Abstract
Introduction:
There is a general interpretation that the distribution and pattern of various cancers exhibit geographical variations between developed and developing countries. However, as far as oral cancer is concerned, these differential patterns of distribution are not much documented.
Aim and Objective:
This review is aimed to bring in the existence of geographical disparities and its pattern for oral cancer incidence and mortality. The objectives of this review are: (1) To compare and comment on the trends in estimates for oral cancer incidence and mortality for the years 2002, 2008, and 2012. (2) To correlate oral cancer incidence and mortality values for 2012 with the human development index (HDI) scores for 2012 for each country. Design: Ecological approach and entire review was carried out using two secondary data sets, and they were (i) Age-standardized oral cancer incidence and mortality value for all countries published by the International Agency on Cancer Research for the years 2002, 2008, and 2012. (ii) HDI score for all countries for the year 2012 released by the United Nations Development Program.
Results:
A diametric pattern of distribution was observed across the two strata of countries. When developed countries have higher rates for incidence, low developed countries have higher rates for mortality.
Keywords: Cancer distribution, global, human development index rank, oral
Introduction
Cancer of any kind is a chronic debilitating condition that affects all spheres of physical, mental, and social well-being of an individual and is also a warning signal of death. The impact of cancer not only affects the individual, but also places a huge burden on the family. Moreover, there are interpretations that there exist geographical differences in the distribution for incidence and mortality from cancers between the developed and developing countries. However, as far as oral cancer is concerned, these differential patterns of distribution are not much documented. Therefore, this review analysis is aimed to bring in the existence of geographical disparities and its pattern for oral cancer incidence and mortality. Specifically, this review is trying to explore correlation between the oral cancer rates and human development status of different countries, thereby hypothesizing a missed relationship between socioeconomic rank and oral cancer burden. This manuscript is prepared as a chapter in the doctoral work of the author.
The objectives of this review are:
To compare and comment on the trend in estimates for oral cancer incidence and mortality for the years 2002, 2008, and 2012
To correlate oral cancer incidence and mortality values for 2012 with the human development index (HDI) scores for 2012 for each country.
Methodology
An ecological study was carried out using secondary data sets and they were
Results
GLOBOCAN is a global cancer database project under IARC, which publishes the estimates of incidence and mortality data on different cancers in the form of crude numbers and age-standardized rates (ASR). Trends in global oral cancer incidence and mortality over 2002, 2008, and 2012 were examined by cross tabulating total and gender-stratified standardized rates [Table 1].
Table 1.
Distribution of individuals according to age and gender
| Parameter | Obese patients (n=25) | Healthy patients (n=25) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (mean±SD) | 54.92±6.82 | 43.24±8.96 | <0.001** |
| BMI (mean±SD) | 31.68±4.16 | 22.42±2.11 | <0.001** |
| Male, n (%) | 18 (72) | 19 (76) | 0.257 (NS) |
| Female, n (%) | 7 (28) | 6 (24) |
P<0.05 is considered statistically significant. **Highly significant (P<0.01), NS: Not significant (P>0.05). BMI: Body mass index; SD: Standard deviation
As per the GLOBOCAN data [Table 1], one positive finding is that there is a declining trend observed for ASR for both incidence and mortality over 3 successive years of 2002, 2008, and 2012.
The GLOBOCAN database also publishes ASR rates separately for more developed and less developed countries. Therefore, tabulation was done to compare the difference for incidence and mortality rates between more developed and less developed countries [Table 2]. Data related to the three periods of 2002, 2008, and 2012 show that ASR incidence rates are higher for more developed countries with respect to less developed countries. On the other hand, ASR mortality rates are showing a diametric pattern with respect to ASR incidence rates, with less developed countries having more mortality in comparison with more developed countries. The point here is that one needs to explore the probable reasons for this diverse pattern between the developed and less developed countries. One assumed reason for the high incidence rates across developed countries could be because of their highly organized health system which facilities and promotes early case detection and thereby improving the rate of prognosis which is exhibited as low rates for mortality in these countries. For less developed countries, the situation may be different with most cases getting reported at late stages, which may affect the prognosis, resulting in high mortality rates.
Table 2.
