Abstract
Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors such as sildenafil citrate and tadalafil are well known for the treatment of erectile dysfunction. However, their use in the presence of pulmonary hypertension can cause ophthalmologic side effects, including non-arteritic optic ischemic neuropathy, chorioretinopathy, glaucoma, and optic atrophy. The present review aimed to identify these visual side effects and provide recommendations. We identified articles published from January 2000 to March 2019 on diseases arising from the management of sexual dysfunction in urology or pulmonary hypertension in pneumonia that could cause pathologic alterations in eye structure based on a literature search of the MEDLINE electronic database using keywords for the most common adverse effects and different kinds of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors. After applying the exclusion criteria, we selected 36 of the 77 articles initially identified to write the narrative review and added 20 additional articles to completely describe the pathological entities. Phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors can cause side effects in the eye including ocular surface abnormalities, increased intraocular pressure and glaucoma, uveitis, non-arteritic ischemic neuropathy, chorioretinopathy, retinal occlusion, and visual field changes. There is an increased need for well-performed studies to better understand these side effects, which are common due to the wide use of sildenafil.
Keywords: Adverse Effects, Eye Manifestations, Physiological, Review, Sexual Dysfunction, Sildenafil Citrate
INTRODUCTION
Erectile dysfunction (ED) is defined as a persistent inability to achieve and/or maintain an erection to allow satisfactory sexual relations. It is a prevalent condition, with over 18 million men affected worldwide. ED affects an estimated 9.1% of men aged 40–49 years, 15.2% of men aged 50–59 years, 29.4% of men aged 60–69 years, and 54.9% of men older than 70 years.[1] The first line of treatment for ED is phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitors (PDE5i). This drug was first developed to treat pulmonary hypertension and muscle spasms; however, its most notable side effect, prolonged erection, soon became the focus of its use in clinical practice. In 1998, the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved its use as a clinically effective and safe treatment for ED.[2]
There are 11 types of PDEs, all of which function to degrade cyclic adenosine monophosphate (AMPc) to adenosine monophosphate (AMP) and GMPc to guanosine monophosphate (GMP).[3] Sildenafil citrate (SC), a selective inhibitor of PDE5i present in the cavernous bodies in the penis, is responsible for smooth muscle relaxation and, consequently, inducing an erection.[1] PDE5i can cross the blood–brain and blood–retinal barriers and may partially inhibit the PDE 6 enzyme present in the retina, with significant dose-dependent changes in photoreceptors and the optical nerve.[4,5,6] The main contraindication for the use of PDE5i is its concomitant use with nitrates, which can lead to hypotension and ischemic events.[4]
The main reported side effects of PDE5i are headaches, dizziness, blushing, nasal congestion, dyspepsia, and visual changes. The most common visual side effects are photophobia, cyanopsia, and haze. Most of the visual effects can be reversed weeks after stopping use of the medication.[3] Other ophthalmologic disturbances described in the literature include keratitis, ocular surface abnormalities, chorioretinopathy, vessel occlusion, retinal detachment, and optic neuropathy.[1,4,5,7]
Considering the wide use of PDE5i, clinicians should know its side effects profile. This study reviewed the most common ocular effects related to the use of PDE5i.
METHODS
A literature search was conducted through the MEDLINE online electronic database for articles written in English published from January 2000 to March 2019. The reason to delimitate the research to this period was to evaluate recent developments regarding PDE5i and their side effects. Thus, this review aimed to perform a current, but thorough, analysis of published articles. We used the following descriptors in sequence, all of which had to be present in the title of the article: (1) Keratitis OR (2) Surface Abnormalities OR (3) Chorioretinopathy OR (4) Ocular OR (5) Intraocular Pressure OR (6) Glaucoma OR (7) Non-arteritic Anterior Ischemic Optic Neuropathy OR (8) Retinal Occlusion OR (9) Optic Atrophy OR (10) Visual Changes OR (11) Electroretinography OR (12) Uveitis OR (13) Retinal AND (14) Sildenafil AND (15) Phosphodiesterase 5 Inhibitors AND (16) Tadalafil AND (17) Viagra AND (18) Vardenafil AND (19) Avanafil AND (20) Udenafil AND (21) Mirodenafil AND (22) Lodenafil AND 2000/01/01: 2019/03/31. The keywords from 1 to 13 were searched again with AND 14 added; the same process was performed to add keywords 15 to 22.
