Abstract
Abstract
Background
The objective of this study was to increase understanding of the complex interactions between diet, obesity, and the gut microbiome of adult female non-human primates (NHPs). Subjects consumed either a Western (n=15) or Mediterranean (n=14) diet designed to represent human dietary patterns for 31 months. Body composition was determined using CT, fecal samples were collected, and shotgun metagenomic sequencing was performed. Gut microbiome results were grouped by diet and adiposity.
Results
Diet was the main contributor to gut microbiome bacterial diversity. Adiposity within each diet was associated with subtle shifts in the proportional abundance of several taxa. Mediterranean diet-fed NHPs with lower body fat had a greater proportion of Lactobacillus animalis than their higher body fat counterparts. Higher body fat Western diet-fed NHPs had more Ruminococcus champaneliensis and less Bacteroides uniformis than their low body fat counterparts. Western diet-fed NHPs had significantly higher levels of Prevotella copri than Mediterranean diet NHPs. Western diet-fed subjects were stratified by P. copri abundance (P. copriHIGH versus P. copriLOW), which was not associated with adiposity. Overall, Western diet-fed animals in the P. copriHIGH group showed greater proportional abundance of B. ovatus, B. faecis, P. stercorea, P. brevis, and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii than those in the Western P. copriLOW group. Western diet P. copriLOW subjects had a greater proportion of Eubacterium siraeum. E. siraeum negatively correlated with P. copri proportional abundance regardless of dietary consumption. In the Western diet group, Shannon diversity was significantly higher in P. copriLOW when compared to P. copriHIGH subjects. Furthermore, gut E. siraeum abundance positively correlated with HDL plasma cholesterol indicating that those in the P. copriLOW population may represent a more metabolically healthy population. Untargeted metabolomics on urine and plasma from Western diet-fed P. copriHIGH and P. copriLOW subjects suggest early kidney dysfunction in Western diet-fed P. copriHIGH subjects.
Conclusions
In summary, the data indicate diet to be the major influencer of gut bacterial diversity. However, diet and adiposity must be considered together when analyzing changes in abundance of specific bacterial taxa. Interestingly, P. copri appears to mediate metabolic dysfunction in Western diet-fed NHPs.
Video abstract
Supplementary Information
The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1186/s40168-021-01069-y.
Keywords: Metagenomic sequencing, Metabolomics, Western and Mediterranean diet, Body fat composition, Prevotella copri, Eubacterium siraeum, Urinary carnitine metabolites, Uremic toxins
Background
Gut microbiome dysbiosis is associated with many adverse health outcomes including multiple sclerosis, cancer, diabetes (types 1 and 2), asthma, allergies, inflammatory bowel disease, obesity, and autism [1–6]. Composition of the gut microbiome is influenced by several factors including maternal delivery method, ethnicity, geography, and lifestyle [7]. Of the multiple factors associated with the term “lifestyle,” diet in particular has a major influence on the microbial composition within the gut. Bacterial abundance is modulated by dietary macronutrient consumption, including proteins, carbohydrates, and fats [6, 8, 9]. Poor diet and obesity often are linked, making it difficult to determine which variable is the major driver of the gut microbiome composition.
The composition of the human gut microbiome is dominated by the Bacteroidetes and Firmicutes bacterial phyla [10]. Within the Bacteroidetes phylum, enterotypes are distinguished by abundance of Bacteroides or Prevotella. While both Prevotella and Bacteroides are saccharolytic bacteria, these genera of bacteria tend to inhibit each other, thereby giving way to two separate enterotypes [11]. The prevalence of either strongly associates with long-term diets; Bacteroides predominate with protein and animal fat consumption and Prevotella are observed with carbohydrate (fiber) consumption [12]. Enteric Prevotella are more common in non-Westernized populations consuming a plant-rich diet or in Western populations with high adherence to a Mediterranean or vegetarian diet [13]. Food and nutrient consumption patterns, such as omnivore versus plant-based diet, are associated with shifts in the human gut microbiome. Subjects consuming an omnivore diet displayed increased Ruminococcus and Streptococcus abundance, while subjects on a vegetable-based diet showed increased abundance of Roseburia, Lachnospira, and Prevotella [14]. High-fat diet and obesity are linked to modulation of these phyla in humans and mice; both factors are associated with increased Firmicutes and decreased Bacteroidetes phyla in the gut metagenome [6, 8, 9, 15–17].
The microbiome of non-human primates (NHP) harbors Bacteroidetes, Firmicutes, and Proteobacteria, similar to the human microbiome [18, 19]. Prominent differences (see [19]) exist between the macaques and human microbiome such as elevated Helicobacter and Spirochaetes in NHPs compared to humans, albeit these NHPs were consuming standard adult monkey chow that would not compare to humanized dietary patterns and may account for some of the noted differences [19]. A study investigating the differences in the gut microbiome between captive and wild NHPs (8 different species) indicate that captivity “humanizes” the primate microbiome [20]. Taken together, these data suggest that application of a humanized dietary pattern in captive NHPs may accurately represent the human microbiome. As an additional benefit, the establishment of a NHP model allows for a closely controlled study without adherence or self-reporting issues, and avoiding medication, all of which often are confounding factors in human studies.
This study examines the impact of a translationally relevant humanized Western and Mediterranean dietary patterns on the gut microbiota, and association with obesity, in female middle-aged cynomolgous macaques. Application of these diets has been shown to significantly influence the gut populations of cynomolgous macaques [18]. Mediterranean diet consumption increased the genera Lactobacillus, Clostridium, Faecalibacterium, and Oscillospira while decreasing Ruminococcus and Coprococcus representation [18]. However, the aforementioned report relied on 16S rRNA sequencing. In the study reported here, we instead utilize metagenomic sequencing, the methodology used in Human Microbiome Project [21]. 16S sequencing is useful in studies where many samples are available, but has poor resolution compared to metagenomics [22]. Shotgun metagenomic sequencing offers enhanced functional and taxonomic resolution to allow identification of specific bacterial species and strains [21–23]. This has allowed us to report bacterial species as well as virulence factor clusters modulated by dietary exposure in cynomolgous macaques, improving understanding of the similarities and differences between NHPs and humans with the respect to influence of diet on the gut microbiome. In addition, we assessed complete metabolic profiling data for each of the animals to correlate gut microbiota populations with body weight (BW), body adiposity, plasma cholesterol levels, insulin tolerance testing, and metabolite signatures in plasma or urine. This enabled the identification of specific microbes that may potentially influence metabolic syndrome development.
Methods
NHP subjects
Adult female Macaca fascicularis were obtained (SNBL USA, Ltd., Alice, Texas) and housed in groups of 4 animals per pen with daylight exposure on a 12/12 light/dark cycle. Animals were aged at study initiation by dentition to be approximately 8.8 years old. The subjects were habituated to their social groups and were metabolically characterized for group randomization during a 7-month baseline phase while consuming standard monkey chow (monkey diet 5037/5038; LabDiet, St. Louis, Missouri). Animal groups were randomized so that no differences in age, body weight (BW), body mass index (BMI), or plasma triglyceride concentrations were observed. No gastrointestinal differences or other health concerns were observed at baseline before animals were randomized to dietary pattern. Animals were then assigned to a dietary pattern (Western n=21 or Mediterranean n=17) for 31 months. All animal manipulations were performed according to the guidelines of state and federal laws, the US Department of Health and Human Services, and the Animal Care and Use Committee of Wake Forest University School of Medicine.
Diet formulation
Experimental diets were formulated to be isocaloric with respect to protein, fat, carbohydrates, and cholesterol content. Experimental diets translationally represent humanized Western and Mediterranean dietary patterns. For further details on diet formulation and ingredients, see Supplemental Table 1 and references [24, 25].
Metabolic characterization
Metabolic parameters were measured in each subject and previously reported [24, 25]. Briefly, BW (kg) and body length (BL, m) were measured throughout the study. BMI was calculated as BW/(BL)2. BW and BMI reported in Table 1 were measured at the endpoint of the dietary intervention study (31 months) in all subjects and subjects were categorized into tertiles by BMI. For this particular analysis, only animals classified in the lowest (N=14) or highest (N=15) tertiles underwent microbiome analysis and comprise the sample included in this report. Body composition was measured by computed tomography in anesthetized subjects during various intervals throughout the study. Body fat composition reported in Table 1 was measured at month 27 of the treatment phase. The fat compartment was defined as tissue with attenuation between −190 and −30 Hounsfield units, and total fat was then determined across the whole body. Intravenous glucose tolerance tests with insulin responses were performed during month 26 of the treatment phase as previously described [18]. In brief, subjects were fasted for 18 h, sedated with ketamine HCl (15 mg/kg), and dosed with 500 mg/kg dextrose. Blood samples were taken at 0, 5, 10, 20, 30, 40, and 60 min. Insulin area under the curve (AUC) was calculated using insulin responses between 10 and 40 min. Insulin was determined using a commercial enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA; Mercodia, Uppsala, Sweden).
Table 1.
Metabolic parameters by body weight group. Values represent mean ± standard deviation
| Mediterranean-lean (n=7) | Mediterranean-heavy (n=7) | Western-lean (n=7) | Western-heavy (n=8) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BW (kg) | 2.5±0.2 | 4.1±1.0 | 2.7±0.2 | 4.9±1.2 |
| BMI (kg/m2) | 36.7±4.2 | 48.2±6.9 | 39.7±4.5 | 60.2±10.4 |
| Body fat composition (%) | 8.4±2.0 | 23.4±9.0 | 11.7±4.3 | 39.1±10.5 |
| Insulin AUC | 1721±335 | 6456±5703 | 3431±4043 | 10526±8427 |
| TPC (mg/dL) | 133.4±29.4 | 163.7±48.0 | 159.5±33.1 | 149.9±28.5 |
| HDL-C (mg/dL) | 48.6±8.6 | 66.7±29.8 | 78.4±40.6 | 72.1±17.2 |
| TPC/HDL-C ratio | 2.78±0.50 | 2.62±0.46 | 2.38±0.95 | 2.13±0.16 |
| Cortisol (µg/dL) | 36.5±4.2 | 29.3±5.6 | 33.7±8.8 | 41.1±5.7 |
Total plasma cholesterol (TPC) and high-density lipoprotein cholesterol (HDL-C) were measured at 24 months from plasma collected after an 18 h fast. TPC and HDL-C levels were determined by the Wake Forest Comparative Medicine Clinical Chemistry and Endocrinology Laboratory using reagents (ACE cholesterol and ACE HDL-C standards) and instrumentation (ACE ALERA auto analyzer) from Alfa Wasserman Diagnostic Technologies (West Caldwell, NJ). TPC and HDL-C were standardized to calibrated controls from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention/National Institutes of Health Lipid Standardization Program [26]. Blood samples for cortisol assay were drawn in the morning within 9 min of staff entering NHP housing, and serum was assayed with RIA kits from DiaSource (IBL America, Minneapolis, MN).
