Abstract
Myosin heavy chain 7b (MYH7b) is an ancient member of the myosin heavy chain motor protein family that is expressed in striated muscles. In mammalian cardiac muscle, MYH7b RNA is expressed along with two other myosin heavy chains, β-myosin heavy chain (β-MyHC) and α-myosin heavy chain (α-MyHC). However, unlike β-MyHC and α-MyHC, which are maintained in a careful balance at the protein level, the MYH7b locus does not produce a full-length protein in the heart due to a posttranscriptional exon-skipping mechanism that occurs in a tissue-specific manner. Whether this locus has a role in the heart beyond producing its intronic microRNA, miR-499, was unclear. Using cardiomyocytes derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells as a model system, we found that the noncoding exon-skipped RNA (lncMYH7b) affects the transcriptional landscape of human cardiomyocytes, independent of miR-499. Specifically, lncMYH7b regulates the ratio of β-MyHC to α-MyHC, which is crucial for cardiac contractility. We also found that lncMYH7b regulates beat rate and sarcomere formation in cardiomyocytes. This regulation is likely achieved through control of a member of the TEA domain transcription factor family (TEAD3, which is known to regulate β-MyHC). Therefore, we conclude that this ancient gene has been repurposed by alternative splicing to produce a regulatory long-noncoding RNA in the human heart that affects cardiac myosin composition.
Keywords: heart failure, myosin heavy chain (MyHC), myosin heavy chain 7b (MYH7b), alternative splicing, long noncoding RNA (lncRNA), gene regulation
Abbreviations: α-MyHC, α-myosin heavy chain; β-MyHC, β-myosin heavy chain; FISH, fluorescent in situ hybridization; FHOD3, formin homology 2 domain containing 3 protein; MYH7b, myosin heavy chain 7b; NMD, nonsense-mediated decay; PTC, premature termination codon; TdT, terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase
The myosin family of motor proteins that drives striated muscle contraction consists of ten genes with distinct functions (1). Three of these genes are expressed in mammalian hearts (MYH6, MYH7, and MYH7b). MYH6 (α-MyHC) and MYH7 (β-MyHC) are the major sarcomeric myosin proteins expressed in mammalian hearts. In humans, >90% of the heart’s myosin protein composition is comprised of β-MyHC with the remaining <10% being α-MyHC and the two are antithetically regulated (1, 2, 3, 4, 5). However, various conditions can shift their relative proportions. The finely tuned balance of these two motors is critical for proper cardiac function since they have very different enzymatic properties, which determine the contractile velocity of the muscle (6). It has been well established that disturbing the β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratio leads to compromised contractility in cardiomyocytes; in human heart failure, there is a shift to ∼100% β-MyHC and α-MyHC becomes undetectable (2, 3, 4, 7). As β-MyHC is the slower, more efficient motor, this shift in expression is thought to be an initial compensatory mechanism to preserve energy in the failing heart. Heart failure patients that show functional improvement upon treatment with β-adrenergic receptor blockers have an increase in α-MyHC expression (4). This suggests that maintenance of the β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratio is fundamental to proper cardiac function.
While MYH6 and MYH7 have been studied for decades, MYH7b was not identified until the sequencing of the human genome and was initially annotated as a sarcomeric myosin based on sequence alignments with other known family members (8). Based on phylogenetic analysis, MYH7b was identified as an ancient myosin, indicating that MYH7b was present before the gene duplication events that led to the other sarcomeric myosins (8). The human MYH7b gene is located on chromosome 20, separate from the two canonical sarcomeric myosin clusters on chromosomes 14 (cardiac myosins) and 17 (skeletal muscle myosins), supporting the idea that MYH7b may have a specialized role in muscle biology (1, 8). In certain species, including snakes and birds, MYH7b is expressed as a typical sarcomeric myosin protein in the heart and skeletal muscle (9). However, MYH7b has a unique expression pattern in mammals: the encoded protein is expressed in specialized muscles and nonmuscle tissues (10, 11, 12). Furthermore, while MYH7b RNA is expressed in mammalian cardiac and skeletal muscle, an alternative splicing event skips an exon, introducing a premature termination codon (PTC) that prevents full-length protein expression (Fig. 1A, Fig. S1) (10). This raises the question of why MYH7b RNA expression has been conserved in the mammalian heart. One obvious hypothesis is that MYH7b transcription is preserved in mammalian heart and skeletal muscle in order to maintain the expression of an intronic MYH7b microRNA, miR-499, in those tissues (10). However, miR-499 knockout mice have no discernible cardiac or skeletal muscle phenotype (13). It is possible that the species-specific regulation of myosin isoforms complicates the interpretation of this mouse model and that miR-499 could play an important role in human muscle (6, 14). Another hypothesis is that a heretofore unknown functional molecule is expressed from the MYH7b gene, resulting in its conserved expression in the sarcomeric muscle tissue. In this report, we performed a thorough dissection of this locus in order to discern the role of MYH7b gene expression in human cardiomyocytes and found a novel long noncoding RNA (lncMYH7b) with roles in cardiac gene expression, leading to changes in cardiomyocyte beat rate and sarcomeric organization.
Figure 1.
