Abstract
It is important for dental care professionals to reliably assess carbon dioxide (CO2) levels and ventilation rates in their offices in the era of frequent infectious disease pandemics. This study was to evaluate CO2 levels in dental operatories and determine the accuracy of using CO2 levels to assess ventilation rate in dental clinics. Mechanical ventilation rate in air change per hour (ACHVENT) was measured with an air velocity sensor and airflow balancing hood. CO2 levels were measured in these rooms to analyze factors that contributed to CO2 accumulation. Ventilation rates were estimated using natural steady-state CO2 levels during dental treatments and experimental CO2 concentration decays by dry ice or mixing baking soda and vinegar. We compared the differences and assessed the correlations between ACHVENT and ventilation rates estimated by the steady-state CO2 model with low (0.3 L/min, ACHSS30) or high (0.46 L/min, ACHSS46) CO2 generation rates, by CO2 decay constants using dry ice (ACHDI) or baking soda (ACHBV), and by time needed to remove 63% of excess CO2 generated by dry ice (ACHDI63%) or baking soda (ACHBV63%). We found that ACHVENT varied from 3.9 to 35.0 in dental operatories. CO2 accumulation occurred in rooms with low ventilation (ACHVENT ≤6) and overcrowding but not in those with higher ventilation. ACHSS30 and ACHSS46 correlated well with ACHVENT (r = 0.83, P = 0.003), but ACHSS30 was more accurate for rooms with low ACHVENT. Ventilation rates could be reliably estimated using CO2 released from dry ice or baking soda. ACHVENT was highly correlated with ACHDI (r = 0.99), ACHBV (r = 0.98), ACHDI63% (r = 0.98), and ACHBV63% (r = 0.98). There were no statistically significant differences between ACHVENT and ACHDI63% or ACHBV63%. We conclude that ventilation rates could be conveniently and accurately assessed by observing the changes in CO2 levels after a simple mixing of household baking soda and vinegar in dental settings.
Keywords: indoor air quality, pathogen transmission, air filter, baking soda, dentistry, COVID-19
Carbon dioxide (CO2) level is an important indicator of ventilation in occupied indoor environments. CO2 is a by-product of human metabolism and exists in high levels in exhaled air. Atmospheric CO2 level is approximately 400 parts per million (ppm) in outdoor environments, but CO2 in human exhaled air reaches on average 40,000 ppm in concentration (Issarow et al. 2015). CO2 level is therefore often used as a proxy for indoor air quality as well as a risk marker for transmission of airborne diseases since it is inert, its indoor emission source (human) is known, and its measurement is inexpensive and accurate (Batterman 2017). Increased CO2 level is often associated with poor ventilation and overcrowding. Accumulation of CO2 occurs concurrently with accumulation of respiratory pathogens in a room where an infected person is present but not wearing a mask, which may increase the risk of disease transmission. High levels of CO2 have long been associated with the transmission of infectious respiratory diseases such as tuberculosis, influenza, and rhinovirus infections (Myatt et al. 2004; Richardson et al. 2014; Wood et al. 2014). Indoor CO2 levels have therefore been widely used to model the risks of airborne infectious disease transmission (Rudnick and Milton 2003; Issarow et al. 2015; Harrichandra et al. 2020), including that of coronavirus infection transmission in dental offices (Zemouri et al. 2020).
Clinical spaces with good ventilation should have CO2 levels close to that of outside air at approximately 400 ppm (ASHRAE 2007; Issarow et al. 2015). Higher CO2 levels indicate poor ventilation, accumulation of exhaled air, and increase in the fraction of “rebreathed air” in the indoor environment, which is proven to be a risk factor for infectious disease transmissions (Rudnick and Milton 2003; Richardson et al. 2014; Wood et al. 2014; Issarow et al. 2015). CO2 levels have been used to estimate ventilation rates in dental offices (Godwin et al. 2003; Helmis et al. 2007; Helmis et al. 2008). Ventilation rate was found to be 1.12 air change per hour (ACH) in a typical dental clinic in the United States (Godwin et al. 2003) and was on average 5 ACH in a dental school clinic in Greece where the doors and windows were opened for cross-ventilation (Helmis et al. 2007). Both studies used natural buildup of CO2 levels in dental clinics to estimate the ventilation rate through mathematic models, but none actually verified the ventilation estimates using standard methodologies such as high-precision airflow sensors (ASHRAE 2017). It is not known if these estimates were accurate as both methods require mathematical modeling based on several assumptions related to CO2 generation, buildup, and dispersion over a relatively lengthy period of time, which may result in erroneous estimates if any of the assumed conditions are not met (Batterman 2017). A simpler and more reliable method is needed if CO2 level is to be used by dental care professionals to assess the ventilation rate of their treatment rooms.
