Abstract
Background
The application of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) has been shown to have some benefits in the treatment of preterm infants with respiratory distress. CPAP has the potential to reduce lung damage, particularly if applied early before atelectasis has occurred. Early application may better conserve an infant's own surfactant stores and consequently may be more effective than later application.
Objectives
• To determine if early compared with delayed initiation of CPAP results in lower mortality and reduced need for intermittent positive‐pressure ventilation in preterm infants in respiratory distress
○ Subgroup analyses were planned a priori on the basis of weight (with subdivisions at 1000 grams and 1500 grams), gestation (with subdivisions at 28 and 32 weeks), and according to whether surfactant was used
▫ Sensitivity analyses based on trial quality were also planned
○ For this update, we have excluded trials using continuous negative pressure
Search methods
We used the standard search strategy of Cochrane Neonatal to search the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL; 2020, Issue 6), in the Cochrane Library; Ovid MEDLINE(R) and Epub Ahead of Print, In‐Process & Other Non‐Indexed Citations Daily and Versions(R); and the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literatue (CINAHL), on 30 June 2020. We also searched clinical trials databases and the reference lists of retrieved articles for randomised controlled trials (RCTs) and quasi‐RCTs.
Selection criteria
We included trials that used random or quasi‐random allocation to either early or delayed CPAP for spontaneously breathing preterm infants in respiratory distress.
Data collection and analysis
We used the standard methods of Cochrane and Cochrane Neonatal, including independent assessment of trial quality and extraction of data by two review authors. We used the GRADE approach to assess the certainty of evidence.
Main results
We found four studies that recruited a total of 119 infants. Two were quasi‐randomised, and the other two did not provide details on the method of randomisation or allocation used. None of these studies used blinding of the intervention or the outcome assessor. Evidence showed uncertainty about whether early CPAP has an effect on subsequent use of intermittent positive‐pressure ventilation (IPPV) (typical risk ratio (RR) 0.77, 95% confidence interval (CI) 0.43 to 1.38; typical risk difference (RD) ‐0.08, 95% CI ‐0.23 to 0.08; I² = 0%, 4 studies, 119 infants; very low‐certainty evidence) or mortality (typical RR 0.93, 95% CI 0.43 to 2.03; typical RD ‐0.02, 95% CI ‐0.15 to 0.12; I² = 33%, 4 studies, 119 infants; very low‐certainty evidence). The outcome 'failed treatment' was not reported in any of these studies. There was an uncertain effect on air leak (pneumothorax) (typical RR 1.09, 95% CI 0.39 to 3.04, I² = 0%, 3 studies, 98 infants; very low‐certainty evidence). No trials reported intraventricular haemorrhage or necrotising enterocolitis. No cases of retinopathy of prematurity were reported in one study (21 infants). One case of bronchopulmonary dysplasia was reported in each group in one study involving 29 infants. Long‐term outcomes were not reported.
Authors' conclusions
All four small trials included in this review were performed in the 1970s or the early 1980s, and we are very uncertain whether early application of CPAP confers clinical benefit in the treatment of respiratory distress, or whether it is associated with any adverse effects.
Further trials should be directed towards establishing the appropriate level of CPAP and the timing and method of administration of surfactant when used along with CPAP.
Plain language summary
Early versus delayed initiation of continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) for respiratory distress in preterm infants
Review question
We wanted to find out whether for preterm infants in respiratory distress, applying continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) early would result in increased benefit and less harm than if it were applied later.
Background
Preterm babies often lack surfactant, a detergent‐like substance produced by the lung. Lack of surfactant causes their lungs to fail to expand properly at birth and results in the need for greater effort in breathing. If left untreated, the breathing difficulty progressively worsens and may lead to lung damage. CPAP improves expansion of the lung, making it easier for the baby to breathe, and might reduce the need for intermittent positive‐pressure ventilation (IPPV), a form of respiratory support that carries greater risks, including the risk of developing a type of lung damage called bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BDP). CPAP might also reduce the risk of the baby dying from respiratory distress. CPAP is applied through a face mask, a nasal mask, or prongs into the nostrils.
Study characteristics
The search is up‐to‐date as of June 2020. We found four small studies including a total of 119 babies. All four studies were performed in the 1970s or early 1980s, when the use of antenatal steroids (given to the mother to help a preterm baby's lung to become more mature) was uncommon.
Key results
From these four small studies, we are very uncertain whether early CPAP provides any benefit or whether it causes any harm.
Certainty of evidence
All four included studies had weaknesses in the way they were conducted, and all were very small. In addition, because they were old studies, study results might not apply to the current care of preterm infants. Therefore, we assessed the certainty of evidence as very low.
Summary of findings
Summary of findings 1. Early compared to late continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) for respiratory distress in preterm infants.
| Early compared to late CPAP for respiratory distress in preterm infants | ||||||
| Patient or population: preterm infants with respiratory distress Setting: neonatal units in UK and USA during the 1970s and 1980s Intervention: early CPAP (FiO₂ approximately ≤ 0.6) Comparison: late CPAP (FiO₂ approximately ≥ 0.6) | ||||||
| Outcomes | Anticipated absolute effects* (95% CI) | Relative effect (95% CI) | № of participants (studies) | Certainty of the evidence (GRADE) | Comments | |
| Risk with late CPAP | Risk with early CPAP | |||||
| Use of IPPV before discharge | Study population | RR 0.77 (0.43 to 1.38) | 119 (4 RCTs) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ VERY LOWa,b | ||
| 299 per 1000 | 230 per 1000 (128 to 412) | |||||
| Mortality (time not specified) | Study population | |||||
| 164 per 1000 | 153 per 1000 (71 to 333) |
RR 0.93 (0.43 to 2.03) | 119 (4 RCTs) |
⊕⊕⊝⊝ LOWb,c | Not downgraded for lack of blinding Objective outcome | |
| Failure of treatment ‐ death or intermittent positive‐pressure ventilation (IPPV) before hospital discharge | Outcome not reported | |||||
| Air leak (pneumothorax) | Study population | RR 1.09 (0.39 to 3.04) | 98 (3 RCTs) | ⊕⊕⊝⊝ LOWb,c | Not downgraded for lack of blinding Objective outcome | |
| 125 per 1000 | 136 per 1000 (49 to 380) | |||||
| Bronchopulmonary dysplasia at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age | Study population | RR 1.42 (0.10 to 20.49) | 29 (1 RCT) | ⊕⊝⊝⊝ VERY LOWb,d | Not downgraded for lack of blinding Objective outcome | |
| 59 per 1000 | 84 per 1000 (6 to 1000) | |||||
| *The risk in the intervention group (and its 95% confidence interval) is based on the assumed risk in the comparison group and the relative effect of the intervention (and its 95% CI). CI: confidence interval; IPPV: intermittent positive‐pressure ventilation; RCT: randomised controlled trial; RR: risk ratio. | ||||||
| GRADE Working Group grades of evidence. High certainty: we are very confident that the true effect lies close to that of the estimate of the effect. Moderate certainty: we are moderately confident in the effect estimate: the true effect is likely to be close to the estimate of the effect, but there is a possibility that it is substantially different. Low certainty: our confidence in the effect estimate is limited: the true effect may be substantially different from the estimate of the effect. Very low certainty: we have very little confidence in the effect estimate: the true effect is likely to be substantially different from the estimate of effect. | ||||||
aDowngraded two levels for risk of bias: selection bias and performance bias.
bDowngraded one level for imprecision. Concerns about indirectness also taken into account (old studies performed before modern day neonatal intensive care).
cDowngraded one level for concerns about selection bias.
dDowngraded two levels for imprecision due to very wide confidence interval and data derived from only one small study.
Background
Description of the condition
Primary surfactant deficiency is responsible for respiratory distress syndrome (RDS) in preterm infants (Avery 1959). This deficiency in surfactant results in low lung volumes, poor lung distensibility, and atelectasis. The resulting hypoxia leads to increased pulmonary vascular resistance and right‐to‐left shunting (Evans 1991; Gribetz 1959). This exacerbates existing ventilation‐perfusion abnormalities. If left untreated, the disease progresses, resulting in alveolar‐capillary leakage, pulmonary oedema, and alveolar cell injury (Barter 1960). These events lead to the formation of hyaline membranes seen on histological examination of diseased lungs. Although in a majority of infants respiratory distress will be due to surfactant deficiency, often described as RDS, there are other causes of respiratory distress, and these might exacerbate the deficiency or might act either alone or along with it as a cause of respiratory distress. Usually it is not possible to determine clinically which factors are causing respiratory distress in a particular preterm infant.
Intermittent positive‐pressure ventilation (IPPV) without positive end‐expiratory pressure was the first mode of assisted ventilation used for treatment of respiratory distress in preterm infants. When it became evident that low lung volume was a consequence of the disease, continuous distending pressure (CDP) was developed as a means of increasing lung volume and improving oxygenation (Gregory 1971). Positive end‐expiratory pressure was also found to improve oxygenation in ventilated infants (Cotton 1998; Herman 1973).
Description of the intervention
CDP refers to the continuous application of pressure either as positive airway pressure (CPAP) or as negative pressure (CNP) to distend the lungs. CNP is no longer in clinical use. This review focuses on CPAP ‐ the application of positive pressure to the airways. This pressure may be applied through binasal prongs, a single nasal‐pharyngeal tube, a face mask, or a nasal mask. It has also been applied directly to the lungs via an endotracheal tube. Application of CPAP has been shown to provide some benefit for the treatment of preterm infants with respiratory distress (Ho 2015). It is beneficial when applied prophylactically or very early after birth, at a time when it is not clear whether the infant will develop established respiratory distress. However, for treatment of respiratory distress, it is not clear whether the effectiveness of CPAP might be modified by early application. The use of nasal CPAP has been established in post‐extubation care (Davis 2003).