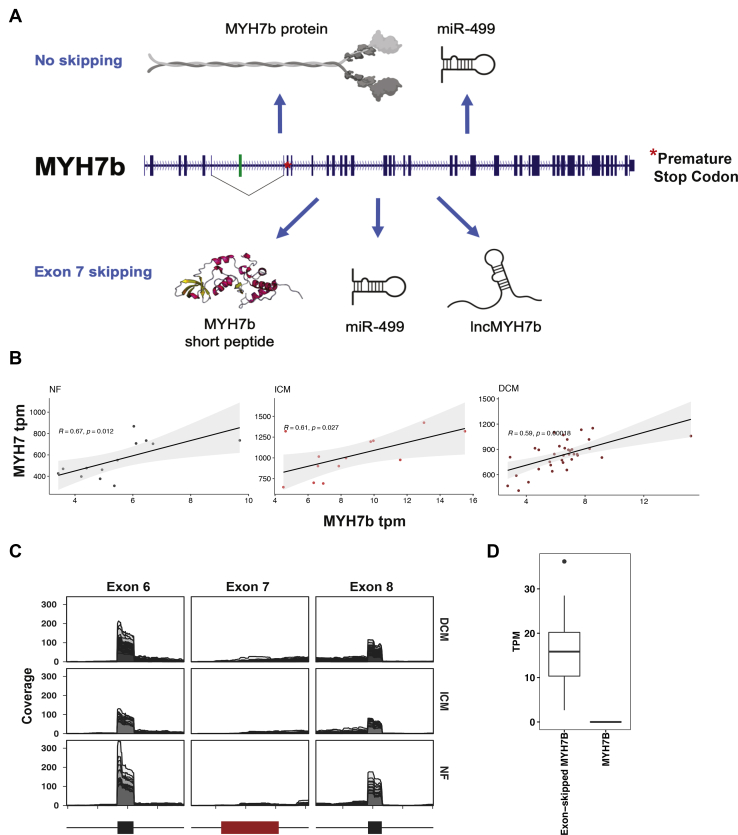
MYH7b is alternatively spliced in the heart and correlates with β-MyHC in heart disease.A, MYH7b is expressed as a full-length sarcomeric myosin protein in the human brain and inner ear, but is alternatively spliced, skipping exon 8 (in green) in the heart and skeletal muscle to become noncoding. A putative short peptide (MYH7b_sp) could be produced from the exon-skipped transcript, and a microRNA (miR-499) is encoded regardless of splicing. B, the expression of exon 7-skipped MYH7b correlates with that of β-MyHC in nonfailing (NF), dilated cardiomyopathy (DCM), and ischemic cardiomyopathy (ICM). Data pulled from GSE116250. C, splicing analysis of MYH7b in 64 human hearts shows that exon 8 is almost nonexistent in the human heart. D, quantification of exon skipping in human hearts.
Results
MYH7b and β-MyHC expression are positively coregulated
The human MYH7b locus is complex. In certain tissues, it encodes a typical striated muscle myosin mRNA and full-length protein. In tissues where exon 7 is skipped, the locus could theoretically produce both a peptide originating from the short open reading frame preceding the PTC in exon 9 (MYH7b_sp) and the exon 7-skipped long-noncoding RNA itself (lncMYH7b, Fig. 1A). In both contexts, the microRNA miR-499 is encoded in intron 19. We analyzed RNA-sequencing (RNA-seq) data from 64 healthy and diseased human heart samples and found that exon 7 (the skipped exon) of the MYH7b RNA is essentially undetectable regardless of disease state, which is consistent with our previous observation that MYH7b has a tissue-specific alternative splicing pattern (Fig. 1, B and C) (10). This transcriptomic analysis suggests that the full-length MYH7b protein is not present in the human heart. This observation is also consistent with our previous results showing that forced expression of full-length MYH7b protein in the mouse heart results in cardiac dilation and dysfunction, despite roles the full-length protein is known to have in other tissues (12, 15, 16).
β-MyHC induction, which shifts the β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratio, is a hallmark of chronic heart disease (2, 3, 4). Intriguingly, we observed that MYH7b RNA levels correlate with β-MyHC expression, including the known increase in β-MyHC expression in diseased human hearts (Fig. 1D and Fig. S2). This raised the possibility that there is a regulatory relationship between the MYH7b locus and β-MyHC expression. Although full-length MYH7b protein and mRNA are essentially absent in the human heart, there are several other molecules originating from the MYH7b gene locus, as mentioned above. The presence of these different molecules prompted further investigation into the locus as a whole.
miR-499 does not regulate β-MyHC expression
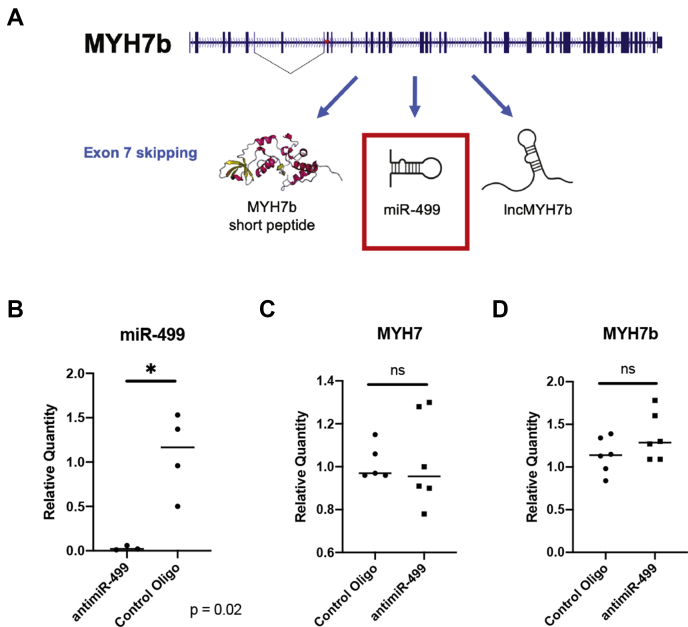
One hypothesis is that the MYH7b locus regulates β-MyHC through the miR-499, which is a miRNA encoded in intron 19 of the MYH7b pre-mRNA. There is no evidence to suggest that miR-499 regulates the expression of either α- or β-MyHC, and the miR-499 knockout mouse still induces β-MyHC in the heart under conditions of hypothyroidism (10, 13, 17). Other microRNAs, such as miR-208a and miR-208b encoded by the α-MyHC and β-MyHC genes, respectively, have been shown to have effects on the β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratio in mouse models (13). However, the adult mouse cardiac β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratio is opposite to the human one (5%:95% compared with 90%:10%), demonstrating species-specific regulation (6, 14). Therefore, it was important to investigate the β-MyHC response to changes in miR-499 activity in a human context. We employed a cellular model of human induced pluripotent stem cells differentiated to cardiomyocytes (hiPS-CMs), which we treated with an anti-miR that targets miR-499 specifically. We observed no changes in MYH7b or β-MyHC levels (Fig. 2). Therefore, we conclude that miR-499 does not regulate β-MyHC expression in human cardiomyocytes.
Figure 2.
miR-499 does not affect the expression of either MYH7b or β-MyHC.A, miR-499 is effectively knocked down by the anti-miR. miR-499 is still produced upon skipping of exon 7 and could have a role in β-MyHC regulation. B, an anti-miR targeted to miR-499 does not change the expression levels of MYH7b or β-MyHC.
