Abstract
Protein-truncating variants (PTVs) affecting dyslipidemia risk may point to therapeutic targets for cardiometabolic disease. Our objective was to identify PTVs that were associated with both lipid levels and the risk of coronary artery disease (CAD) or type 2 diabetes (T2D) and assess their possible associations with risks of other diseases. To achieve this aim, we leveraged the enrichment of PTVs in the Finnish population and tested the association of low-frequency PTVs in 1,209 genes with serum lipid levels in the Finrisk Study (n = 23,435). We then tested which of the lipid-associated PTVs were also associated with the risks of T2D or CAD, as well as 2,683 disease endpoints curated in the FinnGen Study (n = 218,792). Two PTVs were associated with both lipid levels and the risk of CAD or T2D: triglyceride-lowering variants in ANGPTL8 (-24.0[-30.4 to -16.9] mg/dL per rs760351239-T allele, P = 3.4 × 10−9) and ANGPTL4 (-14.4[-18.6 to -9.8] mg/dL per rs746226153-G allele, P = 4.3 × 10−9). The risk of T2D was lower in carriers of the ANGPTL4 PTV (OR = 0.70[0.60–0.81], P = 2.2 × 10−6) than noncarriers. The odds of CAD were 47% lower in carriers of a PTV in ANGPTL8 (OR = 0.53[0.37–0.76], P = 4.5 × 10−4) than noncarriers. Finally, the phenome-wide scan of the ANGPTL8 PTV showed that the ANGPTL8 PTV carriers were less likely to use statin therapy (68,782 cases, OR = 0.52[0.40–0.68], P = 1.7 × 10−6) compared to noncarriers. Our findings provide genetic evidence of potential long-term efficacy and safety of therapeutic targeting of dyslipidemias.
Author summary
Studying the health impacts of protein-truncating variants (PTVs) enables detecting the health impact of drugs that inhibit these same genes. Our study aimed to expand our knowledge of genes associated with cardiometabolic disease, along with the side effects of these genes. To detect PTVs associated with cardiometabolic disease, we first performed a genome-wide scan of PTVs associated with serum lipid levels in Finns. We found PTVs in two genes highly enriched in Finns, which were associated with both serum lipid levels and a lower risk of type 2 diabetes or coronary artery disease: ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8. To evaluate the other health effects of these PTVs, we performed an association scan between the PTVs and 2,683 disease endpoints curated in the FinnGen Study (n = 218,792). We demonstrate that using human populations with PTV-enrichment, such as Finns, offers considerable boosts in statistical power to detect potential long-term efficacy and safety of pharmacologically targeting genes.
Introduction
Dyslipidemia is a major risk factor for cardiovascular disease and is present in nearly half of type 2 diabetes patients [1]. For treating dyslipidemia, there are few alternatives to low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol-lowering therapy. Although common, this therapy often fails to treat the condition effectively, leaving patients with high risk of cardiovascular disease [2]. Therefore, a search for possible new drugs is necessary. Although genome-wide association studies have identified over 200 genetic loci that are related to circulating lipid levels [3–6] these variants are typically common (minor-allele frequency [MAF] greater than 5%) and are located in the noncoding part of the genome. This has made it hard to identify causal genes for blood lipid levels and thus cardiometabolic disease risk for most genetic regions. Recent surveys on the protein-coding variation in lipid-associated loci [4,5,7] have implicated likely causal genes via low-frequency coding variants. However, these types of studies have not been able to show which genes can be pharmacologically inhibited safely to reduce the risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D) or coronary artery disease (CAD).
There is a limited number of drugs for treating dyslipidemia currently on the market or in development. Drugs targeting triglycerides, lipoprotein(a) or high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol that are currently being developed have emerged from studies of PTVs [8–14], and it is uncertain whether they are safe enough to reach the market. Meanwhile, PCSK9 inhibitors and ezetimibe are the only common alternatives to statins for lowering LDL cholesterol levels. More options would be welcome given that statins have common side effects [15].
Besides the small number of alternatives, another issue is the long-term safety of drugs targeting dyslipidemia. Maximizing the long-term safety of these drugs is important because they are often used preventatively and for prolonged periods by wide sectors of the population. Given this use, the long-term, population-level side effects of these drugs are especially important to minimize. Such an understanding could be achieved by investigating health impacts of genetic proxies for protein deficiencies that are associated with lipid levels. A study assessing this question exists for the chief lipoprotein(a)-modulating gene LPA [16]. However, it is less well known what are the health effects of the other major lipid-modifying genes targeted by drugs currently under development: ANGPTL3, ANGPTL4, APOC3 and CETP [8–13]. Although some of these drug targets have undergone clinical trials, they do not consider long-term health impacts and suffer from confounding factors, such as compound-specific off-target effects.
Considering these clinical needs, the present study aimed to further the treatment of dyslipidemia in two ways. The primary goal was to identify PTVs associated with serum lipid levels and the risk of T2D or CAD, as well as assess their associations with other disease risks. Because of the clear deleterious effect of PTVs on the protein levels, studying them makes it possible to determine the effect of individual genes on disease risks and phenotypes over long time periods. Ultimately, such results provide an opportunity to develop safe drug targets for treating dyslipidemia and cardiometabolic diseases. The secondary aim of this study was to evaluate the long-term health consequences of existing dyslipidemia drug targets with the help of PTVs. Studying Finns provides a promising avenue for reaching both of these goals. The Finnish population isolate shows an enrichment of protein-truncating variants (PTVs)[17,18] (stop-gained, frame-shift and essential splice-site mutations), thus enabling the detection of both new and previously-known therapeutic effects through a smaller sample size than in the non-Finnish European population. We restricted the study to low-frequency and rare PTVs (MAF between 0.1% and 5%). On the one hand, associations with common variants (MAF > 5%) would have already been detected by past large consortium efforts. On the other hand, for very rare variants (MAF < 0.1%), our study would have had both insufficient imputation accuracy and statistical power to detect significant associations. Thanks to national health records on Finns, it is also possible to screen for a wide range of long-term health impacts associated with these PTVs. When combined, the data on PTVs and health records provide us with exactly the type of long-term, population-wide, on-target side effect data that is currently lacking, as discussed above.
Results
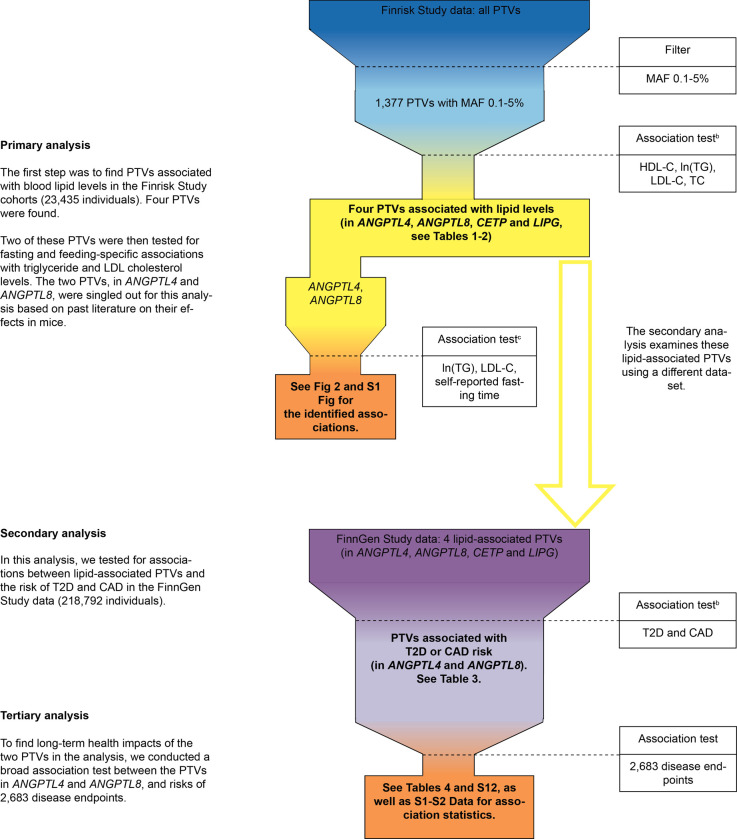
An overview of our study’s analyses and their results is presented in Fig 1. Our results are divided into three parts: the primary, secondary and tertiary analyses. Results of the primary analysis concern associations between 1,377 PTVs with a MAF of 0.1–5% and the serum lipid levels: triglycerides, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol and total cholesterol. Results of the secondary analysis concern associations between lipid-associated PTVs and the risk of CAD and T2D. Finally, results of the tertiary analyses concern the possible side effects of PTVs associated with both lipid levels and the risk of T2D or CAD.
