Abstract
Telomerase plays critical roles in cellular aging, in the emergence and/or development of cancer, and in the capacity for stem-cell renewal, consists of a catalytic telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) and a template-encoding RNA (TER). TERs from diverse organisms contain two conserved structural elements: the template-pseudoknot (T-PK) and a helical three-way junction (TWJ). Species-specific features of the structure and function of telomerase make obtaining a more in-depth understanding of the molecular mechanism of telomerase particularly important. Here, we report the first structural studies of N-terminally truncated TERTs from Candida albicans and Candida tropicalis in apo form and complexed with their respective TWJs in several conformations. We found that Candida TERT proteins perform only one round of telomere addition in the presence or absence of PK/TWJ and display standard reverse transcriptase activity. The C-terminal domain adopts at least two extreme conformations and undergoes conformational interconversion, which regulates the catalytic activity. Most importantly, we identified a conserved tertiary structural motif, called the U-motif, which interacts with the reverse transcriptase domain and is crucial for catalytic activity. Together these results shed new light on the structure and mechanics of fungal TERTs, which show common TERT characteristics, but also display species-specific features.
INTRODUCTION
Telomerase is a specialized ribonucleoprotein that prevents chromosome shortening during replication by synthesizing telomeric DNA repeats from an RNA template de novo (1). Below a critical length threshold, telomere shortening ultimately leads to telomere fusions and cell senescence (2). However, aberrant activation of telomerase is deleterious, providing a mechanism for 90% of human cancers to bypass the tumor-suppressing activity of telomere shortening (3). Thus, a more thorough understanding of telomerase regulation may provide not only a molecular basis of cancer progression, but also a way to manipulate telomerase activity as a potential therapeutic option. The telomerase holoenzyme contains accessory proteins that are important for cell stability and/or activity (4–6); the catalytic core of telomerase consists of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) and template-encoding RNA (TER) (7,8). Human and other eukaryotic TERTs share conserved functional domains including the telomerase essential N-terminal domain (TEN), telomerase RNA binding domain (TRBD), the reverse transcriptase domain (RT) and the C-terminal extension (CTE) (Figure 1A) (9). Although the TERT protein is highly conserved across different species, TER varies dramatically in size, primary sequence, secondary structure and biogenesis pathway (10). Phylogenetic and functional studies have revealed that all TERs contain two conserved structural elements: the catalytically essential template-pseudoknot core domain (T-PK) and a stem-terminus element called the three-way junction (TWJ) (11). Despite much experimental effort, the detailed molecular mechanism of telomerase enzymatic activity regulation and the structural details of the interactions between the different domains and the other components of the complex (RT, TRBD, TER and telomeric DNA) are still not fully understood (12). The absence of a high-resolution, experimentally determined structure for the assembled telomerase core catalytic complex is a serious impediment to elucidating the molecular mechanism of telomerase action.
Figure 1.
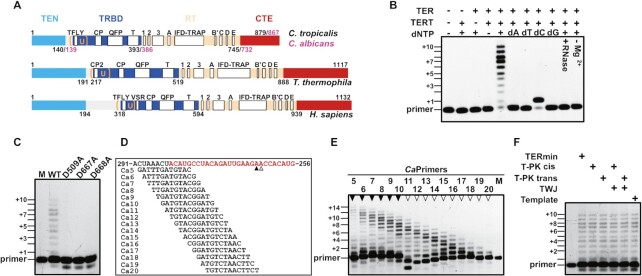
Characterization of the reverse transcriptase activity of Candida TERT. (A) Schematic presentation of the conserved domains/motifs of the TERT protein from yeast to humans. (B) Telomerase activity assays performed from reconstituted CaTERTFL-TERmin. Assays were performed as described in Methods with the telomeric DNA substrate Ca11 (5′-ATGTACGGATGT-3′) in the presence or absence of the TERT, TER, or dNTPs (0.4 mM), as indicated in the figure. Numbers (+1, +3, +5, +7 and +10, etc.) indicate the number of nucleotides incorporated by telomerase at the indicated band. Primer is Ca11. (C) In vitro telomerase activity assay performed with the wild type (CaTERTFL) and mutants (CaTERTFL/D509A, CaTERTFL/D667A, CaTERTFL/D668A) in which the putative active-site amino-acid residues were replaced by alanine. The assay was performed with the primer Ca10 (5′-GATGTACGGATG-3′) and CaTERmin. (D) Primer alignment with various sites of CaTERmin. The red marked nucleotide is template region, the arrowheads below the sequence indicate 3′-end positions of products shown in (E). (E) Recombinant telomerase exhibited varying processivity for primers with different 3′ ends in vitro. Numbers above the gel correspond to the primers shown in (D), while the arrowheads above the lanes indicate the 3′-end position of the product, corresponding to (D). Positions +2, +4, +6, +8 and +10 are indicated. (F) CaTERTFL telomerase activity is independent of the PK and TWJ. The assays were performed with the primer Ca10 under the same experimental conditions, in the presence or absence of various fragments of TER, as indicated.
The past years have seen exciting progress in determining telomerase holoenzyme architecture and the structural basis of telomerase activity (5,6,13–16). Cryo-EM structures of the human telomerase holoenzyme and that of the ciliate Tetrahymena have not only given the first glimpse into differences in subunit composition and architecture between two very distant species, but have also provided an interesting initial model which reveals common, conserved structural features (6,13). The recently refined Cryo-EM structure at 4.8 Å for Tetrahymena has revealed additional structural motifs that play an important role in telomerase activity regulation (16).
Because C-terminal ‘thumb’ domains of reverse transcriptase undergo significant conformational changes that are strictly required for polymerase activity (17), some studies have suggested that the telomerase CTE may also undergo changes from an open to a closed conformation during the catalytic cycle (18). For example, the study of the dynamics of TERT and TER during catalysis using single-molecule Förster resonance energy transfer (smFRET) (19), TERT modelling (14) and based on the structure of TERT in complexes with a BIBR1532 telomerase inhibitor (20) have suggested that CTE may undergo a conformational change. Electron microscopy images of human TERT have also suggested the existence of open and closed conformations (21).
The studies of species-specific features of telomerase structure and function can help understand the mechanistic conservation or divergence of particular pathways and interactions from structural conservation/divergence. Fungal telomerase has been extensively studied in budding yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Kluyveromyces lactis) (22–24), fission yeast (Schizosaccharomyces pombe) (25), Candida species (26–28), and Neurospora crassa (29), particularly their TER sequences, secondary structures and functions. The fungal telomere repeat base composition and length, binding factors and telomerase components are exceptionally diverse and distinct from those found in other eukaryotes (10,30). A unique feature of telomerase, which distinguishes it from other RTs, is its ability to repetitively reverse transcribe its relatively short RNA template after a single primer-binding event, a process known as repeat addition processivity (RAP) (31). However, unlike the core enzymes from humans and ciliates, some fungal telomerases appear to be naturally non-processive in repeat addition (22–24,32,33). One study suggested that yeast telomerase is processive for a single round of replication, and its telomeric repeat addition in cells is accomplished by multiple cycles of distributive action (22), indicating that fungal yeast telomerase may possess fundamentally distinct structural and mechanistic features (33). Very little is known about the fungal telomerase structure (12), because fungal telomerase, as well as other telomerases, have been particularly refractory to structural studies due to their naturally low abundance, their complexity and to the difficulty in obtaining stable recombinant proteins.
We have overcome the various difficulties in fungal recombinant TERT expression and structural analysis, and obtained the first crystal structure of the N-terminally truncated fungal TERT complexed with part of the TER from two Candida species in high resolution. The reconstituted telomerases can perform one round of telomere addition and can act as a standard reverse transcriptase in isolation. We solved several structures of N-terminally truncated Candida TERT alone and in complex with the TWJ and we observed a significant conformational change in the CTE domain, in a closed conformation. Most importantly, our structures reveal a previously unidentified structural motif (the U-motif), whose unique structure may serve to sense and transfer the template boundary definition signal to the active site.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
Protein preparation
The detailed protocols for CtTERT and CaTERT proteins expression and purification have been published under Chinese Patent with number of 202011599625.6. Briefly, the genes corresponding to the full-length CtTERT and CaTERT were cloned into the protein expression vector pET15b-SUMO (Takara) and transformed into the Escherichia coli strain BL21 (DE3) (Invitrogen), respectively. When the culture reached early stationary phase (OD600 = 0.5–0.6) at 37°C, 0.3 mM IPTG was added and the protein was overexpressed for 14 h at 18°C. Cells were harvested and pellets were resuspended in lysis buffer (20 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.8, 500 mM NaCl, 5 mM Imidazole and 5% glycerol) and lysed using an ultra-high pressure cell disrupter (JNBIO). After centrifugation, the supernatants were loaded onto a Ni-NTA column (QIAGEN), then the SUMO fusion protein was eluted with elution buffer (20 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.8, 500 mM NaCl, 500 mM Imidazole and 5% glycerol). The SUMO tag was cleaved with SUMO protease at 4°C overnight, and the protein was further purified by cation-exchange chromatography (HiTrap SP, GE Healthcare). The protein was finally purified by gel-filtration chromatography on HiLoad Superdex 200 pre-equilibrated with 20 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.8, 10% glycerol, 500 mM NaCl. After the final step, the purified proteins were about 95% pure as determined by SDS-PAGE and stored at –80°C. All mutant, truncated, SeMet-CtTERT178–879 and SeMet-CtTERT158–879 proteins were expressed and purified following the similar procedure as described above.