MYH7b short peptide is not expressed in human hearts
The elimination of miR-499 as a regulator of the β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratio left both a putative short peptide and the lncMYH7b itself to investigate (Fig. 3A). The MYH7b locus produces full-length protein in the specialized muscles, brain, and inner ear tissues and therefore encodes all of the essential signals for translation (9). We previously reported increased exon 7-skipped MYH7b RNA levels in C2C12 mouse myotubes after blocking translation with cycloheximide, indicating that the exon-skipped RNA is either translated or shunted to the nonsense-mediated decay (NMD) pathway (10). Using FISH, we determined that MYH7b RNA is localized to the cytoplasm in hiPS-CMs, consistent with translation (Fig. 3, B and C). We confirmed these results by checking for signal upon knockdown and with biochemical fractionation (Fig. S3, B and C). Furthermore, we saw very few transcripts along the nuclear envelope, which is where mRNAs undergoing NMD typically localize (Fig. 3B) (18). This suggests that not all exon 7-skipped MYH7b RNA is degraded by NMD. There is also precedent for small peptides being produced from “non-coding” RNAs, which affect muscle contraction (19, 20). Based on this, we next investigated whether the short open reading frame prior to the PTC in exon 9 is translated and, if so, whether the short peptide (MYH7b_sp) could regulate the β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratio in human cardiomyocytes. The putative MYH7b_sp is predicted to be 206 amino acids in length and approximately 27 kDa. It is possible that MYH7b_sp has escaped detection in previous studies simply because full-length MyHCs are approximately 250 kDa, and a 27 kDa MyHC has not been described. Therefore, we used our anti-MYH7b antibody, which is directed against an epitope that should present in both the full-length MYH7b (as shown in Fig. 3D, mouse cerebellum) and the putative MYH7b_sp to probe for MYH7b_sp expression (11, 15). As a positive control, we infected C2C12 cells with an adenovirus containing only the MYH7b_sp open reading frame and detected a protein of the right size and immunoreactivity (Fig. 3D). We probed human heart tissue from dilated cardiomyopathy patients, where MYH7b transcripts are easily detectable (Fig. 1B), but did not detect it via western blotting (Fig. 3D). In case MYH7b_sp exists at levels below the detection limit of a western blot but does have a regulatory role, we forced expression of the MYH7b_sp using adenovirus infection of hiPS-CMs and performed RNA-seq (Fig. S4). We found no difference in the β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratio at the RNA level, and many differentially expressed genes were chaperones, which is both consistent with an adenoviral infection and production of a foreign peptide (Fig. S4) (21). Thus, we conclude that MYH7b_sp is not expressed at detectable levels in human cardiomyocytes and has no effect on the expression of α- or β-MyHC, even after forced expression.
Figure 3.
MYH7b_sp does not affect the β-/α-MyHC ratio and is undetectable in human hearts.A, miR-499 has been eliminated as the active molecule involved in MyHC regulation in the heart; however, MYH7b_sp could have a regulatory role. B, single-molecule FISH shows that MYH7b RNA is largely is localized in the cytoplasm, but not along the nuclear envelope where NMD largely occurs. C, quantification of MYH7b RNA localization using FISH. D, western blotting of failing human hearts cannot detect MYH7b_sp using a custom MYH7b antibody that does detect full-length MYH7b in mouse cerebellum. E, RNA-seq of MYH7b_sp overexpression shows no significant change in the β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratio.
lncMYH7b has a role in β-MyHC regulation in human cardiomyocytes
Having ruled out the possible regulatory roles of miR-499 and MYH7b_sp in β-MyHC expression, we hypothesized that the lncMYH7b transcript itself regulates β-MyHC. We attempted to overexpress the exon-skipped cDNA (MYH7bΔ7 cDNA) via adenoviral infection as we did with MYH7b_sp. Unfortunately, we discovered that this cDNA expresses large quantities of MYH7b_sp, which we have that shown is not produced from endogenous lncMYH7b (Fig. S5). We hypothesize that this is due to the lack of exon junction complexes that would normally trigger NMD and other RNA quality-control pathways. This led us to postulate that having a spliced transcript is essential to lncMYH7b’s function. Therefore, we decided to move forward with a loss-of-function approach. To achieve this, we knocked down MYH7b RNA with locked nucleic acid antisense oligonucleotides (ASOs) and measured the kinetics of lncMYH7b and β-MyHC expression in hiPS-CMs. Upon treatment with 10 μM ASO, MYH7b RNA was knocked down ∼12-fold by 48 h, which was maintained through 7 days (Fig. 4A). Importantly, we observed decreased β-MyHC expression only after loss of MYH7b RNA (Fig. 4A), supporting an upstream role for the exon-skipped MYH7b RNA in regulating β-MyHC expression. To further support the idea that lncMYH7b is regulating β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratios independently of miR-499, we measured the change in myomiR levels after lncMYH7b knockdown (KD). We observed no change in miR-499 levels, nor in the other two myomiRs encoded by α-MyHC and β-MyHC (miR-208a and miR-208b, respectively) upon treatment with the MYH7b ASO (Fig. 4B).
Figure 4.
lncMYH7b controls β-MyHC expression at both the RNA and protein level.A, MYH7b RNA decreases at least 48 h before there is a change in β-MyHC, RNA levels are reduced. B, ASOs targeted against MYH7b RNA do not affect myomiR levels. C, myosin-separating gels show a reduction in the β-/α-MyHC ratio at the protein level upon lncMYH7b KD in hiPS-CMs. D, representative myosin-separating gel.