Fig 1. An overview of the present study.
a Abbreviations: PTV, protein-truncating variant; MAF, minor-allele frequency; HDL-C, high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level; ln(TG), natural logarithm of triglyceride level; LDL-C, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol level; TC, total cholesterol level; T2D, type 2 diabetes; CAD, coronary artery disease. a Shown in the figure is an overview of the present study. The final results are shown in boxes with a bolded font. b Results for these association tests were also compared with other PTVs in UK Biobank. c These association tests were post-hoc in nature.
Primary analyses
Protein-truncating variants and serum lipid levels
Through a genome-wide association scan between 1,377 PTVs and serum lipid levels we found four PTVs to be associated with serum lipid levels in 23,435 Finrisk Study individuals. PTVs in CETP (rs751916721-T), LIPG (rs200435657-A), and ANGPTL8 (rs760351239-T) showed genome-wide significant associations with HDL cholesterol levels. PTVs in ANGPTL4 (rs746226153-G) and ANGPTL8 (rs760351239-T) had genome-wide significant associations with triglyceride levels (Tables 1 and 2). These observations are supported by previous studies. The splice acceptor variant rs200435657-A in LIPG and the stop-gained variant rs145464906-T in ANGPTL8 have been associated genome-wide significantly with higher HDL cholesterol levels [4,19]. Nominal associations (P < 0.05) between lower triglyceride levels and protein-truncating variation in ANGPTL8[19] and ANGPTL4[9], as well as between CETP protein-truncating variation and higher HDL cholesterol levels [20], have also been reported. The four PTVs showed 27 to 210-fold enrichment in Finns compared to non-Finnish Europeans in the gnomAD database [21], version 2.1.1 (gnomad.broadinstitute.org) (Table 1).
Table 1. Associations between protein-truncating variants and serum lipid levels in the Finrisk Study.a.
| Locus and variant | Chromosome positionb | Type of mutation | MAF in Finrisk Study % | MAF in NFE in gnomAD % | Enrichmentc | Primary association | P | Conditional Pd |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ANGPTL4 rs746226153-G | 19:8364556 | Frameshift | 0.48 | 1.9 × 10−2 | 27.2 | Triglycerides | 4.3 × 10−9 | 3.7 × 10−8 |
| ANGPTL8 rs760351239-T | 19:11240228 | Stop-gained | 0.15 | 2.1 × 10−3 | 85.0 | Triglycerides | 3.4 × 10−9 | - |
| CETP rs751916721-T | 16:56962097 | Splice-site | 0.12 | 3.1 × 10−3 | 46.3 | HDL cholesterol | 1.6 × 10−21 | 5.9 × 10−19 |
| LIPG rs200435657-A | 18:49565316 | Splice-site | 0.20 | 7.8 × 10−4 | 210.1 | HDL cholesterol | 5.0 × 10−13 | 3.6 × 10−12 |
Abbreviations: MAF, minor-allele frequency; NFE, non-Finnish Europeans.
a Shown in the table are the four PTVs associated genome-wide significantly (two-sided P < 5 × 10−8) with at least one serum lipid level measure in the Finrisk Study cohorts. The tested serum lipid levels were LDL, HDL and total cholesterol, as well as natural logarithm transformed triglycerides.
b Chromosome numbers and positions refer to genome build GRCh38.
c The allele frequency enrichment in Finns with respect to non-Finnish Europeans according to the gnomAD database, version 2.1.1 (gnomad.broadinstitute.org).
d The conditional P value is the largest P value from association tests conditioning on other previously reported genome-widely significant markers in the same gene. The conditional P value for rs760351239-T is not available because no genome-widely significant genetic variant in ANGPTL8 has been reported before.
Table 2. Associations between protein-truncating variants and serum lipid levels in the Finrisk Study and UK Biobank.a.
| Locus and variant | Cohort | Triglycerides | LDL cholesterol | HDL cholesterol | Total cholesterol | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Effect (95% CI)b mg/dL | P | Effect (95% CI)b mg/dL | P | Effect (95% CI)b mg/dL | P | Effect (95% CI)b mg/dL | P | ||
| ANGPTL4 rs746226153-G | Finrisk | -14.4 (-18.6 to -9.8) |
4.3 × 10−9 | 2.4 (-2.1 to 7.0) |
0.30 | 1.5 (-0.2 to 3.3) |
0.09 | -0.2 (-5.3 to 4.9) |
0.94 |
| ANGPTL8 rs760351239-T | Finrisk | -24.0 (-30.4 to -16.9) |
3.4 × 10−9 | -16.8 (-24.8 to -8.7) |
4.5 × 10−5 | 9.1 (6.1 to 12.3) |
4.6 × 10−9 | -14.2 (-23.2 to -5.1) |
2.2 × 10−3 |
| ANGPTL8 rs145464906-T | UK Biobank | -18.9 (-21.2 to -15.1) |
3.3 × 10−25 | -4.5 (-7.6 to -1.4) |
4.2 × 10−3 | 6.1 (4.8 to 7.4) |
7.4 × 10−20 | -1.0 (-5.2 to 3.1) |
0.62 |
|
CETP rs751916721-T |
Finrisk | 5.1 (-5.2 to 16.8) |
0.34 | -7.0 (-16.1 to 2.1) |
0.13 | 16.7 (13.2 to 20.1) |
1.6 × 10−21 | 12.0 (1.9 to 22.2) |
0.02 |
|
LIPG rs200435657-A |
Finrisk | 3.7 (-4.6 to 12.8) |
0.40 | 4.1 (-3.4 to 11.7) |
0.28 | 10.2 (7.5 to 13.0) |
5.0 × 10−13 | 17.3 (9.0 to 25.5) |
4.2 × 10−5 |
Abbreviations: CI, confidence interval.
a All association tests in were adjusted for age, age squared, sex. In the Finrisk Study and UK Biobank association tests were additionally adjusted for the study cohort and ten principal components, and assessment center and 40 principal components respectively. In analyses of serum triglycerides, the triglyceride levels were natural logarithm transformed and waist-to-hip ratio was included as an additional covariate. Values for LDL and total cholesterol were adjusted for the use of lipid-lowering medication by dividing by 0.7 and 0.8 respectively.
b The effect is the difference per each copy of the minor-allele in units in mg/dL of triglycerides, LDL, HDL and total cholesterol. To convert the values for cholesterol to mmol/L, multiply by 0.0259. To convert the values for triglycerides to mmol/L, multiply by 0.0113.
To evaluate whether the associations between the serum lipid levels and the four PTVs were independent, we conducted conditional tests of independence and determined which credible sets the PTVs belonged to. In our conditional analysis, the associations between lipid levels and the PTVs in the Finrisk Study [22] data were not explained by previously-reported genome-wide significant variants [3–6] (Tables 1 and S3–S6). The LIPG and ANGPTL8 PTVs alone formed credible sets with posterior probabilities above 99.9%. The CETP and ANGPTL4 PTVs were in high linkage disequilibrium with the noncoding variants rs566571297-T (r2 = 0.99) and rs919624228-G (r2 = 0.97) respectively. With their correlated variant pair, these two PTVs formed credible sets with posterior probabilities higher than 99%. Hence, all the four PTVs were independently associated with changes in lipid levels with a very high probability (S7–S10 Tables).
To inspect if the lipid level associations with PTVs in Finns were concordant with other PTVs in the same genes, we surveyed the UK Biobank data. Using another rare non-Finnish European-enriched ANGPTL8 PTV (rs145464906-T) in Britons, we observed comparable and genome-wide significant HDL cholesterol and triglyceride level associations as with the PTV found in Finns (Table 2). PTVs in ANGPTL4, CETP or LIPG were not present in the UK Biobank data and thus we were not able to investigate the lipid level associations of other protein-truncating variation in these genes.