RNA preparation
The secondary structure of the full-length of TERs were calculated with RNAfold package and the template region, the TWJ structure and the pseudoknot structure were constrained and co-varying motifs were searched using CMfinder as Gunisova et al. (28).
The genes corresponding to the different-length TER fragments were either cloned into the pGEM 9Zf vector (Promega) or amplified by PCR as in vitro transcription templates. RNA was produced using T7 RNA polymerase for 4 h at 37°C. The optimum concentration of MgCl2 for each given RNA was individually determined, and ranged between 20 and 30 mM. RNA was purified on a Mono-Q column with a linear 100–1000 mM NaCl gradient in a buffer containing 20 mM HEPES–KOH, pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl and 5 mM MgCl2 and was concentrated to 5 mg/ml. The constructs with CtTWJ and CaTWJ were optimized to stabilize the P5 end and improve transcription efficiency by the addition of one/two G–C base pairs, respectively.
In vitro reconstitution of telomerase
Full-length or modified (truncated) TERT and the appropriate TER fragment (TERmin, T-PK and/or TWJ) were mixed at a 1:1.2 ratio and incubated in 50 μl reconstitution buffer (final concentrations: 10 mM HEPES–KOH, pH 8.0, 100 mM NaCl, 25% glycerol, 1 mM MgCl2, 3 mM KCl, 0.1 mM phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride, 1 mM DTT and 10 units/μl RNasin) at room temperature for 45 min and then placed at 33°C to produce recombinant telomerase, typically between 10–20 μM.
Telomerase activity assay
The direct primer-extension assay was used to detect telomerase activity. The primer-extension assay was initiated by the addition of 0.2–1 μM 12-nt DNA primer labelled at the 5′-end with 6-FAM into 25 μl reaction buffer (40 mM Tris–HCl, pH 8.0, 2 mM MgCl2, 1 mM spermidine, 100 mM NaCl, 20 mM KCl, 1 mM DTT, 0.2 mM dTTP, dATP, dCTP, and dGTP and 2 mM Mg(AC)2) containing ∼0.5 μM reconstituted recombinant telomerase. The reactions were incubated at 30°C for 40 min and stopped by the addition of 300 μl proteinase K buffer (100 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.4, 150 mM NaCl, 12.5 mM EDTA, 1% SDS and 400 ng/μl proteinase K) and then extracted with phenol/chloroform followed by ethanol precipitation. Extension products were resolved on a 15% polyacrylamide (19:1)/7 M urea denaturing gel. The gel was exposed using ChemiDoc XRS+ (Bio-Rad).
Crystallization
Purified apo proteins of CtTERT178–879 and CtTERT158–745 were concentrated to 8 mg/ml for crystallization. Purified CtTERT158–879 was mixed with the CtTWJ at a molar ratio of 1:1.3 and incubated on ice for 1 h to obtain a stable RNA–protein complex. Then, the complex (CtTERT158–879-TWJ) was purified by gel filtration chromatography over a Superdex 200 10/300 GL column in a buffer containing 250 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.8, 4 mM MgCl2 and 1 mM DTT. The elution peak, corresponding to the ribonucleoprotein, was collected, and concentrated to 8 mg/ml for crystallization. The sitting-drop vapor-diffusion method was performed at 18°C for crystallization. The apo protein (CtTERT178–879) was crystallized with a buffer containing 0.2 M sodium citrate tribasic dihydrate, 0.1 M Bis-Tris propane (pH 6.1), and 15% PEG3350. The crystal of the CTE-truncated protein (CtTERT158–745) was grown in 60% tacsimate (pH 7.0). Crystals of the CtTERT158–879-TWJ complex were grown in 0.2 M sodium citrate tribasic dihydrate, 0.1 M Bis–Tris propane (pH 6.1), and 13% PEG2000-MME as precipitant. All crystals grew to full size within five days. Then, crystals were collected into a cryo-protectant solution and flash frozen in liquid nitrogen. The cryo-protectant solution of CtTERT178–879 contained 0.2 M sodium citrate tribasic dihydrate, 0.1 M Bis–Tris propane (pH 6.1), 25% PEG3350 and 15% glycerol. The crystal of CtTERT158–745 was cryo-protected in 60% tacsimate (pH 7.0). Crystals of CtTERT158–879-TWJ were harvested into cryo-protectant solution containing 0.2 M sodium citrate tribasic dihydrate, 0.1 M Bis-Tris propane (pH 6.1), 28% PEG2000-MME, and 15% glycerol. The growth conditions and cryo-protectant solutions of crystals of SeMet-CtTERT178–879, SeMet-CtTERT158–879-TWJ and CtTERT178–879/366C-774C were the same as those used for their native or wild type crystals.
Purified CaTERT177–867 or CaTERT95–867 were mixed with the CaTWJ at a molar ratio of 1:1.3 and incubated on ice for 1 h to obtain a stable RNA-protein complex. Then, the complex (CaTERT177–867-TWJ or CaTERT95–867-TWJ) was purified by gel filtration chromatography over a Superdex 200 10/300 GL column in a buffer containing 300 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.8, 4 mM MgCl2 and 1 mM DTT. The elution peak, corresponding to the ribonucleoprotein, was collected and concentrated to 8 mg/ml for crystallization. Crystals of CaTERT177–867-TWJ and CaTERT95–867-TWJ were grown by sitting-drop vapor-diffusion at 18°C. Crystals of the CaTERT177–867-TWJ complex were grown in 0.2 M sodium citrate tribasic dihydrate, 0.1 M Bis–Tris propane (pH 7.5) and 17% PEG2000-MME as precipitant. Crystals of the CaTERT95–867-TWJ complex were grown in 0.1 M Buffer System 1 (1 M imidazole, 1 M MES monohydrate), pH 6.5, 0.1 M CA (0.2 M sodium formate, 0.2 M ammonium acetate, 0.2 M sodium citrate tribasic dihydrate; 0.2 M sodium potassium tartrate tetrahydrate, and 0.2 M sodium oxamate), and 30% GOL_P4K (40% glycerol and 20% PEG4000) as precipitant. All crystals grew to full size within five days. Then crystals were collected into cryo-protectant solution and flash frozen in liquid nitrogen. The cryo-protectant solution for CaTERT177–867-TWJ contained 0.2 M sodium citrate tribasic dihydrate, 0.1 M Bis–Tris propane (pH 7.5), 25% PEG2000-MME, and 15% glycerol. The crystal of CaTERT95–867-TWJ was cryo-protected with 0.1 M Buffer System 1, pH 6.5, 0.1 M CA, and 30% GOL_P4K. The growth conditions and cryo-protectant solutions of crystals of SeMet-CaTERT177–867-TWJ were the same as those used for their native type crystals.
Data collection, phasing and refinement
Datasets of CtTERT178–879/366C-774C were collected on the Proxima 2A beamline at the SOLEIL Synchrotron (France) and the rest of the diffraction data were collected on the BL17U1 and BL19U1 beamlines at the SSRF synchrotron (Shanghai, China) and processed using the XDS package (34). Crystals of CtTERT178–879, SeMet-CtTERT178–879 and CtTERT178–879/366C-774C belong to space group P41212. The remaining crystals of CtTERT, including CtTERT158–745, CtTERT158–879-TWJ and SeMet-CtTERT158–879-TWJ are all in the C2221 space groups. The CtTERT178–879 structure was solved by SAD using 2.46 Å data collected at the selenium peak wavelength. Phasing was performed using AutoSHARP software (35), with Se sites primarily found using ShelXD (36). After solvent flattening, the figure of merit was 0.70 and most of the residues could be built automatically with Buccaneer. The model was then manually built with Coot and refined with Phenix (37,38). The CtTERT158–745 and CtTERT178–879/366C-774C structures were solved by Molecular Replacement with Phaser using this model (39). The CtTERT158–879-TWJ structure was determined using the MR-SAD module of Phaser with 2.85 Å data collected at the selenium peak wavelength. The RNA structure was built manually and refined using ERRASER (40).
The CaTERT177–867-TWJ structure was determined using the MR-SAD module of Phaser with 3 Å data collected at the selenium peak wavelength. The RNA structure was built manually and refined using ERRASER (40). The CaTERT95–867-TWJ structure was solved by Molecular Replacement with Phaser using this model (39). Cell parameters and data collection statistics are reported in Supplementary Table S1.
Dynamic light scattering (DLS) assay
DLS measurements were performed at 20°C using a DynaPro NanoStar instrument (Wyatt Technology Corporation) with a thermostat cell holder. The protein concentration was 5–10 μM in DLS buffer (500 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.8, 5% glycerol). The measurement data was recorded every 5 s with a period of 50 s and analyzed with the Dynamics version 7.0 software by using regularization arithmetic (Wyatt Technology) as described previously (41).