How the intervention might work
CPAP improves lung function by reducing the work of breathing, normalizing lung volumes, and improving ventilation‐perfusion mismatch (Cogswell 1975; Cotton 1980; Field 1985; Harris 1996; Richardson 1978; Saunders 1976). CPAP also conserves surfactant (Verder 1994; Wyszogrodski 1975), and it splints the airways during expiration, thus reducing atelectasis in the surfactant‐deficient lung (Miller 1990). Therefore CPAP has the potential to reduce lung damage seen in respiratory distress, and this reduction might be greater if it is applied early, before alveolar collapse and formation of the hyaline membrane occur. Surfactant, a proven treatment for RDS, is more effective if applied early (Bahadue 2012; Rojas‐Reyes 2012), suggesting that CPAP may also be more effective if applied early. CPAP might work differently in infants of lower birth weight (< 1000 grams) or at earlier gestation (< 28 weeks) because the terminal airways are not fully developed in these infants, and they may have pulmonary insufficiency as well as surfactant deficiency (Langston 1984). In addition, respiratory muscle function and respiratory drive might be reduced (Henderson‐Smart 2004).
Why it is important to do this review
The purpose of this review is to establish whether early application of CPAP provides any benefit over later application for preterm infants in respiratory distress. An earlier review on this topic has been done (Bancalari 1992). Another earlier version of this Cochrane Review looked at all forms of CDP (i.e. CPAP and CNP) (Ho 2002). However, more recently, CPAP has become established as the principal means of applying CDP because of its ease of application and provision of nursing care to infants during treatment. For this 2020 update, we have made a post hoc decision to exclude CNP trials and to examine these in a separate review. Another Cochrane Review examines prophylactic or very early CPAP started soon after birth (Subramaniam 2016).
Objectives
-
To determine if early compared with delayed initiation of CPAP results in lower mortality and reduced need for intermittent positive‐pressure ventilation in preterm infants in respiratory distress
-
Subgroup analyses were planned a priori on the basis of weight (with subdivisions at 1000 grams and 1500 grams), gestation (with subdivisions at 28 and 32 weeks), and according to whether surfactant was used
Sensitivity analyses based on trial quality were also planned
For this update, we have excluded trials using continuous negative pressure
-
Methods
Criteria for considering studies for this review
Types of studies
We included randomised and quasi‐randomised controlled trials.
Types of participants
We included preterm infants (i.e. those at < 37 weeks' gestation) in respiratory distress breathing spontaneously at trial entry before application of any assisted ventilation other than for resuscitation at birth.
Types of interventions
We included comparisons of early CPAP (commencing at randomisation) delivered by nasal prongs, mask, single nasopharyngeal tube, or endotracheal tube versus a policy of delayed CPAP (initiated at fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO₂) of approximately 0.6 or more).
We excluded trials in which infants had CPAP initiated prophylactically at birth or very early, before it would be possible to judge whether they had established respiratory distress.
In the first version of the review (Ho 2002), we made a minor post hoc change to the protocol. For the delayed CPAP definition of FiO₂ 0.6 or more, we added the word 'approximately' 0.6 or more because we encountered studies that otherwise qualified for inclusion, in which the early CPAP group used a definition of FiO₂ of 0.6, as well as studies in which the delayed CPAP group was defined as an FiO₂ below 0.5.
Types of outcome measures
Primary outcomes
Use of intermittent positive‐pressure ventilation (IPPV) before discharge
Mortality (first 28 days of life and before discharge)
Failure of treatment ‐ death or IPPV before hospital discharge
For this update, we have changed the order of the outcomes because we judged that for studies comparing two different criteria for initiation of CPAP, the best indicator of failure of CPAP would be use of IPPV, followed by mortality.
Secondary outcomes
Air leak (pneumothorax, pneumomediastinum, or pulmonary interstitial emphysema)
Intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH) (any or grade 3 or 4)
Necrotising enterocolitis (NEC) (Bell criteria stage 2 (Bell 1978))
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP) (any or ≥ stage 3)
Oxygen dependency at 28 days
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia, (BPD) (oxygen dependency at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age)
Long‐term growth and neurodevelopmental outcome (cerebral palsy and abnormal mental development < 2 standard deviations (SD) below the mean on a standardised score)
Search methods for identification of studies
Electronic searches
All Cochrane Neonatal CPAP review searches were updated simultaneously in October 2017. We ran a sensitive search using only CPAP intervention terms, and we used a beginning search date of 1 January 2007 to comprehensively search for all reviews. See Appendix 1 for details of this search.
On 30 June 2020, we updated the search using Cochrane Neonatal's current search practices (see Differences between protocol and review).
We conducted a comprehensive search including the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL; 2020, Issue 6), in the Cochrane Library; Ovid MEDLINE(R) and Epub Ahead of Print, In‐Process & Other Non‐Indexed Citations, Daily and Versions(R) (2017 to 30 June 2020); and the Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) (2017 to 30 June 2020). We have included in Appendix 2 the search strategies for each database. We did not apply language restrictions.
We searched clinical trial registries for ongoing or recently completed trials (International Standard Randomized Controlled Trials Number (ISRCTN) Registry). We searched the World Health Organization International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) (www.who.int/ictrp/search/en/), as well as the US National Library of Medicine ClinicalTrials.gov (clinicaltrials.gov), via Cochrane CENTRAL.
For reviews published before 2017, see search strategies used previously in Appendix 3.
Searching other resources
We searched the reference lists of any articles selected for inclusion in this review to identify additional relevant articles.
Data collection and analysis
We employed the standard methods of Cochrane Neonatal Guidelines.
Selection of studies
We included all randomised and quasi‐randomised controlled trials fulfilling the selection criteria described in the previous section. Two review authors reviewed results of the search and separately selected studies for inclusion.
Data extraction and management
Two review authors (JJH and AS) extracted data independently and assessed and coded all data for each study. We replaced any standard error of the mean with the corresponding standard deviation and resolved disagreements by discussion. For each study, one review author entered final data into RevMan 5, and a second review author checked the data (Review Manager 2020). We performed statistical analyses using RevMan 5 software (Review Manager 2020), and we analysed categorical data using risk ratio (RR) and risk difference (RD). We analysed continuous data using mean difference (MD), reported the 95% confidence interval (CI) for all estimates, and used a fixed‐effect model for meta‐analysis.
Assessment of risk of bias in included studies
Two review authors (JJH and AS), independently assessed the risk of bias (low, high, or unclear) of all included trials using the Cochrane ‘Risk of bias’ tool for the following domains (Higgins 2011).
Sequence generation (selection bias).
Allocation concealment (selection bias).
Blinding of participants and personnel (performance bias).
Blinding of outcome assessment (detection bias).
Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias).
Selective reporting (reporting bias).
Any other bias.
We resolved any disagreements by discussion or by consultation with a third assessor. See Appendix 4 for a more detailed description of risk of bias for each domain.
Measures of treatment effect
We used RR, RD, and number needed to treat for additional benefit (NNTB) or number needed to treat for additional harm (NNTH), derived from 1/RD for categorical outcomes. We used MD for continuous outcomes. For each measure of effect, we calculated the 95% CI. We did not calculate the confidence interval for the number needed to treat when it incorporated both harm and benefit.
Unit of analysis issues
We planned to exclude cross‐over studies because we judged this trial design as unsuitable. We planned to include cluster RCTs and would have adjusted their sample sizes and event rates using the methods described in the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions (Higgins 2017).
We have reported how each study that randomised twins dealt with this potential clustering effect. For trials testing more than two arms, if encountered, we intended to include only the arms relevant to our objective in the analysis. When two or more arms met our inclusion criteria for either the intervention or the control, we intended to combine those arms.
Dealing with missing data
For all outcomes, we carried out analyses, as far as possible, on an intention‐to‐treat basis, that is, we attempted to include all participants randomised to each group in the analyses, and we analysed all participants in the group to which they were allocated, regardless of whether or not they received the allocated intervention. The denominator for each outcome in each trial was the number randomised minus the number of participants whose outcomes were known to be missing. We planned to contact study authors if we encountered any missing data. We did not plan any imputation to account for missing data.
Assessment of heterogeneity
We examined heterogeneity between trials by inspecting forest plots and quantifying the impact of heterogeneity using the I² statistic. If we detected statistical heterogeneity, we would attempt to explain it. We considered an I² value of about 40% or below to represent little or no heterogeneity, 40% to 60% to represent moderate heterogeneity, and 50% to 90% to represent substantial heterogeneity. We planned to explore possible causes using subgroup analyses. If we encountered considerable heterogeneity (> 90%), we planned to not present a meta‐analysis.
Assessment of reporting biases
If we had found sufficient studies (≥ 10), we planned to construct a funnel plot and to inspect this for evidence of asymmetry. If we had found this, we would have attempted to explain it.
Data synthesis
We synthesised data using the standard methods of Cochrane Neonatal. We performed meta‐analysis using Review Manager software (Review Manager 2020), as supplied by Cochrane. For estimates of RR and RD, we used the Mantel‐Haenszel method. We performed all meta‐analyses using the fixed‐effect model.
Certainty of evidence
We used the GRADE approach, as outlined in the GRADE Handbook (Schünemann 2013), to assess the certainty of evidence for the following (clinically relevant) outcomes: use of IPPV, mortality, failure of treatment (death or IPPV), air leak (pneumothorax), and bronchopulmonary dysplasia at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age.
Two review authors (JJH and PS) independently assessed the certainty of evidence for each of the outcomes above. We considered evidence from RCTs as high certainty but downgraded the evidence one level for serious (and two levels for very serious) limitations based upon the following: design (risk of bias), consistency across studies, directness of evidence, precision of estimates, and presence of publication bias. We used the GRADEpro GDT Guideline Development Tool to create Table 1 to report the certainty of evidence.
The GRADE approach results in an assessment of the certainty of a body of evidence as one of four grades.
High certainty: further research is very unlikely to change our confidence in the estimate of effect.
Moderate certainty: further research is likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and may change the estimate.
Low certainty: further research is very likely to have an important impact on our confidence in the estimate of effect and is likely to change the estimate.
Very low certainty: we are very uncertain about the estimate.
