Abstract
Nigella is a small genus of the family Ranunculaceae, which includes some popular species due to their culinary and medicinal properties, especially in Eastern Europe, Middle East, Western, and Central Asia. Therefore, this review covers the traditional uses and phytochemical composition of Nigella and, in particular, Nigella sativa. The pharmacological studies reported in vitro, in vivo, and in humans have also been reviewed. One of the main strength of the use of Nigella is that the seeds are rich in the omega-6 fatty acid linoleic acid and provide an extra-source of dietary phytochemicals, including the bioactive thymoquinone, and characteristics saponins, alkaloids, and flavonoids. Among Nigella species, N. sativa L. is the most studied plant from the genus. Due to the phytochemical composition and pharmacological properties, the seed and seed oil from this plant can be considered as good candidates to formulate functional ingredients on the basis of folklore and scientific knowledge. Nonetheless, the main limations are that more studies, especially, clinical trials are required to standardize the results, e.g. to establish active molecules, dosage, chemical profile, long-term effects and impact of cooking/incorporation into foods.
Keywords: Nigella, cancer, pharmacological properties, functional ingredients, metabolic syndrome, thymoquinone
Introduction
Nigella, also known as fennel flower, is a small genus belonging to the family Ranunculaceae and includes around 20 species (Zohary, 1983; The plant list, 2020). The members of the genus are annuals and survive harsh condition as seed (therophytes) with a short life cycle (Agradi et al., 2002). A popular ornamental species, Nigella damascena L. (commonly known as lady-in-a-mist or ragged lady), and a well-known condiment and spice, Nigella sativa L. (also known as black cumin or black seeds), have a high commercial interest especially in the food, pharmaceutical and cosmetics industries (Ali and Blunden, 2003; Bittkau and Comes, 2009; Malhotra, 2012). As an example, N. sativa is used in foods, pickles, and baked goods (Malhotra, 2012).
The evolutionary origins of Nigella species are presumably in the Aegean and the adjacent Western-Irano-Turanian region; its centre of species diversity (Zohary, 1983; Bittkau and Comes, 2009). The genus is found as wild in southern Europe, Russia, northern Africa, Asia Minor, Turkey, Middle-East, India, Pakistan, and Bangladesh (Tonçer and Kizil, 2004; Zohary, 1983; Dönmez and Mutlu, 2004; Heiss and Oeggl, 2005; Sharma et al., 2009; Iqbal et al., 2010; Heiss et al., 2011; Rabbani et al., 2011; Zhao et al., 2013; Hossan et al., 2018).
The taxonomic position of Nigella has undergone many changes in the past few decades. It has been commonly divided into three sections viz. Komaroffia, Garidella and Nigella (Tutin et al., 1972; Tamura, 1993; Uğurlu Aydın and Dönmez, 2019). Section Komaroffia comprises one species (Nigella integrifolia Regel), section Garidella consists of two species (Nigella nigellastrum (L.) Willk. and Nigella unguicularis (Poir.) Spenn.), whereas section Nigella composed of twelve species, including N. sativa, N. damascena and others (Nigella arvensis L., Nigella fumariifola Kotschy, Nigella hispanica L., Nigella segetalis M. Bieb., Nigella stellaris Boiss., Nigella elata Boiss., Nigella ciliaris DC., Nigella orientalis L., Nigella oxypetala Boiss., and Nigella turcica Dönmez and Mutlu) (Zohary, 1983; Heiss et al., 2011). In the Plant List, a working list of known plant species produced by the botanical community, there are 91 Nigella names, but only 23 are accepted latin names for species (The plant list, 2020). In general, this genus is characterized by angular or discoid seeds and the characteristic black color is related to other common name of Nigella, “black cumin” (Zhao et al., 2013).
Due to their ethnopharmacology as healing herbs and food importance of Nigella spp., the present work reviews their traditional uses and phytochemical composition, as well as various scientific studies related to their health benefit with special emphasis in N. sativa.
Traditional Uses of Nigella
Latest ethno-pharmacological studies showed that Nigella species are among the most usually used for traditional and folk medicinal practices. Among them, N. sativa is probably the best-known species of the Nigella genus and it has been used in many parts of the world as a natural medicine. The traditional use of N. sativa dates from the 1st century A.D.; Pliny the Elder recommended N. sativa as a digestive and an ingredient of antidotes curing snake bites and scorpion stings (Dönmez and Mutlu, 2004), or even at least till Tutankhamen kingdom (Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz et al., 2016). Today, the seed powder of N. sativa is recommended at 0.5–4 g in the Pharmacopoeia of India (Tajmiri et al., 2016), which is used as a stimulant to ease bowel and indigestion problems and as carminative. It has also been administered to manage pain during menstruation and diabetes in India and Bangladesh (Esakkimuthu et al., 2016; Hossan et al., 2018). Similarly, N. sativa is widely used in traditional medicine of Algeria for the treatment of diabetes and also to treat high blood pressure (BP) (Bouzabata, 2013).
Moreover, according to the Bedouins (Egypt), the wooden stem is used to treat jaundice, while seeds are used to treat BP as before, as well as heart diseases, etc. (El-Seedi et al., 2013) (Table 1). Similar uses have been reported in Iranian traditional medicine (Ghazeeri et al., 2012; Amiri and Joharchi, 2013; Bahmani et al., 2016b), in Pakistan (Khan et al., 2014; Yaseen et al., 2015; Aziz et al., 2017) and in Morocco (Eddouks et al., 2002; El-Hilaly et al., 2003; Khabbach et al., 2012; Jamila and Mostafa, 2014; Teixidor-Toneu et al., 2016), where N. sativa seeds and leaves are orally ingested, consumed as a powder, herbal tea, as decoction or as inhalant. In Pakistan N. sativa is also applied to manage lactation, bacterial diseases, etc. (Khan et al., 2014; Aziz et al., 2017), while in Morocco the seeds are recommended to deal with otolaryngological, urological, and nephrological ailments as well as to treat pathologies of the respiratory and skeleton–muscular systems, allergy and hyper-sensibility (Eddouks et al., 2002; El-Seedi et al., 2013; Jamila and Mostafa, 2014). The anti-rheumatic and analgesic properties of N. sativa combined with honey have been reported (Khabbach et al., 2012). In addition, seeds infusion is used to treat malaria in the Malaysian traditional medicine (Al-Adhroey et al., 2010), as well as seeds (fresh, dried, and powdered forms) and leaves in Ethiopia (Alrawi et al., 2017). The use of N. sativa is still more widespread, being recognized as panacea for its healing properties in Qatar (Alrawi et al., 2017) and Bangladesh (Jennings et al., 2015). Some of the latter uses are also common in Mauritius, Nepal, Turkey, Thailand, Lebanon, and Palestine (Ghazeeri et al., 2012; Al-Ramahi et al., 2013; Sreekeesoon and Mahomoodally, 2014; Guler et al., 2015; Jennings et al., 2015; Kunwar et al., 2015; Bahmani et al., 2016a; Neamsuvan et al., 2016; Alrawi et al., 2017; Ahmed et al., 2018). Furthermore, in Bangladesh and Libano N. sativa seeds are used as a spice and food preservative, directly consumed after being ground, while Nigella oil also can be applied topically (Jennings et al., 2015). Similarly, seeds of N. sativa (also named Nigella glandulifera Freyn and Sint.) are consumed in some regions of China and frequently added to “naan” (a crusty pancake). Its water decoction is used in the Uighur's traditional medicine for the treatment of numerous disorders as the other species (Table 1) (Zhao et al., 2013).
TABLE 1.
Some traditional uses of Nigella species.
| Species | Traditional use | Country | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Asia | |||
| N. arvensis (seed) | To treat lung, brain and skin | Palestine | (Jaradat et al., 2016a) |
| N. ciliaris (seed) | To treat abdominal pain and to facilitate delivery | Palestine | (Ali-Shtayeh et al., 2015) |
| N. ciliaris (seed) | To treat menstrual cycle problems | Iran | (Bahmani et al., 2015) |
| N. ciliaris (seed) | To treat cancer | Palestine | ((Jaradat et al., 2016a; Hamarsheh et al., 2017) |
| N. sativa (seed) | To treat diuretic, analgesic, insomnia, dizziness, tinnitus, amnesia, and bronchial disorders | China | (Zhao et al., 2013) |
| N. sativa (seed) | To ease bowel and indigestion problems and to manage diabetes | India | (Tajmiri et al., 2016) (Esakkimuthu et al., 2016) |
| N. sativa (seed) | To manage pain during menstruation and diabetes | Bangladesh | (Esakkimuthu et al., 2016) (Esakkimuthu et al., 2016) (Hossan et al., 2018 |
| N. sativa (seed) | Curative effects in bacterial-caused diseases, sexual tonic, to manage lactation and to decrease mental disturbances | Pakistan | (Khan et al., 2014; Aziz et al., 2017) |
| N. sativa (seed) | To treat malaria | Malaysia | (Al-Adhroey et al., 2010) |
| Africa | |||
| N. sativa (seed) | Hypoglycemic and hypotensive agent | Algeria | (Bouzabata, 2013) |
| N. sativa (wooden stem and seed) | Wooden steem: To treat jaundice. Seeds: Hypotensive agent and to treat heart diseases, headaches, nasal congestion, toothache, and against intestinal worms | Egypt | (El-Seedi et al., 2013) |
| N. sativa (seed, fruit and leaf) | Hypoglycemic and hypotensive agent and to deal with digestive, respiratory, and cardiovascular problems, and allergy | Morocco | (Eddouks et al., 2002; El-Seedi et al., 2013; Jamila and Mostafa, 2014) |
| Europe | |||
| N. damascena | Galactagogue (seed) and against trachoma | Italy | (Geraci et al., 2018) (Leporatti and Ghedira, 2009) |
| N. damascena | Antihelmintic (for children) and to treat haematuria and skin diseases (itchiness and eczema) | Serbia | (Geraci et al., 2018) |
Other Nigella species with a wide range of medicinal properties are N. damascena and N. ciliaris. In Central Europe, the use of N. damascena dates from Bronze Age but it cannot reliably assign any ethnobotanical relevance and its origin is unclear; it has never grown in the wild in central Europe (Heiss and Oeggl, 2005). Alternatively, N. damascena seeds are used for example in Sicilian folk medicine as a galactogogue (Geraci et al., 2018). Other uses are as emmenagogue, vermifugue, and disinfectant (Heiss and Oeggl, 2005). This plant is also used as an helmintic agent and to treat hematuria, and skin diseases in the Serbian medieval medicine (Jarić et al., 2014). The former use has also been reported in Epirus (Greece) (Vokou et al., 1993). Traditionally, N. damascena is used for treating trachoma in Tunisia and Italy (Leporatti and Ghedira, 2009). Besides its use as herbal remedy, N. damascena is used as a condiment in several regions (Heiss and Oeggl, 2005), including in Morocco (Khabbach et al., 2011).
In the folklore medicine of Palestine and Iran, N. ciliaris seeds are used for abdominal pain, to facilitate delivery and to treat menstrual cycle related problems, respectively (Ali-Shtayeh et al., 2015) (Bahmani et al., 2015). In Turkey, Meriç Town, dried flowers of N. arvensis are used as a winter tea (Kartal and Güneş, 2017). On the other hand, in Iran (Kerman), the seed powder of N. arvensis mixed with other seeds are administrated to enhance male potency and to improve memory and intelligence (Khajoei Nasab and Khosravi, 2014). The seeds of both Nigella species are used for the treatment of cancer in Palestine (Jaradat et al., 2016a; Hamarsheh et al., 2017).
Phytoconstituents
Nigella genus is widely used for their culinary and medicinal properties especially in the Eastern Europe, Middle East, Western and Central Asia. The plants are mainly consumed for their seeds and seed oil, as commented before. The main constituents of N. sativa seeds reported in the literature are fixed oil (27–40%), proteins (16–19%), characterized mainly by the amino acids arginine, glutamic acid, leucine, lysine; minerals (1.79–3.74%), like Cu, Zn, P, and Fe; carbohydrates (28.5–33.7%), and solubre dietary fibers (5.5–8.9%) (Al-Naqeep et al., 2009; Tiruppur Venkatachallam et al., 2010; Kooti et al., 2016; El-Naggar et al., 2017; Saxena et al., 2017). Concerning the phytochemical composition of Nigella seeds, the most interesting plant part, it is constituted of alkaloids, terpenes and phenolic compounds (Agradi et al., 2001). Although the number of studies on the chemical composition and pharmacological properties of N. sativa is continuously increasing (Bourgou et al., 2010b), there are other interesting species for their culinary and medicinal properties, as commented before. Thus, this section details phytochemicals found in N. sativa and other Nigella plants.
Fixed Oil: Essential Fatty Acids
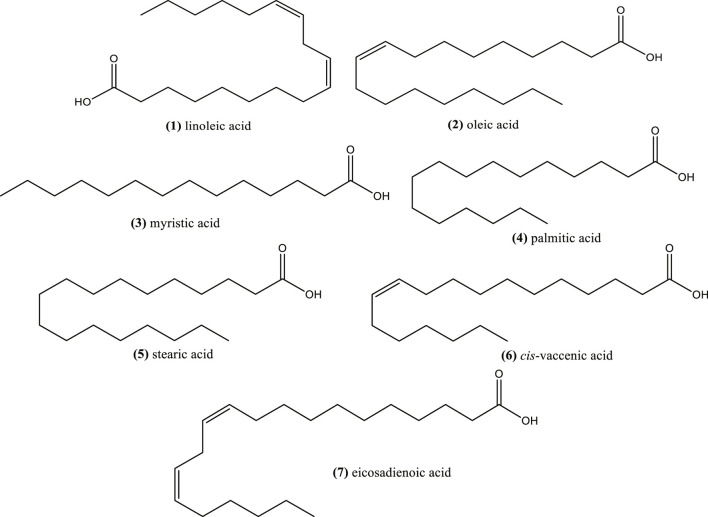
The oil of N. sativa seeds has been highly studied, showing predominance of linoleic acid (1) (50–60%), oleic acid (2) (20%), myristic acid (3) (30%), and palmitic acid (4) (12.5%) (Tiruppur Venkatachallam et al., 2010; Kooti et al., 2016; El-Naggar et al., 2017; Saxena et al., 2017) (Figure 1). Nigella seed oil from Morocco also showed that the major fatty acids were linoleic acid (1) (58.5 and 56.5%), oleic acid (2) (23.8 and 24.9%) and palmitic acid (4) (13.1 and 11.9%) using cold press and solvent extraction, respectively (Gharby et al., 2015). The major compounds were similar to those found in N. sativa seeds from other Mediterranean countries. These fatty acids were also reported as major compounds from the seed oils, extracted by n-hexane, of different N. sativa genotypes from India (Saxena et al., 2017). Other study have shown that fixed oils from N. sativa seed from Turkey and Egypt obtained by supercritical CO2 extraction were similar in fatty acid composition of saturated fatty acids (16%), mainly constituted by palmitic acid (4) and stearic acid (5); monounsaturated acids (23%), mainly oleic acid and cis-vaccenic acid (6), and polyunsaturated acids (58%), mainly linoleic acid (1) and eicosadienoic acid (7) (Piras et al., 2013) (Figure 1). In this work the ratio omega-6/omega-3 ranged between 180 and 221 considering linoleic and alpha-linolenic acid.
FIGURE 1.
Fatty acids in fixed oils from Nigella seeds.
Other Nigella species, including N. damascena, N. orientalis, N. arvensis, N. elata, N. nigellastrum, N. oxypetala, N. segetalis, N. unguicularis, and N. lancifolia Hub.-Mor., also contain linoleic acid (31.2–69.5%) and oleic acid (15.8–36.0%) as the major ones (Kökdil et al., 2005; Matthaus and Özcan, 2011). The abundance relevance of other fatty acids depends on the species.
Volatile Oil Phytochemicals
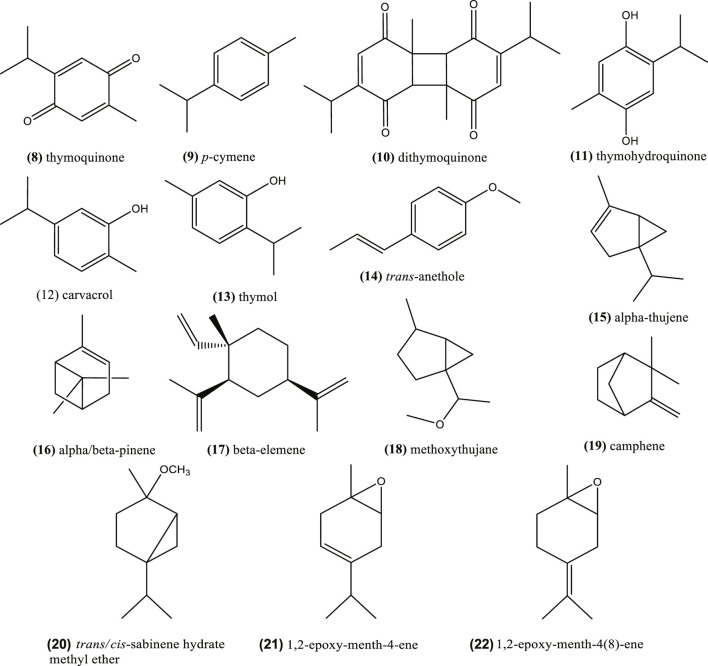
Volatile oils are derived from plant tissues and are characterized to evaporate under room temperature and failure to saponify. Concerning volatile oil (around 0.5–1.5%) of Nigella seeds, it showed high abundance of thymoquinone (8), p-cymene (9) and other phenolic derivatives, such as dithymoquinone (nigellone) (10), thymohydroquinone (11), carvacrol (12), and thymol (13) (Bourgou et al., 2010b; Tiruppur Venkatachallam et al., 2010; Kooti et al., 2016; El-Naggar et al., 2017).
These compounds are considered Nigella active principles (Mahmoudvand et al., 2014), but the composition may vary depending on the chemotype and species, among other factors (Edris, 2010; Zribi et al., 2014; Koshak et al., 2017; Saxena et al., 2017). As an example, N. sativa volatile composition (seeds) presents different chemotypes (Burits and Bucar, 2000; Islam et al., 2004): thymoquinone (8) chemotype in Egypt and Turkey varieties (77.2–86.2%) (Piras et al., 2013); trans-anethole (14) (38.3%) chemotype in Iranian N. sativa essential oil (Nickavar et al., 2003); p-cymene (9) (33%), and thymol (13) (26.8%) chemotype in Moroccan species (Moretti et al., 2004). The volatile oils from N. sativa seeds of Turkey and Egypt obtained by supercritical fractioned extraction with CO2 also showed that thymoquinone was the major constituent (77.2–86.2%) followed by p-cymene (9) (5.4–11.0%) (Piras et al., 2013). An essential oil from Iranian N. sativa seeds was rich in thymoquinone (42.4%), p-cymene (14.1%) and caravacrol (10.3%) (Mahmoudvand et al., 2014). Figure 2 depicts the chemical structure of these phytochemicals and Table 2 the content of the major ones and the source.
FIGURE 2.
Phytochemical components in essential oils from Nigella seeds.
TABLE 2.