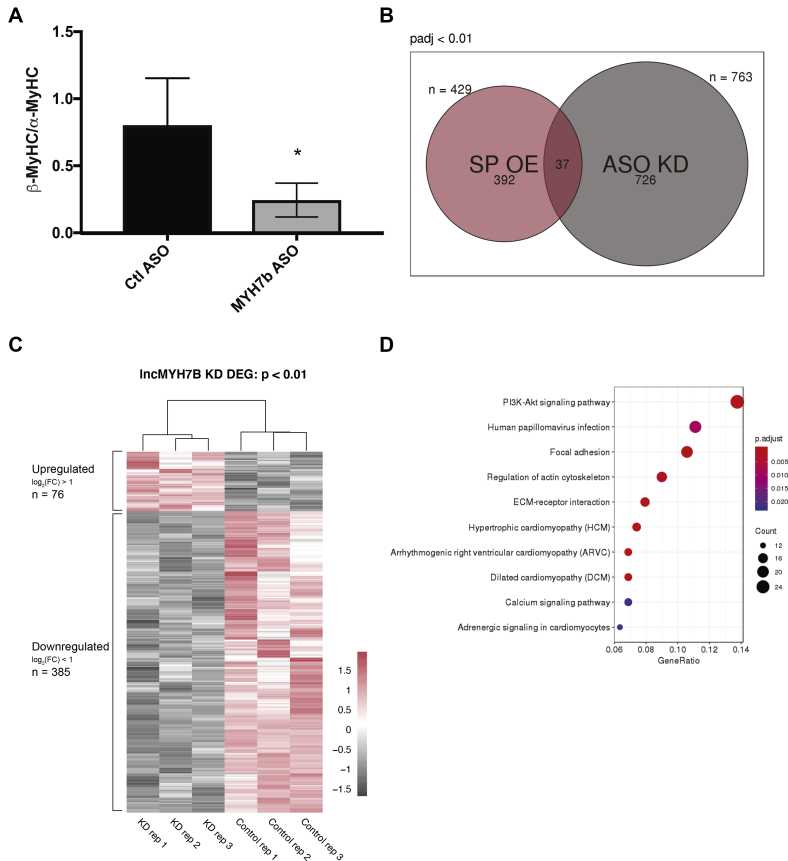
Next, we determined that the change observed in β-MyHC RNA upon MYH7b KD was recapitulated at the protein level. As independent validation, we differentiated hiPS-CMs from a different iPSC line and used a different ASO sequence. A myosin separating gel showed a significant decrease of the β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratio upon KD of MYH7b RNA (Fig. 4C). Together, these data demonstrate a role for lncMYH7b in regulating the β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratio in human cardiomyocytes.
In order to elucidate the potential regulatory impacts of lncMYH7b in a more global and unbiased manner, we performed RNA-seq on MYH7b ASO-treated hiPS-CMs. We used the publicly available NF-core/RNAseq pipeline to analyze differential gene expression (22). Differential expression analysis revealed a large bias toward downregulation (535 downregulated versus 224 upregulated genes) with very little overlap with our MYH7b_sp dataset (Fig. 5B). As knockdown of the RNA would also prevent protein expression, this further supports the lack of MYH7b_sp translated from the endogenous locus. We found that the change in the β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratio was also evident at the RNA level, suggesting that lncMYH7b is affecting β-MyHC pretranslationally (Fig. 5A). To gain functional insight into the role of lncMYH7b in regulating cardiac gene expression, we performed a KEGG pathway analysis of our RNA-seq dataset and found that pathways associated with cardiomyopathies were regulated by the reduction in lncMYH7b expression (Fig. 5D). This is consistent with the increases in lncMYH7b levels observed in the tissue from patients with chronic heart disease (Fig. S2). Of interest, expression of two members of the TEA domain (TEAD) transcription factor family, TEAD1 and TEAD3 (log2(fold change) = −0.67 and −1.68, respectively), was decreased in our lncMYH7b KD dataset. As TEAD3 was the most downregulated, and has been shown to directly regulate β-MyHC transcription, we decided to focus on that transcription factor (23). We independently confirmed a decrease in TEAD3 RNA levels using qPCR, which agrees with TEAD3 being the most downregulated transcription factor in our data (Fig. S6). TEAD family members are known to bind to and enhance transcription at the β-MyHC promoter and are upregulated in hypertrophic cardiomyopathy patient hearts (23). TEAD3 specifically has not been well studied, but has a cardiac-enriched expression pattern (24). TEAD family members can complex with MEF2 transcription factor family members, which are master regulators of muscle formation and are known to enhance β-MyHC transcription (25, 26, 27). Moreover, further interrogation of the dataset revealed a significant decrease in the expression of PTK2, also known as focal adhesion kinase (FAK). FAK can also complex with MEF2 in cardiomyocytes to enhance its activity under stress conditions, and in a mouse model where FAK was knocked out in cardiomyocytes, MEF2A protein levels were downregulated (28, 29, 30). Additionally, the FAK pathway is one of the top five enriched pathways in our KEGG analysis (Fig. 5D). Finally, FAK has also been identified as an upstream activator of TEAD transcriptional networks (31, 32). This, along with lncMYH7b’s cytoplasmic localization, suggests that lncMYH7b is targeting an upstream effector of TEAD transcription in cardiomyocytes.
Figure 5.
lncMYH7b KD shows little overlap with MYH7b_sp overexpression.A, RNA-seq of lncMYH7b KD in iPS-CMs shows a reduction in the β-/α-MyHC ratio, confirming that lncMYH7b is affecting β-MyHC RNA. B, Venn diagram of the differentially expressed genes from the MYH7b_sp overexpression and lncMYH7b KD shows that there is little overlap, which further supports the conclusion that MYH7b_sp is nonconsequential. C, RNA-seq of lncMYH7b KD shows an enrichment of downregulated genes. D, KEGG analysis of the lncMYH7b KD RNA-seq shows enrichment of focal adhesion pathways, indicating possible role of FAK in lncMYH7b regulation.
lncMYH7b KD also causes defects in cardiomyocyte function and sarcomere organization
As we saw effects upon the adrenergic signaling pathway in our RNA-seq data (Fig. 6A), we measured the spontaneous cardiomyocyte beat rate after lncMYH7b KD. As analyzed by the MotionGUI software, we saw a significant (∼25%) decrease in beat rate in the MYH7b ASO-treated cells as compared with the hiPS-CMs treated with the scrambled control ASO (Fig. 6B) (33). To confirm that this is due to the changes in expression seen in the RNA-seq, we decided to measure protein levels of several of the affected proteins by western blot. As seen in Figure 6C, PP2A levels are significantly decreased and RyR2 levels are trending down. This is consistent with the changes in RNA levels detected in our RNA-seq data (Fig. 6A), indicating that lncMYH7b is affecting expression of some key proteins in the adrenergic pathways in cardiomyocytes.
Figure 6.
lncMYH7b KD affects adrenergic signaling and beat rate in hiPS-CMs.A, KEGG pathway diagram showing the effects seen on adrenergic signaling genes upon lncMYH7b KD. B, hiPS-CMs treated with MYH7b ASO have a significantly slower spontaneous beat rate than those treated with control ASO. C, changes in RyR2 and PP2A expression shown by RNA-seq are recapitulated at the protein level.