RESULTS
We selected 36 of the 77 articles initially identified for the literature review, including both clinical and experimental studies. We also included 20 additional articles to completely describe the pathological entities [Figure 1]. We analyzed the articles for the inclusion and exclusion criteria. The inclusion criteria were articles that had in their titles at least one combination of the descriptors in the search strategy, publications written in the English language, and relevant content in the article regarding the research topic. The exclusion criteria were articles that had in the title or abstract nonophthalmic PDE adverse effects related to PDE5i use; reviews and book chapters; non-original studies including editorials, exam alteration studies, preface and brief communication; duplicate articles, articles written in a language other than English; and unavailable study abstract or full text. We added two studies related to non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) since our search method identified few studies. Furthermore, we also included 13 letters to editors that described important side effects. We did not find optic atrophy studies related to our topic; similarly, no studies on mirodenafil, udenafil, or lodenafil were identified. Each retrieved article was carefully read and checked for relevance before being included in the review [Figure 1].
Figure 1.
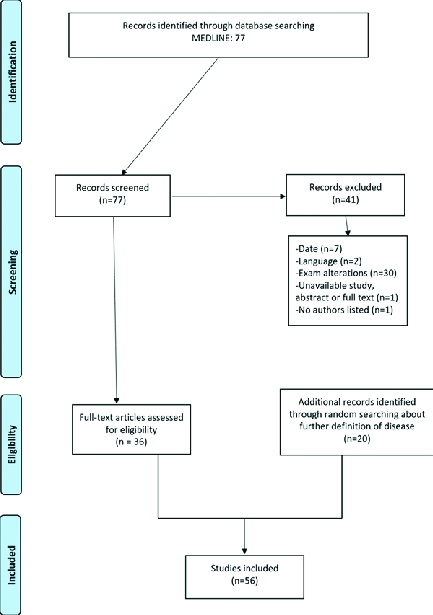
Inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Table 1.
The best studies for each category
|
| ||||
| Finding | Authors | Concise Methods | Brief Outcomes | Strength of Evidence |
| Chart 1: Studies Related to Intraocular Pressure Alterations | ||||
| Increased intraocular pressure | Nazari et al. 2017[20] | -110 patients -Weekly sildenafil of 50mg average dose after 3 months | -Significantly differences between intraocular pressure values -p=0,003 | -Grade B |
| Wirostko et al. 2012[15] | -277 adults | - Changes in Intraocular Pressure mean showed in 95% confidence interval (CI) | -Grade B | |
| Ermis et al. 2004[25] | -28 male volunteers | -No significantly changes in intraocular pressure -p=0.37 | -Grade B | |
| Dündar et al. 2001[26] | -14 healthy male volunteers | - No significantly changes in intraocular pressure | Grade B | |
| No Increased intraocular pressure | Yajima et al. 2000[24] | -Study 1with 16 subjects and study 2with 48 subjects | -No major changes | - Grade B |
| Chart 2: Other Surface Abnormalities | ||||
| Finding | Authors | Concise Methods | Brief Outcomes | Strength of Evidence |
| Surface abnormalities | Matieli et al 2016[8] | -Case control with eyes in case group and 13 eyes in control group | -28 eyes (70%) using sildenafil, while only 13 eyes (35%) in the group control | - Grade B |
| Chart 3: Keratitis | ||||
| Finding | Authors | Concise Methods | Brief Outcomes | Strength of Evidence |
| -Keratitis | Matieli et al 2016[8] | -Case control with 20 patients | -One-third of individuals | - Grade B |
| Chart 4: Chorioretinopathy | ||||
| Finding | Authors | Concise Methods | Brief Outcomes | Strength of Evidence |
| Central Serous Chorioretinopathy | Turkuc et al 2013[11] | -43 patients treated | -Sildenafil citrate did not lead to Central Serous Chorioretinopathy | -Grade B |
| Chart 5: Uveitis | ||||
| Finding | Authors | Concise Methods | Brief Outcomes | Strength of Evidence |
| Uveitis | French et al[12] | -Case report | - 6 episodes of uveitis | - Grade C |
| Pomeranz et al[34] | -Literature review | - 40 case report studies reported | - Grade C | |
| Galvez-Ruiz et al[36] | -Case series | - 10 patients who after regular intake of Sildenafil presented in 1 eye | - Grade C | |
| NAION | Gedik et al[37] | -Case report | - 36-year-old male who presented blurry vision in his left eye after 100 mg Sildenafil intake | - Grade C |
| Hafidi et al[38] | - Case report | - 40-year old man with vision loss after 100 mg Sildenafil for two consecutive days | - Grade C | |
| Pomeranz et al[39] | - Case series | - 5 patients presented after ingestion of 50 to 100 mg of Sildenafil | - Grade C | |
| Pomeranz et al[40] | -Case series | - 6 of 7 patients who took Sildenafil presented vision loss within 24 hours | - Grade C | |
| Chart 7: Retinal Vessel Occlusion | ||||
| Finding | Authors | Concise Methods | Brief Outcomes | Strength of Evidence |
| Supratemporal retinal artery branch occlusion | Tripathi et al[33] | -Case report | 69-year-old male who presented with sudden painless vision loss after two days of Sildenafil 100 mg intake | -Grade C |
| Cilioretinal artery occlusion | Hafidi et al[38] | -Case report | -40-year-old male who presented with acute vision loss after 2 days of Sildenafil 100 mg intake | -Grade C |
| Murthy et al[47] | -Case report | -Bilateral concurrent cilioretinal artery occlusion in a 37-year-old female patient after once daily for four weeks | -Grade C | |
| Cilioretinal vessel occlusion | Pinto et al[49] | -Case report | -36-year-old male presented with cilioretinal vessel occlusion | -Grade C |
| Chart 8: Visual Change | ||||