The purpose of the present study was 2-fold: 1) to evaluate CO2 level and its associated factors in dental operatories and 2) to determine the accuracy of various methods using CO2 levels to assess ventilation rate in dental clinics. Our aim was to find a practical tool that will enable dental care professionals to conveniently and accurately monitor CO2 levels and assess the ventilation rates in order to devise a pragmatic and effective strategy for ventilation improvement in their work environment.
Methods
Study Settings
We conducted the CO2 concentration and ventilation rate assessments in 10 closed treatment rooms ranging from 667 to 1,221 cubic feet (ft3) in size in a multifloor building in an academic dental institute. Mechanical ventilation of the rooms was provided by 3 air handlers that drew 60% outside air to the ventilation system.
Determining Room Airflow and Mechanical Ventilation Rates
Mechanical ventilation in air change per hour (ACHVENT) was measured with an air velocity sensor integrated in an airflow balancing hood (ADM-850L Airdata Multimeter with CFM-850L FlowHood; Shortridge Instruments) as described elsewhere (Ren et al. 2021).
Assessing CO2 Levels during Dental Treatment Procedures
We measured CO2 levels in 2 dental treatment rooms when dental procedures were performed. The 2 rooms represented 2 extremes in ventilation rates, with one at 3.9 air change per hour and the other at 35. The number of persons in the rooms was recorded in real time when a person was entering and leaving the room. CO2 levels were measured at a 1-min interval using a consumer-grade CO2 sensor (Aranet4, range 0–9,999 ppm, accuracy ±50 ppm; SAF Tehnika).
24-h Continuous Monitoring CO2 in Dental Treatment Rooms
To further explore the dynamics of CO2 levels in dental treatment rooms throughout the day and assess accuracies of the steady-state models of CO2 for ventilation assessments, we continuously measured the CO2 levels in 10 dental treatment rooms for 24 h and recorded the procedures performed and number of persons in the room.
Assessing Ventilation Rate by Natural CO2 Level Modeling in Dental Treatment Rooms
We used the steady-state model described by Batterman (2017) to calculate the air change rate of treatment rooms and compared the outcomes with that of measured mechanical ventilation.
The steady-state air change rate (ACHSS) is calculated as follows (Batterman 2017):
| (1) |
where n = number of persons in the room, GP = average CO2 generation rate, V = volume of the room in cubic meters (m3), CSS = steady-state indoor CO2 level in ppm, and CR = CO2 level in outdoor air in ppm.
The CO2 generation rate GP is affected by many factors and may vary by human activity, physical size, sex, and race (Qi et al. 2014; Persily and de Jonge 2017). GP of 0.46 L/min or 0.30 L/min was used in previous studies to represent CO2 generation (Godwin et al. 2003; Batterman 2017). As CO2 generation rates and activity levels by dental care providers and their patients are unknown and may not be constant, we used both values to calculate the air change rate ACHSS and assess the correlations between ACHSS and ACHVENT at 2 GP levels.
Assessing Ventilation Rates by CO2 Decays Using Dry Ice
Ventilation rates by CO2 clearance using dry ice (ACHDI) were determined as described by Batterman (2017) using CO2 concentration decays:
| (2) |
where Δt = period between measurements, C0 and C1 = CO2 levels measured at the beginning and the end of the decay period (ppm), and CR = CO2 level in outdoor air (ppm).
Assessing Ventilation Rates by CO2 Decays Using Baking Soda
Considering that dental care professionals in private practices may not have ready access to dry ice, we developed a method to rapidly generate CO2 in dental offices using baking soda (Arm & Hammer Pure; Church & Dwight) and vinegar (Heinz all-natural distilled white vinegar) (see Appendix for detailed protocol). Mixing baking soda (NaHCO3) with vinegar containing 5% acetic acid (CH3COOH) will generate CO2 as follows:
| (3) |
Ventilation rates by CO2 clearance using baking soda and vinegar (ACHBV) could then be calculated using Equation 2 as above.
Estimating Ventilation Rate by Time to 63% Removal of Excess CO2
Based on a commonly used formula for rate of purging airborne contaminants, 1 complete air change will replace 63% of airborne contaminants in the room with outdoor air (Nardell et al. 1991; Fernstrom and Goldblatt 2013; Jimenez 2020). Ventilation rate can therefore be simply calculated using the time needed to reach a 63% reduction of excess CO2 from its peak level:
| (4) |
where t1 = initial time point with indoor CO2 at peak level, and t2 = time point (min) when excess CO2 is reduced by 63%. Indoor CO2 at peak level (CS) is the sum of outdoor CO2 (CR) and excess CO2 (CE) generated by dry ice or baking soda. As CO2 measurement starts at peak level, t1 is therefore always 0. Time needed to remove 63% CE, or t2, is the time point when indoor CO2 level is at C63%E = CS – 63% CE, where CE = CS – CR.