Comparison of mean values of various clinical parameters in both the groups
| Parameter | Mean±SD |
P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obese patients (n=25) | Healthy patients (n=25) | ||
| PI | 2.24±0.59 | 1.89±0.4 | 0.020* |
| GI | 2.66±0.4 | 2.55±0.17 | 0.018* |
| Probing depth | 6.83±0.99 | 6.44±0.52 | 0.089 (NS) |
| Clinical attachment loss | 3.92±1.09 | 3.95±0.75 | 0.905 (NS) |
*Statistically significant (P<0.05), NS: Not significant (P>0.05). PI: Plaque index; GI: Gingival index; SD: Standard deviation
To corroborate the argument that oral cancer incidence and mortality rates change according to the development status of a country, further analysis was done by comparing GLOBOCAN ASR incidence and mortality rates with HDI for countries. The HDI is a composite index that categorizes 177 countries into four classes, namely very high developed, high developed, medium developed, and low developed countries. This classification is based on the score of a composite index derived through combining three indicators for a country, namely longevity, knowledge, and income. Longevity is assessed through average life expectancy at birth, knowledge through adult literacy rates and mean years of schooling, and income through real gross domestic product per capita in purchasing power parity in US dollars. The concept of HDI reflects achievements in the most basic human capabilities, such as leading a long life, being knowledgeable, and enjoying a descent standard of living. For the purpose of analysis, a separate country-wise list was prepared by ranking the rates for oral cancer that lies above the world standardized rate for 2008 and 2012. Out of the total 177 countries, around sixty countries had rates above the average world standardized rate [Table 3].
Table 3.
Comparison of biochemical parameters in both groups
| Parameter | Mean±SD |
P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Obese patients (n=25) | Healthy patients (n=25) | ||
| Serum leptin | 26.33±4.47 | 1.92±0.55 | <0.001** |
| Serum adiponectin | 11.82±5.13 | 16.96±4.69 | <0.001** |
| Leptin/adiponectin | 2.66±1.23 | 0.131±0.065 | <0.001** |
**Highly significant (P<0.01). SD: Standard deviation
Further, these countries were categorized according to their human development rank as to fit in one among the following groups, namely very high developed, high developed, medium developed, and low-income countries [Table 4].
Table 4.
Correlation of serum leptin values with clinical parameters in obese chronic periodontitis group
| Parameter | Correlation value (r) | P |
|---|---|---|
| PI | 0.001 | 0.009* |
| GI | 0.275 | 0.008* |
| Probing depth | 0.324 | 0.009* |
| Clinical attachment loss | 0.28 | 0.005* |
*Significant (P<0.01). PI: Plaque index; GI: Gingival index
Some major findings from the above data arrangement are mentioned below separately for males and females.
Males: In 2008, there were 61 countries around the world having oral cancer standardized estimates above the world average of 5.3. Among these 61 countries, 42 were from very high and high developed countries and the remaining 19 were medium and low developed countries. That means, 68% of countries are from high and very high strata for incidence estimates. For mortality estimates, the total number of countries scaled down to 46, which is a positive sign representing the survival chance of the patients within those countries. However, the unfortunate scenario is that these reduced numbers from incidence to mortality are completely conglomerated over the very high and high developed countries, pointing toward the poor survival chance within medium- and low-income countries [Table 4].
Females: Similarly, the comparison for the number of countries above the world ASR for female incidence and mortality shows a decline in the total number from 46 countries above ASR for incidence to 24 countries above world ASR for mortality. However, similar to males, the decline in the number of countries is exclusively clustered within very high and high developed countries. The comparison brought appalling clues for female rates in incidence and mortality. Sixty to eighty percent of the countries were from middle-income group in both incidence rate and mortality rates [Table 4].
A similar trend of poor survival in medium- and low-income countries for both the gender is continued in the 2012 data also.
Thus, a categorized view from the number of countries within each developmental status is depicting a different pattern between incidence and mortality. Out of the total number of countries that are above the global ASR, very high developed and developed countries are more within the incidence category and medium developed and low-income countries are more within the mortality category.
To deduce the existence of any linear relationship between human development rank of the countries and their oral cancer rates, data for the year 2012, being the most recent, were used. Five columns were prepared, with each column representing five variables, namely
Name of the country
HDI score of that country
Age-standardized oral cancer incidence rates for males
Age-standardized oral cancer mortality rates for males
Age-standardized oral cancer incidence rates for females
Age-standardized oral cancer mortality rates for females.