Fecal and urine sample collection
Urine and fecal samples were collected after 26 months of dietary treatments. Animals were moved to metabolic cages with wire bottoms, and sample cups were checked every 15 min for feces. Fecal samples were immediately placed in sterile tubes under aseptic conditions and stored at −80 °C until further processing. As soon as adequate urine samples were available, they were collected, and stored at −80 °C until analysis.
Metagenomic sequencing
DNA was isolated from 100 mg of frozen feces using the Qiagen DNeasy PowerSoil Pro kit (Valencia, CA), and metagenomic sequencing was performed by CosmosID Inc. (Rockville, MD). In brief, DNA libraries were prepared using the Illumina Nextera XT library preparation kit (San Diego, CA), with a modified protocol [27, 28]. Library quantity was assessed with a Qubit Fluorometer (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Wilmington, DE). Libraries were then sequenced on an Illumina HiSeq platform to generate 150-bp paired-ends reads.
Metagenomic bioinformatic analysis
Unassembled sequencing reads (≥12M read depth; see Supplemental Figure S1 for individual sample read statistics) were analyzed using the CosmosID bioinformatics platform described elsewhere [29–32] for multi-kingdom microbiome analysis, profiling of antibiotic resistance and virulence genes, and quantification of microbial relative abundance. Briefly, the system utilizes curated genome databases and a high-performance data-mining algorithm that rapidly disambiguates hundreds of millions of metagenomic sequence reads into the discrete microorganisms engendering the particular sequences. CosmosID bioinformatics utilizes high performance data mining algorithms and highly curated dynamic comparator databases (GenBook®). GenBook® comprises 150,000+ bacteria, viruses, fungi and protist genomes, and gene sequences. The GenBook database is organized as phylogenetic tree and comprised of libraries of hundreds of millions of marker sequences, representing both coding and noncoding sequences shared or uniquely identified across different taxa and/or distinct nodes of phylogenetic trees. Comparative metagenomic analyses (principal component analysis, double hierarchical clustering, centroid classification, and other statistical analyses) were done to determine temporal changes, geographical diversity, and shifts in diversity correlated with treatment and to differentiate datasets of the different cohorts. Monkey group housing (pen effect) had no significant effect on microbiota populations (Supplemental Figure S2).
Metabolomics
Untargeted metabolomics from urine and plasma samples collected at 26 months were performed by Metabolon (Raleigh, NC) as previously described [24]. In brief, all experiments used a Waters ACQUITY ultra-performance liquid chromatography (UPLC) and a Thermo Scientific Q-Exactive high resolution/accurate mass spectrometer interfaced with a heated electrospray ionization (HESI-II) source and Orbitrap mass analyzer operated at 35,000 mass resolution. The scan range varied slightly between methods but covered 70-1000 m/z. Raw data were extracted, peak- identified, and processed for quality control using Metabolon’s hardware and software. Compounds were identified by comparison to library entries of purified standards or recurrent unknown entities. Peaks were quantified using area-under-the-curve. The informatics consisted of the Laboratory Information Management System (LIMS), the data extraction and peak-identification software, data processing tools for quality control and compound identification, and a collection of information interpretation and visualization tools for use by data analysts. The hardware and software foundations for these components were the LAN backbone, and a database server running Oracle 10.2.1.1 Enterprise Edition. Values were then log transformed, and missing values, if any, were imputed with the minimum observed value for each compound.
Statistical analysis
Metabolic parameters were summarized using means and standard deviations. Microbiome diversity and bacterial populations were compared by diet group using two group t tests allowing for unequal variance using the Satterthwaite method for degrees of freedom. Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) of bacterial beta diversity based on the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity matrix using relative abundance was used to distinguish groups. Diversity analyses were performed using species taxonomy level. Comparisons by diet and body weight group were assessed by two-way ANOVA of diet, group, and their interaction, estimating different variance components by diet and group; we used linear contrasts to make pairwise comparisons within diet group if the interaction p value was <0.10. Within the Western diet group, animals were split into P. copriLOW and P. copriHIGH groups based on whether they were below the median, and Welch’s two-sample t test was used to compare microbiota and metabolites shifts between Western diet P. copriHIGH and Western diet P. copriLOW experimental groups. Correlations between gut microbial populations and metabolic parameters were summarized by Pearson correlation and expressed as r. A p value of p<0.05 was considered statistically significant in all analyses with the exception of the evaluation of diet × group interaction in the two-way ANOVA which used alpha=0.10.
Results
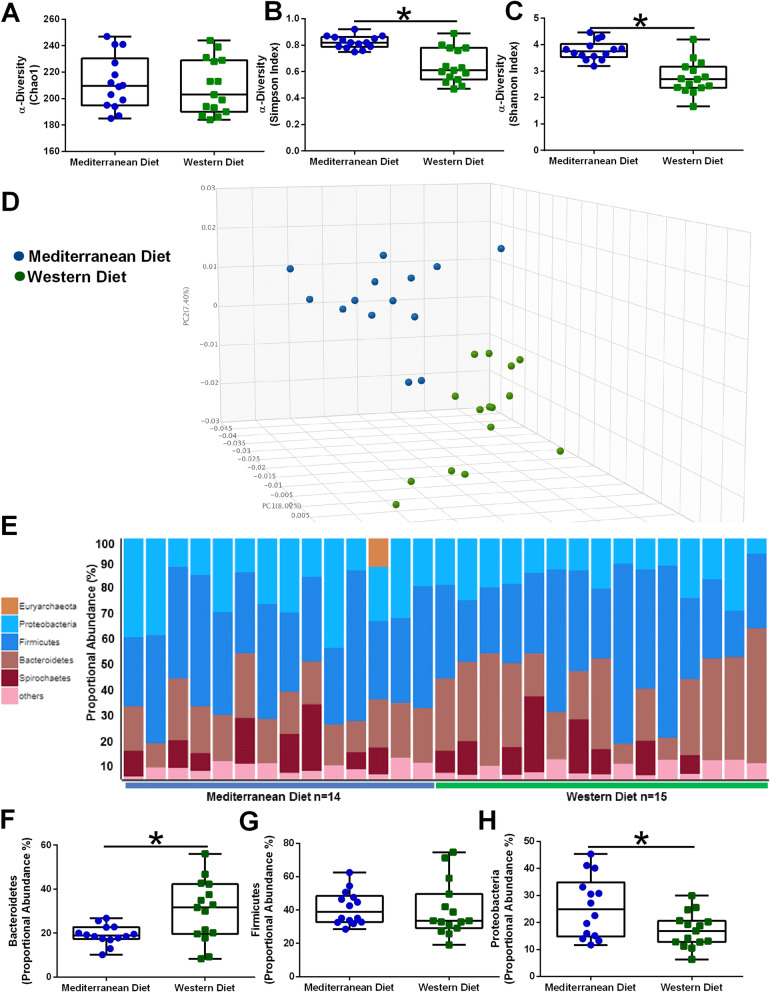
Western and Mediterranean dietary pattern drives gut microbiome populations. While dietary pattern consumption had no significant effects on bacterial richness (Choa1; Fig. 1a), subjects fed a Mediterranean diet displayed higher microbial diversity as indicated by Simpson index (Fig. 1b) and Shannon diversity score (Fig. 1c). PCoA of gut microbial populations by relative abundance indicates that subjects separate by dietary pattern consumption (Fig. 1d). The bulk of the microbial biomass at the phyla level are derived from Bacteroidetes (20-40%), Firmicutes (40%), and Proteobacteria (15-30%). Proportional abundance of each phylum within each animal is shown as bar graph (Fig. 1e). Consumption of a Western diet significantly elevated Bacteroidetes abundance (Fig. 1f), but had no effect on Firmicutes populations (Fig. 1g). Mediterranean diet-fed subjects displayed increased Proteobacteria abundance when compared with Western diet-fed animals (Fig. 1h).
Fig. 1.
