To the editor:
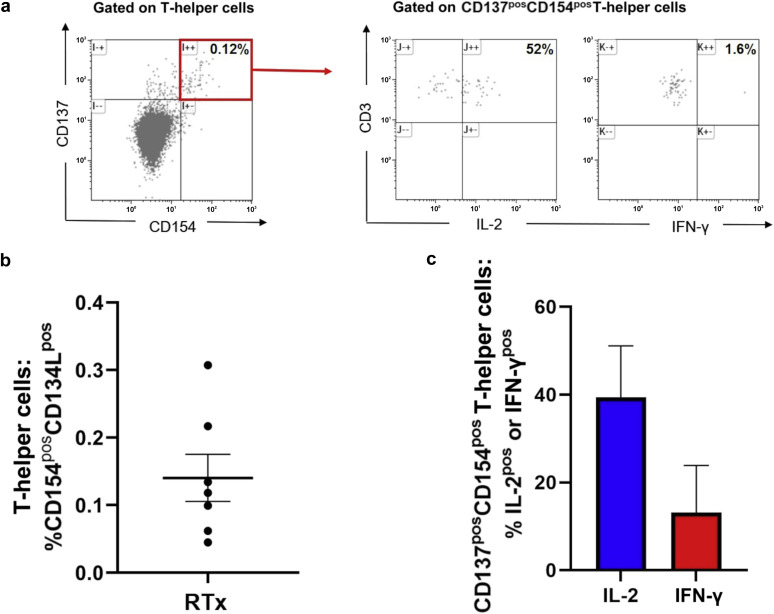
Benotmane et al. have demonstrated that only 48% of renal transplant patients (RTxP) develop a serologic response after vaccination with an mRNA-based severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccine.1 Likewise, we reported that only 22% of RTxP develop anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG after vaccination with the mRNA-based SARS-CoV-2 vaccine BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech).2 To further characterize the immunologic response, we measured the cellular response to BNT162b2 vaccination in 7 RTxP with triple immunosuppression lacking anti–SARS-CoV-2 IgG after vaccination with 2 dosages of BNT162b2 (measured 18–60 days after the second dose). For that purpose, peripheral blood mononuclear cells were isolated from patients and stimulated with overlapping peptide pools for the SARS-CoV-2 spike protein, according to previously published protocols.3 In all 7 patients, S-protein–reactive T-helper cells were detected (Figure 1 ). All patients harbored interleukin-2–producing S-protein–reactive T-helper cells (Figure 1; 39% ± 11% of S-protein–reactive T-helper cells), and in 6 of the 7 patients, interferon-γ–positive S-protein–reactive T-helper cells were present (13% ± 11% of S-protein–reactive T-helper cells).
Figure 1.
S-protein–reactive T-helper cells in renal transplant patients after vaccination. (a) Peripheral blood mononuclear cells were freshly isolated from whole blood and cultured for 16 hours in the presence of overlapping peptide pools for severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) spike protein and brefeldin A. T cells coexpressing CD154 and CD137 were defined as S-protein–specific. The cytokine profile of S-protein–specific T cells was characterized, and interleukin-2 (IL-2)/interferon-γ (IFN-γ) expression was determined. (b) In all 7 patients, S-protein–specific T-helper cells were detectable. (c) S-protein–specific T-helper cells produced IL-2 and IFN-γ. Pos, positive.
Thus, in all of the 7 RTxP, a cellular S-protein–specific immune response was induced by vaccination, despite the lack of S-protein–specific antibodies. The presence of a vaccine-induced T-cell response indicates that mRNA vaccines may well confer T cell–mediated vaccine-specific immunity in immunocompromised patients. Taken together, these findings underscore the importance for a comprehensive immune monitoring and the need for individualized schemes for booster vaccinations in this susceptible patient cohort.
Acknowledgments
Ethical approval was obtained from the local institutional review board, and all patients provided written informed consent. BW was funded by the Dr. Werner Jackstädt-Stiftung, and OW received funding from the Rudolf Ackermann-Stiftung.
References
- 1.Benotmane I., Gautier-Vargas G., Cognard N. Low immunization rates among kidney transplant recipients who received 2 doses of the mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. Kidney Int. 2021;99:1498–1500. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.04.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Korth J., Jahn M., Dorsch O. Impaired humoral response in renal transplant recipients to SARS-CoV-2 vaccination with BNT162b2 (Pfizer-BioNTech) Viruses. 2021;13:756. doi: 10.3390/v13050756. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sattler A., Angermair S., Stockmann H. SARS–CoV-2–specific T cell responses and correlations with COVID-19 patient predisposition. J Clin Invest. 2020;130:6477–6489. doi: 10.1172/JCI140965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]