Subgroup analysis and investigation of heterogeneity
We planned subgroup analyses a priori on the basis of weight (with subdivisions at 1000 grams and 1500 grams) and gestation (with subdivisions at 28 and 32 weeks), and according to whether surfactant was used.
Sensitivity analysis
We performed sensitivity analysis based on trial methods (we analysed randomised controlled trials separately from quasi‐randomised studies).
Results
Description of studies
Results of the search
For this update, after screening titles and abstracts, we retrieved seven full‐text articles (Badiee 2013; Dunn 2011; Finer 2010; Morley 2008; Rojas 2009; Sandri 2010; Tapia 2012), and after examining the full text, we excluded all seven. We included no new studies in the review. Results of the search are shown in Figure 1. We did not find any ongoing studies. We excluded from this update two studies included in previous versions of the review (Ho 2002); we decided to exclude them because the intervention was continuous negative pressure (Gerard 1975; Mockrin 1975).
1.

Study flow diagram: 2020 review update.
Included studies
We included four studies (Allen 1977; Hegyi 1981; Krouskop 1975; Rowe 1978). All were carried out in the pre‐surfactant era. Only one study reported the use of antenatal steroids, stating that no antenatal steroids were used. All four studies used clinical and radiological evidence of respiratory distress as entry criteria. None of the four studies reported whether twins were included.
The FiO₂ required at entry ranged from 0.3 or more to 0.6. Early CPAP was initiated at trial entry, and late CPAP was initiated if further deterioration occurred at FiO₂ ranging from 0.5 up to 1.0. This FiO₂ was given to maintain partial pressure of oxygen of 50 mmHg in four studies, 60 mmHg in one study, and 100 mmHg in another study. Thus the criteria used for initiating early and late CPAP showed variation and overlap.
Of the four studies included in this review, one used face mask CPAP (Allen 1977), and three used binasal CPAP (Hegyi 1981; Krouskop 1975; Rowe 1978).
The primary outcome measures for all studies were use of IPPV and mortality. The point in time at which mortality was measured was not specified in any of the studies, although the age of death for each individual death was given in two trials. Failed treatment (the combined outcome of death before discharge or subsequent use of IPPV) was not reported in any trials. Three studies reported incidence of pneumothorax (Allen 1977; Hegyi 1981, Rowe 1978), one reported BPD (undefined) (Rowe 1978), and one reported ROP (Krouskop 1975), all as secondary outcomes. One study reported a subgroup analysis of mortality among very low birth weight infants (Krouskop 1975). Another study reported duration of oxygen therapy in survivors (time period of survival not stated) (Allen 1977). This was not a prespecified outcome measure but was included post hoc, as it was considered an important secondary outcome.
Allen 1977 included 24 infants with clinical features of hyaline membrane disease (abnormal retractions of the chest wall, cyanosis, tachypnoea, and grunting) and chest X‐ray consistent with the diagnosis. These infants had no previous ventilation except resuscitation and required FiO₂ greater than 0.6. to maintain partial pressure of oxygen (PaO₂) above 60 mmHg. Mean (SD) birth weight was 1641 (509) and 1545 (516) grams, gestation 32.4 (3.8) and 31.1 (3.5) weeks, and age at randomisation 15.8 (12.1) and 11.9 (11.4) hours in early and delayed CPAP groups, respectively. The early group received face mask CPAP at recruitment, and the late group received face mask CPAP or IPPV if the PaO₂ was below 50 mmHg with FiO₂ of 0.95. Ventilation was initiated if PaO₂ was below 50 mmHg with FiO₂ of 0.95 and apnoea was likely, judged by peripheral vasoconstriction, gasps, or heart rate (HR) below 100/min. Outcomes reported were need for ventilation, mortality (time not specified), pneumothorax, and time on oxygen among survivors.
Hegyi 1981 included 38 preterm infants with clinical and radiological evidence of respiratory distress syndrome who required FIO₂ of 0.3 to maintain PaO₂ above 50 mmHg. Mean (SD) birth weight was 1737 (568) and 1950 (581) grams, gestation 33 (2) and 34 (2) weeks, and age at application of CPAP 7.1 (6.2) and 15.1 (12.1) hours for early and delayed groups. The early intervention group received CPAP at recruitment, and the delayed group received CPAP when FiO₂ of 0.5 was needed to maintain PaO₂ above 50 mmHg. All infants received nasal prong CPAP at 6 cm H₂O. PaO₂ was maintained at between 50 and 80 mmHg and CPAP was stopped when FiO₂ was 0.3. All infants had umbilical catheters (in the low position). No antenatal steroids were used. Criteria for ventilation were FiO₂ of 0.9, PaO₂ below 50 mmHg, PaCO₂ above 65 mmHg, and recurrent apnoea. Secondary outcomes included death (time not specified) and pneumothorax.
Krouskop 1975 included 21 infants. Participating infants were preterm infants with clinical and radiological evidence of respiratory distress syndrome who required FIO₂ of 0.4 to maintain PaO₂ at 60 to 100 mmHg on two successive measurements within one hour. The early intervention group received nasal prong CPAP at recruitment, and the delayed intervention group received head box oxygen with nasal prong CPAP, initiated when FiO₂ of 0.7 was required to maintain PaO₂ between 60 and 100 mmHg. Both groups had chin straps, and both groups had PaO₂ measurements every 15 minutes to four hours via an umbilical catheter. CPAP was delivered using heated and humidified gases. The primary outcome was failed therapy and mortality. Failed therapy was defined as requiring FIO₂ of 0.8 or apnoea lasting longer than 15 seconds or with no response to tactile stimulation. Subgroups by birth weight were available for 1500 grams or less and above 1500 grams. Secondary outcomes were pneumothorax, BPD, and ROP. These were not defined.
Rowe 1978 included 36 preterm infants with respiratory distress and requiring FiO₂ of 0.4 to maintain PaO₂ above 50 mmHg. Mean weight and gestation were not reported, but weight groups were reported. Three infants were below 1200 grams and 19 were above 1800 grams birth weight. The early CPAP group received CPAP at FiO₂ of 0.4 and PaO₂ below 50 mmHg, and the delayed CPAP group received CPAP at FiO₂ of 0.7. CPAP was applied using nasal prongs. The pressure level was not reported. Eleven of 19 infants in the delayed CPAP group did not receive CPAP because their FiO₂ requirement did not reach 0.7. Outcomes reported were mortality (time not specified), need for ventilation, air leak, and bronchopulmonary dyplasia (not defined). Data were also available for the combined outcome of death or BPD.
Excluded studies
In addition to the two previously excluded studies (John 1976; Tooley 2003), we excluded seven further studies (Badiee 2013; Dunn 2011; Finer 2010; Morley 2008; Rojas 2009; Sandri 2010; Tapia 2012).
We judged that these seven studies compared treatment with prophylactic or very early CPAP before the onset of established respiratory distress with other interventions including surfactant and mechanical ventilation (Dunn 2011; Finer 2010), surfactant and CPAP (Dunn 2011; Rojas 2009; Sandri 2010), or mechanical ventilation alone (Morley 2008; Tapia 2012).
Badiee 2013 compared prophylactic CPAP within five minutes of birth versus very early CPAP within 30 minutes of birth.
Allocation of infants in John 1976 was quasi‐randomised. John and colleagues excluded after allocation infants who died or required mechanical ventilation. Data on excluded infants were not available; thus, John 1976 provided none of the primary outcomes specified in this Cochrane Review. We excluded this study.
We excluded Tooley 2003, which involved 42 infants, as infants were randomised after intubation and administration of surfactant to extubation and application of nasal CPAP or continued conventional ventilation.
Risk of bias in included studies
Three studies were randomised (Allen 1977; Krouskop 1975; Rowe 1978).
Krouskop 1975 used a sequential design whereby the first eight matched pairs were randomised. Hegyi 1981 was a quasi‐randomised study.
No studies described blinding of the intervention or of outcome assessment. All studies provided complete follow‐up of randomised infants. Only one study stated how many of the potentially eligible infants were entered (Hegyi 1981). The assessment of risk of bias is summarised in Figure 2 and Figure 3.
2.

Risk of bias graph: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item presented as percentages across all included studies.
3.

Risk of bias summary: review authors' judgements about each risk of bias item for each included study.
Allocation
Three studies were randomised, and Hegyi 1981 was quasi‐randomised using the hospital identification number. Two of the three randomised studies did not report the method of sequence generation or whether concealed allocation was used. Krouskop 1975 used concealed allocation (sealed envelopes); however study authors randomised using blocks of two, and the last few allocated infants were alternate. We judged this study to be at high risk of bias.
Blinding
Blinding was not reported in any of the included studies, and because of the nature of the intervention, blinding is unlikely.
Incomplete outcome data
Three of the four included studies reported how many infants were randomised and provided complete outcome data. For Rowe 1978, it is unclear from the report how many infants were randomised.
Selective reporting
None of the study protocols were available. None of the studies reported our primary outcome 'failed treatment'. However because all trials were done in a setting where IPPV was available, and although we do not know the timing of death, it is unlikely that deaths occurred before the use of IPPV. Therefore we judged failure to report this outcome as not due to selective reporting. Other expected outcomes were reported. We judged all studies to be at low risk of selective reporting bias
Other potential sources of bias
Hegyi 1981 had an imbalance between groups, with 13 in one group and 25 in the other. This could be due to the use of hospital number for generation of the sequence. We decided not to include this potential bias here because this has already been taken into consideration under selection bias.
Effects of interventions
See: Table 1
Four studies involving 119 infants met the entry criteria and were included in the analysis (Allen 1977; Hegyi 1981; Krouskop 1975; Rowe 1978).