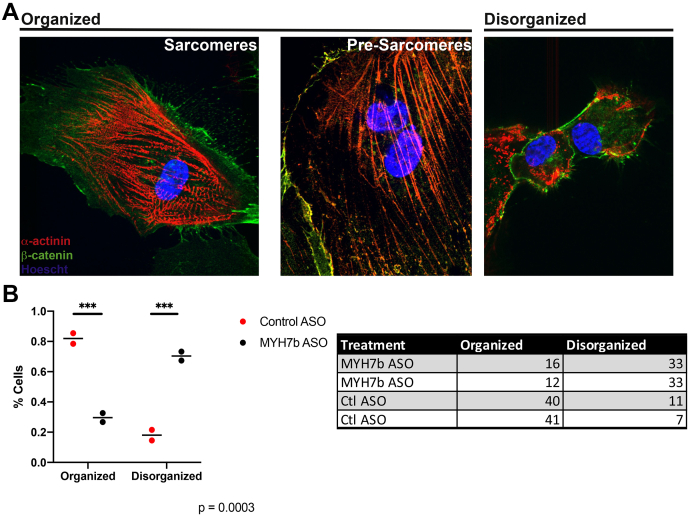
In addition to the adrenergic affects, we were intrigued by the dramatic decrease of the RNA level of Formin Homology 2 Domain Containing 3 Protein (FHOD3). FHOD3 is known to play a significant role in the formation of sarcomeres both in vivo and in maturing hiPS-CMs (34, 35, 36). There was also a significant decrease in the expression of MYH10 upon lncMYH7b KD. Both FHOD3 and MYH10 are essential for sarcomere formation in hiPS-CMs (36). As such, we quantified sarcomere formation in hiPS-CMs treated with the MYH7b ASO. We stained for α-actinin for sarcomere structure across two differentiations and found a distinct phenotypic shift upon lncMYH7b KD (Fig. 7). Cells with clearly defined structures, either fully formed sarcomeres or presarcomeric filaments, predominated in the cells treated with the control ASO. In contrast, most (∼70%) lncMYH7b KD cells have little to no α-actinin organization (Fig. 7). Together, these data suggest that lncMYH7b plays an essential role in cardiomyocyte sarcomeric organization and function.
Figure 7.
lncMYH7b KD causes significant effects on sarcomere organization in hiPS-CMs.A, representative images showing the three phenotypes of α-actinin staining we scored in hiPS-CMs. The “organized” category was broken down into two subphenotypes: organized sarcomeres and presarcomeres that have been shown to transition to fully organized sarcomeres in hiPS-CMs (36). This is in comparison to the disorganized phenotype, where there is no discernible organization of alpha-actinin. B, quantification of the change in α-actinin phenotype upon lncMYH7b knockdown. There is a significant decrease in the percentage of cells with α-actinin organization with MYH7b ASO treatment. Cells from three wells from two independent differentiations were scored.
Discussion
We have discovered that the MYH7b gene not only encodes a myosin heavy chain protein and a miRNA but also a regulatory lncRNA we have named lncMYH7b. This is the first example of a myosin heavy chain sense transcript with a regulatory role. Since MYH7b protein is undetectable in the mammalian heart despite the presence of the RNA, we postulated that the locus is transcribed to enable miR-499 expression. However, miR-499 null mice have no obvious cardiac phenotypes either at baseline or when stressed (13). Importantly, MYH7b RNA levels are preserved in those animals. Although it is a complicated locus encoding several potential active molecules, we present evidence that it is the lncRNA itself that has a regulatory role in cardiac gene expression.
There have been several reports of other lncRNAs having important roles in the heart. Myheart, the antisense transcript of β-MyHC, Chaer, and Charme are just three examples of lncRNAs that regulate genes associated with heart disease (37, 38, 39). However, most known cardiac lncRNAs work at the chromatin level by affecting epigenetic factors. lncMYH7b’s cytoplasmic localization implies a novel posttranscriptional mechanism of regulating gene expression (40, 41). There are examples of annotated lncRNAs encoding micropeptides, but despite MYH7b generating full-length protein in other tissues, there is no evidence for any peptide derived from this locus in the human heart (9, 11, 12, 16, 19, 20). Furthermore, this is an exciting example of the repurposing of an ancient protein-coding gene to produce a regulatory molecule via alternative splicing. The noncoding portion of the genome has been an area of exciting discovery in recent years, and the prospect of more bifunctional RNAs opens up even more possibilities.
The use of human cells was indispensable to this work. The species-specific ratio of β-MyHC and α-MyHC leads to difficulties when using traditional in vivo rodent models. With hiPS-CMs we are more able to investigate regulatory networks specific to humans. We are also able to validate findings against diverse genetic backgrounds. In this study, we were able to use two independent hiPS-CM systems to show the lncMYH7b regulation of the myosin heavy chains. This bodes well for the future of cardiac work in hiPS-CMs, both in the context of reproducibility and studying human-specific gene regulation.
This lncMYH7b dependence of β-MyHC expression at both the RNA and protein levels is an exciting new discovery in the field of cardiac biology. An increase in the β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratio is a hallmark of heart disease (2, 3). This change in myosin heavy chain composition has been shown to compromise the contractility of cardiomyocytes. Heart failure patients that respond functionally to β-adrenergic receptor blocker treatment have a shift back toward the physiological β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratio (4). Therefore, understanding the regulation of β-MyHC expression is of great interest to the cardiac field. Since our FISH data show that lncMYH7b is primarily localized in the cytoplasm (Fig. 3B), we do not think that lncMYH7b acts directly to regulate transcription from the β-MyHC locus. We analyzed the transcriptome of lncMYH7b KD hiPS-CMs to gain insight into potential networks that include this lncRNA. Notably, we found decreased expression of the transcription factors TEAD1, TEAD3, and MEF2A upon lncMYH7b KD. As these factors are known to transcriptionally regulate β-MyHC via a distal MCAT element, we suspect that this is a main driver for the observed decrease in the β-MyHC/α-MyHC ratio (23, 25). How lncMYH7b mediates this change in TEAD and MEF2 family member levels is an area of ongoing investigation. However, it is possible that the expression level changes in these transcription factors are downstream effects of changes in FAK levels. FAK not only affects the levels of MEF2A, but it is also a known upstream regulator of TEAD-mediated transcription (31, 42). All of these factors (FAK, MEF2, and TEADs) have major roles in both normal heart function and response to disease states, indicating that lncMYH7b may also have a role in physiologic cardiac gene expression regulation as well as a role in disease response. This is well represented by the phenotypic changes to beat rate and sarcomere formation we observed. Further dissection of this regulatory network is necessary to better understand lncMYH7b’s role in the transcriptional landscape of the heart. Once fully defined, this offers multiple new target points for therapeutics to treat chronic heart disease.
