Abstract
Background/Aims
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) is a common medical condition, frequently refractory to medical therapy. Nickel is a leading cause of allergic contact dermatitis. Although nickel is widely found in foods, the effect of nickel on GERD is unknown. This pilot study sought to evaluate the effect of a low-nickel diet on GERD and determine if epicutaneous patch testing to nickel could predict responsiveness to a low-nickel diet.
Methods
This prospective, single-site pilot study recruited 20 refractory GERD patients as determined by GERD Health-Related Quality of Life (GERD-HRQL) scores. All patients had epicutaneous patch testing for nickel and were then instructed to follow a low-nickel diet for 8 weeks regardless of patch test results. GERD-HRQL was recorded at baseline and following 8 weeks of a low-nickel diet. Demographic and clinical data associated with GERD and nickel allergy were recorded. A Wilcoxon signed-rank test and nonparametric analysis of longitudinal data were run to determine statistical significance in pre- and post- GERD-HRQL scores in nickel patch test–positive and negative groups.
Results
Nearly all (19/20 [95%]) participants reported reduced GERD symptoms after 8 weeks on a low-nickel diet. Mean total GERD-HRQL, regurgitation, and heartburn scores declined (27.05 ± 16.04, 11.45 ± 6.46, 10.85 ± 8.29). Participants with positive vs. negative patch testing to nickel responded equivalently to a low-nickel diet.
Conclusions
A low-nickel diet improves GERD symptoms, but responsiveness to a low-nickel diet does not correlate with epicutaneous patch testing to nickel.
Trial registration
Clinicaltrials.gov number: NCT03720756
Keywords: Dietary treatment, Esophagus, Food allergy, Gastroesophageal reflux disease, Nickel, Patch test
Graphical Abstract
Introduction
The American Gastroenterological Association states that gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), also known as acid reflux, occurs when acid or other stomach contents back up in the esophagus. It is one of the most commonly diagnosed gastrointestinal (GI) diseases in Western countries [1]. Food allergies and sensitization of the esophageal mucosa to allergens are suspected to play a role [2]. Furthermore, there is frequent co-existence of GERD and food allergy. In infants, this can be up to 40% to 50% [3–5]. In children, GERD can cause vomiting, failure to thrive, and growth and sleep disturbances. Children with refractory GERD showed strong correlation between oral cow’s milk challenge and patch testing to cow’s milk [6]. Patch testing had 79% sensitivity and 91% specificity for cow’s milk allergy in pediatric patients with GI symptoms, predominately GERD [7]. Children with positive patch testing to cow’s milk have higher reflux index compared with patch test-negative GERD patients [8].
In adults, the common symptoms of GERD include heartburn and regurgitation following large or fatty meals. Evaluation of 65 adults with GERD on proton pump inhibitors (PPI) showed 80% improved after a 6-week restriction diet guided by patch testing. Sensitization to foods in refractory GERD was found to be independent of PPI treatment duration [9]. Other studies have shown that patients with GERD are more likely to have nickel sensitization than matched controls [10, 11]. Thus, in both children and adults, there are multiple studies demonstrating an association between cutaneous allergy and GERD.
Nickel is a durable, silver-colored metal frequently found in objects such as jewelry. Nickel is the most common allergen detected in patch test clinics with approximately 20% of those tested reacting positively to nickel [12]. Patch test positivity to nickel is traditionally more common in women due to more prevalent piercing practices compared with men. Despite extensive literature linking nickel to allergic contact dermatitis on the skin, little is known regarding the potential of nickel-rich foods to cause allergic sensitization of the GI mucosa. On the contrary, a nickel-free diet has been shown to have beneficial effects on Helicobacter pylori eradication [13]. Many foods rich in nickel are associated with GERD, yet the relationship between nickel allergy and GERD remains unclear [14].
The primary objectives of this study were to determine whether those with GERD are more likely than the general population to have nickel allergy, evaluate if GERD symptoms improve following a low-nickel diet, and determine if epicutaneous patch testing for nickel could predict responsiveness to a low-nickel diet.
Methods
Participants
We prospectively enrolled patients seen at the West Virginia University Digestive Disease and Dermatology clinics between February 2019 and December 2019. Enrollment criteria included age 18 years or older with a history of GERD as diagnosed by a gastroenterologist, and confirmed symptomatic GERD at the time of initial visit as determined by a score of at least 30 on the validated GERD Health-Related Quality of Life (GERD-HRQL) questionnaire [15]. Patients actively taking a PPI must have been on the PPI for at least 3 months without resolution of GERD symptoms to be considered refractory. Patients were excluded if they had treatment with a steroid (oral or topical) or experienced sunburn within the past 4 weeks because these are known to cause false negative patch test results. Patients with prior history of patch testing were also excluded. All vulnerable populations were excluded. The study protocol was approved by the West Virginia University institutional review board.