| Finding | Authors | Concise Methods | Brief Outcomes | Strength of Evidence |
| -Color discrimination alterations | Cordell et al[56] | -Clinical trial | - Any significant evidence after compared Sildenafil intake for 6 months daily | -Grade A |
We divided the visual side effects into the following categories: keratitis, other surface abnormalities, chorioretinopathy, intraocular pressure and glaucoma, uveitis, NAION, and retinal occlusion. We described each category in different sections; namely, epidemiology and pathophysiology, clinical presentation, literature review, and final statement recommendation.
DISCUSSION
Keratitis
Epidemiology and pathophysiology
In less developed countries, infectious keratitis affects about 10% of the population. Eye injury during agricultural work may predispose infectious agents to cause keratitis. In developed countries, the main cause of this condition is the use of contact lenses.
Clinical presentation
Keratitis presents intense itching accompanied by redness, pain, photophobia, red eye, and a “gritty” sensation.[4]
Literature review
We did not find any association between PDE5i use for ED and keratitis. However, a case–control study that evaluated ocular toxicity in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH) reported a higher incidence of keratitis following chronic SC use. Twenty patients in each group were administered SC from 1 to 60 months at daily doses of 60 mg, except for two patients treated with 120 mg per day. One-third of PAH individuals using SC had severe noninfectious bilateral keratitis. Such patients were not contact lens users. A multivariate analysis using a linear regression model showed that dry eye keratitis was significantly associated with SC use. The patients had no other risk factors for dry eye, suggesting that SC use was possibly the main cause of keratitis in these patients.[8]
Final statement recommendation
Patients who will start chronic PDE5i use and have complaints of dry eye or who use contact lenses should be counseled about an increased risk of keratitis. Referral for routine ophthalmic assessment and use of Preservative-free tear substitutes should be considered.[8]
Other Surface Abnormalities
Epidemiology and pathophysiology
Dry eye disease (DED) is the most common disorder related to surface abnormalities and has been associated with a wide range of traits, including systemic and metabolic conditions.
Clinical presentation
Dryness, burning, itching, watering, stickiness, and crustiness.[9]
Literature review
Only one article was identified related to this topic. In the same case–control study that evaluated ocular toxicity in PAH patients using SC, all participants presented ocular motility, contrast sensitivity, color vision, Schirmer test, intraocular pressure (IOP), and optical coherence tomography (OCT) within the normal ranges. At least one of these other abnormalities of the ocular surface (tarsal gland dysfunction, conjunctival hyperemia, cornea verticillata, and decreased rupture time) were present in 28 eyes (70%) using SC, compared to only 13 eyes (35%) in the control group. Considering the presence of at least one abnormality in biomicroscopy, SC users (40 eyes of 20 patients) had a statistically higher occurrence of anterior superficial anomalies (Fisher's test p = 0.012).[8]
Final statement recommendation
Patients with PAH chronically treated with SC should undergo routine ophthalmologic evaluations to identify ocular surface abnormalities.[8]
Chorioretinopathy
Epidemiology and pathophysiology
Central serous chorioretinopathy (CSC) typically affects men and women between their third and sixth decades of life.[11] The major risk factors are the state of refraction, systemic hypertension, male sex, older age, black ethnicity, and use of corticosteroids.[10]
Clinical presentation
CSC presents as a painless dark, blurred, distorted, dimmed area in the central vision.[11]
Literature review
Two articles on this topic found no association between SC use and CSC. In a prospective study, 43 patients with a mean age of 49.1 years (range 28–67) were treated for ED with SC (50 mg two to three times per week for one month). The patients were evaluated in the first week and at the end of treatment. Macular thickness and volume assessments with OCT did not differ significantly in the central and parafoveal areas (p 0.05). The study concluded that SC in therapeutic doses did not lead to CSC and visual abnormality.[11] French et al[12] studied 577 men aged 59 years and younger with newly diagnosed CSC. To avoid confounding factors, this study did not include individuals with age-related macular degeneration and history of corticosteroid use. The authors found that 111 patients (19.2%) were prescribed PDE5i before CSC onset, and most (99%) were administered SC doses of 100 mg or more [odds ratio: 1.05, 95% confidence interval (CI): 0.74–1.22].[12] In contrast, Gordon-Bennett et al[13] reported an inkblot appearance near the fovea in a 51-year-old male patient 24 hr following the ingestion of more than 20 mg tadalafil.