Statistical Analysis
We performed multiple regression analysis using CO2 levels as the dependent variable and number of persons in the room, ventilation rate, room size, and outdoor CO2 level as independent variables. We analyzed the dynamics of CO2 levels during dental treatment procedures using descriptive analysis and compared the steady-state CO2 levels between rooms with poor and good ventilation using t tests. Mechanical ventilation rate was compared with air change rates calculated with different methods based on CO2 levels to assess the correlation (Pearson’s r) and differences (paired t test) between the 2 methods of ventilation assessments.
Results
Mechanical Ventilation Rate of the Dental Treatment Rooms
The volumetric sizes, airflow rates, and ventilation rates of the rooms are presented in Table 1. The rooms are on average 882 ft3 in volume (range 667–1,221 ft3). Air change rate by ventilation varied from 3.9 to 35.0 with a mean of 13.2 ± 10.6 per hour.
Table 1.
Volumetric Sizes and Mechanical Ventilation Rates of Dental Treatment Rooms.
| Room No. | Volume, ft3 | SAF, ft3/min | EAF, ft3/min | ACHS | ACHE | ACHVENT | Floor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 002 | 815 | 82 | 27 | 6.0 | 2.0 | 6.0 | 0 |
| 003 | 787 | 69 | 27 | 5.3 | 2.1 | 5.3 | 0 |
| 008 | 1,221 | 149 | 103 | 7.3 | 5.1 | 7.3 | 2 |
| 012 | 1,015 | 152 | 64 | 9.0 | 3.8 | 9.0 | 2 |
| 019 | 686 | 59 | 400 | 5.2 | 35.0 | 35.0 | 1 |
| 021 | 861 | 75 | 51 | 5.3 | 3.6 | 5.3 | 1 |
| 022 | 833 | 55 | 46 | 3.9 | 3.3 | 3.9 | 1 |
| 031 | 962 | 337 | 210 | 21.0 | 13.1 | 21.0 | 2 |
| 032 | 667 | 289 | 220 | 26.0 | 19.8 | 26.0 | 2 |
| 033 | 970 | 211 | 220 | 13.1 | 13.6 | 13.6 | 2 |
| Mean | 882 | 148 | 137 | 10.2 | 10.1 | 13.2 | N/A |
| SD | 166 | 101 | 122 | 7.6 | 10.6 | 10.6 | N/A |
ACHE, air change per hour based on exhaust airflow rate; ACHS, air change per hour based on supply airflow rate; ACHVENT, air change per hour based on mechanical ventilation; EAF, exhaust airflow rate in cubic feet per minute; N/A, not applicable; SAF, supply airflow rate in cubic feet per minute.
CO2 Levels during Dental Treatment Procedures
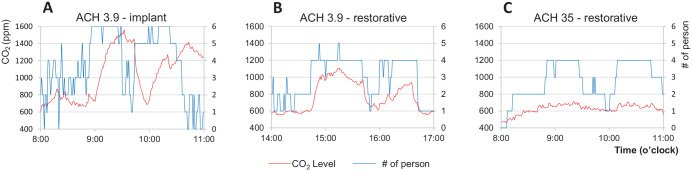
As shown in Figure 1, CO2 levels were significantly higher in the room with low ventilation (less than 4 air change per hour) and reached nearly 1,600 ppm when 6 persons were in the room. The increased number of persons was related to teaching activities involving dental implant surgery where additional graduate students were allowed to observe the procedures. Comparing the 2 rooms with the same number of persons for the same restorative procedures, CO2 levels reached 1,100 ppm at the peak in the room with 3.9 air change per hour but stayed below 700 ppm in the room with 35 air change per hour (P < 0.0001). CO2 accumulation appeared to be associated with crowding and low ventilation rate.
Figure 1.
Carbon dioxide (CO2) levels during dental treatment procedures in operatories with low and high mechanical ventilation. (A) Significant CO2 accumulation occurred in a room with low ventilation (air change per hour [ACH] = 3.9) and multiple persons in the room during clinical teaching activities for dental implant surgery. CO2 level is associated with ventilation rate in rooms with the same number of persons. Peak CO2 level reached 1,100 ppm in the room with 3.9 ACH (B) but stayed under 700 ppm in the rooms with 35 ACH (C).
