Abstract
Background:
Ruxolitinib is a JAK2/JAK1 inhibitor which blocks inflammatory JAK-STAT signaling pathway. Ruxolitinib has been demonstrated to be effective in the treatment of steroid-resistant acute Graft vs Host Disease (GvHD). Ruxolitinib’s effect on inflammatory cells of hematopoietic origin is known. However, its effect on non-hematopoietic cell types with immune modulating and antigen presenting cell competency plausibly involved in pathogenesis of GvHD has not been explored.
Objective(s):
Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (MSCs) are CD45- non-hematopoietic cells of the bone marrow with immune modulatory functions in vivo. MSC’s immunobiology largely depends on their responsiveness to IFNγ. We aimed to define the effect of Ruxolitinib on the immunobiology of MSCs that are modulated by IFNγ.
Study Design:
Human bone marrow derived MSCs, peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMCs) and primary bone marrow aspirates were analyzed for their sensitivity to Ruxolitinib mediated blocking of IFNγ induced STAT-1 phosphorylation and downstream effector molecules, utilizing western blot, flow cytometry, secretome analysis and phosflow techniques.
Results:
IFNγ induced cytostatic effects on MSCs are reversed by Ruxolitinib. Ruxolitinib inhibits IFNγ and secretome of activated peripheral PBMC induced STAT-1 phosphorylation on human bone marrow derived MSCs. In addition, Ruxolitinib inhibits IFNγ induced pro-GVHD pathways on MSCs which includes HLAABC(MHCI), HLADR(MHCII), CX3CL1 and CCL2. IFNγ induced immunosuppressive molecules IDO and PDL-1 were also inhibited by Ruxolitinib on MSCs. Comparative analysis with PBMCs has demonstrated that MSCs are as equal as to HLADR+ PBMCs populations in responding to Ruxolitinib mediated inhibition of IFNγ induced STAT-1 phosphorylation. Ex vivo analysis of human marrow aspirates has demonstrated that Ruxolitinib blocks IFNγ induced STAT-1 phosphorylation in CD45+/−HLADR+/− populations at different levels which is depending on their sensitivity to IFNγ responsiveness.
Conclusion:
These results inform the hypothesis that Ruxolitinib’s immune modulatory effects in vivo may pharmacologically involve marrow and tissue resident MSCs. Ruxolitinib affect the immunobiology of MSCs equivalent to professional HLADR+ APCs which collectively mitigate GvHD.
Keywords: Mesenchymal Stomal/Stem Cells, Ruxolitinib, interferon-γ, HLADR, Bone Marrow, STAT-1 Phosphorylation
Introduction
Ruxolitinib is a small molecule inhibitor of JAK2/JAK1 kinases1. Ruxolitinib was initially approved for the treatment of ABL-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms, including polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia and primary myelofibrosis that are caused by the aberrant activation of the JAK-STAT pathway in hematopoietic cells2, 3. Ruxolitinib is also being clinically investigated for treatment of non-myeloproliferative disorders including irritable bowel disease, rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic skin lesions and Graft versus Host Disease (GVHD)4, 5. These autoimmune diseases are characterized by imbalanced regulation of T-cells with increased plasma levels of interleukins and IFNγ 6, 7. Although ruxolitinib’s mode of action and impact on CD45+ lymphoid and myeloid cells have been studied, its effects on CD45- non-hematopoietic immune modulating cells with antigen presenting cell (APC) competency are largely unexplored. Indeed, it has been suggested that CD45- non-hematopoietic host cells with APC functionalities may be contributors to the onset and pathogenesis of GVHD8. Culture-adapted human mesenchymal stromal cells (MSC) - non-hematopoietic, immunomodulatory cells with conditional APC competency 9, 10 are present in many tissues including bone marrow and adipose tissue 11. Pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IFNγ activate JAK/STAT signaling pathways in MSCs leading to the upregulation of immunosuppressive proteins such as Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase (IDO) and Programmed Death Ligand 1 (PDL-1) as well as upregulation of MHC class I(HLAABC) and Class II (HLADR). Our aim was to test the ability of Ruxolitinib to inhibit IFNγ induced immune licensing of MSCs and provide a biologically plausible rational for non-hematopoietic cellular responders possibly involved in clinical immune modulation and pathogenesis of GVHD.
Materials and Methods
Human Bone marrow MSCs Isolation, Culture and stimulation
Bone marrow mononuclear cells (MNCs) were obtained from the bone marrow aspirates of donors in accordance to the Institutional Review Board of Memorial Health Medical Center, Savannah. Harvested bone marrow was separated by Ficoll density gradient to obtain MNCs. MNCs were either cryopreserved or plated at 200,000 cell/cm2 density on α-MEM culture medium containing 20% FCS and 100 IU/ml penicillin/streptomycin. Non-adherent cells were removed from culture after 3 days and MSCs were allowed to expand for an additional 7 days. All assays were performed using MSCs between passage 3 and 7. MSC identity was confirmed as described earlier (CD45-CD105+CD44+CD90+CD73+) and their responsiveness to IFNg and STAT-1 phosphorylation was also described earlier12. Recombinant human IFNγ (PeProtech, cat. 300–02) was used at 10–20ng/ml concentration. Cells were co-treated with Ruxolitinib (TargetMol, cat.T1829) at concentrations ranging from 1nM-10μM for 48hrs. In the case of phosflow analysis, short term stimulation was performed. For MTT assays, MSCs were seeded on to 96-well plates at a density of 3000 cells per well. Cells were cultured with either medium containing human platelet lysate or fetal calf serum and stimulated with IFNγ 20 ng/ml. MTT assays were performed at the indicated time points by incubating Thiazolyl Blue Tetrazolium Bromide (Sigma, USA) for 5 hours. After 5 hours, formazan crystals were dissolved in DMSO and optical density was measured at 550 nm with 620 nm as reference.
Western Blot Protein Analysis and flow cytometry
Western blots were performed using standard reducing 10% SDS-PAGE protocol with following antibodies from Cell Signaling Technology- pY701STAT1, STAT1, IDO and β-actin. BD FACS Aria flow cytometer was used to analyze the expression of MHCI, MHC, IDO and PDL1 using standard surface staining protocol. Results were analyzed in Flow Jo software.
Phosflow analysis
Culture expanded MSCs or bone marrow mononuclear cells (MNCs) or Peripheral blood Mononuclear Cells (PBMCs) were subjected to phosflow analysis using stimulus either IFNγ or activated PBMC supernatants. Supernatants from Staphylococcal enterotoxin B (SEB) or anti-CD3, anti-CD28 antibodies (Biolegend, USA) activated PBMCs were collected after 4 days and stored at −80°C. Stored supernatants were thawed and centrifuged at 500×g for 3 min to eliminate cell debris and equilibrated at 37°C for an hour. These supernatants or IFNγ (20ng/ml) were used for the stimulation of the MSCs or MNCs for 15 minutes. Prior to stimulation, cells were treated with the appropriate concentrations of Ruxolitinib for 10 minutes. Subsequently cells were fixed with BD cytofix buffer for 10 minutes and were permeabilized with BD Phosflow Perm Buffer for 30 minutes and then were subjected to flow cytometry with antibodies Alexa Fluor® 647 Anti-Stat1 (pY701), PE-HLADR and FITC-CD45 (BD Biosciences, San Jose, CA). Stained cells were acquired in BD FACS Aria. Results were analyzed in Flow Jo software to obtain Mean Fluorescent Intensity (MFI).