Main volatile compounds in essential oils from Nigella seeds.
| Compound name | Source (origin) | Relative amount (%) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Thymoquinone | N. damascena (M), N. sativa seed (C), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (I), N. sativa seed (tk, E), N. sativa seed (ir), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (M) | 0.1, 3.7, 3.0, 33.1–38.4a, 77.2–86.2b, 0.6, ND, 3.8 | (Bourgou et al., 2010b; Geng et al., 2009; Jrah Harzallah et al. (2011); Moretti et al., 2004; (Piras et al., 2013) |
| p-Cymene | N. damascena (M), N. sativa seed (C), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (I), N. sativa seed (tk, E), N. sativa seed (ir), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (M) | ND, 33.8, 60.5, ND, ND, 14.8, 49.5, 33.8 | (Bourgou et al., 2010b; Geng et al., 2009; Jrah Harzallah et al. (2011); Moretti et al., 2004; (Piras et al., 2013) |
| Dithymoquinone | N. damascena (M), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (I), N. sativa seed (tk, E), N. sativa seed (ir), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (M) | ND, ND, ND, ND, ND, ND | (Bourgou et al., 2010b; Jrah Harzallah et al. (2011); Moretti et al., 2004; (Piras et al., 2013) |
| Thymohydroquinone | N. damascena (M), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (I), N. sativa seed (tk, E), N. sativa seed (ir), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (M) | ND, 0.4, 1.1–2.3a, ND, ND, ND | (Bourgou et al., 2010b; Jrah Harzallah et al. (2011); Moretti et al., 2004; (Piras et al., 2013) |
| Carvacrol | N. damascena (M), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (I), N. sativa seed (tk, E), N. sativa seed (ir), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (M) | ND, 2.4, 0.8–2.0a, ND-7.9, 1.6, 0.6, ND | (Bourgou et al., 2010b; Jrah Harzallah et al. (2011); Moretti et al., 2004; (Piras et al., 2013) |
| Thymol | N. damascena (M), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (I), N. sativa seed (tk, E), N. sativa seed (ir), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (M) | ND, ND, 5.3–17.0a, ND, ND, 26.8 | (Bourgou et al., 2010b; Jrah Harzallah et al. (2011); Moretti et al., 2004; (Piras et al., 2013) |
| α-Thujene | N. damascena (M), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (I), N. sativa seed (tk, E), N. sativa seed (ir), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (M) | ND, 6.9, ND, ND-0.4b, 2.4, 18.9, 3.3 | (Bourgou et al., 2010b; Jrah Harzallah et al. (2011); Moretti et al., 2004; (Piras et al., 2013) |
| α-Pinene | N. damascena (M), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (I), N. sativa seed (tk, E), N. sativa seed (ir), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (M) | ND, 1.7, ND, ND, 1.2, 1.2, 5.4, 0.7 | (Bourgou et al., 2010b; Jrah Harzallah et al. (2011); Moretti et al., 2004; (Piras et al., 2013) |
| β-Pinene | N. damascena (M), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (I), N. sativa seed (tk, E), N. sativa seed (ir), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (M) | ND, 2.4, ND-0.4a, ND, 1.3, 4.3, 1.1 | (Bourgou et al., 2010b; Jrah Harzallah et al. (2011); Moretti et al., 2004; (Piras et al., 2013) |
| γ-Terpinene | N. damascena (M), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (I), N. sativa seed (tk, E), N. sativa seed (ir), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (M) | ND, 3.5, 12.9–27.5a, ND-0.6b, 0.5, 2.5, 2.4 | (Bourgou et al., 2010b; Jrah Harzallah et al. (2011); Moretti et al., 2004; (Piras et al., 2013) |
| trans-Anethole | N. damascena (M), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (I), N. sativa seed (tk, E), N. sativa seed (ir), N. sativa seed (T), N. sativa seed (M) | Tr, ND, ND, ND, 38.3 | (Bourgou et al., 2010b; Jrah Harzallah et al. (2011); Moretti et al., 2004; (Piras et al., 2013) |
| β-Elemene | N. arvensis seed, N. damascena seed (M), N. sativa seed (M) | 69.0, 73.2, 5.5 | (Moretti et al., 2004; Edris, 2009) |
ND, Not detected/reported; C, China; I, India; Ir, Iran; E, Egypt; M, Morocco; T, Tunisia; Tk, Turkey; Tr, traces.
Depending on the extraction method and conditions.
Depending on the origin.
The essential oil composition is highly variable and probably more chemotypes exist. As an example, Jrah Harzallah et al. (2011) identified eighty-four compounds in the essential oil obtained by hydrodistillation of N. sativa seeds from Tunisia and the major one was the monoterpenes p-cymene (9) (49.48%), α-thujene (15) (18.93%), α-pinene (16) (5.44%), β-pinene (16) (4.31%). Alternatively, the bioactive compound thymoquinone represented only 0.79%. Similar results were found by Geng et al. (2009); N. sativa seeds contained p-cymene (9) (33.75%) as the major component using the hydrodestillation mode, with low content of thymoquinone (8) (3.73%), while using supercritical CO2 extraction the major one was linoleic acid (1). Another study reported that N. sativa seeds from Tunisia and Morocco showed again that p-cymene (9) occurred in a higher relative concentration (60.5 and 56.7%, respectively) (Bourgou et al., 2010b; Badri et al., 2018). Furthermore, the essential oil extracted by hydrodistillation from Egyptian seeds showed the major components were p-cymene (9) (33.0%) and thymoquinone (8) (32.2%), followed by α-thujene (15) (13.0%) and camphene (19) (2.9%) (Viuda-Martos et al., 2011). Rarely, the composition of N. sativa seeds essential oil from Poland showed that two other monoterpenoids were present: cis- and trans-4-methoxythujane (18) (Wajs et al., 2008). Bourgou et al. (2012) has identified also four terpenoids, trans/cis-sabinene hydrate methyl ether (20), 1,2-epoxy-menth-4-ene (21), and 1,2-epoxy-menth-4(8)-ene (22), in Tunisian N. sativa essential oil from seeds by nuclear magnetic resonance (Figure 2).
Nigella damascena seed oil was characterized by almost 100% sesquiterpenes, of which β-elemene (17) (73.2%) was the most representative one (Moretti et al., 2004; Geng et al., 2009). Edris (2009) also remarked that this compound could be present even up to 73.0% in the essential oils of in N. orientalis and N. arvensis. Alternatively, N. arvensis could also contain other compounds in major levels, e.g. a methylated derivative of carvacrol (19) (26.4%), carvacrol methyl ether, followed by β-pinene (16) (21.4%).
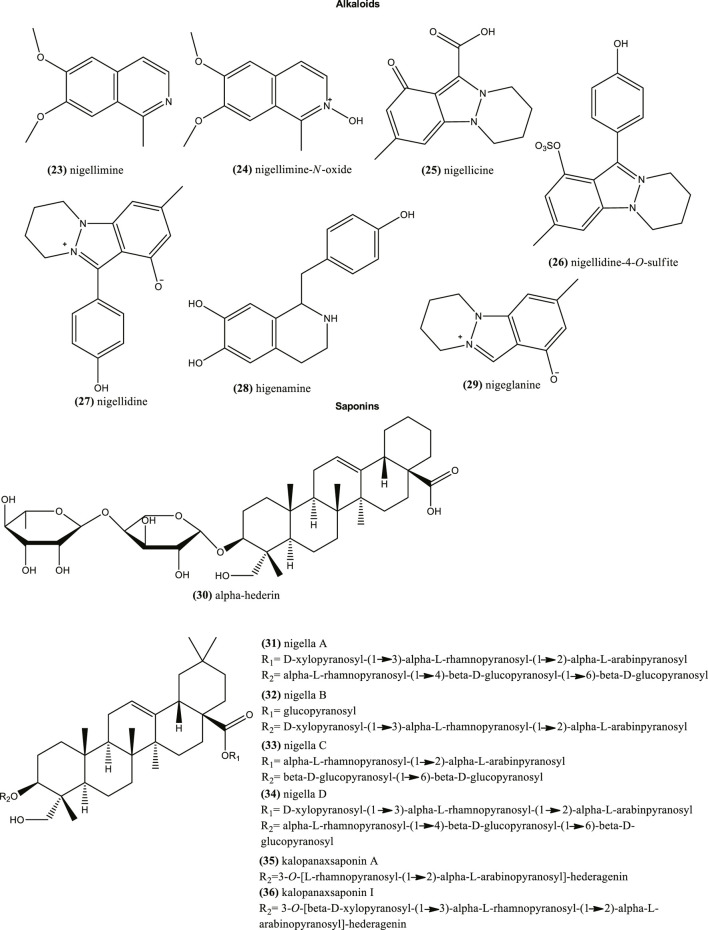
Alkaloids
The bio-potential of nitrogen-containing heterocycles has been recently revised (Thakral and Singh, 2019). In plants, alkaloids contain one or more nitrogen atoms and usually are situated in some cyclic system. Similarly, these nitrogen-containing heterocycles, such as isoquinoline alkaloids and their N-oxides, can be a source of leads for drug discovery (Dembitskya et al., 2015). This included compound such as nigellimine (23) and nigellimine-N-oxide (24) from N. sativa seeds. This species also contains other type of alkaloids such as nigellicine (25), and nigellidine-4-O-sulfite (26) (Figure 3). Nigellidine (27) and its derivative methyl nigellidine, higenamine (28), and nigeglanine (29) were also characterized in N. sativa seeds (Atta Ur et al., 1995; Yun et al., 2014). Among them, methyl nigellidine, nigeglanoside and nigelloside could be used as markers to differentiate both species (Yun et al., 2014).
FIGURE 3.
Example of chemical structures of alkaloids and saponins reported in N. sativa.
Saponins
Other studies also suggest the presence of phenolic compounds and triterpenes like saponins in the seeds of N. sativa and other Nigella species (Ali et al., 2008; Atta Ur, 1985; Atta Ur, 1992; El-Naggar et al., 2017; Kooti et al., 2016; Tiruppur Venkatachallam et al., 2010; Zribi et al., 2014). Saponins are a heterogeneous group of glycosides, which have one or more hydrophilic moieties combined with a lipophilic triterpene or steroid derivative. In particular, triterpene saponins are highly characteristic compounds in Nigella seeds. Besides alpha-hederin (30) (Boubertakh et al., 2013), other relative saponins are: 3-O-[d-xylopyranosyl-(1→3)-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-α-l-arabinpyranosyl]-28-O-[-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-d-glucopyranosyl] hederagenin (nigella A) (31), 3-O-[d-xylopyranosyl-(1→3)-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-α-l-arabinpyranosyl]-28-O-β-d-glucopyranosyl hederagenin (nigella B) (32), 3-O-[α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-α-l-arabinpyranosyl]-28-O-[β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-d-glucopyranosyl] hederagenin (nigella C) (33), 3-O-[d-xylopyranosyl-(1→3)-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-α-l-arabinpyranosyl]-28-O-[-α-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→4)-β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→6)-β-d-glucopyranosyl] hederagenin (nigella D) 34) (Figure 3). The latter were reported in the seeds of N. sativa and exhibit a broad spectrum of bioactivities (Chen et al., 2018; Dönmez and Mutlu, 2004). Others also found in the latter species are: 3-O-[l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-l-arabinopyranosyl]-hederagenin (kalopanaxsaponin A) (35) and 3-O-[-d-xylopyranosyl-(1→3)-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→2)-l-arabinopyranosyl]-hederagenin (kalopanaxsaponin I) (36) (Figure 3), with anticancer properties reported in vitro (Tian et al., 2006).
Phenolic Compounds
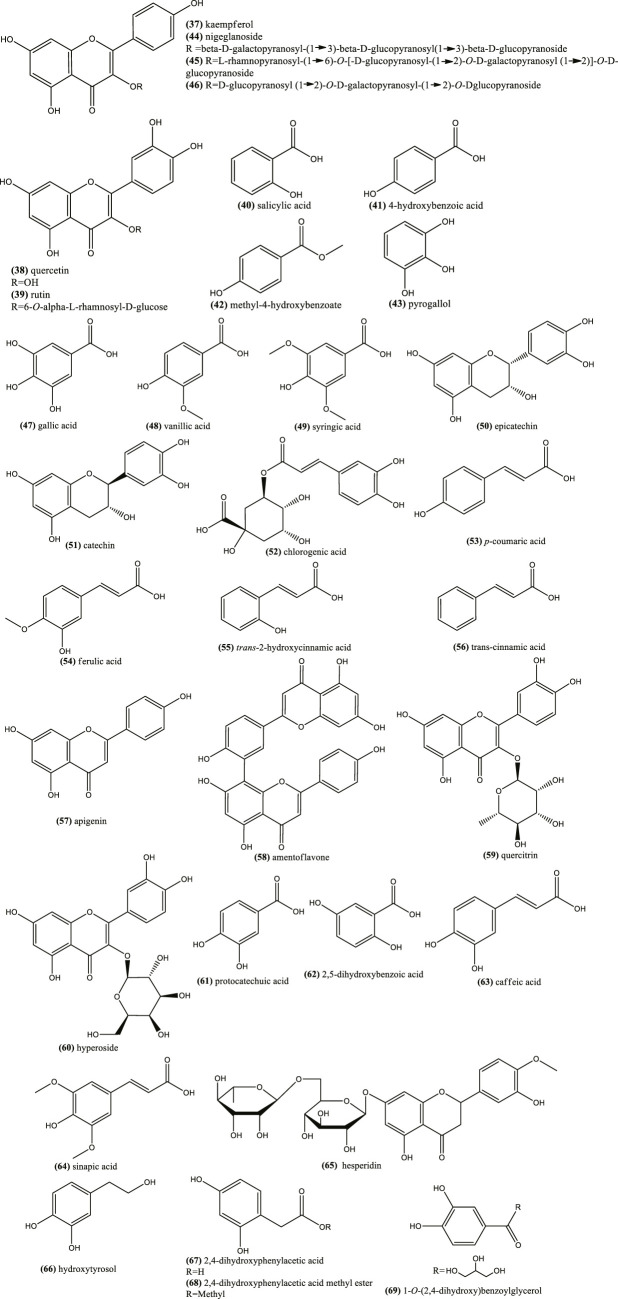
Concerning phenolic compounds, a recent study suggested that N. sativa, N. arvensis, N. damascena, and N. hispanica seeds have more flavonoids and phenolic acid derivatives than N. nigellastrum and N. orientalis seeds (Farag et al., 2014). Phenolic compounds are characterized to be small molecules with at least one phenol unit. Some common ones have been reported in the seeds of N. sativa seeds, e.g. kaempferol (37), quercetin (38), rutin (39), salicylic acid (40), p-hydroxybenzoic acid (41), methyl-4-hydroxybenzoate (42) and pyrogallol (43) (Xin et al., 2008; Boubertakh et al., 2013) (Figure 4). Table 3 shows examples of phenolic compounds described in Nigella plants and their contents.
FIGURE 4.
Example of chemical structures of phenolic compouds reported in N. glandulifera, N. sativa, N. damascena, and N. arvensis.
TABLE 3.
Example of phenolic compounds found in Nigella species.
| Compound name | Source (origin) | Amount (mg/g) | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| p-Hydroxybenzoic acid | N. sativa seed (C), N. sativa seed (T) | NR, 0.002 | (Bourgou et al., 2008; Bourgou et al., 2010a) |
| Gallic acid | N. sativa seed (T), shoot (T), root (T) | 0.3–1.0 a , 0.3, 0.3 | (Bourgou et al., 2008; Bourgou et al., 2010a) |
| Chlorogenic acid | N. sativa seed (T), shoot (T), root (T) | 0.02–0.04 a , 0.015, 0.004 | (Bourgou et al., 2008; Bourgou et al., 2010a) |
| Syringic acid | N. sativa seed (T) | 0.01–0.02 a | (Bourgou et al., 2008; Bourgou et al., 2010a) |
| Vanillic acid | N. sativa seed (T), shoot (T), root (T) | 2.2–3.5 a , 1.4, 0.9 | (Bourgou et al., 2008; Bourgou et al., 2010a) |
| p-Coumaric acid | N. sativa seed (T), root (T) | 0.01–0.02 a , 0.004 | (Bourgou et al., 2008; Bourgou et al., 2010a) |
| Ferulic acid | N. sativa seed (T), root (T) | 0.04–0.13 a , 0.002 | (Bourgou et al., 2008; Bourgou et al., 2010a) |
| trans-Cinnamic acid | N. sativa seed (T), shoot (T), root (T) | 0.03–0.05 a , 0.2, 0.01 | (Bourgou et al., 2008; Bourgou et al., 2010a) |
| (–)-Epicatechin | N. sativa seed (T), shoot (T), root (T) | 0.01–0.02 a , 0.01, 0.01 | (Bourgou et al., 2008; Bourgou et al., 2010a) |
| (+)-catechin | N. sativa seed (T) | 0.1–0.3 a | (Bourgou et al., 2008; Bourgou et al., 2010a) |
| Quercetin | N. sativa seed (C), N. sativa seed (T), shoot (T), root (T) | NR, 0.002–0.005 a , 0.03, 0.03 | (Bourgou et al., 2008; Bourgou et al., 2010a) |
| Apigenin | N. sativa seed (T), shoot (T), root (T) | 0.003–0.005 a , 0.07, 0.02 | (Bourgou et al., 2008; Bourgou et al., 2010a) |
| Amentoflavone | N. sativa seed (T), shoot (T) | 0–0.001 a , 0.03 | (Bourgou et al., 2008; Bourgou et al., 2010a) |
| Quercetin | N. damascena seed (R), N. damascena seed (J), N. arvensis seed (J) | 0.014, NR, NR | (Toma et al., 2015) |
| Quercitrin | N. damascena seed (R), N. sativa seed (R) | 0.020, 0.004 | (Toma et al., 2015) |
| Hyperoside | N. damascena seed (R) | 0.001 | (Toma et al., 2015) |
| Kaempferol | N. arvensis seed (J), N. damascena seed (J), N. sativa seed (C), N. sativa seed (R) | 0.006, NR, NR, NR | (Toma et al., 2015) |
| Kaempferol-3-O-[β-d-glucopyranosyl-(1ê2)-β-d-galactopyranosyl-(1ê2)-β-d-glucopyranoside] | N. arvensis seed (G), N. damascena seed (A, I), N. sativa seed (C), N. hispanica seed (G, F), N. nigellastrum seed (CR), N. orientalis seed (tk), N. sativa seed (E, et, S, SA, tk) | ND, tr, ND, ND, tr, 3.4–6.1 a , NR | (Farag et al., 2014) |
A, Austria; C, China; CR, Czech Republic; E, Egypt; Et, Ethiopia; F, France; G, Germany; I, Italy; J, Jordan; NR, Not reported; R, Romania; S, Syria; T, Tunisia; Tk, Turkey; SA, Saudi Arabia.
It depends on the salinity tested.
Kaempferol and quercetin derivatives are also common in other Nigella species (Farag et al., 2014). Moreover, characteristic glycosilated flavonoids, also found in the seeds, are: kaempferol 3-O-beta-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→3)-beta-d-glucopyranosyl(1→3)-beta-d-glucopyranoside (nigeglanoside) (44) (Hao et al., 1996), kaempferol 3-O-l-rhamnopyranosyl-(1→6)-O-[-d-glucopyranosyl (1→2)-O-d-galactopyranosyl (1→2)]-O-d-glucopyranoside (45) and kaempferol 3-O-d-glucopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-d-galactopyranosyl-(1→2)-O-d-glucopyranoside 46) (Figure 4), which were reported in N. sativa (Liu et al., 2011; Xin et al., 2008) (Figure 4). The latter flavonoid is a taxonomic marker for distinguishing N. sativa from other Nigella species (Farag et al., 2014).