Analytical size exclusion chromatography (SEC)
SEC measurements were performed using a Superdex 200 10/300 GL (24 ml) column at 20°C, which was equilibrated with S200 buffer (500 mM NaCl, 20 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.8, 4 mM MgCl2) at a flow rate of 0.3 ml/min. Approximately 100 μg purified protein was loaded onto the column and eluted in the S200 buffer at same rate and monitored the ultraviolet absorption at 280 nm. The calibration graph of log RS versus Kav was constructed using a calibration kit from Sigma: cytochrome c (12.4 kDa), carbonic anhydrase (29 kDa), albumin (67 kDa), phosphorylase b (97.4 kDa), and thyroglobulin (669 kDa). Assuming similar shape factors, the corresponding molecular weights of the Candida TERT were calculated with the plot calibration of log Mw versus Kav.
Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS)
All samples were buffer exchanged into 20 mM HEPES–KOH, pH 7.8, 250 mM NaCl, 4 mM MgCl2 and 5% glycerol and concentrated to 10 mg/ml. Data were collected at beamlines BL19U2 (SSRF, China) and SWING (SOLEIL synchrotron, France) in HPLC mode. For BL19U2 data, ∼40–60 μl of sample were injected into the size-exclusion chromatography column Superdex 200 10/300 (GE Healthcare) attached on an HPLC system at a flow rate of 0.3 ml/min and SAXS data were collected using a Pilatus 1M detector (Dectris) at a rate of 1 frame per second (2500 frames for total elution). For SWING data, ∼40–60 μl of sample were injected into the size-exclusion chromatography column Superdex 200 Increase 5/150 GL (GE Healthcare) attached on an Agilent 1100 HPLC system at a flow rate of 0.3 ml/min and SAXS data were collected using a Eiger 4M detector (Dectris) at a rate of 1 frame per second (560 frames for total elution) (42). The sample to detector distance covers the range of scattering vectors q from 0.001 to 0.5 Å−1. 2D data were processed and reduced with either BioXtas RAW for data from BL19U2 or Foxtrot software (Xenocs) for data from SWING (43). Further data processing, evaluation and calculation were done with programs of ATSAS 2.8 software package (44). Radius of gyration (Rg) was analyzed using the Guinier approximation with low angle data (q.Rg < 1.3) using PRIMUS. Ab initio modeling was done with program DAMMIF or MONSA for protein-RNA complexes. Fifty independent models were aligned, filtered and averaged with DAMAVER to provide the final ab initio envelope, which quality is estimated by averaged normalized spatial discrepancies (NSD). Full-atom models were generated with MODELLER (see Molecular modeling section). Rigid-body modeling of structures for orientation and position of individual domains in the structure modes were done with SASREF and SREFLEX programs. Further flexible modeling was done with DADIMODO (45). The comparison of experimental scattering intensities and calculated scattering intensities from the model are computed using program CRYSOL (v2.8.3).
Isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC)
Binding between TERT and TWJ was determined by Nano ITC (TA Instruments) at 20°C. TERT and wild type or mutant TWJ were dialyzed in reaction buffer containing 20 mM Tris–HCl, pH 7.8, 250 mM NaCl and 4 mM MgCl2. The titration was performed by injecting 10 μl TERT (50 μM) into the TWJ solution (10 μM) 24 times. The binding stoichiometry and dissociation constants were calculated by concatenating the three runs. Binding parameters were determined from the fit.
Molecular modelling
Since the crystal structures have some unresolved fragments, missing parts were predicted with Rosetta ab initio protocol and full-atom models were further generated with Modeller (46). CtTERT open structure was modelled from the CtTERT closed crystal structure and CaTERT open crystal structure as reference for CTE position. CtTERT open structure was superimposed in the cryoEM structure of TtTERT holoenzyme and DNA (5′-AGGATGTCACGATCATTGG-3′) and RNA (5′-UACACCAAUGAUC-3′) were modeled based on this structure (PDB: 6D6V). After manual inspection for clashes, the CtTERT open structure with DNA substrate and RNA template was energy minimized with Gromacs (47). From this structure, complex of closed CtTERT structure with DNA and RNA was modelled. CTE was moved in 1000 steps from open to closed position and each intermediate structure minimized. DNA and RNA were moving during this process, leading to the final CtTERT closed DNA/RNA model structure. Molecular dynamics calculation was done from CtTERT open structure with DNA and RNA using CHARMM36 forcefield during 0.5 s in periodic boundary box with TIP3 solvent at 298 K and 1 bar. Molecular dynamics trajectory was analyzed with the tools provided by Gromacs.
RESULTS
Telomerase activity from Candida is PK/TWJ-independent and non-processive in telomeric repeat addition
Recombinant telomerase proteins from C. albicans (CaTERT) and C. tropicalis (CtTERT) were highly purified and reconstituted with their core TER (TERmin), which were mostly composed of two ubiquitous structural domains: the template–proximal pseudoknot (T-PK) and a template–distal stem–loop moiety that consists of the P5, P6 and P6.1 stems connected in a three-way junction (TWJ) (Supplementary Figure S1) (28). The telomerase activity of the assembled ribonucleoprotein (CaTERTFL−TERmin) depended on the presence of the cognate template and dNTPs (Figure 1B). Pretreatment of the complex with RNase, omission of Mg2+ from the reaction buffer or replacement of one of the three conserved active site residues (D509, D667 or D668) of CaTERTFL completely eliminated activity (Figure 1B-C), indicating that the reconstituted telomerases possess intrinsic telomerase activity. Recombinant TERTs of both Candida species were able to perform one round of processive telomere addition, but without repeat addition processivity, as demonstrated by assays performed with a set of primers designed to align with the template region of the TERmin at different registration sites (Figure 1D and E). Furthermore, although the TERTs were assembled with isolated template or linked with the PK and/or TWJ in cis or in trans, the determined activities were identical to those with TERmin (Figure 1F). CtTERT showed essentially the same properties as CaTERT (Supplementary Figure S2A–C).
Thus, the above results revealed at least two distinct characteristics of Candida TERTs. First, although it is widely recognized that a unique property of telomerase as a reverse transcriptase is its ability to make consecutive copies of telomere repeats, the Candida telomeres are nonprocessive in terms of telomere repeat addition. This may be an intrinsic property of Candida TERTs and is consistent with previous observations that yeast telomerase add only one telomeric repeat to a DNA oligonucleotide primer (22–24,32,33). Further investigations are required to identify whether these TERTs have evolved a multiple-cycle distributive mechanism to handle the unusually long telomeric sequence (23–26 nt) (28). Secondly, it has been documented that at least two conserved structural motifs in TER (T-PK and TWJ) are essential for stimulatory functions in vertebrates, the filamentous fungus N. crassa and the fission yeast S. pombe (10,29). However, budding yeast (S. cerevisiae) TERT has exceptionally evolved to not rely on the TWJ for enzymatic function (48). Surprisingly, we found that Candida TERT replicates the telomeric sequence in vitro with just its RNA template, raising the possibility that Candida TERT acts as a conventional reverse transcriptase with a non-telomerase RNA template. To confirm this point, DNA primer extension assays were performed with three additional RNAs that were non-telomeric templates and/or random RNA templates with differences in base composition and length (Supplementary Figure S3). As shown in Supplementary Figure S3, Candida TERTs efficiently replicate the ‘input’ RNA templates, indicating that Candida TERTs indeed function as a typical reverse transcriptase. Although this finding is striking, it is far from unprecedented. A similar phenomenon has been observed in TERT from T. castaneum in which the TERT bound to an RNA–DNA hairpin resembling the putative RNA-templating region and telomeric DNA extended three bases in the presence of an non-telomerase RNA template (49). The mechanistic basis through which fungal TERT has evolved less dependence on RNA structures for catalytic activity remains to be clarified. It is noteworthy that fungal telomerase ribonucleoprotein structure and organization is more complex than most other telomerases (12). Candida TERs are unusually long both in the whole sequence and in the template region, which can be as long as 25–28 bp, but less G-rich (28). These peculiarities in TER structure may provide evolutionary pressure for TERT to behave more like a conventional reverse transcriptase.