Luminex analysis
Supernatants from human MSCs cultured with IFNγ and Ruxolitinib was collected after 4 days and stored at −80°C. Stored supernatants were thawed and centrifuged at 500×g for 3 min to eliminate cell debris and analyzed by magnetic bead based multiplex Luminex assays for CCL2, VEGF and CX3CL1 (R&D Biosystems) according to the manufacturer’s instructions using Luminex® xMAP® (multi-analyte profiling) technology. Results were plotted as picogram/milliliter.
Statistical Analysis
All statistically analyzed data is represented as mean ± SD. Differences between groups were analyzed by Two-Way ANOVA multiple comparison tests and unpaired t tests using GraphPad Prism 7. Statistically significant differences were represented as *P ≤0.05, ** P ≤0.01, *** P≤0.001, ****P<0.0001. Correlation between Ruxolitinib inhibition and IFNγ responsiveness were determined by linear regression analyses to obtain R2 and p values using GraphPad Prism 7.0 software.
Results
Ruxolitinib inhibits JAK/STAT1 pathway mediated IDO expression in IFNγ stimulated MSCs
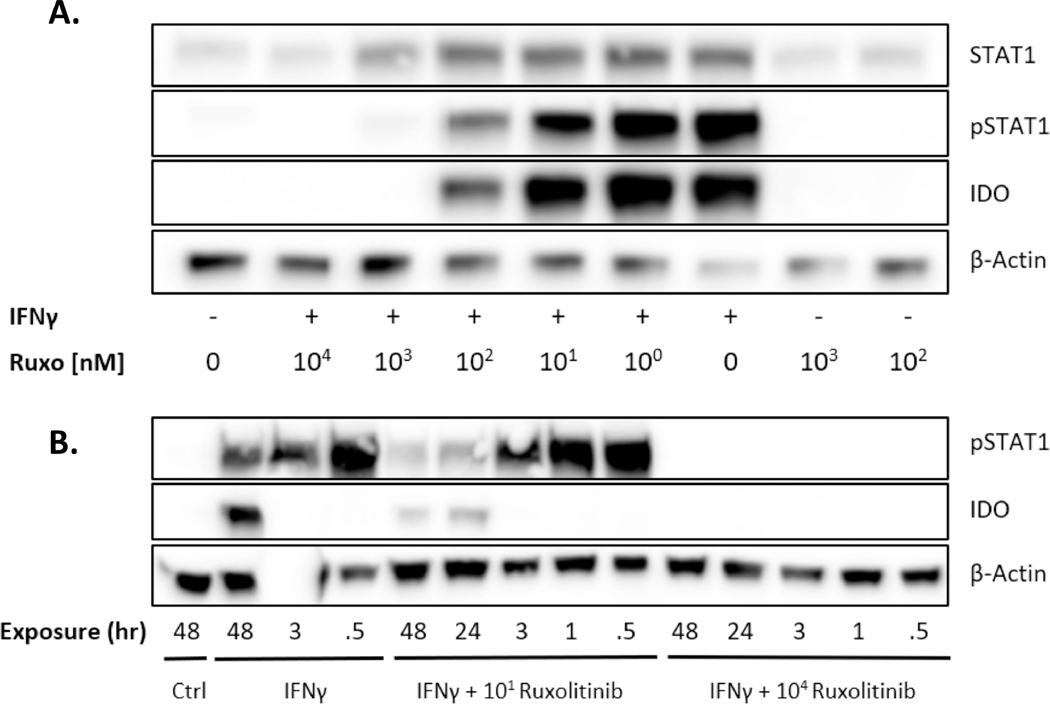
IFNγ activates STAT1 phosphorylation (pSTAT1) at Tyr701 on MSCs 13. MSCs are known to upregulate the production of immunosuppressive enzyme Indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase (IDO) by IFNγ 14. We treated human bone marrow MSCs with IFNγ and varying concentrations of Ruxolitinib. MSCs treated with IFNγ induced STAT1 phosphorylation within 30 minutes and IDO is detectable within 48hrs post treatment, pointing towards a transcriptional regulation (Fig 1A, B). We also observed that 10nM Ruxolitinib blunted pSTAT1 and IDO upregulation over time and that 10000nM abolished pSTAT1 and IDO activation at all time points (Fig 1A, B).
Figure 1. Ruxolitinib inhibits IFN γ mediated expression of IDO protein via JAK-STAT1 pathway.
MSCs were treated with IFNγ (20ng/mL) and/or Ruxolitinib (at concentrations shown) (A) Cells were collected post 48 hrs. of treatment to perform western blot. Cells were probed with antibodies against pSTAT1, total STAT1 and IDO. Beta Actin was used as a loading control. (B) Cells were treated with IFNγ (20ng/mL) with two representative concentrations of Ruxolitinib (10nM and 10 μM). Lysates were collected at various time points to determine the ruxolitinib’s kinetics on JAK/STAT inhibition. Similar results were obtained in a repeat experiment.
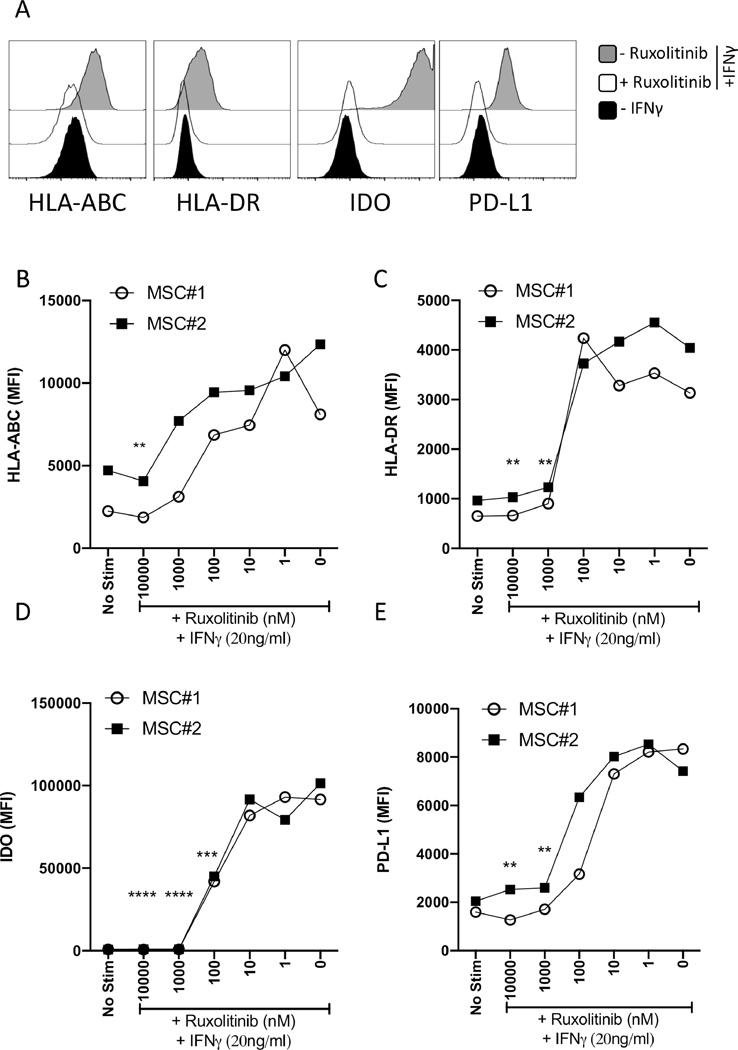
Ruxolitinib blocks the upregulation of HLA-ABC, HLA-DR, PDL-1 and IDO on MSCs at comparable levels.