Methanolic extracts from seeds, shoots and roots of Tunisian N. sativa contained phenolic compounds, including: gallic acid (47), p-hydroxybenzoic acid (41), vanillic acid (48), syringic acid (49), (–)-epicatechin (50), (+)-catechin (51), chlorogenic acid (52), p-coumaric acid (53), ferulic acid (54), trans-2-hydroxycinnamic acid (55), trans-cinnamic acid (56), quercetin (38), apigenin (57), and amentoflavone (58) (Figure 4). Nonetheless, among them, vanillic acid (48) was the major phenolic compound (Bourgou et al., 2008; Bourgou et al., 2010a).
A recent study has shown that there are qualitative and quantitative differences between the phenolic compounds of ethanolic extracts from N. sativa and N. damascena seeds (Toma et al., 2015). For example, quercitrin (59) was detected in both extracts, hyperoside (60) and quercetin (38) in N. damascena, while kaempferol (37) was found only in N. sativa. Moreover, a recent study has reported a more complex phenolic profile, which was found complexed with N. damascena seeds proteins: gallic acid (47), protocatechuic acid (61), 2,5-dihydroxybenzoic acid (62), vanillic acid (48), (+)-catechin (51), caffeic acid (63), chlorogenic acid (52), syringic acid (49), (–)-epicatechin (50), p-coumaric acid (53), sinapic acid (64), hesperidin (65), quercetin 38) and kaempferol (37).
Some of these compounds were also present in N. arvensis seeds (Alu'datt et al., 2016), while 7-methylkaempferol (rhamnocitrin) was also reported in the epigeal part of this species (Kirichenko et al., 1972). Other type of phenolic compounds reported in N. damascena seeds were hydroxytyrosol (66), 2,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid (67) and its methyl derivative (68), as well as a new phenolic ester, 1-O-(2,4-dihydroxy) benzoylglycerol 69) (Fico et al., 2000) (Figure 4).
Others
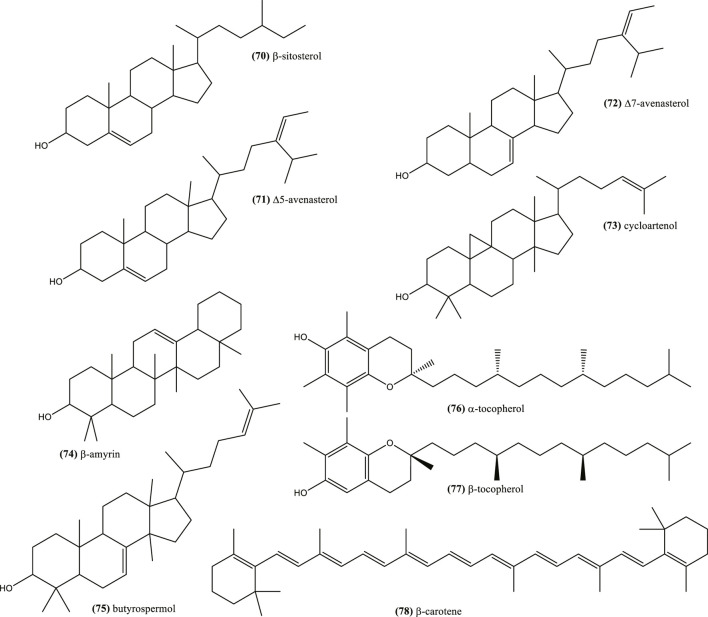
Examples of other reported terpene chemicals include phytosterols such as β-sitosterol (70), ∆5-avenasterol (71), and ∆7-avenasterol (72), as well as stanols such as cycloartenol (73) (Figure 5). Other triterpenes like β-amyrin (74) and butyrospermol (75) (Ramadan and Mörsel, 2002; Ahmad et al., 2013; Ijaz et al., 2017), as well as α-tocopherol (76), γ-tocopherol (77), and β-carotene (78) are also found in seeds (Ramadan and Mörsel, 2004) (Figure 5).
FIGURE 5.
Example of phytosterols and stanols reported and other terpenes in Nigella.
Factors that Affect the Phytochemical Composition
Phytoconstituents of Nigella may vary even within the same species and this is related to many factors such as growing and climatic conditions, location, different organs of the plants and the extraction methods used (Edris, 2010; Manju et al., 2016; Saxena et al., 2017) (Tables 2 and 3). Secondary metabolites, compounds which are not directly related to the development, growth and reproduction of plants but they have significant performance in chemical communication, primary defense against biotic and abiotic stress (Sarkar and Shetty, 2014) and also in epigenetic memory. The chemical composition may vary also during development stage and this was confirmed by Zribi et al. (2014) who demonstrated that the total phenolics, flavonoids, flavonols and flavones, alkaloids and proanthocyanidins contents of Tunisian and Indian N. sativa aqueous extracts were the highest in the vegetative stage. Moreover, the aerial parts from the two varieties were richer in total phenolics and flavonoids, including flavonols, flavones and proanthocyanidins, than seeds. Salinity is also another factor that greatly influenced the phenolic composition of Nigella seeds; e.g. generally the content of certain phenolic compounds decreased, including the major one vanillic acid (45), while the content of trans-cinnamic acid (53), quercetin (38), and apigenin (54) increased. This was related with a decrease of the antioxidant activity (Bourgou et al., 2010a). Today, this is essential information since water scarcity and salinization of arable lands may occur in a future scenario exposed to drastic changes caused by climate (Selim et al., 2019), affecting not only crop growth but also its phytochemical content and antioxidant properties.
This means that a high variability in the content of phytochemicals can be found in Nigella plant parts, and in particular in N. sativa seeds, and from a functional point of view each essential oil/extract should be further characterized in order to elucidate the real active molecules inside for further standardization and quality control.
Biological Activities: Preclinical In Vitro/In Vivo Studies of the Genus Nigella and active compounds
This section collects the results of in vitro, ex vivo, and in vivo studies on the antioxidant, anticancer, cardioprotective, antidiabetic, antiobesity and neurological properties of Nigella species, mainly, N. sativa, as well as some active principles, including thymoquinone.
Antioxidant Activity and Effects on Oxidative Stress
Some studies suggest that N. sativa oil and extracts have antioxidant properties and can modulate oxidative stress, which could be beneficial for oxidative stress related diseases/disorders. In this sense, oils and solvent extracts from N. sativa seeds possessed antioxidant activity in vitro (Toma et al., 2015; Mohammed et al., 2016; Abedi et al., 2017; Singhal et al., 2017), ex vivo (Ghoreyshi et al., 2020), in vivo (Mahmoudi et al., 2018; Rasoli et al., 2018) and in humans (Nikkhah-Bodaghi et al., 2019). Moreover, in vivo regular intake of ethanolic extract of N. sativa seed (400 mg/kg) lowered the lipid peroxidation, and enhanced catalase activity in Wistar rats (Rasoli et al., 2018). Another work suggested that hydroalcoholic and hexane extracts of N. sativa seed as well as thymoquinone may counteract oxidative stress caused by high-fat diets (HFDs), e.g. malondialdehyde (MDA) levels decreased, while the activity of catalase enzyme and serum total antioxidant capacity increased (Mahmoudi et al., 2018). Concerning other Nigella species, N. damacena 70% ethanolic extract (seeds) has shown antioxidant properties in vitro, even higher generally than N. sativa seeds (Toma et al., 2015); the former contained higher amounts of quercetin derivatives. Also, the fixed oil from the seeds of another species, Nigella unguicularis Spenner, showed favorable oxidant/antioxidant balance and blood lipids profile when it was administered to rats (1 ml/kg orally for 4 weeks) (Kökdil et al., 2005). However, the responsible active compounds were not determined in the latter case.
As commented before, thymoquinone can have a protective role against oxidative stress (Woo et al., 2013). Thymoquine has shown antioxidant properties in vitro, in particular using the oxygen radical absorbance capacity (Tesarova et al., 2011). Essential oil extracted from N. sativa seeds with higher thymoquinone content showed stronger antioxidant activity than other essential oils (Abedi et al., 2017). In this context, Usta and Dede (2017) assessed role of thymoquinone on oxidative DNA damage and NF-κB levels in diabetic rats. The results revealed that the oxidative DNA damage (8 hydroxy-2-deoxyguanosine) and NF-κB levels were insignificantly lowered after treatment. Moreover, it also reduced glycosylated hemoglobin, glucose levels and aspartate aminotransferase (AST), alanine aminotransferase and gamma-glutamyl transpeptidase activities. In recent in vitro and in vivo studies, thymoquinone in combination with iron oxide nanoparticles showed attenuation in genetic and oxidative damage, and caused an enhancement in the levels of anti-oxidant enzymes (Ansari et al., 2019).
Nonetheless, other Nigella phytochemicals constituents have antioxidant activity, which is not strictly dependent on the thymoquinone content (Bordoni et al., 2019). Thymohydroquinone (11) has also shown scavenging properties in vitro, while no effects were found for dithymoquinone (10) (Tesarova et al., 2011). Trans-anethole (14), isolated from the essential oil of N. sativa seeds by thin-layer chromatography, also showed free radical scavenging properties using several methods (Burits and Bucar, 2000). Moreover, the phenolic nature of thymol (13) and carvacrol (12) makes them to possess higher antioxidant activity than other volatile constituents in oils (see reviews by (Salehi et al., 2018; Sharifi-Rad et al., 2018; Salehi et al., 2019). In an antioxidant activity guided fractionation of the essential oil from N. sativa seeds it was found that thymoquinone 11) (51%), thymol (25%) and carvacrol (8%) were the main antioxidant compounds (Kazemi, 2015). Moreover, in oxidative stress induced experimental subjects, thymol (12) (thymol 10 mg/kg) has been shown significant impact on sperm quality via increasing the spermatozoa concentration and motility, and lowering the MDA level. It also decreases the dead sperm ratio and enhances the glutathione concentrations in the testicles, liver and kidney tissues (Fangfang et al., 2017). The antioxidative properties of thymol (12) and carvacrol (13), through improving the antioxidants, suppressing lipid peroxidation markers and ameliorating oxidative stress, have also been shown in other in vivo studies (Bakir et al., 2016; Samarghandian et al., 2016; Saravanan and Pari, 2016).
It should be notice that polar extracts from Nigella could have a wide spectrum of other phenolic compounds, which are antioxidant in nature (see section 4.5), and thus it should be taken into account in further studies. As an example, free and bound phenolic compounds, which were associated to N. damascena and N. arvensis proteins from the seeds, have shown antioxidant properties in vitro (Alu'datt et al., 2016). As noted before, N. damascena seeds contain quercetin derivatives, including quercetin aglycone, hyperoside and quercitrin, as well as the total phenolic content showed enhanced antioxidant properties (Toma et al., 2015). Furthermore, total saponins from N. sativa seeds increased the plasma superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase (GSH-Px) activities and decreased MDA level compared to control group in d-galactose-induced aging model (6–24 mg/kg). These seeds also showed (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl) DPPH radical scavenging properties (Dönmez and Mutlu, 2004).
Anti-cancer Properties
Nigella sativa has anti-proliferative, pro-apoptotic, anti-oxidant, cytotoxic, anti-mutagenic, and anti-metastatic effects, underlined by several mechanisms reviewed by (Majdalawieh and Fayyad, 2016). Studies in cell lines, including in human lung (A-549 cells), epithelial cervical (HeLa and SiHa) and Michigan Cancer Foundation-7 (MCF-7) breast cancer cells, have shown that the administration of N. sativa alcoholic seed extracts, seed oil and nanoemulsions markedly lowered the cell viability, inducing apoptotic cell death, and/or altered the cellular morphology, with IC50 values between 0.41-82 μL/mL in some cases (Shafi et al., 2009; Hasan et al., 2013; Al-Sheddi et al., 2014; Periasamy et al., 2016; Butt et al., 2019). Among these studies, Hasan et al. (2013) revealed the presence of thymoquinone as the potential active Nigella constituent. Concerning in vivo studies, supplementation of different doses of N. sativa ethanolic extract (seed) on daily basis (150, 250, 350 mg/kg), thymoquinone (20 mg/kg), and daily dose of silymarin (100 mg/kg) prevented from the hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation provoked by diethylnitrosamine through multiple pathways: reduction in p-EGFR and p-ERK1/2, deactivation of EGFR/ERK1/2 signaling, down regulation of target genes (c−fos, PCNA, and Bcl2), suppression of cell proliferation, reduction in alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) and hepatic enzymes, and enhancement in the levels of antioxidant enzymes (Shahin et al., 2018). Other in vivo studies suggested a protective effect of N. sativa seeds oil and thymoquinone against breast carcinogens (Linjawi et al., 2015) with dosages between 1 and 10 mg/kg. The water extract of N. sativa has shown immunomodulatory and anti-tumor effects on Ehrlich ascites carcinoma in mouse model (Aikemu et al., 2013), but its composition was not characterized.
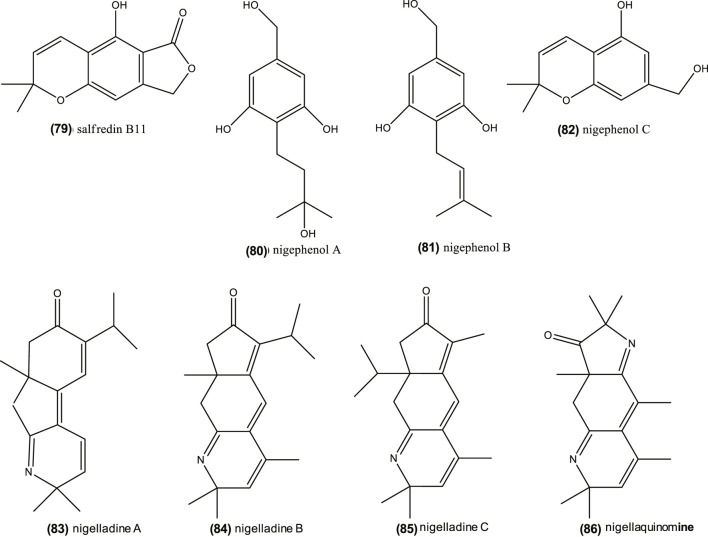
Thymoquinone is one of the potential active compounds in Nigella, as commented before (Woo et al., 2012; Siveen et al., 2014; Shanmugam et al., 2018a; Shanmugam et al., 2018b). It also demonstrated anti-tumor activity on human liver HepG2 cancer cells lines (IC50 = 46 μM) by: enhanced caspase-3 enzyme activity, decreased MDA contents, induced cell apoptosis, and inhibited cell growth (Ismail et al., 2018). This compound also revealed to be a potential therapeutic adjuvant in human breast cancer cell lines (MCF-7, IC50 = 64.93 µM, and T47D, IC50 = 165 µM). In other cases, thymoquinone in combination with anti-cancer drugs, can exhibit antagonistic and synergistic effects (Bashmil et al., 2018). Nonetheless, as shown in “Phytoconstituents” section, Nigella genus is a rich source of phytochemicals, including dithymoquinone (10), thymohydroquinone (11), carvacrol (12), thymol (13), nigellimine-N-oxide (24), nigellicine (25), nigellidine (27), which may contribute to the anticancer properties (see reviews by Majdalawieh and Fayyad, 2016; Salehi et al., 2018; Sharifi-Rad et al., 2018; Salehi et al., 2019). Edris (2009) also remarked that β-elemene (17), which is one of the most abundant compounds in Nigella species like N. orientalis, N. damascena, and N. arvensis, has also anti-cancer properties. Moreover, recent studies suggest that Nigella saponins, including α-hederin (30), nigella A (31) and B (32), have an anti-cancer protective role (Chen et al., 2018; Dönmez and Mutlu, 2004; Kumara and Huat, 2001; Rooney and Ryan, 2005; Tian et al., 2006). Remarkably, nigella A (31) and B (32) (40 mg/kg, intragastric administration), extracted from N. sativa, inhibited tumor growth in nude mice by 42.82 and 37.20%, respectively, when compared with vehicle-administered animals (Chen et al., 2018). Furthermore, phenolic derivatives isolated in the seeds of N. sativa, salfredin B11 (79), nigephenol A (80) and B (81), and nigephenol C (82) (Figure 6), showed inhibition against HepG2 cells (Sun et al., 2015). Globally, seeds, their extracts and essential oils from Nigella are complex sources of anti-cancer compounds, whose level and synergism/antagonism require further study.
FIGURE 6.
Chemical structure of salfredin B11, nigephenol A-C and of nigelladine A–C and nigellaquinomine.
Cardioprotective Properties
Nigella sativa has a high potential for the prevention and treatment of cardiovascular diseases, while little is known about the cardiovascular properties of other Nigella species. As an example, N. sativa seeds powder improved lipid profile and prevented atherosclerosis in hypercholesterolemic rabbits when it was supplied in their diet (5%). It significantly decreased fatty streak formation, total cholesterol and low-density lipoprotein (LDL) (Asgary et al., 2013). A recent study also suggests that diabetic rats treated with an ethanolic extract from N. sativa seeds (100–400 mg/kg) for six weeks reduced serum glucose and lipids, while it improved atherogenic index of plasma, vasoreactivity, endothelial dysfunction, and vascular inflammation (Abbasnezhad et al., 2019). Nigella sativa (seed, oil and extracts) has a potential role in the management of hypertension, as shown ex vivo (Hebi et al., 2016; Abbasnezhad et al., 2019) and in vivo studies (Khattab and Nagi, 2007; Leong et al., 2013; Enayatfard et al., 2018) due to vasorelaxant properties. It also may increase endothelial nitric oxide (NO) synthesis, attenuate cardiovascular effects of the vasoconstrictor angiotensin II, and inhibit the parasympathetic tone (Khattab and Nagi, 2007).