Protein-truncating variants and serum lipid levels as a function of fasting time
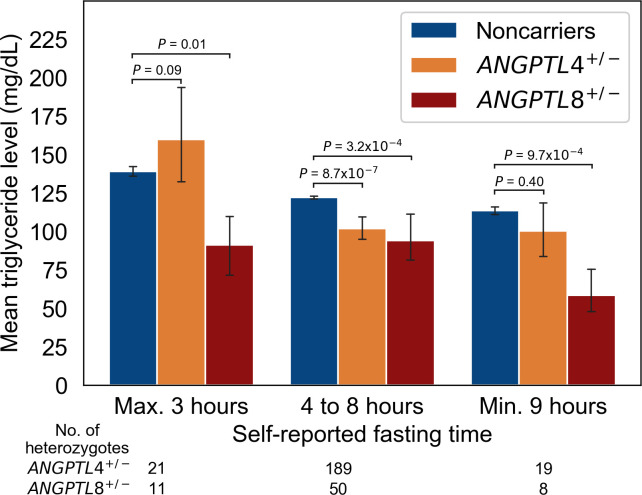
Angptl4 and Angptl8 have previously been linked to specific circulating lipid profiles in response to fasting and feeding respectively [23–25]. Therefore, we tested two hypotheses relating to the association of ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 with lipid levels as a function of fasting time. The first hypothesis was that ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 are associated with lower fasting and postprandial triglyceride levels respectively. We found that ANGPTL4 PTV heterozygotes had 16.6% (20.2 mg/dL, P = 8.7 × 10−7) lower triglyceride levels than non-carriers when the time since the last meal was from 4 to 8 hours. On the other hand, the heterozygotes’ triglyceride levels were not significantly lower than non-carriers’ when the fasting time was 3 hours or less (14.8% higher [20.6 mg/dL], P = 0.09). The ANGPTL8 PTV heterozygotes in turn had 34.3% (47.8 mg/dL, P = 0.01) lower triglyceride levels than non-carriers when the fasting time was up to 3 hours. From 4 to 8 hours after the last meal, the carriers had only 22.9% (27.9 mg/dL, P = 3.2 × 10−4) lower triglyceride levels than noncarriers.
The second hypothesis was that the ANGPTL8 PTV is associated with lower fasting LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels. We observed that ANGPTL8 PTV heterozygotes had 13.4% (18.0 mg/dL, P = 4.5 × 10−5) lower LDL cholesterol levels than noncarriers with a fasting time between 4 and 8 hours. Moreover, the heterozygotes had 48.6% (55.1 mg/dL, P = 9.7 × 10−4) and 26.2% (36.9 mg/dL, P = 0.007) lower triglyceride and LDL cholesterol levels respectively than noncarriers when fasting for 9 hours or longer. The triglyceride and LDL cholesterol levels as a function of ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 PTV genotype and fasting time are shown in Figs 2 and S1 respectively.
Fig 2. Mean serum triglyceride levels of ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 PTV heterozygotes at their self-reported fasting time in the Finrisk Study.
a a The figure shows the mean serum triglyceride level by ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 PTV carrier status with respect to self-reported fasting time. The number of ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 heterozygotes for each fasting time interval are reported below the fasting time legend. The height of the bars indicate means and the error bars 95% confidence intervals. The P values are for the two-sided Welch’s t-test of the natural logarithm of triglyceride levels between noncarriers and heterozygotes.
Secondary analyses
Lipid-associated protein-truncating variants and the risk of T2D and CAD
Given that the primary analysis suggested that ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 PTVs may reduce triglyceride levels, we tested these PTVs’ impact on type 2 diabetes (T2D), coronary artery disease (CAD) risk in 218,792 individuals from the FinnGen Study. The ANGPTL8 PTV was associated (two-tailed P < 4.1 × 10−3) with lower odds of CAD (OR = 0.53[0.37–0.76], P = 4.5 × 10−4). The ANGPTL4 PTV heterozygotes had 30% lower odds of T2D (OR = 0.70[0.60–0.81], P = 2.2 × 10−6). Finally, we tested if the four PTVs identified in our primary analysis were associated with available traditional non-lipid risk factors for CAD in the FinnGen Study (S11 Table). Briefly, ANGPTL4, ANGPTL8 and CETP PTVs were associated with lower risks of using statin medication. ANGPTL4 and LIPG PTV carriers in turn had lower risks of hypertension compared to noncarriers.
Finally, as in the primary analysis, we checked if our findings for the Finnish-enriched ANGPTL8 PTV (rs760351239-T) were congruent with the other ANGPTL8 PTV enriched in UK Biobank. In specific, we tested if the non-Finnish European-enriched ANGPTL8 PTV (rs145464906-T) was associated with T2D and CAD risk. Although rs145464906-T in the UK Biobank data alone was not significantly associated with the risk of T2D or CAD, a meta-analysis of the rs760351239-T and rs145464906-T PTVs strengthened both of these associations (Table 3).
Table 3. Association between protein-truncating variants and T2D and CAD risk in the FinnGen Study and UK Biobank.a.
| Locus and variant | Cohort | Type 2 diabetes; 29,166 cases in FinnGen and 18,945 cases in UK Biobank | Coronary artery disease; 23,363 cases in FinnGen and 20,023 cases in UK Biobank | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Allele frequencyb | ORc (95% CI) |
P | Allele frequencyb | ORc (95% CI) |
P | ||||
| Cases % | Controls % | Cases % | Controls % | ||||||
|
ANGPTL4 rs746226153-G |
FinnGen | 0.41 | 0.53 | 0.70 (0.60–0.81) |
2.2 × 10−6 | 0.51 | 0.51 | 0.94 (0.80–1.12) |
0.50 |
|
ANGPTL8 rs760351239-T |
FinnGen | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.67 (0.49–0.93) |
0.02 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.53 (0.37–0.76) |
4.5 × 10−4 |
|
ANGPTL8 rs145464906-T |
UK Biobank | 0.04 | 0.05 | 0.79 (0.48–1.30) |
0.35 | 0.03 | 0.05 | 0.73 (0.44–1.19) |
0.21 |
|
ANGPTL8 PTV meta-analysisd |
FinnGen and UK Biobank | 0.06 | 0.07 | 0.70 (0.54–0.92) |
0.01 | 0.05 | 0.07 | 0.59 (0.44–0.79) |
3.3 × 10−4 |
|
CETP rs751916721-T |
FinnGen | 0.08 | 0.11 | 0.66 (0.48–0.92) |
0.01 | 0.11 | 0.10 | 1.06 (0.73–1.53) |
0.76 |
|
LIPG rs200435657-A |
FinnGen | 0.13 | 0.13 | 0.87 (0.65–1.15) |
0.33 | 0.14 | 0.13 | 0.79 (0.58–1.09) |
0.15 |
Abbreviations: T2D, type 2 diabetes; CAD, coronary artery disease; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
a Shown in the table are the association statistics between the serum lipid-associated PTVs and type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease risk.
b The allele frequencies are reported in percent. The rs145464906-T allele frequencies in cases and controls were calculated in 343,687 unrelated individuals in UK Biobank and are based on PheCodes [38] 250.2 and 411.4 for type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease respectively.
c In the FinnGen data the odds ratios were calculated using SAIGE [31] saddle-point approximation-based score test after adjustment for age, sex, genotyping batch and ten principal components of ancestry. The odds ratios for the associations between the disease risks and PTVs in UK Biobank were obtained from Zhou et al. [31]
d The rs760351239-T and rs145464906-T PTVs present in FinnGen and UK Biobank genotype data respectively have been meta-analyzed
Tertiary analyses
Phenome-wide associations of protein-truncating variants in ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8
To evaluate a wide range of possible long-term health effects of the PTVs associated with both lipid levels and the risk of T2D or CAD, we tested the association between these PTVs and 2,683 curated disease endpoints. In addition to T2D risk, the ANGPTL4 PTV was phenome-wide significantly associated (two-tailed P < 1.8 × 10−5) with multiple T2D-related disease endpoints and comorbidities (S12 Table). The ANGPTL8 PTV was phenome-wide significantly associated with 48% lower odds of statin therapy (OR = 0.52[0.40–0.68], P = 1.7 × 10−6) (Table 4). See Online Tables 1 and 2 for the complete phenome-wide association statistics of the PTVs.
Table 4. Phenome-wide associations with the ANGPTL8 protein-truncating variant in the FinnGen Study.a.
| ANGPTL8 PTV rs760351239-T | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Phenotype | No. of cases | Allele frequencyb | ORc (95% CI) | P | |
| Cases % | Controls % | ||||
| Statin medication | 68,782 | 0.09 | 0.12 | 0.52 (0.40–0.68) | 1.7 × 10−6 |
Abbreviations: PTV, protein-truncating variant; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
a Shown in the table are the phenome-wide significant associations (P < 1.8 × 10−5) for the rs760351239-T allele in the FinnGen Study.
b The allele frequencies are reported in percent.
c Odds ratios were calculated using SAIGE [31] saddle-point approximation-based score test after adjustment for age, sex, genotyping batch and ten principal components of ancestry.
