Dear Editor,
Severe acute respiratory syndrome Coronavirus-2 (SARS-CoV-2) virus associated COVID-19 (coronavirus disease) pandemic, has led to more than 2.5 million deaths worldwide. Hematopoietic stem cell transplant (HCT) recipients may be at a greater risk of morbidity and mortality due to their immunosupressed state [1]. Here, we report 6 cases of SARS-CoV-2 infection in HCT recipients.
Between May and September 2020, six HCT recipients were diagnosed with SARS-CoV-2 infection at our centre, based on reverse transcriptase polymerase chain reaction (RTPCR) on nasopharyngeal swab. Baseline characteristics of all the six patients are shown in Table 1. Severity of COVID-19 disease was graded as per WHO ordinal scale [2]. We used triplet antiviral combination with Lopinavir/Ritonavir (LPV/r), Ribavirin (RBV) and Interferon β1b (IFN β1b) in the initial period of pandemic and then remdesivir (once available in India) for moderate-severe COVID-19 or for mild COVID-19 with ongoing immunosuppressants. Tocilizumab was used for severe COVID-19, as per physician discretion. Nasopharyngeal swab was repeated every 2 weeks till negativity and antibodies to SARS-CoV-2 were tested after 2 weeks of initial RTPCR positivity and then 2 weekly.
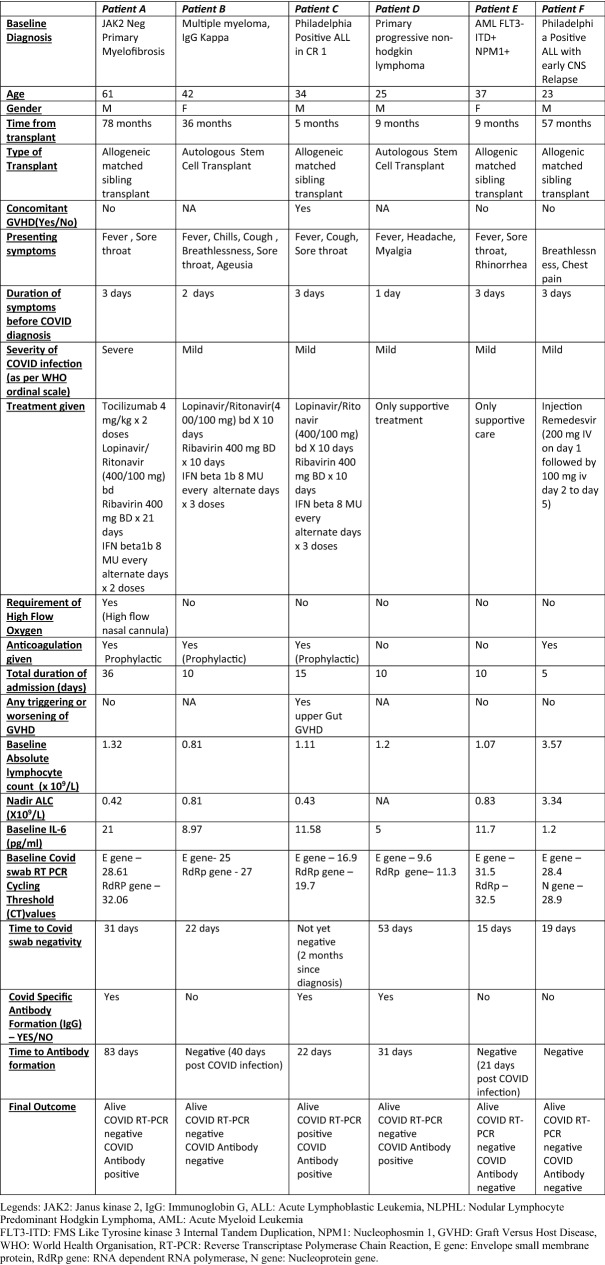
Table 1.