Once the data for 177 countries were entered, bivariate analysis was done using HDI rank as an independent variable and with gender-specific rates in incidence and mortality for each country. The summary of the results is shown in Table 5.
Table 5.
Correlation of serum adiponectin values with clinical parameters
| Parameter | Correlation value (r) | P |
|---|---|---|
| PI | 0.218 | 0.001* |
| GI | 0.230 | 0.001* |
| Probing depth | 0.309 | 0.132 (NS) |
| Clinical attachment loss | 0.330 | 0.107 (NS) |
*Highly significant (P<0.01), NS: Not significant (P>0.05). PI: Plaque index; GI: Gingival index
Except for rates in incidence for females, all the three other variables are related with the HDI rank. When rates for the age-standardized incidence of males show a positive linear association, mortality rates for both sexes are negatively related with HDI rankings. This negative correlation of human development rank with mortality rates from oral cancer is suggesting the existence of a relation between the developmental indicators and probability of survival from oral cancer. Further linear regression analyses were done to predict the values of dependent variable for the given values of independent variable. HDI score was considered as the independent variable, and separate estimate was done with incidence and mortality rate as dependent variable [Table 6 and Graph 1-3].
Table 6.
Correlation of serum leptin/adiponectin values with clinical parameters
| Parameter | Correlation value (r) | P |
|---|---|---|
| PI | 0.150 | 0.474 (NS) |
| GI | 0.228 | 0.272 (NS) |
| Probing depth | 0.380 | 0.061 (NS) |
| Clinical attachment loss | 0.372 | 0.067 (NS) |
*Statistically significant (P<0.05), NS: Not significant (P>0.05). PI: Plaque index; GI: Gingival index
Graph 1.
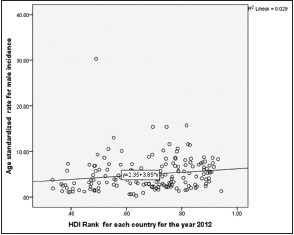
Linear regression model for predicting age.standardized incidence rates for males by country-specified human development index ranks
Graph 3.
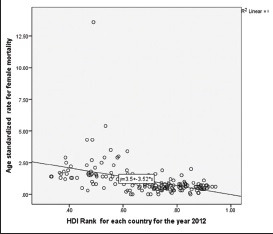
Linear regression model for predicting age-standardized mortality rates for females by country-specified human development index ranks
Graph 2.
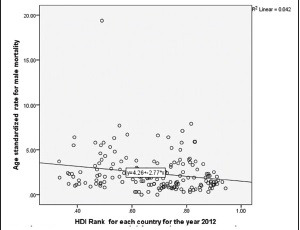
Linear regression model for predicting age-standardized mortality rates for males by country-specified human development index ranks
Table 6 gives important information that beyond a mere correlation, developmental indicators in the form of educational level, income, and life expectancy are predictors for incidence and mortality for oral malignancies, with more specificity exhibited across mortality rates. Thus, irrespective of gender, mortality rates for oral malignancies are significantly depended on the developmental indicators of the country.
On the basis of country-specific HDI rank, UNDP has categorized each country into very high, high, medium, and low developed groups. Utilizing these, an analysis of variance (ANOVA) was performed to see whether these groups of development order show a difference in means with respect to incidence and mortality for oral cancer. The results of the ANOVA test are presented in Table 7, which also show a significant difference between the categories of countries for average mortality rates, especially marked differences within female mortality.
Table 7.