Final statement recommendation
Patients who are about to start ED treatment with PDE5i should be advised to consult an ophthalmologist in case they experience vision problems.[11]
Intraocular Pressure and Glaucoma
Epidemiology and pathophysiology
The global prevalence of glaucoma was over 57 million individuals in 2015 and is expected to increase to over 65 and 111 million individuals by 2020 and 2040, respectively. Angle closure and reduction of ocular blood flow are additional mechanisms for the development of glaucoma, which can be triggered by the systemic use of vasodilators, including some PDE5i.[14,15,16,17]
Clinical presentation
In primary open-angle glaucoma, which is the most common type of glaucoma, the patient is usually oligosymptomatic and visual changes are present only in advanced stages. In acute-angle glaucoma, sudden visual pain followed by nausea and vomiting is usually the initial presentation.[18]
Literature review
Nine articles discussed this topic. Some authors reported increased IOP after SC use.[19] Nazari et al[20] reported increased mean IOP after three months in 110 patients aged 42–60 years with weekly SC doses of 25–100 mg (p = 0.002).[20] Furthermore, Chen et al[21] evaluated the prevalence of self-reported glaucoma in a telephone-based interview in men aged over 40 years. They found that 482 of 7,081 participants reported a diagnosis of glaucoma and the use of SC in the previous year. However, the dose and frequency of PDE5i intake were not investigated.[21] Gerometta et al[22] studied nine healthy male and female volunteers aged 18–74 years, in which the IOP increased 60 min after SC administration (p 0.005) and returned to the control values within 2 hr.[22] Gerometta et al[23] also demonstrated increased IOP in 21 normal sheep after ingestion of both SC (50 and 100 mg) and tadalafil. Other research has shown no association between SC use and IOP increase. Yajima et al[24] did not detect any major changes in IOP 24 hr after the oral administration of 10–150 mg SC I. Furthermore, Wirostko et al[15] reported no changes in IOP among 277 adults with idiopathic PAH in a double-blind study using oral SC (20, 40 or 80 mg) or placebo (1:1:1:1) three times daily for 12 weeks.[15] Ermis et al[25] failed to show any significant effects of SC use on IOP in 28 healthy volunteers with a mean age of 51 years receiving SC (50 and 100 mg).[25] Moreover, in a double-blind, randomized, placebo-controlled, crossover study, Grunwald et al[16] reported no significant acute changes on IOP after a single oral dose of SC l 100 mg in 15 subjects aged 63 14 years with bilateral chronic open-angle glaucoma.[16] Dündar et al[26] also showed no change in IOP after the administration of a single oral dose of 50 mg SC to 14 healthy male volunteers tested immediately before and 1 hr after SC administration.[26]
Final statement recommendation
There is a lack of prospective randomized trials to determine whether there is a true causal association between PDE5i use and elevation of IOP leading to glaucoma development or deterioration. However, it is advisable to monitor IOP periodically in high-risk patients[20] [Table 1].
