Abstract
Sialoperoxidase and myeloperoxidase are the two main peroxidase enzymes found in the oral cavity. Sialoperoxidase is present in salivary secretions and in the biofilms that line the oral surfaces, while myeloperoxidase is abundant in the dento-gingival sulcus area. In the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), oral peroxidases catalyze the oxidation of the pseudohalide anion thiocyanate (SCN−) to hypothiocyanite (OSCN−), a strong oxidant that serves an antimicrobial role. Furthermore, oral peroxidases consume bacteria-produced H2O2 and could help inactivate toxic carcinogenic and genotoxic substances. Numerous in vitro studies have reported the antibacterial, antimycotic and antiviral role of peroxidases, suggesting possible applications in oral therapy. However, the use of oral hygiene products incorporating peroxidase systems has not yet been shown to be beneficial for the treatment or prevention of oral infections. This paradox reflects our incomplete knowledge of the physiological role of peroxidases in a complex environment, such as the oral region. While hygiene is crucial for restoring oral microbiota to a symbiotic state, there are no data to suggest that the addition of a peroxidase per se can create a dysbiotic state. Recent investigations have associated the presence of peroxidase activity with gram-positive cocci microbial flora, and its insufficiency with dysbiosis has been linked to pathologies, such as caries, periodontitis or infections of the oral mucosa. Therefore, oxidants generated by oral peroxidases appear to be an essential ecological determinant for oral health through the selection of a symbiotic microbiota capable of resisting oxidative stress. The objective of the present review was to update the current knowledge of the physiological aspects and applications of oral peroxidases in clinical practice.
Keywords: biofilm, hypoiodite, hypothiocyanite, myeloperoxidase, oral hygiene, oral microflora, salivary peroxidase
1. Introduction
Oral peroxidases are part of the innate non-immune defense mechanism of the saliva (1,2). In the oral medium in the presence of hydrogen peroxide (H2O2), these enzymes catalyze the oxidation of thiocyanate (SCN−), a pseudohalide, into hypothiocyanite (OSCN−), a powerful oxidant capable of inhibiting numerous bacterial species, mycoplasmas, fungi and viruses in vitro (Fig. 1). Sialoperoxidase and myeloperoxidase are the two main peroxidases found in the oral cavity. Sialoperoxidase is present in salivary secretions and in the biofilms that line the oral surfaces, while myeloperoxidase is abundant in the dento-gingival sulcus area (3,4). By regulating the commensal oral flora, as well as by consuming bacterial H2O2, which is toxic for the oral mucosa, oral peroxidases help protect the tissues bordering the oral cavity from microbial injuries. Although numerous studies have demonstrated an antimicrobial role in vitro, only a few studies have documented the use of oral hygiene products incorporating peroxidase systems for the treatment or prevention of oral infections. This paradox reflects our incomplete knowledge of the physiological role of these enzymes in a complex environment, such as the oral environment. The aim of this review was to update our current knowledge of the physiological aspects of oral peroxidases, as well as their potential applications in the oral clinic. The relevant articles published in English until August 2020 were retrieved from the literature indexed by PubMed (https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov). The MeSH terms were ‘thiocyanate’, ‘hydrogen peroxide’ and ‘iodide’ with ‘oral peroxidases’ in different combinations without exclusion criteria, provided they are related to the interested topic area. The systematic attention to the bibliographic section of the papers so-selected was a second source of references. The review data have been neither statically processed nor organized into flowcharts. The quality of evidence for clinical trials follows the recommendations of the Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation system.
Figure 1.
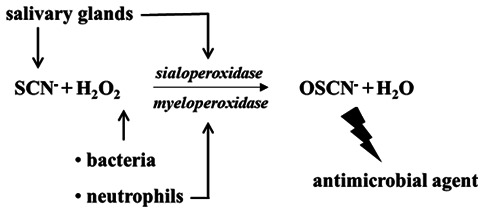
Peroxidase system in the oral cavity leading to the production of OSCN−, which controls the oral microflora. SCN−, thiocyanate; H2O2, hydrogen peroxide; OSCN−, hypothiocyanite.
2. Oral peroxidases: Enzymes and substrates
Peroxidase activity in the saliva was first suspected due to the restoration of an anti-lactobacillus effect following the addition of lactoperoxidase purified from bovine milk in heat-treated saliva (5,6). Salivary peroxidase was then considered to be similar, if not identical, to lactoperoxidase. Salivary peroxidase (or sialoperoxidase) was not considered to be an enzyme different from lactoperoxidase until later. Indeed, these two enzymes have the same amino acid composition (7) and exhibit immunological cross-reactivity (8). However, they differ in their carbohydrate composition and certain kinetic characteristics (7). The whole saliva also contains a significant amount of myeloperoxidase from neutrophils, which enter the oral cavity through the dento-gingival sulci (3). The coexistence of sialoperoxidase and myeloperoxidase in the oral environment may mask the activity of other peroxidases that may be present in much lower quantities (microbial peroxidases) or transiently (lactoperoxidase in dairy products).
Sialoperoxidase
The parotid and submaxillary salivary glands secrete human sialoperoxidase from birth at adult concentrations (9,10). Human sialoperoxidase occurs in different forms based on molecular weight and electrophoretic migration; sialoperoxidase may be free or linked to other salivary molecules, such as mucin (11–13). When unbound and monomeric, its molecular weight is ~78,000 (7), and its isoelectric point is 8–10 (11,14). This enzyme adsorbs different oral surfaces, while retaining its enzymatic activity (15–17), including enamel (15), dental plaque (18), salivary sediments (16) and bacteria such as streptococci (17). Other exocrine secretions, such as tears, sweat, airways or digestive secretions, also have a similar activity (usually referred to as lactoperoxidase and, at times, lacrimal peroxidase in tears). Salivary peroxidase, along with other proteins secreted by salivary glands (i.e. lysozyme and lactoferrin), participates in the antimicrobial protection of oral surfaces, such as mucosa and dental crowns.
Myeloperoxidase
Myeloperoxidase in saliva comes from the lysis of neutrophils entering the oral cavity by the dento-gingival sulci from the first dental eruptions (19–24). The leukocyte count in saliva decreases in edentulous patients and increases in oral inflammation processes (25). The number of neutrophils migrating into the oral cavity is ~106 cells/min in healthy subjects, and higher in patients with periodontal disease (3,26,27). In the saliva, neutrophils undergo hypo-osmotic shock and release myeloperoxidase along with other antimicrobial proteins, such as lysozyme and lactoferrin; in a similar manner, the salivary glands secrete the same two proteins, in addition to sialoperoxidase. Myeloperoxidase represents up to 20–25% of the total peroxidase activity in total centrifuged resting saliva, while it predominates in the salivary sediment and in the liquid of the dento-gingival sulci, where it participates in antimicrobial tissue protection (3,23). The primary substrate for myeloperoxidase is chloride (Cl−) in the tissues [with the production of hypochlorite (OCl−)] and SCN− in the saliva (with the production of OSCN−).
Lactoperoxidase in dairy products
Lactoperoxidase, similarly to sialoperoxidase, catalyzes the oxidation of SCN− in vivo and iodide (I−) in vitro, in the presence of H2O2. Easily purified from bovine milk, lactoperoxidase was first characterized and its enzymatic aspects were specifically documented by Aune and Thomas in 1977 and 1978 (28,29). Lactoperoxidase was commonly used to study the effects of a peroxidase-H2O2-SCN− system on cariogenic bacteria, such as oral streptococci (30) or Lactobacillus acidophilus (31), on periodontopathogenic bacteria (32). The lactoperoxidase-SCN− combination is used as a preservative for vegetables and as a supplement in several oral hygiene products. The lactoperoxidase-I− combination allows for the radioactive labelling of proteins. Lactoperoxidase has the property of adsorbing different surfaces, including that of biomaterials, such as titanium (33).
H2O2
Oral H2O2 comes from the salivary glands [DUOX family of oxidases, reviewed in (34)], neutrophils [NOX family of oxidases, reviewed in (35)] and particularly certain bacterial species present in the mouth through the action of pyruvate oxidase (36). H2O2 is one of the reactive oxygen species (ROS) synthesized by neutrophils during phagocytosis and secreted by the salivary glands as a trigger for sialoperoxidase activity. Determination of H2O2 in the saliva is challenging, given its rapid consumption by oral peroxidases and bacterial catalases. Most of the oral H2O2 comes from bacteria of the genus Streptococcus (37–39) and, to a much lesser extent, from optional anaerobes (40,41). Based on the equilibrium constant of the SCN− peroxidation reaction (3.7×103 M−1) in the oral medium, the mean salivary H2O2 concentration has been estimated at 10 µM (42), the maximum dose tolerable by mammalian cells (43,44). At low concentrations (1–10 nM), H2O2 plays a role as a signaling molecule in bacteria-bacteria interactions (45,46). For example, H2O2 can promote the formation of Streptococcus parasanguinis biofilms co-cultured with Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans in vitro (47).