Discussion
In this study, we first presented associations between serum lipid levels and PTVs in four genes; ANGPTL4, ANGPTL8, CETP and LIPG. Especially the ANGPTL8 PTV carriers showed an overall improved serum lipid level profile compared to noncarriers: significantly lower triglyceride and higher HDL cholesterol levels but also suggestively lower LDL and total cholesterol levels. We then showed that carriers of PTVs in ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 had lower risk of T2D and CAD, respectively, than noncarriers. Finally, we showed that the PTVs in ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 were associated with lower risks of diabetes-related endpoints and statin therapy respectively.
Firstly, our study points to ANGPTL8 as a potential new therapeutic target for lowering triglyceride levels. This is interesting because while CETP, LIPG and ANGPTL4 are well-known lipid genes, a genome-wide significant association between a PTV in ANGPTL8 and triglyceride levels has not previously been reported in humans. ANGPTL8 is known to inhibit triglyceride-hydrolyzing lipoprotein lipase [26,27]. In our data, the association between ANGPTL8 PTV and lower triglyceride levels had the strongest effects soon after a meal in a post-prandial state, and after prolonged fasting. These findings are in line with animal studies which show that Angptl8 is secreted after feeding and has a very short half-life [23,24], and that hepatic very low-density lipoprotein (VLDL) secretion is decreased in Angptl8 knockout mice [28].
Our results also show that carriers of a Finnish-enriched ANGPTL8 PTV had 47% lower odds of CAD than noncarriers. This is in line with genetic evidence of triglycerides being a causal factor for CAD risk [29]. Examining another non-Finnish European-enriched ANGPTL8 PTV (rs145464906-T) in the UK Biobank data, we observed that also this PTV was genome-wide significantly associated with lower triglyceride levels. In addition, a meta-analysis of the ANGPTL8 PTVs in FinnGen and UK Biobank data increased the statistical significance of T2D and CAD risk associations observed in FinnGen data alone. On the whole, an improved lipid profile and lower risk of CAD in ANGPTL8 PTV carriers compared to noncarriers lends support to the efficacy of an antibody-based inhibition of ANGPTL8 in treating dyslipidemia and CAD.
Our results concerning the link between ANGPTL8 and T2D risk are less certain, but still contribute to the existing literature. A previous study by Clapham et al. tested for the association between the rs145464906-T variant and T2D risk but found no significant association [30]. In UK Biobank data, Zhou et al. reported an odds ratio of 0.79[31] which marks a non-zero effect, but a wide confidence interval (0.48–1.30), indicating insufficient statistical power. Lack of statistical power was also a challenge in our study: in the FinnGen data, the association between the Finnish-enriched ANGPTL8 PTV was nominally significant (P < 0.05) but not after multiple-testing correction. However, the statistical power to detect an association between T2D risk and ANGPTL8 protein-truncating variation was higher in the FinnGen data due to a considerably higher number of T2D cases (29,166) compared to both the previous study by Clapham et al. [30] (14,824 cases and 80,734 controls) and Zhou et al. [31] (18,945 cases 388,756 controls). To conclusively confirm the association between ANGPTL8 protein-truncating variation and T2D risk, a dataset with an even higher statistical power is needed.
Lastly, in addition to this main contribution on the potential benefits of the ANGPTL8 PTV, our study also found associations between the ANGPTL4 PTV and a lower risk of T2D, as well as multiple diabetes-related disease endpoints. An earlier report also found that ANGPTL4 PTV carriers had a lower risk of T2D than noncarriers [32]. Also, a low-frequency missense variant in ANGPTL4 has been associated with T2D and CAD risk [3,4].
Our study also has some limitations. Firstly, our study was observational in nature and consequently unable to directly reveal causal effects between genes and outcomes. The results of the tests for conditional variant association and credible sets do however increase the probability that the shortlisted PTVs indeed are causal variants underlying the observed association due to their statistical independence. The ANGPTL8 and LIPG PTVs formed their respective 95% credible sets alone and the ANGPTL4 and CETP in turn with only one other non-coding variant in high linkage disequilibrium with the respective PTV. Additional support for the robust lipid-level associations observed in this study comes from previous publications or replications using other high-confidence PTVs. Associations between lipid levels and the LIPG, CETP and ANGPTL4 PTVs using the same [4] or other high-confidence PTVs in the same gene [20,33] have been reported before. In the case of ANGPTL8, we replicated the associations between HDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels using the high-confidence PTV rs145464906-T present in the UK Biobank data. Despite a replication using the rs145464906-T, a formal replication of the Finnish-enriched rs760351239-T using the same variant is warranted. A formal replication using exactly the same variant was unfeasible due to a combination of rarity, regionality and Finnish population specificity of rs760351239-T. Nevertheless, to confirm the causality between the associated disease risks and the Finnish-enriched PTVs, our findings need to be studied using human cell lines. Secondly, while utilizing samples from the bottlenecked Finnish population offered us considerable boosts in statistical power to test Finnish-enriched variants compared to samples from non-bottlenecked populations, variants at lower frequencies in Finns than other populations lack this particular boost.
In summary, we identified PTVs in ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 that were associated with lower triglyceride levels and PTVs in CETP and LIPG that were associated with higher HDL cholesterol levels. The carriers of PTVs in ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 had lower risks of T2D and CAD respectively. These findings point to potential target genes for development of novel preventive medication against T2D and CAD and highlight the utility of bottleneck populations in search of associations between protein-truncating variation and biomarkers.
Methods
Ethics statement
All participants gave written informed study-specific consent. Patients and control subjects in the FinnGen Study provided informed consent for biobank research, based on the Finnish Biobank Act. Alternatively, older Finnish research cohorts, collected prior the start of FinnGen Study (August 2017), were collected based on study-specific consents and later transferred to the Finnish biobanks after approval by Fimea, the National Supervisory Authority for Welfare and Health. Recruitment protocols followed the biobank protocols approved by Fimea. The Coordinating Ethics Committee of the Hospital District of Helsinki and Uusimaa (HUS) approved the FinnGen Study protocol No. HUS/990/2017.
The FinnGen project is approved by Finnish Institute for Health and Welfare (THL), approval number THL/2031/6.02.00/2017, amendments THL/1101/5.05.00/2017, THL/341/6.02.00/2018, THL/2222/6.02.00/2018, THL/283/6.02.00/2019, THL/1721/5.05.00/2019), Digital and population data service agency VRK43431/2017-3, VRK/6909/2018-3, VRK/4415/2019-3, the Social Insurance Institution (KELA) KELA 58/522/2017, KELA 131/522/2018, KELA 70/522/2019, KELA 98/522/2019, and Statistics Finland TK-53-1041-17.
The Biobank Access Decisions for FinnGen Study samples and data utilized in FinnGen Data Freeze 5 include: THL Biobank BB2017_55, BB2017_111, BB2018_19, BB_2018_34, BB_2018_67, BB2018_71, BB2019_7, BB2019_8, BB2019_26, Finnish Red Cross Blood Service Biobank 7.12.2017, Helsinki Biobank HUS/359/2017, Auria Biobank AB17-5154, Biobank Borealis of Northern Finland_2017_1013, Biobank of Eastern Finland 1186/2018, Finnish Clinical Biobank Tampere MH0004, Central Finland Biobank 1–2017, and Terveystalo Biobank STB 2018001.
Overview of the study
We identified PTVs associated with both lipid levels and the risk of T2D or CAD, and then examined their associations with other disease endpoints. In our primary analysis, we studied 23,435 Finns to find PTVs associated with serum lipid levels. Using data from the FinnGen Study, which is based on 218,792 individuals, we then studied the association between these mutations and the risk of T2D and CAD. We refer to this as our secondary analysis. In our tertiary and final analysis, using FinnGen data, we assessed the long-term health impacts of the PTVs’ associations with T2D and CAD risk by screening them for modified risk of 2,683 diseases. An overview of our study is depicted in Fig 1.
Study populations
We used three different data sets for our study: the Finrisk Study cohorts, the FinnGen Study and UK Biobank. In total, the Finrisk Study dataset contained 23,435 chip-genotyped and imputed samples, selected randomly from the Finnish population in 1992, 1997, 2002, 2007 and 2012[22]. The first and second-degree relatives were limited in the set by limiting the identity by descent to 25% (the —rel-cutoff option set to 0.25 in PLINK). The baseline characteristics of the Finrisk Study participants are shown in S1 Table.
The FinnGen Study contains biobank data and national health registry data for 218,792 individuals. The health registry information of participants from the Finrisk and FinnGen Study was followed up until 31.12.2018. The details of the individual FinnGen cohorts are shown in S2 Table. All Finrisk and FinnGen Study participants were of Finnish descent. The genotyping and imputation data release of UK Biobank data was from 5th March 2018 and included 343,687 unrelated white British individuals.