Primary outcomes
Use of IPPV (outcomes 1.1 and 1.2)
None of the four individual trials showed that early versus delayed CPAP affected the requirement for IPPV. The meta‐analysis showed there is uncertainty about the effect of early CPAP on use of IPPV (typical RR 0.77, 95% CI 0.43 to 1.38; RD ‐0.08, 95% CI ‐0.23 to 0.08; NNTB 13, 95% CI from infinity to 5 (benefit) to 13 (harmed); I² = 0%, 4 studies, 119 participants; very low‐certainty evidence; Analysis 1.1). Krouskop 1975 reported subgroup analysis by birth weight for this outcome. None of the infants weighing 1500 grams or more at birth required IPPV, and for infants weighing less than 1500 grams, three of four participants in each group required IPPV (Analysis 1.2; Figure 4).
1.1. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Early versus late CPAP, Outcome 1: Use of IPPV
1.2. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Early versus late CPAP, Outcome 2: Use of IPPV by birth weight
4.

Forest plot of comparison: 1 early versus late CPAP, outcome: 1.1 use of IPPV.
Mortality at 28 days (outcome 1.3)
The effect of early CPAP on mortality at 28 days, as reported in Hegyi 1981, is uncertain (typical RR 0.62, 95% CI 0.03 to 14.22; 1 study, 38 participants; very low‐certainty evidence; Analysis 1.3).
1.3. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Early versus late CPAP, Outcome 3: Mortality at 28 days
Mortality (outcomes 1.4 and 1.5)
Mortality (explicitly specified as mortality before discharge) was not reported in any of the studies. For mortality (time not specified), there was uncertainty of effect in each of the four trials (119 participants), and the meta‐analysis indicates that intervention may make little or no difference (typical RR 0.93, 95% CI 0.43 to 2.03; typical RD ‐0.02, 95% CI ‐0.15 to 0.12; I² = 33%; very low‐certainty evidence; Analysis 1.4; Figure 5).
1.4. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Early versus late CPAP, Outcome 4: Mortality (time not specified)
5.

Forest plot of comparison: 1 early versus late CDP, outcome: 1.2 mortality (time not specified).
Krouskop 1975 reported subgroup analysis by birth weight (≥ 1500 grams versus < 1500 grams) for this outcome. No death occurred in the seven infants weighing 1500 grams or more at birth. For both early and delayed CPAP, three of four infants weighing less than 1500 grams died in each group (Analysis 1.5). No data were available for a subgroup analysis by gestation to be performed.
1.5. Analysis.
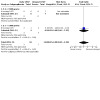
Comparison 1: Early versus late CPAP, Outcome 5: Mortality (time not specified) by birth weight
Failed treatment
None of the included studies reported this outcome. All infants in all trials who failed CPAP received IPPV. Therefore for the included studies, failed treatment equates to IPPV.
Secondary outcomes
Air leak (pneumothorax) (outcome 1.6)
Four trials reported this outcome. However, only Krouskop 1975 reported this outcome in five participants, and it is unclear to which treatment group these participants were assigned. For the three trials that had sufficient information for inclusion in the meta‐analysis, there was uncertainty of effect (RR 1.09, 95% CI 0.39 to 3.04; RD 0.01, 95% CI ‐0.13 to 0.14; 3 trials, 98 participants, I² = 0%; very low‐certainty evidence; Analysis 1.6).
1.6. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Early versus late CPAP, Outcome 6: Air leak (pneumothorax)
Use of surfactant
Surfactant was not used in any of the included studies.
Intraventricular haemorrhage (IVH)
No trial reported this outcome.
Necrotising enterocolitis (NEC)
No studies reported this outcome.
Retinopathy of prematurity (ROP)
This outcome was reported in one study (Krouskop 1975). Study authors reported no ROP in either group.
Oxygen dependency at 28 days (outcome 1.7)
No trial assessed oxygen dependency at 28 days. However, Allen 1977 reported the number of days on oxygen among survivors. Mean days for the early CPAP group were 11.1 (SD 5.7) and 9.4 (SD 4.5) for the delayed group (MD ‐1.70, 95% CI ‐6.4 to 3.0; 20 participants; Analysis 1.7). Rowe 1978 reported no difference in the time spent in FiO₂ greater than 0.3 or greater than 0.7.
1.7. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Early versus late CPAP, Outcome 7: Duration of oxygen in survivors (days)
Bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BDP) (outcome 1.8)
BPD at 36 weeks (in survivors) was reported in one study (Rowe 1978). One baby in each group had this outcome (typical RR 1.42, 95% CI 0.10 to 20.49; very low‐certainty evidence; Analysis 1.8).
1.8. Analysis.

Comparison 1: Early versus late CPAP, Outcome 8: Bronchopulmonary dysplasia at 36 weeks
Neurodevelopmental outcomes
No included study reported this outcome.
Sensitivity analysis
Excluding the quasi‐random study of Krouskop 1975 had no substantive effect on primary outcomes and hence did not change the conclusion.
Discussion
Summary of main results
We identified four eligible trials, including 119 babies, performed in the 1970s and early 1980s. For two of the primary outcomes ‐ use of intermittent positive‐pressure ventilation (IPPV) and mortality ‐ although reported in all four studies, data were insufficient to indicate whether early application of continued positive airway pressure (CPAP) is beneficial. None of the studies reported the outcome of treatment failure. Data were also insufficient to indicate whether early compared with late CPAP could reduce adverse effects such as pneumothorax, intraventricular haemorrhage, bronchopulmonary dysplasia, or necrotising enterocolitis. No study reported long‐term outcomes.
Overall completeness and applicability of evidence
The applicability of this evidence to current practice is questionable for the following reasons. First, the studies were conducted in an era when antenatal steroids were not widely used and surfactant was not yet available for use. Mean birth weight and gestation of the treatment groups ranged from 1545 to 2113 grams and 31 to 34 weeks ‐ considerably higher than most infants receiving treatment for respiratory distress in current practice. In addition, across studies, the age at application of early CPAP ranged from a mean of 7.1 to 18 hours ‐ later than what would currently be considered early intervention for the treatment of respiratory distress (Finer 2010; Morley 2008; Narendran 2003; Tooley 2003). Wide variation was evident in the criteria used for initiating early and late CPAP, resulting in some overlap between intervention and control groups. The incidence of pneumothorax (> 10%) was higher than that seen today (Dunn 2011; Sandri 2010). Since the time this review was first published (Ho 2002), CPAP research has focused on the effect of prophylactic or very early CPAP initiated in the delivery room compared with early mechanical ventilation and early surfactant (Dunn 2011; Finer 2010; Morley 2008; Rojas 2009; Sandri 2010; Tapia 2012). We included trials using any interface for delivering CPAP, including face mask and nasal prongs. We were not able to assess whether publication bias has had any effect on these results.
Quality of the evidence
We noted high or unclear risk of selection bias in all included studies. Two studies were quasi‐randomised. Blinding of the intervention is not possible in these studies, and blinding of outcome assessment would be extremely difficult. Our primary outcomes were failed CPAP, death, and mechanical ventilation. Mortality could be considered an objective outcome; therefore we have downgraded only one level for risk of bias. However even if clear objective criteria for use of IPPV are used, there is room for clinical judgement, which in the context of an unblinded study could contribute to the overall risk of bias. Therefore we downgraded risk of bias two levels for very serious concerns. Follow‐up was complete in three studies and uncertain in the remaining study. In addition, the overall information size is small, and precision of the results is lacking, contributing to uncertainty of evidence. We have downgraded all outcomes one level for this. However, the included studies showed little or no heterogeneity. For reasons outlined above, the applicability of results to today's clinical practice is limited. Use of antenatal steroids and surfactant could reduce baseline risk and hence the potential effect size of early CPAP. Therefore, we downgraded all outcomes one level for this. Hence we present very low‐certainty evidence for all outcomes.
Potential biases in the review process
The findings of this review are limited by the small number of participants in the included studies. Although subgroup analyses by birth weight were reported by at least one trial for the primary outcome, the numbers were too small to be meaningful. Previous versions of the review included studies using continuous negative pressure (Ho 2002). For this update, we excluded these trials because negative pressure is seldom used in current clinical practice, and we believe that users of this review would therefore be interested in the effects of early versus delayed CPAP. Since this is a 'post hoc' change in the process of the review, potential bias could be introduced.
Agreements and disagreements with other studies or reviews
The findings of this review do not contradict the findings of other reviews examining the use of CPAP in preterm infants (Ho 2015; Subramaniam 2016). These two reviews suggest benefit for CPAP whether used prophylactically or very early or as treatment for respiratory distress. In this Cochrane Review, no adverse effects were found, whereas in the other two reviews, an increase in pulmonary air leaks in the CPAP group was suggested. This Cochrane Review does not provide sufficient data to conclusively identify the effects of early CPAP on bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD). However when used prophylactically, CPAP reduces the risk of BPD at 36 weeks' postmenstrual age.
Authors' conclusions
Implications for practice.
From the four small trials included in this review, all performed in the 1970s or early 1980s, we are very uncertain whether early application of CPAP provides clinical benefit for the treatment of respiratory distress, or whether it has any adverse effects.
However, the applicability of these findings to the current practice of neonatal intensive care is uncertain, given that all trials in this Cochrane Review were conducted in the pre‐surfactant era, when antenatal steroid usage was uncommon and infants were heavier and more mature than those currently treated for respiratory distress.
Implications for research.
Re‐evaluation of the strategy of early CPAP in the era of antenatal steroid and surfactant administration may be indicated, but given that CPAP has become standard practice, further trials are unlikely. The main direction of future research in this area should be towards establishing the preferred level of CPAP. Future studies should also attempt to answer questions about preferred timing, dose, and mode of administration of surfactant when used in conjunction with CPAP. Long‐term follow‐up of neurodevelopmental and respiratory outcomes is also important.