Continuous CO2 Monitoring in Dental Treatment Rooms
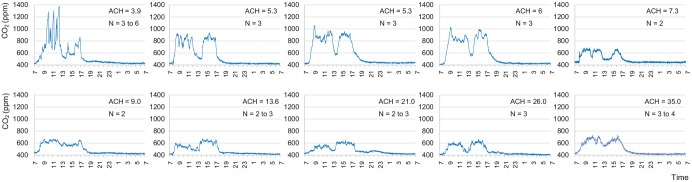
We continuously monitored the CO2 levels for 24 h in the 10 treatment rooms. The dental procedures included exams, hygiene, extractions, restoratives, endodontics, dental implant surgery, and periodontal surgery. Number of persons in the rooms varied from 2 to 6, with more people in the room during dental implant surgeries. The CO2 levels in early morning (5:00–7:00 a.m.) were at a level of 421 ± 10 ppm, similar to outdoor levels (413 ± 15 ppm) (Fig. 2). The steady-state CO2 level (CSS) during dental procedures, which is the mean concentration of CO2 at the plateau level when the number of persons in the room stays unchanged for at least 5 min, ranged from 543 ppm to 1,374 ppm (786 ± 207 ppm) (Appendix Table 1). Multiple regression analysis showed that CO2 levels were significantly correlated to the number of persons in the room (β = 90.2, P = 0.006), ventilation rate (β = 11.0, P = 0.001), and volumetric size of the room (β = −0.50, P = 0.049) but not to outdoor CO2 levels (β = 4.15, P = 0.160).
Figure 2.
The 24-h continuous measurements of carbon dioxide (CO2) levels in 10 dental treatment rooms with various ventilation rates. CO2 accumulation occurred in rooms with lower ventilation rates (air change per hour [ACH] ≤6). CO2 levels stayed under 800 ppm in rooms with a higher ventilation rate and lower number of persons. CO2 level in nonworking hours is close to that of outdoors at 400 ppm in all rooms.
As shown in Figure 2, CO2 levels in rooms with more than 6 air change per hour rarely reached 800 ppm. In rooms with less than 6 air change per hour, however, the CO2 levels were consistently greater than 800 ppm and approached 1,400 ppm in a room with 3.9 air change per hour when number of persons in the room increased.
Ventilation Rates by Steady-State CO2 Level Modeling
Ventilation rates with CO2 generation at 0.30 L/min (ACHSS30) and 0.46 L/min (ACHSS46) were calculated using equation (1) for 2 dental procedures in each room (Appendix Table 1). Both ACHSS30 and ACHSS46 were similarly correlated with ACHVENT (r = 0.83, P = 0.003). ACHSS30 approximated closely to mechanical ventilation rates in rooms with less than 6 air change per hour (mean difference = −0.6, paired t = −1.24, P = 0.304) but significantly underestimated those in rooms with greater than 6 air change per hour (mean difference = −8.7, paired t = −2.59, P = 0.049). The opposite is true for ACHSS46; it significantly overestimated the ventilation rates in rooms with 6 air change per hour or less (mean difference = 3.7, paired t = 6.78, P = 0.007) but approximated closer to those in rooms with greater than 6 air change per hour (mean difference = −3.5, pairedt = −1.14, P = 0.307) (Table 2).
Table 2.
Comparisons between Mechanical Ventilation Rates and Ventilation Rates Estimated from Natural CO2 Levels and CO2 Released by Dry Ice or Baking Soda.
| Room No. | ACHVENT | ACHSS30 | ACHSS46 | ACHDI | ACHBV | ACHDI63 | ACHBV63 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 002 | 6.0 | 5.4 | 8.2 | 5.6 | 6.1 | 5.6 | 6.1 |
| 003 | 5.3 | 6.1 | 9.5 | 4.8 | 4.7 | 4.9 | 4.9 |
| 008 | 7.3 | 4.9 | 7.5 | 5.2 | 6.9 | 6.7 | 6.8 |
| 012 | 9.0 | 6.1 | 9.3 | 9.2 | 9.2 | 9.2 | 9.4 |
| 019 | 35.0 | 11.0 | 16.8 | 28.5 | 27.0 | 30.8 | 27.3 |
| 021 | 5.3 | 5.9 | 9.0 | 4.4 | 4.8 | 4.4 | 5.3 |
| 022 | 3.9 | 5.6 | 8.6 | 3.6 | 4.8 | 4.1 | 4.6 |
| 031 | 21.0 | 11.2 | 17.2 | 17.6 | 16.3 | 17.2 | 16.7 |
| 031 | 26.0 | 16.3 | 24.9 | 19.0 | 22.5 | 17.3 | 22.2 |
| 033 | 13.6 | 10.2 | 15.5 | 14.3 | 15.8 | 14.3 | 16.2 |
| Mean | 13.2 | 12.6 | 8.3 | 11.2 | 11.8 | 11.5 | 11.9 |
| SD | 10.6 | 5.7 | 3.7 | 8.4 | 8.1 | 8.2 | 8.1 |
ACHBV, ventilation rate estimate by carbon dioxide (CO2) decay constants using baking soda and vinegar; ACHBV63, ventilation rate estimate by time needed to remove 63% excess CO2 by baking soda and vinegar; ACHDI, ventilation rate estimate by CO2 decay constants using dry ice; ACHDI63, ventilation rate estimate by time needed to remove 63% excess CO2 by dry ice; ACHSS30, ventilation estimate by steady-state CO2 level with CO2 generation at 0.3 L/min per person; ACHSS46, ventilation estimate by steady-state CO2 level with CO2 generation at 0.46 L/min per person; ACHVENT, mechanical ventilation rate.