SCN−
SCN− is secreted by the parotid, submaxillary, sublingual and minor salivary glands (48,49) at a concentration that is dependent on exogenous intake, mainly brassica vegetables (50), as well as the smoking habits of individuals (51), and on endogenous production coupled with the detoxification of food cyanide, such as cassava (52). The salivary concentration of SCN− is 0.5–2 mM in non-smokers and may be up to 10 mM in heavy smokers (12,51,53); its concentrations in the gingival crevicular fluid is ~40 µM, but may be higher in smokers (12). Of note, the optimal levels for peroxidase activity are in the order of mM. To the best of our knowledge, no study to date has documented the harmful effect of smoking on oral health through the inhibition of the natural peroxidase systems. SCN− has already been proposed as a vasodilator to combat hypertension or as an antimicrobial agent in combination with a peroxidase system. In this context, various studies [reviewed in (54)] have suggest the absence of SCN− toxicity up to concentrations sufficient to activate the enzymatic production of OSCN−. A more significant increase in plasma SCN− concentration is linked to the inhibition of thyroid function, particularly in cases of iodine deficiency. Indeed, SCN− is a competitive inhibitor of the Na+/I− symport in thyroid follicular cells. This competition between a halogen and SCN− for peroxidases explains the etymology of the word ‘pseudohalogen’ to qualify for SCN−.
I−
The ability of the salivary glands to concentrate I− into the salivary compartment (20–100 times higher than the plasma concentration) has long been known (55). This capacity for concentrating iodine in saliva before intestinal re-absorption contributes to the preservation of the iodine pool for optimal thyroid function (56). Iodine deficiency, which is marked by lower urinary and salivary rates, has been correlated with an increase in the incidence of dental caries (57), but no association between iodine deficiency and oral peroxidases has been reported in these studies. Other studies have implicated iodine deficiency in immune dysfunctions (56). Excess iodine has been reported to induce alterations of the salivary glands, including lymphocytic infiltrations (58), in an animal model. In vitro, I− is another substrate for sialoperoxidase, myeloperoxidase or lactoperoxidase in antimicrobial systems. The salivary concentration of I− in humans is estimated to be insufficient for antimicrobial action in vivo. Indeed, the salivary levels reported in the literature are in the order of µM (1,59,60), while those of SCN− are in the mM range. The ability of SCN− to inhibit the uptake of I− by the parotid cells in parallel with thyroid cells has long been known (61). The presence of SCN− at higher concentrations in the saliva should limit the metabolism of I− (oxidation, iodination of tyrosine and iodination of proteins) (12,62,63). However, certain studies have suggested a synergy between the two substrates (64), whereas others have documented the in vitro formation of iodine-SCN− complexes as a more active/stable antimicrobial component, as compared with OI− and OSCN− alone (65–68).
3. Oxidant production by oral peroxidases
Both peroxidases that present in the oral cavity transform SCN− into OSCN−. In vitro, sialoperoxidase turns I− into hypoiodite (OI−). In tissues, myeloperoxidase forms OCl− from Cl− but not in saliva due to the presence of SCN−. In vitro, myeloperoxidase can also produce OI−. In the oral environment, the two peroxidases oxidize SCN− more abundantly than I−. H2O2 is a factor limiting the activity of oral peroxidases. These non-Michaelian enzymes are characterized by optimal concentrations, above which their substrates become their inhibitors (69).
It should be noted that the oral cavity is not a single homogeneous compartment, but rather a juxtaposition of sites, each characterized by its own ecosystem. The intraoral sites to be considered are indeed numerous and can be grouped into the saliva, biofilms and dento-gingival sulci (70). The peroxidase activity varies across sites, depending on the concentrations of available substrates (H2O2 and SCN−). The parotid production of H2O2 is already sufficient for generating OSCN− in the excretory Stenson's duct (71). The preferred method for determining salivary OSCN− is based on the oxidation of the 5,5′-dithiobis-2-nitrobenzoic acid (72). Other procedures are based on the oxidation of pyrogallol, guaiacol or ABTS (73). However, these methods, which are not specific to OSCN−, do not make it possible to specifically analyze the products of the peroxidase activity in the presence of several substrates during the same test, in this case SCN− together with I−. A colorimetric method in the presence of tetramethylbenzidine was recently developed to more specifically assess OI− (74). Fluorides have been described as inhibitors of lactoperoxidase and sialoperoxidase at acid pH regardless of the substrate, SCN− or I− (75).
OSCN−
OSCN− is considered to be the major oxidant produced by oral peroxidases in the oral cavity. Concentrations of OSCN− up to 300 µM have been reported in the literature for the whole saliva (12). However, methodological problems when collecting samples may lead to default errors due to the instability of the molecule and the large number of oxidizable targets in saliva and oral biofilms. As SCN− is metabolized by both myeloperoxidase and sialoperoxidase, the production of OSCN− alone cannot be used to characterize the activity of one of these two enzymes (76). OSCN− at the doses required for an antibacterial effect does not appear to cause damage to the genetic material of the mucous membranes (77). However, selective oxidation of cell/tissue targets containing thiol groups could initiate significant cell damage, such as damage to gingival epithelial cells (78).
OI−
In vitro, OI− decreases the survival rate of some microbial species at a lower concentration, as compared with that observed for OSCN−, especially in Candida albicans (79). Some authors (80) have been able to demonstrate that 125I only binds to a limited number of membrane molecules of Candida albicans, which is particularly sensitive to OI−. However, the hypohalous ion present in the oral cavity is OSCN− rather than OI−, as the substrate SCN− at the origin of the former is 1,000 times more abundant, as compared with I− at the source of the latter. The salivary SCN− concentration reaches the mM level, while OI− barely reaches concentrations in the µM range. At equal (pseudo)halide concentrations, lactoperoxidase has a higher affinity for SCN− than for I−. However, experimentally, the substitution of SCN− by I− increases the innate antiviral defences of the respiratory mucosa against adenoviruses and the respiratory syncytial virus (81). Oral administration of KI vs. NaI increases iodemia, allowing for the accumulation of I− in the mucous secretions of the upper respiratory tract in humans (81) as well as animals (82,83). Although it has already been demonstrated that I− accumulates in submandibular glands in hamsters (84), no similar observations have been reported in humans. It would be interesting to be able to specifically assess salivary OI− in excretory ducts, such as the Stenson's duct, where the oral biofilms do not extend, except in the case of infectious parotitis. Finally, the success of topical formulations based on povidone-iodine to reduce bacterial growth in the oral cavity in ventilated patients may be attributed to the increase in I− available for the patient's peroxidases (85).
Iodine-thiocyanate complexes
The two substrates of peroxidase, SCN− and I−, have been mostly tested independently in suspensions, and less frequently in combination (64). Moreover, few articles reporting that the activity of lactoperoxidase produces a mixture of OSCN/OI− in the presence of a mixture of SCN−/I− substrates have effectively analyzed the products generated under their experimental conditions (1,64,86). Mixtures of the two substrates, SCN− and I−, however, appear to lead to the formation of a more stable oxidative complex over time (65,66,87–90). Under well-defined in vitro experimental conditions (high ionic strength; KI:KSCN ratio, ~4.5; neutral or acidic buffer; presence of H2O2), lactoperoxidase produces stable iodine-SCN− complexes, such as I2(SCN)−, objectified by carbon-13 (C13) nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy (66) with antimicrobial properties against Candida (67). Oxidant concentrations are then less toxic to epithelial cells in the mouth, as compared with chlorhexidine (67). The resistance of epithelial cells may be explained by the presence of bacteria covering their surface and forming a protective biofilm, and/or by the detoxification of enzymatic activities in certain commensal species present in the oral environment (91). The use of these complexes for rinsing dentures ex vivo further limits the possible effect on epithelial cells in vivo. The efficacy of the iodine-SCN− complexes prepared without peroxidase activity has already been demonstrated in vitro on Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Staphylococcus aureus, both in suspension and in biofilms (92). Other studies will have to analyze the interference between this solution of iodine-SCN− complexes and oral microbial ecology.
4. Biological roles of oral peroxidases
Over several decades, oral peroxidases have been recognized as being essential for oral health (93), despite the absence of clinical evidence. Indeed, no specific deficit in sialoperoxidase or its association with a particular pathology have been described. Although the decrease in salivary flow leads to carries or mucosa infections (for example, candidiasis), the deficiency of no particular salivary molecule (in this case, sialoperoxidase) has been definitively proven to cause these infections. Similarly, neutropenia leads to gingivitis/periodontitis, but it is not possible to definitively deduce that myeloperoxidase deficiency is individually responsible. The demonstration of the biological roles of peroxidases is based more on in vitro studies carried out under physiological conditions.