What's new
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 30 June 2020 | New search has been performed |
|
| 30 June 2020 | New citation required and conclusions have changed | No new studies were found, but with negative distending pressure trials removed, and in the current context of care, the conclusions have changed |
History
Protocol first published: Issue 4, 2000 Review first published: Issue 2, 2002
| Date | Event | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 30 November 2018 | Amended | Title was changed |
| 30 October 2013 | New search has been performed | The title has been changed to "Early versus delayed initiation of continuous distending pressure for respiratory distress in preterm infants". It is not possible to establish the cause of respiratory distress before the intervention is provided. No new trials were found |
| 22 December 2009 | New search has been performed | This review updates the existing review "Early versus delayed initiation of continuous distending pressure for respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants", published in the Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews (Ho 2007) An updated search found no new trials No changes were made to review conclusions |
| 17 September 2008 | Amended | This review has been converted to new review format |
| 4 December 2006 | New search has been performed | This review updates the existing review "Early versus delayed initiation of continuous distending pressure for respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants," first published in the Cochrane Library, Issue 2, 2002 (Ho 2015) The literature search was repeated on 1 October 2006, and no further studies eligible for inclusion were found The overall conclusions of the review have not changed |
| 12 February 2002 | New citation required and conclusions have changed | Substantive amendments were made |
Acknowledgements
The late David Henderson‐Smart (DHS) inspired and guided the initial version (Ho 2002), as well as the first two amended versions, of this review (Ho 2007; Ho 2010).
The methods section of this review is based on a standard template used by Cochrane Neonatal.
We would like to thank Cochrane Neonatal: Colleen Ovelman, Managing Editor; Jane Cracknell, Assistant Managing Editor; Roger Soll, Co‐coordinating Editor; and Bill McGuire, Co‐coordinating Editor, who provided editorial and administrative support. Carol Friesen, Information Specialist, designed and ran the literature searches.
As a Cochrane Neonatal Editor, Prakeshkumar Shah has peer‐reviewed and offered feedback for this review.
Appendices
Appendix 1. 2017 search methods
In 2017, we conducted a comprehensive search including: Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL; 2017, Issue 10) in the Cochrane Library; MEDLINE via PubMed (01 January 2007 to October 2017); Embase (01 January 2007 to October 2017); and CINAHL (01 January 2007 to October 2017) using the following search terms:
PubMed
(continuous positive airway pressure[MeSH] OR continuous positive pressure OR continuous positive airway pressure OR CPAP OR continuous distending airway pressure OR continuous positive transpulmonary pressure OR continuous transpulmonary pressure OR continuous inflating pressure OR continuous negative distending pressure OR continuous negative pressure OR continuous airway pressure) AND ((infant, newborn[MeSH] OR infan* OR newborn OR neonat* OR premature OR low birth weight OR VLBW OR LBW) AND (randomized controlled trial [pt] OR controlled clinical trial [pt] OR randomized [tiab] OR placebo [tiab] OR drug therapy [sh] OR randomly [tiab] OR trial [tiab] OR groups [tiab]) NOT (animals [mh] NOT humans [mh]))
Embase
((exp positive end expiratory pressure) OR (continuous positive pressure OR continuous positive airway pressure OR CPAP OR continuous distending airway pressure OR continuous positive transpulmonary pressure OR continuous transpulmonary pressure OR continuous inflating pressure OR continuous negative distending pressure OR continuous negative pressure OR continuous airway pressure)) AND ((exp infant) OR (infan* OR newborn or neonat* OR premature or very low birth weight or low birth weight or VLBW or LBW).mp AND (human not animal) AND (randomized controlled trial or controlled clinical trial or randomized or placebo or clinical trials as topic or randomly or trial or clinical trial).mp
CINAHL
(continuous positive airway pressure OR continuous positive pressure OR CPAP OR continuous distending airway pressure OR continuous positive transpulmonary pressure OR continuous transpulmonary pressure OR continuous inflating pressure OR continuous negative distending pressure OR continuous negative pressure OR continuous airway pressure) AND (infan* OR newborn OR neonat* OR premature OR low birth weight OR VLBW OR LBW) AND (randomized controlled trial OR controlled clinical trial OR randomized OR placebo OR clinical trials as topic OR randomly OR trial OR PT clinical trial)
CRS
(continuous positive airway pressure[MeSH]) OR (continuous positive airway pressure OR continuous positive pressure OR CPAP OR continuous distending airway pressure OR continuous positive transpulmonary pressure OR continuous transpulmonary pressure OR continuous inflating pressure OR continuous negative distending pressure OR continuous negative pressure OR continuous airway pressure) AND (infan* or newborn or neonat* or premature or preterm or very low birth weight or low birth weight or VLBW or LBW)
We did not apply language restrictions.
We searched clinical trials registries for ongoing or recently completed trials (clinicaltrials.gov; the World Health Organization’s International Trials Registry; and Platform, and the ISRCTN Registry).
Appendix 2. 2020 Search methods
The RCT filters have been created using Cochrane's highly sensitive search strategies for identifying randomised trials (Higgins 2017). The neonatal filters were created and tested by the Cochrane Neonatal Information Specialist.
CENTRAL via CRS Web
1. MESH DESCRIPTOR continuous positive airway pressure EXPLODE ALL AND CENTRAL:TARGET
2. MESH DESCRIPTOR positive‐pressure respiration EXPLODE ALL AND CENTRAL:TARGET
3. (continuous positive airway pressure OR continuous positive pressure OR CPAP OR continuous distending airway pressure OR continuous positive transpulmonary pressure OR continuous transpulmonary pressure OR continuous inflating pressure OR continuous negative distending pressure OR continuous negative pressure OR continuous airway pressure OR ncpap) AND CENTRAL:TARGET
4. 1 or 2 or 3
5. MESH DESCRIPTOR Infant, Newborn EXPLODE ALL AND CENTRAL:TARGET
6. (infant or infants or infant’s or “infant s” or infantile or infancy or newborn* or "new born" or "new borns" or "newly born" or neonat* or baby* or babies or premature or prematures or prematurity or preterm or preterms or "pre term" or premies or "low birth weight" or "low birthweight" or VLBW or LBW or ELBW or NICU) AND CENTRAL:TARGET
7. 5 or 6
8. 4 AND 7
9. 2017 TO 2020:YR AND CENTRAL:TARGET
MEDLINE via Ovid
1. exp positive‐pressure respiration/ or exp continuous positive airway pressure/ 2. (continuous positive airway pressure OR continuous positive pressure OR continuous distending airway pressure OR continuous positive transpulmonary pressure OR continuous transpulmonary pressure OR continuous inflating pressure OR continuous negative distending pressure OR continuous negative pressure OR continuous airway pressure).mp. 3. (cpap or ncpap).mp. 4. 1 or 2 or 3 5. exp infant, newborn/ 6. (newborn* or new born or new borns or newly born or baby* or babies or premature or prematurity or preterm or pre term or low birth weight or low birthweight or VLBW or LBW or infant or infants or 'infant s' or infant's or infantile or infancy or neonat*).ti,ab. 7. 5 or 6 8. randomized controlled trial.pt. 9. controlled clinical trial.pt. 10. randomized.ab. 11. placebo.ab. 12. drug therapy.fs. 13. randomly.ab. 14. trial.ab. 15. groups.ab. 16. or/8‐15 17. exp animals/ not humans.sh. 18. 16 not 17 19. 7 and 18 20. randomi?ed.ti,ab. 21. randomly.ti,ab. 22. trial.ti,ab. 23. groups.ti,ab. 24. ((single or doubl* or tripl* or treb*) and (blind* or mask*)).ti,ab. 25. placebo*.ti,ab. 26. 20 or 21 or 22 or 23 or 24 or 25 27. 6 and 26 28. limit 33 to yr="2019 ‐Current" 29. 19 or 28 30. 4 and 29 31. limit 30 to yr="2017 ‐Current"
CINAHL via EBSCOhost
(infant or infants or infant’s or infantile or infancy or newborn* or "new born" or "new borns" or "newly born" or neonat* or baby* or babies or premature or prematures or prematurity or preterm or preterms or "pre term" or premies or "low birth weight" or "low birthweight" or VLBW or LBW) AND (randomized controlled trial OR controlled clinical trial OR randomized OR randomised OR placebo OR clinical trials as topic OR randomly OR trial OR PT clinical trial) AND (continuous positive airway pressure OR continuous positive pressure OR CPAP OR continuous distending airway pressure OR continuous positive transpulmonary pressure OR continuous transpulmonary pressure OR continuous inflating pressure OR continuous negative distending pressure OR continuous negative pressure OR continuous airway pressure OR ncpap)
Limit 2017 to present
Appendix 3. Previous search methods
The search included the Oxford Database of Perinatal Trials, Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL, in the Cochrane Library; Issue 3, 2006), and MEDLINE (1966 to September week 4, 2006; all languages). The MEDLINE search terms used were newborn, neonate, respiratory distress syndrome, hyaline membrane disease, continuous distending pressure, continuous distending airway pressure, continuous positive airway pressure, continuous positive transpulmonary pressure, continuous transpulmonary pressure, continuous inflating pressure, continuous negative distending pressure, continuous negative pressure, or continuous airway pressure.
In November 2009, we updated the search as follows: MEDLINE (search via PubMed), CINAHL, Embase, and CENTRAL (the Cochrane Library) were searched from 2006 to 2009. Search terms: respiratory distress syndrome OR hyaline membrane disease OR continuous distending pressure OR continuous distending airway pressure OR continuous positive airway pressure OR continuous positive transpulmonary pressure OR continuous transpulmonary pressure OR continuous inflating pressure OR continuous negative distending pressure OR continuous negative pressure OR continuous airway pressure. Limits: human, infant and clinical trial. No language restrictions were applied. We repeated this search in April 2015.