As ventilation rate is likely below 6 air change per hour in private dental practices in small freestanding buildings in the United States (Godwin et al. 2003), CO2 generation rate (GP) of 0.30 L/min is more appropriate for ventilation estimates using equation (1). We list the corresponding CO2 levels and ventilation rates in Appendix Table 2. Dental care professionals may use the CO2 levels measured in their treatment rooms to roughly estimate the ventilation rate using this table.
Ventilation Rates by CO2 Decays Using Dry Ice or Baking Soda
Results of ventilation estimates by CO2 decay using dry ice or baking soda are shown in Table 2. CO2 decay curves demonstrate that CO2 levels decreased faster over time in rooms with high air change rate (Fig. 3A, B). ACHDI values ranged from 3.6 to 28.5 (11.2 ± 8.4) and were highly correlated with the mechanical ventilation rate (r = 0.99, P < 0.0001) (Fig. 3C). ACHDI was slightly lower than the mechanical ventilation rate (mean difference = 2.0, paired t = 2.32, P = 0.046). Similarly, ACHBV ranged from 4.7 to 27.0 (11.8 ± 8.1) and also correlated highly with mechanical ventilation rate (r = 0.98, P < 0.0001) (Fig. 3D). There was no statistically significant difference between ACHBV and the mechanical ventilation rate (mean difference = 1.4, paired t = 1.48, P = 0.174) or between ACHBV and ACHDI (mean difference = 0.59, paired t = 1.26, P = 0.239).
Figure 3.
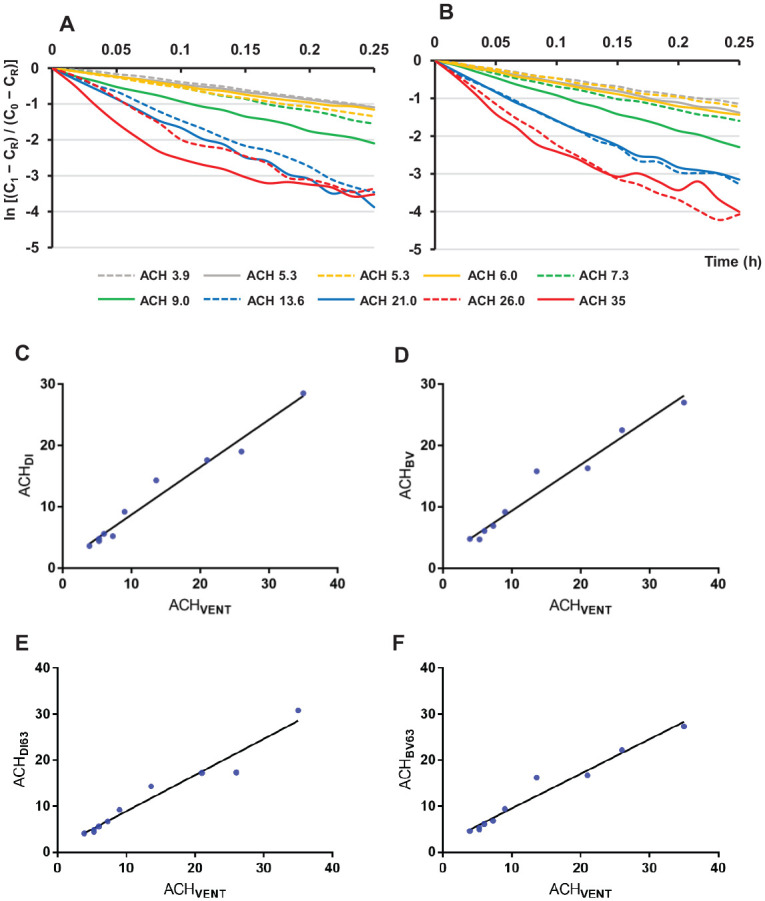
Correlations between ventilation rate and carbon dioxide (CO2) clearance in dental treatment rooms. (A) CO2 decay constants by dry ice and (B) CO2 decay constants by baking soda and vinegar. (C, D) Correlations between mechanical ventilation rates measure by airflow (ACHVENT) and ventilation rates measured by CO2 decay using dry ice (ACHDI) and baking soda and vinegar (ACHBV) in dental treatment rooms. Rooms with high mechanical ventilation rates showed a rapid decrease of CO2 concentrations over time (A, B). Both ACHDI and ACHBV are linearly correlated with ACHVENT (C, D). (E, F) Correlations between ventilation rate by airflow (ACHVENT) and ventilation rates by time needed to reach 63% removal of excess CO2 generated using (E) dry ice (ACHDI63) and (F) baking soda and vinegar (ACHBV63).