The overall structures of the TERT-TWJ complexes from Candida species are conserved
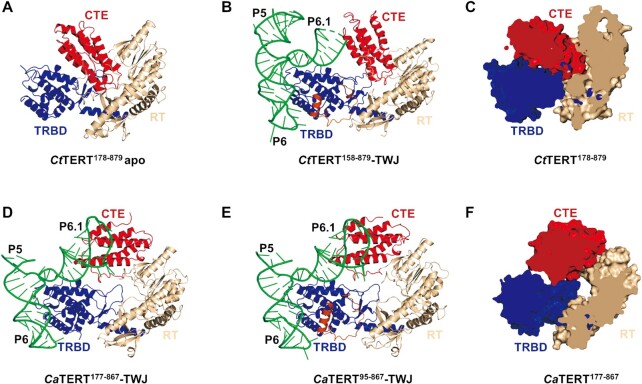
We explored the structural basis of the observed functional properties by carrying out structural studies on TERTs from Candida. Although full-length TERT is not easily crystallized, N-terminally truncated TERT from C. tropicalis in apo form (CtTERT178–879) and complexed with its TWJ (CtTERT158–879-TWJ), as well as TERT from C. albicans complexed with its TWJ (CaTERT177–867-TWJ, CaTERT95–867-TWJ), were crystallized and diffracted to 2.47, 2.85, 2.98 and 3.46 Å, respectively (Figure 2A–C and D–F, respectively, Supplementary Table S1). Consistent with the high levels of sequence conservation between CaTERT and CtTERT (with 44% identity and 81.05% similarity, Supplementary Figure S2D), folding of the individual domains, including TRBD, RT domain and the CTE domain, was very similar between the two Candida TERTs, with a root mean square deviation (r.m.s.d.) of 0.782–0.958 Å (Supplementary Figures S4–S6). In contrast, structural alignment across the available TERT structures for either the full-length T. castaneum (TcTERT, PDB 3DU6) (50) and T. thermophila (TtTERT, PDB 6D6V) (16) or isolated domain O. latipes (OlTERT, PDB 4O26) (14) showed an r.m.s.d. of 2.98, 3.51 and 3.77 Å over 160 Cα, respectively, with CtTRBD (Supplementary Figure S4). The r.m.s.d. values of the CtRT domain calculated from TcTERT and TtTERT over 224 Cα ranged from 3.63 to 4.92 Å (Supplementary Figure S5). The CTE domain superimposed on those of TcTERT and TtTERT over 128 Cα yielded an r.m.s.d. of 3.67 and 3.92 Å, respectively (Supplementary Figure S6). Noteworthily, the individual domains of TERT from different species are generally structurally conserved, and there are no specific regions except for the lack of TRAP-motif in the TcRT domain (Supplementary Figure S5) (16,50). Moreover, the TRAP-motif from the RT domain was only partially visible by electron density and fragments 552–564 and 578–582 were not defined for CaTERT177–867, nor were fragments 568–593 for CtTERT178–879 (Supplementary Figure S5A–B).
Figure 2.
Structures of Candida TERT proteins in apo and complexed with the TWJ. (A) Overview of the organization of the apo CtTERT178–879 domain. The RNA-binding domain (TRBD) is shown in blue, the reverse transcriptase domain (RT) domain is in wheat, and the C-terminal domain (CTE) in red. (B) Structural view of CtTERT158–879 complexed with the CtTWJ. The TWJ is shown in green and the U-motif is orange. (C) and (F) Cut-away views of CtTERT178–879 (C) and CaTERT177–867 (F) are shown, respectively. (D) and (E) Structural view of the CaTERT177–867-TWJ complex (D) and CaTERT95–867-TWJ (E), respectively.
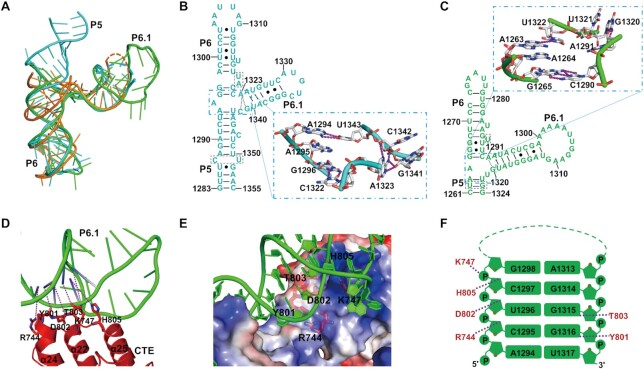
The TWJ has been proposed to be necessary for vertebrate telomerase activity and potentially interacts with the CTE domain (14,51–53). In contrast to the previously determined structure of the TWJ complexed with an isolated TRBD domain (14), our TERT-TWJ complex structures were solved with the catalytic core telomerases of Candida, revealing TWJ binding and its spatial configuration in the context of the N-terminally truncated TERT molecule (Figure 2B, D–E). Candida TWJs adopt similar folding and spatial conformation as the OlTWJ, except that CtTWJ appears as a Y-form due to a 12 base-pair-long double strand in its stem (P5) (Figure 3A). Although, P6 and P5 are maintained by coaxial stacking as a contiguous helix, as observed in the OlTRBD-CR4/5 complex (Figure 3B–C), the previously described two-base triple helix at the P5–P6 junction in the OlTWJ was absent in Candida TWJ (Supplementary Figure S7A–C) (14), indicating that such RNA base stacking is not necessary for maintaining the three-branch junction conformation of the TWJ in fungi. The global geometry of the intermolecular interactions between the TWJ and TRBD are similar to those shown for OlTRBD-CR4/5 (14). For example, the triangular protrusion of TRBD is wedged into the cleft composed of P6 and P6.1 (Figure 2B, D–E) and the amino acids involved in the TWJ interactions are highly conserved. Mutations of the highly conserved adenine base at the invariant P6–6.1 junction (A1323 in CtTWJ or A1291 in CaTWJ) hindered TWJ folding, maintaining its conformation and thus TERT binding (Supplementary Figure S7D–E).
Figure 3.
Structural view of the TWJ solved from the TERT-TWJ complexes. (A) Superposition of the crystal structures of CtTWJ and CaTWJ with that of OlTWJ (Ol-CR4/5, PDB: 4O26). CtTWJ is shown in cyan, CaTWJ in green, and Ol-CR4/5 in orange. (B, C) Secondary structures of CtTWJ and CaTWJ in which the bases involved in the three way junction (P5-P6-P6.1) were enlarged as the crystal structure presentation. (D) Detailed structural view of the interactions between CTE and P6.1 of CaTWJ. (E) RNA backbone–mediated interactions between the TWJ and CTE domain of CaTERT. The CTE domain is shown as an electrostatic potential surface in which the amino acids interacting with the RNA sugar-phosphate backbone are indicated. (F) Schematic diagram of the TWJ-CTE interactions from CaTERT. Stems P6.1 of the TWJ are shown in green and their interacting CTE residues are shown in red. Hydrogen bonds are represented by purple dashed lines.
Although the interactions between P6.1 and the CTE domain in CtTERT158–879-TWJ cannot be precisely determined because of poor electron density for the stem-loop of P6.1, the structure of CaTERT177–867 complexed with the TWJ provided accurate information on the recognition of the CTE domain by P6.1 (Figure 3D–F). Stem P6.1 consists of eight base-pairs, adopting a double-helical conformation in the A-form, essentially composed of the canonical Watson-Crick helix with two wobble base-pairs (Figure 3D-F). Major positively charged residues from the CTE domain of helix α22 and those from the loop interact with helix α24, and helix α25 mainly interacts with the sugar-phosphate backbone of the minor groove of stem P6.1 (Figure 3D-F). Our crystal structures obtained with apo-TERT and those complexed with the TWJ from CaTERT and CtTERT shed new light on the mechanism underlying the recognition of the CTE domain by the TWJ.
The CTE domain assumes two extreme conformations in crystals
Although the overall structures of TERT and/or TWJ are conserved, there was a substantial difference in the spatial orientation of the CTE domain between CaTERT177–867 and CtTERT178–879. The previously determined structures of TcTERT and TtTERT show that the conserved TRBD, RT, and CTE domains create a ring-shaped cavity in which the RNA-DNA helix appears to be docked (5,49,50). However, although the conserved domains in the CaTERT177–867-TWJ structure form a ring-like shape, as observed in TtTERT, the CTE domain of CtTERT178–879 collapses by 108° relative to that of CaTERT177–867 and occludes the cavity, making the CTE domain perpendicular to the RT domain and vertically parallel to the TRDB (Figure 2A, C). Such spatial orientation of the CtCTE is surprising and raises the question of whether the observed CTE orientation is an intrinsic structural property in solution or just an artifact of crystal packing. First, close inspection of our crystal structure revealed that the spatial configuration of CTE is determined by a network of polar contacts between TRBD and RT (Supplementary Figures S8A, C–D and S9C). It is particularly evident that when the molecule assumes the rotational configuration of 45°, the CTE appears to be sitting on a sofa which is composed of TRBD and RT as the main body and the T-motif and IFD-TRAP motif as the armrest on both sides (Supplementary Figure S8B). Thus, the CTE conformation constrained by extensive and exquisite interactions is unlikely to be due to the crystal packing. Second, to further probe the configuration of CTE in solution, small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) coupled with size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) was used to determine the spatial conformations of the CTE in the context of the full-length TERT (CtTERTFL) and the N-terminal domain (TEN) truncated form (CtTERT178–879). Two models corresponding respectively to CtTERTFL and CtTERT178–879 were established from ab initio SAXS envelops followed by rigid body refinement of our crystal structure or/and homologous TEN structure from H. polymorpha TERT (54). The full-length (CtTERTFL) and TEN-truncated TERT (CtTERT178–879) are well accommodated with the corresponding SAXS envelops, in which the CTE has always occupied the central position of the cavity (Supplementary Figure S8E-F). Finally, in fact, crystals grew from the same protein (CtTERT178–879) under multiple conditions, and the resolved structures were the same. Altogether, these findings and arguments indicate that the collapsed conformation of CTE is an intrinsic structural property.