Our published results have demonstrated that IFNγ upregulates HLAABC (MHC-I), HLADR (MHC-II), B7-H1 (PD-L1), and IDO molecules on MSCs 14. Evaluation of IFNγ mediated regulation of these effector molecules serve as the surrogate assay measure of MSC’s functionality. Since all of these effector molecules are at the downstream of IFNγ mediated JAK-STAT signaling, we investigated the effect of Ruxolitinib on their regulation. Our results with MSC populations from independent donors have demonstrated that Ruxolitinib blocks the upregulation of HLA-ABC (Fig. 2A, B), HLA-DR (Fig. 2A, C), IDO (Fig. 2A, D) and PD-L1 (Fig. 2A, E).
Figure 2. IFNγ induced HLA-ABC, HLA-DR, PDL-1 and IDO expression in MSCs are suppressed by Ruxolitinib.
MSCs were treated with contemporaneous Ruxolitinib and IFNγ (20ng/mL) for 48 hours. Cells were stained for flow cytometry analysis using antibodies against MHC I (HLA ABC), MHC II (HLA-DR), IDO and PDL1. (A) Representative histograms are shown. Grey and white histograms represent – and + Ruxolitinib in the presence of IFNγ. Black histogram represents unstimulated control. Dose dependent effect of Ruxolitinib on the mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) of (B) MHC I (HLA ABC), (C) MHC II (HLA-DR), (D) IDO and (E) PDL1 is shown on two independent MSC donors. Similar results were obtained in a repeat experiment. Two-Way ANOVA multiple comparison test was performed between 0 nM and other Ruxolitinib concentrations. **, ***, **** represents P ≤ 0.01, P ≤ 0.001 and P ≤ 0.0001 respectively. Cumulative statistical significance with both MSC donors is shown.
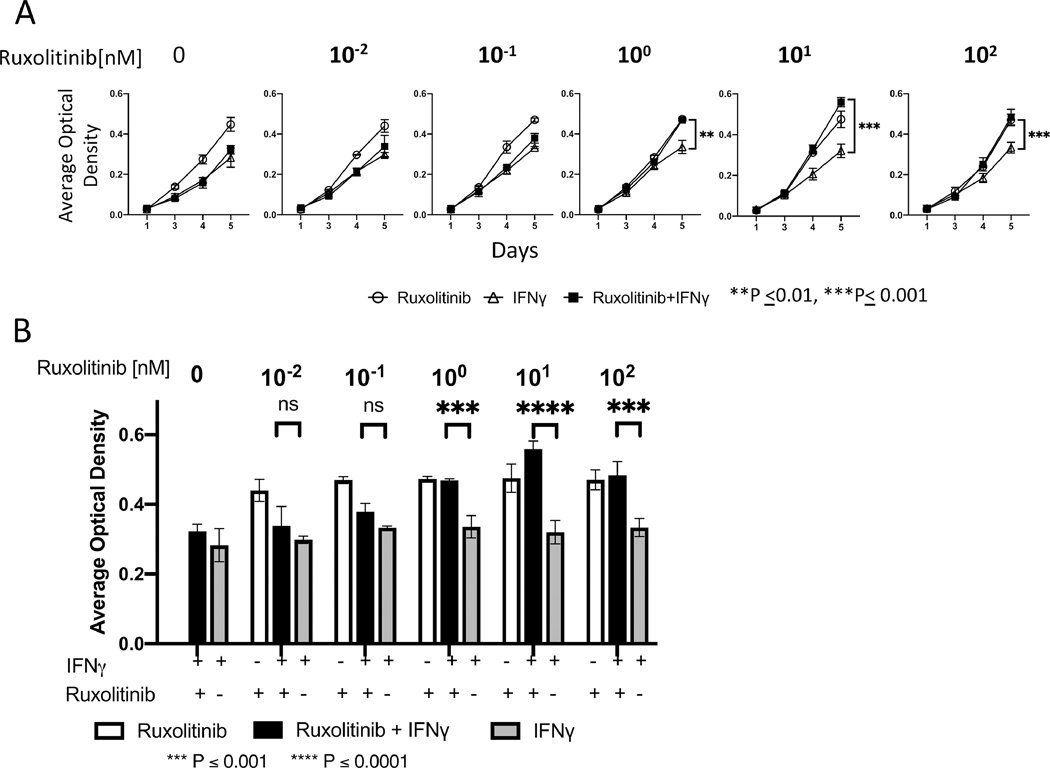
Cytostatic effects of IFNγ on MSCs are reversed by Ruxolitinib treatment
IFNγ regulates the proliferation and differentiation of MSCs via activation of IDO and thus causes cytostatic effect15. Using cell replication as physiological endpoint, we examined effect of Ruxolitinib on IFNγ mediated cytostatic effect on MSCs. We performed MTT assays longitudinally (days 1,3, 4 and 5) on MSCs treated in the presence and absence of IFNγ and varying concentrations of Ruxolitinib (Fig. 3A). We observed that IFNγ causes cytostatic effect on MSC proliferation (Fig. 3A). Ruxolitinib reverses IFNγ mediated cytostatic effect on MSCs (Fig. 3A, B). Statistical significance in reversing IFNγ mediated cytostatic effect was observed with the concentrations of 1nM, 10nM and 100nM of Ruxolitinib (Fig. 3A, B).
Figure 3. Cytostatic effects of IFNy on MSCs are reversed by Ruxolitinib treatment.
MSCs (3000 cells/ well) were seeded in 96 well plate and treated with IFNγ (20 ng/mL) and/or different concentrations of Ruxolitinib for up to 5 days. MTT dye was added 5 hours prior to measuring optical density at 550 nm with 620 nm as reference in a plate reader. Observations were made at the same time each day for 5 days. (A) The effect of different concentrations of Ruxolitinib over 5-day period is shown. (B) Day 5 data is shown in a bar graph format to specific impact of different Ruxolitinib concentration. Data shown are means ±SD of three independent experiments. Two-Way ANOVA multiple comparison test was performed between IFNγ and IFNγ +Ruxolitinib. **, ***, **** represents P ≤ 0.01, P ≤ 0.001 and P ≤ 0.0001 respectively.
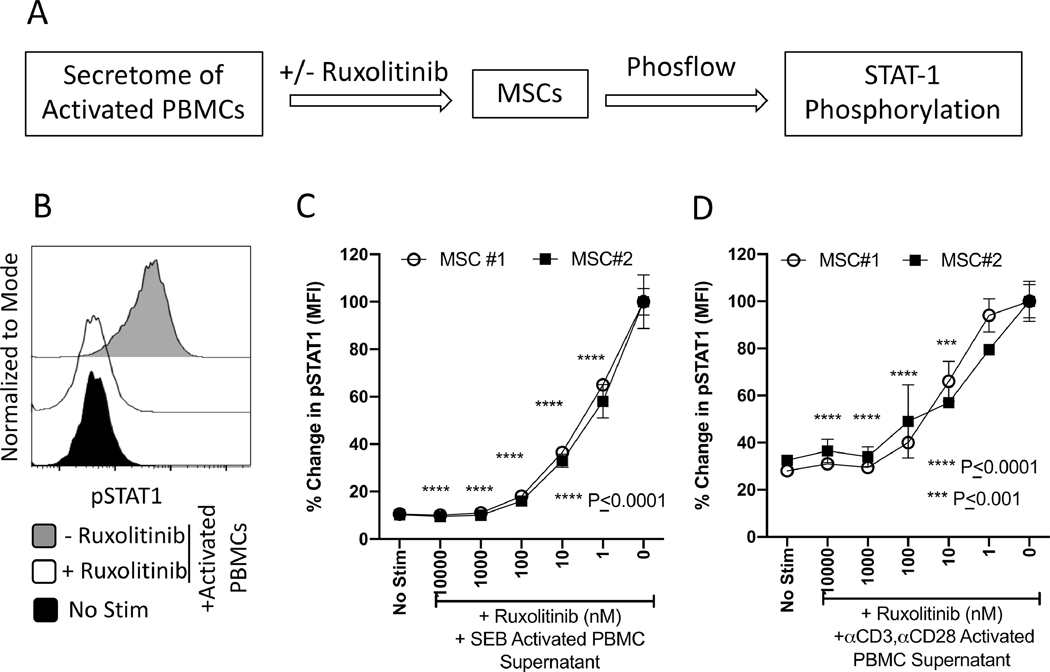
Ruxolitinib inhibits PBMC secretome induced STAT-1 phosphorylation on MSCs
Activated T cells not only secrete IFNγ but also other inflammatory cytokines and chemokines which collectively amplify inflammatory cascade loop at the target visceral tissue and marrow microenvironment. Effect of Ruxolitinib on this process of inflammatory T cell mediated activation of MSCs is unknown. To define these, we have utilized an in vitro model of MSC and PBMC interaction. In this model, PBMCs were stimulated with either Staphylococcus Enterotoxin B (SEB) or anti-CD3, anti-CD28 antibodies. Three days later, total secretome was collected. Total secretome of activated PBMCs was then used for the stimulation of MSCs in the presence of various concentrations of Ruxolitinib (Fig. 4A). Phosflow analysis was performed to determine the phosphorylation levels of STAT-1 on MSCs (Fig 4B). Our results with independent MSC donors have demonstrated that Ruxolitinib blocks the phosphorylation of STAT-1 on MSCs that are induced with the secretome of activated PBMCs (Fig. 4C, D).