Patch testing
Epicutaneous patch testing was performed under occlusive chamber application preferentially to the patient’s upper back using a 2 × 5 panel Finn Chambers AQUA® (Smart Practice, Phoenix, Arizona, US) system secured with non-adhesive surgical tape. In total, four allergens including nickel sulfate hexahydrate, cobalt (II) chromium hexahydrate, balsam of Peru, and cinnamic aldehyde were used as test allergens (allergEAZE, Brial Allergen GmbH, Germany) along with a negative control. The additional allergens were chosen to aid in patient blinding and because they have previously been implicated in GI allergy [2]. The patch test was occluded for 48 h. All subjects were asked to photograph the patch-tested skin after 48 and 96 h to allow two visual readings. Two board-certified dermatologists assessed patch test reactions using the established International Contact Dermatitis Research Group (ICDRG) system for clinical scoring of allergic reactions as shown in Table 1 [16]. All doubtful reactions were classified as patch test-negative reactions. Patients were blinded to patch test results until completion of the 8-week low-nickel diet (Supplementary Table 1) and the follow-up GERD-HRQL questionnaire.
Table 1.
International Contact Dermatitis Research Group patch test scaling recommendations
| Symbol | Morphology | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|
| - | No reaction | Negative |
| ?+ | Non-palpable, faint erythema | Doubtful reaction |
| 1+ | Erythema, infiltration, possibly discrete papules | Weak positive |
| 2+ | Erythema, infiltration, papules, vesicles | Strong positive |
| 3+ | Erythema, infiltration, confluent vesicles | Extreme positive |
| ir | Different types of reactions (blisters, soap effect) | Irritant reaction |
GERD-HRQL scoring
The GERD-HRQL instrument, as recommended for use by the European Association for Endoscopic Surgery, assessed GERD symptoms before and after low-nickel diet implementation [17]. This questionnaire uses a numerical Likert-type response, whereby each patient assesses the severity of symptoms on an ordinal scale. The GERD-HRQL has a possible maximum score of 75 and a minimum score of 0, with the heartburn and regurgitation arms having maximum and minimum scores of 30 and 0 each. Patients returned for a follow-up appointment within 2 weeks of completion of the low-nickel diet to complete the follow-up GERD-HRQL.
Statistical analysis
Study participants who reacted positive to nickel sulfate hexahydrate were compared with participants who tested negative. Data analyses were performed using R (version 3.6.2, R development core team, Vienna, Austria). A Wilcoxon signed-rank test was conducted to determine statistical significance between GERD-HRQL score distribution before and after low-nickel diet implementation. A nonparametric analysis of the longitudinal data model was conducted, where the outcome variable was GERD-HRQL scoring and the classification factors included time and group, to determine if a significant difference existed between nickel patch test-positive and negative total GERD-HRQL, regurgitation, and heartburn scores [18]. Fisher’s exact test was conducted to determine if there was a significant difference between the prevalence of nickel allergy in GERD and the general population.
Results
Demographics
The characteristics of study participants are presented in Table 2. All patients presented with a positive history of regurgitation, heartburn, and gastroesophageal reflux. The total cohort included 20 patients, 16 females and 4 males with a mean age of 49.95 ± 12.74 years. All participants were Caucasian. Smoking history was positive in 8/20 (40%) participants. The average BMI of the study participants was 35.24 ± 9.04 (Table 3).
Table 2.
Baseline characteristics of GERD patients. GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease, HRQL health-related quality of life, BMI body mass index
| Characteristic | Number (%)* |
|---|---|
| Age, mean ± SD, years | 49.95 ± 12.74 |
| Gender | |
| Female | 16 (80) |
| Male | 4 (20) |
| Race | |
| White | 20 (100) |
| Non-white | 0 (0) |
| Smoking history | |
| Yes | 8 (40) |
| No | 12 (60) |
| Asthma | |
| Yes | 12 (60) |
| No | 8 (40) |
| BMI, mean ± SD | 35.24 ± 9.04 |
| Baseline GERD-HRQL, mean ± SD | 48.60 ± 11.44 |
| GERD satisfaction rating | |
| Satisfied | 0 (0) |
| Neutral | 1 (5) |
| Dissatisfied | 19 (95) |
Unless otherwise specified
Table 3.