Experimental procedures
Cell culture
The WTC-11 iPSC line was used for all RNA-seq and fluorescent in situ hybridization (FISH) experiments. A small-molecule differentiation protocol was followed (43). Wnt signaling was activated for 48 h using Chiron 99021 (GSK3 inhibitor) at 5 μM in RPMI base media with BSA and L-ascorbic acid. Wnt was then inhibited for 48 h using Wnt-C59 at 2 μM in the same base media. The media was then switched to a B27 supplement with insulin in RPMI for the remainder of the culture time. All cells were matured for 35 days before treatment with ASO or virus.
iCell Cardiomyocytes were purchased from Cellular Dynamics International (CMC-100-010-001, donor 01434), cultured to manufacturer’s protocols, and used for all qPCR experiments. qPCR probes were purchased from Applied Biosystems and performed according to manufacturer’s protocols.
Antisense oligonucleotide treatment
Matured cardiomyocytes were passively treated with either a scrambled (control) ASO or one targeting MYH7b at 2 μM for 96 h. ASO was refreshed with media changes, every 48 h. ASO was manufactured and verified by miRagen (sequence found in Table S1, chemistry proprietary). For the kinetic study, iCell Cardiomyocytes were treated with 10 μM ASO targeting MYH7b for indicated timepoints. ASO was refreshed with media changes every 24 h and RNA was collected at indicated timepoints.
Fluorescent in situ hybridization probe design
Probes were designed against the human MYH7b using the LGC Biosearch Technologies’ Stellaris probe designer (Stellaris Probe Designer v. 4.2). As there was a concern for cross-reaction with both β-MyHC and α-MyHC due to high sequence conservation in the myosin II family, these probes were ranked according to how many mismatches they had with the other two transcripts. The selected sequences can be found in Table S2. The top 29 were ordered from Integrated DNA Technologies and labeled with ATTO-550 dye using terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT) as described in Gaspar et al. 2017. Briefly, TdT was incubated with 5-Propargylamino-ddUTP-ATTO-550 and an equimolar mix of the 29 probes at 37 °C for 16 h, refreshing the TdT at 8 h. The labeled probes were then purified through ethanol precipitation. We checked for cross-reaction with β-MyHC and α-MyHC by transfecting Cos7 cells with each cDNA and subjecting them to our anti-MYH7b FISH probes (Fig. S3A).
Matured cardiomyocytes were replated on plasma cleaned coverslips coated in a GelTrex cushion. 48 h after, the cardiomyocytes were washed three times with PBS, then fixed with 4% PFA for 10 min at room temperature. After washing again, coverslips were transferred to 70% ethanol and kept at 4 °C for at least 1 h. The 70% ethanol was then removed and 1 ml Stellaris RNA FISH Wash Buffer A (Biosearch Technologies Cat# SMF-WA1-60) with 10% deionized formamide was added for 5 min at room temperature. A humidifying chamber was assembled in a 15 cm tissue culture plate using a wet paper towel covered in Parafilm. For each coverslip, 2 μl of the TdT-labeled probes was added to 98 μl of Stellaris RNA FISH Hybridization Buffer (Biosearch Technologies Cat# SMF-HB1-10); 100 μl of this mixture was dotted onto the Parafilm in the humidifying chamber. The chamber was sealed with Parafilm, then left in the dark at 37 °C overnight. Coverslips were then transferred back into a 12-well culture plate and washed twice with 1 ml Buffer A for 30 min at 37 °C, then in 1 ml Stellaris RNA FISH Wash Buffer B (Biosearch Technologies Cat# SMF-WB1-20) with Hoechst stain at 1:10,000 dilution for 5 min at RT. Coverslips were then mounted using Vectashield antifade mounting medium and sealed with clear nail polish. Cells were imaged with a DeltaVision confocal microscope, and images were deconvolved using the Softworx software. Localization was determined using Imaris to detect all dots, then only dots within nuclei, and taking the ratio of those two measurements; 100 nuclei were analyzed across eight field of views in two independent experiments.
Adenovirus production
Adenovirus for recombinant expression of MYH7b_sp and MYH7bΔ7 cDNA was produced as previously described using the pAdEasy system (44). Cells were infected with a multiplicity of infection of 400 and collected after 48 h.
Tissue samples
Tissue samples from four individuals were obtained upon left ventricular assist device implantation under IRB approval CRV019-1 from UCD Anschutz Medical Campus.
Whole cell lysates, myosin separating gels, and western blotting
All tissue samples were powdered with a BioPulverizer, then nutated in RIPA buffer (140 mM NaCl, 50 mM Tris, 0.5 mM EGTA, 1 mM EDTA, 1% Triton X-100, 0.1% SDS, 0.5% deoxycholate) for 45 min at 4 °C, then spun at 15,000 rpm for 15 min to pellet the insoluble fraction. Cell lysates were prepared in the same manner. Lysates were quantified using a BioRad DC Assay. To determine the myosin isoform percentages in control versus MYH7b KD samples, we followed the protocol in Warren and Greaser (45). Briefly, 4 μg of each sample was run on a 6% poly-acrylamide–N,N0 -diallyltartardiamide (DATD) gel and stained with Sypro. Relative percentages of α-MyHC and β-MyHC were determined for each lane using ImageQuant. For western blotting, 40 μg of protein was run on a 10% SDS-PAGE gel and transferred to a PVDF membrane. An anti-MYH7b antibody was used at 1:100 (11, 15). Commercial antibodies used were: anti-RyR2 (Thermo Fisher, #MA3-916),anti-TEAD3 (Cell Signaling Technologies [CST], #13224S), PP2A C subunit (CST, #2038T), anti-vinculin (Sigma, #V9131), anti-GAPDH (CST #2118). Westerns were quantified using FIJI open source software.