Figure 4. Ruxolitinib blocks PBMC secretome induced STAT-1 phosphorylation on MSCs.
(A) PBMCs were activated with SEB or anti-CD3, anti-CD28 antibodies and four days later supernatants were collected. Collected supernatants were used for the stimulation of MSCs in the presence of varying concentrations of Ruxolitinib. Phosflow analysis was performed on MSC populations for pSTAT1 expression. (B) Representative histogram is shown for pSTAT1 expression. Grey and white histograms represent – and + Ruxolitinib in the presence of IFNγ. Black histogram represents unstimulated control. Dose dependent effect of Ruxolitinib on the mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) of pSTAT1 is shown on two independent MSC donors stimulated with the secretome of (C) SEB and (D) anti-CD3, ant-CD28 activated PBMCs. Percentage MFI change is calculated based on pSTAT1 expression in the conditions of absence and presence of Ruxolitinib and PBMC secretome, respectively. Assays were done in duplicates. Average and Standard deviation is shown. Two-Way ANOVA multiple comparison test was performed between 0 nM and other Ruxolitinib concentrations. ***, **** represents P ≤ 0.001 and P ≤ 0.0001 respectively. Cumulative statistical significance with both MSC donors is shown.
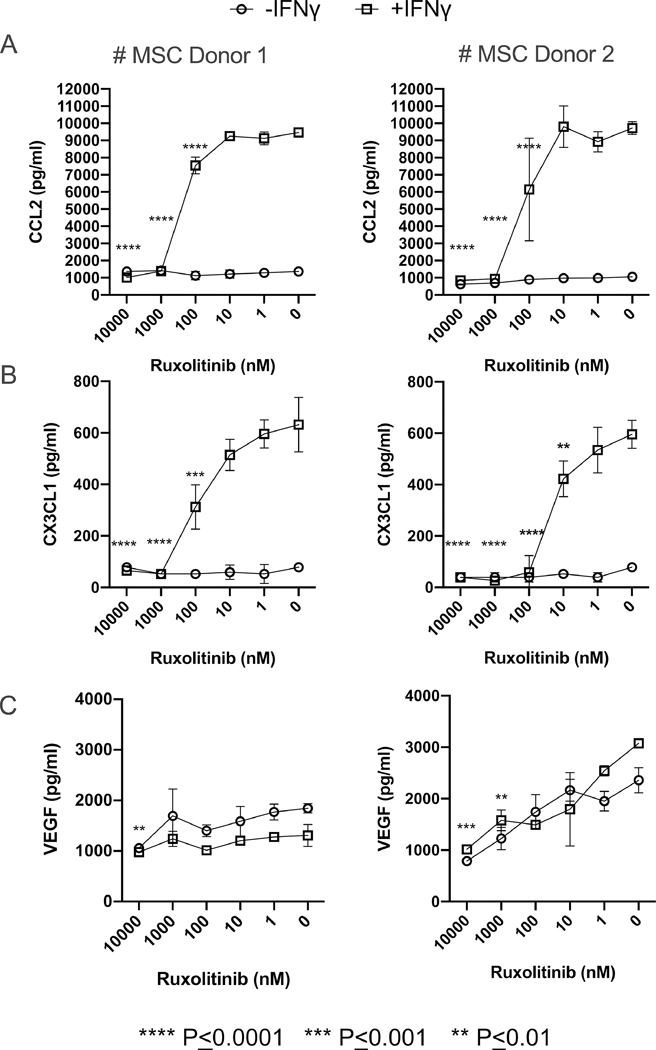
Ruxolitinib inhibits MSC driven pro-GvHD chemokines CX3CL1 and CCL2
Previous studies have shown that CX3CL1(Fractalkine) levels correlate with the incidence of grade II-IV acute GvHD and could serve as a biomarker for GvHD16. Similarly, CCR2-CCL2 axis play an important role in the onset of GvHD17. In addition, recent studies shed lights on the pro-GvHD role of VEGF (Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor) and angiogenesis on GvHD onset and inflammation 18, 19. In order to define the regulation of these secretory molecules on MSCs and Ruxolitinib interference, we performed a Luminex XMAP technology based 3-plex (CCL2, CX3CL1 and VEGF) analysis of the secretome of MSCs stimulated with and without IFNγ and varying concentrations of Ruxolitinib. Our results have demonstrated that Ruxolitinib blocks IFNγ mediated upregulation of CCL2 and CX3CL1 on MSCs (Fig 5A, B). Although, VEGF is constitutively secreted on MSCs, it is not modulated by IFNγ while Ruxolitinib moderately inhibits its secretion (Fig. 5C).
Figure 5. Ruxolitinib blocks IFNγ induced CX3CL1 and CCL2 on MSCs.
MSCs (10000 cells/ well) were seeded in 96 well plate and treated with +/− IFNγ (20 ng/mL) and different concentrations of Ruxolitinib for up to 3 days. The supernatants were collected on day 3 and quantitative levels of CCL2, CX3CLl and VEGF were assayed through Luminex xMAP (multi-analyte profiling) technology. Dose dependent effect of Ruxolitinib on the concentrations of (A) CCL2, (B) CX3CLl and (C) VEGF is shown on two independent MSC donors (Left: MSC Donor#1, Right: MSC Donor#2). Y axis represents the concentration in Picogram/milliliter. Average concentration with standard deviation is plotted. Assays were done in duplicates and were run in the Luminex system independently. Two-Way ANOVA multiple comparison test was performed between 0 nM and other Ruxolitinib concentrations. **, ***, **** represents P ≤ 0.01, P ≤ 0.001 and P ≤ 0.0001 respectively.
