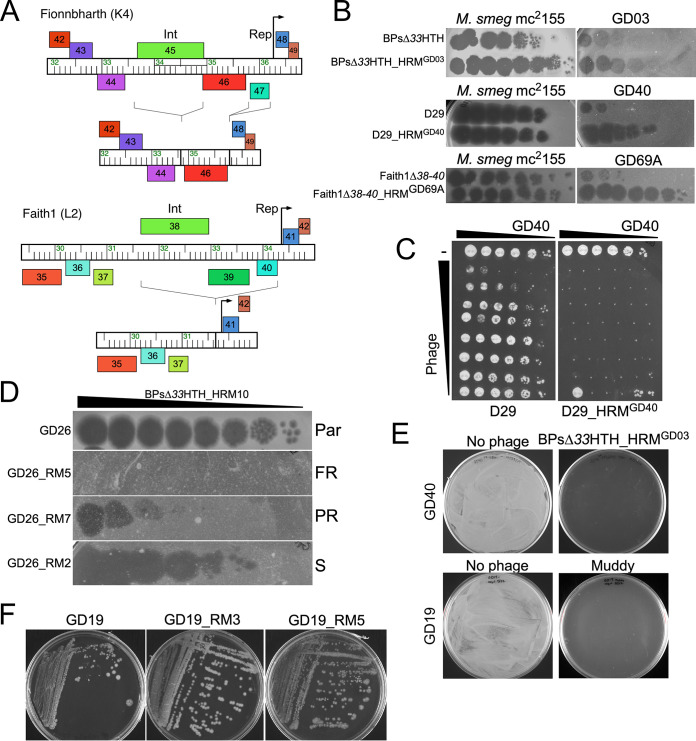
FIG 4.
M. abscessus phage mutants and resistance. (A) Engineering lytic derivatives of phage Fionnbharth and Faith1. Central genomic regions are shown for each phage with rightward- and leftward-transcribed genes shown above and below the genome ruler, respectively. The subcluster K4 phage Fionnbharth genome was edited to remove the integrase (int) and repressor (rep) genes as indicated. The subcluster L2 phage Faith1 was edited to remove genes 38 to 40 including int and rep. (B) Ten-fold serial dilutions of host range mutants (HRM) of BPsΔ33HTH, D29, and Faith1Δ38-40 were plated from left to right on M. smegmatis and the M. abscessus strain on which the HRM was isolated. (C) Killing assay of M. abscessus strain GD40 with phages D29 (left) and D29_HRMGD40 (right). Each column has 10-fold serial dilutions of M. abscessus GD40 (leftmost column, 3 × 105 CFU), and each row has 10-fold serial dilutions of either phage D29 or D29_HRMGD40 (topmost row, 107 PFU). Cells and phage were mixed and incubated for 48 h prior to plating on solid medium. (D) Phage susceptibility assay illustrating that strains recovered from BPsΔ33HTH_HRM10 challenge of GD26: Par, parental; FR, fully resistant GD26_RM5; PR, partially resistant GD26_RM7; and S, fully sensitive GD26_RM2. Spots are 10-fold serial dilutions of BPsΔ33HTH_HRM10 from left to right. (E) Efficient killing of M. abscessus strains GD40 and GD19 (as indicated) with phages BPsΔ33HTH_HRMGD03 or Muddy. Aliquots of 107 CFU were incubated with or without phage (multiplicity of infection [MOI] 10) for 48 h and plated on solid medium. (F) Colony morphotypes of GD19 and Muddy-resistant mutants GD19_RM3 and GD19_RM5. GD19 and GD19_RM3 are rough, and GD19_RM5 is smooth.