Genotyping and quality control
The Finrisk Study samples were genotyped using the HumanCoreExome BeadChip, Human610-Quad BeadChip, Affymetrix6.0 and Infinium HumanOmniExpress (Illumina Inc., San Diego, CA, USA) chips and a Finnish-ancestry-specific imputation panel consisting of 2,690 deep-coverage (25-30x) whole-genome and 5,092 whole-exome sequences. In the primary analysis, the 1,377 PTVs (stop-gained, frameshift and essential splice-site mutations) were located in 1,209 genes and had a MAF between 0.1 and 5%. These PTVs in the Finrisk Study cohorts were imputed and had a IMPUTE2[34] genotype information score with a mean of 0.95 (standard deviation of 0.05) and a minimum of 0.75. The FinnGen Study samples were genotyped with various Illumina and a custom AxiomGT1 Affymetrix array (www.finngen.fi/en/researchers/genotyping). All the lipid-associated PTVs were directly genotyped in at least 70.0% of the FinnGen Study individuals with the AxiomGT1 Affymetrix array. The genotypes of the PTVs in our secondary and tertiary analyses that were not genotyped on chip were imputed using a genotype panel that consisted of 3,775 deep-coverage (25-30x) whole-genome sequenced individuals of Finnish ancestry. The PTVs in our secondary and tertiary analyses had IMPUTE2[34] genotype information scores above 0.93 in the FinnGen data. Detailed description of the genotyping methods, genotype imputation and quality-control procedures are described in S2 Text.
For the association analyses between lipid levels and the rs145464906-T ANGPTL8 PTV we included only white British individuals from UK Biobank and removed samples with excess heterozygosity or genotype missingness, sex chromosome aneuploidies and a mismatch between inferred and reported sex. Finally, related individuals were removed by limiting KING’s (http://people.virginia.edu/~wc9c/KING/) [35] kinship value to 0.0442.
Study outcomes
A blood sample and the self-reported fasting time since the previous meal at the time of blood sample collection of each Finrisk Study participant were collected during a clinical visit. The total cholesterol, HDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels were measured directly from serum or plasma and LDL cholesterol was either directly measured or estimated using the Friedewald formula [36]. In UK Biobank the blood lipid levels were measured from serum directly. LDL and total cholesterol levels of individuals with lipid-lowering therapy were divided by 0.7 and 0.8 [37] respectively.
Information on diagnoses in the FinnGen data were collected and confirmed by examining national healthcare registries and recorded using the International Classification of Diseases [ICD] revisions 8–10. Purchase information on prescription drugs since 1995 were obtained from the Finnish social insurance institution (KELA) reimbursement records and coded using the Anatomical Therapeutic Chemical [ATC] classification). All FinnGen Study participants’ healthcare registry information were followed up until 31.12 2017. Cancer diagnoses and causes of death were obtained from their respective national registries. The clinical expert groups of the FinnGen Study have defined disease events using ICD and ATC codes. For a complete list of the considered clinical endpoints and corresponding ICD and ATC codes, see the link: www.finngen.fi/en/researchers/clinical-endpoints. For the T2D and CAD statuses in UK Biobank participants we used PheCodes [38] 250.2 and 411.4 respectively.
Study design and statistical analyses
Primary analysis
In this analysis, we sought to identify associations between lipid levels and PTVs in the Finrisk Study. The lipid levels tested were plasma or serum levels of HDL cholesterol, LDL cholesterol, total cholesterol and logarithmically transformed triglycerides on a natural log scale. Our model was additive, and included age, age squared, sex, collection year, and ten principal components of ancestry as fixed-effects covariates. To correct for the effect of adiposity on triglyceride levels, we adjusted the triglyceride association tests for waist-to-hip ratio as well. We considered the genome-wide association significance threshold of a two-sided P value of less than 5.0 × 10−8 to be significant. Genetic association analyses were carried out using the PLINK [39], version v1.90b3.45 (www.cog-genomics.org/plink/1.9/), file format, Python, version 3.6 (www.python.org) and the statsmodels Python package, version 0.8.0 (www.statsmodels.org). In our scan, we only considered variants with a MAF 0.1–5% to account for adequate statistical power and the expected low frequency of high-impact alleles. To assess the statistical independence of the associations, we performed conditional analyses with previously associated variants [3–6] (Table 1 and S3–S6 Tables) and determined the 95% credible sets of variants in each gene locus with a 1 Mb window (S7–S10 Tables). The credible sets were determined using FINEMAP [40], version 1.4.3 (www.finemap.me).
Next, we carried out a post-hoc analysis to test the hypotheses that ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 PTVs are associated with triglycerides and LDL cholesterol levels as a function of fasting time. These hypotheses were based on animal studies that we reviewed after finding four PTVs associated with lipids in our genome-wide analysis. Firstly, we found studies that showed that in mice, Angptl4 and Angptl8 inhibit lipoprotein lipase (LPL) as a function of fasting time [23–25]. LPL inhibition is important because it is the mechanism by which several triglyceride-lowering drugs currently under development work [8,9,12]. If the association between triglyceride levels and ANGPTL8 and ANGPTL4 PTVs depends on fasting time, then fasting time dependent effects on triglyceride levels of these PTVs are very relevant for our study, which aims to assess the effect of these PTVs on hypertriglyceridemia risk.
Literature similarly suggested that, to determine whether ANGPTL8 is a viable drug target, it might also be important to test its association with LDL cholesterol levels as a function of fasting time. A mouse study found that ANGPTL8 modulates VLDL secretion [28]. Given our goal of testing the viability of ANGPTL8 as a drug target, the effect of ANGPTL8 on VLDL levels would be important to assess in humans because high VLDL levels are associated with a higher risk of CAD [41]. We could not directly test whether human ANGPTL8 PTV carriers had lower VLDL levels than noncarriers, so we instead tested the association between the ANGPTL8 PTV and levels of LDL cholesterol and triglycerides after fasting. Our rationale for this test was that fasting triglyceride and LDL cholesterol levels in particular can be considered a proxy for VLDL. This is due to the deficiency of chylomicron and chylomicron remnant particles in the bloodstream in a fasted state [42].
We examined the serum lipid level associations of other PTVs in the same genes as in our findings, using UK Biobank data. For this we used another rare non-Finnish European-enriched ANGPTL8 PTV (rs145464906-T). PTVs in ANGPTL4, CETP or LIPG were not present in the UK Biobank data and thus we were not able to analyze the lipid level associations of protein-truncating variation in these genes.
Secondary and tertiary analyses
In the secondary analyses, we examined associations between the risk of T2D and CAD, and the lipid-associated PTVs identified in the primary analysis. The associations were tested on data from the FinnGen Study and we regarded a two-sided P value below 4.1 × 10−3 (Bonferroni-corrected threshold for 12 tests) to be statistically significant.
As in the primary analysis, we checked if our findings for the Finnish-enriched ANGPTL8 PTV (rs760351239-T) were consistent with another rare ANGPTL8 PTV in UK Biobank. We tested if the non-Finnish European-enriched ANGPTL8 PTV (rs145464906-T) was associated with T2D and CAD risk. In addition, we conducted an inverse-variance-weighted meta-analysis of the rs760351239-T and rs145464906-T PTVs in the FinnGen and UK Biobank data.
In the tertiary analyses we examined the other health impacts of the PTVs associated with both serum lipid levels and the risk of T2D or CAD. We screened these PTVs broadly for modified risk of 2,683 diseases in the FinnGen data. We regarded a two-sided P value below 1.8 × 10−5 (Bonferroni-corrected threshold for 2,683 traits) to be statistically significant.
In both the secondary and tertiary analyses in the FinnGen data, the odds ratios for disease outcomes were estimated using SAIGE [31], version 0.35.8.8 (www.github.com/weizhouUMICH/SAIGE/releases/tag/0.35.8.8). Age, sex, genotyping batch and ten principal components of ancestry and the kinship matrix were included as fixed-effects covariates. See S1–S2 Data for the association statistics between disease risks and the ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 PTVs and the link: https://www.finngen.fi/en/researchers/clinical-endpoints for disease endpoint definitions in FinnGen. The details of computing the associations in the FinnGen data are described in the Supporting information. The T2D and CAD risk associations were also computed using SAIGE and were obtained from Zhou et al. [31].
Supporting information
People who contributed to the FinnGen Study are listed in the supplementary text.
(PDF)
A detailed description of the measures used in genotyping, quality control and statistical analyses of the Finrisk and FinnGen Study samples is included in this document.