Uveitis
Epidemiology and pathophysiology
The prevalence of idiopathic uveitis is similar in studies from different countries. Although the understanding of the pathogenesis of uveitis is evolving, approximately 24–55% of patients with uveitis have idiopathic or undifferentiated uveitis.[27]
Clinical presentation
Uveitis is an intraocular inflammation due to an inflammation of the uvea presenting as redness and swelling of the uvea.[28]
Literature review
Only one article discussed this topic. The association of PDE5i and the onset of uveitis is limited to one case report, which described a 38-year-old man diagnosed with Behçet's disease 15 years prior and without any occurrence of uveitis for the past 12 years. After starting SC for ED, he developed recurrent posterior uveitis in his left eye. The uveitis episode started after the second or third dose of SC, with a total of six episodes.[29]
Final statement recommendation
Patients with ED who plan to start PDE5i should be informed of the risk for ocular side effects. If a recurrence of ocular symptoms is observed concomitant to PDE5i intake, patients should be informed to stop treatment.[29]
NAION
Epidemiology and pathophysiology
The annual incidence of NAION is 1 in 10,000 cases and affects men and women equally. It is more common in Caucasians than in African, American, and Hispanic descendants. NAION is a multifactorial disorder[30] and is believed to be related to vascular insufficiency in the optic nerve head. The condition is also associated with short posterior ciliary artery dysfunction. However, the mechanisms related to the vasculopathy and ischemia remain unclear and there is no consensus regarding the possible associations between NAION and PDE5i.[31,32]
Clinical presentation
The primary presentation includes acute, painless, unilateral visual loss, which confers an increased risk of contralateral vision loss. The condition may worsen over hours or days, with optic disc edema and an afferent pupillary defect. Altitudinal defects are a more common presentation in the visual field.[16,33]
Literature review
In their literature review, Pomeranz et al[34] described 40 case reports of NAION. Posterior ischemic optic neuropathy was also related to SC use in some letters to the editor.[30,35] Galvez-Ruiz et al[36] reported a series of 10 patients who presented with NAION with routine exposure to SC (2–3 times per week) during the weeks and months before the ocular ischemia. NAION was diagnosed based on clinical presentations, fundus features consistent with NAION, and exclusion of other possible etiologies. Half of the patients in the study had a primary episode of unilateral ischemic optic neuropathy. Despite the initial adverse event (first episode of NAION), all patients continued to use the medication and developed a second episode of NAION in the contralateral eye. Only 1 of the 10 patients presented with bilateral simultaneous NAION.[36] Another report described a 36-year-old male patient presenting with blurred vision in his left eye and afferent pupillary defect after the ingestion of 100 mg of SC. Funduscopy revealed hyperemia and edema in the lower portion of the left optic disc.[37] Hafidi et al[38] reported an acute unilateral visual loss in a previously healthy 40-year-old man after ingestion of 100 mg SC for two consecutive days before the onset of this visual symptom. In this particular case, SC was associated with NAION and cilioretinal and central retinal vein occlusion (CRVO).[38] Pomeranz et al[39] (2002) reported on five patients ranging in age from 42 to 69 years after SC ingestion. They demonstrated the characteristic findings of NAION, including altitudinal visual field loss and associated optic disc and/or peripapillary hemorrhages. Pomeranz et al[39] later reported on seven patients aged 50–69 years who had typical symptoms of NAION within 36 hr after the ingestion of SC for ED.[37,40] However, in a cohort of 8,893 patients prescribed SC by their primary care physicians in England between April and June 1999, NAION was reported only in a 61-year-old patient who had other risk factors for NAION; thus, it was not possible to confirm any association between SC and NAION.[40,41] However, Peter et al[42] reported an NAION case in a patient with no known vasculopathy risk factors.
Final statement recommendation
A history of NAION should be an absolute contraindication to PDE5i therapy[43] and patients who are at higher risk for NAION (such as small cup-to-disc ratio and systemic arterial hypertension) should be counseled and undergo ophthalmologic assessments.[35,38,44]
Retinal Vessel Occlusion
Epidemiology and pathophysiology
Central retinal artery occlusion (CRAO) occurs in an estimated 1 in 100,000 individuals in the general population and accounts for 1 in 10,000 ophthalmological outpatient visits.[45] An embolism is the most common cause of CRAO.[46]
Clinical presentation
CRAO appears as a sudden, catastrophic visual loss.[46]
Literature review
Tripathi et al[33] reported a case of a 69-year-old man presenting with a sudden painless loss of vision in the left eye two days previously. Fundus examination of the right eye was normal whereas the left eye showed a supratemporal branch retinal artery occlusion. As the patient did not have any of the risk factors for arterial occlusion, a more detailed history was sought. The patient indicated that he had taken SC (100 mg) a few hours before he experienced the loss of vision in his left eye.[33] Murthy et al[47] reported a case of bilateral concurrent CRAO in a 37-year-old female African–American patient with sickle cell disease and PAH. She had been treated with tadalafil (40 mg) once daily for four weeks. Fluorescein angiography (FA) revealed delayed transit time with areas of blocked fluorescence due to retinal edema,[48] and spectral-domain OCT revealed inner retinal edema in the macula.[47] Hafidi et al[38] reported a case of CRAO and CRVO observed by OCT and FA. The 40-year-old male patient was previously healthy and presented with acute visual loss of the left eye after two days of 100 mg SC use.[47] Pinto et al[49] reported a case of a 36-year-old man with chronic renal failure who was diagnosed with CRVO by FA after ingesting 100 mg SC.