Nigella sativa seed oil used in the study by Asgary et al. (2013) contained predominantly terpenoids, including p-cymene 9) (37.3%) and thymoquinone 8) (13.7%). In other studies, N. sativa seeds extracts contained thymoquinone (8), which were standardized (0.05–0.06% extract weight) (Enayatfard et al., 2018; Abbasnezhad et al., 2019). In fact, thymoquinone has demonstrated very good cardioprotective benefits and antihypertensive effects (Enayatfard et al., 2018). Liu et al. (2019) reported that thymoquinone has protective effects against cardiac damage in BALB/c mice via multiple mechanisms including reduction in intestinal histological alterations, suppressions of p62, NLRP3, IL-1β, TNF-α, caspase-1, IL-6 and 18, as well as MCP-1 expressions, inhibition of troponin-T levels in serum, enhancement in ATP, improvement in IL-10 and beclin 1 levels, and decrement in phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase level. Convincingly, thymoquinone effectively modulates pyroptosis, autophagy, and pro-inflammatory markers in cardiac stress (Liu et al., 2019). Likewise, thymoquinone reverted doxorubicine-induced cardiotoxicity when administered to mice. of the administration of thymoquinone (10–20 mg/kg p.o) significantly ameliorated oxidative stress markers involving lipid peroxidation, creatine kinase (CK)-MB, lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), and AST. Alongside, meaningful improvement in antioxidant enzymes like SOD, catalase, glutathione reductase, and glutathione-S-transferase has also been noticed (Alam et al., 2018). Another recent study reported by Atta et al. (2018) showed the protective role of thymoquinone on diabetes-caused cardiac complications in Wistar male rats. Lu et al. (2018) reported that thymoquinone (8) provides shield against myocardial ischemia/reperfusion (I/R) injury in isolated rat hearts and neonatal rat cardiomyocytes models via: improving left ventricular function, lowering myocardial infarct size, attenuating mitochondrial oxidative damage, producing LDH, and lowering MDA levels and H2O2 concentrations, alongside improving antioxidant enzymes levels. Additionally, the cardioprotective role of this compound was also linked to the up-regulation of sirtuin 1 (SIRT1) expression and inhibition of p53 acetylation (Lu et al., 2018). Thymoquinone 8) showed prophylactic effect from myocardial I/R injury in Langendorff perfused rat hearts. It encouraged autophagy, favored cardiac function, lowered infarct size, LDH and CK-MB levels, and suppressed oxidative stress (Xiao et al., 2018). Finally, Salahshoor and their co-workers highlighted that the supplementation of thymoquinone (4.5–18 mg/kg) in mice significantly increased the mean diameter of central hepatic vein, blood serum NO level, and liver enzymes level, while it decreased the liver weight (Salahshoor et al., 2018).
Two other interesting molecules are again carvacrol (12) and thymol (13). The latter was a cardioprotective agent against carotid tissue of hypercholesterolemic rats. The supplementation of thymol (24 mg/kg) in experimental subjects prevents from cardio complications through several mechanisms such as reduction in low density lipoprotein, triglycerides, increment in high-density lipoprotein level, reduction in apoptotic proteins and inflammatory expressions, phosphorylation of p38 (p-p38) and the protein expression of cleaved caspase-3 (Bayatmakoo et al., 2017). In another work, thymol (13) administration (7.5 mg/kg) reversed changes produced by isoproterenol in rats. It also enhanced the caspase-8 and 9, as well as Fas genes expression while lowered Bcl-xL gene expression in myocardium (Meeran et al., 2016). Among other effects, previous investigation revealed that multiple pathways are involved in this effect: a lowered serum cardiac troponin-Y, lysosomal thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS), high sensitivity C-reactive protein (hsCRP), and lowered activities of β-glucuronidase, β-galactosidase, cathepsin-B and D activities in lysosomes. Thymol down-regulated the proinflammatory cytokines involving IL-6 and 1β genes expression and TNF-α in myocardium of rats, and lowered heart weight, left ventricular hypertrophy and increased ST segments and tachycardia (Nagoor Meeran et al., 2015a; Nagoor Meeran et al., 2015b; Nagoor Meeran et al., 2016). El-Sayed et al. (2016) evidenced the protective role of both thymol (13) (20 mg/kg p.o.) and/or carvacrol (12) (25 mg/kg) against doxorubicin induced cardiotoxicity, ameliorating the heart function and oxidative stress parameters.
Antidiabetic
Nigella sativa could play a role against diabetes and obesity, and thereby it could be an interesting agent to treat/prevent the metabolic syndrome. In cell in vitro assays, the ethanol extract from N. sativa seeds has shown antidiabetic activity using adipocytes (Benhaddou-Andaloussi et al., 2008; Benhaddou-Andaloussi et al., 2010). In particular, it was able to activate the AMPK pathway and the insulin signaling pathway, as well as it acted as an agonist of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPARγ) (Benhaddou-Andaloussi et al., 2010), which plays a role in the regulation of metabolism. The seed oil from N. sativa, which contained compounds such as thymoquinone (8), anethole (14), p-cymene (9), saturated and unsaturated fatty acids, had also antidiabetic properties in vivo. In this concern, N. sativa oil (500 mg/kg/day) was co-administered orally along with high-fructose water (20%, w/v) for 45 days. It was able to reduce fructose-induced insulin resistance by reduction of hepatic insulin-degrading enzyme protein and activation of insulin receptor signaling. It also decreased body weight (BW), serum lipids, and glucagon (Elseweidy et al., 2018). In addition, n-hexane and petroleum ether from the seeds of N. sativa has shown inhibitory properties against protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B, with half maximal inhibitory concentration values of 33.15 and 18.50 μg/mL, respectively. This could be another mechanism of action since this enzyme is involved in the down regulation of insulin and leptin signaling and thus this plant could have antidiabetic potential (Xin et al., 2010).
Among the bioactive constituents of Nigella, the antidiabetic and antiobesity properties of thymoquinone have been also revealed. The administration (20 mg/kg/day) to diet-induced obesity mice was able to reduce decrease fasting blood glucose (FBG) and insulin levels, and enhanced glucose tolerance and insulin sensitivity. Moreover, this compound decreased the level of liver triglycerides and serum cholesterol, increased protein expression of phosphorylated Akt, decreased serum levels of inflammatory markers, and decreased NADH/NAD+ ratio. It was related to the capacity of thymoquinone to increase insulin sensitivity in insulin-resistant HepG2 cells through a SIRT1-dependent mechanism (Karandrea et al., 2017). Glycemic parameters were momentously controlled by the administration of thymoquinone (8) to the diabetic rats (Usta and Dede, 2017). El-Aarag et al. (2017) also investigated the effects of this compound to boost anti-diabetic properties of metformin in streptozotocin-induced diabetes in male rats. Their investigation unveiled that negative impacts of streptozotocin were corrected and normal biochemical functions were restored by combined treatment of thymoquinone (8) and metformin. This combination also up-regulated the expression level of glucose transporter-2 (Glut-2). The elevated MDA level was reduced in liver homogenates of the thymoquinone (8) treated rats (Zribi et al., 2014). Thymoquinone (8) in nano-formulation (20–80 mg/kg) showed significant decrease in blood glucose and HbA1c levels and showed a dose dependent antihyperglycemic effect. It can result in better antihyperglycemic effect in type-2 diabetic rats than the non-capsulated compound (Rani et al., 2018). In another research, intraperitoneal administration of thymoquinone (8) (50 mg/kg) resulted in amelioration of dyslipidemia, hypoinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, impaired antioxidant defense system and upregulation of the expression of PPAR-γ and GLUT4 genes in diabetic rats (Moneim et al., 2018).
Concerning thymol (13), intragastric administration (40 mg/kg/day) for the subsequent 5 weeks momentously lowered kidney weight and blood and urinary markers of kidney injury by HFD-induced nephropathy in diabetic mice (Saravanan and Pari, 2016). It further reduced the HbA1c, leptin and adiponectin levels in the mice receiving thymol treatment. The plasma triglyceride, cholesterol, LDL and free fatty acids were reported to be significantly lowered and HDL was momentously elevated in thymol treated mice (Saravanan and Pari, 2016). It also represented beneficial effects on HFD-induced cognitive deficits via activating Nrf2/HO-1 signaling and improving hippocampal insulin resistance (Fangfang et al., 2017). The neuroprotective effect of carvacrol (12) has been also demonstrated on diabetes-associated cognitive deficit in a rat model of diabetes treated with this compound (25–100 mg/kg, 7 weeks). It prevented behavioral, biochemical, and molecular changes associated with diabetes in a dose-dependently way (Deng et al., 2013).
However, the aforementioned in vitro study on adipocytes (Benhaddou-Andaloussi et al., 2010) suggests that compounds other than thymol, such as carvacrol (12), hederin (30), nigellimine (23), and thymoquinone (8), could be active forms. In this regards, four alkaloids, nigelladines A–C (83–85) and nigellaquinomine 86) (Figure 6) have been isolated in N. sativa seeds and possessed inhibitory activity protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B) inhibitory activity, which is key negative regulator of insulin signaling (Chen et al., 2014). Active n-hexane and petroleum ether extracts from this plant were also rich in palmitic acid and unsaturated fatty acids like oleic and linoleic acids, and their methyl esters (Xin et al., 2010).
Antiobesity
Nigella sativa fruit and seed extracts and oil (33% thymoquinone) have shown antiobesity potential using in vitro and in vivo studies, and the mechanisms include the inhibition of pancreatic lipase and α-amylase (15–100%, depending on the extract and enzyme), proinflammatory cytokine production in pre-adipocytes (a model of low-grade inflammation in Simpson–Golabi–Behmel syndrome human) and weight loss, by positively affecting the uncoupling protein-1 (UCP-1), which the index protein of the brown adipose tissue used in the obesity studies (Buchholz and Melzig, 2016; Mahmoudi et al., 2018; Bordoni et al., 2019).
The latter in vivo study, which was performed in mice feed with HFD, suggested that the weight loss effect was less dependent on tymoquinone, while other phenolic compounds may affect (Mahmoudi et al., 2018). Alternatively, studies on female C57BL/6 mice, which were also subjected to HFD and supplemented with thymoquinone (10–20%), showed that this compound ameliorated obesity-induced metabolic dysfunction and impaired positive effects on ovarian and mammary gland metabolic functions (Harphoush et al., 2019). In another context, obesity markers were significantly down-regulated while momentous control over obesity-induced changes in biochemical profile of the body by thymol (13) treatment. It also modified fat and glucose metabolism in such a way to favor the control over obesity in mice partly via hypolipidemic, hypoglycemic, hypo-insulinemic, hypoleptinemic, and pancreatic lipase inhibition action (Haque and Ansari, 2018). This compound has also been endorsed to possess anti-obesity properties by controlling obesity markers in HFD induced obese male Wistar rats. They recorded significant reduction in body and liver weights, visceral fat pad weight, food intake, leptin and inhibition of pancreatic lipase (Haque et al., 2014). Among molecular mechanisms, Choi et al. (2017) assessed the role of thymol (13) in 3T3-L1 white adipocytes via promoting mitochondrial biogenesis, enhancing expression of a core set of brown fat-specific markers as well as enhancing the protein levels of PPARγ, PPARδ, pAMPK, pACC, HSL, PLIN, CPT1, ACO, PGC-1α, and UCP1. It also augmented lipolysis, thermogenesis and fat oxidation. In the case of carvacrol (12), it can act by reduction of autophagy (essential for adipocyte maturation) and on carbohydrate-responsive element-binding protein ChREBP activity, reducing adipogenic differentiation (Spalletta et al., 2018). The supplementation of this compound in the diet (0.1%) may prevent diet-induced obesity by modulating gene expressions involved and protein associated with the signaling cascades in adipogenesis, as well as inflammation (Cho et al., 2012). Overall, it seems that N. sativa has an interesting profile of phytochemicals, which can act in different ways and require attention.
Neuroprotection
The role of N. sativa and its components as promising neuropharmacological agents (Beheshti et al., 2016) in facitilating learning and memory have been recently reviewed (Sahak et al., 2016). In rats, 1 ml/kg of N. sativa oil for 14 days depleted reactive oxygen species (ROS)/NO levels, improved neurogenic proteins, acetylcholinesterase (AChE) activities and neuro-cognitive markers depletions in chlopyrifos exposure (Imam et al., 2018). Moreover, N. sativa oil improved neurocognicives indices such as Morris water maze. In other study performed in rats, the hydroalcoholic extracts of N. sativa seeds (200 and 400 mg/kg, 5 days) were used to investigate its effects on memory and brain tissues oxidative damage in penthylenetetrazole-induced repeated seizures (Vafaee et al., 2015). The results showed a beneficial effects of N. sativa on learning and memory impairments (Morris water maze) and improved antioxidant effects in the rat brain (lower MDA levels).
Health-Promoting Effects: Clinical Trials in Humans
Clinical studies have mostly confirmed some effects of the seeds of N. sativa and their derivatives (seed extract and seed oil) obtained in the aforementioned in vitro and in vivo animal studies. Particularly, in the on line database about clinical trials “www.clinicaltrials.gov”, there are 16 studies on N. sativa. Among them, the status of four studies on blood lipids, obesity and diabetes management has been completed, while other two were about palmer arsenical keratosis and asthma. The administration of N. sativa seeds (or seeds oil/extract) was alone or with other herbal substances (e.g., Curcuma longa extract), with different dosages and up to 60 days. Some of the results were positive, e.g. in total cholesterol and asthma, and subject of publications (Qidwai et al., 2009; Koshak et al., 2017).
Furthermore, in the following section the results of other clinical studies regarding preventive and relieving effects of N. sativa on metabolic disorders and risk factors (diabetes, obesity and hypertension), as well as other effects are shown. In Table 4, we have summarized these effects. The effects of other Nigella plants are also commented.
TABLE 4.
Clinical trials on effect of Nigella sativa to various system disorders, diseases and conditions.
| Intervention | Application, duration | Type of study | Number of patients/study designa | Control | Main effectsa | References | |
| Powdered N. sativa seed | Oral application for 8 weeks, 2 g of powder per day | Double-blind placebo controlled randomized clinical trial | 40 patients with HT (aged between 22 and 50 years) | Placebo (starch) | ↓ body weight and BMI, ↓ TSH and anti-TPO antibodies, ↑ T3, ↓ serum VEGF concentration | (Farhangi et al., 2016) | |
| N. sativa powder | Oral application for eight weeks | Randomized double-blind trial | 40 patients with HT, 22–50 years | Placebo (starch) | ↓ serum IL-23, ↓ TSH and anti-TPO antibodies, ↑ serum T3, ↓ body weight | (Tajmiri et al., 2016) | |
| N. sativa seed powder | Oral application for 8 weeks, 2 g per day | Double-blind placebo controlled randomized clinical trial | 40 patients with HT (aged between 22 and 50 years) | Placebo (starch) | ↓ serum LDL and T3, ↑ HDL | (Farhangi et al., 2018) | |
| N. sativa powdered seed | Oral application of 500 mg in combination with 500 mg of metformin, 10 mg atorvastatine, 150 mg aspirin | Randomized clinical trial | 80 patients with metabolic syndrome and poor glycemic control (HbA1C>7%) | 500 mg of metformin, 10 mg atorvastatine, 150 mg aspirin | ↓ FBG, PPBG, HbA1c, LDL | (Najmi et al., 2012) | |
| N. sativa seed oil | Oral application for 3 months, 2.5 mL two times daily | Double-blind placebo controlled randomized clinical trial | 70 patients with type II diabetes | Mineral oil | ↓ FBG, PPBG, HbA1c | (Hosseini et al., 2013) | |
| N. sativa seed powder | Oral application of 2g powder daily, for one year in addition to their standard medications | Double-blind placebo controlled randomized clinical trial | 114 patients with type 2 diabetes on standard oral hypoglycemic drugs | Placebo (charcoal) | ↓ FBG, HbA1c, TBARS ↑ TAC, SOD, GSH | (Kaatabi et al., 2015) | |
| N. sativa oil soft gel capsules | Oral application of 3g oil daily, for 12 weeks | Double-blind placebo controlled randomized clinical trial | 72 patients with diabetes type 2 | Sunflower oil gel capsules | ↓ FBG, HbA1c, TG, LDL | (Heshmati et al., 2015) | |
| N. sativa seed oil | Oral application of 2.5 mL two times daily for two months | Double-blind placebo controlled randomized clinical trial | 68 healthy men 20–45 years of age with infertility lasting more than one year | Liquid paraffin | Sperm count, motility, morphology and semen volume, pH and round cells were improved significantly | (Kolahdooz et al., 2014) | |
| N. sativa seed extract | Two test groups received 100 and 200 mg of extract twice a day for 8 weeks | Double-blind placebo controlled randomized clinical trial | 119 healthy male volunteers, aged 35 to 50 | Placebo | ↓ systolic and diastolic BP in a dose-dependent manner | (Dehkordi and Kamkhah, 2008) | |
| N. sativa seed oil | Oral application of 2.5 mL oil two times per day for 8 weeks | Randomized, double-blind placebo-controlled trial | 70 healthy volunteers aged 34–63 years | Mineral oil | ↓ systolic and diastolic BPs | (Fallah Huseini et al., 2013) | |
| N. sativa oil | 6 mg/kg daily, for 30 days | Prospective and double-blind clinical study | 66 patients with allergic rhinitis | Placebo | ↓ nasal mucosal congestion, nasal itching, sneezing attack, runny nose, turbinate hypertrophy, and mucosal pallor during the first 2 weeks of the study | (Nikakhlagh et al., 2011) | |
| N. sativa nasal spray | 2 puffs/day of N. sativa nasal spray (1 g/day of N. sativa) for 8 weeks | Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial | 65 patients with mild to moderate chronic rhinosinusitis | Placebo (2 puffs/day of sodium chloride spray 0.65%) | Lund–McKay, lund Kennedy, and Sino-nasal outcome Test-22 scores significantly decreased in the intervention group | (Rezaeian and Amoushahi Khouzani, 2018) | |
| N. sativa oil | Topical application, twice a day for 6 months | Randomized, double-blind clinical trial | 52 patients with vitiligo lesions | Fish oil | Reduction in size of lesions | (Ghorbanibirgani et al., 2014) | |
| N. sativa ointment (2%) | Ointment (1 G) topically applied on eczematous lesions twice a day for a period of 4 weeks | Randomized double-blind placebo-controlled trial | 60 patients with hand eczema, 18–60 years | Betamethasone and eucerin | ↓ Dermatology life quality index score in Nigella and betamethasone groups compared to eucerin | (Yousefi et al., 2013) | |
| N. sativa seed powder and ointment | 12 weeks, group I: 10% w/w ointment with N. sativa oil extract; group II: capsules with 500 mg of N. sativa powder, three times daily; group III: Combination of ointment and capsules | Randomized clinical trial | 60 patients with mild to moderate plaque and palmoplanter psoriasis | - | Group I—total healing of psoriatic lesions, with good response in 65% of patients, and a relapse rate of 31% four weeks after cessation of treatment; group II—good response in 50% of patients, with a relapse rate of 50% observed four weeks after application; group III—total cure of lesions, and good responses in 85% of patients, with a relapse rate of 18% | (Jawad et al., 2014) | |
| N. sativa oil | Two placebo capsules daily for 1 month, followed by a month of NS oil capsules 500 mg twice per day | Placebo controlled clinical trial | 40 female atients with rheumatoid artritis | Placebo (two starch capsules per day) | ↓ disease activity score, ↓ number of swollen joints and the duration of morning stiffness | (Gheita and Kenawy, 2012) | |
| N. sativa oil | 500 mg oil capsules two times daily for 8 weeks | Randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial | 42 patients with rheumatoid artritis | Placebo | ↑ IL-10, ↓ MDA, ↓ NO | (Hadi et al., 2016) | |
| N. sativa oil | Topical application twice a day (in the morning and night) for 21 days | Double-blind, parallel, clinical trial | 52 pateints with osteoarthritis, 60–80 years | Diclofenac gel | Better pain relief effect compared to diclofenac gel according to KOOS score (38.88 ± 17.84 and 50.33 ± 20.38, respectively) | (Azizi et al., 2019) | |
| N. sativa seed | Oral administration: 500 mg in capsules (twice a day for 9 weeks) | Randomized study | 20 healthy humans | Placebo: Psyllium seed husk in capsuels | Improvement in the parameters studied: Score of logical memory tests, attention test (letter cancenlation test and trail making test), cognitive test (Scroop)etc. | (Bin Sayeed et al., 2013) | |
aBMI, body mass index; BP, blood pressure; FBG, fasting blood glucose; HbA1c, hemoglobin A1c; HT, Hashimoto’s thyroiditis; IL, interleukin; LDL, low density lipoprotein; MDA, malondialdehyde; PPBG, postprandial blood glucose; T3, total triiodothyronine; TAC, total antioxidant capacity; TBARS, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances; TG, triglycerides; TPO, thyroid peroxidase; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.