(DOCX)
a Shown in the table are the baseline characteristics of the Finrisk Study participants used for finding the PTVs associated with blood lipid levels.
(XLSX)
a AxiomGT1 batches 9 and 11 had possibly contaminated samples identified by excessive relatedness (pihat linkage cutoff ≥ 0.1 for more than 30 samples). Therefore, in the QC step before imputation, an additional 83 and 50 samples were removed from batches 9 and 11 respectively.
(XLSX)
a This table shows the association statistics in Finrisk Study data of previously reported genome-wide associations in the CETP locus and the association statistics when the rs751916721-T variant is tested in a joint model with the earlier associations. Missing results are due to the rarity of a previously known variant in the Finrisk genotype data. b rs821840 is located in a low complexity region and was thus excluded from the Finrisk genotype data; hence the missing data.
(XLSX)
a This table shows the association statistics in Finrisk Study data of previously reported genome-wide associations in the LIPG locus and the association statistics when the rs200435657-A variant is tested in a joint model with the earlier associations. Missing results are due to the rarity of a previously known variant in the Finrisk genotype data.
(XLSX)
a This table shows the association statistics in Finrisk Study data of previously reported genome-wide associations in the ANGPTL4 locus and the association statistics when the rs746226153-G variant is tested in a joint model with the earlier associations. Missing results are due to the rarity of a previously known variant in the Finrisk Study genotype data.
(XLSX)
a This table shows the association statistics in Finrisk Study data of previously reported genome-wide associations in the ANGPTL8 locus and the association statistics when the rs760351239-T variant is tested in a joint model with the earlier associations. Missing results are due to the rarity of a previously known variant in the Finrisk Study genotype data.
(XLSX)
a Shown in the table are the variants with the highest posterior probability in each 95% credible set in the CETP locus. The columns cred1-cred5 and prob1-prob5 indicate these variants and their respective posterior probabilities in each credible set. b The noncoding rs566571297 and protein-truncating rs751916721 variants are in very high linkage disequilibrium (r2 = 0.99).
(XLSX)
a Shown in the table are the variants with the highest posterior probability in each 95% credible set in the LIPG locus. The columns cred1-cred4 and prob1-prob4 indicate these variants and their respective posterior probabilities in each credible set.
(XLSX)
a Shown in the table are the variants with the highest posterior probability in each 95% credible set in the ANGPTL4 locus. The columns cred1-cred2 and prob1-prob2 indicate these variants and their respective posterior probabilities in each credible set. b The noncoding rs919624228 and protein-truncating rs746226153 variants are in very high linkage disequilibrium (r2 = 0.97).
(XLSX)
a Shown in the table are the variants with the highest posterior probability in each 95% credible set in the ANGPTL8 locus. The columns cred1 and prob1 indicate the variant and its posterior probability in each credible set.
(XLSX)
a Shown in the table are the associations between the lipid-associated PTVs, and hypertension and statin medication in the FinnGen Study. b The allele frequencies are reported in percent. c The ORs were calculated using SAIGE saddle-point approximation-based score test after adjustment for age, sex, genotyping batch and ten principal components of ancestry in the FinnGen Study.
(XLSX)
a Abbreviations: PTV, protein-truncating variant; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval. a Shown in the table are the phenome-wide significant associations (P < 1.8 × 10−5) for the rs746226153-G allele in the FinnGen Study. b The allele frequencies are reported in percent. c Odds ratios were calculated using SAIGE saddle-point approximation-based score test after adjustment for age, sex, genotyping batch and ten principal components of ancestry.
(XLSX)
For a complete list of the considered clinical endpoints and the corresponding ICD and ATC codes in the fifth data release of the FinnGen data see the link: www.finngen.fi/en/researchers/clinical-endpoints.
(XLSX)
For a complete list of the considered clinical endpoints and the corresponding ICD and ATC codes in the fifth data release of the FinnGen data see the link: www.finngen.fi/en/researchers/clinical-endpoints.
(XLSX)
a The figure shows the mean plasma LDL cholesterol level by ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 PTV carrier status with respect to self-reported fasting time. The number of ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 heterozygotes for each fasting time interval are reported below the fasting time legend. The points indicate means and the error bars 95% confidence intervals. The P values are for the two-sided Welch’s t-test between triglyceride levels of noncarriers and heterozygotes. LDL cholesterol levels of individuals with lipid-lowering therapy were divided by 0.7.
(TIFF)
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Heidi Silvennoinen and Katri Silvennoinen for proofreading the manuscript, and Sari Kivikko, Huei-Yi Shen and Ulla Tuomainen for management assistance. Many thanks go to Kalle Pärn, Marita A. Isokallio, Javier Nunez Fontarnau and Priit Palta for the genotype imputation of Finrisk Study participants.
The members behind the FinnGen Study are listed in S1 Text. Following biobanks are acknowledged for collecting the FinnGen project samples: Auria Biobank (https://www.auria.fi/biopankki), THL Biobank (https://thl.fi/fi/web/thl-biopankki), Helsinki Biobank (https://www.terveyskyla.fi/helsinginbiopankki), Biobank Borealis of Northern Finland (https://www.oulu.fi/university/node/38474), Finnish Clinical Biobank Tampere (https://www.tays.fi/enUS/Research_and_development/Finnish_Clinical_Biobank_Tampere), Biobank of Eastern Finland (https://itasuomenbiopankki.fi), Central Finland Biobank (https://www.ksshp.fi/fi-FI/Potilaalle/Biopankki), Finnish Red Cross Blood Service Biobank (https://www.veripalvelu.fi/verenluovutus/biopankkitoiminta) and Terveystalo Biobank (https://www.terveystalo.com/fi/Yritystietoa/Terveystalo-Biopankki/Biopankki/). All Finnish Biobanks are members of BBMRI.fi infrastructure (www.bbmri.fi). We also thank study participants for their generous participation at THL Biobank, the National FINRISK Study (https://thl.fi/en/web/thlfi-en/research-and-expertwork/population-studies/the-national-finrisk-study) and UK Biobank (https://www.ukbiobank.ac.uk/). This research has been conducted using the UK Biobank Resource with the application number 22627.
Data Availability
The FinnGen data may be accessed through Finnish Biobanks’ FinnBB portal (www.finbb.fi) and THL Biobank data through THL Biobank (https://thl.fi/en/web/thl-biobank).
