P. A global agenda for older adult immunization in the COVID-19 era: a roadmap for action. Vaccine. 2020 doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2020.06.082. S0264-410X(20)30885-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.M.F. Haidere, Z.A. Ratan, S. Nowroz, S.B. Zaman, Y.J. Jung, H. Hosseinzadeh, J.Y. Cho, COVID-19 vaccine: critical questions with complicated answers, Biomol. Ther. (Seoul), 29(1), 1–10, doi: 10.4062/biomolther.2020.178. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Nindrea R.D., Sari N.P., Harahap W.A., Haryono S.J., Kusnanto H., Dwiprahasto I. Survey data of COVID-19 awareness, knowledge, preparedness and related behaviors among breast cancer patients in Indonesia. Data Brief. 2020;32 doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2020.106145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Nindrea R.D., Sari N.P., Harahap W.A., Haryono S.J., Kusnanto H., Dwiprahasto I. Survey data of multidrug-resistant tuberculosis, Tuberculosis patients characteristics and stress resilience during COVID-19 pandemic in West Sumatera province Indonesia. Data Brief. 2020;32 doi: 10.1016/j.dib.2020.106293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.