Effect of N. sativa Supplementation on Patients with Metabolic Disorders and Risk Factors
Metabolic Syndrome
The possibility of application of N. sativa seed in patients with metabolic syndrome was firstly investigated by Najmi et al. (2008). They found that the administration with N. sativa seed oil (2.5 mL twice a day for 6 weeks) in patients with metabolic syndrome significantly decreased FBG and LDL and increased HDL levels. The same group of authors (Najmi et al., 2012) analyzed the effect of supplementation with powdered N. sativa seed (500 mg/day for two months) in patients with low glycemic control (glycate hemoglobin—HbA1C was lower than 7%). As a result, in the intervention group significant lowering of FBG, postprandial blood glucose (PPBG) and HbA1c was observed.
Conversely, a recent cross-over study (2 months treatment, 2 weeks washout period) evaluated the effects of N. sativa, as a form of traditional bread spiked with seeds (2 g), on FBG, BP and anthropometric indices (BW, waist circumference or WC, and BMI body mass index) in patients with metabolic syndrome. It found no significant effect between the mean of changes of parameters in the beginning and end of study (time effect), with the exception of diastolic BP (Mohtashami, 2019).
Diabetes
Oxidation and inflammation are important factors connected with occurrence of various chronic diseases, such as diabetes mellitus type 2 (Pouvreau et al., 2018). Due to the antioxidant, antiobesity and antidiabetic effects of N. sativa seeds and their constituents, this plant species can offer potential in prevention and treatment of type 2 diabetes. A recent review suggests that N. sativa can improve glycemic stages and lipid profile in diabetes (Heshmati and Namazi, 2015).
Hosseini et al. (2013) investigated anti-hyperglycemic effect of N. sativa seed oil in type II diabetic patients. As a result of supplementation with 5 mL of oil/day for three months, blood levels of fasting and 2 h PPBG, as well as HbA1c were significantly decreased compared to placebo group. This hypoglycemic effect can be result of an insulin senzitation and stimulation of pancreatic beta-cell function, resulting in intensified activity and consequent decrease in glucose level. Moreover, Kaatabi et al. (2015) reported pronounced antidiabetic activity after three-month application of N. sativa powdered seed (2 g/day) in combination with oral hypoglycemic agent in patients with type 2 diabetes. In this study, N. sativa received group showed significant reduction of FBG, HbA1C, and TBARS, and at the same time noticeable increase of the total antioxidant capacity, SOD, and glutathione levels were recorded in the intervention group. Heshmati et al. (2015) investigated effect of N. sativa seed oil application (3 g/day) on glucose metabolism and lipid concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes. According to this study, FBG, HbA1C, and levels of triglycerides (TG) and LDL significantly changed in the intervention group compared to the placebo one. On the other hand, insulin level and its resistance decreased and HDL increased in the intervention group, but after adjusting for confounder factors, these parameters were not significant. Overall, the potential antidiabetic mechanisms of N. sativa could be mediated through a change in the oxidative status (either via upregulation of endogenous antioxidants or reduction of oxidative species), reduction of inflammation, and improvement of lipid profiles (Yimer et al., 2019). Furthermore, a recent meta-analysis confirms that supplementation with N. sativa could be a suitable choice to manage the complications of type 2 diabetes, including FBS (−17.84 mg/dL), HbA1c (−0.71%), total cholesterol (−22.99 mg/dL), and LDL (−22.38 mg/dL) (Daryabeygi-Khotbehsara et al., 2017).
Hypercholesterolemia and Obesity
Nigella sativa powder supplementation (1 g/day) for sixty days caused momentous reductions in concentrations of LDL, TG levels and enhancement in HDL level in hypercholesterolemic patients (Tasawar et al., 2011). Moreover, a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled 4-weeks trial showed that the administration of N. sativa seeds (1g/day) can reduce total cholesterol and LDL. Thus, it can be interesting as lowering lipid agent in hyperlipidaemic subjects (Pelegrin et al., 2019). Nigella sativa oil (3 g/day for 8 weeks) was also tested in a low-calorie diet on cardiometabolic risk factors in obese women. Compared to the placebo group, in the N. sativa treated group, weight (−6.0%) and WC (−6.9%) decreased. It also favored a reduction in triglyceride and LDL levels (Mahdavi et al., 2015). Recently, a recent meta-analysis (literature till June 2017) has been performed on the effects of supplementation with N. sativa on some anthropometric indices in adult subjects. It indicated that N. sativa supplementation exerts a moderate effect on reduction in BW (−2.11 kg), BMI (−1.16 kg/m2) and WC (−3.52 cm) (Namazi et al., 2018). Nonetheless, other meta-analysis performed till January 2018 suggested that N. sativa supplementation have only an effect on BW (−1.76 kg) and BMI (−0.85 kg/m2) in adults compared to placebo (Mousavi et al., 2018).
Hypertension
There are several clinical studies reporting positive effect of N. sativa application on hypertension. Dehkordi and Kamkhah (2008) demonstrated that application of N. sativa seeds extract (100 and 200 mg for eight weeks) in patients with mild hypertension led to significant reduction of systolic and diastolic BP compared to placebo. At the same time, a significant decrease in total and LDL cholesterol was observed and no other complications caused by the treatment were found. Similar results were obtained for N. sativa seed oil. Fallah Huseini et al. (2013) exhibited that its application in a dose 2.5 mL two times per day for 8 weeks reduced systolic and dyastolic BP in healthy volunteers. Authors suggested that the exhibited effect could be attributed to the activity of thymoquinone (8), one of main constituents of the volatile oil from N. sativa seed, as commented before.
Some of the cardiovascular benefits evidenced in vitro and now in vivo through risk factors, such as blood lipids, and BP, could be related to the presence of omega-6 fats as linoleic acid, which is the major fatty acid of the seed oil. Nonetheless, the cardiovascular health benefits of linoleic acid are controversial (Hooper et al., 2018; Marklund et al., 2019), and the positive effects of minor phytochemicals remains unclear.
Other Effects of N. sativa
Effect of N. sativa Supplementation in Patients with Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis (HT)
HT is one of the most common human autoimmune diseases influencing the thyroid glands and an organ-specific T-cell mediated disease (Chistiakov, 2005). The disease is ten times more frequent in women than in men and it affects 2% of general population. HT is associated with serious alterations in composition and the transport of lipoproteins. Several clinical studies have demonstrated the efficacy of N. sativa application in patients with HT. According to the study conducted by Farhangi et al. (2016), the application of powdered N. sativa seeds (2 g) for eight weeks significantly decreased BW and BMI compared to placebo. Also, a positive effect has been achieved on thyroid function. A decrease in the serum concentrations of thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and anti-thyroid peroxidase (anti-TPO) has been shown, while serum concentrations of T3 increased in N. sativa treated group. In the same study, significant reduction of vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) was noted in the intervention group. It has been observed that its concentration grows during pathological states characterized by increased TSH secretion (Farhangi et al., 2016).
These results were confirmed by Tajmiri et al. (2016) and Farhangi et al. (2018), who showed lower BMIs in the group of patients with HT after the treatment with N. sativa seeds. This positive effect was exhibited through hypolipidemic effect: lowering serum LDL cholesterol and TG concentrations, while raising the level of HDL cholesterol. Beside this effect, Tajmiri et al. (2016) showed that treatment with N. sativa seed powder for eight weeks reduced levels of serum TSH, anti-TPO and IL-23, while level of serum T3 was increased.
Effect of N. sativa Supplementation on Patients with Reproductive System Disorders
Kolahdooz et al. (2014) studied effect of N. sativa seed oil on abnormal semen quality in infertile man. These authors showed that the daily application of 5 mL for two months significantly improved sperm count, morphology and motility and volume of semen, pH, and number of round cells. The exact mechanism of the exhibited effect is not determined, but it is likely related to strong antioxidant activity of the oil. Namely, it is well known that high level of oxidative stress contributes to decreased semen quality (Schulte et al., 2010).
Effect of N. sativa Supplementation on Patients with Allergic Rhinitis
The potential of application of N. sativa seeds and its oil in patients with allergic rhinitis has been also confirmed in clinical studies. Nikakhlagh et al. (2011) showed in prospective and double blind clinical trial that the oral administration of N. sativa seed oil (6 mg/kg daily) for 30 days in patients with allergic rhinitis significanly decreased the severity of respiratory symptoms, such as the presence of the nasal mucosal congestion, nasal itching, runny nose, sneezing attacks, turbinate hypertrophy, and mucosal pallor. Moreover, Rezaeian and Amoushahi Khouzani (2018) investigated the effect of N. sativa nasal spray in randomized clinical study. In this study patients in the intervention group received 2 puffs/day of N. sativa nasal spray (i.e. 1 g/day of N. sativa) and in the placebo group received 2 puffs/day of sodium chloride spray (0.65%). Lund–McKay, Lund Kennedy, and Sino-Nasal Outcome Test-22 scores were used and the outcomes were significantly lower in the intervention group compared to the placebo group. These findings are in line with previous reports about the antihistamine properties of N. sativa (Boskabady and Sheiravi, 2002; Kanter et al., 2006).
Effect of N. sativa Supplementation on Patients with Skin Diseases
Several clinical trials demonstrated positive effects of N. sativa application in resolving symptoms related to some skin diseases. Ghorbanibirgani et al. (2014) showed positive effects of 6 months topical application of N. sativa oil on vitiligo lesions compared to fish oil according to Vitiligo Area Scoring Index. In another study, Yousefi et al. (2013) investigated the therapeutic potential of 2% ointment topically applied (twice/day during 4 weeks) in patients with hand eczema compared to eucerin and betamethasone. According to scores obtained using Hand Eczema Severity index and Dermatology Life Quality Index, they showed that N. sativa ointment could have the same efficacy as betamethasone, while it is more efficient compared to eucerin. Jawad et al. (2014) investigated effect of various preparations of N. sativa in psoriasis treatment. A first group has been receiving Nigella ointment topically (10% w/w, twice daily), the second group took crude pulverized plant (capsules with 500 mg three times daily), while the third group received the combination of both treatments. The inspected reaction has been estimated following the Psoriasis Area and Severity Index score, while MDA serum level was used as indicator of the oxidative stress. After 12 weeks of treatment ointment reached total healing of psoriatic lesions, with good response in 65% of patients, and a relapse rate of 31% four weeks after cessation of treatment. Oral doses of N. sativa developed good response in 50% of patients, with a relapse rate of 50% observed four weeks after application. The combination of ointment and oral doses gained best results—total cure of lesions, and good responses in 85% of patients, with a relapse rate of 18%. All of these positive effects of N. sativa in dermatological diseases could be attributed to its antimicrobial, antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and anti-inflammatory effects.
Effect of Nigella sativa Supplementation in Patients with Rheumatic Artritis
The efficacy of black cumin oil in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA) was evaluated in female patients diagnosed with RA. Application of N. sativa oil in capsules (500 mg) twice daily exhibited improvement in disease activity score compared to placebo. Respectively, a pronounced improvement was demonstrated in amount of inflamed joints and occurrence of morning stiffness (Gheita and Kenawy, 2012). These results were confirmed by Hadi et al. (2016) with higher doses of N. sativa oil (1 g of oil/day, divided in two capsules). They showed that after 8 weeks of application in patients with RA noticeable decrease of serum MDA and NO was observed in the intervention group, while at the same time the serum level of anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 was increased (Hadi et al., 2016).
Azizi et al. (2019) compared the effects of topical application of N. sativa oil and diclofenac gel in patients with osteoartritis, one of the most common diseases in aging population. In this study, pain score has been expressed as average number obtained using Knee injury and Osteoarthritis Outcome Score scale. It has been observed that first ten days there has been no significant differences in placebo and the intervention group. Still, after 21 days of application better pain relief effect was observed after treatment with N. sativa oil compared to diclofenac gel.
Effects on Memory, Attention and Cognition
In a randomized study with 20 healthy humans, the effects of 500 mg of N. sativa seeds (twice a day for 9 weeks) on memory, attention, and cognition were studied. The results showed an improvement in the score of the tests studied, without an alteration of the biochemical markers of cardiac, liver and kidney functions (Bin Sayeed et al., 2013).
Effects of Other Nigella Species
Among other herbs, there are several studies on the clinical use of N. ciliaris during childbirth and postpartum (Ali-Shtayeh et al., 2015), against diabetes (Ali-Shtayeh et al., 2012) and hypertension (Ali-Shtayeh et al., 2013), as well as N. arvensis against psoriasis (Jaradat et al., 2016b) and cancer (Jaradat et al., 2016a), which were performed in Palestine using questionnaires. Some patients seem to be satisfied with the outcomes of herbal therapy (Ali-Shtayeh et al., 2012; Ali-Shtayeh et al., 2013), but the authors did not reveal the herb treatment that was successful to manage the latter diseases/conditions. In any case, clinical evidences are still lacking and no studies have been found in the abovementioned database https://clinicaltrials.gov/.
Conclusion
Nigella seeds and extracts have a wide range of bioactivities, which have been demonstrated in vitro and in vivo. Nonetheless, N. sativa is the most studied species probably due to their popularity in folklore medicine. In all cases, future perspectives should be oriented to perform a better characterization of the constituents of the extracts since most studies were only focused on determining the concentration of thymoquinone, but other phytochemicals could be present as in this review more than 80 compounds have been reported. This is also important to remark that bioavailability could affect the way that Nigella components act in vivo, e.g., some studies administered Nigella products orally, while other intravenously.
When referring to clinical trials, it seems that the supplementation of N. sativa can exert some effects on diabetes, obesity, and hypertension, among others. Nonetheless, the administration way (seeds, powder, oil, etc.), the dose and the treatment period are highly variable and should be further established from a therapeutic point of view, as well the chemical and phytochemical composition. This should be further study in order to formulate functional ingredients/nutraceuticals to promote the health benefit and how should be added into food. Moreover, besides the pleiotropic health applications of Nigella, it can be useful in nanotechnology applications as well as to modulate the activity of other therapeutic agents.
It is important to highlight that the culinary and medicinal use of some Nigella seeds as spice, condiment or infusion (e.g., N. sativa, N. damascena, and N. arvensis) suggests that their consumption is safe. The seeds are characterized by a low toxicity degree (Ali and Blunden, 2003) and no serious side effects in clinical trials (Namazi et al., 2018), but more studies were focused on N. sativa. In fact, toxicity studies performed in animal models also suggest a wide of margin of safety for using N. sativa fixed oil, with high LD50 value (28.8 ml of oil/kg BW administered orally to mice) (Zaoui et al., 2002), in powder form (Dollah et al., 2013) and as extracts (Vahdati-Mashhadian et al., 2005).
Acknowledgments
M. d. M. Contreras thanks the FEDER UJA project 1260905 funded by “Programa Operativo FEDER 2014–2020” and “Consejería de Economía y Conocimiento de la Junta de Andalucía”. This work was also supported by CONICYT PIA/APOYO CCTE AFB170007.
