Fig. 5. Univariate analysis of bile acid variables for time-to-event (hepatic decompensation) in PSC.
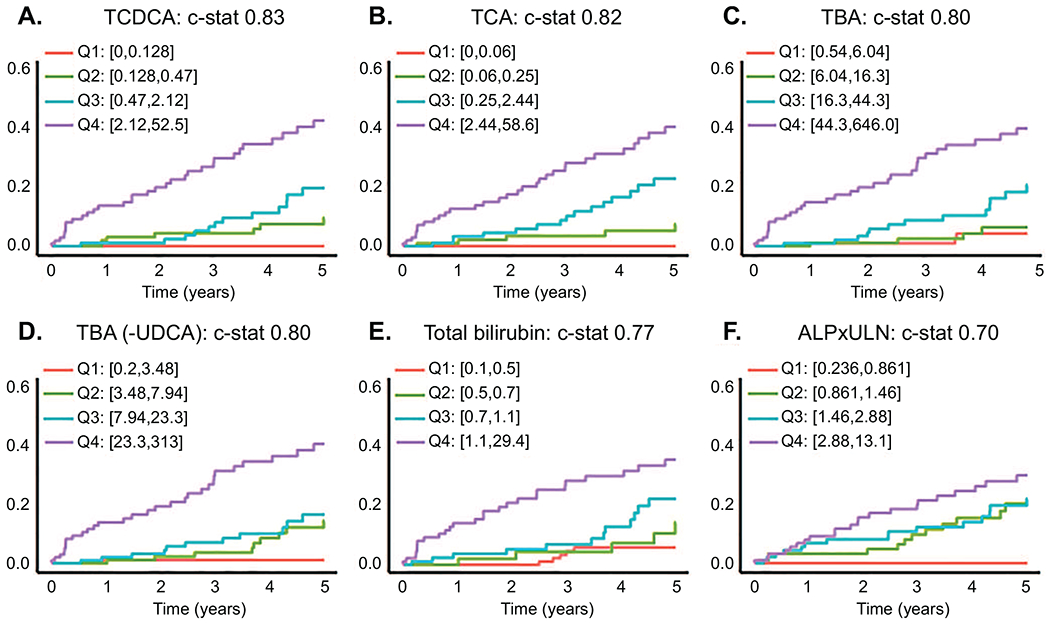
(A) TCDCA, (B) TCA and (C) total bile acids (TBA) were the top 3 variables capable of predicting hepatic decompensation (HD; defined as ascites, esophageal varices or encephalopathy) in PSC over a 5 year window. (D) TBA with UDCA and it’s conjugates subtracted performed similar to TBA. These variables outperformed (E) Total bilirubin and (F) alkaline phosphatase expressed as times upper limit of normal (ALPxULN). Cox proportional hazard models were used to evaluate risk of HD (p<0.001 all variables). The Harrell’s concordance statistic (c-stat) was used to measure discrimination ability of the variables. Data is presented using Aalen-Johansen curves based on quartiles of variable values, accounting for death and liver transplantation as competing risks.