Biochemical fractionation
The following was performed on a full 12-well plate of hiPS-CMs. The cells were collected by Versene treatment followed by cell scraping. Cells were washed three times with cold PBS. They were then resuspended in five volumes of lysis buffer (10 mM Tris, pH 7.5, 3 mM MgCl2, 10 mM NaCl, 5 mM EGTA, 0.05% NP40) and nutated at 4 °C for 30 min. Cells were then dounced ten times. This was spun for 10 min at 2000g at 4 °C. The cytoplasmic fraction (supernatant) was then collected. The nuclear fraction was washed three times with cold nuclear wash buffer (10 mM HEPES, pH 6.8, 300 mM sucrose, 3 mM MgCl2, 25 mM NaCl, 1 mM EGTA) and pelleted at 400g for 5 min at 4 °C. Nuclei were then lysed in five volumes of nuclear lysis buffer (50 mM HEPES pH 7.0, 150 mM NaCl, 0.1% NP-40), nutated at 4 °C for 30 min. They were then dounced 20 times and spun at 15,000 rpm for 30 min. The supernatant was collected as the nuclear fraction.
RNA isolation
Total RNA was isolated using Tri reagent. Samples were suspended in Tri reagent, then total RNA was organically extracted using chloroform. RNA was then alcohol precipitated with isopropanol and resuspended in sterile water.
Quantitative PCR (qPCR)
Reverse transcription was performed using Superscript III (Life Technologies, #18080044) and random hexamers. Quantitative PCR analysis was performed with the SYBR Green master mix (Invitrogen #4312704) on a BioRad CFX96 Touch Real-Time PCR Detection system. Results were analyzed with the CFX96 software, using the standard curve method of quantitation. The primers used can be found in Table S3.
RNA-sequencing and analysis
RNA samples were submitted to Novogene for library preparation, by PolyA selection, and sequencing. All samples had a sequencing depth of at least 20 million 150 bp paired end reads. The reads were mapped and extensive quality control was performed using the nf-core/rnaseq v1.4.2 pipeline. Reads were mapped to hg38 and gene quantification used Gencode v34. Differential expression analysis was performed using DESeq2 in R v3.5.1. Functional enrichment was performed with ClusterProfiler in R. All scripts are available on GitHub at: https://github.com/libr8211/lncMYH7b.
RNA-seq reads for the human heart data were retrieved from GEO (accession number GSE116250). Since the exon-skipped transcript is not present in the Gencode v34 annotation, we appended the specific exon-skipped transcript entry for MYH7b to the Gencode human annotation v34 and ran the same bioinformatic analysis as above to quantify the amount of exon skipped versus full length transcript. Details are available in the same Github repository as above.
Immunostaining
Cells were replated onto plasma-cleaned coverslips coated with a GelTrex cushion 48 h before ASO treatment began. ASO treatment was consistent with above methods. After treatment, coverslips were removed from culture and the remaining cells were collected to confirm MYH7b KD by qPCR. Coverslips were fixed with 4% paraformaldehyde in PBS for 10 min at room temperature. The fixed cells were then permeabilized by 0.1% Triton X-100 in PBS for 5 min at room temperature. Then cells were blocked in 0.1% Triton X-100, 1% BSA, and 5% normal goat serum in PBS for 30 min at room temperature. The primary solution of 1:1000 α-actinin and 1:100 β-catenin (Cell Signaling Technologies, #8480T) was made in the block solution, and cells were left in primary solution overnight in a humidifying chamber at 4 °C. The next day, cells were washed three times for 5 min in PBS, then transferred to secondary: 1:1000 IgG goat α-mouse Alexa 568 (Invitrogen, #A21144) and 1:1000 IgG donkey α-rabbit Alexa 488 in block solution, for 1 h at room temperature in a humidifying chamber. Cells were then washed three times for 5 min in PBS and incubated for 10 min in 1:8000 Hoescht stain in PBS. Cells were washed one more time in PBS, then coverslips were mounted on microscopy slides with FluoroMount G. Images were taken with a Nikon spinning disc confocal microscope in the CU Biofrontiers Advanced Light Microscopy core. To help prevent bias, images were taken after only identifying nuclei without looking at the α-actinin and β-catenin staining, therefore blinding the sarcomere phenotype. Images were analyzed with the FIJI open-source software. This was repeated for two separate differentiations, three wells each time. The three α-actinin phenotypes (sarcomeres, pre-sarcomeres, and disorganized) were decided upon after a blind scoring of images from the first differentiation. Sarcomeres in the second differentiation were not well organized, so the images were identified to be certain that we had a consistent phenotype across the control samples.
Beat rate analysis
Cells were treated on day 35 with ASO as above. Brightfield videos of 10 s each, with the frame rate set to “no-delay,” were obtained with the Nikon Te-2000 Widefield microscope in the BioFrontiers Advanced Light Microscopy core. This produced videos of 33 fps, which were analyzed with the MotionGUI software in Matlab (33). This was repeated for two separate differentiations, three wells each time.
Statistical analysis
We used a t-test with Welch’s correction to compare treated with control groups. All groups had at least a biological replicate number of 3, the specific n for each experiment is noted in individual figure legends. Any outliers were determined and eliminated based on the GraphPad QuickCalcs Grubbs test (https://www.graphpad.com/quickcalcs/grubbs1/, alpha = 0.05). For the RNA-sequencing analysis, the statistics used were the default within the bioinformatic programs. Details are available within the Github repository as above.
Data availability
The RNA-seq datasets generated for this study are available on NCBI GEO GSE157260 (MYH7b_sp overexpression) and GSE157217 (KD study).
Supporting information
This article contains supporting information.
Conflict of interest
No conflicts of interest were reported.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Dr Michael Bristow for helpful discussions and Deepa Puthenvadu and Ariana Combs for their work on myosin-separating gels.
Author contributions
L. J. B. experimental plan, data collection and analysis, intellectual contributions, article preparation. M. J. S. data collection and analysis, article editing. K. M. R. data collection and analysis, experimental plan. J. S. N. data collection and analysis. R. L. M. intellectual contributions, raw materials, article editing. J. L. R. intellectual contributions, experimental plan, article editing. L. A. L. intellectual contributions, funding, experimental plan, article editing.
Funding and additional information
This work was primarily funded by NIH R01 GM029090 (to L. A. L.), the NIH-CU Biophysics Training Grant (to L. J. B.), and NIH NRSA F31HL147487 (to L. J. B.). The content is solely the responsibility of the authors and does not necessarily represent the official views of the National Institutes of Health.