Diet is a driver of gut microbiome diversity. Alpha diversity was estimated with the Chao1 index (a), Simpson index (b), and Shannon index (c) on raw OTU abundance in Mediterranean diet and Western diet-fed subjects. d Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) of bacterial beta diversity based on the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity of gut microbial populations by relative abundance indicates that subjects separate by dietary pattern consumption. Mediterranean diet-fed subjects are shown in blue, while Western diet-consuming animals are shown in green. e Relative abundance of bacterial phyla in different fecal samples is visualized by bar plots. Each bar represents a subject and each colored box a bacterial phylum. The height of a color box represents the relative abundance of that organism within the sample. “Other” represents lower abundance taxa. f Western diet-fed NHPs displayed higher Bacteroidetes. g Diet had no significant effects on shifting Firmicute abundance. h Mediterranean diet-fed subjects showed higher proportional abundance of Proteobacteria. n=14-15; *p<0.05. Error bars in box plots show the min to max distribution
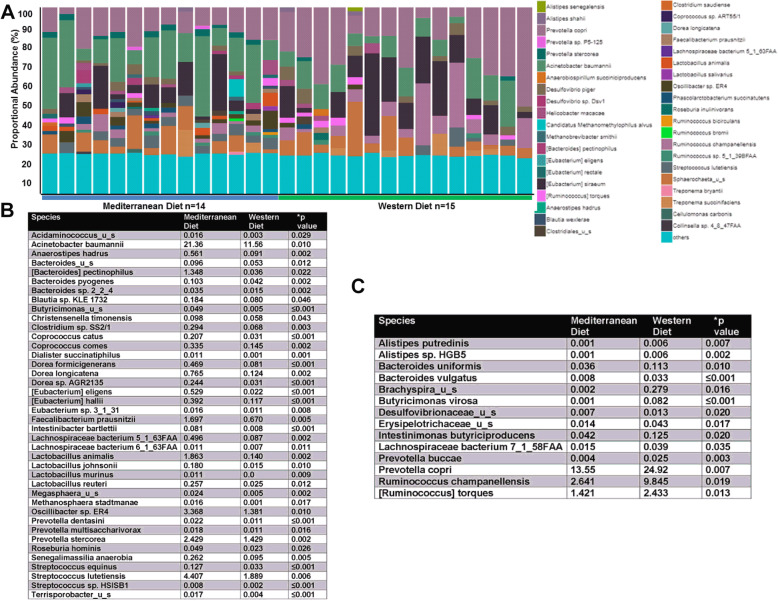
At the species level, 507 different species of bacteria were detected in the fecal samples obtained from diet-treated subjects. The proportional abundance of the more abundant species is shown in Fig. 2a in which each bar represents a fecal sample from an individual subject. Diet significantly shifted the proportional abundance of 54 different species. See Fig. 2b-c for all 54 species. Of specific interest, Mediterranean diet-fed subjects displayed increased proportional abundance of Bacteroides (B.) pectinophilus, Clostridium sp. SS2/1, Coprococcus catus, Coprococcus comes, Dorea formicigenerans, Dorea longicatena, Eubacterium (E.) eligens, E. hallii, Faecalibacterium prausnitzii, Lachnospiraceae bacterium 5_1_63FAA, Lachnospiraceae bacterium 6_1_63FAA, Lactobacillus (L.) animalis, L. johnsonii, L. murinus, L. reuteri, Oscillibacter sp. ER4, Prevotella (P.) dentasini, P. stercorea, Roseburia hominis, and Streptococcus lutetiensis (Fig. 2b). Western diet-fed subjects displayed elevated proportional abundance of Alistipes putredinis, B. uniformis, B. vulgatus, Butyricimonas virosa, Lachnospiraceae bacterium 7_1_58FAA, P. buccae, P. copri, Ruminococcus champanellensis, and Ruminococcus torques (Fig. 2c). While 44 of these diet-associated species have less than a 1% proportional abundance within the samples, 10 species display up to 25% abundance within the sample.
Fig. 2.
Consumption of Mediterranean diet leads to significant variation in distinct gut microbiota species. a Relative abundance of bacterial species in different fecal samples is visualized by bar plots. Each bar represents a subject and each colored box a bacterial taxon. The height of a color box represents the relative abundance of that organism within the sample. “Other” represents lower abundance taxa. Mediterranean diet-fed subjects are shown in blue; Western diet-fed subjects are shown in green. b Species elevated in Mediterranean diet-consuming animals when compared with Western diet-fed subjects (mean values and p values) are shown in the table. c Species elevated in Western diet-fed animals when compared with Mediterranean diet-consuming subjects (mean values and p values) are shown in the table
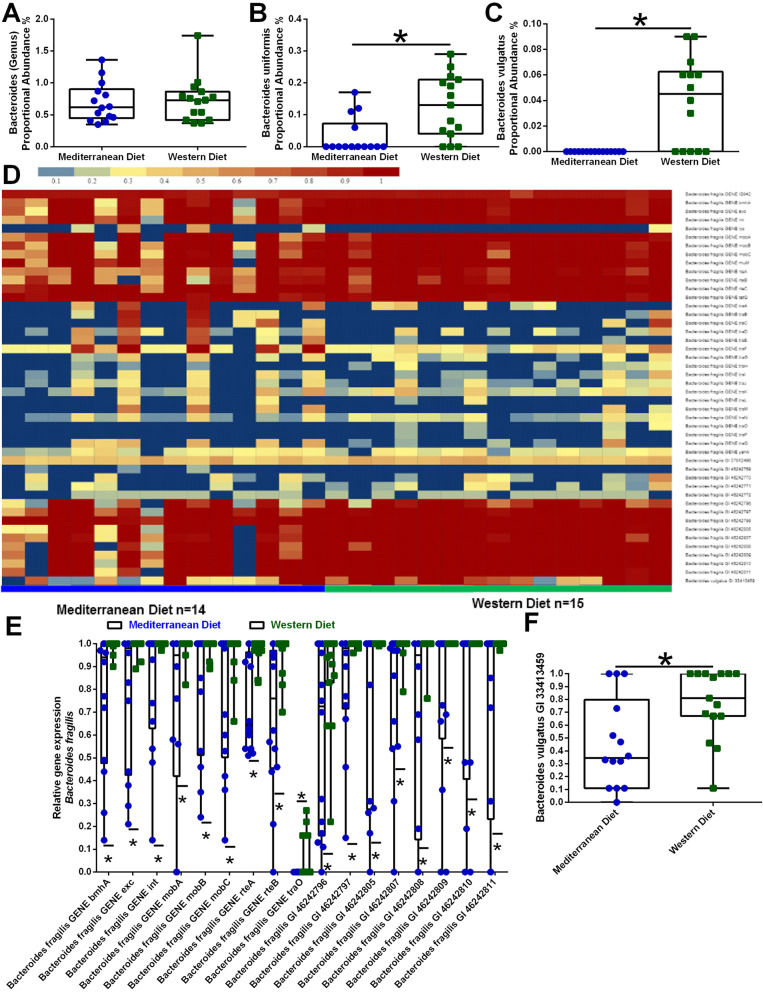
While not a major component of the NHP gut microbiota (≤1%), Bacteroides genus did not differ by diet (Fig. 3a), distinct Bacteroides species differed by dietary pattern consumption. B. uniformis (Fig. 3b, p=0.005) and B. vulgatus (Fig. 3c, p<0.001) were higher in animals fed the Western diet than the Mediterranean diet. Furthermore, virulence factor gene measurements from the shotgun metagenomics sequencing highlighted elevated B. fragilis (Fig. 3d and e) and B. vulgaris (Fig. 3d and f) in Western diet consuming NHPs (all p values <0.05).
Fig. 3.
Virulence factor clustering analysis highlights Bacteroides populations varied by dietary consumption. a At the genus level, Bacteroides did not differ by diet (p=0.79). Bacteroides uniformis (b) and Bacteroides vulgatus (c) populations were elevated in Western diet fed NHPs. Furthermore, virulence factor measurements from the shotgun metagenomics sequencing highlighted increased Bacteroides fragilis (d and e) and Bacteroides vulgaris (f) in Western diet-consuming NHPs. n=14-15. *p<0.05 using two group t test for unequal variance with Satterthwaite adjustment. Error bars on box plots show the min to max distribution
Shotgun metagenomics sequencing allows for identification of viruses, fungi, protozoa, and phages in addition to the more commonly investigated bacteria populations. We show that dietary patterns also modulate gut viral and protist communities with no effect on fungal or phage populations (Supplemental Figure S3). There were approximately 32 different viral species identified in the NHP fecal samples, of which five species were associated by diet. Western diet-fed NHP displayed elevated fecal baboon endogenous virus strain M7 and RD114 retrovirus. Mediterranean diet-fed NHP displayed elevated fecal human mastadenovirus G, Sfi11 virus u_s, and Streptococcus virus 7201 (Supplemental Figure S3A). In the protozoa community, approximately 12 species were identified in the NHP fecal samples. Western diet-fed NHP displayed elevated fecal Endolimax nana abundance and reduced Neobalantidium coli abundance when compared with fecal samples obtained from Mediterranean diet-fed NHPs (Supplemental Figure S3B).
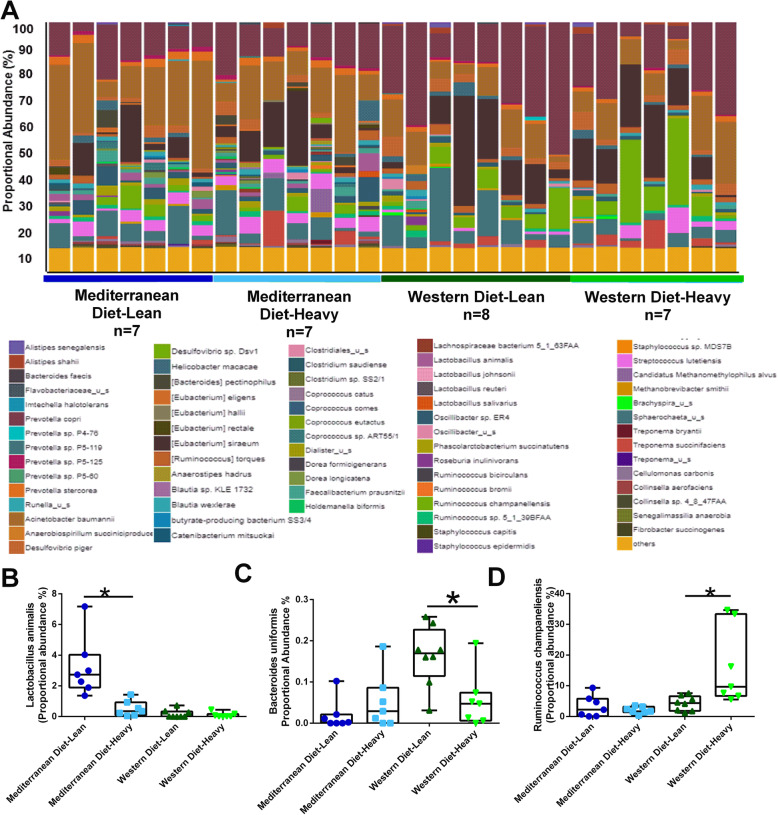
Adiposity within dietary pattern consumption cohort shifts differential microbiota abundance. Some of the effect of dietary pattern on gut microbiota species differed by body adiposity. The gut microbiota species within each subject is shown in a bar graph of proportional abundance with each bar representing an individual subject and separate colors for distinct bacterial species (Fig. 4a). Specifically, there was a significant interaction between diet and adiposity. Microbe abundance within dietary patterns differed by adiposity for L. animalis (Fig. 4b, p interaction=0.005), B. uniformis (Fig. 4c, p=0.064), and Ruminococcus champaneliensis (Fig. 4d, p=0.034). Within Mediterranean diet-fed subjects, monkeys with increased body adiposity displayed decreased L. animalis (Fig. 4b) when compared to their leaner Mediterranean diet-fed counterparts. Adiposity did not regulate L. animalis in Western diet-fed animals. Lean Western diet-fed monkeys had increased B. uniformis (Fig. 4c) when compared with the proportional abundance in heavier Western diet-fed animals, but Mediterranean diet-fed animals did not have different levels of abundance by adiposity. Heavier Western diet consuming subjects displayed elevated Ruminococcus champaneliensis (Fig. 4d) compared to lean Western diet-fed animals, but Mediterranean diet-fed animals did not have different levels of abundance by adiposity.