Results of analysis of variance test comparing development status and age-standardized rates
| Age Standardized Rates | Development Status | n | Mean | Std. Deviation | Std. Error | 95% Confidence Interval for Mean |
df | Mean Square | F | Sig. | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lower Bound | Upper Bound | ||||||||||
| Age standardized rate for male incidence | Very High Human Development | 45 | 5.7267 | 2.96268 | 0.44165 | 4.8366 | 6.6168 | 3 | 14.965 | 1.134 | 0.337 |
| High Human Development | 42 | 5.0381 | 3.2326 | 0.4988 | 4.0307 | 6.0454 | |||||
| Medium human Development | 39 | 4.5538 | 3.25761 | 0.52164 | 3.4979 | 5.6098 | |||||
| Low Human Development | 42 | 4.431 | 4.80414 | 0.74129 | 2.9339 | 5.928 | |||||
| Total | 168 | 4.9583 | 3.63703 | 0.2806 | 4.4043 | 5.5123 | |||||
| Age standardized rate for female incidence | Very High Human Development | 45 | 2.6333 | 1.31079 | 0.1954 | 2.2395 | 3.0271 | 3 | 7.713 | 1.961 | 0.122 |
| High Human Development | 42 | 1.8571 | 0.97309 | 0.15015 | 1.5539 | 2.1604 | |||||
| Medium human Development | 39 | 2.3821 | 1.5595 | 0.24972 | 1.8765 | 2.8876 | |||||
| Low Human Development | 42 | 2.85 | 3.26946 | 0.50449 | 1.8312 | 3.8688 | |||||
| Total | 168 | 2.4351 | 2.00036 | 0.15433 | 2.1304 | 2.7398 | |||||
| Age standardized rate for male mortality | Very High Human Development | 45 | 1.9756 | 1.60923 | 0.23989 | 1.4921 | 2.459 | 3 | 13.898 | 3.073 | 0.029 |
| High Human Development | 42 | 2.0857 | 1.73761 | 0.26812 | 1.5442 | 2.6272 | |||||
| Medium human Development | 39 | 2.2538 | 1.76439 | 0.28253 | 1.6819 | 2.8258 | |||||
| Low Human Development | 42 | 3.2262 | 3.06658 | 0.47318 | 2.2706 | 4.1818 | |||||
| Total | 168 | 2.3804 | 2.16572 | 0.16709 | 2.0505 | 2.7102 | |||||
| Age standardized rate for female mortality | Very High Human Development | 45 | 0.6222 | 0.34502 | 0.05143 | 0.5186 | 0.7259 | 3 | 21.003 | 15.869 | 0 |
| High Human Development | 42 | 0.5881 | 0.37168 | 0.05735 | 0.4723 | 0.7039 | |||||
| Medium human Development | 39 | 1.159 | 0.88011 | 0.14093 | 0.8737 | 1.4443 | |||||
| Low Human Development | 42 | 2.0952 | 2.07611 | 0.32035 | 1.4483 | 2.7422 | |||||
Inferences from the above analysis
The major inferences from the entire review are that:
A declining trend is observed for ASR for both incidence and mortality across a 10-year period of 2002, 2008, and 2012
Incidence and mortality rates are showing a specific pattern of distribution across different strata of countries. In developed countries, incidence rates are on a higher side in comparison with the mortality rates. However, in the case of less developed countries, mortality rates are on a higher side in comparison with incidence rates
Human development rank of countries and oral cancer rates, especially mortality rates, are negatively correlated
There is a significant difference in mean mortality rates, for males and females, across four categories of countries, with mortality rates higher within medium and low developed countries.
Discussion and Conclusion
Through this ecological approach, the article is trying to highlight few aspects with respect to the epidemiology of oral malignancies. Incidence and mortality from oral cancer is on a declining trend, and the probable reasons could be the initiation of early case detection and prompt management. The question here is, whether this decline is cluttered around a group of countries, especially the developed countries? If it is, then one needs to be cautious in generalizing the declining trend. A diametric pattern of distribution was observed across the two strata of countries. When developed countries have higher rates for incidence, low developed countries have higher rates for mortality. The data published by IARC are based on cancer registries of different countries; it is obvious that developed countries will have an edge over the underdeveloped countries in data collection methods and facilities. Moreover, health facilities and resources can facilitate an early detection for incident cases and prompt management of incident cases in these countries. These opportunities can not only result in a higher case number in incidence, but also result in low number for mortality. A reverse situation can be expected from the low developed countries where most cases may be detected in the late stages, thus reducing the probability of survival which can contribute to higher rates in mortality in comparison with developed countries.
Financial support and sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
Acknowledgment
Hereby, the authors acknowledge UNDP and IACR for sharing data and Dr. Jayan Jacob Mathew, department of periodontics, for reviewing the manuscript.
References
- 1.Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Dikshit R, Eser S, Mathers C, Rebelo M, et al. Cancer incidence and mortality worldwide: sources, methods and major patterns in GLOBOCAN 2012. Int J Cancer. 2015;136:E359–86. doi: 10.1002/ijc.29210. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.United Nations Development Programme. Human Development Report. New York, USA: United Nations Development Programme; 2012. [Google Scholar]