We used the following database‐specific limiters for RCTs and neonates:
PubMed: ((infant, newborn[MeSH] OR infan* OR newborn OR neonat* OR premature OR low birth weight OR VLBW OR LBW) AND (randomized controlled trial [pt] OR controlled clinical trial [pt] OR randomized [tiab] OR placebo [tiab] OR drug therapy [sh] OR randomly [tiab] OR trial [tiab] OR groups [tiab]) NOT (animals [mh] NOT humans [mh]))
Embase: ((exp infant) OR (infan* OR newborn or neonat* OR premature or very low birth weight or low birth weight or VLBW or LBW).mp AND (human not animal) AND (randomized controlled trial or controlled clinical trial or randomized or placebo or clinical trials as topic or randomly or trial or clinical trial).mp
CINAHL: (infan* OR newborn OR neonat* OR premature OR low birth weight OR VLBW OR LBW) AND (randomized controlled trial OR controlled clinical trial OR randomized OR placebo OR clinical trials as topic OR randomly OR trial OR PT clinical trial)
Cochrane Library: (infan* or newborn or neonat* or premature or preterm or very low birth weight or low birth weight or VLBW or LBW)
Appendix 4. Risk of bias tool
1. Sequence generation (checking for possible selection bias). Was the allocation sequence adequately generated?
For each included study, we categorised the method used to generate the allocation sequence as:
low risk (any truly random process, e.g. random number table; computer random number generator);
high risk (any non‐random process, e.g. odd or even date of birth; hospital or clinic record number); or
unclear risk.
2. Allocation concealment (checking for possible selection bias). Was allocation adequately concealed?
For each included study, we categorised the method used to conceal the allocation sequence as:
low risk (e.g. telephone or central randomisation; consecutively numbered sealed opaque envelopes);
high risk (open random allocation; unsealed or non‐opaque envelopes, alternation; date of birth); or
unclear risk.
3. Blinding of participants and personnel (checking for possible performance bias). Was knowledge of the allocated intervention adequately prevented during the study?
For each included study, we categorised the methods used to blind study participants and personnel from knowledge of which intervention a participant received. Blinding was assessed separately for different outcomes or classes of outcomes. We categorised the methods as:
low risk, high risk, or unclear risk for participants; and
low risk, high risk, or unclear risk for personnel.
4. Blinding of outcome assessment (checking for possible detection bias). Was knowledge of the allocated intervention adequately prevented at the time of outcome assessment?
For each included study, we categorised the methods used to blind outcome assessment. Blinding was assessed separately for different outcomes or classes of outcomes. We categorised the methods as:
low risk for outcome assessors;
high risk for outcome assessors; or
unclear risk for outcome assessors.
5. Incomplete outcome data (checking for possible attrition bias through withdrawals, dropouts, protocol deviations). Were incomplete outcome data adequately addressed?
For each included study and for each outcome, we described the completeness of data including attrition and exclusions from the analysis. We noted whether attrition and exclusions were reported, numbers included in the analysis at each stage (compared with the total randomised participants), reasons for attrition or exclusion where reported, and whether missing data were balanced across groups or were related to outcomes. When sufficient information was reported or supplied by the trial authors, we re‐included missing data in the analyses. We categorised the methods as:
low risk (< 20% missing data);
high risk (≥ 20% missing data); or
unclear risk.
6. Selective reporting bias. Are reports of the study free of the suggestion of selective outcome reporting?
For each included study, we described how we investigated the possibility of selective outcome reporting bias and what we found. For studies in which study protocols were published in advance, we compared prespecified outcomes versus outcomes eventually reported in the published results. If the study protocol was not published in advance, we contacted study authors to gain access to the study protocol. We assessed the methods as:
low risk (when it is clear that all of the study's prespecified outcomes and all expected outcomes of interest to the review have been reported);
high risk (when not all of the study's prespecified outcomes have been reported; one or more reported primary outcomes were not prespecified outcomes of interest and are reported incompletely and so cannot be used; study fails to include results of a key outcome that would have been expected to have been reported); or
unclear risk.
7. Other sources of bias. Was the study apparently free of other problems that could put it at high risk of bias?
For each included study, we described any important concerns we had about other possible sources of bias (e.g. whether there was a potential source of bias related to the specific study design, whether the trial was stopped early due to some data‐dependent process). We assessed whether each study was free of other problems that could put it at risk of bias as:
low risk;
high risk; or
unclear risk.
If needed, we explored the impact of the level of bias through undertaking sensitivity analyses.
Data and analyses
Comparison 1. Early versus late CPAP.
| Outcome or subgroup title | No. of studies | No. of participants | Statistical method | Effect size |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.1 Use of IPPV | 4 | 119 | Risk Difference (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐0.08 [‐0.23, 0.08] |
| 1.2 Use of IPPV by birth weight | 1 | 21 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.45, 2.23] |
| 1.2.1 ≥ 1500 grams | 1 | 13 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Not estimable |
| 1.2.2 < 1500 grams | 1 | 8 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.45, 2.23] |
| 1.3 Mortality at 28 days | 1 | 38 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.62 [0.03, 14.22] |
| 1.4 Mortality (time not specified) | 4 | 119 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 0.93 [0.43, 2.03] |
| 1.5 Mortality (time not specified) by birth weight | 1 | 21 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.45, 2.23] |
| 1.5.1 ≥ 1500 grams | 1 | 13 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | Not estimable |
| 1.5.2 < 1500 grams | 1 | 8 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.00 [0.45, 2.23] |
| 1.6 Air leak (pneumothorax) | 3 | 98 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.09 [0.39, 3.04] |
| 1.7 Duration of oxygen in survivors (days) | 1 | 20 | Mean Difference (IV, Fixed, 95% CI) | ‐1.70 [‐6.40, 3.00] |
| 1.8 Bronchopulmonary dysplasia at 36 weeks | 1 | 29 | Risk Ratio (M‐H, Fixed, 95% CI) | 1.42 [0.10, 20.49] |
Characteristics of studies
Characteristics of included studies [ordered by study ID]
Allen 1977.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | Preterm infants with clinical features of hyaline membrane disease (abnormal retractions of the chest wall, cyanosis, tachypnoea, and grunting) and chest X‐ray consistent with the diagnosis. No previous ventilation except for resuscitation. PaO₂ < 8 kPa (60 mmHg) in FiO₂ > 0.6 (n = 24) | |
| Interventions | Early group: face mask CPAP initiated at randomisation (PaO₂ < 60 mmHg in FIO₂ 0.6) vs late group: face mask CPAP or IPPV at PaO₂ < 50 mmHg in FiO₂ 0.95 Criteria for ventilation:i
|
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Study conducted at University College Hospital, UK | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: 'infants were randomly assigned...' Method of sequence generation not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Not described |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | Blinding not reported Comment: we judged blinding not possible Need for ventilation could be affected by lack of blinding, but mortality unlikely to be affected |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Follow‐up complete |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No study protocol. All expected outcomes reported |
| Other bias | Low risk | None detected |
Hegyi 1981.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Described as randomised | |
| Participants | 38 (13 study and 25 control) preterm infants with clinical and radiological RDS requiring FiO₂ ≥ 0.3 to maintain PaO₂ > 50 mmHg | |
| Interventions | Nasal prong CPAP at 6 cm H₂O at allocation (FiO₂ 0.3) vs CPAP at FiO₂ ≥ 0.5 to maintain PaO₂ > 50 mmHg All infants had umbilical catheter (low position). No antenatal steroids |
|
| Outcomes |
Study authors also reported numbers of infants who required FiO₂ > 0.6 |
|
| Notes | Reason for inequality in group sizes not stated. Study conducted at a regional newborn centre in Monmouth Medical Centre, USA | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Quote: "randomised by hospital number", but the way in which the hospital number was used to determine randomisation is not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Concealment of allocation not reported but highly unlikely |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | No blinding of intervention or outcome assessment reported Comment: blinding unlikely |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | Complete follow‐up. All infants accounted for |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No study protocol. All expected outcomes reported |
| Other bias | Low risk | There was an imbalance between groups (i.e. 13 in 1 group, 25 in the other group). This could be due to selection bias (use of hospital number). We decided not to include this potential bias as other bias because we have already accounted for this under selection bias |
Krouskop 1975.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Quasi‐randomised | |
| Participants | Preterm infants (n = 21) with RDS, spontaneously breathing on FiO₂ of 0.4 to maintain PaO₂ 60 to 100 mmHg on 2 blood gases within 1 hour, or an R‐to‐L shunt > 40% (by Klaus and Meyer). Diagnosis made by clinical and radiological means | |
| Interventions | Early group: nasal prong CPAP started at allocation (i.e. at FiO₂ 0.4) Late group: head box oxygen with FiO₂ < 0.7 to maintain PaO₂ 60 to 100 mmHg. Nasal prong CPAP started when FiO₂ 0.7 and PaO₂ < 0.6 twice within 1 hour Both groups: warmed and humidified CPAP pressure 8 to 14 cm H₂O CPAP pressure was lowered in increments of 2 cm H₂O after FiO₂ reached 0.4 down to atmospheric pressure. Both groups used a chin strap and had an umbilical artery catheter; ABG measured every 15 minutes to 4 hours Failed therapy defined as:
|
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Hours on CPAP and hours on oxygen for survivors also reported. Study conducted at Perinatal Clinical Research Center at Cleveland Metropolitan General Hospital, USA | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | High risk | Sequential randomisation in blocks of 2 matched for age at study entry and birth weight. Actual generation of the sequence is not reported The last 5 participants were allocated alternatively |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | High risk | Sealed envelopes provided by the biometry department Comment: because infants were allocated in blocks of 2, it is possible that allocation for the second of the pair would be known. The last 5 participants were allocated alternatively, so it is unlikely that allocation concealment would have been used for these patients |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | Blinding not reported Comment: it is unlikely that blinding would have been performed for caregivers or outcome assessors |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Low risk | All infants accounted for. Follow‐up complete |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No protocol available. All expected outcomes reported |
| Other bias | Low risk | None detected |
Rowe 1978.
| Study characteristics | ||
| Methods | Randomised controlled trial | |
| Participants | 36 infants with RDS spontaneously breathing and PaO₂ < 50 mmHg in FiO₂ > 0.4 | |
| Interventions | Nasal prong CPAP at allocation (FiO₂ > 0.4) vs FiO₂ > 0.7 in PaO₂ < 50 mmHg 11 out of 19 in the delayed intervention group did not require CPAP because they did not require FiO₂ of 0.7 |
|
| Outcomes |
|
|
| Notes | Data from conference abstract. Study author clarification sought regarding definition of BPD. No full‐text publication. Weight groups used were < 1200 grams, 1201 to 1800 grams, and > 1800 grams. Data were not available for our subgroup analysis by prespecified weight groups. Study conducted at University of Washington, USA | |
| Risk of bias | ||
| Bias | Authors' judgement | Support for judgement |
| Random sequence generation (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Quote: "infants were randomised by weight group to either the early or late CPAP group" Actual sequence generation is not described |
| Allocation concealment (selection bias) | Unclear risk | Concealment of allocation not reported |
| Blinding (performance bias and detection bias) All outcomes | High risk | No blinding of intervention or outcome assessment reported Comment: blinding unlikely |
| Incomplete outcome data (attrition bias) All outcomes | Unclear risk | Unclear how many infants were recruited |
| Selective reporting (reporting bias) | Low risk | No protocol available. All expected outcomes reported |
| Other bias | Low risk | None detected |
ABG: arterial blood gas.