Fig. 4.
Body adiposity shifts gut microbiota patterns within dietary patterns. a Relative abundance of bacterial species in different fecal samples is visualized by bar plots. Each bar represents a subject and each colored box a bacterial taxon. The height of a color box represents the relative abundance of that organism within the sample. “Other” represents lower abundance taxa. Lean Mediterranean diet-fed subjects are shown in dark blue; heavy Mediterranean diet-fed subjects are shown in light blue; lean Western diet-fed subjects are shown in dark green; and heavy Western diet-fed animals are shown in light green. b Lean Mediterranean diet-fed animals display higher Lactobacillus animalis abundance when compared to heavy Mediterranean diet-fed subjects, lean Western diet-fed subjects, and heavy Western diet-fed subjects. Lean Western diet-fed monkeys displayed increased gut abundance of Bacteroides uniformis (c) when compared to heavy animals fed the same diet. Heavy Western diet-fed subjects displayed increased Ruminococcus champaneliensis (d) when compared to the relative abundance of these species within lean Western diet-fed NHPs. n=7-8. *p from pairwise comparison in two-way ANOVA diet × group interaction used alpha=0.10. Error bars show the min to max distribution
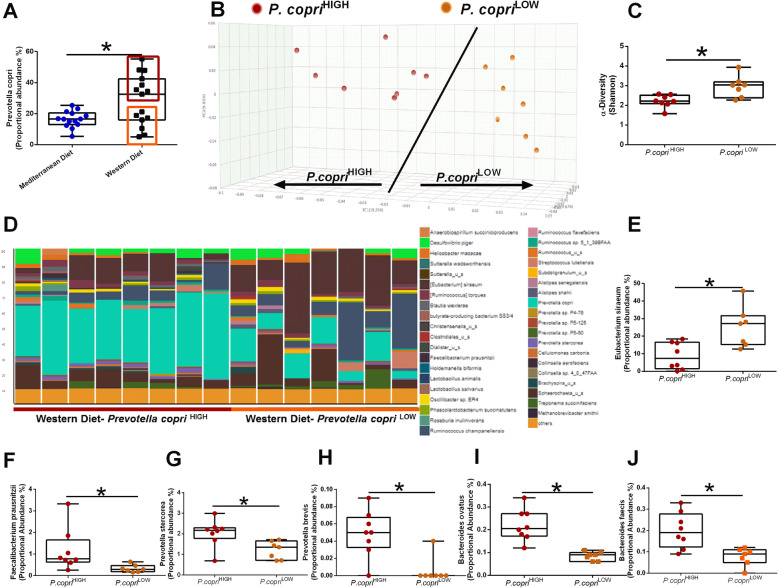
P. copri enterotypes categorize two distinct populations within Western diet consuming subjects. NHPs consuming a Western diet display elevated abundance of P. copri when compared with Mediterranean diet-fed animals (Fig. 5a). Within Western diet-fed animals, subjects could be stratified into two distinct enterotypes: P. copriHIGH and P. copriLOW. As shown in the PCoA (Fig. 5b), the two enterotypes are distinct from each other as indicated by increased distance between clusters. Shannon diversity was reduced in the Western diet-fed P. copriHIGH group (Fig. 5c). Animals in the P. copriLOW group displayed elevated E. siraeum (Fig. 5d and e). Animals in the P. copriHIGH displayed increased Faecalibacterium prausnitzii (Fig. 5f), P. stercorea (Fig. 5g), P. brevis (Fig. 5h), B. ovatus (Fig. 5i), and B. faecis (Fig. 5j).
Fig. 5.
Western diet-fed subjects cluster into two different enterotypes based upon Prevotella copri abundance. a Proportional abundance of Prevotella copri in Mediterranean and Western diet-fed NHPs. n = 14–15, *p < 0.05 from Welch’s two group t test. Error bars show the min to max distribution. b Principal coordinates analysis (PCoA) of bacterial beta diversity based on the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity using relative abundance. P. copriHIGH samples (n=8) are shown in red circles and P. copriLOW samples are shown in orange circles. c Alpha diversity was estimated with the Shannon index on raw OTU abundance based upon P. copri abundance. Shannon diversity is significantly higher in P. copriLOW animals. d Relative abundance of bacterial species in different fecal samples is visualized by bar plots. Each bar represents a subject and each colored box a bacterial taxon. The height of a color box represents the relative abundance of that organism within the sample. “Other” represents lower abundance taxa. e Proportional abundance of Eubacterium siraeum is elevated in P. copriLOW subjects. P copriHIGH samples are characterized by elevated Faecalibacterium prausnitzii (f), Prevotella stercorea (g), Prevotella brevis (h), Bacteroides ovatus (i), and Bacteroides faecis (j). n=6-8; *p<0.05 from Welch’s two group t test
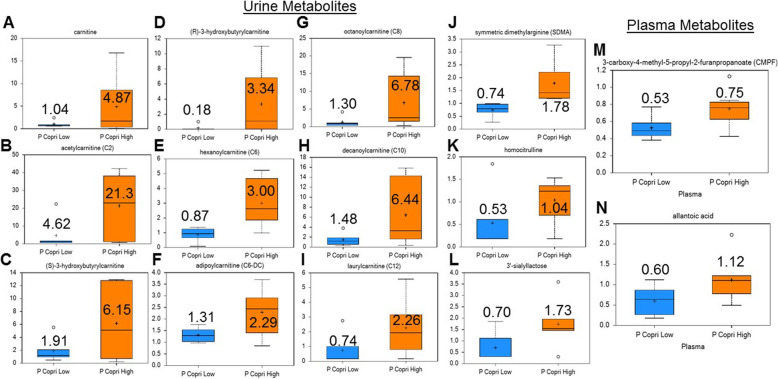
Untargeted metabolomics was performed on urine and plasma samples from Western diet-fed P. copriHIGH and P. copriLOW subjects. Urinary biomarkers elevated in Western diet-fed P. copriHIGH subjects (Fig. 6) include carnitine-based metabolites (carnitine, acetylcarnitine, (S)-3-hydroxybutyrylcarnitine, (R)-3-hydroxybutyrylcarnitine, adipoylcarnitine (C6-DC), hexanoylcarnitine (C6), octanoylcarnitine (C8), decanoylcarnitine (C10), and laurylcarnitine (C12)), uremic toxin symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA), homocitrulline, and 3′-sialyllactose. While urinary levels of 3-carboxy-4-methyl-5-propyl-2-furanpropanoate (CMPF) and allantoic acid were not different between Western diet-fed P. copriHIGH and P. copriLOW subjects, plasma levels of CMPF and allantoic acid were significantly higher in the P. copriHIGH group. P. copriLOW subjects displayed elevated levels of plasma gamma glutamyl amino acids and phosphodtidylethanolamine (PE) metabolites (Supplemental Figure S4), suggesting potential lipid and amino acid metabolism regulation.
Fig. 6.
Western diet-fed subjects display differential urine and plasma metabolites regulation based upon gut Prevotella copri abundance. Urinary biomarkers elevated in Western diet-fed P. copriHIGH subjects include carnitine-based metabolites (carnitine, acetylcarnitine, (S)-3-hydroxybutyrylcarnitine, (R)-3-hydroxybutyrylcarnitine, adipoylcarnitine (C6-DC), hexanoylcarnitine (C6), octanoylcarnitine (C8), decanoylcarnitine (C10), and laurylcarnitine (C12)), uremic toxin symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA), homocitrulline, and 3′-sialyllactose. Plasma levels of 3-carboxy-4-methyl-5-propyl-2-furanpropanoate (CMPF) and allantoic acid were elevated between Western diet-fed P. copriHIGH and P. copriLOW subjects. n = 6-8, p < 0.05 from Welch’s two group t test. Error bars show the min to max distribution; the mean value is displayed within/next to whisker plot
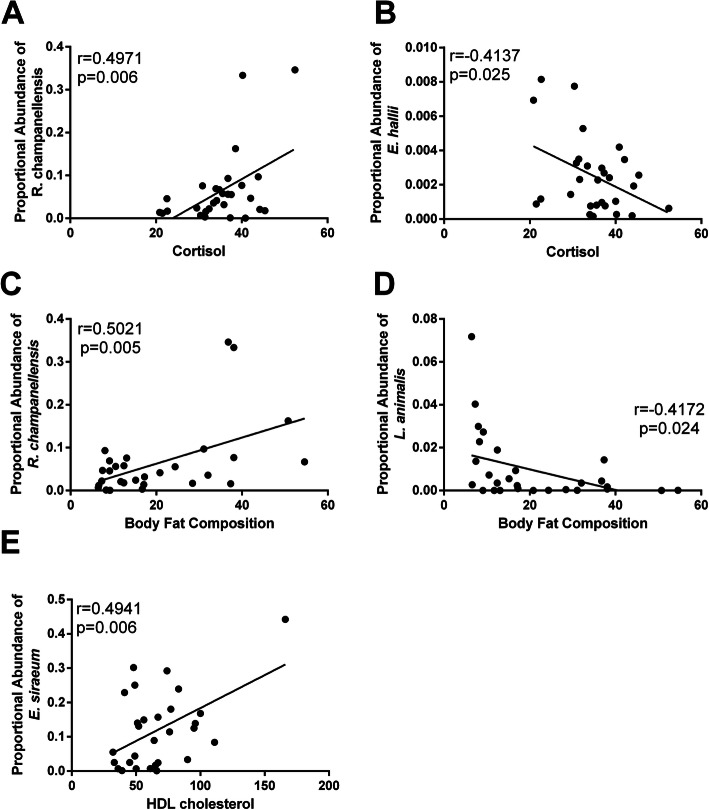
Gut microbiota populations correlate with metabolic parameters. Regardless of dietary pattern consumption, certain gut microbiota populations correlated with plasma cortisol levels; gut Ruminococcus champanellensis positively correlated with plasma cortisol (Fig. 7a) and with percent body fat composition (Fig. 7c), while E. hallii abundance negatively correlated with plasma cortisol (Fig. 7b). Furthermore, we observed L. animalis abundance negatively correlated with percent body fat composition (Fig. 7d) and gut E. siraeum positively correlated with plasma HDL levels (Fig. 7e).