Antimicrobial effects
Oral peroxidases control the oral microbiota while detoxifying the environment of H2O2. By oxidizing thiol groups (29) and nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NAD(P)H) (94), OSCN− exerts antimicrobial, antimycotic and antiviral effects (1,2). In particular, the bacterial hexokinase activity, which initiates the Emden-Meyerhoff pathway, decreases in the presence of OSCN−. Acid production by dental plaque is reduced in the presence of OSCN− (95). In vitro, OSCN− slows the growth of cariogenic bacteria belonging to the genera Streptococcus or Lactobacillus (1). Periodontopathogenic bacteria are also inhibited (32,96–98), as are yeasts of the Candida genus, which are responsible for mucosal pathologies (99). Some viruses are sensitive to this oxidant, such as the herpes virus (100), HIV (101) or influenza virus (102,103). Antisepsis research suggests using peroxidase-generated OSCN− as a putative prophylactic agent to prevent contamination with SARS-CoV-2 (104).
Some bacteria have developed various strategies to resist the ROS produced by neutrophils (105). Similarly, commensal oral surface bacteria, such as Streptococcus sanguis (one of the first colonizers of the dental plaque) have the biochemical equipment to protect themselves from OSCN−. By contrast, Streptococcus mutans (a cariogenic bacterial species) does not have this detoxifying system (91). Thus, peroxidases operate more like ecological selectors by allowing commensal bacteria capable of reducing OSCN− to survive in the oral environment. Moreover, peroxidases coupled to a system detoxifying the environment of hypohalous compounds (of the thioredoxin type) participate in the protection of tissues against oxidants resulting from the metabolism of activated oxygen, such as the superoxide anions or H2O2 (106). There appears to be an interconnection between resistance to oxidative stress and the ability to form biofilms via quorum-sensing molecules, such as farnesol (107). On the other hand, non-active lactoperoxidase, after the depletion of the substrate, can promote the in vitro growth of certain anaerobes (98). At the same time, a clinical study (108) suggested a rebound in periodontitis after a phase of clinical improvement, possibly due to an accumulation of lactoperoxidase without substrate. The association of a peroxidase system with another innate non-immune defence factor further strengthens the inhibition of some bacteria in vitro. For example, lysozyme improves the inhibition of glucose metabolism by the peroxidase system in Streptococcus mutans (109).
Biofilm control
Sialoperoxidase, similar to lactoperoxidase in vitro, adsorbs enamel surfaces irreversibly (15) while retaining its activity. This property contributes to controlling the formation of dental plaque and regulating the bacterial microflora attached to the surfaces of the oral cavity. The activity of peroxidases present in dental plaque depends on the availability of its two substrates (SCN− and H2O2) in the thickness of oral biofilms. SCN− diffuses deeper into the biofilms from the salivary film that covers them. At the same time, H2O2 relies on the oxygen supply allowing certain bacteria to produce it in situ. Certain studies (12,106) have described a virtuous cycle summarizing the beneficial effect of sialoperoxidase on oral microflora control. After a supply of food sugars, commensal bacteria of the genus Streptococcus grow and produce more H2O2, which activates the production of OSCN− in the presence of sialoperoxidase and SCN−, thereby limiting bacterial growth or even killing microorganisms. Theoretically, these mechanisms work less effectively deeper inside thick biofilms, given the consumption of peroxidase substrates in the most superficial layers. Similarly, mouth rinsing with solutions containing an OSCN−-generating system is likely to further impact the more superficial layers of biofilms. These remarks suggested that a peroxidase system may act both on the formation of biofilms and on already formed biofilms.
In addition to protecting the walls of the oral cavity, sialoperoxidase may also protect the excretory ducts of the salivary glands, which are rarely infected when they open into an oral cavity abundantly colonized by microbial germs; however, to the best of our knowledge, no scientific study has yet considered this physiological aspect.
Protection against oxidative stress
The uncontrolled production of activated oxygen species (ROS: Superoxides, H2O2, free radicals, hypohalous compounds) or reactive nitrogen species (RNS: Compounds derived from nitric oxide and superoxides, such as peroxynitrite, nitrogen dioxide and dinitrogen trioxide) is implicated in various oral pathologies (110). These oxidative derivatives damage cells and are considered to be mutagenic and carcinogenic. They are controlled in the salivary environment by scavengers (mainly uric acid) and antioxidant enzymes (bacterial catalase and oral peroxidases). Lactoperoxidase transforms cytotoxic H2O2 into a less toxic product, as suggested by in vitro experiments on fibroblast cultures (44). The coupling of peroxidases to a bacterial thioredoxin system helps protect tissues from oxidants produced from peroxidase activities. In tissues (including gingival), catalase and glutathione peroxidase help remove H2O2.
Certain studies [reviewed in (12)] considered that the enzymatic peroxidation of mutagenic and carcinogenic molecules bound to diet as another function of oral peroxidases. However, the related data are currently insufficient to assess its actual significance in the detoxification of toxic molecules introduced into the oral cavity, through food or other means.
5. Mimicking biological systems
Manufacturers have attempted to mimic the peroxidase activity of saliva by incorporating lactoperoxidase into oral hygiene products [reviewed in (111)]. A ‘peroxidase system’ is a galenic formulation associating a peroxidase with one of its substrates of the (pseudo)halide type plus H2O2 or an H2O2 donor. The formulation of such a system requires a methodical step-by-step approach to optimize the volume and rinsing time, the concentration of H2O2 and SCN−, as well as the pH, in order to achieve the production of an adequate antimicrobial level in the oral cavity (112). Even before the launch of oral hygiene products with a peroxidase system, Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO)/World Health Organization (WHO) recommended its use for the safe preservation of raw milk or vegetables (113). Articles on proteins derived from milk list the oral benefits of lactoperoxidase, sometimes associated with other proteins, such as lactoferrin or lysozyme (114). Numerous preclinical in vitro tests (through saliva sample collection, solid or liquid cultures, biofilm models) have evaluated peroxidase systems for pharmacokinetics (115), antimicrobial effects on the oral microflora (116), as well as toxicity on epithelial cells (117). Some ex vivo studies have reported the decontamination of materials that have remained in an oral environment, while others describe the advantage of their use in vivo. The SCN−/lactoperoxidase system is the most extensively investigated, but there have been few clinical studies on the I−/lactoperoxidase system (118). Unfortunately, these investigations often test a peroxidase system coupled with other milk antimicrobial proteins also found in the saliva (119). Such systems have been introduced into oral hygiene products with a curative intent (periodontitis, halitosis) or with a preventive perspective (dry mouth, caries). However, the efficacy of these products has not been sufficiently documented (117), and there are only a limited number of small-scale phase I/II clinical trials. Investigators face the difficulty of finding adequate biological markers to demonstrate the effects of a peroxidase system on the regulation of oral microflora in the oral environment. Another dilemma could be to choose between quantitative (bacterial count) or qualitative (metabolic markers) markers. For example, a mouth-rinse/tooth-wash with an in vivo peroxidase system increases the concentration of OSCN− in the saliva (120) but does not change the total number of salivary bacteria, while it could reduce bacterial ATP (an indicator of their metabolic potential). Several studies have thoroughly evaluated peroxidase systems by following clinical indices (gingival index, plaque index, etc.) and some others, as dry mouth, settle for satisfaction surveys. The determination of an appropriate control is challenging. Moreover, the short half-life of the oxidants produced and the bacterial resistance constitute other limitations to their use. Recently, the SCN−/I− combination has made it possible to obtain more stable products. Molecular techniques (16SrRNA gene sequencing analysis) demonstrated that the use of lactoperoxidase coupled with lactoferrin promotes supragingival and lingual biofilms with more gram-positive and fewer gram-negative bacteria (119).
Tables I and II list the clinical studies evaluating a peroxidase system used alone (108,121–130) or in combination (131–140) with other exocrine proteins.
Table I.
