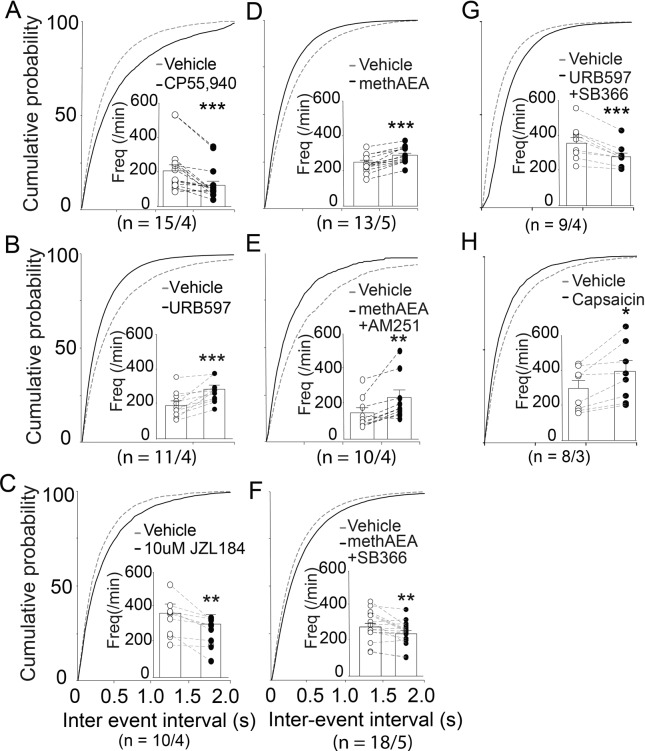
Fig. 2. AEA increases sEPSC frequency in the NAcore of saline group via TRPV1 rather than CB1Rs.
Cumulative distributions of inter-event intervals and mean event frequencies (insets) pre- and post-drug perfusion. The CB1Rs agonist CP55,940 (0.3 μM) or 2-AG hydrolase inhibitor JZL184 (10 μM) significantly reduced sEPSC frequency (A, C), while methAEA (30 μM), AEA hydrolase inhibitor URB597 (10 μM), methAEA (30 μM) or TRPV1 agonist capsaicin (10 μM) increased sEPSC frequency (B, D, H). MethAEA increased sEPSC frequency in the presence of the CB1R antagonist, AM251 (5 μM), but decreased sEPSC frequency in the presence of the TRPV1 antagonist, SB366791 (1 μM) (E, F). Hence, the action of AEA on increasing synaptic glutamate release probability may be mediated by TRPV1. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001, compared with vehicle perfusion using paired t test. The first and second N numbers in parentheses correspond to the numbers of recorded neurons and rats, respectively.