Fig. 7.
Certain microbiota species correlate with metabolic parameters. a Serum cortisol levels positively correlates with gut Ruminococcus champanellensis abundance. b Serum cortisol levels negatively correlates with gut Eubacterium hallii abundance. c Gut Ruminococcus champanellensis abundance correlates with increasing % body fat composition. d Proportional abundance of Lactobacillus animalis negatively correlates with % body fat composition. e Gut Eubacterium siraeum correlates with plasma HDL cholesterol levels. n=29; Pearson correlation coefficient (r)
Discussion
Our data indicates that diet composition impacts gut microbiota structure and that a Mediterranean diet pattern is associated with increased gut bacterial diversity in female cynomolgous macaques. In accordance with human diet studies in which subjects with high adherence to a Mediterranean diet display elevated Proteobacteria populations [33], Mediterranean diet-fed NHPs also show increased Proteobacteria phyla proportional abundance in response to this diet. While NHPs have similar gut microbiota populations in comparison to humans [34] and respond to translationally relevant diets concordantly in regards to alpha diversity, the response to Western diet at the phyla level appears to differ. In humans, consumption of high fat animal-based Westernized diet leads to decreased Bacteroidetes: Firmicutes ratio, mainly due to enrichment of Firmicutes. We confirmed previous results from 16S sequencing data demonstrating that Western diet-fed NHPs displayed increased proportional abundance of Bacteroidetes phylum with no significant shifts in Firmicutes populations [18]. Consumption of a Western-like diet in the African green monkey led to a similar outcome, although important to note that this study relied on 16S sequencing and was unable to identify species level classifications [35]. The elevated Bacteroidetes abundance observed in the NHPs is driven by an enrichment in P. copri. Gut P. copri displays an interesting case of duality in human health and disease. Non-westernized lifestyle is associated with increased gut P. copri abundance [36]. Literature strongly supports the association of gut P. copri abundance with improved glucose and insulin tolerance when diets are also fiber rich [37, 38]. On the other hand, in studies from Westernized populations Prevotella dominated enterotypes (in particular P. copri) have been linked with autoimmune disease, new onset rheumatoid arthritis, hypertension, and diabetes [39–42]. Taken together, these data suggest that any potential health benefits from P. copri could be dependent on host diet background.
While overall Bacteroides abundance is low in NHP subjects, possibly due to the mutually exclusive dominance of Prevotella, monkey subjects consuming a Westernized diet did display elevated B. uniformis and B. vulgatus species when compared with Mediterranean diet-fed animals. In this regard, monkeys responded to translationally relevant diets in a similar pattern to humans (consumption of animal product diet increased Bacteroides in human subjects [12];). The duodenum, ileum, and colon of NHPs (while consuming standard monkey lab chow) are more acidic than what is observed in humans [43], which could lead to some differences in microbiota populations. Bacteroides have weak acidic tolerance (pH preference 6.5-6.9 [44, 45];) while Prevotella display slight acidic preference (pH 5.5-6.0 [46];), which could potentially explain the dominance of Prevotella in the gut of NHPs (human versus NHP colon pH: 6.4-7.0 (proximal to distal colon pH range) in humans compared to NHP colon pH 5.1 [41].)
We showed two distinct enterotypes in Western diet-consuming animals based upon P. copri abundance. The P. copriLOW subgroup displayed increased bacterial diversity and elevated E. siraeum (strain: V10Sc8a). Gut E. siraeum abundance in NHP from either diet correlated with elevated HDL-C levels, suggesting a more metabolic healthy subgroup. Devillard et al. demonstrated novel biosynthetic activity of E. siraeum mediating the bioconversion of linoleic acid to form conjugated linoleic acids (CLA; mainly cis-9,trans-11-18:2 [47];). Consumption of CLA is associated with various health benefits (including elevating HDL-C [48]), further supporting the association between E. siraeum and HDL-C observed in our study. In a small monozygotic Korean twin study (n=20), E. siraeum negatively correlated with obesity [49], giving evidence in support of the E. siraeum-enriched P. copriLOW subgroup displaying a healthier enterotype.
Our metabolic data in urine and plasma samples obtained from Western diet-fed P. copriHIGH and P. copriLOW subjects indicates potential early stage kidney damage in P. copriHIGH animals. Hypertensive adolescents display elevated urinary excretion of carnitine metabolites [50] which also serve as a marker for proximal tubular damage [51]. Therefore, the observed elevated urinary carnitine, acteylcarnitine, and acyl-carnitine metabolites (but not plasma levels) may represent an attenuated capacity for reabsorption and possibly are an early mark of renal tubular damage. The uremic toxin, SDMA, inhibits nitric oxide production and is associated with coronary artery disease, type 2 diabetes mellitus, and stroke [52]. Hence, the elevated urinary SDMA observed in P. copriHIGH animals further associates this enterotype with kidney dysfunction and may contribute to proximal tubule damage by reducing local levels of nitric oxide. Additionally, we observed elevated plasma allantoic acid concentrations in Western diet-fed P. copriHIGH subjects. Elevated plasma allantoic acid was evident in a pre-clinical mouse model of cystic kidney disease [53]. Moreover, plasma allantoin levels were increased in both a pre-clinical rat model of kidney fibrosis [54] and in chronic kidney disease patients [55], highlighting the potential relevance of this metabolite in the assessment and/or contribution to reduced renal function (lower glomerular filtration rate). In generally healthy individuals, urine 3′sialyllactose levels correlate with chronic low-grade inflammation as measured by elevated C-reactive protein concentrations [56]. Elevated serum 3′sialyllactose served as a biomarker for mastitis development in clinically healthy dairy cows [57], giving evidence in support of 3′sialyllactose serving as a pro-inflammatory marker. The close link between chronic low-grade inflammation and the development of many metabolic diseases suggests that the elevated 3′sialyllactose observed in the urine of P. copriHIGH may indicate a sub-clinical pro-inflammatory phenotype mediated by this gut microbiota enterotype. Elevated plasma CMPF is observed in gestational diabetes and in type 2 diabetes patients [58]. In mice, CMPF treatment (at diabetic levels) resulted in β cell dysfunction through oxidative stress demonstrating a dose-dependent causality of this metabolite to induce diabetes. However, it is important to note that fish oil administration also raises plasma CMPF levels but not to the extent observed in diabetic patients [59], suggesting key dose-dependent activity of circulating CMPF. Taken together, the identified plasma and urinary metabolomics profile support a metabolic unhealthy potential of Western diet-fed P. copriHIGH enterotype when compared with Western diet-fed P. copriLOW animals.
In our study, obesity (as a single variable) did not appear to be significantly associated with gut microbiome composition (Supplemental Figure S5). However, body adiposity within each diet pattern was associated with subtle shifts in the proportional abundance of several key microbiota species. Among Mediterranean diet-consuming subjects, leaner animals displayed a higher proportional abundance of L. animalis compared to monkeys with more adipose tissue. Several Lactobacillus species, including L. animalis, are considered healthy probiotic commensal organisms. Administration of Lactobacillus for 6 weeks as a probiotic supplement was shown to reduce systolic blood pressure in a controlled, randomized, double-blind trial of smokers [60]. Several preclinical studies indicate positive health benefits of Lactobacillus supplementation in regards to cholesterol lowering potential [61–64].
Among Western diet-fed animals, lower adiposity subjects displayed increased B. uniformis abundance compared to their higher adiposity counterparts. Supplementation of B. uniformis in obese mice fed a high-fat diet ameliorated metabolic dysfunction and reduced inflammation, indicating the elevated B. uniformis observed in lean Western diet-fed monkeys may be associated with a healthier phenotype [65, 66]. Heavier Western diet-fed NHPs had elevated Ruminococcus champaneliensis compared to their lean counterparts. R. champanelienses is a cellulose degrading bacterium that may supplement host metabolism by releasing digestible substrate from normally indigestible carbohydrates, potentially contributing to obesity. Within NHP on either diet, R. champaneliensis correlated with circulating cortisol and body fat composition, suggesting that while this species is associated with body adiposity, higher R. champaneliensis abundance may also modulate stress hormones in a gut-brain signaling axis.
Literature indicates that E. rectale, F. prausnitzii, Roseburia spp., Dorea and Coprococcus metabolism produce SCFA from plant-vegetables products within the gastro-intestinal system for potential health benefits [67, 68]. We identified other Eubacterium species (E. eligens, E. hallii, and Eubacterium sp. 3_1_31), F. prausnitzii, Roseburia hominis, multiple Dorea sp. (D. formicigenerans, D. longicatena, and Dorea sp. AGR2135), and several Coprococcus species (C. catus and C. comes) to be significantly higher in Mediterranean diet-fed NHP subjects than Western diet consuming animals. Our previous work demonstrated an increase in plasma bacterial modified bioactive compounds in Mediterranean diet-fed NHPs [24]. Consumption of Mediterranean diet elevated p-cresol-glucuronide, 3-indoxyl sulfate, and indole-3-propionate (IPA). IPA is the deamination product of tryptophan mediated by gut Clostridium and Lactobacillus species, which we observed elevated Lactobacillus sp. (L. animalis, L. johnsonii, L. murinus, and L. reuteri) and Clostridium sp. SS2/1 in our Mediterranean diet-fed monkeys. Metabolomic analysis of conventional-housed and germ-free mice have indicated that germ-free mice cannot produce plasma 3-indoxyl sulfate and IPA, demonstrating the reliance on bacteria to produce these metabolites [69]. Furthermore, administration of IPA improves intestinal barrier function and decrease circulating LPS thereby reducing systemic inflammation [70]. The reduction in inflammation often observed by Mediterranean diet consumption [71–75] may result from modulation of key gut microbiota populations and the production of beneficial bacterial-derived bioactive compounds.