Patch test reactions and GERD-HRQL scores. GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease, HRQL health-related quality of life
| Participant ID | Nickel patch test reactions | Baseline GERD-HRQL |
Follow-up GERD-HRQL |
Follow-up GERD satisfaction rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | - | 63 | 46 | Dissatisfied |
| 2 | - | 61 | 8 | Satisfied |
| 3 | - | 66 | 7 | Satisfied |
| 4 | - | 52 | 4 | Satisfied |
| 5 | - | 48 | 28 | Neutral |
| 6 | ?+ | 38 | 15 | Neutral |
| 7* | 2+ | 45 | 51 | Dissatisfied |
| 8 | - | 75 | 26 | Satisfied |
| 9 | ?+ | 36 | 11 | Neutral |
| 10 | - | 39 | 1 | Satisfied |
| 11 | - | 39 | 39 | Dissatisfied |
| 12 | - | 33 | 12 | Neutral |
| 13 | - | 59 | 40 | Neutral |
| 14 | - | 48 | 17 | Neutral |
| 15 | - | 56 | 38 | Dissatisfied |
| 16* | 1+ | 49 | 27 | Dissatisfied |
| 17 | - | 38 | 13 | Satisfied |
| 18 | - | 38 | 22 | Satisfied |
| 19 | - | 37 | 2 | Satisfied |
| 20* | 2+ | 52 | 24 | Satisfied |
Nickel allergy–positive participants with at least 1+ on patch testing according to International Contact Dermatitis Research Group criteria
Patch test reactions
Among the study participants, 3 (15%) had patch test positivity to nickel sulfate hexahydrate, 6 (30%) to balsam of Peru, 1 (5%) to cinnamic aldehyde, and none to cobalt (II) chloride hexahydrate. Nickel patch test reactions are shown in Table 2. The prevalence of nickel allergy in GERD was not significantly different than the known prevalence in the general population [19].
GERD-HRQL scores
At baseline, study participants reported GERD-HRQL of 48.60 ± 11.44. Average baseline heartburn and regurgitation scores were 21.10 ±4.25 and 19.65 ±5.44, respectively. Nearly all (19/20 [95%]) study participants saw marked improvement in GERD-HRQL following the implementation of a low-nickel diet. Among all participants, the mean total GERD-HRQL decreased by 27.05 ± 16.04 following low-nickel diet implementation. The mean heartburn score decreased by 11.45 ± 6.46, and the mean regurgitation score decreased by 10.85 ± 8.29. When comparing all study participants, a low-nickel diet significantly decreased total GERD-HRQL (p <0.001), heartburn (p <0.001), and regurgitation scores (p < 0.001).
The subset of participants with patch test positivity to nickel also had improvement with decreased mean total GERD-HRQL, heartburn, and regurgitation scores (14.67 ± 14.82, 6.67 ± 7.59, and 4.67 ± 7.72, respectively), but the improvement was more modest than that of participants with patch test negativity to nickel (29.24 ± 15.23, 12.29 ± 5.85, and 11.94 ± 7.90, respectively). GERD-HRQL, heartburn, and regurgitation scores following a low-nickel diet were not significantly different between those who tested positive vs. negative on patch testing to nickel. Before and after GERD-HRQL scores are shown in Fig. 1.
Fig. 1.