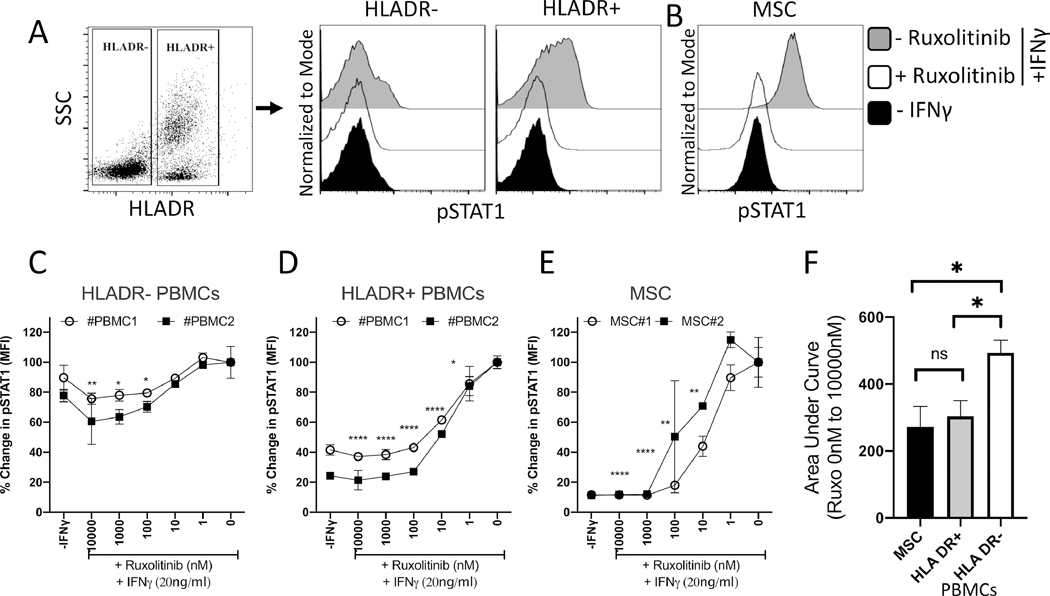
Ruxolitinib blocks STAT-1 phosphorylation on MSCs equivalent to HLADR+ populations of the peripheral blood
Previous studies have demonstrated that MHC Class II+ (HLADR+) antigen presenting cells of recipient origin in allogeneic bone marrow transplant individuals initiate and perpetuate GvHD 8, 20–23. Hence, we aim to compare total HLADR+ and HLADR- populations of PBMCs which include both lymphoid and myeloid lineages. This informs the relative effect of Ruxolitinib on PBMC populations based on HLADR expression. In addition, MSCs share antigen presenting cell functionalities by upregulating MHC-Class II (HLADR) molecules upon sensing IFNγ 9, 10. Hence, we compared the effect of Ruxolitinib on HLADR+/− populations with bone marrow MSCs. Utilizing a phosflow method, we analyzed IFNγ induced STAT1 phosphorylation levels in HLADR+/− populations of peripheral blood and marrow MSCs in the presence of varying concentrations of Ruxolitinib (Fig. 6A, B). IFNγ efficiently induced STAT-1 phosphorylation on HLADR+ than HLADR- populations (Fig. 6C, D). This reflects Ruxolitinib’s efficient blocking of STAT-1 phosphorylation on HLADR+ cells than HLADR- cells (Fig. 6C, 6D, F). Importantly, these experimental analyses were done in parallel with bone marrow derived MSCs and our results demonstrated that bone marrow MSCs were comparable to HLADR+ PBMC populations in responding to Ruxolitinib in blocking IFNγ induced STAT-1 phosphorylation (Fig. 6E, F).
Figure 6. Relative inhibition STAT-1 phosphorylation on MSCs and HLADR+ populations of PBMCs.
PBMCs and MSCs were stimulated with IFNγ in the presence of varying concentrations of Ruxolitinib. Phosflow analysis was performed on PBMCs and MSCs for pSTAT1 expression. PBMCs were additionally stained for phosflow compatible HLADR antibody. (A) Gating strategy for PBMCs based on Side scatter and HLADR expression is shown. Representative histogram is shown for pSTAT1 expression in (A) HLADR+ and HLADR- populations and (B) bone marrow MSCs. Grey and white histograms represent – and + Ruxolitinib in the presence of IFNγ. Black histogram represents unstimulated control. Dose dependent effect of Ruxolitinib on the mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) of pSTAT1 is shown on two independent PBMC and MSC donors. (C) HLADR- PBMCs (D) HLADR+ PBMCs (E) MSCs. Assays were done in duplicates. Average and Standard deviation is shown. Percentage MFI change is calculated based on pSTAT1 expression in the conditions of absence and presence of Ruxolitinib and IFNγ, respectively. Two-Way ANOVA multiple comparison test was performed between 0 nM and other Ruxolitinib concentrations. *, **, ***, **** represents P≤0.05, P ≤ 0.01, P ≤ 0.001 and P ≤ 0.0001 respectively. (F) Area Under Curve (AUC) values of HLADR- PBMCs, HLADR+ PBMCs and MSCs were plotted with average and standard deviation. Unpaired t test was perfored in Graphpad Prism to obtain statistical significance. * represents P≤0.05.
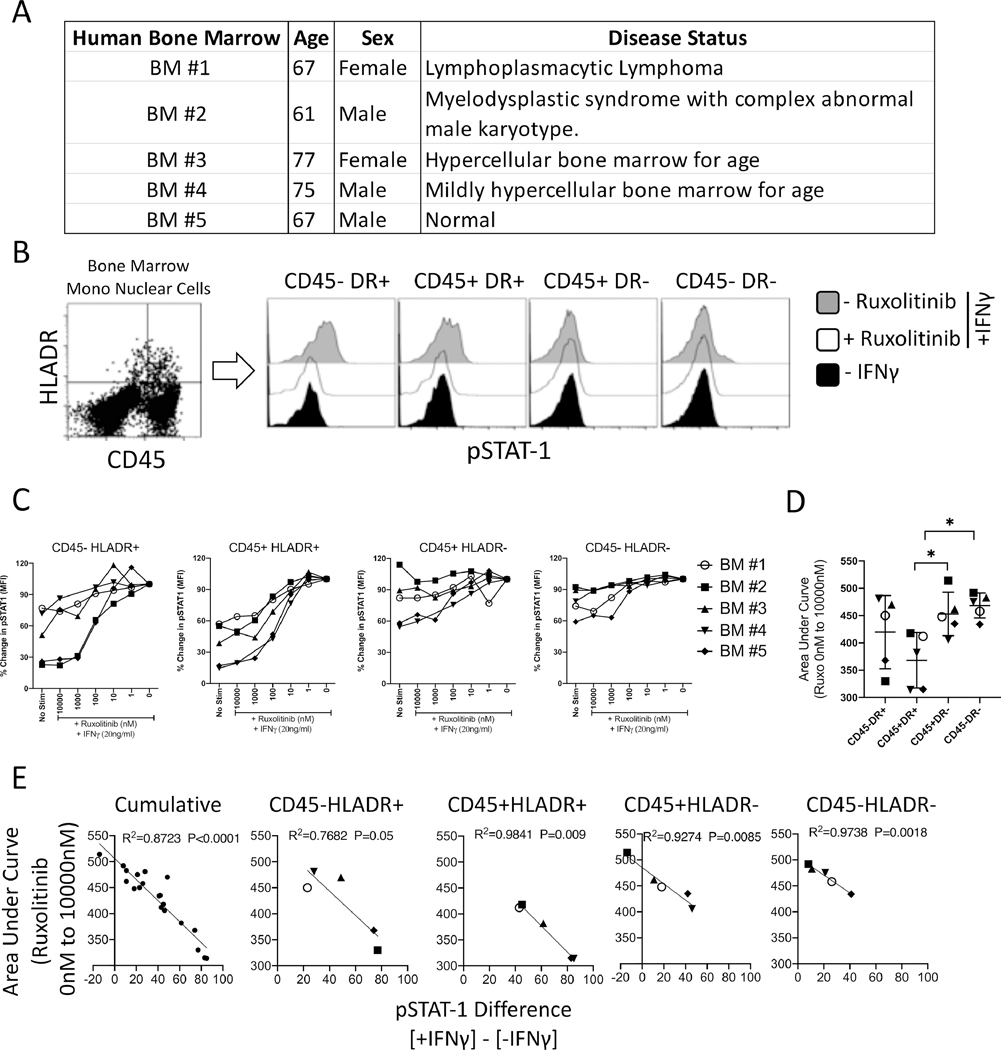
Ruxolitinib’s ex vivo effect on primary bone marrow CD45+/− and HLADR+/− populations of various hematological conditions
MSCs are non-hematopoietic progenitors of the marrow microenvironment and thus are the descent lineage of CD45- population and can upregulate HLADR. To define the direct effect of Ruxolitinib on CD45+/− and HLADR+/− ancestry populations at large, we investigated marrow aspirates from 5 independent donors (Fig. 7A). Bone marrow mononuclear cells were stimulated with IFNγ in the presence of varying concentrations of Ruxolitinib. Phosflow analysis was performed to determine STAT-1 phosphorylation in CD45+/− and HLADR+/− populations (Fig. 7B). Basal pSTAT-1 expression was also analyzed with appropriate isotype controls. CD45+/− and HLADR+/− bone marrow populations do not express basal pSTAT-1 expression and are not different to isotype controls (Fig. S1). Our results show that CD45+/− and HLADR+/− populations display differential sensitivity to Ruxolitinib mediated inhibition of IFNγ induced STAT-1 phosphorylation (Fig. 7C). Area Under Curve (AUC) analysis (Low and high AUC values represent high and low sensitivity to Ruxolitinib respectively) has demonstrated that Ruxolitinib significantly block STAT-1 phosphorylation on CD45+HLADR+ populations compared to CD45+HLADR- and CD45-HLADR- populations (Fig. 7D). Other comparisons did not yield statistical significance (Fig. 7D). Next, we investigated if sensitivity of CD45+/− and HLADR+/− populations to Ruxolitinib mediated inhibition correlate with their IFNγ responsiveness status. Our results have demonstrated that IFNγ induced STAT-1 phosphorylation levels directly correlates with sensitivity to Ruxolitinib mediated inhibition (Fig. 7E).
