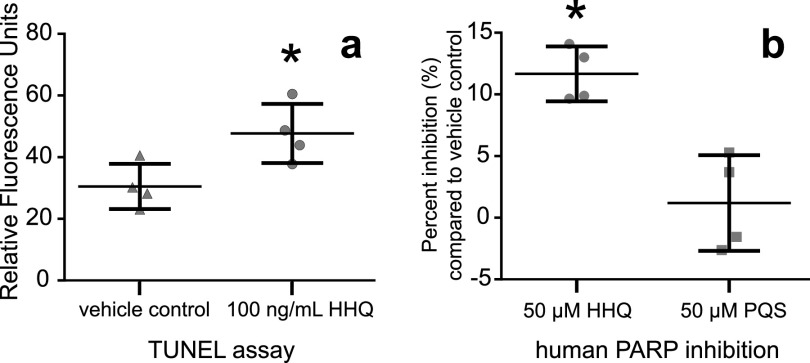
FIG 4.
Exposure to HHQ leads to cellular DNA damage and inhibition of human PARP. (a) Cultures (n = 4) of E. huxleyi were exposed to 100 ng ml−1 HHQ or the vehicle control (DMSO) for 46 h before pigments were removed and cells were stained using an in vivo TUNEL assay to detect the presence of DNA ends, a proxy for DNA breaks. (b) Inhibition of the human PARP-1 enzyme by 50 μM HHQ and 2-heptyl-3-hydroxy-4(1H)-quinolone (PQS). Percent PARP inhibition was measured using the PARP universal colorimetric assay kit (R&D Systems). The absorbance values for quadruplicate wells containing HHQ or PQS were compared to those of the vehicle control, and this ratio was subtracted from 100% to determine PARP inhibition. Points represent individual replicates. Asterisks indicate a significant difference between the treatment and the vehicle control (P value of <0.05 by Welch’s approximate t test).