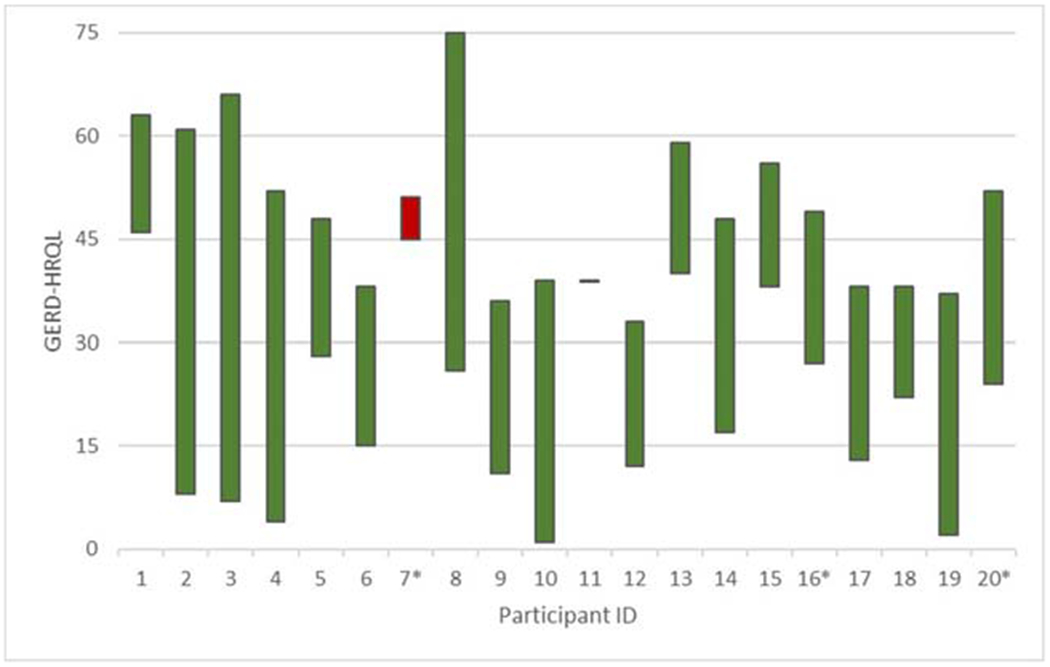
GERD-HRQL score change following low-nickel diet implementation. A candlestick chart depicts the change in GERD-HRQL scores of study participants who completed the 8-week low-nickel diet. A decline in GERD symptom severity is noted in green, while worsening symptom severity is noted in red. Asterisk indicates nickel allergy positive–participants with at least 1+ on patch testing according to ICDRG criteria. GERD gastroesophageal reflux disease, HRQL health-related quality of life, ICDRG International contact dermatitis research group
Satisfaction ratings
Nearly all (19/20 [95%]) participants reported dissatisfaction with GERD symptoms prior to low-nickel diet implementation, with a single participant reporting neutral feelings to GERD symptoms. Following low-nickel diet implementation, 9/20 (45%) participants changed their rating from dissatisfied to satisfied with GERD symptoms, 5/20 (25%) changed from dissatisfied to neutral, 5/20 (25%) stayed dissatisfied, and 1/20 (5%) remained neutral (Fig. 2).
Fig. 2.
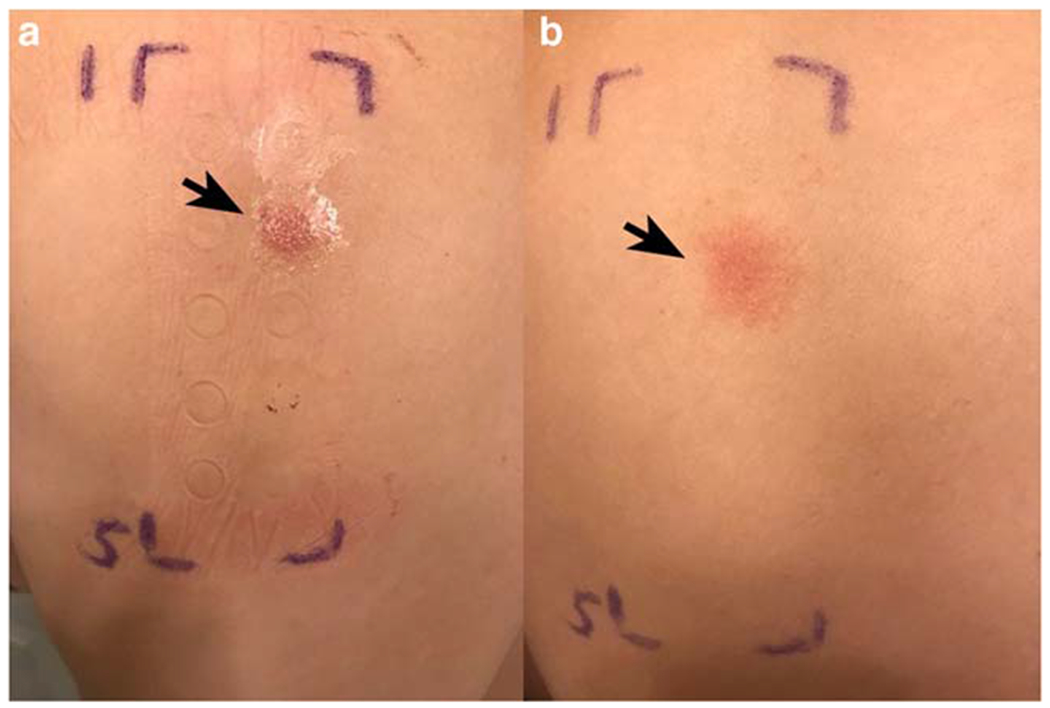
Weak positive reaction at 48 and 96 h. a At 48 h, palpable erythema (arrow) is noted on the upper back located at the site of nickel sulfate hexahydrate Finn Chambers AQUA® (Smart Practice, Phoenix, Arizona, US) system occlusion. b At 96 h, the erythema and infiltration (arrow) have spread to all skin contacted by nickel sulfate hexahydrate. According to International contact dermatitis research group criteria, this patch test was read as 1+
Discussion
Nickel, a metal commonly found in jewelry and other environmental products, is the most common allergen to elicit a positive response on patch testing. Nickel is a well-known cause of allergic contact dermatitis, classically appearing on the earlobes from earrings and near the umbilicus from contact with belt buckles. Ingestion of nickel-rich food products such as cocoa, chocolate, legumes, cereals, and canned foods has been shown to flare dermatitis in nickel-sensitive patients. Likewise, nickel ingestion in foods can cause similar inflammatory reactions in the intestinal mucosa [20]. Thus, dietary consumption of nickel has documented inflammatory effects on the cutaneous and GI epithelium.