BPD: bronchopulmonary dysplasia.
CPAP: continuous positive airway pressure.
FiO₂: fraction of inspired oxygen.
HR: heart rate.
IPPV: intermittent positive‐pressure ventilation.
L: left.
PaCO₂: partial pressure of carbon dioxide.
PaO₂: partial pressure of oxygen.
PO₂: partial pressure of oxygen.
R: right.
RDS: respiratory distress syndrome.
Characteristics of excluded studies [ordered by study ID]
| Study | Reason for exclusion |
|---|---|
| Badiee 2013 | Randomised controlled trial of preterm infants who received either prophylactic CPAP initiated within 5 minutes of birth or very early CPAP initiated within 30 minutes of birth |
| Dunn 2011 | Randomised controlled trial in preterm infants at birth of 3 interventions applied immediately after birth
|
| Finer 2010 | Randomised controlled trial 2 × 2 factorial design comparing prophylactic CPAP or intubation and surfactant followed by mechanical ventilation. At the same time, infants were randomised to 1 of 2 target ranges for oxygen saturation. Infants did not need to have respiratory distress to be enrolled in the study |
| Gerard 1975 | Early vs delayed application of continuous negative pressure |
| John 1976 | Quasi‐random study of 42 infants at ≥ 29 weeks with RDS. Deaths and individuals requiring mechanical ventilation were excluded post allocation. We judged that with these exclusions, the study did not meet our objectives |
| Mockrin 1975 | Early vs delayed application of continuous negative pressure |
| Morley 2008 | Randomised controlled trial of preterm infants 25 to 28 weeks with respiratory distress at 5 minutes of age allocated to nasal CPAP or intermittent positive‐pressure ventilation. Excluded because there was no control group for standard treatment |
| Rojas 2009 | Randomised controlled trial of preterm infants 27 to 31 weeks with respiratory distress in the delivery room comparing surfactant and nasal CPAP with nasal CPAP alone. No standard treatment control group |
| Sandri 2010 | Randomised controlled trial of early prophylactic surfactant followed by extubation to CPAP compared with early CPAP followed by selective surfactant. Infants did not need to have respiratory distress to participate |
| Tapia 2012 | Randomised controlled trial of prophylactic CPAP compared with standard care (oxygen by head box or nasal cannula when indicated). CPAP was followed by surfactant via INSURE technique (intubate‐surfactant‐extubate), and standard care was followed by mechanical ventilation and surfactant |
| Tooley 2003 | Study of 42 infants including infants at 25 to 28 weeks' gestation who were all intubated at birth, given a single dose of surfactant and positive‐pressure ventilation, then randomised at about 1 hour of age to extubation to nasal CPAP or to continued conventional IPPV. No criteria for the diagnosis of RDS were given |
CPAP: continuous positive airway pressure.
INSURE technique: intubate‐surfactant‐extubate.
IPPV: intermittent positive‐pressure ventilation.
RDS: respiratory distress syndrome.
Differences between protocol and review
For the 2020 update, the most important difference from the protocol was the exclusion of continuous negative‐pressure trials. Justification for this change is noted in the text of the review. We also changed the order of the primary outcomes.
-
For the 2020 update, we changed the search methods as follows.
As of July 2019, Cochrane Neonatal no longer searches Embase for its reviews. RCTs and controlled clinical trials (CCTs) from Embase are added to the Cochrane Central Register of Controlled Trials (CENTRAL) via a robust process (see How CENTRAL is created). Cochrane Neonatal has validated its searches to ensure that relevant Embase records are found while searching CENTRAL.
Also starting in July 2019, Cochrane Neonatal no longer searches for RCTs and CCTs on the following platforms ‐ ClinicalTrials.gov and the World Health Organization’s International Clinical Trials Registry Platform (ICTRP) ‐ as records from both platforms are added to CENTRAL on a monthly basis (see How CENTRAL is created). Comprehensive search strategies are executed in CENTRAL to retrieve relevant records. The ISRCTN (at www.isrctn.com/ ‐ formerly Controlled‐trials.com) is searched separately.
For the 2020 update, we developed a new search strategy (Appendix 2). The 2020 update also includes the results of a search run in 2017 (Appendix 1). The previous search methods are available in Appendix 3.
For the 2007 amended version, we made a change to the criteria for early and late comparison groups. In the protocol, the early group was defined as CPAP starting at randomisation, and the late group as needing an FiO₂ of 0.6 or more. Because we found that one trial defined late as FiO₂ 0.5 or more, we inserted the word 'approximately' 0.6 or more for the delayed group.
Contributions of authors
For the first two versions of this review, JJH conducted the search with input from DHS. JJH and DHS independently evaluated the trials and extracted data. JJH entered the data and wrote the paper with input from the other two review authors (Ho 2002; Ho 2007).
The 2010 amended version was conducted centrally by Cochrane Neonatal staff (Yolanda Montagne, Diane Haughton, and Roger Soll), and was reviewed and approved by JJH.
In 2013, JJH and PGD reviewed the search results and JJH conducted this amendment with input from PGD.
For the 2020 update, two new review authors (PS and AS) were included. JJH and AS re‐extracted data from the original studies using a redesigned and expanded data extraction format. JJH wrote the update with input from the remaining review authors.
Sources of support
Internal sources
Penang Medical College, Georgetown, Penang, Malaysia
Royal Women's Hospital, Melbourne, Australia
Royal Prince Alfred Hospital, Sydney, Australia
Centre for Perinatal Health Services Research, University of Sydney, Australia
Royal College of Medicine Perak, Malaysia
Department of Paediatrics, Hospital Ipoh, Malaysia
External sources
-
Vermont Oxford Network, USA
Cochrane Neonatal Reviews are produced with support from Vermont Oxford Network, a worldwide collaboration of health professionals dedicated to providing evidence‐based care of the highest quality for newborn infants and their families.
Declarations of interest
JJH has no interest to declare.
PS has no interest to declare.
AS has no interest to declare.
PGD's institution has a grant pending from the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council (government salary and project support).
New search for studies and content updated (conclusions changed)
References
References to studies included in this review
Allen 1977 {published data only}
- Allen AP, Reynolds EOR, Rivers RPA, Le Souef PN, Wimberley PD. Controlled trial of continuous positive airway pressure given by face mask for hyaline membrane disease. Archives of Disease in Childhood 1977;52(5):373-8. [DOI: 10.1136/adc.52.5.373] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Hegyi 1981 {published data only}
- Hegyi T, Hiatt IM. The effect of continuous positive airway pressure on the course of respiratory distress syndrome: the benefits of early initiation. Critical Care Medicine 1981;9(1):38-41. [DOI: 10.1097/00003246-198101000-00009] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Krouskop 1975 {published data only}
- Krouskop RW, Brown EG, Sweet AY. The early use of continuous positive airway pressure in the treatment of idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome. Journal of Pediatrics 1975;87(2):263-6. [DOI: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80599-3] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rowe 1978 {unpublished data only}
- Rowe JC, Guthrie RD, Hinkes P, Prueitt J, Murphy J, Woodrum DZ, et al. 1017 Time of initiation of CPAP in HMD (Abstract ). Pediatric Research 1978;12:533. [DOI: 10.1203/00006450-197804001-01023] [DOI] [Google Scholar]
References to studies excluded from this review
Badiee 2013 {published data only}
- Badiee Z, Naseri F, Sadeghnia A. Early versus delayed initiation of nasal continuous positive airway pressure for treatment of respiratory distress syndrome in premature newborns: a randomized clinical trial. Advanced Biomedical Research 2013;2:4. [DOI: 10.4103/2277-9175.107965] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Dunn 2011 {published data only}
- Dunn MS, Kaempf J, Klerk A, Klerk R, Reilly M, Howard D, et al. Randomized trial comparing 3 approaches to the initial respiratory management of preterm neonates. Pediatrics 2011;128(5):e1069-76. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.2010-3848] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Finer 2010 {published data only}
- SUPPORT Study Group of the Eunice Kennedy Shriver NICHD Neonatal Research Network, Finer NN, Carlo WA, Walsh MC, Rich W, Gantz MG, Laptook AR, et al. Early CPAP versus surfactant in extremely preterm infants. New England Journal of Medicine 2010;362(21):1970-9. [DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa0911783] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gerard 1975 {published data only}
- Gerard P, Fox WW, Outerbridge EW, Beaudry PH, Stern L. Early versus late introduction of continuous negative pressure in the management of the idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome. Journal of Pediatrics 1975;87(4):591-5. [DOI: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80832-8] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
John 1976 {published data only}
- John E, Thomas DB, Burnard ED. Influence of early introduction of continuous positive pressure breathing on the course of hyaline membrane disease. Australian Paediatric Journal 1976;12(4):276-80. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1440-1754.1976.tb02516.x] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Mockrin 1975 {published data only}
- Mockrin LD, Bancalari EH. Early versus delayed initiation of continuous negative pressure in infants with hyaline membrane disease. Journal of Pediatrics 1975;87(4):596-600. [DOI: 10.1016/s0022-3476(75)80833-x] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Morley 2008 {published data only}
- Morley CJ, Davis PG, Doyle LW, Brion LP, Hascoet JM, Carlin JB, et al. Nasal CPAP or intubation at birth for very preterm infants. New England Journal of Medicine 2008;358:700-8. [DOI: 10.1056/NEJMoa072788] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rojas 2009 {published data only}
- Rojas MA, Lozano JM, Rojas MX, Laughon M, Bose CL, Rondon MA, et al. Very early surfactant without mandatory ventilation of premature infants treated with early continuous positive airway pressure: a randomized, controlled trial. Pediatrics 2009;123(1):137-42. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.2007-3501] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Sandri 2010 {published data only}