Overlaying the apo-CtTERT178–879 and TWJ-bound CtTERT158–879 structures showed that TWJ binding does not turn the CTE domain to the equivalent spatial position as in TcTERT to form a ring-like conformation, but rather the CTE domain is pushed away by 29.5° in the forward direction (Supplementary Figure S9A). In addition, TWJ binding disrupts the amino-acid interactions between the CTE domain and both the T-motif and TRAP-motif, maintaining the spatial position of the CTE domain relative to TRAP-motif and the T-motif in apo-TERT (Supplementary Figure S9B-D).
The flexible CTE domain plays a regulatory role
We determined the spatial conformation of the CTE domain in solution using SEC, dynamic light scattering (DLS), and SEC-SAXS. Characterization of the full-length and/or N-terminally truncated TERTs (CaTERT and CtTERT) in their apo-form with SEC and DLS showed these proteins to be monomeric in solution, in concordance with the crystal structures (Supplementary Figure S10G). SEC-SAXS was further used to correlate the conformation of the entire molecules, particularly the spatial configurations of the CTE domain in solution, with those in the crystallographic structures (Supplementary Tables S2–3). The SAXS data obtained with the same apo-TERTs used for the crystal-structure determinations (CaTERT177–867 and CtTERT158–879) could be fitted with the rigid-body models, in which the CTE domain assumes either an open or closed conformation (Supplementary Figure S10A-F and Supplementary Tables S2–S3). However, the χ2 values calculated from the crystal structure, leaving the CTE domain as a mobile rigid body, improved significantly from 1.36 to 1.07 and 2.23 to 1.15 for CaTERT177–867 and CtTERT158–879, respectively (Supplementary Figure S10A–F and Supplementary Tables S2–S3). Overall, the combined structural and SAXS evidence suggests that the open conformation of the CTE domain in CaTERT and the closed conformation of the CTE domain in CtTERT represent two extreme conformations as the CTE domain freely rotates in solution.
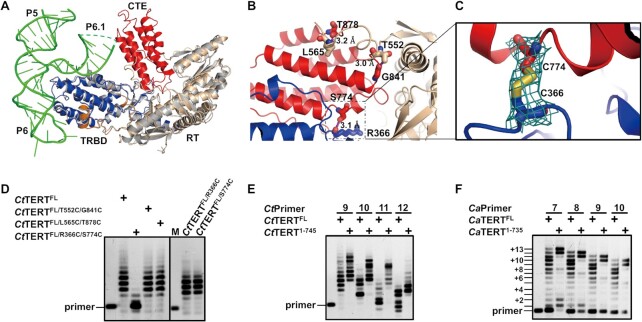
We further speculated that if the CTE domain does rotate freely, then the conformation of the TRBD and RT domains should be independent of the presence of the CTE domain. To confirm this hypothesis, we crystallized the CTE-domain deleted mutant CtTERT158–745 (CtTERTΔCTE), in which the C-terminal residues 746–879 were entirely deleted. Superimposition of the crystal structures of CtTERT158–879 and CtTERTΔCTE over the entire TRBD and RT domain (475 Cα) yielded an r.m.s.d. value of 0.911 Å (Figure 4A), showing that the folding and spatial positions of TRBD and the RT domain are independent of the CTE domain. We next sequentially replaced three pairs of residues at the interface between the CTE and RT domains with cysteine residues to restrain CTE in its closed conformation through disulfide bonds to better understand the functional impact of the CTE domain on telomerase activity (Figure 4B). Biochemical and crystal structure analysis of the three mutants showed only CtTERTR366C/S774C to form the expected disulfide bond (Figure 4B and C). Activity assays performed with the wild type and mutants including individual mutations (CtTERTFL/R366C and CtTERTRFL/S774C) showed that although the mutants without disulfide-bond formation (CtTERTFL/T552C/G841C and CtTERTFL/L565C/T878C) displayed the same activity as the wild type enzyme (CtTERTFL), the activity of CtTERTFL/R366C/S774C was fully impaired (Figure 4D). Overall, these results show that the CTE domain freely rotates and constraining it in a closed conformation is prohibitive to primer extension activity.
Figure 4.
Structural and functional analysis of CTE domain. (A) Structural superposition of apo-CtTERT158–745 (gray) and CtTERT158–879 complexed with TWJ indicates that the TRBD and RT domains can overlap completely. (B) Presentation of the replaced three pairs of residues with cysteine residue to constrain CTE in closed conformation. (C) Electron density map of the disulfide bonds between C774-C366 of CtTERT178–879/R366C/S774C. (D) Telomerase activity of the wild type and mutant CtTERT, as indicated. The experiments were initiated by adding 2 μM in vitro-reconstituted TERT-TERmin complex in the presence of 1 μM telomeric DNA primer (5′-TTAGTGTAAGGA-3′). (E, F) Telomerase assays with the full-length wild type (CtTERTFL and CaTERTFL), CTE-truncated (CtTERT1–745 and CaTERT1–735). The assays were performed as indicated in (D), but with different telomeric DNA primers, as indicated above the gel.
CTE-domain rotation may affect the stability of the RNA/DNA duplex and regulate processivity
Based on the spatial configuration of the heteroduplex formed between the RNA template and telomeric DNA relative to the RT:TRBD:CTE subcomplex in the Cryo-EM structure of Tetrahymena (16), we first modelled the open conformation of CtTERT178–879 complexed with its endogenous RNA/DNA duplex. In the pre-initiation state, the primer-template duplex adopted a helical structure and docked into the cavity in which the 3′-end of the telomeric primer, paired with the RNA template, interacts with the putative residues of the active site (Supplementary Figure S11). Modelling the closed conformation, in which the CTE domain turns in a counterclockwise direction, resulted in steric clashes between the CTE domain and the DNA/RNA duplex, in which the double-stranded RNA/DNA is destabilized and pushed apart (Supplementary Figure S11). Further modelling and energy minimization of the closed structure showed that the DNA/RNA duplex is clipped by the CTE domain and finally separated (Supplementary Figure S11 and Supplementary Movie S1). Similarly, molecular dynamic simulation from the open structure of CaTERT towards the closed conformation of CtTERT further confirmed the flexibility of the CTE domain. Based on the above modelling results, we reasoned that a C-terminal truncated version of TERT would display enhanced processivity during one round of telomere addition, because the destabilizing effect of the CTE domain on the RNA/DNA duplex would be eliminated (Supplementary Figure S17). Consistent with this hypothesis, telomerase activity assays performed with the full-length wild type (CaTERTFL and CtTERTFL) and CTE-truncated mutants (CaTERT1–735 and CtTERT1–745) under the same experimental conditions demonstrated that both CTE-truncated TERTs display markedly enhanced processivity (Figure 4E-F and Supplementary Figure S17).
A conserved U-motif is critical for telomerase activity and regulation
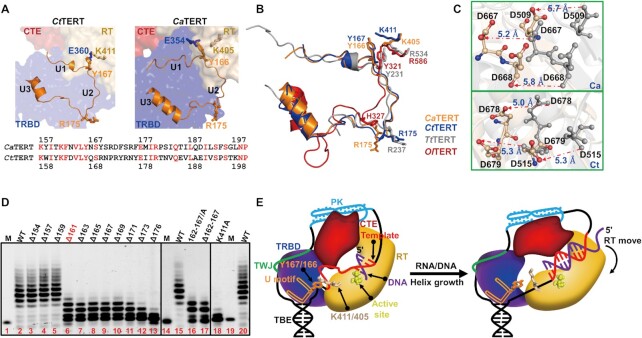
A conserved structural motif looks like a chain of mountains placed in a fixed and orderly fashion on the TRBD surface (Figure 5A and Supplementary Figure S12A, E). The motif is composed of connected U-like structure (that we hereafter call a U-motif) that spans amino acids 157–199 in CaTERT and 158–200 in CtTERT (Figure 5A and Supplementary Figure S12A, E). The U-motif averages about 45 amino acids and consists of two short α-helices connected by unstructured loops (Supplementary Figure S13). The unstructured loops/linkers are not completely disordered, relatively constrained by extensive interactions as described and demonstrated in Supplementary Figure S12 (Supplementary Figure S12). The U1 fragment (157–166) closely resembles the TFLY (vertebrate) (55) and the first half of the CP2 (ciliate) (15,56) motifs (Supplementary Figure S14). The U2 fragment (167–175) is mainly constrained through hydrogen bonds with residues (A354, V358, E360 and H374) of the T-motif. The extended U2 loop with α-helices constitute the U3 fragment (176–192), which extends in parallel with α-helix 12 of the TRBD through a set of hydrophobic interactions (Supplementary Figure S12D). Y167 at the outer corner 1 (between U1 and U2) directly interacts with K411 on the β-strand 4 of the RT domain through a strong cation-π interaction (Figure 5B, Supplementary Figure S15A-B), whereas R175 at the outer corner 2 (U2-U3) occupies the equivalent position of R237 in CP2, which wedges into the template boundary element (TBE) stem-loop in Tetrahymena (15) (Figure 5B). Sequence alignment showed that the whole amino-acid sequence of U-motif—not just that constrained around CP2/TFLY, but particularly the residues involved in the spatial conformation between the U-motif and the RT domain, including Y167 of corner 1 and K411 of the RT domain, are highly conserved among telomerases (Supplementary Figure S13 and Supplementary Figure S15F). Consistently, the U-motif and its interactions with the RT domain are perfectly conserved across the available structures of TERTs, including those from T. thermophila (15,16), O. latipes (14) and T. rubripes (55) (Figure 5B and Supplementary Figure S15A–E). The significant differences and similarities between the U-motif and the previously identified CP2/TFLY motif will be further summarized after the functional characterization of the U-motif (below).