Author Contributions
All authors contributed equally to the manuscript. Conceptualization, BS, CQ, MI, IU-H, JŽ, IA-R, SS, YT, KA, HA, AS-C, DM, GS, MM, US, RK, HS; validation investigation—data curation writing—all authors; review and editing, MdMC, AR, and JS-R. All the authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Abbasnezhad A., Niazmand S., Mahmoudabady M., Rezaee S. A., Soukhtanloo M., Mosallanejad R., et al. (2019). Nigella sativa L. seed regulated eNOS, VCAM-1 and LOX-1 genes expression and improved vasoreactivity in aorta of diabetic rat. J. Ethnopharmacol 228, 142–147. 10.1016/j.jep.2018.09.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abedi A. S., Rismanchi M., Shahdoostkhany M., Mohammadi A., Mortazavian A. M. (2017). Microwave-assisted extraction of Nigella sativa L. essential oil and evaluation of its antioxidant activity. J. Food Sci. Technol. 54, 3779–3790. 10.1007/s13197-017-2718-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agradi E., Fico G., Cillo F., Francisci C., Tome F. (2002). Estrogenic activity of Nigella damascena extracts, evaluated using a recombinant yeast screen. Phytother Res. 16, 414–416. 10.1002/ptr.905 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agradi E., Fico G., Cillo F., Francisci C., Tome F. (2001). Estrogenic activity of phenolic compounds from Nigella damascena evaluated using a recombinant yeast screen. Planta Med. 67, 553–555. 10.1055/s-2001-16485 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmad A., Husain A., Mujeeb M., Khan S. A., Najmi A. K., Siddique N. A., et al. (2013). A review on therapeutic potential of Nigella sativa: a miracle herb. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Biomed. 3, 337–352. 10.1016/S2221-1691(13)60075-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ahmed M., Hwang J. H., Hasan M. A., Han D. (2018). Herbal medicine use by pregnant women in Bangladesh: a cross-sectional study. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 18, 333. 10.1186/s12906-018-2399-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aikemu A., Xiaerfuding X., Shiwenhui C., Abudureyimu M., Maimaitiyiming D. (2013). Immunomodulatory and anti-tumor effects of Nigella glandulifera freyn and sint seeds on ehrlich ascites carcinoma in mouse model. Pharmacogn Mag. 9, 187–191. 10.4103/0973-1296.113258 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Adhroey A. H., Nor Z. M., Al-Mekhlafi H. M., Mahmud R. (2010). Ethnobotanical study on some Malaysian anti-malarial plants: a community based survey. J. Ethnopharmacol 132, 362–364. 10.1016/j.jep.2010.08.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Naqeep G. N., Ismail M. M., Al-Zubairi A. S., Esa N. M. (2009). Nutrients composition and minerals content of three different samples of Nigella sativa L. Cultivated in Yemen. Asian J. Biol. Sci. 2, 43–48. 10.3923/ajbs.2009.43.48 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Ramahi R., Jaradat N., Adawi D. (2013). Use of herbal medicines during pregnancy in a group of Palestinian women. J. Ethnopharmacol 150, 79–84. 10.1016/j.jep.2013.07.041 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Al-Sheddi E. S., Farshori N. N., Al-Oqail M. M., Musarrat J., Al-Khedhairy A. A., Siddiqui M. A. (2014). Cytotoxicity of Nigella sativa seed oil and extract against human lung cancer cell line. Asian Pac. J. Cancer Prev. 15, 983–987. 10.7314/apjcp.2014.15.2.983 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alam M. F., Khan G., Safhi M. M., Alshahrani S., Siddiqui R., Sivagurunathan Moni S., et al. (2018). Thymoquinone ameliorates doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity in Swiss albino mice by modulating oxidative damage and cellular inflammation. Cardiol. Res. Pract. 2018, 1483041. 10.1155/2018/1483041 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali B. H., Blunden G. (2003). Pharmacological and toxicological properties of Nigella sativa . Phytother Res. 17, 299–305. 10.1002/ptr.1309 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali Z., Ferreira D., Carvalho P., Avery M. A., Khan I. A. (2008). Nigellidine-4-O-sulfite, the first sulfated indazole-type alkaloid from the seeds of Nigella sativa . J. Nat. Prod. 71, 1111–1112. 10.1021/np800172x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali-Shtayeh M. S., Jamous R. M., Jamous R. M. (2012). Complementary and alternative medicine use amongst Palestinian diabetic patients. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 18, 16–21. 10.1016/j.ctcp.2011.09.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali-Shtayeh M. S., Jamous R. M., Jamous R. M. (2015). Plants used during pregnancy, childbirth, postpartum and infant healthcare in Palestine. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 21, 84–93. 10.1016/j.ctcp.2015.03.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ali-Shtayeh M. S., Jamous R. M., Jamous R. M., Salameh N. M. (2013). Complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) use among hypertensive patients in Palestine. Complement. Ther. Clin. Pract. 19, 256–263. 10.1016/j.ctcp.2013.09.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alrawi S. N., Khidir A., Elnashar M. S., Abdelrahim H. A., Killawi A. K., Hammoud M. M., et al. (2017). Traditional Arabic & Islamic medicine: validation and empirical assessment of a conceptual model in Qatar. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 17, 157. 10.1186/s12906-017-1639-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alu'datt M. H., Rababah T., Alhamad M. N., Gammoh S., Ereifej K., Alodat M. D., et al. (2016). Antioxidant and antihypertensive properties of phenolic–protein complexes in extracted protein fractions from Nigella damascena and Nigella arvensis . Food Hydrocolloids 56, 84–92. 10.1016/j.foodhyd.2015.12.008 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Amiri M. S., Joharchi M. R. (2013). Ethnobotanical investigation of traditional medicinal plants commercialized in the markets of Mashhad, Iran. Avicenna J. Phytomed 3, 254–271. 10.1201/9780203502327-26 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ansari M. O., Parveen N., Ahmad M. F., Wani A. L., Afrin S., Rahman Y., et al. (2019). Evaluation of DNA interaction, genotoxicity and oxidative stress induced by iron oxide nanoparticles both in vitro and in vivo: attenuation by thymoquinone. Sci. Rep. 9, 6912. 10.1038/s41598-019-43188-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Asgary S., Ghannadi A., Dashti G., Helalat A., Sahebkar A., Najafi S. (2013). Nigella sativa L. improves lipid profile and prevents atherosclerosis: evidence from an experimental study on hypercholesterolemic rabbits. J. Funct. Foods 5, 228–234. 10.1016/j.jff.2012.10.011 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Atta M. S., El-Far A. H., Farrag F. A., Abdel-Daim M. M., Al Jaouni S. K., Mousa S. A. (2018). Thymoquinone attenuates cardiomyopathy in streptozotocin-treated diabetic rats. Oxid Med. Cel Longev 2018, 7845681. 10.1155/2018/7845681 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atta Ur R., Malik S., Ahmad S., Chaudhary I., Habib Ur R. (1985). Nigellimine N-oxide—a new isoquinoline alkaloid from the seeds of Nigella sativa . Heterocycles 23, 953–955. [Google Scholar]
- Atta Ur R., Malik S., Hasan S. S., Choudhary M. I., Ni C.-Z., Clardy J. (1995). Nigellidine—a new indazole alkaloid from the seeds of Nigella sativa . Tetrahedron Lett. 36, 1993–1996. [Google Scholar]
- Atta Ur R., Malik S., Zaman K. (1992). Nigellimine: a new isoquinoline alkaloid from the seeds of Nigella sativa . J. Nat. Prod. 55, 676–678. [Google Scholar]
- Aziz M. A., Khan A. H., Adnan M., Izatullah I. (2017). Traditional uses of medicinal plants reported by the indigenous communities and local herbal practitioners of Bajaur Agency, Federally Administrated Tribal Areas, Pakistan. J. Ethnopharmacol 198, 268–281. 10.1016/j.jep.2017.01.024 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Azizi F., Ghorat F., Hassan Rakhshani M., Rad M. (2019). Comparison of the effect of topical use of Nigella sativa oil and diclofenac gel on osteoarthritis pain in older people: a randomized, double-blind, clinical trial. J. Herbal Med. 16, 100259. 10.1016/j.hermed.2019.100259 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Badri W., El Asbahani A., Miladi K., Baraket A., Agusti G., Nazari Q. A., et al. (2018). Poly (ε-caprolactone) nanoparticles loaded with indomethacin and Nigella sativa L. essential oil for the topical treatment of inflammation. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 46, 234–242. 10.1016/j.jddst.2018.05.022 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bahmani M., Abaszadeh A., Rafieian-Kopaei M., Naghdi N. (2016a). A review of the most important native medicinal plants of Iran effective on diarrhea. J. Chem. Pharm. Sci. 9, 1294–1304. 10.25258/ijcprr.v8i02.9192 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bahmani M., Eftekhari Z., Jelodari M., Saki K., Majlesi M., Rafieian-Kopaei M., et al. (2015). Effect of Iranian herbal medicines in dysmenorrhea phytotherapy. J. Chem. Pharm. Res. 7, 519–526. 10.1002/ptr.6055 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bahmani M., Tajeddini P., Ezatpour B., Rafieian-Kopaei M., Nasrollahnaghdi, Asadi-Samani M. (2016b). Ethenobothanical study of medicinal plants against parasites detected in Shiraz, southern part of Iran. Der Pharmacia Lettre 8, 153–160. 10.32598/cjns.6.20.200.3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bakir M., Geyikoglu F., Colak S., Turkez H., Bakir T. O., Hosseinigouzdagani M. (2016). The carvacrol ameliorates acute pancreatitis-induced liver injury via antioxidant response. Cytotechnology 68, 1131–1146. 10.1007/s10616-015-9871-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bashmil H. A., Alamoudi A. A., Noorwali A., Hegazy G. A., Ajabnoor G., Al-Abd A. M. (2018). Thymoquinone influences the anticancer properties of paclitaxel and gemcitabine against breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 78, 5813. 10.1158/1538-7445.am2018-5813 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bayatmakoo R., Rashtchizadeh N., Yaghmaei P., Farhoudi M., Karimi P. (2017). Thymol decreases apoptosis and carotid inflammation induced by hypercholesterolemia through a discount in oxidative stress. Crescent J. Med. Biol. Sci. 4, 186–193. 10.1158/1538-7445.am2018-5813 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Beheshti F., Khazaei M., Hosseini M. (2016). Neuropharmacological effects of Nigella sativa . Avicenna J. Phytomed 6, 104–116. 10.1201/9781420028256-14 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benhaddou-Andaloussi A., Martineau L. C., Spoor D., Vuong T., Leduc C., Joly E., et al. (2008). Antidiabetic activity of nigella sativa. Seed extract in cultured pancreatic β-cells, skeletal muscle cells, and adipocytes. Pharm. Biol. 46, 96–104. 10.1080/13880200701734810 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Benhaddou-Andaloussi A., Martineau L. C., Vallerand D., Haddad Y., Afshar A., Settaf A., et al. (2010). Multiple molecular targets underlie the antidiabetic effect of Nigella sativa seed extract in skeletal muscle, adipocyte and liver cells. Diabetes Obes. Metab. 12, 148–157. 10.1111/j.1463-1326.2009.01131.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bin Sayeed M. S., Asaduzzaman M., Morshed H., Hossain M. M., Kadir M. F., Rahman M. R. (2013). The effect of Nigella sativa Linn. seed on memory, attention and cognition in healthy human volunteers. J. Ethnopharmacol 148, 780–786. 10.1016/j.jep.2013.05.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bittkau C., Comes H. P. (2009). Molecular inference of a Late Pleistocene diversification shift in Nigella s. lat. (Ranunculaceae) resulting from increased speciation in the Aegean archipelago. J. Biogeogr. 36, 1346–1360. 10.1111/j.1365-2699.2008.02003.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bordoni L., Fedeli D., Nasuti C., Maggi F., Papa F., Wabitsch M., et al. (2019). Antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of Nigella sativa oil in human pre-adipocytes. Antioxidants 8, 51. 10.3390/antiox8020051 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boskabady M. H., Sheiravi N. (2002). Inhibitory effect of Nigella sativa on histamine (H1) receptors of isolated Guinea pig tracheal chains. Pharm. Biol. 40, 596–602. 10.1076/phbi.40.8.596.14653 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Boubertakh B., Liu X.-G., Cheng X.-L., Li P. (2013). A Spotlight on Chemical Constituents and Pharmacological Activities of Nigella glandulifera Freyn et Sint Seeds. J. Chem. 2013, 820183. 10.1155/2013/820183 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgou S., Kchouk M. E., Bellila A., Marzouk B. (2010a). Effect of salinity on phenolic composition and biological activity of Nigella sativa. Leuven, Belgium: International Society for Horticultural Science (ISHS), 57–60. 10.17660/actahortic.2010.853.5 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgou S., Ksouri R., Bellila A., Skandrani I., Falleh H., Marzouk B. (2008). Phenolic composition and biological activities of Tunisian Nigella sativa L. shoots and roots. Comptes Rendus Biologies 331, 48–55. 10.1016/j.crvi.2007.11.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgou S., Pichette A., Lavoie S., Marzouk B., Legault J. (2012). Terpenoids isolated from Tunisian Nigella sativa L. essential oil with antioxidant activity and the ability to inhibit nitric oxide production. Flavour Fragr. J. 27, 69–74. 10.1002/ffj.2085 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgou S., Pichette A., Marzouk B., Legault J. (2010b). Bioactivities of black cumin essential oil and its main terpenes from Tunisia. South Afr. J. Bot. 76, 210–216. 10.1016/j.sajb.2009.10.009 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bouzabata A. (2013). Traditional treatment of high blood pressure and diabetes in Souk ahras district. J. Pharmacognosy Phytotherapy 5, 12–20. [Google Scholar]
- Buchholz T., Melzig M. F. (2016). Medicinal plants traditionally used for treatment of obesity and diabetes mellitus—screening for pancreatic lipase and alpha-amylase inhibition. Phytother Res. 30, 260–266. 10.1002/ptr.5525 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burits M., Bucar F. (2000). Antioxidant activity of Nigella sativa essential oil. Phytother Res. 14, 323–328. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butt A. S., Nisar N., Ghani N., Altaf I., Mughal T. A. (2019). Isolation of thymoquinone from Nigella sativa L. and Thymus vulgaris L., and its anti-proliferative effect on HeLa cancer cell lines. Trop. J. Pharm. Res. 18, 37–42. 10.4314/tjpr.v18i1.6 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Chen L., Han H., Amin A., Zhang L., Ma S. (2018). Hydrolysis product of Nigella A obtained from Nigella glandulifera Freyn seeds promotes apoptosis and AMPK-mediated autophagy in human colon cancer SW620 cells. Arch. Biol. Sci. 70, 603–612. 10.2298/abs171108021c [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Q. B., Xin X. L., Yang Y., Lee S. S., Aisa H. A. (2014). Highly conjugated norditerpenoid and pyrroloquinoline alkaloids with potent PTP1B inhibitory activity from Nigella glandulifera . J. Nat. Prod. 77, 807–812. 10.1021/np4009078 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chistiakov D. A. (2005). Immunogenetics of Hashimoto's thyroiditis. J. Autoimmune Dis. 2, 1–21. 10.1186/1740-2557-2-1 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho S., Choi Y., Park S., Park T. (2012). Carvacrol prevents diet-induced obesity by modulating gene expressions involved in adipogenesis and inflammation in mice fed with high-fat diet. J. Nutr. Biochem. 23, 192–201. 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2010.11.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Choi J. H., Kim S. W., Yu R., Yun J. W. (2017). Monoterpene phenolic compound thymol promotes browning of 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Eur. J. Nutr. 56, 2329–2341. 10.1007/s00394-016-1273-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daryabeygi-Khotbehsara R., Golzarand M., Ghaffari M. P., Djafarian K. (2017). Nigella sativa improves glucose homeostasis and serum lipids in type 2 diabetes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Complement. Ther. Med. 35, 6–13. 10.1016/j.ctim.2017.08.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dehkordi F. R., Kamkhah A. F. (2008). Antihypertensive effect of Nigella sativa seed extract in patients with mild hypertension. Fundam. Clin. Pharmacol. 22, 447–452. 10.1111/j.1472-8206.2008.00607.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng W., Lu H., Teng J. (2013). Carvacrol attenuates diabetes-associated cognitive deficits in rats. J. Mol. Neurosci. 51, 813–819. 10.1007/s12031-013-0069-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dembitsky V. M., Gloriozova T. A., Poroikov V. V. (2015). Naturally occurring plant isoquinoline N‐oxide alkaloids: their pharmacological and SAR activities. Phytomedicine 22 (1), 183–202. 10.1016/j.phymed.2014.11.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dollah M. A., Parhizkar S., Latiff L. A., Bin Hassan M. H. (2013). Toxicity effect of Nigella sativa on the liver function of rats. Adv. Pharm. Bull. 3, 97–102. 10.5681/apb.2013.016 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dönmez A., Mutlu B. (2004). A new species of Nigella (Ranunculaceae) from Turkey. Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 146, 251–255. 10.1111/j.1095-8339.2004.00325.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Eddouks M., Maghrani M., Lemhadri A., Ouahidi M. L., Jouad H. (2002). Ethnopharmacological survey of medicinal plants used for the treatment of diabetes mellitus, hypertension and cardiac diseases in the south-east region of Morocco (Tafilalet). J. Ethnopharmacol. 82, 97–103. 10.1016/s0378-8741(02)00164-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edris A. E. (2009). Anti-cancer properties of Nigella spp. essential oils and their major constituents, thymoquinone and beta-elemene. Curr. Clin. Pharmacol. 4, 43–46. 10.2174/157488409787236137 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edris A. E. (2010). Evaluation of the volatile oils from different local cultivars of Nigella sativa L. Grown in Egypt with emphasis on the effect of extraction method on thymoquinone. J. Essent. Oil Bearing Plants 13, 154–164. 10.1080/0972060x.2010.10643805 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- El-Aarag B., Hussein W. M., Ibrahim W. M., Zahran M. A. (2017). Thymoquinone improves anti-diabetic activity of metformin in streptozotocin-induced diabetic male rats. J. Diabetes Metab. 8, 1–8. 10.4172/2155-6156.1000780 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- El-Hilaly J., Hmammouchi M., Lyoussi B. (2003). Ethnobotanical studies and economic evaluation of medicinal plants in Taounate province (Northern Morocco). J. Ethnopharmacol 86, 149–158. 10.1016/s0378-8741(03)00012-6 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Naggar T., Carretero M. E., Arce C., Gomez-Serranillos M. P. (2017). Methanol extract of Nigella sativa seed induces changes in the levels of neurotransmitter amino acids in male rat brain regions. Pharm. Biol. 55, 1415–1422. 10.1080/13880209.2017.1302485 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Sayed E.-S. M., Mansour A. M., Abdul-Hameed M. S. (2016). Thymol and carvacrol prevent doxorubicin-induced cardiotoxicity by abrogation of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in rats. J. Biochem. Mol. Toxicol. 30, 37–44. 10.1002/jbt.21740 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- El-Seedi H., Burman R., Mansour A., Turki Z., Boulos L., Gullbo J., et al. (2013). The traditional medical uses and cytotoxic activities of sixty-one Egyptian plants: discovery of an active cardiac glycoside from Urginea maritima. J. Ethnopharmacol 145, 746–757. 10.1016/j.jep.2012.12.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elseweidy M. M., Amin R. S., Atteia H. H., Aly M. A. (2018). Nigella sativa oil and chromium picolinate ameliorate fructose-induced hyperinsulinemia by enhancing insulin signaling and suppressing insulin-degrading enzyme in male rats. Biol. Trace Elem. Res. 184, 119–126. 10.1007/s12011-017-1167-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enayatfard L., Mohebbati R., Niazmand S., Hosseini M., Shafei M. N. (2018). The standardized extract of Nigella sativa and its major ingredient, thymoquinone, ameliorates angiotensin II-induced hypertension in rats. J. Basic Clin. Physiol. Pharmacol. 30, 51–58. 10.1515/jbcpp-2018-0074 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esakkimuthu S., Mutheeswaran S., Arvinth S., Paulraj M. G., Pandikumar P., Ignacimuthu S. (2016). Quantitative ethnomedicinal survey of medicinal plants given for cardiometabolic diseases by the non-institutionally trained siddha practitioners of Tiruvallur district, Tamil Nadu, India. J. Ethnopharmacol 186, 329–342. 10.1016/j.jep.2016.04.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fallah Huseini H., Amini M., Mohtashami R., Ghamarchehre M. E., Sadeqhi Z., Kianbakht S., et al. (2013). Blood pressure lowering effect of Nigella sativa L. seed oil in healthy volunteers: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytother Res. 27, 1849–1853. 