Ventilation Rates by Time to 63% Removal of Excess CO2
Ventilation rates calculated by time needed to remove 63% of excess CO2 generated by dry ice or baking soda are presented in Table 2. ACHDI63 values ranged from 4.1 to 30.8 (11.5 ± 8.6) and were highly correlated with the mechanical ventilation rate (r = 0.98, P < 0.0001) (Fig. 3E). There was no statistically significant difference between ACHDI63 and mechanical ventilation rate (mean difference = 1.8, paired t = 1.93, P = 0.086).
Similarly, ACHBV63 ranged from 4.6 to 27.3 (11.9 ± 8.1) and correlated highly with the mechanical ventilation rate (r = 0.98, P < 0.0001) (Fig. 3F). There was no statistically significant difference between ACHBV63 and mechanical ventilation rate (mean difference = 1.3, paired t = 1.34, P = 0.213) or between ACHBV63 and ACHDI63 (mean difference = 0.50, paired t = 0.76, P = 0.467).
In Appendix Table 4, a Microsoft Excel template is provided that will allow dental care professionals to calculate the ventilation rate of their offices by inputting the values of peak CO2 level (CS), outdoor CO2 level (CR), and time (min) needed to reach 63% removal of excess CO2 generated by baking soda (Jimenez 2020).
Discussion
Our findings affirmed that dental operatories with low ventilation rates and overcrowding facilitate CO2 accumulation. Ventilation can be measured by assessing natural or experimental buildup of CO2 levels in dental treatment rooms using a consumer-grade CO2 sensor. Ventilation rates in air change per hour could be accurately assessed by observing CO2 levels after a simple mixing of household baking soda and vinegar in dental settings. Time needed to remove 63% of excess CO2 generated by baking soda could be used to accurately calculate the ventilation rates with the help of a basic calculator.
Our findings show that CO2 level may consistently stay above 800 ppm in rooms with ventilation rates below 6 ACH, especially when 3 or more persons (including the patient who is not wearing a mask) are in the room during dental treatments. We observed that CO2 level stayed above 1,000 ppm and approached 1,600 ppm when 3 to 6 persons were in a room with 3.9 ACH in clinical teaching scenarios. High levels of CO2 indicate high concentrations of respiratory aerosols in the room. It is possible that these aerosols contain pathogens if the patient is not wearing a mask and is infected but asymptomatic or presymptomatic. Effective mitigation measures will be required in these rooms to improve air quality even without the ongoing infectious disease pandemics. Overcrowding should be avoided in rooms with poor ventilation. In dental operatories with ventilation rates higher than 10 ACH, the CO2 levels stayed consistently below 700 ppm in most cases with 3 persons in the room. Our data demonstrated a clear dependency of CO2 levels on number of persons in the room and the ventilation rate. CO2 level is a proxy for indoor air quality as it represents the fraction of rebreathed air, or the proportion of inhaled air that was exhaled by others in the same indoor environment. Although numerous epidemiological studies indicate CO2 begins to have negative health effects at 700 ppm and respiratory symptoms may occur when indoor CO2 is above 1,000 ppm (Azuma et al. 2018), our main concern is the concurrent accumulation of respiratory aerosols that may contain infectious disease pathogens. Numerous studies have shown that exhaled air from infected patients contains respiratory disease pathogens, including rhinovirus, influenza virus, and Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Fabian et al. 2009; Issarow et al. 2015; Lindsley et al. 2016; Yip et al. 2019). Patients with early stages of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) may release millions of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) viral copies per hour in exhaled air (Qian et al. 2020). In a recent study that modeled factors associated with the spread of respiratory infectious disease in dental offices, CO2 levels were found to play the most important role in the risk of disease transmission. CO2 levels at 774 ppm were considered low risk, but those at or above 1,135 ppm may increase the risk of disease transmission in dental offices (Zemouri et al. 2020).
Ventilation rates varied greatly between rooms on the same air handling system due to variations in their sizes and locations and the addition of separate air exhaust fans in some rooms designated for nitrous oxide conscious sedation (Ren et al. 2021). Accurate measurements of ventilation rate in dental settings are important for risk assessment and for risk mitigation planning in an era of frequent infectious disease pandemics. Mechanical ventilation rate is usually assessed by quantifying the amount of outdoor air flowing into and out of an indoor space using highly sophisticated instruments operated by trained professionals (ASHRAE 2017). Technical barriers may have contributed to the scarcity of information regarding ventilation in dental settings. Besides direct airflow measurements, ventilation rate could be estimated using CO2 as a tracer gas. CO2 in an indoor space could be built up to a significantly higher level than in outdoor air, either through natural generation by the occupants or through experimental release of the gas (Cheng and Li 2014; Stuart et al. 2015; Batterman 2017). Analysis of steady-state CO2 levels or the rate of CO2 concentration decays, which are directly dependent on the outdoor airflow rate from the ventilation system, will allow an estimate of the ventilation rate of the indoor space. We found that modeling CO2 levels using equation (1) correlated reasonably well with mechanical ventilation but may either under- or overestimate the ventilation rate based on different assumptions of human CO2 generation rates. In comparison, CO2 concentration decay method relied on actual CO2 levels measured at the beginning and the end of a decay period and provided accurate assessments and better approximation to mechanical ventilation rates. CO2 concentrations in dental operatories could be built up to a level of about 1,500 to 2,500 ppm in 2 min using either dry ice or baking soda. CO2 decays could then be monitored using a CO2 sensor that logs data in 1-min intervals. Many affordable consumer-grade CO2 sensors are readily available and suitable for the purpose of observing CO2 level changes over a period of time. The CO2 sensor used in the present study was purchased online for $159 and appeared to be a reliable tool for measuring CO2 levels in dental settings.