GERD is one of the most common medical conditions requiring clinical care. Response to available therapy is frequently unsatisfactory resulting in a specialist referral [21]. Additional treatment options for GERD are warranted, especially diet-based approaches rather than pharmacotherapy. Patch test–guided dietary restriction in GERD has previously been shown to be helpful. This study is the first to examine the effect of a low-nickel diet on GERD symptoms and the first to determine if epicutaneous patch testing to nickel could predict responsiveness to a low-nickel diet.
Low-nickel diet decreased GERD symptom severity in both heartburn and regurgitation in 19/20 (95%) participants and led 14/20 (70%) participants to improve satisfaction ratings pertaining to GERD symptoms. This striking improvement in GERD symptomatology is noteworthy, particularly given high participant satisfaction with results. When asked about changes in GERD symptoms, most participants acknowledged significant improvement, some planning to continue the low-nickel diet due to complete resolution of GERD. Strengths of the study include 100% study completion rate among participants, with 80% (16/20) of participants finding the low-nickel diet tolerable over the 8-week study period. Also, participants and study coordinators were blinded to patch test results until completion of the 8-week low-nickel diet. Limitations of the study include lack of a dietary placebo (i.e. all 20 participants followed the same diet) and small sample size which limited the ability to detect small variations in GERD symptomatology between nickel positive vs. nickel negative participants. Also, participants without a positive patch test reaction may have determined their patch test was negative thereby introducing bias. Furthermore, participants lost 0.3 kg on average after the 8-week intervention, and dietary restriction alone may have led to the improvement in GERD symptoms. Since all participants were Caucasian, these results may not be generalizable to all populations. Finally, some participants may have had alternative diagnoses other than GERD, such as eosinophilic esophagitis.
In conclusion, a low-nickel diet over an 8-week period leads to a marked reduction in GERD symptomatology in 95% of participants. All participants completed the 8-week period of dietary restriction without dropout noting the limited adverse effect on quality of life. Epicutaneous patch testing for nickel was unable to predict responsiveness of GERD symptomatology to a low-nickel diet. Further studies with larger sample size and placebo-controlled dietary intervention are needed to validate these findings. The authors are hopeful this pilot study will stimulate future prospective, randomized clinical trials evaluating the effect of a low-nickel diet in GERD.
Supplementary Material
Bullet points of the study highlights.
What is already known?
Nickel sensitization is more prevalent in gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) patients.
The effect of a low nickel diet on GERD symptoms has not been explored.
What is new in this study?
Among 20 participants placed on a low nickel diet, nearly all (19/20) participants reported reduced GERD symptoms after 8 weeks.
Participants with positive vs. negative patch testing to nickel responded equivalently to a low nickel diet.
What are the future clinical and research implications of the study findings?
A low nickel diet reduces GERD symptoms, regardless of nickel sensitization.
Funding Research reported in this publication was supported by the National Institute of General Medical Sciences of the National Institutes of Health under the West Virginia Clinical Translational Science Institute Award Number 5U54GM104942-04. The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Footnotes
Ethics statement The study was performed in accordance with the Helsinki Declaration of 1975, as revised in 2000 and 2008 concerning human rights, and the authors followed the policy concerning informed consent as shown on Springer.com. The study was conducted after obtaining proper ethical clearance from the institutional ethics committee.