10.1002/ptr.4944 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fangfang, Li H., Qin T., Li M., Ma S. (2017). Thymol improves high-fat diet-induced cognitive deficits in mice via ameliorating brain insulin resistance and upregulating NRF2/HO-1 pathway. Metab. Brain Dis. 32, 385–393. 10.1007/s11011-016-9921-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farag M. A., Gad H. A., Heiss A. G., Wessjohann L. A. (2014). Metabolomics driven analysis of six Nigella species seeds via UPLC-qTOF-MS and GC-MS coupled to chemometrics. Food Chem. 151, 333–342. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.11.032 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farhangi M. A., Dehghan P., Tajmiri S., Abbasi M. M. (2016). The effects of Nigella sativa on thyroid function, serum Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor (VEGF)—1, Nesfatin-1 and anthropometric features in patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis: a randomized controlled trial. BMC Complement. Med. Therapies 16, 471. 10.1186/s12906-016-1432-2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farhangi M. A., Dehghan P., Tajmiri S. (2018). Powdered black cumin seeds strongly improves serum lipids, atherogenic index of plasma and modulates anthropometric features in patients with Hashimoto's thyroiditis. Lipids Health Dis. 17, 59. 10.1186/s12944-018-0704-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fico G., Braca A., Tomè F., Morelli I. (2000). Phenolic derivatives from Nigella damascena seeds. Pharm. Biol. 38, 371–373. 10.1076/phbi.38.5.371.5967 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Geng D., Zhang S., Lan J. (2009). Analysis on chemical components of volatile oil and determination of thymoquinone from seed of Nigella glandulifera . Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 34, 2887–2890. 10.1021/acs.orglett.7b03189.s001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geraci A., Polizzano V., Schicchi R. (2018). Ethnobotanical uses of wild taxa as galactagogues in Sicily (Italy). Acta Societatis Botanicorum Poloniae 87, 1–18. 10.5586/asbp.3580 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Gharby S., Harhar H., Guillaume D., Roudani A., Boulbaroud S., Ibrahimi M., et al. (2015). Chemical investigation of Nigella sativa L. seed oil produced in Morocco. J. Saudi Soc. Agric. Sci. 14, 172–177. 10.1016/j.jssas.2013.12.001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ghazeeri G. S., Awwad J. T., Alameddine M., Younes Z. M. H., Naja F. (2012). Prevalence and determinants of complementary and alternative medicine use among infertile patients in Lebanon: a cross sectional study. BMC Complement. Med. Therapies 12, 129. 10.1186/1472-6882-12-129 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gheita T. A., Kenawy S. A. (2012). Effectiveness of Nigella sativa oil in the management of rheumatoid arthritis patients: a placebo controlled study. Phytother Res. 26, 1246–1248. 10.1002/ptr.3679 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghorbanibirgani A., Khalili A., Rokhafrooz D. (2014). Comparing Nigella sativa oil and fish oil in treatment of vitiligo. Iran Red Crescent Med. J. 16, e4515. 10.5812/ircmj.4515 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghoreyshi M., Mahmoudabady M., Bafadam S., Niazmand S. (2020). The protective effects of pharmacologic postconditioning of hydroalcoholic extract of Nigella sativa on functional activities and oxidative stress injury during ischemia-reperfusion in isolated rat heart. Cardiovasc. Toxicol. 20, 130–138. 10.1007/s12012-019-09540-x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guler B., Manav E., Ugurlu E. (2015). Medicinal plants used by traditional healers in Bozuyuk (Bilecik-Turkey). J. Ethnopharmacol 173, 39–47. 10.1016/j.jep.2015.07.007 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hadi V., Kheirouri S., Alizadeh M., Khabbazi A., Hosseini H. (2016). Effects of Nigella sativa oil extract on inflammatory cytokine response and oxidative stress status in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Avicenna J. Phytomed 6, 34–43. 10.1002/ptr.5417 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hamarsheh O., Azmi K., Amro A., Schultheis M., Abdeen Z., Firdessa R., et al. (2017). Antileishmanial potential of crude plant extracts derived from medicinal plants in Palestine. Ann. Clin. Cytol. Pathol. 3, 1065. 10.17221/464-pps [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hao H. F., Ren L. J., Chen Y. W. (1996). Studies on the chemical constituents of seed from Nigella glandulifera . Yao Xue Xue Bao 31, 689–694. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haque M. R., Ansari H. S. (2018). Anti-obesity effect of arq zeera and its main components thymol and cuminaldehyde in high fat diet induced obese rats. Drug Res. (Stuttg) 68, 637–647. 10.1055/a-0590-1956 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haque M. R., Ansari S. H., Najmi A. K., Ahmad M. A. (2014). Monoterpene phenolic compound thymol prevents high fat diet induced obesity in murine model. Toxicol. Mech. Methods 24, 116–123. 10.3109/15376516.2013.861888 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harphoush S., Wu G., Qiuli G., Zaitoun M., Ghanem M., Shi Y., et al. (2019). Thymoquinone ameliorates obesity-induced metabolic dysfunction, improves reproductive efficiency exhibiting a dose-organ relationship. Syst. Biol. Reprod. Med. 65, 367–382. 10.1080/19396368.2019.1626933 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hasan T. N., Shafi G., Syed N. A., Alfawaz M. A., Alsaif M. A., Munshi A., et al. (2013). Methanolic extract of Nigella sativa seed inhibits SiHa human cervical cancer cell proliferation through apoptosis. Nat. Prod. Commun. 8, 213–216. 10.1177/1934578x1300800221 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hebi M., Zeggwagh N., Hajj L., Bouhali B. E., Eddouks M. (2016). Cardiovascular effect of Nigella sativa L. Aqueous extract in normal rats. Cardiovasc. Hematol. Disord. Drug Targets 16, 47–55. 10.2174/1871529x16666160729115249 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heiss A. G., Kropf M., Sontag S., Weber A. (2011). Seed morphology of nigella s.l. (Ranunculaceae): identification, diagnostic traits, and their potential phylogenetic relevance. Int. J. Plant Sci. 172, 267–284. 10.1086/657676 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Heiss A. G., Oeggl K. (2005). The oldest evidence of Nigella damascena L. (Ranunculaceae) and its possible introduction to central Europe. Veget Hist. Archaeobot 14, 562–570. 10.1007/s00334-005-0060-4 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Heshmati J., Namazi N. (2015). Effects of black seed (Nigella sativa) on metabolic parameters in diabetes mellitus: a systematic review. Complement. Ther. Med. 23, 275–282. 10.1016/j.ctim.2015.01.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heshmati J., Namazi N., Memarzadeh M.-R., Taghizadeh M., Kolahdooz F. (2015). Nigella sativa oil affects glucose metabolism and lipid concentrations in patients with type 2 diabetes: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Food Res. Int. 70, 87–93. 10.1016/j.foodres.2015.01.030 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hooper L., Al-Khudairy L., Abdelhamid A. S., Rees K., Brainard J. S., Brown T. J., et al. (2018). Omega-6 fats for the primary and secondary prevention of cardiovascular disease. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 11, Cd011094. 10.1002/14651858.CD011094.pub2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hossan M. S., Jindal H., Maisha S., Samudi Raju C., Devi Sekaran S., Nissapatorn V., et al. (2018). Antibacterial effects of 18 medicinal plants used by the Khyang tribe in Bangladesh. Pharm. Biol. 56, 201–208. 10.1080/13880209.2018.1446030 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hosseini M. S., Mirkarimi S. A., Amini M., Mohtashami R., Kianbakht S., Fallah Huseini H. (2013). Effects of Nigella sativa L. Seed oil in type 2 diabetic patients: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J. Med. Plants 12, 93–99. 10.1002/ptr.4944 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ijaz H., Tulain U. R., Qureshi J., Danish Z., Musayab S., Akhtar M. F., et al. (2017). Review: Nigella sativa (prophetic medicine): a review. Pak J. Pharm. Sci. 30, 229–234. 10.4172/2327-5162.1000209 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imam A., Lawal A., Oyewole L. A., Ajibola M. I., Williams V., Chengetanai S., et al. (2018). Nigella sativa conserved hippocampal oxidative and neurogenic activities to salvage neuro-cognitive integrities in chlorpyrifos insult. Scientific Afr. 1, e00008. 10.1016/j.sciaf.2018.e00008 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal M. S., Qureshi A. S., Ghafoor A. (2010). Evaluation of Nigella sativa L., for genetic variation and ex-situ conservation. Pakistan J. Bot. 42, 2489–2495. 10.1016/0006-3207(95)90018-7 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Islam S. N., Begum P., Ahsan T., Huque S., Ahsan M. (2004). Immunosuppressive and cytotoxic properties of Nigella sativa . Phytother Res. 18, 395–398. 10.1002/ptr.1449 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ismail N., Abdel–Mottaleb Y., Eissa Ahmed A. A., El-Maraghy N. N. (2018). Novel combination of thymoquinone and resveratrol enhances anticancer effect on hepatocellular carcinoma cell line. Future J. Pharm. Sci. 4, 41–46. 10.1016/j.fjps.2017.08.001 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jamila F., Mostafa E. (2014). Ethnobotanical survey of medicinal plants used by people in Oriental Morocco to manage various ailments. J. Ethnopharmacol 154, 76–87. 10.1016/j.jep.2014.03.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaradat N. A., Al-Ramahi R., Zaid A. N., Ayesh O. I., Eid A. M. (2016a). Ethnopharmacological survey of herbal remedies used for treatment of various types of cancer and their methods of preparations in the West Bank-Palestine. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 16, 93. 10.1186/s12906-016-1070-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jaradat N. A., Shawahna R., Eid A. M., Al-Ramahi R., Asma M. K., Zaid A. N. (2016b). Herbal remedies use by breast cancer patients in the West Bank of Palestine. J. Ethnopharmacol 178, 1–8. 10.1016/j.jep.2015.11.050 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jarić S., Mitrović M., Karadžić B., Kostić O., Djurjević L., Pavlović M., et al. (2014). Plant resources used in Serbian medieval medicine. Ethnobotany and Ethnomedicine. Genet. Resour. Crop Evol. 61, 1359–1379. 10.1007/s10722-014-0118-1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jawad A. H., Azhar I. Y., Khalil I. a. H. (2014). Evaluation of efficacy, safety and antioxidant effect of Nigella sativa in patients with psoriasis: a randomized clinical trial. J. Clin. Exp. Invest. 5, 188–193. 10.5799/ahinjs.01.2014.02.0387 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Jennings H. M., Merrell J., Thompson J. L., Heinrich M. (2015). Food or medicine the food-medicine interface in households in Sylhet. J. Ethnopharmacol 167, 97–104. 10.1016/j.jep.2014.09.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jrah Harzallah H., Kouidhi B., Flamini G., Bakhrouf A., Mahjoub T. (2011). Chemical composition, antimicrobial potential against cariogenic bacteria and cytotoxic activity of Tunisian Nigella sativa essential oil and thymoquinone. Food Chem. 129, 1469–1474. 10.1016/j.foodchem.2011.05.117 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatabi H., Bamosa A. O., Badar A., Al-Elq A., Abou-Hozaifa B., Lebda F., et al. (2015). Nigella sativa improves glycemic control and ameliorates oxidative stress in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus: placebo controlled participant blinded clinical trial. PLoS One 10, e0113486. 10.1371/journal.pone.0113486 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanter M., Coskun O., Uysal H. (2006). The antioxidative and antihistaminic effect of Nigella sativa and its major constituent, thymoquinone on ethanol-induced gastric mucosal damage. Arch. Toxicol. 80, 217–224. 10.1007/s00204-005-0037-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karandrea S., Yin H., Liang X., Slitt A. L., Heart E. A. (2017). Thymoquinone ameliorates diabetic phenotype in Diet-Induced Obesity mice via activation of SIRT-1-dependent pathways. PLoS One 12, e0185374. 10.1371/journal.pone.0185374 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartal Ç., Güneş F. (2017). Medicinal plants used in Meriç Town from Turkey. Indian J. Pharm. Educ. Res. 51, S249–S253. 10.5530/ijper.51.3s.23 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kazemi M. (2015). Chemical composition and antioxidant properties of the essential oil of Nigella sativa L. Bangladesh . J. Bot. 44, 111–116. 10.3329/bjb.v44i1.22732 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Khabbach A., Libiad M., Ennabili A., Bousta D. (2012). Medicinal and cosmetic use of plants from the province of Taza, Northern Morocco. Boletín Latinoamericano y Del. Caribe de Plantas Medicinales y Aromáticas 11, 46–60. 10.35248/2167-0412.20.9.349 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Khabbach A., Libiad M., Ennabili A. (2011). Plant resources use in the province of taza (north of Morocco). Proenvironment 4, 347–356. 10.17151/luaz.2013.36.7 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Khajoei Nasab F., Khosravi A. R. (2014). Ethnobotanical study of medicinal plants of sirjan in kerman province, Iran. J. Ethnopharmacol 154, 190–197. 10.1016/j.jep.2014.04.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khan N., Abbasi A. M., Dastagir G., Nazir A., Shah G. M., Shah M. M., et al. (2014). Ethnobotanical and antimicrobial study of some selected medicinal plants used in Khyber Pakhtunkhwa (KPK) as a potential source to cure infectious diseases. BMC Complement. Altern. Med. 14, 122. 10.1186/1472-6882-14-122 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khattab M. M., Nagi M. N. (2007). Thymoquinone supplementation attenuates hypertension and renal damage in nitric oxide deficient hypertensive rats. Phytother Res. 21, 410–414. 10.1002/ptr.2083 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirichenko B. M., Koreshchuk K. E., Drozd G. A. (1972). Rhamnocitrin — a new component of Nigella arvensis . Chem. Nat. Compd. 8, 656. 10.1007/bf00564348 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kökdil G., Tamer L., Ercan B., İlci A., Aras N., Atik U. (2005). Effects of Nigella unguicularis fixed oil on blood biochemistry and oxidant/antioxidant balance in rats. J. Ethnopharmacology 99, 131–135. 10.1016/j.jep.2005.02.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolahdooz M., Nasri S., Modarres S. Z., Kianbakht S., Huseini H. F. (2014). Effects of Nigella sativa L. seed oil on abnormal semen quality in infertile men: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Phytomedicine 21, 901–905. 10.1016/j.phymed.2014.02.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kooti W., Hasanzadeh-Noohi Z., Sharafi-Ahvazi N., Asadi-Samani M., Ashtary-Larky D. (2016). Phytochemistry, pharmacology, and therapeutic uses of black seed (Nigella sativa). Chin. J. Nat. Med. 14, 732–745. 10.1016/S1875-5364(16)30088-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshak A., Wei L., Koshak E., Wali S., Alamoudi O., Demerdash A., et al. (2017). Nigella sativa supplementation improves asthma control and biomarkers: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Phytother Res. 31, 403–409. 10.1002/ptr.5761 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumara S. S., Huat B. T. (2001). Extraction, isolation and characterisation of antitumor principle, alpha-hederin, from the seeds of Nigella sativa . Planta Med. 67, 29–32. 10.1055/s-2001-10628 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunwar R. M., Acharya R. P., Chowdhary C. L., Bussmann R. W. (2015). Medicinal plant dynamics in indigenous medicines in farwest Nepal. J. Ethnopharmacol 163, 210–219. 10.1016/j.jep.2015.01.035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leong X. F., Rais Mustafa M., Jaarin K. (2013). Nigella sativa and its protective role in oxidative stress and hypertension. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2013, 120732. 10.1155/2013/120732 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leporatti M. L., Ghedira K. (2009). Comparative analysis of medicinal plants used in traditional medicine in Italy and Tunisia. J. Ethnobiol. Ethnomed 5, 31. 10.1186/1746-4269-5-31 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linjawi S. A., Khalil W. K., Hassanane M. M., Ahmed E. S. (2015). Evaluation of the protective effect of Nigella sativa extract and its primary active component thymoquinone against DMBA-induced breast cancer in female rats. Arch. Med. Sci. 11, 220–229. 10.5114/aoms.2013.33329 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu H., Sun Y., Zhang Y., Yang G., Guo L., Zhao Y., et al. (2019). Role of thymoquinone in cardiac damage caused by sepsis from BALB/c mice. Inflammation 42, 516–525. 10.1007/s10753-018-0909-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y. M., Liu Q. H., Chen B. Q. (2011). A new flavonol glycoside from the seeds of Nigella glandulifera . Nat. Prod. Res. 25, 1334–1338. 10.1080/14786419.2010.534470 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y., Feng Y., Liu D., Zhang Z., Gao K., Zhang W., et al. (2018). Thymoquinone attenuates myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury through activation of SIRT1 signaling. Cell Physiol Biochem. 47, 1193–1206. 10.1159/000490216 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahdavi R., Namazi N., Alizadeh M., Farajnia S. (2015). Effects of Nigella sativa oil with a low-calorie diet on cardiometabolic risk factors in obese women: a randomized controlled clinical trial. Food Funct. 6, 2041–2048. 10.1039/c5fo00316d [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoudi A., Ghatreh Samani K., Farrokhi E., Heidarian E. (2018). Effects of Nigella sativa extracts on the lipid profile and uncoupling protein-1 gene expression in Brown adipose tissue of mice. Adv. Biomed. Res. 7, 121. 10.4103/abr.abr_91_18 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahmoudvand H., Sepahvand A., Jahanbakhsh S., Ezatpour B., Ayatollahi Mousavi S. A. (2014). Evaluation of antifungal activities of the essential oil and various extracts of Nigella sativa and its main component, thymoquinone against pathogenic dermatophyte strains. J. Mycol. Med. 24, e155–161. 10.1016/j.mycmed.2014.06.048 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Majdalawieh A. F., Fayyad M. W. (2016). Recent advances on the anti-cancer properties of Nigella sativa, a widely used food additive. J. Ayurveda Integr. Med. 7, 173–180. 10.1016/j.jaim.2016.07.004 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malhotra S. K. (2012). Handbook of herbs and spices. Second Edition. Berlin: Springer, 391–416. [Google Scholar]