Funding Statement
The FinnGen project is funded by two grants from Business Finland (https://www.businessfinland.fi/) (HUS 4685/31/2016 and UH 4386/31/2016) and by the following industry partners: AbbVie Inc, AstraZeneca UK Ltd, Biogen MA Inc, Celgene Corporation, Celgene International II Sàrl, Genentech Inc, Merck Sharp & Dohme Corp, Pfizer Inc., GlaxoSmithKline, Sanofi, Maze Therapeutics Inc., Janssen Biotech Inc and Novartis AG. This work was supported by the Sigrid Jusélius Foundation (https://sigridjuselius.fi/en/) (to S.R., A.P.); University of Helsinki HiLIFE (https://www.helsinki.fi/en/helsinki-institute-of-life-science) Fellow grants 2017-2020 and HiLIFE Grand Challenge (to S.R.); Academy of Finland (https://www.aka.fi/en) Center of Excellence in Complex Disease Genetics (grant number 312062 and 336820 to S.R., 312074 and 336824 to A.P., 312075 and 336821 to M.J.D.); Academy of Finland (grant number 285380 to S.R., 128650 to A.P., 321356 to A.S.H.); Foundation and the Horizon 2020 Research and Innovation Programme (https://ec.europa.eu/programmes/horizon2020/en) (grant number 101016775 [INTERVENE] to S.R., grant number 667301 [COSYN] to A.P.); The Finnish Foundation for Cardiovascular Research (https://www.sydantutkimussaatio.fi/en/foundation) (to S.R., A.P., V.S.); Precision Health Scholars Award from the University of Michigan Medical School (https://precisionhealth.umich.edu/tools-resources/grants/u-m-precision-health-scholars-awards/2018-scholars-awards/) (to I.S.); Doctoral Programme in Population Health, University of Helsinki (https://www.helsinki.fi/en/research/doctoral-education/doctoral-schools-and-programmes/doctoral-school-in-health-sciences/doctoral-programme-in-population-health) (to P.H., T.K.); Emil Aaltonen Foundation (https://emilaaltonen.fi/) (to P.H.). The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
References
- 1.Kannel WB, McGee DL. Diabetes and cardiovascular disease. The Framingham study. JAMA. 1979;241(19):2035–8. Epub 1979/05/11. 10.1001/jama.241.19.2035 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Fruchart JC, Sacks F, Hermans MP, Assmann G, Brown WV, Ceska R, et al. The Residual Risk Reduction Initiative: a call to action to reduce residual vascular risk in patients with dyslipidemia. Am J Cardiol. 2008;102(10 Suppl):1K–34K. Epub 2008/12/17. 10.1016/S0002-9149(08)01833-X . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Klarin D, Damrauer SM, Cho K, Sun YV, Teslovich TM, Honerlaw J, et al. Genetics of blood lipids among ~300,000 multi-ethnic participants of the Million Veteran Program. Nat Genet. 2018;50(11):1514–23. Epub 2018/10/03. 10.1038/s41588-018-0222-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Liu DJ, Peloso GM, Yu H, Butterworth AS, Wang X, Mahajan A, et al. Exome-wide association study of plasma lipids in >300,000 individuals. Nat Genet. 2017;49(12):1758–66. Epub 2017/10/31. 10.1038/ng.3977 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Lu X, Peloso GM, Liu DJ, Wu Y, Zhang H, Zhou W, et al. Exome chip meta-analysis identifies novel loci and East Asian-specific coding variants that contribute to lipid levels and coronary artery disease. Nat Genet. 2017;49(12):1722–30. Epub 2017/10/31. 10.1038/ng.3978 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Willer CJ, Schmidt EM, Sengupta S, Peloso GM, Gustafsson S, Kanoni S, et al. Discovery and refinement of loci associated with lipid levels. Nat Genet. 2013;45(11):1274–83. Epub 2013/10/08. 10.1038/ng.2797 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Surakka I, Horikoshi M, Magi R, Sarin AP, Mahajan A, Lagou V, et al. The impact of low-frequency and rare variants on lipid levels. Nat Genet. 2015;47(6):589–97. Epub 2015/05/12. 10.1038/ng.3300 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Dewey FE, Gusarova V, Dunbar RL, O’Dushlaine C, Schurmann C, Gottesman O, et al. Genetic and Pharmacologic Inactivation of ANGPTL3 and Cardiovascular Disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(3):211–21. Epub 2017/05/26. 10.1056/NEJMoa1612790 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Dewey FE, Gusarova V, O’Dushlaine C, Gottesman O, Trejos J, Hunt C, et al. Inactivating Variants in ANGPTL4 and Risk of Coronary Artery Disease. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(12):1123–33. Epub 2016/03/05. 10.1056/NEJMoa1510926 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Gaudet D, Alexander VJ, Baker BF, Brisson D, Tremblay K, Singleton W, et al. Antisense Inhibition of Apolipoprotein C-III in Patients with Hypertriglyceridemia. N Engl J Med. 2015;373(5):438–47. Epub 2015/07/30. 10.1056/NEJMoa1400283 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Gaudet D, Brisson D, Tremblay K, Alexander VJ, Singleton W, Hughes SG, et al. Targeting APOC3 in the familial chylomicronemia syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2014;371(23):2200–6. Epub 2014/12/04. 10.1056/NEJMoa1400284 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Graham MJ, Lee RG, Brandt TA, Tai LJ, Fu W, Peralta R, et al. Cardiovascular and Metabolic Effects of ANGPTL3 Antisense Oligonucleotides. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(3):222–32. Epub 2017/05/26. 10.1056/NEJMoa1701329 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Group HTRC, Bowman L, Hopewell JC, Chen F, Wallendszus K, Stevens W, et al. Effects of Anacetrapib in Patients with Atherosclerotic Vascular Disease. N Engl J Med. 2017;377(13):1217–27. Epub 2017/08/30. 10.1056/NEJMoa1706444 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tsimikas S, Karwatowska-Prokopczuk E, Gouni-Berthold I, Tardif JC, Baum SJ, Steinhagen-Thiessen E, et al. Lipoprotein(a) Reduction in Persons with Cardiovascular Disease. N Engl J Med. 2020;382(3):244–55. Epub 2020/01/02. 10.1056/NEJMoa1905239 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Collins R, Reith C, Emberson J, Armitage J, Baigent C, Blackwell L, et al. Interpretation of the evidence for the efficacy and safety of statin therapy. Lancet. 2016;388(10059):2532–61. Epub 2016/09/13. 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31357-5 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Emdin CA, Khera AV, Natarajan P, Klarin D, Won HH, Peloso GM, et al. Phenotypic Characterization of Genetically Lowered Human Lipoprotein(a) Levels. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2016;68(25):2761–72. Epub 2016/12/23. 10.1016/j.jacc.2016.10.033 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chheda H, Palta P, Pirinen M, McCarthy S, Walter K, Koskinen S, et al. Whole-genome view of the consequences of a population bottleneck using 2926 genome sequences from Finland and United Kingdom. Eur J Hum Genet. 2017;25(4):477–84. Epub 2017/02/02. 10.1038/ejhg.2016.205 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Lim ET, Wurtz P, Havulinna AS, Palta P, Tukiainen T, Rehnstrom K, et al. Distribution and medical impact of loss-of-function variants in the Finnish founder population. PLoS Genet. 2014;10(7):e1004494. Epub 2014/08/01. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1004494 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Peloso GM, Auer PL, Bis JC, Voorman A, Morrison AC, Stitziel NO, et al. Association of low-frequency and rare coding-sequence variants with blood lipids and coronary heart disease in 56,000 whites and blacks. Am J Hum Genet. 2014;94(2):223–32. Epub 2014/02/11. 10.1016/j.ajhg.2014.01.009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Nomura A, Won HH, Khera AV, Takeuchi F, Ito K, McCarthy S, et al. Protein-Truncating Variants at the Cholesteryl Ester Transfer Protein Gene and Risk for Coronary Heart Disease. Circ Res. 2017;121(1):81–8. Epub 2017/05/17. 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311145 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Lek M, Karczewski KJ, Minikel EV, Samocha KE, Banks E, Fennell T, et al. Analysis of protein-coding genetic variation in 60,706 humans. Nature. 2016;536(7616):285–91. Epub 2016/08/19. 10.1038/nature19057 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Vartiainen E, Laatikainen T, Peltonen M, Juolevi A, Mannisto S, Sundvall J, et al. Thirty-five-year trends in cardiovascular risk factors in Finland. Int J Epidemiol. 2010;39(2):504–18. Epub 2009/12/05. 10.1093/ije/dyp330 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Dang F, Wu R, Wang P, Wu Y, Azam MS, Xu Q, et al. Fasting and Feeding Signals Control the Oscillatory Expression of Angptl8 to Modulate Lipid Metabolism. Sci Rep. 2016;6:36926. Epub 2016/11/16. 10.1038/srep36926 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Fu Z, Abou-Samra AB, Zhang R. A lipasin/Angptl8 monoclonal antibody lowers mouse serum triglycerides involving increased postprandial activity of the cardiac lipoprotein lipase. Sci Rep. 2015;5:18502. Epub 2015/12/22. 10.1038/srep18502 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Kersten S, Mandard S, Tan NS, Escher P, Metzger D, Chambon P, et al. Characterization of the fasting-induced adipose factor FIAF, a novel peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor target gene. J Biol Chem. 2000;275(37):28488–93. Epub 2000/06/23. 10.1074/jbc.M004029200 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Chi X, Britt EC, Shows HW, Hjelmaas AJ, Shetty SK, Cushing EM, et al. ANGPTL8 promotes the ability of ANGPTL3 to bind and inhibit lipoprotein lipase. Mol Metab. 2017;6(10):1137–49. Epub 2017/10/17. 10.1016/j.molmet.2017.06.014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Haller JF, Mintah IJ, Shihanian LM, Stevis P, Buckler D, Alexa-Braun CA, et al. ANGPTL8 requires ANGPTL3 to inhibit lipoprotein lipase and plasma triglyceride clearance. J Lipid Res. 2017;58(6):1166–73. Epub 2017/04/18. 10.1194/jlr.M075689 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wang Y, Quagliarini F, Gusarova V, Gromada J, Valenzuela DM, Cohen JC, et al. Mice lacking ANGPTL8 (Betatrophin) manifest disrupted triglyceride metabolism without impaired glucose homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110(40):16109–14. Epub 2013/09/18. 