IRB statement The study protocol was approved by the West Virginia University institutional review board.
Guarantor of the article Senior author Swapna Gayam, MD, accepts full responsibility for the conduct of the study, has had access to the data, and controls the decision to publish.
Publisher's Disclaimer: Disclaimer The authors are solely responsible for the data and the contents of the paper. In no way, the Honorary Editor-in-Chief, Editorial Board Members, the Indian Society of Gastroenterology or the printer/publishers are responsible for the results/findings and content of this article.
Electronic supplementary material The online version of this article (https://doi.org/10.1007/s12664-020-01090-3) contains supplementary material, which is available to authorized users.
Conflict of interest AY, RH, MM, EG, WF, RC, ZZ, and SG declare that they have no conflict of interest. All authors had access to study data and approved the final manuscript.
References
- 1.Peery AF, Crockett SD, Murphy CC, et al. Burden and cost of gastrointestinal, liver, and pancreatic diseases in the United States: update 2018. Gastroenterology. 2019;156:254–72.e11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Gayam S, Zinn Z, Chelliah M, Teng J. Patch testing in gastrointestinal diseases-a systematic review of the patch test and atopy patch test. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol. 2018;32:e349–51. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Lacono G, Carroccio A, Cavataio F, et al. Gastroesophageal reflux and cow’s milk allergy in infants: a prospective study. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1996;97:822–7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Cavataio F, Carroccio A, Iacono G. Milk-induced reflux in infants less than one year of age. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2000;30: S36–44. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Salvatore S, Vandenplas Y. Gastroesophageal reflux and cow milk allergy: is there a link? Pediatrics. 2002;110:972–84. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Yukselen A, Celtik C. Food allergy in children with refractory gastroesophageal reflux disease. Pediatr Int. 2016;58:254–8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.de Boissieu D, Waguet J, Dupont C. The atopy patch tests for detection of cow’s milk allergy with digestive symptoms. J Pediatr. 2003;142:203–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Nielsen R, Bindslev-Jensen C, Kruse-Andersen S, Husby S. Severe gastroesophageal reflux disease and cow milk hypersensitivity in infants and children: disease association and evaluation of a new challenge procedure. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2004;39:383–91. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pomiecinski F, Yang AC, Navarro-Rodrigues T, et al. Sensitization to foods in gastroesophageal reflux disease and its relation to eosinophils in the esophagus: is it of clinical importance? Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2010;105:359–63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Stanghellini V, Tosetti C, Benedetto E, et al. Nickel sensitization in patients with gastro-esophageal reflux disease. United European Gastroenterol J. 2016;4:184–90. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Aslan N, Sezikli M, Erdal E. Nickel sensitivity in patients with gastroesophageal reflux disease. Cutan Ocul Toxicol. 2017;36: 347–50. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Zug KA, Pham AK, Belsito DV, et al. Patch testing in children from 2005 to 2012: results from the North American contact dermatitis group. Dermatitis. 2014;25:345–55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Campanale M, Nucera E, Ojetti V, et al. Nickel free-diet enhances the Helicobacter pylori eradication rate: a pilot study. Dig Dis Sci. 2014;59:1851–5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sharma AD. Relationship between nickel allergy and diet. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 2007;73:307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Velanovich V The development of the GERD-HRQL symptom severity instrument. Dis Esophagus. 2007;20:130–4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Fregert S Manual of Contact Dermatitis. 2nd ed. Copenhagen: Munksgaard; 1981. p. 71–6. [Google Scholar]
- 17.Korolija D, Sauerland S, Wood-Dauphinee S, et al. Evaluation of quality of life after laparoscopic surgery: evidence-based guidelines of the European Association for Endoscopic Surgery. Surg Endosc Other Interv Tech. 2004;18:879–97. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Domhof S, Langer F. Nonparametric analysis of longitudinal data in factorial experiments: Wiley-Interscience; 2002. [Google Scholar]
- 19.Shah N, Jalali O, Glover B, Zinn Z. A 5 year retrospective review of contact dermatitis patch testing in West Virginia. W V Med J. 2018;114:36–40. [Google Scholar]
- 20.Di MG, Masci S, Cavallucci E, et al. Immuno-histopathologic changes in the gastrointestinal mucosa in patients with nickel contact allergy. G Ital Med Lav. 1995;17:33–6. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Sifrim D, Zerbib F. Diagnosis and management of patients with reflux symptoms refractory to proton pump inhibitors. Gut. 2012;61:1340–54. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.