Bibliographic references for clinical trial reports evaluating the efficiency of a peroxidase system in oral medicine when used alone (references cited until August 2020 in the PubMed database).
| First author/s, year | Field | Pathology | Peroxidase system tested | N | Marker | Effect | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Koch et al, 1973 | H | Plaque accumulation | AGC, GOD | 15 | PI | Yes | (121) |
| Hugoson et al, 1974 | H | Caries, gingivitis | AGC, GOD | 22 | CI, GI, PI | Yes | (122) |
| Koch and Strand, 1979 | H | Caries | AGC, GOD | 750 | CI, dental X-rays | Yes | (123) |
| Rotgans and Hoogendoorn, 1979 | A | Caries | AGC, GOD | 48 | Histology | Yes | (124) |
| Afseth and Rølla, 1983 | H | Plaque accumulation | AGC, GOD | 8 | PI, plaque pH | No | (125) |
| Midda and Cooksey, 1986 | H | Plaque accumulation, gingivitis | AGC, GOD, SCN− | 135 | GI, PI | Yes | (126) |
| van Steenberghe et al, 1994 | H | Post-irradiation xerostomia | G/GOD/SCN−/LPO | 12 | PI, SBI | Yes | (108) |
| Bánóczy et al, 1994 | H | Xerostomia | G/GOD/SCN−/LPO | 41 | Self-rating survey/bacteria monitoring/cytological tests | Yes/no/yes | (127) |
| Toljanic et al, 1996 | H | Post-irradiation xerostomia | G/GOD/SCN−/LPO | 60 | GI, PI | Yes | (128) |
| Epstein et al, 1999 | H | Post-irradiation xerostomia | G/GOD/SCN−/LPO | 19 | Self-rating survey/bacteria monitoring | Yes/no | (129) |
| Warde et al, 2000 | H | Post-irradiation xerostomia | G/GOD/SCN−/LPO | 28 | Self-rating survey | Yes | (130) |
A, animal; AGC, amyloglucosidase; CI, caries index; H, human; GI, gingival index; GOD, glucose oxidase; SCN−, thiocyanate; LPO, lactoperoxidase; N, number of cases; PI, plaque index; SBI, sulcus blood index.
Table II.
Bibliographic references for clinical trial reports evaluating the efficiency of a peroxidase system in oral medicine when used in combination with other exocrine proteins (references cited until August 2020 in the PubMed database).
| First author/s, year | Field | Pathology | Peroxidase system tested | N | Marker | Effect | (Refs.) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Kirstilä et al, 1996 | H | Xerostomia | G/GOD/SCN−/LPO | 20 | Chemical monitoring/bacteria monitoring/self-rating survey | No/no/no | (131) |
| Matear and Barbaro, 2005 | H | Xerostomia | G/GOD/SCN−/LPO + Lf + Lz | 20 | Self-rating survey | Yes | (132) |
| Hatti et al, 2007 | H | Plaque accumulation | G/GOD/SCN−/LPO + Lf + Lz | 20 | PI/bacteria monitoring | Yes/yes | (133) |
| Gil-Montoya et al, 2008 | H | Xerostomia | G/GOD/SCN−/LPO + Lf + Lz | 20 | Candida monitoring/self-rating survey | No/yes | (134) |
| Shin et al, 2011 | H | Halitosis | G/GOD/LPO + Lf | 15 | Chemical monitoring/bacteria monitoring | Yes/yes | (135) |
| Jose et al, 2016 | H | Xerostomia | LPO + Lf + Lz | 396 | Self-rating survey | Yes | (136) |
| Nakano et al, 2016 | H | Halitosis | GOD/LPO + Lf | 39 | Chemical monitoring | Yes | (137) |
| Morita et al, 2017 | H | Oral hygiene in the elderly | LPO + Lf | 37 | Bacteria monitoring | Yes | (138) |
| Barbe et al, 2018 | H | Xerostomia | G/GOD/SCN−/LPO + Lf + Lz | 40 | PI/organoleptic score | Yes/yes | (139) |
| Nakano et al, 2019 | H | Gingivitis | LPO + Lf | 150 | GI, PI, self-rating survey | Yes | (140) |
H, human; G, glucose; GI, gingival index; GOD, glucose oxidase; SCN−, thiocyanate; LPO, lactoperoxidase; Lf, lactoferrin; Lz, lysozyme; N, number of cases; PI, plaque index.
Curative vs. preventive
The use of peroxidase systems may be considered as topical administration to protect oral surfaces in vivo as a prophylactic measure. Recommending these galenic preparations may not be of value as a curative approach, as the infection itself indicates that a deregulated oral flora has overtaken physiological systems, including peroxidase. Reserving or even developing these galenic preparations as prophylactic treatment would avoid the appearance of strains resistant to antimicrobials used continuously to prevent the occurrence of certain infections (for example, oral candidiasis in patients with AIDS).
In vitro vs. in vivo
Peroxidase systems present a paradox: Although they have been shown to be active in vitro for a long time, the definitive evidence of their effects in vivo is still lacking. A possible explanation is the actual availability of H2O2 in the oral environment, which is rich in bacterial catalase. In this case, the increased availability of H2O2 can compensate for its consumption by other enzymatic activities (141,142), thus allowing the exogenous lactoperoxidase to be active. Another explanation would be to consider a transient metabolic suppression demonstrated, for example, by assaying ATP, but not observed on culture media.
In vivo vs. ex vivo
Peroxidases adsorb different biomaterials used in dentistry: Titanium and resin are two examples. Ex vivo use may be employed to disinfect removable prostheses by short-circuiting in vivo use; the intra-oral administration is indeed considered by some to be dangerous, due to cytotoxicity and potential immunogenicity. The toxicity of peroxidase systems on the oral mucosa appears to be limited by the oral biofilms covering them. However, the accumulation of inactive lactoperoxidase in biofilms may favor certain anaerobic bacteria, such as Porphyromonas gingivalis (98). On the other hand, the accumulation of I− during regular use would not be advised for some patients. With regards to health and safety, it should be noted that the FAO recommends the SCN−/lactoperoxidase system for the decontamination of milk and vegetables for food sales (113).
Toxicity
Few reports have analyzed the oral toxicity of peroxidase systems when recommended in oral care products. Indirectly, these products may be beneficial for patients who have aphthous ulcers secondary to the toxicity of lauryl sulfate, often used as a detergent in toothpaste (143). Indeed, the incorporation of such enzymes in oral hygiene products implies the no-use of detergent foaming agents, which have the ability to denature proteins, and therefore enzymes.
Perspective in oral hygiene
Numerous investigations have analyzed the effects of peroxidase systems on the various pathogens present in the oral cavity, including viruses. In vivo, oral peroxidases defend the gingival sulcus against microbial invasion (myeloperoxidase) and help regulate the microflora adhering to the surfaces of the oral cavity (sialoperoxidase). Incorporating lactoperoxidase with other salivary antimicrobial proteins in salivary substitutes may mimic the antimicrobial effect of the salivary exocrine fluid (144). The beneficial effect of oral sprays with such peroxidase preparations in combating dryness of the oral mucosa in patients on respirator treatment has already been proposed. However, their benefit in daily oral hygiene has not yet been quantified or even demonstrated by clinical studies. Certain studies have suggested considering peroxidases as ecological selectors directing the oral microflora towards a Gram-positive cocci microflora poor in cariogenic or periodontopathogenic germs, thereby preserving the mucosa and protecting it from yeast overgrowth, among others. Thus, the administration of an efficient lactoperoxidase system in a toothpaste also containing lactoferrin and lysozyme may prevent oral dysbiosis (145). A few studies have demonstrated an inverse association between the activity of sialoperoxidase and the depth of the periodontal pockets (146). On the other hand, the administration of inactive peroxidase without substrate seems to disturb in vitro the balance between commensals and periodontopathogens to the latter's advantage (98,147). The peroxidase systems' clinical benefit in oral hygiene must still be demonstrated on a large scale through evidence-based practice.
6. Conclusion
Oral peroxidases are involved in the control of the oral microflora as ecological selectors favoring a commensal flora, which can develop or survive in the presence of OSCN− (148,149). The use of peroxidase systems may be beneficial for preventing topical administration to protect the oral surfaces in vivo. By contrast, they may be used ex vivo to disinfect removable prostheses. The efficacy of formulations with peroxidase activity is not yet sufficiently documented, and there are no large-scale clinical trials to date. The short half-life of the produced oxidants and bacterial resistance constitute limiting factors for their use. However, the SCN−/I− combination has recently made it possible to obtain more stable products.
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Funding
No funding was received.
Availability of data and materials
Not applicable.
Author's contributions
PC conceived and designed the study, and drafted the manuscript. Data authentication is not applicable. The author read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Patient consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The author declares that he has no competing interests.