Figure 7. Effect of Ruxolitinib on CD45+/− and HLADR+/− populations of primary human bone marrow aspirates.
(A)Age, sex and disease status of primary bone marrow aspirates that are analyzed in this study is shown in a table format. (B) Primary bone marrow mononuclear cells (MNCs) were stimulated with IFNγ in the presence of varying concentrations of Ruxolitinib. Phosflow analysis was performed for pSTAT1 expression. MNCs were additionally stained for phosflow compatible HLADR and CD45 antibodies. (B) Representative histogram is shown for pSTAT1 expression in CD45-HLADR+, CD45+HLADR+, CD45+HLADR-, CD45-HLADR- populations of BM#5. Grey and white histograms represent – and + Ruxolitinib in the presence of IFNγ. Black histogram represents unstimulated control. (C) Dose dependent effect of Ruxolitinib on the mean fluorescent intensity (MFI) of pSTAT1 is shown on CD45-HLADR+, CD45+HLADR+, CD45+HLADR-, CD45-HLADR- populations of 5 independent primary bone marrow aspirates. Percentage MFI change is calculated based on pSTAT1 expression in the conditions of absence and presence of Ruxolitinib and IFNγ, respectively. (D) Area Under Curve (AUC) values of CD45-HLADR+, CD45+HLADR+, CD45+HLADR-, CD45-HLADR- populations were plotted with average and standard deviation. Unpaired t test was performed in GraphPad prism to obtain statistical significance. * represents P≤0.05. (E) Cumulative or independent Area Under Curve (AUC) values of CD45-HLADR+, CD45+HLADR+, CD45+HLADR-, CD45-HLADR- populations were subjected to linear regression analysis with the corresponding values of pSTAT-1 difference between + and -IFNγ stimulation. Regression analysis was performed in Graphpad Prism to obtain R2values and p values.
Discussion
Allogeneic bone marrow transplantation is the major treatment option for patients with advanced hematological malignancies. However, the major complication of allogeneic bone marrow transplantation is Graft vs Host Disease (GvHD). Allo immune response is initiated in GvHD through presentation of recipient tissue antigens by Antigen presenting Cells (APCs) to donor T cells. Although both donor and recipient APCs present tissue antigens to donor T cells, recipient non-hematopoietic APCs are substantially more potent than donor APCs in inducing severe GvHD 20–22. In addition, presentation of alloantigen by recipient APC is more significant in initiating GvHD than non-APC target tissues such as epithelium 23. All these studies suggested that MHC class II+ fibroblast and/or pericyte like cells of mesenchymal origin initiate GvHD. We hypothesized that recipient tissue/marrow resident MSCs drive GvHD based on two rationale: (1) MSCs are non-hematopoietic antigen presenting cells and up regulate MHC Class I and II by IFNγ, and thus can present tissue antigens to donor T cells 9, 10, 14, 24, 25. (2) MSCs derived from the bone marrow aspirates of GvHD patients are exclusively recipient origin. MSCs in donor bone marrow never engraft or replace recipient MSCs and lack chimerism 26–29. Thus, recipient MSCs could be a fuel for inflammation in GvHD and our results supports the hypothesis that anti-inflammatory drug Ruxolitinib affect the immunobiology of MSCs equivalent to professional HLADR+ APCs which collectively mitigate GvHD.
Ruxolitinib is shown to be beneficial to the patients with GvHD by blocking the inflammatory responses 30–32. Our finding appends to its mechanism of action by demonstrating that the cellular targets of Ruxolitinib are both HLADR+ lympho-myeloid populations and non-hematopoietic MSCs. Ruxolitinib’s comparability in blocking IFNγ mediated STAT-1 phosphorylation on both HLADR+ professional APCs and MSCs further suggests that MSCs are non-canonical cellular targets of Ruxolitinib and are as significant as HLADR+ populations in containing inflammation. Our results show that HLADR-populations of bone marrow and peripheral blood are less responsive to IFNγ mediated STAT-1 phosphorylation compared to HLADR+ populations. This is in contrast to marrow MSCs since they are HLADR- in their resting stage while IFNγ activates STAT-1 phosphorylation and downstream HLADR expression 13, 33. Thus, Ruxolitinib blocks IFNγ induced STAT-1 phosphorylation on HLADR negative MSCs. Based on these premises we propose that MSCs are the robust HLADR- immune responders of Ruxolitinib.
Our results have shown that Ruxolitinib blocks IFNγ mediated upregulation of both MHC Class I (HLA-ABC) and MHC Class II (HLADR) on MSCs which supports the hypothesis that Ruxolitinib interferes with MSC and T cell interaction. In fact, MSC and T cell coculture experiments to demonstrate the function of Ruxolitinib on MSCs are challenging as this drug affects T cell proliferation on its own [Data not shown]. Hence, we utilized a loop approach where we have demonstrated that the secretome of activated PBMCs induces STAT1 phosphorylation while Ruxolitinib blocks this effect. This mechanistic data provides two distinct insights. 1. Ruxolitinib blocks PBMC mediated activation of MSC thereby interfering with the loop interaction of MSCs and PBMCs. 2. Ruxolitinib blocks STAT-1 phosphorylation on MSCs that are either stimulated with IFNγ or total secretome of activated PBMCs which suggests that Ruxolitinib prevents pan STAT1 phosphorylation on MSCs irrespective of the stimuli.