- Manju S., Malaikozhundan B., Withyachumnarnkul B., Vaseeharan B. (2016). Essential oils of Nigella sativa protects Artemia from the pathogenic effect of Vibrio parahaemolyticus Dahv2. J. Invertebr Pathol. 136, 43–49. 10.1016/j.jip.2016.03.004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marklund M., Wu J. H. Y., Imamura F., Del Gobbo L. C., Fretts A., De Goede J., et al. (2019). Biomarkers of dietary omega-6 fatty acids and incident cardiovascular disease and mortality. Circulation 139, 2422–2436. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.118.038908 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthaus B., Özcan M. M. (2011). Fatty acids, tocopherol, and sterol contents of some Nigella species seed oil. Czech J. Food Sci. 29, 145–150. 10.17221/206/2008-cjfs [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Meeran M. F., Jagadeesh G. S., Selvaraj P. (2016). Synthetic catecholamine triggers beta1-adrenergic receptor activation and stimulates cardiotoxicity via oxidative stress mediated apoptotic cell death in rats: abrogating action of thymol. Chem. Biol. Interact 251, 17–25. 10.1016/j.cbi.2016.03.017 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohammed N. K., Abd Manap M. Y., Tan C. P., Muhialdin B. J., Alhelli A. M., Meor Hussin A. S. (2016). The effects of different extraction methods on antioxidant properties, chemical composition, and thermal behavior of black seed (Nigella sativa L.) oil. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2016, 6273817. 10.1155/2016/6273817 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohtashami A. (2019). Effects of bread with Nigella sativa on blood glucose, blood pressure and anthropometric indices in patients with metabolic syndrome. Clin. Nutr. Res. 8, 138–147. 10.7762/cnr.2019.8.2.138 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moneim A. A., Abdel-Reheim E. S., Helmy H., Addaleel W. (2018). Antidiabetic Effect of Thymoquinone via modulation of PPAR-γ, GLUT4, hyperlipidemia and antioxidant status in diabetic rats. Asian J. Biol. Sci. 11, 203–209. 10.3923/ajbs.2018.203.209 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Moretti A., D'antuono L. F., Elementi S. (2004). Essential oils of Nigella sativa L. And Nigella damascena L. Seed. J. Essent. Oil Res. 16, 182–183. 10.1080/10412905.2004.9698690 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mousavi S. M., Sheikhi A., Varkaneh H. K., Zarezadeh M., Rahmani J., Milajerdi A. (2018). Effect of Nigella sativa supplementation on obesity indices: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Complement. Ther. Med. 38, 48–57. 10.1016/j.ctim.2018.04.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mrozek-Wilczkiewicz A., Musiol R., Spaczynska E. (2016). Nigella sativa—a functional spice from a pharaoh’s tomb to modern healthcare. Nat. Prod. J. 6, 13–26. 10.2307/30107802 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nagoor Meeran M. F., Jagadeesh G. S., Selvaraj P. (2015a). Thymol attenuates altered lipid metabolism in β-adrenergic agonist induced myocardial infarcted rats by inhibiting tachycardia, altered electrocardiogram, apoptosis and cardiac hypertrophy. J. Funct. Foods 14, 51–62. 10.1016/j.jff.2015.01.013 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nagoor Meeran M. F., Jagadeesh G. S., Selvaraj P. (2015b). Thymol attenuates inflammation in isoproterenol induced myocardial infarcted rats by inhibiting the release of lysosomal enzymes and downregulating the expressions of proinflammatory cytokines. Eur. J. Nutr. 754, 153–161. 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.02.028 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagoor Meeran M. F., Jagadeesh G. S., Selvaraj P. (2016). Thymol, a dietary monoterpene phenol abrogates mitochondrial dysfunction in beta-adrenergic agonist induced myocardial infarcted rats by inhibiting oxidative stress. Chemico-Biological Interactions 244, 159–168. 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.12.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najmi A., Nasiruddin M., Khan R. A., Haque S. F. (2008). Effect of Nigella sativa oil on various clinical and biochemical parameters of insulin resistance syndrome. Int. J. Diabetes Developing Countries 28, 11–14. 10.4103/0973-3930.41980 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najmi A., Nasiruddin M., Khan R. A., Haque S. F. (2012). Therapeutic effect of Nigella sativa in patients of poor glycemic control. Asian J. Pharm. Clin. Res. 5, 224–228. 10.5580/1554 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Namazi N., Larijani B., Ayati M. H., Abdollahi M. (2018). The effects of Nigella sativa L. on obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Ethnopharmacol 219, 173–181. 10.1016/j.jep.2018.03.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neamsuvan O., Phumchareon T., Bunphan W., Kaosaeng W. (2016). Plant materials for gastrointestinal diseases used in chawang district, nakhon Si thammarat province, Thailand. J. Ethnopharmacol 194, 179–187. 10.1016/j.jep.2016.09.001 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nickavar B., Mojab F., Javidnia K., Amoli M. A. (2003). Chemical composition of the fixed and volatile oils of Nigella sativa L. from Iran. Z. für Naturforschung. C, A J. biosciences 58, 629–631. 10.1515/znc-2003-9-1004 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikakhlagh S., Rahim F., Aryani F. H., Syahpoush A., Brougerdnya M. G., Saki N. (2011). Herbal treatment of allergic rhinitis: the use of Nigella sativa . Am. J. Otolaryngol. 32, 402–407. 10.1016/j.amjoto.2010.07.019 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikkhah-Bodaghi M., Darabi Z., Agah S., Hekmatdoost A. (2019). The effects of Nigella sativa on quality of life, disease activity index, and some of inflammatory and oxidative stress factors in patients with ulcerative colitis. Phytother Res. 33, 1027–1032. 10.1002/ptr.6296 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelegrin S., Galtier F., Chalancon A., Gagnol J. P., Barbanel A. M., Pelissier Y., et al. (2019). Effects of Nigella sativa seeds (black cumin) on insulin secretion and lipid profile: a pilot study in healthy volunteers. Br. J. Clin. Pharmacol. 85, 1607–1611. 10.1111/bcp.13922 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Periasamy V. S., Athinarayanan J., Alshatwi A. A. (2016). Anticancer activity of an ultrasonic nanoemulsion formulation of Nigella sativa L. essential oil on human breast cancer cells. Ultrason. Sonochem. 31, 449–455. 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.01.035 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piras A., Rosa A., Marongiu B., Porcedda S., Falconieri D., Dessì M. A., et al. (2013). Chemical composition and in vitro bioactivity of the volatile and fixed oils of Nigella sativa L. extracted by supercritical carbon dioxide. Ind. Crops Prod. 46, 317–323. 10.1016/j.indcrop.2013.02.013 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pouvreau C., Dayre A., Butkowski E. G., De Jong B., Jelinek H. F. (2018). Inflammation and oxidative stress markers in diabetes and hypertension. J. Inflamm. Res. 11, 61–68. 10.2147/JIR.S148911 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qidwai W., Hamza H. B., Qureshi R., Gilani A. (2009). Effectiveness, safety, and tolerability of powdered Nigella sativa (kalonji) seed in capsules on serum lipid levels, blood sugar, blood pressure, and body weight in adults: results of a randomized, double-blind controlled trial. J. Altern. Complement. Med. 15, 639–644. 10.1089/acm.2008.0367 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabbani M. A., Ghafoor A., Masood M. S. (2011). NARC-kalonji: an early maturing and high yielding variety of Nigella sativa released for cultivation in Pakistan. Pakistan J. Bot. 43, 191–195. 10.25301/jpda.294.205 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadan M. F., Mörsel J.-T. (2002). Neutral lipid classes of black cumin (Nigella sativa L.) seed oils. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 214, 202–206. 10.1007/s00217-001-0423-8 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Ramadan M. F., Mörsel J.-T. (2004). Oxidative stability of black cumin (Nigella sativa L.), coriander (Coriandrum sativum L.) and Niger (Guizotia abyssinica Cass.) crude seed oils upon stripping. Eur. J. Lipid Sci. Technol. 106, 35–43. 10.1002/ejlt.200300895 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rani R., Dahiya S., Dhingra D., Dilbaghi N., Kim K. H., Kumar S. (2018). Improvement of antihyperglycemic activity of nano-thymoquinone in rat model of type-2 diabetes. Chem. Biol. Interact 295, 119–132. 10.1016/j.cbi.2018.02.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasoli M. S., Khalili M., Mohammadi R., Soleimani A., Kohzadi R., Ilkhanipour M., et al. (2018). The chemical composition of Nigella sativa L. and its extract effects on lipid peroxidation levels, total antioxidant capacity and catalase activity of the liver and kidney in rats under stress. Gene, Cell and Tissue 5, e61323. 10.5812/gct.61323 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Rezaeian A., Amoushahi Khouzani S. (2018). Effect of Nigella sativa nasal spray on the treatment of chronic rhinosinusitis without a nasal polyp. Allergy Rhinol (Providence) 9, 2152656718800059. 10.1177/2152656718800059 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rooney S., Ryan M. F. (2005). Effects of alpha-hederin and thymoquinone, constituents of Nigella sativa, on human cancer cell lines. Anticancer Res. 25, 2199–2204. 10.22541/au.158879398.87850730 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahak M. K. A., Kabir N., Abbas G., Draman S., Hashim N. H., Hasan Adli D. S. (2016). The role of Nigella sativa and its active constituents in learning and memory. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2016, 6075679. 10.1155/2016/6075679 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salahshoor M. R., Vahabi A., Roshankhah S., Darehdori A. S., Jalili C. (2018). The effects of thymoquinone against morphine-induced damages on male mice liver. Int. J. Prev. Med. 9, 1–8. 10.4103/ijpvm.ijpvm_144_16 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salehi B., Abu-Darwish M. S., Tarawneh A. H., Cabral C., Gadetskaya A. V., Salgueiro L., et al. (2019). Thymus spp. plants—food applications and phytopharmacy properties. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 85, 287–306. 10.1016/j.tifs.2019.01.020 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Salehi B., Mishra A. P., Shukla I., Sharifi-Rad M., Contreras M. D. M., Segura-Carretero A., et al. (2018). Thymol, thyme, and other plant sources: health and potential uses. Phytother Res. 32, 1688–1706. 10.1002/ptr.6109 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Samarghandian S., Farkhondeh T., Samini F., Borji A. (2016). Protective effects of carvacrol against oxidative stress induced by chronic stress in rat's brain, liver, and kidney. Biochem. Res. Int. 2016, 2645237. 10.1155/2016/2645237 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saravanan S., Pari L. (2016). Protective effect of thymol on high fat diet induced diabetic nephropathy in C57BL/6J mice. Chem. Biol. Interact 245, 1–11. 10.1016/j.cbi.2015.11.033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar D., Shetty K. (2014). Metabolic stimulation of plant phenolics for food preservation and health. Annu. Rev. Food Sci. Technol. 5, 395–413. 10.1146/annurev-food-030713-092418 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxena S. N., Rathore S. S., Diwakar Y., Kakani R. K., Kant K., Dubey P. N., et al. (2017). Genetic diversity in fatty acid composition and antioxidant capacity of Nigella sativa L. genotypes. LWT 78, 198–207. 10.1016/j.lwt.2016.12.033 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Schulte R. T., Ohl D. A., Sigman M., Smith G. D. (2010). Sperm DNA damage in male infertility: etiologies, assays, and outcomes. J. Assist. Reprod. Genet. 27, 3–12. 10.1007/s10815-009-9359-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selim T., Karlsson L., Bouksila F., Ben Slimane A., Persson M. (2019). Evaluation of different irrigation treatments with saline water in a future climate in Tunisia. Irrig. Drain. 68, 281–296. 10.1002/ird.2307 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Shafi G., Munshi A., Hasan T. N., Alshatwi A. A., Jyothy A., Lei D. K. (2009). Induction of apoptosis in HeLa cells by chloroform fraction of seed extracts of Nigella sativa . Cancer Cel Int. 9, 29. 10.1186/1475-2867-9-29 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shahin Y. R., Elguindy N. M., Abdel Bary A., Balbaa M. (2018). The protective mechanism of Nigella sativa against diethylnitrosamine-induced hepatocellular carcinoma through its antioxidant effect and EGFR/ERK1/2 signaling. Environ. Toxicol. 14, 121. 10.1002/tox.22574 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam M. K., Ahn K. S., Hsu A., Woo C. C., Yuan Y., Tan K. H. B., et al. (2018a). Thymoquinone inhibits bone metastasis of breast cancer cells through abrogation of the CXCR4 signaling Axis . Front. Pharmacol. 9, 1294. 10.3389/fphar.2018.01294 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shanmugam M. K., Arfuso F., Kumar A. P., Wang L., Goh B. C., Ahn K. S., et al. (2018b). Modulation of diverse oncogenic transcription factors by thymoquinone, an essential oil compound isolated from the seeds of Nigella sativa Linn. Pharmacol. Res. 129, 357–364. 10.1016/j.phrs.2017.11.023 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi-Rad M., Varoni E. M., Iriti M., Martorell M., Setzer W. N., Del Mar Contreras M., et al. (2018). Carvacrol and human health: a comprehensive review. Phytother Res. 32, 1675–1687. 10.1002/ptr.6103 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma N. K., Ahirwar D., Jhade D., Gupta S. (2009). Medicinal and pharmacological potential of Nigella sativa: a review. Ethnobotanical Rev. 13, 946–955. 10.5897/jmpr11.1341 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Singhal P., Singla N., Sakhare D., Sharma A. (2017). A Comparative evaluation of in-vitro antioxidant activity of some commonly used spices of Northern India. Nat. Prod. J. 7, 1–6. 10.2174/2210315506666161123120821 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Siveen K. S., Mustafa N., Li F., Kannaiyan R., Ahn K. S., Kumar A. P., et al. (2014). Thymoquinone overcomes chemoresistance and enhances the anticancer effects of bortezomib through abrogation of NF-kappaB regulated gene products in multiple myeloma xenograft mouse model. Oncotarget 5, 634–648. 10.18632/oncotarget.1596 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spalletta S., Flati V., Toniato E., Di Gregorio J., Marino A., Pierdomenico L., et al. (2018). Carvacrol reduces adipogenic differentiation by modulating autophagy and ChREBP expression. PLoS One 13, e0206894. 10.1371/journal.pone.0206894 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sreekeesoon D. P., Mahomoodally M. F. (2014). Ethnopharmacological analysis of medicinal plants and animals used in the treatment and management of pain in Mauritius. J. Ethnopharmacol 157, 181–200. 10.1016/j.jep.2014.09.030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun L., Liu Y.-M., Chen B.-Q., Liu Q.-H. (2015). New phenolic compounds from the seeds of Nigella glandulifera and their inhibitory activities against human cancer cells. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 25, 3864–3866. 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.07.055 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tajmiri S., Farhangi M. A., Dehghan P. (2016). Nigella sativa treatment and serum concentrations of thyroid hormones, transforming growth factor β (TGF-β) and interleukin 23 (IL-23) in patients with Hashimoto’s Thyroiditis. Eur. J. Integr. Med. 8, 576–580. 10.1016/j.eujim.2016.03.003 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M. (1993). “Ranunculaceae,” in The families and genera of vascular plants. Vol II. Editors Kubitzki K., Rohwer J. G., Bittrich V. (Berlin: Springer; ), 563–583. [Google Scholar]
- Tasawar Z., Siraj Z., Ahmad N., Lashari M. H. (2011). The effects of Nigella sativa (kalonji) on lipid profile in patients with stable coronary artery disease in multan, Pakistan. Pakistan J. Nutr. 10, 162–167. 10.3923/pjn.2011.162.167 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Teixidor-Toneu I., Martin G. J., Ouhammou A., Puri R. K., Hawkins J. A. (2016). An ethnomedicinal survey of a Tashelhit-speaking community in the High Atlas, Morocco. J. Ethnopharmacol 188, 96–110. 10.1016/j.jep.2016.05.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tesarova H., Svobodova B., Kokoska L., Marsik P., Pribylova M., Landa P., et al. (2011). Determination of oxygen radical absorbance capacity of black cumin (Nigella sativa) seed quinone compounds. Nat. Prod. Commun. 6, 213–216. 10.1177/1934578x1100600214 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thakral S., Singh V. (2019). 2,4‐Dichloro‐5‐[(N‐aryl/alkyl)sulfamoyl]benzoic acid derivatives: in vitro antidiabetic activity, molecular modeling and in silico ADMET screening. Med Chem. 15 (2), 186–195. 10.2174/1573406414666180924164327 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The Plant List (2020). Version 1.1. Available at: http://www.theplantlist.org/ (Accessed April).
- Tian Z., Liu Y. M., Chen S. B., Yang J. S., Xiao P. G., Wang L., et al. (2006). Cytotoxicity of two triterpenoids from Nigella glandulifera . Molecules 11, 693–699. 10.3390/11090693 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tiruppur Venkatachallam S. K., Pattekhan H., Divakar S., Kadimi U. S. (2010). Chemical composition of Nigella sativa L. seed extracts obtained by supercritical carbon dioxide. J. Food Sci. Technol. 47, 598–605. 10.1007/s13197-010-0109-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toma C. C., Olah N. K., Vlase L., Mogosan C., Mocan A. (2015). Comparative studies on polyphenolic composition, antioxidant and diuretic effects of Nigella sativa L. (Black cumin) and Nigella damascena L. (Lady-in-a-Mist) seeds. Molecules 20, 9560–9574. 10.3390/molecules20069560 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tonçer Ö., Kizil S. (2004). Effect of seed rate on agronomic and technologic characters of Nigella sativa L. Int. J. Agric. Biol. 3, 529–532. 10.1007/978-981-15-4194-0_13 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tutin T. G., Heywood V. H., Burgess N. A., Moore D. M., Valentine D. H., Walters S. M., et al. (1972). Flora europaea. Edinburgh: Royal Botanic Garden Edinburgh. [Google Scholar]
- Usta A., Dede S. (2017). The effect of thymoquinone on nuclear factor kappa B levels and oxidative DNA damage on experimental diabetic rats. Pharmacogn Mag. 13, S458–s461. 10.4103/pm.pm_134_17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uğurlu Aydın Z., Dönmez A. A. (2019). Numerical analyses of seed morphology and its taxonomic significance in the tribe Nigelleae (Ranunculaceae). Nordic J. Bot. 37, 121. 10.1111/njb.02323 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Vafaee F., Hosseini M., Hassanzadeh Z., Edalatmanesh M. A., Sadeghnia H. R., Seghatoleslam M., et al. (2015). The effects of Nigella sativa hydro-alcoholic extract on memory and brain tissues oxidative damage after repeated seizures in rats. Iranian J. Pharm. Res. 14, 547–557. 10.26226/morressier.5785edc8d462b80296c99763 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vahdati-Mashhadian N., Rakhshandeh H., Omidi A. (2005). An investigation on LD50 and subacute hepatic toxicity of Nigella sativa seed extracts in mice. Pharmazie 60, 544–547. 10.7176/fsqm/102-06 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Viuda-Martos M., Mohamady M. A., Fernández-López J., Abd Elrazik K. A., Omer E. A., Pérez-Alvarez J. A., et al. (2011). In vitro antioxidant and antibacterial activities of essentials oils obtained from Egyptian aromatic plants. Food Control 22, 1715–1722. 10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.04.003 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Vokou D., Katradi K., Kokkini S. (1993). Ethnobotanical survey of Zagori (Epirus, Greece), a renowned centre of folk medicine in the past. J. Ethnopharmacol 39, 187–196. 10.1016/0378-8741(93)90035-4 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wajs A., Bonikowski R., Kalemba D. (2008). Composition of essential oil from seeds of Nigella sativa L. cultivated in Poland. Flavour Fragr. J. 23, 126–132. 10.1002/ffj.1866 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Woo C. C., Hsu A., Kumar A. P., Sethi G., Tan K. H. (2013). Thymoquinone inhibits tumor growth and induces apoptosis in a breast cancer xenograft mouse model: the role of p38 MAPK and ROS. PLoS One 8, e75356. 10.1371/journal.pone.0075356 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woo C. C., Kumar A. P., Sethi G., Tan K. H. (2012). Thymoquinone: potential cure for inflammatory disorders and cancer. Biochem. Pharmacol. 83, 443–451. 10.1016/j.bcp.2011.09.029 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao J., Ke Z. P., Shi Y., Zeng Q., Cao Z. (2018). The cardioprotective effect of thymoquinone on ischemia-reperfusion injury in isolated rat heart via regulation of apoptosis and autophagy. J. Cel Biochem. 119, 7212–7217. 10.1002/jcb.26878 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xin X. L., Aisa H. A., Wang H. Q. (2008). Flavonoids and phenolic compounds from seeds of the Chinese plant Nigella glandulifera . Chem. Nat. Compd. 44, 368–369. 10.1007/s10600-008-9066-3 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Xin X., Wang Q., Aisa H. A., Wang H. (2010). Antidiabetes properties of n-hexane and petroleum ether extracts from seeds of Nigella glandulifera Freyn. J. Food Biochem. 34, 811–824. 10.1111/j.1745-4514.2009.00318.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Yaseen G., Ahmad M., Zafar M., Sultana S., Kayani S., Cetto A. A., et al. (2015). Traditional management of diabetes in Pakistan: ethnobotanical investigation from traditional health practitioners. J. Ethnopharmacol 174, 91–117. 10.1016/j.jep.2015.07.041 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yimer E. M., Tuem K. B., Karim A., Ur-Rehman N., Anwar F. (2019). Nigella sativa L. (black cumin): a promising natural remedy for wide range of illnesses. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2019, 1528635. 10.1155/2019/1528635 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yousefi M., Barikbin B., Kamalinejad M., Abolhasani E., Ebadi A., Younespour S., et al. (2013). Comparison of therapeutic effect of topical Nigella with Betamethasone and Eucerin in hand eczema. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 27, 1498–1504. 10.1111/jdv.12033 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yun Q., Liu Q., He C., Ma X., Gao X., Talbi A., et al. (2014). UPLC-Q-TOF/MS characterization, HPLC fingerprint analysis and species differentiation for quality control of Nigella glandulifera Freyn et Sint seeds and Nigella sativa L. seeds. Anal. Methods 6, 4845–4852. 10.1039/c4ay00775a [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zaoui A., Cherrah Y., Alaoui K., Mahassine N., Amarouch H., Hassar M. (2002). Effects of Nigella sativa fixed oil on blood homeostasis in rat. J. Ethnopharmacol 79, 23–26. 10.1016/s0378-8741(01)00342-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao J., Xu F., Huang H., Gu Z., Wang L., Tan W., et al. (2013). Evaluation on anti-inflammatory, analgesic, antitumor, and antioxidant potential of total saponins from Nigella glandulifera seeds. Evid. Based Complement. Alternat Med. 2013, 827230. 10.1155/2013/827230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zohary M. (1983). The genus Nigella (Ranunculaceae) — a taxonomic revision. Pl Syst. Evol. 142, 71–105. 10.1007/bf00989605 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zribi I., Omezzine F., Haouala R. (2014). Variation in phytochemical constituents and allelopathic potential of Nigella sativa with developmental stages. South Afr. J. Bot. 94, 255–262. 10.1016/j.sajb.2014.07.009 [DOI] [Google Scholar]