References
- 1.Pruitt KM, Reiter B. Biochemistry of peroxidase system: Antimicrobial effects. In: Pruitt KM, Tenovuo JO, editors. The lactoperoxidase system: Chemistry and Biological Significance. Marcel Dekker; New York: 1985. pp. 143–178. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Bafort F, Parisi O, Perraudin JP, Jijakli MH. Mode of action of lactoperoxidase as related to its antimicrobial activity: A review. Enzyme Res. 2014;2014:517164. doi: 10.1155/2014/517164. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Thomas EL, Jefferson MM, Joyner RE, Cook GS, King CC. Leukocyte myeloperoxidase and salivary lactoperoxidase: Identification and quantitation in human mixed saliva. J Dent Res. 1994;73:544–555. doi: 10.1177/00220345940730021001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Ihalin R, Loimaranta V, Tenovuo J. Origin, structure, and biological activities of peroxidases in human saliva. Arch Biochem Biophys. 2006;445:261–268. doi: 10.1016/j.abb.2005.07.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Morrison M, Allen PZ, Bright J, Jayasinghe W. Lactoperoxidase. V. Identification and isolation of lactoperoxidase from salivary gland. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1965;111:126–133. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(65)90330-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Slowey RR, Eidelman S, Klebanoff SJ. Antibacterial activity of the purified peroxidase from human parotid saliva. J Bacteriol. 1968;96:575–579. doi: 10.1128/JB.96.3.575-579.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Mansson-Rahemtulla B, Rahemtulla F, Baldone DC, Pruitt KM, Hjerpe A. Purification and characterization of human salivary peroxidase. Biochemistry. 1988;27:233–239. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Mansson-Rahemtulla B, Rahemtulla F, Humphreys-Beher MG. Human salivary peroxidase and bovine lactoperoxidase are cross-reactive. J Dent Res. 1990;69:1839–1846. doi: 10.1177/00220345900690121001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Gothefors L, Marklund S. Lactoperoxidase activity in human milk and in saliva of newborn infants. Infect Immun. 1975;11:1210–1215. doi: 10.1128/IAI.11.6.1210-1215.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Tenovuo J, Lehtonen OP, Aaltonen AS, Vilja P, Tuohimaa P. Antimicrobial factors in whole saliva of human infants. Infect Immun. 1986;51:49–53. doi: 10.1128/IAI.51.1.49-53.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Tenovuo J. The peroxidase system in human secretions. In: Pruitt KM, Tenovuo J, editors. The lactoperoxidase system: Chemistry and Biological Significance. Marcel Dekker; New York: 1985. pp. 101–122. [Google Scholar]
- 12.Tenovuo J. Nonimmunoglobulin defense factors in human saliva. In: Tenovuo J, editor. Human saliva: Clinical chemistry and microbiology. Vol. 2. Boca Raton, FL: CRC Press; 1989. pp. 55–91. [Google Scholar]
- 13.Mäkinen KK, Tenovuo J. Chromatographic separation of human salivary peroxidases. Acta Odontol Scand. 1976;34:141–150. doi: 10.3109/00016357609002561. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Tenovuo J. Different molecular forms of human salivary lactoperoxidase. Arch Oral Biol. 1981;26:1051–1055. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(81)90116-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Pruitt KM, Adamson M. Enzyme activity of salivary lactoperoxidase adsorbed to human enamel. Infect Immun. 1977;17:112–116. doi: 10.1128/IAI.17.1.112-116.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Tenovuo J, Valtakoski J, Knuuttila ML. Antibacterial activity of lactoperoxidase adsorbed by human salivary sediment and hydroxyapatite. Caries Res. 1977;11:257–262. doi: 10.1159/000260277. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Pruitt KM, Adamson M, Arnold R. Lactoperoxidase binding to streptococci. Infect Immun. 1979;25:304–309. doi: 10.1128/IAI.25.1.304-309.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Cole MF, Hsu SD, Baum BJ, Bowen WH, Sierra Ll, Aquirre M, Gillepsie G. Specific and nonspecific immune factors in dental plaque fluid and saliva from young and old populations. Infect Immun. 1981;31:998–1002. doi: 10.1128/IAI.31.3.998-1002.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Wright DE. The differential leucocyte count of human saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 1968;13:1159–1161. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90069-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Raeste AM. The differential count of oral leukocytes. Scand J Dent Res. 1972;80:63–67. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0722.1972.tb00263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Skapski H, Lehner T. A crevicular washing method for investigating immune components of crevicular fluid in man. J Periodontal Res. 1976;11:19–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1976.tb00046.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Kowolik MJ, Grant M. Myeloperoxidase activity in human gingival crevicular neutrophils. Arch Oral Biol. 1983;28:293–295. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(83)90070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Smith QT, Yang CH. Salivary myeloperoxidase of young adult humans. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1984;175:468–475. doi: 10.3181/00379727-175-41822. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Vidović A, Vidović Juras D, Vučićević Boras V, Lukač J, Grubišić-Ilić M, Rak D, Sabioncello A. Determination of leucocyte subsets in human saliva by flow cytometry. Arch Oral Biol. 2012;57:577–583. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2011.10.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Calonius PE. The leukocyte count in saliva. Oral Surg Oral Med Oral Pathol. 1958;11:43–46. doi: 10.1016/0030-4220(58)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Woolweaver DA, Koch GG, Crawford JJ, Lundblad RL. Relation of the orogranulocytic migratory rate to periodontal disease and blood leukocyte count: A clinical study. J Dent Res. 1972;51:929–939. doi: 10.1177/00220345720510043401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Cao CF, Smith QT. Crevicular fluid myeloperoxidase at healthy, gingivitis and periodontitis sites. J Clin Periodontol. 1989;16:17–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.1989.tb01606.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Aune TM, Thomas EL. Accumulation of hypothiocyanite ion during peroxidase-catalysed oxidation of thiocyanate ion. Eur J Biochem. 1977;80:209–214. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11873.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Aune TM, Thomas EL. Oxidation of protein sulfhydryls by products of peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation of thiocyanate ion. Biochemistry. 1978;17:1005–1010. doi: 10.1021/bi00599a010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Thomas EL, Milligan TW, Joyner RE, Jefferson MM. Antibacterial activity of hydrogen peroxide and the lactoperoxidase-hydrogen peroxide-thiocyanate system against oral streptococci. Infect Immun. 1994;62:529–535. doi: 10.1128/IAI.62.2.529-535.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Clem WH, Klebanoff SJ. Inhibitory effect of saliva on glutamic acid accumulation by Lactobacillus acidophilus and the role of the lactoperoxidase-thiocyanate system. J Bacteriol. 1966;91:1848–1853. doi: 10.1128/JB.91.5.1848-1853.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Courtois P, Majerus P, Labbé M, Vanden Abbeele A, Yourassowsky E, Pourtois M. Susceptibility of anaerobic microorganisms to hypothiocyanite produced by lactoperoxidase. Acta Stomatol Belg. 1992;89:155–162. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Ahariz M, Mouhyi J, Louette P, Van Reck J, Malevez C, Courtois P. Adsorption of peroxidase on titanium surfaces: A pilot study. J Biomed Mater Res. 2000;52:567–571. doi: 10.1002/1097-4636(20001205)52:3<567::AID-JBM16>3.0.CO;2-K. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Sarr D, Tóth E, Gingerich A, Rada B. Antimicrobial actions of dual oxidases and lactoperoxidase. J Microbiol. 2018;56:373–386. doi: 10.1007/s12275-018-7545-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Winterbourn CC, Kettle AJ, Hampton MB. Reactive oxygen species and neutrophil function. Annu Rev Biochem. 2016;85:765–792. doi: 10.1146/annurev-biochem-060815-014442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Redanz S, Cheng X, Giacaman RA, Pfeifer CS, Merritt J, Kreth J. Live and let die: Hydrogen peroxide production by the commensal flora and its role in maintaining a symbiotic microbiome. Mol Oral Microbiol. 2018;33:337–352. doi: 10.1111/omi.12231. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Kraus FW, Nickerson JF, Perry WI, Walker AP. Peroxide and peroxidogenic bacteria in human saliva. J Bacteriol. 1957;73:727–735. doi: 10.1128/JB.73.6.727-735.1957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Carlsson J, Iwami Y, Yamada T. Hydrogen peroxide excretion by oral streptococci and effect of lactoperoxidase-thiocyanate-hydrogen peroxide. Infect Immun. 1983;40:70–80. doi: 10.1128/IAI.40.1.70-80.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ryan CS, Kleinberg I. Bacteria in human mouths involved in the production and utilization of hydrogen peroxide. Arch Oral Biol. 1995;40:753–763. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(95)00029-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Amano A, Tamagawa H, Takagaki M, Murakami Y, Shizukuishi S, Tsunemitsu A. Relationship between enzyme activities involved in oxygen metabolism and oxygen tolerance in black-pigmented bacteroides. J Dent Res. 1988;67:1196–1199. doi: 10.1177/00220345880670090901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Sheng J, Nguyen PT, Marquis RE. Multi-target antimicrobial actions of zinc against oral anaerobes. Arch Oral Biol. 2005;50:747–757. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2005.01.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Pruitt KM, Tenovuo J, Mansson-Rahemtulla B, Harrington P, Baldone DC. Is thiocyanate peroxidation at equilibrium in vivo? Biochim Biophys Acta. 1986;870:385–391. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(86)90245-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Hänström L, Johansson A, Carlsson J. Lactoperoxidase and thiocyanate protect cultured mammalian cells against hydrogen peroxide toxicity. Med Biol. 1983;61:268–274. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Tenovuo J, Larjava H. The protective effect of peroxidase and thiocyanate against hydrogen peroxide toxicity assessed by the uptake of (3H)-thymidine by human gingival fibroblasts cultured in vitro. Arch Oral Biol. 1984;29:445–451. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(84)90025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Jakubovics NS, Yassin SA, Rickard AH. Community interactions of oral streptococci. Adv Appl Microbiol. 2014;87:43–110. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800261-2.00002-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Sies H. Hydrogen peroxide as a central redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress: Oxidative eustress. Redox Biol. 2017;11:613–619. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2016.12.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Duan D, Scoffield JA, Zhou X, Wu H. Fine-tuned production of hydrogen peroxide promotes biofilm formation of Streptococcus parasanguinis by a pathogenic cohabitant aggregatibacter actinomycetemcomitans. Environ Microbiol. 2016;18:4023–4036. doi: 10.1111/1462-2920.13425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Logothetopoulos JH, Myant NB. Concentration of radio-iodide and 35-S-thiocyanate by the salivary glands. J Physiol. 1956;134:189–194. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1956.sp005634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Stephen KW, Robertson JW, Harden RM, Chisholm DM. Concentration of iodide, pertechnetate thiocyanate, and bromide in saliva from parotid, submandibular, and minor salivary glands in man. J Lab Clin Med. 1973;81:219–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Felker P, Bunch R, Leung AM. Concentrations of thiocyanate and goitrin in human plasma, their precursor concentrations in brassica vegetables, and associated potential risk for hypothyroidism. Nutr Rev. 2016;74:248–258. doi: 10.1093/nutrit/nuv110. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Narkowicz S, Jaszczak E, Polkowska Ż, Kielbratowska B, Kotłowska A, Namieśnik J. Determination of thiocyanate as a biomarker of tobacco smoke constituents in selected biological materials of human origin. Biomed Chromatogr. 2018;32:e4111. doi: 10.1002/bmc.4111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Bourdoux P, Delange F, Gerard M, Mafuta M, Hanson A, Ermans AM. Evidence that cassava ingestion increases thiocyanate formation: A possible etiologic factor in endemic goiter. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1978;46:613–621. doi: 10.1210/jcem-46-4-613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Tenovuo J, Mäkinen KK. Concentration of thiocyanate and ionizable iodine in saliva of smokers and non-smokers. J Dent Res. 1976;55:661–663. doi: 10.1177/00220345760550042001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Chandler JD, Day BJ. Biochemical mechanisms and therapeutic potential of the pseudohalide thiocyanate in human health. Free Radic Res. 2015;49:695–710. doi: 10.3109/10715762.2014.1003372. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Schiff L, Stevens CD, Molle WE, Steinberg H, Kumpe CW, Stewart P. Gastric (and salivary) excretion of radioiodine in man: Preliminary report. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1947;7:349–354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Venturi S, Venturi M. Iodine in evolution of salivary glands and in oral health. Nutr Health. 2009;20:119–134. doi: 10.1177/026010600902000204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Gulaboglu M, Akgül HM, Akgül N, Cetin M. Urine and saliva iodine levels in patients with dental caries and normal healthy volunteers. Trace Elem Electroly. 2012;29:28–33. doi: 10.5414/TEX01186. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Ross GR, Fabersani E, Russo M, Gómez A, Japaze H, González SN, Gauffin Cano P. Effect of excess iodide intake on salivary glands in a Swiss Albino mice model. Biomed Res Int. 2017;2017:6302869. doi: 10.1155/2017/6302869. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Ren H, Qiu H, Liang X, Wang X, Jiang S. Determination of inorganic anions in saliva by electroosmotic flow controlled counterflow isotachophoretic stacking under field-amplified sample injection. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci. 2013;935:75–79. doi: 10.1016/j.jchromb.2013.07.022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Novo DR, Mello JE, Rondan FS, Henn AS, Mello PA, Mesko MF. Bromine and iodine determination in human saliva: Challenges in the development of an accurate method. Talanta. 2019;191:415–421. doi: 10.1016/j.talanta.2018.08.081. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Moss BR, Hall RF, Miller JK, Swanson EW. Effect of thiocyanate on iodide concentrating systems of the calf. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1968;129:153–155. doi: 10.3181/00379727-129-33272. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Tenovuo J. Lactoperoxidase-catalyzed iodine metabolism in human saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23:253–258. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90014-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Sarimo SS, Tenovuo J. Enzymically iodinated human salivary proteins. Fractionation and characterization by column chromatography and electrofocusing. Biochem J. 1977;167:23–29. doi: 10.1042/bj1670023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Bosch EH, van Doorne H, de Vries S. The lactoperoxidase system: The influence of iodide and the chemical and antimicrobial stability over the period of about 18 months. J Appl Microbiol. 2000;89:215–224. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2672.2000.01098.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Schlorke D, Flemmig J, Birkemeyer C, Arnhold J. Formation of cyanogen iodide by lactoperoxidase. J Inorg Biochem. 2016;154:35–41. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2015.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Bafort F, Damblon C, Smargiasso N, De Pauw E, Perraudin JP, Jijakli MH. Reaction product variability and biological activity of the lactoperoxidase system depending on medium ionic strength and pH, and on substrate relative concentration. Chem Biodivers. 2018;15:e1700497. doi: 10.1002/cbdv.201700497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Sebaa S, Faltot M, De Breucker S, Boucherit-Otmani Z, Bafort F, Perraudin JP, Courtois Ph. Ex vivo decontamination of yeast-colonized dentures by iodine-thiocyanate complexes. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2018;10:149–158. doi: 10.2147/CCIDE.S165377. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Tonoyan L, Boyd A, Fleming GTA, Friel R, Gately CM, Mc Cay PH, O'Flaherty V. In vitro comparative cytotoxicity study of a novel biocidal iodo-thiocyanate complex. Toxicol In Vitro. 2018;50:264–273. doi: 10.1016/j.tiv.2018.03.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Pruitt KM, Mansson-Rahemtulla B, Baldone DC, Rahemtulla F. Steady-state kinetics of thiocyanate oxidation catalyzed by human salivary peroxidase. Biochemistry. 1988;27:240–245. doi: 10.1021/bi00401a036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Ashby MT. Inorganic chemistry of defensive peroxidases in the human oral cavity. J Dent Res. 2008;87:900–914. doi: 10.1177/154405910808701003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Pruitt KM, Mansson-Rahemtulla B, Tenovuo J. Detection of the hypothiocyanite (OSCN-) ion in human parotid saliva and the effect of pH on OSCN- generation in the salivary peroxidase antimicrobial system. Arch Oral Biol. 1983;28:517–525. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(83)90184-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Thomas EL, Bates KP, Jefferson MM. Hypothiocyanite ions: Detection of the antimicrobial agent in human saliva. J Dent Res. 1980;59:1446–1472. doi: 10.1177/00220345800590090201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Pruitt KM, Kamau DN, Miller K, Månsson-Rahemtulla B, Rahemtulla F. Quantitative, standardized assays for determining the concentrations of bovine lactoperoxidase, human salivary peroxidase, and human myeloperoxidase. Anal Biochem. 1990;191:278–286. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(90)90220-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Bafort F, Barthelemy JP, Parisi O, Perraudin JP, Jijakli HM. Development of a colorimetric method for the dosage of OI- anions and I2 in aqueous media. Commun Agric Appl Biol Sci. 2014;79:155–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Thibodeau EA, Bowen WH, Marquis RE. pH-dependent fluoride inhibition of peroxidase activity. J Dent Res. 1985;64:1211–1213. doi: 10.1177/00220345850640100601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Mansson-Rahemtulla B, Baldone DC, Pruitt KM, Rahemtulla F. Specific assays for peroxidases in human saliva. Arch Oral Biol. 1986;31:661–668. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(86)90095-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.White WE, Jr, Pruitt KM, Mansson-Rahemtulla B. Peroxidase-thiocyanate-peroxide antibacterial system does not damage DNA. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1983;23:267–272. doi: 10.1128/AAC.23.2.267. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Altman LC, Baker C, Fleckman P, Luchtel D, Oda D. Neutrophil-mediated damage to human gingival epithelial cells. J Periodontal Res. 1992;27:70–79. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1992.tb02088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Ahariz M, Courtois P. Candida albicans susceptibility to lactoperoxidase-generated hypoiodite. Clin Cosmet Investig Dent. 2010;2:69–78. doi: 10.2147/CCIDE.S10891. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Molloy C, Shepherd MG, Sullivan PA. Identification of envelope proteins of Candida albicans by vectorial iodination. Microbios. 1989;57:73–83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Fischer AJ, Lennemann NJ, Krishnamurthy S, Pócza P, Durairaj L, Launspach JL, Rhein BA, Wohlford-Lenane C, Lorentzen D, Bánfi B, McCray PB., Jr Enhancement of respiratory mucosal antiviral defenses by the oxidation of iodide. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2011;45:874–881. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2010-0329OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Derscheid RJ, van Geelen A, Berkebile AR, Gallup JM, Hostetter SJ, Banfi B, McCray PB, Jr, Ackermann MR. Increased concentration of iodide in airway secretions is associated with reduced respiratory syncytial virus disease severity. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2014;50:389–397. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2012-0529OC. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Shoemake BM, Vander Ley BL, Newcomer BW, Heller MC. Efficacy of oral administration of sodium iodide to prevent bovine respiratory disease complex. J Vet Intern Med. 2018;32:516–524. doi: 10.1111/jvim.14903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Kumlien A, Carlsöö B, Bloom GD. Iodide accumulation and peroxidase activity in the submandibular salivary gland of the normal and castrated male hamster. Arch Oral Biol. 1974;19:577–582. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(74)90075-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Tsuda S, Soutome S, Hayashida S, Funahara M, Yanamoto S, Umeda M. Topical povidone iodine inhibits bacterial growth in the oral cavity of patients on mechanical ventilation: A randomized controlled study. BMC Oral Health. 2020;20:62. doi: 10.1186/s12903-020-1043-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Bafort F, Parisi O, Perraudin JP, Jijakli H. The lactoperoxidase system: A natural biochemical biocontrol agent for pre- and post-harvest applications. J Phytopathol. 2017;165:22–34. doi: 10.1111/jph.12532. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Lewis C, Skoog DA. Spectrophotometric study of a thiocyanate complex of iodine. J Am Chem Soc. 1962;84:1101–1106. doi: 10.1021/ja00866a007. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Long C, Skoog DA. A thiocyanate complex of Iodine (I) Inorg Chem. 1966;5:206–210. doi: 10.1021/ic50036a011. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Országh I, Bazsa G, Beck MT. Spectrophotometric study of the reversible iodine-thiocyanate interaction. Inorganica Chim Acta. 1972;6:271–274. doi: 10.1016/S0020-1693(00)91797-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Scott McIndoe J, Tuck DG. Studies of polyhalide ions in aqueous and non-aqueous solution by electrospray mass spectrometry. Dalt Trans. 2003;2003:244–248. doi: 10.1039/b208035b. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Courtois PH, Pourtois M. Purification of NADH: Hypothiocyanite oxidoreductase in Streptococcus sanguis. Biochem Mol Med. 1996;57:134–138. doi: 10.1006/bmme.1996.0019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Tonoyan L, Fleming GTA, Mc Cay PH, Friel R, O'Flaherty V. Antibacterial potential of an antimicrobial agent inspired by peroxidase-catalyzed systems. Front Microbiol. 2017;8:680. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2017.00680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Tenovuo J, Pruitt KM. Relationship of the human salivary peroxidase system to oral health. J Oral Pathol. 1984;13:573–584. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1984.tb01459.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Hogg DM, Jago GR. The oxidation of reduced nicotinamide nucleotides by hydrogen peroxide in the presence of lactoperoxidase and thiocyanate, iodide or bromide. Biochem J. 1970;117:791–797. doi: 10.1042/bj1170791. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Tenovuo J, Mansson-Rahemtulla B, Pruitt KM, Arnold R. Inhibition of dental plaque acid production by the salivary lactoperoxidase antimicrobial system. Infect Immun. 1981;34:208–214. doi: 10.1128/IAI.34.1.208-214.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Ihalin R, Loimaranta V, Lenander-Lumikari M, Tenovuo J. The effects of different (pseudo)halide substrates on peroxidase-mediated killing of Actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans. J Periodontal Res. 1998;33:421–427. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0765.1998.tb02338.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Fadel M, Courtois P. Effect of peroxidase-generated hypothiocyanite on the survival rate of Porphyromonas gingivalis NCTC 11834. Med Sci Res. 1999;27:667–669. [Google Scholar]
- 98.Fadel M, Courtois P. Inhibitory effect of lactoperoxidase-generated hypothiocyanite upon black pigmented anaerobe growth. Int J Mol Med. 2001;8:59–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Majerus PM, Courtois PA. Susceptibility of Candida albicans to peroxidase-catalyzed oxidation products of thiocyanate, iodide and bromide. J Biol Buccale. 1992;20:241–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Courtois P, van Beers D, de Foor M, Mandelbaum IM, Pourtois M. Abolition of herpes simplex cytopathic effect after treatment with peroxidase generated hypothiocyanite. J Biol Buccale. 1990;18:71–74. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Pourtois M, Binet C, Van Tieghem N, Courtois P, Vandenabbeele A, Thiry L. Saliva can contribute in quick inhibition of HIV infectivity. AIDS. 1991;5:598–600. doi: 10.1097/00002030-199105000-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Cegolon L, Salata C, Piccoli E, Juarez V, Palu' G, Mastrangelo G, Calistri A. In vitro antiviral activity of hypothiocyanite against A/H1N1/2009 pandemic influenza virus. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2014;217:17–22. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2013.03.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Patel U, Gingerich A, Widman L, Sarr D, Tripp RA, Rada B. Susceptibility of influenza viruses to hypothiocyanite and hypoiodite produced by lactoperoxidase in a cell-free system. PLoS One. 2018;13:e0199167. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0199167. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Cegolon L, Javanbakht M, Mastrangelo G. Nasal disinfection for the prevention and control of COVID-19: A scoping review on potential chemo-preventive agents. Int J Hyg Environ Health. 2020;230:113605. doi: 10.1016/j.ijheh.2020.113605. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Nguyen GT, Green ER, Mecsas J. Neutrophils to the ROScue: Mechanisms of NADPH oxidase activation and bacterial resistance. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2017;7:373. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2017.00373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Carlsson J. Salivary peroxidase: An important part of our defense against oxygen toxicity. J Oral Pathol. 1987;16:412–416. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0714.1987.tb02077.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Cáp M, Váchová L, Palková Z. Reactive oxygen species in the signaling and adaptation of multicellular microbial communities. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2012;2012:976753. doi: 10.1155/2012/976753. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.van Steenberghe D, Van den Eynde E, Jacobs R, Quirynen M. Effect of a lactoperoxidase containing toothpaste in radiation-induced xerostomia. Int Dent J. 1994;44:133–138. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Lenander-Lumikari M, Månsson-Rahemtulla B, Rahemthulla F. Lysozyme enhances the inhibitory effects of the peroxidase system on glucose metabolism of Streptococcus mutans. J Dent Res. 1992;71:484–490. doi: 10.1177/00220345920710031201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Sardaro N, Della Vella F, Incalza MA, DI Stasio D, Lucchese A, Contaldo M, Laudadio C, Petruzzi M. Oxidative stress and oral mucosal diseases: An overview. In Vivo. 2019;33:289–296. doi: 10.21873/invivo.11474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Magacz M, Kędziora K, Sapa J, Krzyściak W. The significance of lactoperoxidase system in oral health: Application and efficacy in oral hygiene products. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20:1443. doi: 10.3390/ijms20061443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Mansson-Rahemtulla B, Pruitt KM, Tenovuo J, Le TM. A mouthrinse which optimizes in vivo generation of hypothiocyanite. J Dent Res. 1983;62:1062–1066. doi: 10.1177/00220345830620101101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.FAO/WHO report, corp-author. Report of an FAO/WHO technical meeting. FAO Headquarters; Rome, Italy: 2006. Benefits and potential risks of the lactoperoxidase system of raw milk preservation. 28 November-2 December 2005. [Google Scholar]