10.1073/pnas.1315292110 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Do R, Willer CJ, Schmidt EM, Sengupta S, Gao C, Peloso GM, et al. Common variants associated with plasma triglycerides and risk for coronary artery disease. Nat Genet. 2013;45(11):1345–52. Epub 2013/10/08. 10.1038/ng.2795 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Clapham KR, Chu AY, Wessel J, Natarajan P, Flannick J, Rivas MA, et al. A null mutation in ANGPTL8 does not associate with either plasma glucose or type 2 diabetes in humans. BMC Endocr Disord. 2016;16:7. Epub 2016/01/30. 10.1186/s12902-016-0088-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Zhou W, Nielsen JB, Fritsche LG, Dey R, Gabrielsen ME, Wolford BN, et al. Efficiently controlling for case-control imbalance and sample relatedness in large-scale genetic association studies. Nat Genet. 2018;50(9):1335–41. Epub 2018/08/15. 10.1038/s41588-018-0184-y [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Gusarova V, O’Dushlaine C, Teslovich TM, Benotti PN, Mirshahi T, Gottesman O, et al. Genetic inactivation of ANGPTL4 improves glucose homeostasis and is associated with reduced risk of diabetes. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):2252. Epub 2018/06/15. 10.1038/s41467-018-04611-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Myocardial Infarction G, Investigators CAEC, Stitziel NO, Stirrups KE, Masca NG, Erdmann J, et al. Coding Variation in ANGPTL4, LPL, and SVEP1 and the Risk of Coronary Disease. N Engl J Med. 2016;374(12):1134–44. Epub 2016/03/05. 10.1056/NEJMoa1507652 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Howie BN, Donnelly P, Marchini J. A flexible and accurate genotype imputation method for the next generation of genome-wide association studies. PLoS Genet. 2009;5(6):e1000529. Epub 2009/06/23. 10.1371/journal.pgen.1000529 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Manichaikul A, Mychaleckyj JC, Rich SS, Daly K, Sale M, Chen WM. Robust relationship inference in genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics. 2010;26(22):2867–73. Epub 2010/10/12. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btq559 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Friedewald WT, Levy RI, Fredrickson DS. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin Chem. 1972;18(6):499–502. Epub 1972/06/01. . [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Cholesterol Treatment Trialists C, Baigent C, Blackwell L, Emberson J, Holland LE, Reith C, et al. Efficacy and safety of more intensive lowering of LDL cholesterol: a meta-analysis of data from 170,000 participants in 26 randomised trials. Lancet. 2010;376(9753):1670–81. Epub 2010/11/12. 10.1016/S0140-6736(10)61350-5 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Denny JC, Bastarache L, Ritchie MD, Carroll RJ, Zink R, Mosley JD, et al. Systematic comparison of phenome-wide association study of electronic medical record data and genome-wide association study data. Nat Biotechnol. 2013;31(12):1102–10. Epub 2013/11/26. 10.1038/nbt.2749 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Chang CC, Chow CC, Tellier LC, Vattikuti S, Purcell SM, Lee JJ. Second-generation PLINK: rising to the challenge of larger and richer datasets. Gigascience. 2015;4:7. Epub 2015/02/28. 10.1186/s13742-015-0047-8 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Benner C, Spencer CC, Havulinna AS, Salomaa V, Ripatti S, Pirinen M. FINEMAP: efficient variable selection using summary data from genome-wide association studies. Bioinformatics. 2016;32(10):1493–501. Epub 2016/01/17. 10.1093/bioinformatics/btw018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Ren J, Grundy SM, Liu J, Wang W, Wang M, Sun J, et al. Long-term coronary heart disease risk associated with very-low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in Chinese: the results of a 15-Year Chinese Multi-Provincial Cohort Study (CMCS). Atherosclerosis. 2010;211(1):327–32. Epub 2010/03/13. 10.1016/j.atherosclerosis.2010.02.020 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Nordestgaard BG. A Test in Context: Lipid Profile, Fasting Versus Nonfasting. J Am Coll Cardiol. 2017;70(13):1637–46. Epub 2017/09/25. 10.1016/j.jacc.2017.08.006 . [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
People who contributed to the FinnGen Study are listed in the supplementary text.
(PDF)
A detailed description of the measures used in genotyping, quality control and statistical analyses of the Finrisk and FinnGen Study samples is included in this document.
(DOCX)
a Shown in the table are the baseline characteristics of the Finrisk Study participants used for finding the PTVs associated with blood lipid levels.
(XLSX)
a AxiomGT1 batches 9 and 11 had possibly contaminated samples identified by excessive relatedness (pihat linkage cutoff ≥ 0.1 for more than 30 samples). Therefore, in the QC step before imputation, an additional 83 and 50 samples were removed from batches 9 and 11 respectively.
(XLSX)
a This table shows the association statistics in Finrisk Study data of previously reported genome-wide associations in the CETP locus and the association statistics when the rs751916721-T variant is tested in a joint model with the earlier associations. Missing results are due to the rarity of a previously known variant in the Finrisk genotype data. b rs821840 is located in a low complexity region and was thus excluded from the Finrisk genotype data; hence the missing data.
(XLSX)
a This table shows the association statistics in Finrisk Study data of previously reported genome-wide associations in the LIPG locus and the association statistics when the rs200435657-A variant is tested in a joint model with the earlier associations. Missing results are due to the rarity of a previously known variant in the Finrisk genotype data.
(XLSX)
a This table shows the association statistics in Finrisk Study data of previously reported genome-wide associations in the ANGPTL4 locus and the association statistics when the rs746226153-G variant is tested in a joint model with the earlier associations. Missing results are due to the rarity of a previously known variant in the Finrisk Study genotype data.
(XLSX)
a This table shows the association statistics in Finrisk Study data of previously reported genome-wide associations in the ANGPTL8 locus and the association statistics when the rs760351239-T variant is tested in a joint model with the earlier associations. Missing results are due to the rarity of a previously known variant in the Finrisk Study genotype data.
(XLSX)
a Shown in the table are the variants with the highest posterior probability in each 95% credible set in the CETP locus. The columns cred1-cred5 and prob1-prob5 indicate these variants and their respective posterior probabilities in each credible set. b The noncoding rs566571297 and protein-truncating rs751916721 variants are in very high linkage disequilibrium (r2 = 0.99).
(XLSX)
a Shown in the table are the variants with the highest posterior probability in each 95% credible set in the LIPG locus. The columns cred1-cred4 and prob1-prob4 indicate these variants and their respective posterior probabilities in each credible set.
(XLSX)
a Shown in the table are the variants with the highest posterior probability in each 95% credible set in the ANGPTL4 locus. The columns cred1-cred2 and prob1-prob2 indicate these variants and their respective posterior probabilities in each credible set. b The noncoding rs919624228 and protein-truncating rs746226153 variants are in very high linkage disequilibrium (r2 = 0.97).
(XLSX)
a Shown in the table are the variants with the highest posterior probability in each 95% credible set in the ANGPTL8 locus. The columns cred1 and prob1 indicate the variant and its posterior probability in each credible set.
(XLSX)
a Shown in the table are the associations between the lipid-associated PTVs, and hypertension and statin medication in the FinnGen Study. b The allele frequencies are reported in percent. c The ORs were calculated using SAIGE saddle-point approximation-based score test after adjustment for age, sex, genotyping batch and ten principal components of ancestry in the FinnGen Study.
(XLSX)
a Abbreviations: PTV, protein-truncating variant; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval. a Shown in the table are the phenome-wide significant associations (P < 1.8 × 10−5) for the rs746226153-G allele in the FinnGen Study. b The allele frequencies are reported in percent. c Odds ratios were calculated using SAIGE saddle-point approximation-based score test after adjustment for age, sex, genotyping batch and ten principal components of ancestry.
(XLSX)
For a complete list of the considered clinical endpoints and the corresponding ICD and ATC codes in the fifth data release of the FinnGen data see the link: www.finngen.fi/en/researchers/clinical-endpoints.
(XLSX)
For a complete list of the considered clinical endpoints and the corresponding ICD and ATC codes in the fifth data release of the FinnGen data see the link: www.finngen.fi/en/researchers/clinical-endpoints.
(XLSX)
a The figure shows the mean plasma LDL cholesterol level by ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 PTV carrier status with respect to self-reported fasting time. The number of ANGPTL4 and ANGPTL8 heterozygotes for each fasting time interval are reported below the fasting time legend. The points indicate means and the error bars 95% confidence intervals. The P values are for the two-sided Welch’s t-test between triglyceride levels of noncarriers and heterozygotes. LDL cholesterol levels of individuals with lipid-lowering therapy were divided by 0.7.
(TIFF)
Data Availability Statement
The FinnGen data may be accessed through Finnish Biobanks’ FinnBB portal (www.finbb.fi) and THL Biobank data through THL Biobank (https://thl.fi/en/web/thl-biobank).