It is important to note several key limitations of our current study. This study only includes female NHP; sex differences may exist impacting dietary influences on the gut microbiome and metabolic outcomes in males. Baseline fecal samples were not collected during the metabolic characterization phase while the NHP were on standard monkey chow. Therefore, the data we show in this study does not accurately reflect a response to diet, but reports metabolic and microbiome patterns associated with dietary pattern consumption.
Conclusions
In conclusion, our study demonstrated several similarities and key differences in the gut microbiome mediated by human translationally relevant diet administration. However, the key difference (stimulation of P. copri by Western diet administration) may represent a potential model to elucidate signaling differences observed in human Westernized populations with gut P. copri associations with several disease states. Furthermore, our metabolomic data indicates potential deleterious metabolite regulation in the urine and plasma of P. copriHIGH Western diet-fed subjects, suggesting that the P. copriHIGH enterotype in subjects eating a Westernized diet may potentiate the development of metabolic disease.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1: Supplemental Table 1. Non-human primate diets replicating human Western and Mediterranean dietary patterns. Supplemental Figure S1. Individual read statistics on each sample. Samples ranged from 13,694,588 to 28,756,486 reads with no significant differences in reads between dietary patterns. Supplemental Figure S2. Diet, not pen effects, drive microbiome populations. A. PCoA of bacterial beta diversity based on the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity; different solid color spheres indicates subjects housed in same pen. B. Shannon diversity of each subject; different solid color spheres indicates subjects housed in same pen. Supplemental Figure S3. Diet shifts viral and protozoa populations in the gut microbiome. A. Relative abundance of viral species in different fecal samples is visualized by bar plots. Samples are aggregated by diet cohort. Each colored box represents a viral species. The height of a color box represents the relative abundance of that organism within the sample. “Other” represents lower abundance taxa (<5%). B. Relative abundance of protozoa species in different fecal samples is visualized by bar plots. Samples are aggregated by diet cohort. Each colored box represents a protist species. The height of a color box represents the relative abundance of that organism within the sample. “Other” represents lower abundance taxa (<5%). C. Relative abundance of fungal species in different fecal samples is visualized by bar plots. Samples are aggregated by diet cohort. Each colored box represents a fungal species. The height of a color box represents the relative abundance of that organism within the sample. “Other” represents lower abundance taxa (<5%). D. A. Relative abundance of phages in different fecal samples is visualized by bar plots. Samples are aggregated by diet cohort. Each colored box represents a bacteriophage species. The height of a color box represents the relative abundance of that organism within the sample. “Other” represents lower abundance taxa (<5%). Supplemental Figure S4. Western diet-fed subjects with low P. copri abundance display elevated plasma gamma-glutamyl amino acid and phosphatidylethanolamine metabolites. Supplemental Figure S5. Obesity regardless of diet does not significantly regulate the gut microbiome. A. Shannon diversity. B. PCoA of bacterial beta diversity based on the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity. C. Relative abundance of bacterial species in different fecal samples is visualized by bar plots. Each bar represents a subject and each colored box a bacterial taxon. The height of a color box represents the relative abundance of that organism within the sample. “Other” represents lower abundance taxa. D. Proportional abundance of Treponema (Genus) in obese and lean NHP regardless of dietary pattern. E. Proportional abundance of Treponema succinifaciens in obese and lean NHP regardless of dietary pattern.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- ANOVA
Analysis of variance
- AUC
Area under the curve
- BL
Body length
- BW
Body weight
- CLA
Conjugated linoleic acid
- CMPF
3-carboxy-4-methyl-5-propyl-2-furanpropanoate
- HDL-C
High-density lipoprotein-cholesterol
- IPA
Indole propionic acid
- LPS
Lipopolysaccharide
- NHP
Non-human primate
- PCoA
Principal coordinate analysis
- SCFA
Short chain fatty acid
- SDMA
Symmetric dimethylarginine
- TPC
Total plasma cholesterol
Authors’ contributions
C.A.S., T.C.R., and S.E.A. designed the in vivo portion of the NHP experiment. B.U., K.Y.J.C., and A.S.W. performed the experiments. B.F, M.D., and K.G. from CosmosID performed and optimized metagenomic sequencing of fecal samples. J.A.T. supplied urine and plasma metabolomics data. U.N and S.R. Metabolon re-analyzed data to determine differences by P. copri abundance. T.M.N., C.A.S., T.C.R., H.Y, A.C., K.D.R, J.A.T., and K.L.C. wrote and revised the manuscript. K.L.C. created the conceptual design of approaches to microbiome data analysis. C.A.S. and K.L.C. supervised the study. All authors discussed the results and commented on the manuscript. The authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was supported by the Department of Defense Breast Cancer Research Program Breakthrough Level 2 Award W81XWH-20-1-0014 (to K.L.C.), American Cancer Society Research Scholar Grant RSG-16-204-01-NEC (to K.L.C.), Career Catalyst Grant from the Susan G. Komen foundation CCR18547795 (to K.L.C.), and NIH grants HL-087103 (to C.A.S.), HL-122393 (to T.C.R.), and HL-146818 (M.C.C). Wake Forest Claude Pepper Older Americans Independence Center grant P30 AG21332 (to T.C.R.). Shared resource services were provided by the Wake Forest Baptist Comprehensive Cancer Center’s NCI Cancer Center Support Grant (P30CA012197).
Availability of data and materials
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal manipulations were performed according to the guidelines of state and federal laws, the US Department of Health and Human Services, and the Animal Care and Use Committee of Wake Forest University School of Medicine.
Consent for publication
Not applicable
Competing interests
As an author from an industry sponsor, RC, BF, MD, KG, UN, and SR from Metabolon and CosmosID declare that they have a non-financial interests in relation to the work described in the manuscript. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Trompette A, Gollwitzer ES, Yadava K, Sichelstiel AK, Sprenger N, Ngom-Bru C, Blanchard C, Junt T, Nicod LP, Harris NL, Marsland BJ. Gut microbiota metabolism of dietary fiber influences allergic airway disease and hematopoiesis. Nat Med. 2014;20(2):159–166. doi: 10.1038/nm.3444. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Backhed F, Fraser CM, Ringel Y, Sanders ME, Sartor RB, Sherman PM, Versalovic J, Young V, Finlay BB. Defining a healthy human gut microbiome: current concepts, future directions, and clinical applications. Cell Host Microbe. 2012;12(5):611–622. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2012.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Petersen C, Round JL. Defining dysbiosis and its influence on host immunity and disease. Cell Microbiol. 2014;16(7):1024–1033. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Hsiao EY, McBride SW, Hsien S, Sharon G, Hyde ER, McCue T, Codelli JA, Chow J, Reisman SE, Petrosino JF, et al. Microbiota modulate behavioral and physiological abnormalities associated with neurodevelopmental disorders. Cell. 2013;155(7):1451–1463. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.11.024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Garrett WS. Cancer and the microbiota. Science. 2015;348(6230):80–86. doi: 10.1126/science.aaa4972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ley RE, Backhed F, Turnbaugh P, Lozupone CA, Knight RD, Gordon JI. Obesity alters gut microbial ecology. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102(31):11070–11075. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0504978102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Khan MJ, Gerasimidis K, Edwards CA, Shaikh MG. Role of gut microbiota in the aetiology of obesity: proposed mechanisms and review of the literature. J Obes. 2016;2016:7353642. doi: 10.1155/2016/7353642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Hildebrandt MA, Hoffmann C, Sherrill-Mix SA, Keilbaugh SA, Hamady M, Chen YY, Knight R, Ahima RS, Bushman F, Wu GD. High-fat diet determines the composition of the murine gut microbiome independently of obesity. Gastroenterology. 2009;137(5):):1716–):1724. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2009.08.042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Turnbaugh PJ, Ridaura VK, Faith JJ, Rey FE, Knight R, Gordon JI. The effect of diet on the human gut microbiome: a metagenomic analysis in humanized gnotobiotic mice. Sci Transl Med. 2009;1(6):6ra14. doi: 10.1126/scitranslmed.3000322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Qin J, Li R, Raes J, Arumugam M, Burgdorf KS, Manichanh C, Nielsen T, Pons N, Levenez F, Yamada T, et al. A human gut microbial gene catalogue established by metagenomic sequencing. Nature. 2010;464(7285):59–65. doi: 10.1038/nature08821. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Costea PI, Hildebrand F, Arumugam M, Backhed F, Blaser MJ, Bushman FD, de Vos WM, Ehrlich SD, Fraser CM, Hattori M, et al. Enterotypes in the landscape of gut microbial community composition. Nat Microbiol. 2018;3(1):8–16. doi: 10.1038/s41564-017-0072-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Wu GD, Chen J, Hoffmann C, Bittinger K, Chen YY, Keilbaugh SA, Bewtra M, Knights D, Walters WA, Knight R, Sinha R, Gilroy E, Gupta K, Baldassano R, Nessel L, Li H, Bushman FD, Lewis JD. Linking long-term dietary patterns with gut microbial enterotypes. Science. 2011;334(6052):105–108. doi: 10.1126/science.1208344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.De Filippo C, Cavalieri D, Di Paola M, Ramazzotti M, Poullet JB, Massart S, Collini S, Pieraccini G, Lionetti P. Impact of diet in shaping gut microbiota revealed by a comparative study in children from Europe and rural Africa. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107(33):14691–14696. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1005963107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.De Filippis F, Pellegrini N, Vannini L, Jeffery IB, La Storia A, Laghi L, Serrazanetti DI, Di Cagno R, Ferrocino I, Lazzi C, et al. High-level adherence to a Mediterranean diet beneficially impacts the gut microbiota and associated metabolome. Gut. 2016;65(11):1812–1821. doi: 10.1136/gutjnl-2015-309957. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Lloyd-Price J, Abu-Ali G, Huttenhower C. The healthy human microbiome. Genome Med. 2016;8(1):51. doi: 10.1186/s13073-016-0307-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ley RE, Turnbaugh PJ, Klein S, Gordon JI. Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature. 2006;444(7122):1022–1023. doi: 10.1038/4441022a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Newman TM, Vitolins MZ, Cook KL. From the table to the tumor: the role of Mediterranean and Western dietary patterns in shifting microbial-mediated signaling to impact breast cancer risk. Nutrients. 2019;11(11):2565-80. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 18.Nagpal R, Shively CA, Appt SA, Register TC, Michalson KT, Vitolins MZ, Yadav H. Gut microbiome composition in non-human primates consuming a Western or Mediterranean diet. Front Nutr. 2018;5:28. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2018.00028. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Yasuda K, Oh K, Ren B, Tickle TL, Franzosa EA, Wachtman LM, Miller AD, Westmoreland SV, Mansfield KG, Vallender EJ, Miller GM, Rowlett JK, Gevers D, Huttenhower C, Morgan XC. Biogeography of the intestinal mucosal and lumenal microbiome in the rhesus macaque. Cell Host Microbe. 2015;17(3):385–391. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2015.01.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Clayton JB, Vangay P, Huang H, Ward T, Hillmann BM, Al-Ghalith GA, Travis DA, Long HT, Tuan BV, Minh VV, et al. Captivity humanizes the primate microbiome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(37):10376–10381. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1521835113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Aagaard K, Petrosino J, Keitel W, Watson M, Katancik J, Garcia N, Patel S, Cutting M, Madden T, Hamilton H, Harris E, Gevers D, Simone G, McInnes P, Versalovic J. The Human Microbiome Project strategy for comprehensive sampling of the human microbiome and why it matters. FASEB J. 2013;27(3):1012–1022. doi: 10.1096/fj.12-220806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Jovel J, Patterson J, Wang W, Hotte N, O'Keefe S, Mitchel T, Perry T, Kao D, Mason AL, Madsen KL, et al. Characterization of the gut microbiome using 16S or shotgun metagenomics. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:459. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Norman JM, Handley SA, Virgin HW. Kingdom-agnostic metagenomics and the importance of complete characterization of enteric microbial communities. Gastroenterology. 2014;146(6):1459–1469. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2014.02.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Shively CA, Register TC, Appt SE, Clarkson TB, Uberseder B, Clear KYJ, Wilson AS, Chiba A, Tooze JA, Cook KL. Consumption of Mediterranean versus Western diet leads to distinct mammary gland microbiome populations: implications for breast cancer. Cell Reports. 2018;25(1):47–56. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.08.078. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Shively CA, Appt SE, Vitolins MZ, Uberseder B, Michalson KT, Silverstein-Metzler MG, Register TC. Mediterranean versus Western diet effects on caloric intake, obesity, metabolism, and hepatosteatosis in nonhuman primates. Obesity (Silver Spring) 2019;27(5):777–784. doi: 10.1002/oby.22436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Anantharamaiah GM, Garber DW, Goldberg D, Morrel E, Datta G, Palgunachari MN, Register TC, Appt SE, White CR. Novel fatty acyl apoE mimetic peptides have increased potency to reduce plasma cholesterol in mice and macaques. J Lipid Res. 2018;59(11):2075–2083. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M085985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Connelly S, Fanelli B, Hasan NA, Colwell RR, Kaleko M. Oral beta-lactamase protects the canine gut microbiome from oral amoxicillin-mediated damage. Microorganisms. 2019;7(5):150. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 28.Leonard MM, Karathia H, Pujolassos M, Troisi J, Valitutti F, Subramanian P, Camhi S, Kenyon V, Colucci A, Serena G, et al. Multi-omics analysis reveals the influence of genetic and environmental risk factors on developing gut microbiota in infants at risk of celiac disease. Microbiome. 2020;8(1):130. doi: 10.1186/s40168-020-00906-w. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ottesen A, Ramachandran P, Reed E, White JR, Hasan N, Subramanian P, Ryan G, Jarvis K, Grim C, Daquiqan N, Hanes D, Allard M, Colwell R, Brown E, Chen Y. Enrichment dynamics of Listeria monocytogenes and the associated microbiome from naturally contaminated ice cream linked to a listeriosis outbreak. BMC Microbiol. 2016;16(1):275. doi: 10.1186/s12866-016-0894-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ponnusamy D, Kozlova EV, Sha J, Erova TE, Azar SR, Fitts EC, Kirtley ML, Tiner BL, Andersson JA, Grim CJ, Isom RP, Hasan NA, Colwell RR, Chopra AK. Cross-talk among flesh-eating Aeromonas hydrophila strains in mixed infection leading to necrotizing fasciitis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016;113(3):722–727. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1523817113. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Hasan NA, Young BA, Minard-Smith AT, Saeed K, Li H, Heizer EM, McMillan NJ, Isom R, Abdullah AS, Bornman DM, et al. Microbial community profiling of human saliva using shotgun metagenomic sequencing. PLoS One. 2014;9(5):e97699. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0097699. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Lax S, Smith DP, Hampton-Marcell J, Owens SM, Handley KM, Scott NM, Gibbons SM, Larsen P, Shogan BD, Weiss S, Metcalf JL, Ursell LK, Vazquez-Baeza Y, van Treuren W, Hasan NA, Gibson MK, Colwell R, Dantas G, Knight R, Gilbert JA. Longitudinal analysis of microbial interaction between humans and the indoor environment. Science. 2014;345(6200):1048–1052. doi: 10.1126/science.1254529. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Garcia-Mantrana I, Selma-Royo M, Alcantara C, Collado MC. Shifts on gut microbiota associated to Mediterranean diet adherence and specific dietary intakes on general adult population. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:890. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.00890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Nagpal R, Wang S, Solberg Woods LC, Seshie O, Chung ST, Shively CA, Register TC, Craft S, McClain DA, Yadav H. Comparative microbiome signatures and short-chain fatty acids in mouse, rat, non-human primate, and human feces. Front Microbiol. 2018;9:2897. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2018.02897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Amato KR, Yeoman CJ, Cerda G, Schmitt CA, Cramer JD, Miller ME, Gomez A, Turner TR, Wilson BA, Stumpf RM, et al. Variable responses of human and non-human primate gut microbiomes to a Western diet. Microbiome. 2015;3(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s40168-015-0120-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Tett A, Huang KD, Asnicar F, Fehlner-Peach H, Pasolli E, Karcher N, Armanini F, Manghi P, Bonham K, Zolfo M, de Filippis F, Magnabosco C, Bonneau R, Lusingu J, Amuasi J, Reinhard K, Rattei T, Boulund F, Engstrand L, Zink A, Collado MC, Littman DR, Eibach D, Ercolini D, Rota-Stabelli O, Huttenhower C, Maixner F, Segata N. The Prevotella copri complex comprises four distinct clades underrepresented in Westernized populations. Cell Host Microbe. 2019;26(5):666–679. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2019.08.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.De Vadder F, Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Zitoun C, Duchampt A, Backhed F, Mithieux G. Microbiota-produced succinate improves glucose homeostasis via intestinal gluconeogenesis. Cell Metab. 2016;24(1):151–157. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.06.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Kovatcheva-Datchary P, Nilsson A, Akrami R, Lee YS, De Vadder F, Arora T, Hallen A, Martens E, Bjorck I, Backhed F. Dietary fiber-induced improvement in glucose metabolism is associated with increased abundance of Prevotella. Cell Metab. 2015;22(6):971–982. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.10.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Scher JU, Sczesnak A, Longman RS, Segata N, Ubeda C, Bielski C, Rostron T, Cerundolo V, Pamer EG, Abramson SB, Huttenhower C, Littman DR. Expansion of intestinal Prevotella copri correlates with enhanced susceptibility to arthritis. Elife. 2013;2:e01202. doi: 10.7554/eLife.01202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Wen C, Zheng Z, Shao T, Liu L, Xie Z, Le Chatelier E, He Z, Zhong W, Fan Y, Zhang L, et al. Quantitative metagenomics reveals unique gut microbiome biomarkers in ankylosing spondylitis. Genome Biol. 2017;18(1):142. doi: 10.1186/s13059-017-1271-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Pedersen HK, Gudmundsdottir V, Nielsen HB, Hyotylainen T, Nielsen T, Jensen BA, Forslund K, Hildebrand F, Prifti E, Falony G, et al. Human gut microbes impact host serum metabolome and insulin sensitivity. Nature. 2016;535(7612):376–381. doi: 10.1038/nature18646. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Li J, Zhao F, Wang Y, Chen J, Tao J, Tian G, Wu S, Liu W, Cui Q, Geng B, Zhang W, Weldon R, Auguste K, Yang L, Liu X, Chen L, Yang X, Zhu B, Cai J. Gut microbiota dysbiosis contributes to the development of hypertension. Microbiome. 2017;5(1):14. doi: 10.1186/s40168-016-0222-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hatton GB, Yadav V, Basit AW, Merchant HA. Animal farm: considerations in animal gastrointestinal physiology and relevance to drug delivery in humans. J Pharm Sci. 2015;104(9):2747–2776. doi: 10.1002/jps.24365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Chung WS, Walker AW, Louis P, Parkhill J, Vermeiren J, Bosscher D, Duncan SH, Flint HJ. Modulation of the human gut microbiota by dietary fibres occurs at the species level. BMC Biol. 2016;14(1):3. doi: 10.1186/s12915-015-0224-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Ilhan ZE, Marcus AK, Kang DW, Rittmann BE, Krajmalnik-Brown R. pH-mediated microbial and metabolic interactions in fecal enrichment cultures. mSphere. 2017;2(3):e00047-17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 46.Kianoush N, Adler CJ, Nguyen KA, Browne GV, Simonian M, Hunter N. Bacterial profile of dentine caries and the impact of pH on bacterial population diversity. PLoS One. 2014;9(3):e92940. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092940. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Devillard E, McIntosh FM, Duncan SH, Wallace RJ. Metabolism of linoleic acid by human gut bacteria: different routes for biosynthesis of conjugated linoleic acid. J Bacteriol. 2007;189(6):2566–2570. doi: 10.1128/JB.01359-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Wanders AJ, Brouwer IA, Siebelink E, Katan MB. Effect of a high intake of conjugated linoleic acid on lipoprotein levels in healthy human subjects. PLoS One. 2010;5(2):e9000. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0009000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Yassour M, Lim MY, Yun HS, Tickle TL, Sung J, Song YM, Lee K, Franzosa EA, Morgan XC, Gevers D, Lander ES, Xavier RJ, Birren BW, Ko GP, Huttenhower C. Sub-clinical detection of gut microbial biomarkers of obesity and type 2 diabetes. Genome Med. 2016;8(1):17. doi: 10.1186/s13073-016-0271-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kepka A, Kuroczycka-Saniutycz E, Chojnowska S, Filonowicz R, Korzeniecka-Kozerska A, Wasilewska A. Urine L-carnitine excretion in hypertensive adolescents. Ir J Med Sci. 2015;184(1):219–225. doi: 10.1007/s11845-014-1091-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Haschke M, Vitins T, Lude S, Todesco L, Novakova K, Herrmann R, Krahenbuhl S. Urinary excretion of carnitine as a marker of proximal tubular damage associated with platin-based antineoplastic drugs. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2010;25(2):426–433. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfp456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Tain YL, Hsu CN. Toxic dimethylarginines: asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA) and symmetric dimethylarginine (SDMA). Toxins (Basel). 2017;9(3):92.