Clinical characteristics of patients with SARS-CoV-2 infections post BMT
We found that 5 of these 6 patients required prolonged time to clear the viral infection, with median time to RTPCR negativity of 31 days (Table 1). Three patients (patient A, C and D) developed neutralising IgG antibodies (IgG) to SARS-CoV-2 at 83 days, 22 days and 31 days post infection respectively. However, Patient C who developed antibodies at day 22, continued to remain persistently RTPCR positive for SARS-CoV-2 (Table 1). At a median follow-up of 40 days, all patients in our cohort are alive.
With emerging evidence, treatment options in COVID-19 are becoming clearer. However, there is no standard of care for immunocompromised patients, especially post HCT recipients.
In a phase II randomized trial, triplet combination consisting of oral LPV/r (400 mg/100 mg) and RBV 400 mg twice daily (14 days) along with IFN β1b was compared with LPV/r alone. Along with significantly improved clinical response, the triplet combination resulted in early nasopharyngeal negativity [3]. Amongst the 6 patients in our series, 3 received triplet antivirals, and showed rapid defervesence with clinical improvement. However, in contrast to Hung et al. [3], the time to negative nasopharyngeal swab was longer in our patients who received this combination. Production of excessive cytokines results in severe inflammatory responses in the lung resulting in severe COVID-19 manifestations and use of Tocilizumab, has been found to abrogate this inflammation [4]. In patient A, Tocilizumab was used twice in view of impending respiratory failure on third day and fifth day of infection resulting in rapid clinical benefit and radiological response. Thus, this case series highlights that use of antivirals (triplet antivirals and Remdesivir) and tocilizumab results in favorable outcome in post HCT patients with COVID-19 infection.
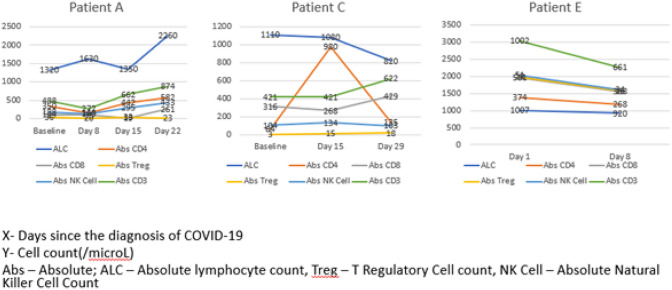
We recorded the immune kinetics of our allogeneic HCT patients during the course of illness (Fig. 1). In the early phases of infection, there was a decrease in the Absolute NK Cell, CD3, CD4 and CD8. By Day 8–15 there was a rise in these parameters. The graph pattern of patient E is in stark contrast to those of patients A and C. All the T-cell subsets and NK-cells appear to have stabilized, likely because this patient was diagnosed in late stages of the infection.
Fig. 1.
Immune cell profile of Allogeneic stem cell transplant recipients post COVID infection
With the FDA authorizing the use of remdesivir, a more tolerated drug with better outcomes, for the treatment of moderate and severe COVID-19 infection, the place of triplet combination of LPV/r, RBV and IFN β1b in the therapeutic armamentarium is not clear, nevertheless, it still remains an alternative, if remdesivir is unavailable.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Saraceni F, et al Severe COVID-19 in a patient with chronic graft-versus-host disease after hematopoietic stem cell transplant successfully treated with ruxolitinib. Transpl Infect Dis n/a: e13401. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 2.https://www.who.int/blueprint/priority-diseases/key-action/COVID-19_Treatment_Trial_Design_Master_Protocol_synopsis_Final_18022020.pdf. Last Accessed 10 Jan 2021.
- 3.Hung IF-N, et al. Triple combination of interferon beta-1b, lopinavir–ritonavir, and ribavirin in the treatment of patients admitted to hospital with COVID-19: an open-label, randomised, phase 2 trial. Lancet. 2020;395:1695–1704. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)31042-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Toniati P, et al. (2020) Tocilizumab for the treatment of severe COVID-19 pneumonia with hyperinflammatory syndrome and acute respiratory failure: a single center study of 100 patients in Brescia, Italy. Autoimmun Rev 19, 102568 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]