Chemokines play an important role in perpetuating GvHD and it has been suggested that targeting of chemokine pathways reduce the disease severity 34. Our results demonstrated that Ruxolitinib blocks the production of pro-GvHD chemokines CX3CL1 and CCL2 on MSCs. The receptor for CX3CL1 is CX3CR1 and its expression has been well reported on T cells with high perforin and granzyme B activities 35. CX3CL1-CX3CR1 axis has been suggested as target for inflammatory disorders and GvHD 36, 37. Similarly, CCL2-CCR2 axis play a significant role in GvHD induction 17. Our results add to the existing data that targeting of chemokines CX3CL1 and CCL2 by Ruxolitinib is a strategy in mitigating GvHD. We observed differences in the dose sensitivity between Ruxolitinib’s rescue effect on IFNγ induced cytostatic effect and IFNγ induced effector molecules. This could be due to the differences in the biological endpoints, variations in the sensitivity and duration of the assay systems. It is also possible that Ruxolitinib activates other cell regulating pathways in the presence of IFNγ which warrants future investigations.
Previous studies have shown the role of immunosuppressive pathways IDO and PD-L1 in suppressing GvHD 38–41. Our results demonstrated that Ruxolitinib also blocks IDO and PD-L1 on MSCs. Thus, although Ruxolitinib blocks immunostimulatory molecules on MSCs which is beneficial to mitigate GvHD, it also defuses MSC driven anti-GvHD molecules IDO and PD-L1. Although, future studies are required to define the relative significance of immunostimulatory vs inhibitory pathways in endogenous recipient MSCs in modulating GvHD, it is entirely possible that immunostimulatory pathways dominate and neutralize anti-GvHD effectors in MSCs.
The limitation of the present study is the lack of demonstration of the effect of Ruxolitinib on non-culture expanded MSC progenitors in primary bone marrow aspirates. Methodologies to perform phosflow technologies on low frequency endogenous MSC progenitors using multicolor flowcytometry panel is limited. Future studies are warranted to define the identity and characteristics of endogenous MSC progenitors. Notwithstanding, our ex vivo analysis of marrow aspirates from healthy individuals and patients with hematological conditions demonstrated that CD45+/− and HLADR+/− bone marrow populations show sensitivity to Ruxolitinib depending on their responsiveness to IFNγ induced STAT-1 phosphorylation. This is significant since MSCs respond to IFNγ and hence are sensitive to Ruxolitinib. In addition, MSCs are the descent of CD45- bone marrow population and upregulate HLADR upon IFNγ activation. Thus, endogenous MSC progenitors could be either CD45-HLADR+ or CD45-HLADR-. Altogether, combination of our data using culture expanded MSCs and primary bone marrow aspirates provided insights that marrow MSCs are the targets of Ruxolitinib. The present study investigates bone marrow from control and hematological conditions and future investigations are warranted with bone marrow of GvHD patients.
Recent clinical evidences have demonstrated that infusion of random donor MSCs as cell therapy showed efficacy in mitigating pediatric steroid-refractory acute GvHD and thus are considered as an attractive cell therapy agent to mitigate GVHD42, 43. IFNγ prelicensed MSCs can be tested as an augmented MSC therapy since IFNγ prelicensing enhances MSC’s immunosuppressive properties 44, 45. Importantly, the mechanism of action of MSCs based cell therapy in mitigating GvHD needs to be understood in human clinical trials prior to moving forward with IFNγ prelicensed MSC therapy. It has been shown that MSC viability is dispensable for anti-GVHD effect in the animal model studies 11, 46. Infused MSCs undergo apoptosis which execute immunomodulation and mitigate GvHD. Thus, the relative significance of immunomodulatory factors (which can be improved by IFNγ prelicensing) on viable MSCs in mitigating GvHD irrespective of apoptosis yet to be understood. There are also challenges in translating MSC studies from GvHD animal models into human outcome. Infusion of human MSCs in the GvHD animal models do not provide insights on the mechanism of action of MSCs due to their xenogenecity. In contrary, infusion of mouse MSCs in the GvHD animal models also do not provide insights since mouse MSCs are not equal to human counter parts in executing immune suppression 47. Despite this conundrum on MSC based cell therapy for GvHD, the role of endogenous MSCs in modulating GvHD is also yet to be understood in future studies. The significant challenge in analyzing endogenous MSCs prior to culture expansion/adaptation and by direct ex vivo analysis is their rare frequency in marrow aspirates. However, analyzing culture expanded MSCs still provide part of insights on endogenous MSCs as they share mesenchymal lineage characteristics. Our results provided indications that recipient endogenous MSCs could be a target for therapeutic interventions for the management of GvHD.
Supplementary Material
Highlights.
Ruxolitinib blocks IFNγ and PBMC secretome induced STAT-1 phosphorylation on MSCs
Ruxolitinib blocks IFNγ induced downstream effector molecules on MSCs
MSCs are as equal as to HLADR+ PBMCs in responding to Ruxolitinib
Bone marrow populations display differential sensitivity to IFNγ and Ruxolitinib
Acknowledgements:
This study was directly supported by the WES Leukemia Research Foundation (RC). This research was also supported by Mercer University School of Medicine’s research funds (RC) and generous support from the Landings Women’s Golf Association (Savannah, GA) (RC). This work was also partly supported by National Institutes of Health, National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases award R01DK109508 (JG).
Footnotes
Publisher's Disclaimer: This is a PDF file of an unedited manuscript that has been accepted for publication. As a service to our customers we are providing this early version of the manuscript. The manuscript will undergo copyediting, typesetting, and review of the resulting proof before it is published in its final form. Please note that during the production process errors may be discovered which could affect the content, and all legal disclaimers that apply to the journal pertain.