We recommend that mitigation measures be taken for dental operatories that have ventilation rates below 15 ACH, which is required for procedure rooms in outpatient health care facilities by Centers for Disease Control and Prevention guidelines (Chinn et al. 2003). While in theory the most effective measure for air quality improvement in dental offices is to increase outdoor airflow rate through the ventilation system or through natural ventilation by opening doors and windows, such measures are severely limited by the weather or climate conditions. An effective alternative is to improve air filtration using upgraded filters in the ventilation system and portable air cleaners (PACs) equipped with high-efficiency particulate air (HEPA) filters (Ren et al. 2021).
In summary, this study showed that CO2 level in dental treatment rooms could be measured with a simple consumer-grade CO2 sensor and that ventilation rate could be determined by either natural or experimental buildup of CO2 levels in dental settings. Assessing CO2 levels will allow dental care professionals to conveniently and accurately calculate the ventilation rates in their offices and help them to devise an effective strategy for ventilation improvement.
Author Contributions
Q. Huang, contributed to conception, design, data acquisition, and analysis, critically revised the manuscript; T. Marzouk, R. Cirligeanu, contributed to data acquisition, critically revised the manuscript; H. Malmstrom, E. Eliav, contributed to conception, design, and data interpretation, critically revised the manuscript; Y.-F. Ren, contributed to conception, design, data acquisition, analysis, or interpretation, drafted the manuscript. All authors gave final approval and agree to be accountable for all aspects of the work.
Supplemental Material
Supplemental material, sj-pdf-1-jdr-10.1177_00220345211014441 for Ventilation Assessment by Carbon Dioxide Levels in Dental Treatment Rooms by Q. Huang, T. Marzouk, R. Cirligeanu, H. Malmstrom, E. Eliav and Y.-F. Ren in Journal of Dental Research
Acknowledgments
We thank building engineers Dan Mateer and Kevin McLellan at Johnson Control Inc. and mechanical engineers Ray Richard and Karen Pembroke at Facility Operations, University of Rochester Medical Center for their technical expertise and assistance with the present study.
Footnotes
A supplemental appendix to this article is available online.
Declaration of Conflicting Interests: The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Funding: The authors disclosed receipt of the following financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article: This study is supported in part by the Eastman Institute for Oral Health Foundation, Rochester, New York.
ORCID iDs: Q. Huang  https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0891-650X
https://orcid.org/0000-0003-0891-650X
Y.-F. Ren  https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6428-2252
https://orcid.org/0000-0001-6428-2252
References
- ASHRAE. 2007. Ventilation for acceptable indoor air quality. ANSI/ASHRAE Standard 62.1-2007. Atlanta (GA): ASHRAE. p. 1–48. [Google Scholar]
- ASHRAE. 2017. Measurement, testing, adjusting and balancing of building HVAC systems. ASHRAE/ANSI Standard 111-2008 (RA 2017). Atlanta (GA): ASHRAE. [Google Scholar]
- Azuma K, Kagi N, Yanagi U, Osawa H. 2018. Effects of low-level inhalation exposure to carbon dioxide in indoor environments: a short review on human health and psychomotor performance. Environ Int. 121(Pt 1):51–56. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Batterman S. 2017. Review and extension of CO2-based methods to determine ventilation rates with application to school classrooms. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 14(2):145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng PL, Li X. 2014. Air change rate measurements using tracer gas carbon dioxide from dry ice. Int J Vent. 13(3):235–246. [Google Scholar]
- Chinn RY, Sehulster L; CDC; HICPAC. 2003. Guidelines for environmental infection control in health-care facilities; recommendations of CDC and healthcare infection control practices advisory committee (HICPAC). MMWR Recomm Rep. 52(RR-10):1–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fabian P, McDevitt JJ, Lee WM, Houseman EA, Milton DK. 2009. An optimized method to detect influenza virus and human rhinovirus from exhaled breath and the airborne environment. J Environ Monit. 11(2):314–317. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernstrom A, Goldblatt M. 2013. Aerobiology and its role in the transmission of infectious diseases. J Pathog. 2013:493960. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Godwin CC, Batterman SA, Sahni SP, Peng CY. 2003. Indoor environment quality in dental clinics: potential concerns from particulate matter. Am J Dent. 16(4):260–266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harrichandra A, Ierardi AM, Pavilonis B. 2020. An estimation of airborne SARS-CoV-2 infection transmission risk in New York City nail salons. Toxicol Ind Health. 36(9):634–643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmis CG, Tzoutzas J, Flocas HA, Halios CH, Assimakopoulos VD, Stathopoulou OI, Panis V, Apostolatou M. 2008. Emissions of total volatile organic compounds and indoor environment assessment in dental clinics in Athens, Greece. Int Dent J. 58(5):269–278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmis CG, Tzoutzas J, Flocas HA, Halios CH, Stathopoulou OI, Assimakopoulos VD, Panis V, Apostolatou M, Sgouros G, Adam E. 2007. Indoor air quality in a dentistry clinic. Sci Total Environ. 377(2–3):349–365. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Issarow CM, Mulder N, Wood R. 2015. Modelling the risk of airborne infectious disease using exhaled air. J Theor Biol. 372:100–106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jimenez J-L. 2020. How to quantify the ventilation rate of an indoor space using an affordable CO2 monitor [accessed 2021 Feb 4]. https://medium.com/@jjose_19945/how-to-quantify-the-ventilation-rate-of-an-indoor-space-us ing-a-cheap-co2-monitor-4d8b6d4dab44.
- Lindsley WG, Blachere FM, Beezhold DH, Thewlis RE, Noorbakhsh B, Othumpangat S, Goldsmith WT, McMillen CM, Andrew ME, Burrell CN, et al. 2016. Viable influenza A virus in airborne particles expelled during coughs versus exhalations. Influenza Other Respir Viruses. 10(5):404–413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myatt TA, Johnston SL, Zuo Z, Wand M, Kebadze T, Rudnick S, Milton DK. 2004. Detection of airborne rhinovirus and its relation to outdoor air supply in office environments. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 169(11):1187–1190. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nardell EA, Keegan J, Cheney SA, Etkind SC. 1991. Airborne infection: theoretical limits of protection achievable by building ventilation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 144(2):302–306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persily A, de Jonge L. 2017. Carbon dioxide generation rates for building occupants. Indoor Air. 27(5):868–879. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi MW, Li XF, Weschler LB, Sundell J. 2014. CO2 generation rate in Chinese people. Indoor Air. 24(6):559–566. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qian H, Miao T, Liu L, Zheng X, Luo D, Li Y. 2020. Indoor transmission of SARS-CoV-2. Indoor Air [epub ahead of print 31 Oct 2020]. doi: 10.1111/ina.12766 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ren Y-F, Huang Q, Marzouk T, Richard R, Pembroke K, Martone P, Venner T, Malmstrom H, Eliav E. 2021. Effects of mechanical ventilation and portable air cleaner on aerosol removal from dental treatment rooms. J Dent. 105:103576. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richardson ET, Morrow CD, Kalil DB, Ginsberg S, Bekker LG, Wood R. 2014. Shared air: a renewed focus on ventilation for the prevention of tuberculosis transmission. PLoS One. 9(5):e96334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudnick SN, Milton DK. 2003. Risk of indoor airborne infection transmission estimated from carbon dioxide concentration. Indoor Air. 13(3):237–245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart R, Sweet E, Batchelder A. 2015. Assessing general ventilation effectiveness in the laboratory. J Chem Health Saf. 22(2):2–7. [Google Scholar]
- Wood R, Morrow C, Ginsberg S, Piccoli E, Kalil D, Sassi A, Walensky RP, Andrews JR. 2014. Quantification of shared air: a social and environmental determinant of airborne disease transmission. PLoS One. 9(9):e106622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yip L, Finn M, Granados A, Prost K, McGeer A, Gubbay JB, Scott J, Mubareka S. 2019. Influenza virus RNA recovered from droplets and droplet nuclei emitted by adults in an acute care setting. J Occup Environ Hyg. 16(5):341–348. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zemouri C, Awad SF, Volgenant CMC, Crielaard W, Laheij AMGA, de Soet JJ. 2020. Modeling of the transmission of coronaviruses, measles virus, influenza virus, Mycobacterium tuberculosis, and Legionella pneumophila in dental clinics. J Dent Res. 99(10):1192–1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Supplemental material, sj-pdf-1-jdr-10.1177_00220345211014441 for Ventilation Assessment by Carbon Dioxide Levels in Dental Treatment Rooms by Q. Huang, T. Marzouk, R. Cirligeanu, H. Malmstrom, E. Eliav and Y.-F. Ren in Journal of Dental Research