- Sandri F, Plavka R, Ancora G, Simeoni U, Stranak Z, Martinelli S, et al. Prophylactic or early selective surfactant combined with nCPAP in very preterm infants. Pediatrics 2010;124(6):e1402-9. [DOI: 10.1542/peds.2009-2131] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tapia 2012 {published data only}
- Tapia JL, Urzua S, Bancalari A, Meritano J, Torres G, Fabres J, et al. Randomized trial of early bubble continuous positive airway pressure for very low birth weight infants. Journal of Pediatrics 2012;161(1):75-80.e1. [DOI: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2011.12.054] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Tooley 2003 {published data only}
- Tooley J, Dyke M. Randomized study of nasal continuous positive airway pressure in the preterm infant with respiratory distress syndrome. Acta Paediatrica 2003;92:1170-4. [DOI: 10.1080/08035250310004496] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Additional references
Avery 1959
- Avery ME, Mead J. Surface properties in relation to atelectasis and hyaline membrane disease. American Journal of Diseases of Children 1959;97(5, Part 1):517-23. [DOI: 10.1001/archpedi.1959.02070010519001] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bahadue 2012
- Bahadue FL, Soll R Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews Art No: CD001456. Early versus delayed selective surfactant treatment for neonatal respiratory distress syndrome. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 11. Art. No: CD001456. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001456.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bancalari 1992
- Bancalari E, Sinclair JC. Mechanical ventilation. In: Sinclair JC, Bracken MB, editors(s). Effective Care of the Newborn Infant. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 1992:200-20. [Google Scholar]
Barter 1960
- Barter RA, Maddison TG. The nature of the neonatal pulmonary hyaline membrane. Archives of Disease in Childhood 1960;35(183):460-4. [DOI: 10.1136/adc.35.183.460] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Bell 1978
- Bell MJ, Ternberg JL, Feigin RD, Keating JP, Marshall R, Barton L, et al. Neonatal necrotizing enterocolitis. Therapeutic decisions based upon clinical staging. Annals of Surgery 1978;187(1):1-7. [DOI: 10.1097/00000658-197801000-00001] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cogswell 1975
- Cogswell JJ, Hatch DJ, Kerr AA, Taylor B. Effects of continuous positive airway pressure on lung mechanics of babies after operation for congenital heart disease. Archives of Disease in Childhood 1975;50(10):799-804. [DOI: 10.1136/adc.50.10.799] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cotton 1980
- Cotton RB, Lindstrom DP, Kanarek KS, Sundell H, Stahlman MT. Effect of positive-end-expiratory-pressure on right ventricular output in lambs with hyaline membrane disease. Acta Paediatrica Scandinavica 1980;69(5):603-6. [DOI: 10.1111/j.1651-2227.1980.tb07329.x] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Cotton 1998
- Cotton RB. Pathophysiology of hyaline membrane disease (excluding surfactant). In: Polin RA, Fox WW, editors(s). Fetal and Neonatal Physiology. 2nd edition. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1998:1165-74. [Google Scholar]
Davis 2003
- Davis PG, Henderson-Smart DJ. Nasal continuous positive airways pressure immediately after extubation for preventing morbidity in preterm infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2003, Issue 2. Art. No: CD000143. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000143] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Evans 1991
- Evans NJ, Archer LN. Doppler assessment of pulmonary artery pressure and extrapulmonary shunting in the acute phase of hyaline membrane disease. Archives of Disease in Childhood 1991;66(1 Spec No):6-11. [DOI: 10.1136/adc.66.1_spec_no.6] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Field 1985
- Field D, Milner AD, Hopkins IE. Effects of positive end expiratory pressure during ventilation of the preterm infant. Archives of Disease in Childhood 1985;60(9):843-7. [DOI: 10.1136/adc.60.9.843] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
GRADEpro GDT [Computer program]
- McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime) GRADEpro GDT. Version 3rd September 2020. Hamilton (ON): McMaster University (developed by Evidence Prime), 2015. Available at gradepro.org.
Gregory 1971
- Gregory GA, Kitterman JA, Phibbs RH, Tooley WH, Hamilton WK. Treatment of the idiopathic respiratory distress syndrome with continuous positive airway pressure. New England Journal of Medicine 1971;284(24):1333-40. [DOI: 10.1056/NEJM197106172842401] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Gribetz 1959
- Gribetz I, Frank NR, Avery ME. Static volume-pressure relations of excised lungs of infants with hyaline membrane disease, newborn and stillborn infants. Journal of Clinical Investigation 1959;38(12):2168-75. [DOI: 10.1172/JCI103996] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Harris 1996
- Harris TR, Wood ER. Physiologic principles. In: Goldsmith JP, Karotkin EH, editors(s). Assisted Ventilation. 3rd edition. Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1996:21-68. [Google Scholar]
Henderson‐Smart 2004
- Henderson‐Smart DJ. Recurrent apnoea. In: Evidence Based Pediatrics. Oxford: Blackwell, 2004. [Google Scholar]
Herman 1973
- Herman S, Reynolds EOR. Methods of improving oxygenation in infants mechanically ventilated for severe hyaline membrane disease. Archives of Disease in Childhood 1973;48(8):612-7. [DOI: 10.1136/adc.48.8.612] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Higgins 2011
- Higgins JP, Altman DG, Sterne JA; on behalf of the Cochrane Statistical Methods Group and the Cochrane Bias Methods Group [Green S, editor(s). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.1.0 (updated March 2011). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2011]. Available from handbook.cochrane.org.
Higgins 2017
- Higgins JPT, Green S (editors). Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions Version 5.2.0 (updated June 2017). The Cochrane Collaboration, 2017. Available from training.cochrane.org/handbook.
Ho 2015
- Ho JJ, Subramaniam P, Davis PG. Continuous distending pressure for respiratory distress in preterm infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2015, Issue 7. Art. No: CD002271. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002271.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Langston 1984
- Langston C, Kida K, Reed M, Thurlbeck WM. Human lung growth in late gestation and in the neonate. American Review of Respiratory Disease 1984;129(4):607-13. [PMID: ] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Miller 1990
- Miller MJ, DiFiore JM, Strohl KP, Martin RJ. Effects of nasal CPAP on supraglottic and total pulmonary resistance in preterm infants. Journal of Applied Physiology 1990;68(1):141-6. [DOI: 10.1152/jappl.1990.68.1.141] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Narendran 2003
- Narendran V, Donovan EF, Hoath SB, Akinbi HT, Steichen JJ, Jobe AH. Early bubble CPAP and outcomes in ELBW preterm infants. Journal of Perinatology 2003;23(3):195-9. [DOI: 10.1038/sj.jp.7210904] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Review Manager 2020 [Computer program]
- The Cochrane Collaboration Review Manager (RevMan). Version 5.4. The Cochrane Collaboration, 2020.
Richardson 1978
- Richardson CP, Jung AL. Effects of continuous positive airway pressure on pulmonary function and blood gases of infants with respiratory distress syndrome. Pediatric Research 1978;12(7):771-4. [DOI: 10.1203/00006450-197807000-00006] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Rojas‐Reyes 2012
- Rojas-Reyes MX , Morley CJ, Soll R. Prophylactic versus selective use of surfactant for preventing morbidity and mortality in preterm infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2012, Issue 3. Art. No: CD000510. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD000510.pub2] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Saunders 1976
- Saunders RA, Milner AD, Hopkin IE. The effect of CPAP on lung mechanics and lung volumes in the neonate. Biology of the Neonate 1976;29(3-4):178-81. [DOI: 10.1159/000240862] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Schünemann 2013
- Schünemann H, Brożek J, Guyatt G, Oxman A, editor(s). Handbook for grading the quality of evidence and the strength of recommendations using the GRADE approach (updated October 2013). GRADE Working Group, 2013. Available from gdt.guidelinedevelopment.org/app/handbook/handbook.html.
Subramaniam 2016
- Subramaniam P, Ho JJ, Davis PG. Prophylactic nasal continuous positive airway pressure for preventing morbidity and mortality in very preterm infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2016, Issue 6. Art. No: CD001243. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD001243.pub3] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Verder 1994
- Verder H, Richardson B, Griesen G, Ebbesen F, Albertsen P, Lundstrom K, et al. The Danish-Swedish Multicentre Study Group. Surfactant therapy and respiratory distress syndrome. New England Journal of Medicine 1994;331(16):1051-5. [DOI: 10.1056/NEJM199410203311603] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Wyszogrodski 1975
- Wyszogrodski I, Kyei-Aboagye K, Taeusch HW Jr, Avery ME. Surfactant inactivation by hyperventilation: conservation by end-expiratory pressure. Journal of Applied Physiology 1975;38(3):461-6. [DOI: 10.1152/jappl.1975.38.3.461] [PMID: ] [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
References to other published versions of this review
Ho 2002
- Ho JJ, Henderson-Smart DJ, Davis PG. Early versus delayed initiation of continuous distending pressure for respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2002, Issue 2. Art. No: CD002975. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002975] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ho 2007
- Ho JJ, Henderson-Smart DJ, Davis PG. Early versus delayed initiation of continuous distending pressure for respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants (amended). Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2007, Issue 2. Art. No: CD002975. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002975] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Ho 2010
- Ho JJ , Henderson-Smart DJ, Davis PG. Early versus delayed initiation of continuous distending pressure for respiratory distress syndrome in preterm infants.. Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews 2010, Issue 3. Art. No: CD002975. [DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD002975] [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