- 53.Taylor SL, Ganti S, Bukanov NO, Chapman A, Fiehn O, Osier M, Kim K, Weiss RH. A metabolomics approach using juvenile cystic mice to identify urinary biomarkers and altered pathways in polycystic kidney disease. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 2010;298(4):F909–F922. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.00722.2009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hanifa MA, Skott M, Maltesen RG, Rasmussen BS, Nielsen S, Frokiaer J, Ring T, Wimmer R. Tissue, urine and blood metabolite signatures of chronic kidney disease in the 5/6 nephrectomy rat model. Metabolomics. 2019;15(8):112. doi: 10.1007/s11306-019-1569-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Toyohara T, Akiyama Y, Suzuki T, Takeuchi Y, Mishima E, Tanemoto M, Momose A, Toki N, Sato H, Nakayama M, Hozawa A, Tsuji I, Ito S, Soga T, Abe T. Metabolomic profiling of uremic solutes in CKD patients. Hypertens Res. 2010;33(9):944–952. doi: 10.1038/hr.2010.113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Pietzner M, Kaul A, Henning AK, Kastenmuller G, Artati A, Lerch MM, Adamski J, Nauck M, Friedrich N. Comprehensive metabolic profiling of chronic low-grade inflammation among generally healthy individuals. BMC Med. 2017;15(1):210. doi: 10.1186/s12916-017-0974-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Zandkarimi F, Vanegas J, Fern X, Maier CS, Bobe G. Metabotypes with elevated protein and lipid catabolism and inflammation precede clinical mastitis in prepartal transition dairy cows. J Dairy Sci. 2018;101(6):5531–5548. doi: 10.3168/jds.2017-13977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Prentice KJ, Luu L, Allister EM, Liu Y, Jun LS, Sloop KW, Hardy AB, Wei L, Jia W, Fantus IG, Sweet DH, Sweeney G, Retnakaran R, Dai FF, Wheeler MB. The furan fatty acid metabolite CMPF is elevated in diabetes and induces beta cell dysfunction. Cell Metab. 2014;19(4):653–666. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2014.03.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Prentice KJ, Wendell SG, Liu Y, Eversley JA, Salvatore SR, Mohan H, Brandt SL, Adams AC, Serena Wang X, Wei D, FitzGerald GA, Durham TB, Hammond CD, Sloop KW, Skarke C, Schopfer FJ, Wheeler MB. CMPF, a metabolite formed upon prescription omega-3-acid ethyl ester supplementation, prevents and reverses steatosis. EBioMedicine. 2018;27:200–213. doi: 10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.12.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Naruszewicz M, Johansson ML, Zapolska-Downar D, Bukowska H. Effect of Lactobacillus plantarum 299v on cardiovascular disease risk factors in smokers. Am J Clin Nutr. 2002;76(6):1249–1255. doi: 10.1093/ajcn/76.6.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Usman HA. Effect of administration of Lactobacillus gasseri on serum lipids and fecal steroids in hypercholesterolemic rats. J Dairy Sci. 2000;83(8):1705–1711. doi: 10.3168/jds.S0022-0302(00)75039-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Kumar R, Grover S, Batish VK. Bile salt hydrolase (Bsh) activity screening of Lactobacilli: in vitro selection of indigenous Lactobacillus strains with potential bile salt hydrolysing and cholesterol-lowering ability. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2012;4(3):162–172. doi: 10.1007/s12602-012-9101-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.London LE, Kumar AH, Wall R, Casey PG, O'Sullivan O, Shanahan F, Hill C, Cotter PD, Fitzgerald GF, Ross RP, et al. Exopolysaccharide-producing probiotic Lactobacilli reduce serum cholesterol and modify enteric microbiota in ApoE-deficient mice. J Nutr. 2014;144(12):1956–1962. doi: 10.3945/jn.114.191627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Qu T, Yang L, Wang Y, Jiang B, Shen M, Ren D. Reduction of serum cholesterol and its mechanism by Lactobacillus plantarum H6 screened from local fermented food products. Food Funct. 2020;11(2):1397–1409. doi: 10.1039/C9FO02478F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Gauffin Cano P, Santacruz A, Moya A, Sanz Y. Bacteroides uniformis CECT 7771 ameliorates metabolic and immunological dysfunction in mice with high-fat-diet induced obesity. PLoS One. 2012;7(7):e41079. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0041079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Fernandez-Murga ML, Sanz Y. Safety assessment of bacteroides uniformis CECT 7771 isolated from stools of healthy breast-fed infants. PLoS One. 2016;11(1):e0145503. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0145503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Riviere A, Selak M, Lantin D, Leroy F, De Vuyst L. Bifidobacteria and butyrate-producing colon bacteria: importance and strategies for their stimulation in the human gut. Front Microbiol. 2016;7:979. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2016.00979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Rinninella E, Raoul P, Cintoni M, Franceschi F, Miggiano GAD, Gasbarrini A, et al. What is the healthy gut microbiota composition? A changing ecosystem across age, environment, diet, and diseases. Microorganisms. 2019;7(1):14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 69.Wikoff WR, Anfora AT, Liu J, Schultz PG, Lesley SA, Peters EC, Siuzdak G. Metabolomics analysis reveals large effects of gut microflora on mammalian blood metabolites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106(10):3698–3703. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0812874106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Jennis M, Cavanaugh CR, Leo GC, Mabus JR, Lenhard J, Hornby PJ. Microbiota-derived tryptophan indoles increase after gastric bypass surgery and reduce intestinal permeability in vitro and in vivo. Neurogastroenterol Motil. 2018;30(2):e13178. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 71.Estruch R, Ros E, Martinez-Gonzalez MA. Mediterranean diet for primary prevention of cardiovascular disease. N Engl J Med. 2013;369(7):676–677. doi: 10.1056/NEJMc1306659. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Urpi-Sarda M, Casas R, Chiva-Blanch G, Romero-Mamani ES, Valderas-Martinez P, Salas-Salvado J, Covas MI, Toledo E, Andres-Lacueva C, Llorach R, et al. The Mediterranean diet pattern and its main components are associated with lower plasma concentrations of tumor necrosis factor receptor 60 in patients at high risk for cardiovascular disease. J Nutr. 2012;142(6):1019–1025. doi: 10.3945/jn.111.148726. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Sureda A, Bibiloni MDM, Julibert A, Bouzas C, Argelich E, Llompart I, et al. Adherence to the Mediterranean diet and inflammatory markers. Nutrients. 2018;10(1):62. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 74.Esposito K, Marfella R, Ciotola M, Di Palo C, Giugliano F, Giugliano G, D’Armiento M, D’Andrea F, Giugliano D. Effect of a mediterranean-style diet on endothelial dysfunction and markers of vascular inflammation in the metabolic syndrome: a randomized trial. JAMA. 2004;292(12):1440–1446. doi: 10.1001/jama.292.12.1440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Llorente-Cortes V, Estruch R, Mena MP, Ros E, Gonzalez MA, Fito M, Lamuela-Raventos RM, Badimon L. Effect of Mediterranean diet on the expression of pro-atherogenic genes in a population at high cardiovascular risk. Atherosclerosis. 2010;208(2):442–450. doi: 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2009.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Additional file 1: Supplemental Table 1. Non-human primate diets replicating human Western and Mediterranean dietary patterns. Supplemental Figure S1. Individual read statistics on each sample. Samples ranged from 13,694,588 to 28,756,486 reads with no significant differences in reads between dietary patterns. Supplemental Figure S2. Diet, not pen effects, drive microbiome populations. A. PCoA of bacterial beta diversity based on the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity; different solid color spheres indicates subjects housed in same pen. B. Shannon diversity of each subject; different solid color spheres indicates subjects housed in same pen. Supplemental Figure S3. Diet shifts viral and protozoa populations in the gut microbiome. A. Relative abundance of viral species in different fecal samples is visualized by bar plots. Samples are aggregated by diet cohort. Each colored box represents a viral species. The height of a color box represents the relative abundance of that organism within the sample. “Other” represents lower abundance taxa (<5%). B. Relative abundance of protozoa species in different fecal samples is visualized by bar plots. Samples are aggregated by diet cohort. Each colored box represents a protist species. The height of a color box represents the relative abundance of that organism within the sample. “Other” represents lower abundance taxa (<5%). C. Relative abundance of fungal species in different fecal samples is visualized by bar plots. Samples are aggregated by diet cohort. Each colored box represents a fungal species. The height of a color box represents the relative abundance of that organism within the sample. “Other” represents lower abundance taxa (<5%). D. A. Relative abundance of phages in different fecal samples is visualized by bar plots. Samples are aggregated by diet cohort. Each colored box represents a bacteriophage species. The height of a color box represents the relative abundance of that organism within the sample. “Other” represents lower abundance taxa (<5%). Supplemental Figure S4. Western diet-fed subjects with low P. copri abundance display elevated plasma gamma-glutamyl amino acid and phosphatidylethanolamine metabolites. Supplemental Figure S5. Obesity regardless of diet does not significantly regulate the gut microbiome. A. Shannon diversity. B. PCoA of bacterial beta diversity based on the Bray-Curtis dissimilarity. C. Relative abundance of bacterial species in different fecal samples is visualized by bar plots. Each bar represents a subject and each colored box a bacterial taxon. The height of a color box represents the relative abundance of that organism within the sample. “Other” represents lower abundance taxa. D. Proportional abundance of Treponema (Genus) in obese and lean NHP regardless of dietary pattern. E. Proportional abundance of Treponema succinifaciens in obese and lean NHP regardless of dietary pattern.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article [and its supplementary information files].