- 114.Artym J, Zimecki M. Milk-derived proteins and peptides in clinical trials. Postepy Hig Med Dosw (Online) 2013;67:800–816. doi: 10.5604/17322693.1061635. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Welk A, Meller CH, Schubert R, Schwahn CH, Kramer A, Below H. Effect of lactoperoxidase on the antimicrobial effectiveness of the thiocyanate hydrogen peroxide combination in a quantitative suspension test. BMC Microbiol. 2009;9:134. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-9-134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Modesto A, Lima KC, de Uzeda M. Effects of three different infant dentifrices on biofilms and oral microorganisms. J Clin Pediatr Dent. 2000;24:237–243. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Tenovuo J. Clinical applications of antimicrobial host proteins lactoperoxidase, lysozyme and lactoferrin in xerostomia: Efficacy and safety. Oral Dis. 2002;8:23–29. doi: 10.1034/j.1601-0825.2002.1o781.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Vanden Abbeele A, De Meel H, Courtois P, Pourtois M. Influence of a hypoiodite mouth-wash on dental plaque formation in vivo. Bull Group Int Rech Sci Stomatol Odontol. 1996;39:57–61. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Nakano M, Wakabayashi H, Sugahara H, Odamaki T, Yamauchi K, Abe F, Xiao JZ, Murakami K, Ishikawa K, Hironaka S. Effects of lactoferrin and lactoperoxidase-containing food on the oral microbiota of older individuals. Microbiol Immunol. 2017;61:416–426. doi: 10.1111/1348-0421.12537. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Lenander-Lumikari M, Tenovuo J, Mikola H. Effects of a lactoperoxidase system-containing toothpaste on levels of hypothiocyanite and bacteria in saliva. Caries Res. 1993;27:285–291. doi: 10.1159/000261552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Koch G, Edlund K, Hoogendoorn H. Lactoperoxidase in the prevention of plaque accumulation, gingivitis and dental caries. II. Effect of mouthrinses with amyloglucosidase and glucoseoxidase on plaque accumulation on teeth in individuals on a sucrose diet. Odontol Revy. 1973;24:367–372. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Hugoson A, Koch G, Thilander H, Hoogendoorn H. Lactoperoxidase in the prevention of plaque accumulation, gingivitis and dental caries. 3. Effect of mouthrinses with amyloglucosidase and glucoseoxidase in the model system of experimental gingivitis and caries in man. Odontol Revy. 1974;25:69–80. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Koch G, Strand G. Effect of an enzyme dentifrice on caries. A two-year clinical pilot study. Swed Dent J. 1979;3:9–13. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Rotgans J, Hoogendoorn H. The effect of brushing with a toothpaste containing amyloglucosidase and glucose oxidase on dental caries in rats. Caries Res. 1979;13:150–153. doi: 10.1159/000260394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Afseth J, Rølla G. Clinical experiments with a toothpaste containing amyloglucosidase and glucose oxidase. Caries Res. 1983;17:472–475. doi: 10.1159/000260704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Midda M, Cooksey MW. Clinical uses of an enzyme-containing dentifrice. J Clin Periodontol. 1986;13:950–956. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-051X.1986.tb01433.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Bánóczy J, Dombi C, Czegledly A, Sari K. A clinical study with lactoperoxidase-containing gel and toothpaste in patients with dry mouth syndrome. J Clin Dent. 1994;5:65–69. [Google Scholar]
- 128.Toljanic JA, Siddiqui AA, Patterson GL, Irwin ME. An evaluation of a dentifrice containing salivary peroxidase elements for the control of gingival disease in patients with irradiated head and neck cancer. J Prosthet Dent. 1996;76:292–296. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3913(96)90174-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Epstein JB, Emerton S, Le ND, Stevenson-Moore P. A double-blind crossover trial of Οral Βalance gel and Biotene® toothpaste versus placebo in patients with xerostomia following radiation therapy. Oral Oncol. 1999;35:132–137. doi: 10.1016/S1368-8375(98)00109-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Warde P, Kroll B, O'Sullivan B, Aslanidis J, Tew-George E, Waldron J, Maxymiw W, Liu FF, Payne D, Cummings B. A phase II study of Biotene in the treatment of postradiation xerostomia in patients with head and neck cancer. Support Care Cancer. 2000;8:203–208. doi: 10.1007/s005200050286. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Kirstilä V, Lenander-Lumikari M, Söderling E, Tenovuo J. Effects of oral hygiene products containing lactoperoxidase, lysozyme, and lactoferrin on the composition of whole saliva and on subjective oral symptoms in patients with xerostomia. Acta Odontol Scand. 1996;54:391–397. doi: 10.3109/00016359609003557. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Matear DW, Barbaro J. Effectiveness of saliva substitute products in the treatment of dry mouth in the elderly: A pilot study. J R Soc Promot Health. 2005;125:35–41. doi: 10.1177/146642400512500113. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Hatti S, Ravindra S, Satpathy A, Kulkarni RD, Parande MV. Biofilm inhibition and antimicrobial activity of a dentifrice containing salivary substitutes. Int J Dent Hyg. 2007;5:218–224. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5037.2007.00249.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Gil-Montoya JA, Guardia-López I, González-Moles MA. Evaluation of the clinical efficacy of a mouthwash and oral gel containing the antimicrobial proteins lactoperoxidase, lysozyme and lactoferrin in elderly patients with dry mouth-a pilot study. Gerodontology. 2008;25:3–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1741-2358.2007.00197.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Shin K, Yaegaki K, Murata T, Ii H, Tanaka T, Aoyama I, Yamauchi K, Toida T, Iwatsuki K. Effects of a composition containing lactoferrin and lactoperoxidase on oral malodor and salivary bacteria: A randomized, double-blind, crossover, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Clin Oral Investig. 2011;15:485–493. doi: 10.1007/s00784-010-0422-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Jose A, Siddiqi M, Cronin M, DiLauro TS, Bosma ML. A randomized clinical trial in subjects with dry mouth evaluating subjective perceptions of an experimental oral gel, an oral rinse and a mouth spray compared to water. Am J Dent. 2016;29:58–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Nakano M, Shimizu E, Wakabayashi H, Yamauchi K, Abe F. A randomized, double-blind, crossover, placebo-controlled clinical trial to assess effects of the single ingestion of a tablet containing lactoferrin, lactoperoxidase, and glucose oxidase on oral malodor. BMC Oral Health. 2016;16:37. doi: 10.1186/s12903-016-0199-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Morita Y, Ishikawa K, Nakano M, Wakabayashi H, Yamauchi K, Abe F, Ooka T, Hironaka S. Effects of lactoferrin and lactoperoxidase-containing food on the oral hygiene status of older individuals: A randomized, double blinded, placebo-controlled clinical trial. Geriatr Gerontol Int. 2017;17:714–721. doi: 10.1111/ggi.12776. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Barbe AG, Schmidt-Park Y, Hamacher S, Derman SHM, Noack MJ. Efficacy of GUM® Hydral versus Biotène® Oralbalance mouthwashes plus gels on symptoms of medication-induced xerostomia: A randomized, double-blind, crossover study. Clin Oral Investig. 2018;22:169–180. doi: 10.1007/s00784-017-2096-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Nakano M, Yoshida A, Wakabayashi H, Tanaka M, Yamauchi K, Abe F, Masuda Y. Effect of tablets containing lactoferrin and lactoperoxidase on gingival health in adults: A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled clinical trial. J Periodontal Res. 2019;54:702–708. doi: 10.1111/jre.12679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Pruitt KM, Tenovuo J, Fleming W, Adamson M. Limiting factors for the generation of hypothiocyanite ion, an antimicrobial agent, in human saliva. Caries Res. 1982;16:315–323. doi: 10.1159/000260614. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Sebaa S, Lybaert P, Boucherit-Otmani Z, Courtois PH, Ahariz M. Ex vivo yeast-decontamination of denture by H2O2/Iodide/Lactoperoxidase system: Need to overpass the microbial H2O2 catabolism. Oral Health Dent Manag. 2015;14:62–69. [Google Scholar]
- 143.Herlofson BB, Barkvoll P. Sodium lauryl sulfate and recurrent aphthous ulcers. A preliminary study. Acta Odontol Scand. 1994;52:257–259. doi: 10.3109/00016359409029036. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Cawley A, Golding S, Goulsbra A, Hoptroff M, Kumaran S, Marriott R. Microbiology insights into boosting salivary defences through the use of enzymes and proteins. J Dent. 2019;80(Suppl 1):S19–S25. doi: 10.1016/j.jdent.2018.10.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Adams SE, Arnold D, Murphy B, Carroll P, Green AK, Smith AM, Marsh PD, Chen T, Marriott RE, Brading MG. A randomised clinical study to determine the effect of a toothpaste containing enzymes and proteins on plaque oral microbiome ecology. Sci Rep. 2017;7:43344. doi: 10.1038/srep43344. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Memarzadeh Zahedani M, Schwahn C, Baguhl R, Kocher T, Below H, Welk A. Association of salivary peroxidase activity and concentration with periodontal health: A validity study. J Clin Periodontol. 2017;44:803–812. doi: 10.1111/jcpe.12754. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Herrero ER, Boon N, Bernaerts K, Slomka V, Verspecht T, Quirynen M, Teughels W. Clinical concentrations of peroxidases cause dysbiosis in in vitro oral biofilms. J Periodontal Res. 2018;53:457–466. doi: 10.1111/jre.12534. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Miller DP, Fitzsimonds ZR, Lamont RJ. Metabolic signaling and spatial interactions in the oral polymicrobial community. J Dent Res. 2019;98:1308–1314. doi: 10.1177/0022034519866440. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Diaz PI, Valm AM. Microbial interactions in oral communities mediate emergent biofilm properties. J Dent Res. 2020;99:18–25. doi: 10.1177/0022034519880157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.