Figure 5.
Newly identified U-motif structure and function. (A) The identified U-motif conformation and key residues in CtTERT (left) and CaTERT (right). The detailed interactions are shown in Supplementary Figure S12. The residues of U-motif from CaTERT and CtTERT are shown below the figure. (B) Superimposition of the identified U-motif structures in CaTERT (orange), CtTERT (blue), TtTERT (gray, PDB: 6D6V), and OlTERT (red, PDB: 4O26). (C) Significant movement of the key residues in the active site of CaTERT (above) and that of CtTERT (bottom) in the presence of the integral U-motif (gray) and partially truncated U-motif proteins (wheat). Additional conformational changes and the detailed interactions are shown in Supplementary Figure S16B-C. (D) Telomerase activity assays performed with a series N-terminally truncated or structure-guided point mutants from CtTERT. WT is CtTERTFL, Δ154 means residues 1–154 are deleted, namely CtTERT155–879, and others are similar to this; 162–167/A and Δ162–167 mean residues from 162 to 167 either systematically substituted by alanine or entirely deleted on the basis of the full-length CtTERT; K411A means residue K411 substituted by alanine, namely CtTERT1–879/K411A. The experiments were carried out under experimental conditions as described in Figure 4D. (E) Proposed model for the U-motif-mediated conformational change upon the completion of telomeric synthesis. The RNA template is bound between the TBE stem at its 5′-end and a PK motif at its 3′-end. Similarly, as observed in the TtTERT-TER complex structure determined by Cryo-EM, TER embraces the TERT. While the spatial positions of the TBE and PK are mobilized by the U-motif and other regions of TERT, the single stranded RNA template is flexible prior to replication (left). However, as the RNA template is replicated, the RNA/DNA hybrid becomes shorter than the ssRNA. The produced tension rotates the global conformation between the TRBD and RT domain and consequently disrupts the cation-π interaction between Y167/166 and K411/405 (right), which is essential for maintaining TERT in an active conformation.
The CP2 motif in Tetrahymena located at the corner 2 position has been structurally characterized (15). We focus our attention on the function of corner 1. To this end, the N-terminal residues of full-length CtTERT were successively truncated to N176. Telomerase activity assays showed that proteins bearing truncations up to position 159 display telomerase activity identical to that of full-length TERT, whereas further truncation beyond residue 161 severely impaired primer extension, indicating that the complete overall corner 1 plays an essential role in telomere addition (Figure 5D). We confirmed these results by constructing two additional types of mutants, in which residues K162 to Y167 of the full-length TERT were either systematically substituted by alanine or entirely deleted, resulting in mutants CtTERT162/A-167/A and CtTERTΔ162–167. The mutants showed the same level of reduction in telomerase activity as those bearing truncations beyond Y161 (Figure 5D). CaTERT showed essentially the same properties as CtTERT (Supplementary Figure S16A).
To understand the structural basis of how corner 1 in the U-motif affects telomerase activity, even though it is distant from the active site, the structures of CtTERT158–879 complexed with the TWJ bearing the full-length U-motif (CtTERT158–879) and CtTERT178–879, in which both corner 1 and 2 were completely truncated, were superimposed based on the Cα or backbone atoms of the TRBD (r.m.s.d. of 2.58 Å for 472 Cα). This analysis showed marked structural rearrangement, with notable changes in the RT domain of CtTERT178–879. Truncation of the U-motif resulted in disruption between Y167 and K411 and thus the overall RT domain is distorted by 16.9° and pushed up 15 Å, which twists the entire active site by 24.6° and moves it away by ≈ 5 Å (Figure 5C and Supplementary Figure S16B-C). In accordance with the above interpretation, the replacement of K411 with alanine significantly reduced telomerase activity (Figure 5D). It is noteworthy that the above results are consistent with the previous observations from the studies with telomerases of other species. Both mutants R503A (S. pombe) and R534A (ciliate) at the equivalent position of K411 of CtTERT severely impair telomerase activity (25,57). Of note, the integral U-motif and its interaction with the RT domain was identified with CtTERT158–879 complexed with the TWJ, whereas such a structural interaction was absent in CtTERT178–879. This raises the question of whether folding of the U-motif and the interaction between Y167 and K411 results from TWJ binding. We thus superimposed the crystal structure of CtTERT158–745, which bears an integral U-motif, with that of CtTERT158–879. The resulting r.s.m.d. of 0.911 Å showed the conformations and interactions of Y167 at corner 1 and K411 at the RT domain to be nearly identical between the two crystal structures (Figure 4A), indicating that the newly identified U-motif is an intrinsic structure of TERT that stabilizes the active conformation of telomerase independently of the TWJ. Overall, mutational and structural analysis shows that the interaction between the U-motif and the RT domain is very important for maintaining the structural integrity of TERT and, therefore, orientating the spatial configuration of the active site relative to the RNA template (Figure 5A, E).
Putting the previously identified CP2/TFLY into the U-motif framework could offer a new perspective on the organization of previously recognized isolated components and potential functions, which have not formerly been recognized. The distinct features and the novelty of the U-motif can be summarized as: (i) the U-motif concept expands our knowledge of CP2/TFLY. The CP2 motif, which harbors the α-helix of TFLY, was previously defined just as a 12-amino-acid sequence conserved across ciliate species (56). It is now clear that both CP2 and TFLY are partial components of the U-motif and may possess additional functions (Supplementary Figure S13 and Supplementary S14); (ii) the U-motif is not just analogous to CP2/TFLY; under this framework, previous findings may be better understood and potential functions of some residues in the U-motif can be deduced. For example, realizing that the two residues (H234 and R237 in ciliates) (15) are located in the rigid corner 2, but not in an unstructured flexible loop, will help understand how the two residues remain at their physical position to serve as a wedge, rather than moving together with the TBE while the RNA template is stretched. Furthermore, only when the corner organization feature was taken into account, did we identify the interaction between Y167-K411 at corner 1, which is structurally and functionally conserved across different species; (iii) the two physical corners may play distinct functions and coordinately communicate with each other. It is possible that corner 2 acts as a sensor to perceive the replication stop signal and results in the disruption of Y167-K411 interaction at corner 1. Additional studies on the U-motif will be required to gain a better understanding of the precise regulation of telomere synthesis.
DISCUSSION
In this study, we determined several crystal structures of N-terminally truncated fungal TERTs in apo- and TWJ-bound forms. These data, together with our biophysical and biochemical data, provide important insights into the domain or motif organization and the potential molecular mechanisms of telomerase activity regulation.
Studies previously demonstrated that two conserved TER structural elements (the PK and the TWJ) are particularly important for the telomerase activity in vertebrates and ciliates, but not for S. cerevisiae telomerase in which the telomeric sequence can be added in the absence of TWJ (10). We surprisingly found that the fungal TERTs characterized in this work can act as standard reverse transcriptases and neither PK nor TWJ are required to efficiently catalyze primer extension. The mechanisms of TWJ/PK-dependent and -independent activity are completely unknown (10,11). The fact that the spatial conformation of the U-motif relative to the RT domain is well assembled into an active state in the absence of a TWJ/PK in Candida TERTs may explain why the telomerase activity of Candida is TWJ/PK-independent. These observations in turn raise the possibility that the cation-π interaction between the U-motif and the RT domain does not occur in the absence of the TWJ/PK for the TWJ-dependent telomerase in the apo-form and that TWJ binding promotes the necessary interaction between the U-motif and the RT domain, probably through the highly conserved tyrosine residue in the U-motif and the lysine in the TR domain, thereby activating telomerase activity. The above interpretation needs to be verified by comparing the structures determined with TWJ/PK-dependent telomerase in apo- form and complexed with the TWJ/PK.