References
- 1.Zhou T, Georgeon S, Moser R, Moore DJ, Caflisch A, Hantschel O. Specificity and mechanism-of-action of the JAK2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors ruxolitinib and SAR302503 (TG101348). Leukemia. 2014;28:404–407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bose P, Verstovsek S. JAK Inhibition for the Treatment of Myelofibrosis: Limitations and Future Perspectives. Hemasphere. 2020;4:e424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Rumi E, Barate C, Benevolo G, Maffioli M, Ricco A, Sant’Antonio E. Myeloproliferative and lymphoproliferative disorders: State of the art. Hematol Oncol. 2020;38:121–128. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Risitano AM, Peffault de Latour R. Ruxolitinib for steroid-resistant acute GVHD. Blood. 2020;135:1721–1722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Zeiser R, von Bubnoff N, Butler J, et al. Ruxolitinib for Glucocorticoid-Refractory Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease. The New England journal of medicine. 2020;382:1800–1810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Spoerl S, Mathew NR, Bscheider M, et al. Activity of therapeutic JAK 1/2 blockade in graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2014;123:3832–3842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Welsch K, Holstein J, Laurence A, Ghoreschi K. Targeting JAK/STAT signalling in inflammatory skin diseases with small molecule inhibitors. Eur J Immunol. 2017;47:1096–1107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Blazar BR, Murphy WJ, Abedi M. Advances in graft-versus-host disease biology and therapy. Nature reviews. Immunology. 2012;12:443–458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Stagg J, Pommey S, Eliopoulos N, Galipeau J. Interferon-gamma-stimulated marrow stromal cells: a new type of nonhematopoietic antigen-presenting cell. Blood. 2006;107:2570–2577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Francois M, Romieu-Mourez R, Stock-Martineau S, Boivin MN, Bramson JL, Galipeau J. Mesenchymal stromal cells cross-present soluble exogenous antigens as part of their antigen-presenting cell properties. Blood. 2009;114:2632–2638. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Galipeau J, Sensebe L. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells: Clinical Challenges and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cell stem cell. 2018;22:824–833. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Chinnadurai R, Rajakumar A, Schneider AJ, Bushman WA, Hematti P, Galipeau J. Potency Analysis of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Using a Phospho-STAT Matrix Loop Analytical Approach. Stem cells. 2019;37:1119–1125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Loisel S, Dulong J, Menard C, et al. Brief Report: Proteasomal Indoleamine 2,3-Dioxygenase Degradation Reduces the Immunosuppressive Potential of Clinical Grade-Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Undergoing Replicative Senescence. Stem cells. 2017;35:1431–1436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chinnadurai R, Copland IB, Patel SR, Galipeau J. IDO-independent suppression of T cell effector function by IFN-gamma-licensed human mesenchymal stromal cells. Journal of immunology. 2014;192:1491–1501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Croitoru-Lamoury J, Lamoury FM, Caristo M, et al. Interferon-gamma regulates the proliferation and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells via activation of indoleamine 2,3 dioxygenase (IDO). PloS one. 2011;6:e14698. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Brissot E, Bossard C, Malard F, et al. Involvement of the CX3CL1 (fractalkine)/CX3CR1 pathway in the pathogenesis of acute graft-versus-host disease. Journal of leukocyte biology. 2015;97:227–235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Terwey TH, Kim TD, Kochman AA, et al. CCR2 is required for CD8-induced graft-versus-host disease. Blood. 2005;106:3322–3330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Riesner K, Shi Y, Jacobi A, et al. Initiation of acute graft-versus-host disease by angiogenesis. Blood. 2017;129:2021–2032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Haen SP. Vessels, T cells, and GVHD: time matters. Blood. 2017;129:1898–1899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Ordemann R, Hutchinson R, Friedman J, et al. Enhanced allostimulatory activity of host antigen-presenting cells in old mice intensifies acute graft-versus-host disease. The Journal of clinical investigation. 2002;109:1249–1256. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Matte CC, Liu J, Cormier J, et al. Donor APCs are required for maximal GVHD but not for GVL. Nature medicine. 2004;10:987–992. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Shlomchik WD, Couzens MS, Tang CB, et al. Prevention of graft versus host disease by inactivation of host antigen-presenting cells. Science. 1999;285:412–415. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Teshima T, Ordemann R, Reddy P, et al. Acute graft-versus-host disease does not require alloantigen expression on host epithelium. Nature medicine. 2002;8:575–581. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Romieu-Mourez R, Francois M, Boivin MN, Bouchentouf M, Spaner DE, Galipeau J. Cytokine modulation of TLR expression and activation in mesenchymal stromal cells leads to a proinflammatory phenotype. Journal of immunology. 2009;182:7963–7973. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Chinnadurai R, Copland IB, Ng S, et al. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells Derived From Crohn’s Patients Deploy Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase-mediated Immune Suppression, Independent of Autophagy. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy. 2015;23:1248–1261. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Bartsch K, Al-Ali H, Reinhardt A, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells remain host-derived independent of the source of the stem-cell graft and conditioning regimen used. Transplantation. 2009;87:217–221. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Rieger K, Marinets O, Fietz T, et al. Mesenchymal stem cells remain of host origin even a long time after allogeneic peripheral blood stem cell or bone marrow transplantation. Experimental hematology. 2005;33:605–611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wang J, Liu K, Lu DP. Mesenchymal stem cells in stem cell transplant recipients are damaged and remain of host origin. International journal of hematology. 2005;82:152–158. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Copland IB, Qayed M, Garcia MA, Galipeau J, Waller EK. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Patients with Acute and Chronic Graft-versus-Host Disease Deploy Normal Phenotype, Differentiation Plasticity, and Immune-Suppressive Activity. Biology of blood and marrow transplantation : journal of the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. 2015;21:934–940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Zeiser R, Socie G. The development of ruxolitinib for glucocorticoid-refractory acute graft-versus-host disease. Blood advances. 2020;4:3789–3794. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Mohty M, Holler E, Jagasia M, et al. Refractory acute graft-versus-host disease: a new working definition beyond corticosteroid refractoriness. Blood. 2020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Przepiorka D, Luo L, Subramaniam S, et al. FDA Approval Summary: Ruxolitinib for Treatment of Steroid-Refractory Acute Graft-Versus-Host Disease. Oncologist. 2020;25:e328–e334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Chinnadurai R, Rajan D, Ng S, et al. Immune dysfunctionality of replicative senescent mesenchymal stromal cells is corrected by IFNgamma priming. Blood advances. 2017;1:628–643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Castor MG, Pinho V, Teixeira MM. The role of chemokines in mediating graft versus host disease: opportunities for novel therapeutics. Front Pharmacol. 2012;3:23. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Umehara H, Bloom ET, Okazaki T, Nagano Y, Yoshie O, Imai T. Fractalkine in vascular biology: from basic research to clinical disease. Arteriosclerosis, thrombosis, and vascular biology. 2004;24:34–40. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Barrett AJ. A new checkpoint in the path to GVHD? How bedside-to-bench stem cell transplant studies can inform human GVHD biology. Journal of leukocyte biology. 2015;97:213–215. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Imai T, Yasuda N. Therapeutic intervention of inflammatory/immune diseases by inhibition of the fractalkine (CX3CL1)-CX3CR1 pathway. Inflamm Regen. 2016;36:9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Jasperson LK, Bucher C, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, Mellor AL, Munn DH, Blazar BR. Inducing the tryptophan catabolic pathway, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO), for suppression of graft-versus-host disease (GVHD) lethality. Blood. 2009;114:5062–5070. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Jasperson LK, Bucher C, Panoskaltsis-Mortari A, et al. Indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase is a critical regulator of acute graft-versus-host disease lethality. Blood. 2008;111:3257–3265. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Saha A, Aoyama K, Taylor PA, et al. Host programmed death ligand 1 is dominant over programmed death ligand 2 expression in regulating graft-versus-host disease lethality. Blood. 2013;122:3062–3073. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Hossain MS, Kunter GM, El-Najjar VF, et al. PD-1 and CTLA-4 up regulation on donor T cells is insufficient to prevent GvHD in allo-HSCT recipients. PloS one. 2017;12:e0184254. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Kurtzberg J, Abdel-Azim H, Carpenter P, et al. A Phase 3, Single-Arm, Prospective Study of Remestemcel-L, Ex Vivo Culture-Expanded Adult Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for the Treatment of Pediatric Patients Who Failed to Respond to Steroid Treatment for Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease. Biology of blood and marrow transplantation : journal of the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. 2020;26:845–854. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Galipeau J. Mesenchymal Stromal Cells for Graft-versus-Host Disease: A Trilogy. Biology of blood and marrow transplantation : journal of the American Society for Blood and Marrow Transplantation. 2020;26:e89–e91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Guess AJ, Daneault B, Wang R, et al. Safety Profile of Good Manufacturing Practice Manufactured Interferon gamma-Primed Mesenchymal Stem/Stromal Cells for Clinical Trials. Stem Cells Transl Med. 2017;6:1868–1879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Burnham AJ, Daley-Bauer LP, Horwitz EM. Mesenchymal stromal cells in hematopoietic cell transplantation. Blood advances. 2020;4:5877–5887. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Galleu A, Riffo-Vasquez Y, Trento C, et al. Apoptosis in mesenchymal stromal cells induces in vivo recipient-mediated immunomodulation. Sci Transl Med. 2017;9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chinnadurai R, Sands J, Rajan D, et al. Molecular Genetic and Immune Functional Responses Distinguish Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stromal Cells from Hepatic Stellate Cells. Stem cells. 2019;37:1075–1082. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.