Final statement recommendation
Acute and severe complaints should alert clinicians to CRAO. Patients with increased risks for thromboembolic events should be counseled about CRAO. Despite the anecdotal cases, it is not possible to establish a link between PDE5i use and CRAO.[47,50]
Visual Changes
Epidemiology and pathophysiology
Most cases of visual changes after PDE5i are believed to be dose dependent and lead to mild alterations in the visual system. These alterations lead to complaints of blue-tinged vision and increased brightness perception.[51] SC also inhibits phosphodiesterase type 6 (PDE6),[52] an essential enzyme involved in the activation and modulation of the phototransduction cascade, impairing the ability of PDE6 to shorten the time of integration between the visual system and light level.[53] The sensitivity of SC for PDE6 isoenzymes is thought to be the basis for the reduced electrophysiological response on electroretinograms (ERG) in patients prescribed 50 mg SC, as well as the transient color vision abnormalities more likely to be observed with higher doses of SC.[54]
Clinical presentation
Patients report changes related to color perception.[55]
Literature review
In a comparative case series study, Matieli et al[8] analyzed the visual effects of SC use for PAH by assessing symptoms such as bluish vision, photophobia, and green or blue or yellow patterns on Farnsworth D15-Color Test Saturated Panels. SC was used from 1 to 60 months. The SC user and control groups included 17 women each. One-third of the treated group showed severe bilateral keratitis. In contrast, Cordell et al[56] randomized 244 subjects to receive tadalafil (5 mg, 85 patients), SC (50 mg, 77 patients), or placebo (82 patients) daily for six months. No significant differences in the visual function of color discrimination by the Farnsworth–Munsell 100-Hue Color Vision Test were observed between the treatment and placebo groups.[56]
Final statement recommendation
Despite its low occurrence, patients should be counseled about transient color changes associated with PDE5i use for ED or PAH.[8]
SUMMARY
PDE5i are one of the most prescribed drugs worldwide, with a very good safety profile. However, NAION, chorioretinopathy, and color changes are important issues reported in the literature. Although these visual side effects have been reported in patients using PDE5i, there is not enough evidence to prove a causal association. Given the low incidence of such side effects, these should not preclude the usual indications for PDE5i. However, patients with histories of ophthalmologic conditions or optic nerve issues or those at high risk for any eye disease require specific clearance before the commencement of therapy.
Financial Support and Sponsorship
Nil.
Conflicts of Interest
There is no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank Federal University of Ceara and Christus University Center for collaboration and Editage (www.editage.com) for English language editing.
References
- 1.Selvin E, Burnett AL, Platz EA. Prevalence and risk factors for erectile dysfunction in the US. Am J Med 2007;120:151–157. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 2.Kehat R, Bonsall DJ, North R, Connors B. Ocular findings of oral sildenafil use in term and near-term neonates. J AAPOS 2010;14:159–162. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 3.Sowka JW, Neiberg MN, Vollmer LA. Optic atrophy after sildenafil use. Optometry 2007;78:122–128. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 4.Hom MM, Nguyen AL, Bielory L. Allergic conjunctivitis and dry eye syndrome. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol 2012;108:163–166. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 5.Keay L, Stapleton F, Schein O. Epidemiology of contact lens-related inflammation and microbial keratitis: a 20-year perspective. Eye Contact Lens 2007;33:346–353, discussion 62–63. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 6.Gupta N, Tandon R, Gupta SK, Sreenivas V, Vashist P. Burden of corneal blindness in India. Indian J Community Med 2013;38:198–206. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 7.Nirmalan PK, Katz J, Tielsch JM, Robin AL, Thulasiraj RD, Krishnadas R, et al. Ocular trauma in a rural south Indian population: the Aravind Comprehensive Eye Survey. Ophthalmology 2004;111:1778–1181. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 8.Matieli L, Berezovsky A, Salomao SR, Allemann N, Martins EN, Hirai FE, et al. Ocular toxicity assessment of chronic sildenafil therapy for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 2016;254:1167–1174. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 9.The definition and classification of dry eye disease: report of the Definition and Classification Subcommittee of the International Dry Eye WorkShop (2007). Ocul Surf 2007;5:75–92. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 10.Damar E, Toklu Y, Tuncel A, Balci M, Aslan Y, Simsek S, et al. Does therapeutic dose of sildenafil citrate treatment lead to central serous chorioretinopathy in patients with erectile dysfunction? Am J Mens Health 2013;7:439–443. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 11.Turkcu FM, Yuksel H, Sahin A, Murat M, Bozkurt Y, Caca I. Central serous chorioretinopathy due to tadalafil use. Int Ophthalmol 2013;33:177–180. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 12.French DD, Margo CE. Central serous chorioretinopathy and phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitors: a case-control postmarketing surveillance study. Retina 2010;30:271–274. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 13.Gordon-Bennett P, Rimmer T. Central serous chorioretinopathy following oral tadalafil. Eye 2012;26:168–169. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 14.Kapetanakis VV, Chan MP, Foster PJ, Cook DG, Owen CG, Rudnicka AR. Global variations and time trends in the prevalence of primary open angle glaucoma (POAG): a systematic review and meta-analysis. Br J Ophthalmol 2016;100:86–93. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 15.Wirostko BM, Tressler C, Hwang LJ, Burgess G, Laties AM. Ocular safety of sildenafil citrate when administered chronically for pulmonary arterial hypertension: results from phase III, randomised, double masked, placebo controlled trial and open label extension. BMJ 2012;344:e554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 16.Grunwald JE, Jacob SS, Siu K, Piltz J, Dupont J. Acute effects of sildenafil citrate (Viagra) on intraocular pressure in open-angle glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 2001;132:872–874. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 17.Lee WJ, Seong M. Sildenafil citrate and choroidal thickness. Retina 2011;31:1742; author reply -3. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 18.Garg A, Gazzard G. Selective laser trabeculoplasty: past, present, and future. Eye 2018;32:863–876. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 19.Ramasamy B, Rowe F, Nayak H, Peckar C, Noonan C. Acute angle-closure glaucoma following sildenafil citrate-aided sexual intercourse. Acta Ophthalmol Scand 2007;85:229–230. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 20.Nazari A, Tabrizi YT, Mokhtaree M. Effect of periodic sildenafil dosage on intraocular pressure in patients with erectile dysfunction. Electron Physician 2017;9:5229–5232. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 21.Chen SP, Singh K, Lin SC. Use of phosphodiesterase inhibitors and prevalence of self-reported glaucoma in the United States. PLoS ONE 2017;12:e0183388. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 22.Gerometta R, Alvarez LJ, Candia OA. Effect of sildenafil citrate on intraocular pressure and blood pressure in human volunteers. Exp Eye Res 2011;93:103–107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 23.Gerometta R, Alvarez LJ, Candia OA. Effects of sildenafil and tadalafil on intraocular pressure in sheep: implications for aqueous humor dynamics. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2010;51:3139–3144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 24.Yajima T, Yajima Y, Koppiker N, Grunwald JE, Laties AM. No clinically important effects on intraocular pressure after short-term administration of sildenafil citrate (Viagra). Am J Ophthalmol 2000;129:675–676. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 25.Ermis SS, Inan UU, Samli M, Ozturk F. Acute effects of sildenafil on Humphrey visual field and intraocular pressure. Int Ophthalmol 2004;25:69–72. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 26.Dundar SO, Dundar M, Kocak I, Dayanir Y, Ozkan SB. Effect of sildenafil on ocular haemodynamics. Eye 2001;15:507–510. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 27.Han YS, Rivera-Grana E, Salek S, Rosenbaum JT. Distinguishing uveitis secondary to sarcoidosis from idiopathic disease: cardiac implications. JAMA Ophthalmol 2018;136:109–115. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 28.Krishna U, Ajanaku D, Denniston AK, Gkika T. Uveitis: a sight-threatening disease which can impact all systems. Postgrad Med J 2017;93:766–773. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 29.Isik M, Kilic L, Dogan I. Recurrent uveitis due to sildenafil usage in a patient with Bechet's disease. Rheumatol Int 2013;33:803. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 30.Su DH, Ang PS, Tow SL. Bilateral posterior ischemic optic neuropathy associated with use of sildenafil. J Neuroophthalmol 2008;28:75. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 31.Li A, Li L, Li M, Shi X. A new characterization for nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Int J Clin Exp Med 2015;8:18681–18688. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 32.Boshier A, Pambakian N, Shakir SA. A case of nonarteritic ischemic optic neuropathy (NAION) in a male patient taking sildenafil. Int J Clin Pharmacol Ther 2002;40:422–423. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 33.Tripathi A, O'Donnell NP. Branch retinal artery occlusion; another complication of sildenafil. Br J Ophthalmol 2000;84:934–935. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 34.Pomeranz HD. Erectile dysfunction agents and nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Neurol Clin 2017;35:17–27. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 35.Coca MN, Morgan ML, Gupta P, Elkeeb A, Lee AG. Bilateral posterior ischemic optic neuropathy associated with the use of Sildenafil for pulmonary hypertension. Can J Ophthalmol 2016;51:e96–e99. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 36.Galvez-Ruiz A, Arishi N. Sequential, non-arteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy in patients taking sildenafil: a report of ten cases. Saudi J Ophthalmol 2013;27:241–246. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 37.Gedik S, Yilmaz G, Akova YA. Sildenafil-associated consecutive nonarteritic anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy, cilioretinal artery occlusion, and central retinal vein occlusion in a haemodialysis patient. Eye 2007;21:129–130. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 38.Hafidi Z, Handor H, Laghmari M, Daoudi R. Cilioretinal artery and central retinal vein occlusion after sildenafil use. Emerg Med J 2014;31:535. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 39.Pomeranz HD, Smith KH, Hart WM Jr, Egan RA. Sildenafil-associated nonarteritic anterior ischemic optic neuropathy. Ophthalmology 2002;109:584–587. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 40.Pomeranz HD, Bhavsar AR. Nonarteritic ischemic optic neuropathy developing soon after use of sildenafil (Viagra): a report of seven new cases. J Neuroophthalmol 2005;25:9–13. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 41.Oguz H. Sildenafil-associated vascular casualties. Eye 2007;21:676–677; author reply 7–8. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 42.Peter NM, Singh MV, Fox PD. Tadalafil-associated anterior ischaemic optic neuropathy. Eye 2005;19:715–717. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 43.Pepin S, Pitha-Rowe I. Stepwise decline in visual field after serial sildenafil use. J Neuroophthalmol 2008;28:76–77. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 44.Fraunfelder FW, Fraunfelder FT. Central serous chorioretinopathy associated with sildenafil. Retina 2008;28:606–609. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 45.Varma D, Lee AW, Chen CS. Reply: 'a review of central retinal artery occlusion: clinical presentation and management'. Eye 2014;28:1270. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 46.Rudkin AK, Lee AW, Chen CS. Vascular risk factors for central retinal artery occlusion. Eye 2010;24:678–681. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 47.Murthy RK, Perez L, Priluck JC, Grover S, Chalam KV. Acute, bilateral, concurrent central retinal artery occlusion in sickle cell disease after use of tadalafil (Cialis). JAMA Ophthalmol 2013;131:1471–1473. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 48.Bertolucci A, Latkany RA, Gentile RC, Rosen RB. Hemi-retinal artery occlusion associated with sexual activity and sildenafil citrate (Viagra). Acta Ophthalmol Scand 2003;81:198–200. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 49.Pinto LM, Morekar S, Mahashur AA. Central retinal vein occlusion in a patient after being commenced on sildenafil citrate for pulmonary arterial hypertension. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci 2009;51:249–251. [PubMed]
- 50.Li AS, Pomeranz HD. Food and drug administration adverse event reports of retinal vascular occlusions associated with phosphodiesterase type 5 inhibitor use. J Neuroophthalmol 2016;36:480–481. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 51.Kinoshita J, Iwata N, Shimoda H, Kimotsuki T, Yasuda M. Sildenafil-induced reversible impairment of rod and cone phototransduction in monkeys. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 2015;56:664–673. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 52.Laties AM, Fraunfelder FT. Ocular safety of Viagra, (sildenafil citrate). Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 1999;97:115–125; discussion 25–28. [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 53.Stockman A, Sharpe LT, Tufail A, Kell PD, Ripamonti C, Jeffery G. The effect of sildenafil citrate (Viagra) on visual sensitivity. J Vis 2007;7:4. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 54.Farooq MU, Naravetla B, Moore PW, Majid A, Gupta R, Kassab MY. Role of sildenafil in neurological disorders. Clin Neuropharmacol 2008;31:353–362. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 55.Sinha S, Pathak-Ray V, Ahluwalia H, Morgan JE. Viagra or what? Eye 2004;18:446–448. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 56.Cordell WH, Maturi RK, Costigan TM, Marmor MF, Weleber RG, Coupland SG, et al. Retinal effects of 6 months of daily use of tadalafil or sildenafil. Arch Ophthalmol 2009;127:367–373. [DOI] [PubMed]