The addition of consecutive copies of telomeric repeats involves extremely complex and delicate processes, including dissociation, translocation and realignment of the RNA-DNA hybrid (31). Telomerase must undergo extensive domain or motif rearrangements for each round of telomere addition to accomplish these tasks (58). However, such structural mobility remains speculative and direct structural evidence is still lacking (12). Here, we not only trapped two extreme conformations of the CTE domain, an ‘open’ state and a ‘closed’ state, but also demonstrated that the CTE domain can undergo rapid conformational interconversion. The discovery that CTE collapses into a TERT cavity and forms a closed conformation is surprising, although this tremendous flexibility of the CTE domain is analogous to the flexibility of the thumb domain observed in structures of HIV-1 RT (59) and pol ν (60). Since the significance of the closed conformation of TERT is not yet fully understood, it is tempting to speculate that the closed conformation may exist as a stable intermediate form before binding to TER and the correct positioning of template in active site. It may also prevent binding of TERT with other non-specific long non-coding RNAs. However, although deletion of the CTE domain does not affect telomerase activity, constraining the CTE into the closed conformation results in impaired primer extension activity. This confusing phenomenon can be best interpreted to mean that CTE is not absolutely required for telomerase activity, but it plays a regulating effect to adjust primer extension. Although we were unable to obtain a crystal structure of TERT complexed with the putative RNA-template and telomeric DNA, our molecular modelling results show that the movement/rotation of the CTE domain can alter the steric position of the DNA/RNA hybrid relative to the active site (Supplementary Figure S11 and Supplementary Movie S1). Therefore, further studies are needed to confirm that conformational flexibility of the CTE domain revealed here is a general mechanism of telomerase regulation.
The detailed mechanism by which telomerase concurrently senses the completion of one round of telomere addition and triggers dissociation of the DNA/RNA hybrid from the active site remains unknown. The identified U-motif-bound TBE may assume such a double role. As shown in Figure 5E, the RNA template is linked to the PK at its 3′ end and the TBE, as an RNA hairpin, is fixed via corner 2 of the U-motif at its 5′ end. Because the TBE is anchored to the U-motif and NTPs are incorporated into the active site, the end-to-end distance of the 25–30 nt single-stranded RNA template will be significantly reduced due to the formation of the RNA/DNA double helix. The produced tension distorts the relative spatial conformational arrangement between the TRBD and RT domains, which accompanies disruption of the cation-π interaction between Y167 and K411, as observed in the crystal structure of CtTERT158–879. The resulting alteration in the spatial conformation between the active site and RNA template simultaneously drives dissociation of the RNA/DNA hybrid and halts telomeric synthesis (Figure 5E and Supplementary Figure S17 and Supplementary Movie S1).
DATA AVAILABILITY
Structures of CtTERT and CaTERT have been deposited in the PDB with the following accession numbers: 6ZD1 (CtTERT178–879 apo), 6ZD2 (CtTERT158–745), 6ZDP (CtTERT158–879-TWJ), 6ZD6 (CtTERT178–879/R366C-S774C), 6ZDQ (CaTERT177–867-TWJ), 6ZDU (CaTERT95–867-TWJ).
Supplementary Material
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Dr Qian Zhang performed many CaTERT177–867-TWJ complex crystallization assays at the early stage of this work. We thank beamline scientists at BL17U1 of the Shanghai Synchrotron Radiation Facility, and at BL18U1, BL19U1 and BL19U2 of the National Center for Protein Science Shanghai, for assistance with data collection. We are grateful for access to the SOLEIL (SWING and Proxima 2A) synchrotron radiation facility for SAXS and crystal data collection. We also acknowledge Dr Na-Nv Liu for much help in the manuscript editing.
Authors contributions: L.-T.Z. carried out the bulk of the experiments. L.-T.Z. and W.-F.C. collected crystal diffraction data. S.R. determined the crystal structures, performed SAXS experiments and analyzed SAXS data. S.R. and D.A. performed MD simulations. Z.-Y.S. participated in additional protein and RNA purifications. X.-G.X., S.R., S.-X. D., B.S. and L.-T.Z. analyzed the data and X.-G.X. established the procedures including the plasmids construction, expression, and purification of the two recombinant TERTs, conceived the project and wrote the paper.
Contributor Information
Liu-Tao Zhai, State Key Laboratory of Crop Stress Biology in Arid Areas, College of Life Sciences, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, Shaanxi 712100, China.
Stephane Rety, University Lyon, ENS de Lyon, University Claude Bernard, CNRS UMR 5239, INSERM U1210, LBMC, 46 Allée d’Italie Site Jacques Monod, F-69007 Lyon, France.
Wei-Fei Chen, State Key Laboratory of Crop Stress Biology in Arid Areas, College of Life Sciences, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, Shaanxi 712100, China.
Ze-Yu Song, State Key Laboratory of Crop Stress Biology in Arid Areas, College of Life Sciences, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, Shaanxi 712100, China.
Daniel Auguin, Laboratoire de Biologie des Ligneux et des Grandes Cultures (LBLGC), Université d’Orléans, INRA, USC1328, 45067 Orléans; Structural Motility, Institut Curie, CNRS, UMR 144 Paris, France.
Bo Sun, School of Life Science and Technology, ShanghaiTech University, Shanghai 201210, China.
Shuo-Xing Dou, Beijing National Laboratory for Condensed Matter Physics and CAS Key Laboratory of Soft Matter Physics, Institute of Physics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China; School of Physical Sciences, University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100049, China.
Xu-Guang Xi, State Key Laboratory of Crop Stress Biology in Arid Areas, College of Life Sciences, Northwest A&F University, Yangling, Shaanxi 712100, China; Laboratoire de Biologie et de Pharmacologie Appliquée (LBPA), UMR 8113 CNRS, Institut D’Alembert, École Normale Supérieure Paris-Saclay, Université Paris-Saclay, 4, Avenue des Sciences, 91190 Gif sur Yvette, France.
SUPPLEMENTARY DATA
Supplementary Data are available at NAR Online.
FUNDING
National Natural Science Foundation of China [31870788]; LIA of CNRS (“Helicase-mediated G-quadruplex DNA unwinding and genome stability"). Funding for open access charge: National Natural Science Foundation of China [31870788].
Conflict of interest statement. None declared.
REFERENCES
- 1. Armanios M., Blackburn E.H.. The telomere syndromes. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012; 13:693–704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Aubert G., Lansdorp P.M.. Telomeres and aging. Physiol. Rev. 2008; 88:557–579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3. Kim N.W., Piatyszek M.A., Prowse K.R., Harley C.B., West M.D., Ho P.L., Coviello G.M., Wright W.E., Weinrich S.L., Shay J.W.. Specific association of human telomerase activity with immortal cells and cancer. Science. 1994; 266:2011–2015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4. Schmidt J.C., Cech T.R.. Human telomerase: biogenesis, trafficking, recruitment, and activation. Genes Dev. 2015; 29:1095–1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5. Jiang J., Chan H., Cash D.D., Miracco E.J., Ogorzalek Loo R.R., Upton H.E., Cascio D., O’Brien Johnson R., Collins K., Loo J.A.et al.. Structure of Tetrahymena telomerase reveals previously unknown subunits, functions, and interactions. Science. 2015; 350:aab4070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6. Nguyen T.H.D., Tam J., Wu R.A., Greber B.J., Toso D., Nogales E., Collins K.. Cryo-EM structure of substrate-bound human telomerase holoenzyme. Nature. 2018; 557:190–195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7. Weinrich S.L., Pruzan R., Ma L., Ouellette M., Tesmer V.M., Holt S.E., Bodnar A.G., Lichtsteiner S., Kim N.W., Trager J.B.et al.. Reconstitution of human telomerase with the template RNA component hTR and the catalytic protein subunit hTRT. Nat. Genet. 1997; 17:498–502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8. Licht J.D., Collins K.. Telomerase RNA function in recombinant Tetrahymena telomerase. Genes Dev. 1999; 13:1116–1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9. Autexier C., Lue N.F.. The structure and function of telomerase reverse transcriptase. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006; 75:493–517. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10. Podlevsky J.D., Chen J.J.. Evolutionary perspectives of telomerase RNA structure and function. RNA Biol. 2016; 13:720–732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11. Musgrove C., Jansson L.I., Stone M.D.. New perspectives on telomerase RNA structure and function. Wiley Interdiscip. Rev. RNA. 2018; 9:e1456. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12. Wang Y., Sušac L., Feigon J.. Structural biology of telomerase. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019; 11:a032383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13. Jiang J., Miracco E.J., Hong K., Eckert B., Chan H., Cash D.D., Min B., Zhou Z.H., Collins K., Feigon J.. The architecture of Tetrahymena telomerase holoenzyme. Nature. 2013; 496:187–192. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14. Huang J., Brown A.F., Wu J., Xue J., Bley C.J., Rand D.P., Wu L., Zhang R., Chen J.J., Lei M.. Structural basis for protein-RNA recognition in telomerase. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2014; 21:507–512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15. Jansson L.I., Akiyama B.M., Ooms A., Lu C., Rubin S.M., Stone M.D.. Structural basis of template-boundary definition in Tetrahymena telomerase. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015; 22:883–888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16. Jiang J., Wang Y., Susac L., Chan H., Basu R., Zhou Z.H., Feigon J.. Structure of telomerase with telomeric DNA. Cell. 2018; 173:1179–1190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17. Choi W.S., He P., Pothukuchy A., Gollihar J., Ellington A.D., Yang W.. How a B family DNA polymerase has been evolved to copy RNA. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2020; 117:21274–21280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18. Yang W., Lee Y.S.. A DNA-hairpin model for repeat-addition processivity in telomere synthesis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015; 22:844–847. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19. Parks J.W., Stone M.D.. Coordinated DNA dynamics during the human telomerase catalytic cycle. Nat. Commun. 2014; 5:4146. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20. Bryan C., Rice C., Hoffman H., Harkisheimer M., Sweeney M., Skordalakes E.. Structural basis of telomerase inhibition by the highly specific BIBR1532. Structure. 2015; 23:1934–1942. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21. Sauerwald A., Sandin S., Cristofari G., Scheres S.H., Lingner J., Rhodes D. Structure of active dimeric human telomerase. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013; 20:454–460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22. Prescott J., Blackburn E.H.. Telomerase RNA mutations in Saccharomyces cerevisiae alter telomerase action and reveal nonprocessivity in vivo and in vitro. Genes Dev. 1997; 11:528–540. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23. Fulton T.B., Blackburn E.H.. Identification of Kluyveromyces lactis telomerase: discontinuous synthesis along the 30-nucleotide-long templating domain. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998; 18:4961–4970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24. Cohn M., Blackburn E.H.. Telomerase in yeast. Science. 1995; 269:396–400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25. Haering C.H., Nakamura T.M., Baumann P., Cech T.R.. Analysis of telomerase catalytic subunit mutants in vivo and in vitro in Schizosaccharomycespombe. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2000; 97:6367–6372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26. Hsu M., McEachern M.J., Dandjinou A.T., Tzfati Y., Orr E., Blackburn E.H., Lue N.F.. Telomerase core components protect Candida telomeres from aberrant overhang accumulation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2007; 104:11682–11687. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27. Yu E.Y. Telomeres and telomerase in Candida albicans. Mycoses. 2012; 55:e48–59. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28. Gunisova S., Elboher E., Nosek J., Gorkovoy V., Brown Y., Lucier J.F., Laterreur N., Wellinger R.J., Tzfati Y., Tomaska L.. Identification and comparative analysis of telomerase RNAs from Candida species reveal conservation of functional elements. RNA. 2009; 15:546–559. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29. Qi X., Li Y., Honda S., Hoffmann S., Marz M., Mosig A., Podlevsky J.D., Stadler P.F., Selker E.U., Chen J.J.. The common ancestral core of vertebrate and fungal telomerase RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013; 41:450–462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30. Egan E.D., Collins K.. Biogenesis of telomerase ribonucleoproteins. RNA. 2012; 18:1747–1759. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31. Wu R.A., Upton H.E., Vogan J.M., Collins K.. Telomerase mechanism of telomere synthesis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2017; 86:439–460. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32. Liao X.H., Zhang M.L., Yang C.P., Xu L.X., Zhou J.Q.. Characterization of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae telomerase core enzyme purified from yeast. Biochem. J. 2005; 390:169–176. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33. Bosoy D., Lue N.F.. Yeast telomerase is capable of limited repeat addition processivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004; 32:93–101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34. Kabsch W. Xds. Acta Crystallogr. D. 2010; 66:125–132. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35. Vonrhein C., Blanc E., Roversi P., Bricogne G.. Automated structure solution with autoSHARP. Methods Mol. Biol. 2007; 364:215–230. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36. Sheldrick G.M. A short history of SHELX. Acta Crystallogr. A, Found. Crystallogr. 2008; 64:112–122. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37. Emsley P., Lohkamp B., Scott W.G., Cowtan K.. Features and development of Coot. Acta Crystallogr. D. 2010; 66:486–501. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38. Adams P.D., Afonine P.V., Bunkóczi G., Chen V.B., Davis I.W., Echols N., Headd J.J., Hung L.W., Kapral G.J., Grosse-Kunstleve R.W.et al.. PHENIX: a comprehensive Python-based system for macromolecular structure solution. Acta Crystallogr. D. Biol. Crystallogr. 2010; 66:213–221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39. McCoy A.J., Grosse-Kunstleve R.W., Adams P.D., Winn M.D., Storoni L.C., Read R.J.. Phaser crystallographic software. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2007; 40:658–674. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40. Chou F.C., Echols N., Terwilliger T.C., Das R.. RNA structure refinement using the ERRASER-Phenix pipeline. Methods Mol. Biol. 2016; 1320:269–282. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41. Liu N.N., Duan X.L., Ai X., Yang Y.T., Li M., Dou S.X., Rety S., Deprez E., Xi X.G.. The Bacteroides sp. 3_1_23 Pif1 protein is a multifunctional helicase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015; 43:8942–8954. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42. David G., Perez J.. Combined sampler robot and high-performance liquid chromatography: a fully automated system for biological small-angle X-ray scattering experiments at the Synchrotron SOLEIL SWING beamline. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2009; 42:892–900. [Google Scholar]
- 43. Hopkins J.B., Gillilan R.E., Skou S.. BioXTAS RAW: improvements to a free open-source program for small-angle X-ray scattering data reduction and analysis. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2017; 50:1545–1553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44. Franke D., Petoukhov M.V., Konarev P.V., Panjkovich A., Tuukkanen A., Mertens H.D.T., Kikhney A.G., Hajizadeh N.R., Franklin J.M., Jeffries C.M.et al.. ATSAS 2.8: a comprehensive data analysis suite for small-angle scattering from macromolecular solutions. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2017; 50:1212–1225. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45. Evrard G., Mareuil F., Bontems F., Sizun C., Perez J.. DADIMODO: a program for refining the structure of multidomain proteins and complexes against small-angle scattering data and NMR-derived restraints. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2011; 44:1264–1271. [Google Scholar]
- 46. Webb B., Sali A.. Comparative protein structure modeling using MODELLER. Curr. Protoc. Protein Sci. 2016; 86:2.9.1–2.9.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47. Van Der Spoel D., Lindahl E., Hess B., Groenhof G., Mark A.E., Berendsen H.J.. GROMACS: fast, flexible, and free. J. Comput. Chem. 2005; 26:1701–1718. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48. Zappulla D.C., Goodrich K., Cech T.R.. A miniature yeast telomerase RNA functions in vivo and reconstitutes activity in vitro. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2005; 12:1072–1077. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49. Mitchell M., Gillis A., Futahashi M., Fujiwara H., Skordalakes E.. Structural basis for telomerase catalytic subunit TERT binding to RNA template and telomeric DNA. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2010; 17:513–518. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50. Gillis A.J., Schuller A.P., Skordalakes E.. Structure of the Tribolium castaneum telomerase catalytic subunit TERT. Nature. 2008; 455:633–637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51. Robart A.R., Collins K.. Human telomerase domain interactions capture DNA for TEN domain-dependent processive elongation. Mol. Cell. 2011; 42:308–318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52. Bley C.J., Qi X., Rand D.P., Borges C.R., Nelson R.W., Chen J.J.. RNA-protein binding interface in the telomerase ribonucleoprotein. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2011; 108:20333–20338. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53. Mitchell J.R., Collins K.. Human telomerase activation requires two independent interactions between telomerase RNA and telomerase reverse transcriptase. Mol. Cell. 2000; 6:361–371. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54. Petrova O.A., Mantsyzov A.B., Rodina E.V., Efimov S.V., Hackenberg C., Hakanpaa J., Klochkov V.V., Lebedev A.A., Chugunova A.A., Malyavko A.N.et al.. Structure and function of the N-terminal domain of the yeast telomerase reverse transcriptase. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018; 46:1525–1540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55. Harkisheimer M., Mason M., Shuvaeva E., Skordalakes E.. A motif in the vertebrate telomerase N-terminal linker of TERT contributes to RNA binding and telomerase activity and processivity. Structure. 2013; 21:1870–1878. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56. Akiyama B.M., Gomez A., Stone M.D.. A conserved motif in Tetrahymena thermophila telomerase reverse transcriptase is proximal to the RNA template and is essential for boundary definition. J. Biol. Chem. 2013; 288:22141–22149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57. Bryan T.M., Goodrich K.J., Cech T.R.. Telomerase RNA bound by protein motifs specific to telomerase reverse transcriptase. Mol. Cell. 2000; 6:493–499. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58. Jansson L.I., Stone M.D.. Single-molecule analysis of reverse transcriptase enzymes. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2019; 11:a032458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59. Schmidt T., Tian L., Clore G.M.. Probing conformational states of the finger and thumb subdomains of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase using double electron-electron resonance electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 2018; 57:489–493. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60. Lee Y.S., Gao Y., Yang W.. How a homolog of high-fidelity replicases conducts mutagenic DNA synthesis. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2015; 22:298–303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
Structures of CtTERT and CaTERT have been deposited in the PDB with the following accession numbers: 6ZD1 (CtTERT178–879 apo), 6ZD2 (CtTERT158–745), 6ZDP (CtTERT158–879-TWJ), 6ZD6 (CtTERT178–879/R366C-S774C), 6ZDQ (CaTERT177–867-TWJ), 6ZDU (CaTERT95–867-TWJ).