Edited by Ronald Wek
Supporting information
References
- 1.Weiss A., Leinwand L. The mammalian myosin heavy chain gene family. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 1996;12:417–439. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cellbio.12.1.417. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nakao K., Minobe W., Roden R., Bristow M.R., Leinwand L.A. Myosin heavy chain gene expression in human heart failure. J. Clin. Invest. 1997;100:2362–2370. doi: 10.1172/JCI119776. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Miyata S., Minobe W., Bristow M.R., Leinwand L.A. Myosin heavy chain isoform expression in the failing and nonfailing human heart. Circ. Res. 2000;86:386–390. doi: 10.1161/01.res.86.4.386. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lowes B.D., Gilbert E.M., Abraham W.T., Minobe W.A., Larrabee P., Ferguson D., Wolfel E.E., Lindenfeld J.A., Tsvetkova T., Robertson A.D., Quaife R.A., Bristow M.R. Myocardial gene expression in dilated cardiomyopathy treated with beta-blocking agents. N. Engl. J. Med. 2002;346:1357–1365. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa012630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Hasegawa K., Lee S.J., Jobe S.M., Markham B.E., Kitsis R.N. cis-Acting sequences that mediate induction of beta-myosin heavy chain gene expression during left ventricular hypertrophy due to aortic constriction. Circulation. 1997;96:3943–3953. doi: 10.1161/01.cir.96.11.3943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Krenz M., Robbins J. Impact of beta-myosin heavy chain expression on cardiac function during stress. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004;44:2390–2397. doi: 10.1016/j.jacc.2004.09.044. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Rundell V.L.M., Manaves V., Martin A.F., de Tombe P.P. Impact of beta-myosin heavy chain isoform expression on cross-bridge cycling kinetics. Am. J. Physiol. Heart Circ. Physiol. 2005;288:H896–H903. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00407.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Desjardins P.R., Burkman J.M., Shrager J.B., Allmond L.A., Stedman H.H. Evolutionary implications of three novel members of the human sarcomeric myosin heavy chain gene family. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2002;19:375–393. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a004093. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Lee L.A., Karabina A., Broadwell L.J., Leinwand L.A. The ancient sarcomeric myosins found in specialized muscles. Skelet. Muscle. 2019;9:1–15. doi: 10.1186/s13395-019-0192-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Bell M.L., Buvoli M., Leinwand L.A. Uncoupling of expression of an intronic microRNA and its myosin host gene by exon skipping. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010;30:1937–1945. doi: 10.1128/MCB.01370-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rossi A.C., Mammucari C., Argentini C., Reggiani C., Schiaffino S. Two novel/ancient myosins in mammalian skeletal muscles: MYH14/7b and MYH15 are expressed in extraocular muscles and muscle spindles. J. Physiol. 2010;588:353–364. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2009.181008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Rubio M.D., Johnson R., Miller C.A., Huganir R.L. Regulation of synapse structure and function by distinct myosin II motors. J. Neurosci. 2011;31:1448–1460. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3294-10.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.van Rooij E., Quiat D., Johnson B.A., Sutherland L.B., Qi X., Richardson J.A., Kelm R.J., Olson E.N. A family of microRNAs encoded by myosin genes governs myosin expression and muscle performance. Dev. Cell. 2009;17:662–673. doi: 10.1016/j.devcel.2009.10.013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Sadayappan S., Gulick J., Klevitsky R., Lorenz J.N. Cardiac myosin binding protein-C phosphorylation in a “humanized” mouse heart. Physiology. 2010;119:1253–1262. doi: 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.798983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Peter A.K., Rossi A.C., Buvoli M., Ozeroff C.D., Crocini C., Perry A.R., Buvoli A.E., Lee L.A., Leinwand L.A. Expression of normally repressed myosin heavy chain 7b in the mammalian heart induces dilated cardiomyopathy. J. Am. Heart Assoc. 2019;8 doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.013318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Haraksingh R.R., Jahanbani F., Rodriguez-Paris J., Gelernter J., Nadeau K.C., Oghalai J.S., Schrijver I., Snyder M.P. Exome sequencing and genome-wide copy number variant mapping reveal novel associations with sensorineural hereditary hearing loss. BMC Genomics. 2014;15:1155. doi: 10.1186/1471-2164-15-1155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Chistiakov D.A., Orekhov A.N., Bobryshev Y.V. Cardiac-specific miRNA in cardiogenesis, heart function, and cardiac pathology (with focus on myocardial infarction) J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2016;94:107–121. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Trcek T., Sato H., Singer R.H., Maquat L.E. Temporal and spatial characterization of nonsense-mediated mRNA decay. Genes Dev. 2013;27:541–551. doi: 10.1101/gad.209635.112. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Nelson B.R., Makarewich C.A., Anderson D.M., Winders B.R., Troupes C.D., Wu F., Reese A.L., McAnally J.R., Chen X., Kavalali E.T., Cannon S.C., Houser S.R., Bassel-duby R., Olson E.N. A peptide encoded by a transcript annotated as long noncoding RNA enhances SERCA activity in muscle. Science. 2016;351:271–275. doi: 10.1126/science.aad4076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Anderson D.M., Anderson K.M., Chang C.L., Makarewich C.A., Nelson B.R., McAnally J.R., Kasaragod P., Shelton J.M., Liou J., Bassel-Duby R., Olson E.N. A micropeptide encoded by a putative long noncoding RNA regulates muscle performance. Cell. 2015;160:595–606. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.01.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zhao H., Dahlö M., Isaksson A., Syvänen A.C., Pettersson U. The transcriptome of the adenovirus infected cell. Virology. 2012;424:115–128. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2011.12.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ewels P.A., Peltzer A., Fillinger S., Alneberg J., Patel H., Wilm A., Garcia M.U., Tommaso P. Di, Nahnsen S. nf-core: Community curated bioinformatics pipelines. bioRxiv. 2019 doi: 10.1101/610741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Iwaki H., Sasaki S., Matsushita A., Ohba K., Matsunaga H. Essential role of TEA domain transcription factors in the negative regulation of the MYH 7 gene by thyroid hormone and its receptors. PLoS One. 2014;9 doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0088610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Jin Y., Messmer-Blust A.F., Li J. The role of transcription enhancer factors in cardiovascular biology. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 2011;21:1–5. doi: 10.1016/j.tcm.2011.12.009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Karasseva N., Tsika G., Ji J., Zhang A., Mao X., Tsika R. Transcription enhancer factor 1 binds multiple muscle MEF2 and A/T-rich elements during fast-to-slow skeletal muscle fiber type transitions. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2003;23:5143–5164. doi: 10.1128/MCB.23.15.5143-5164.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wales S., Hashemi S., Blais A., McDermott J.C. Global MEF2 target gene analysis in cardiac and skeletal muscle reveals novel regulation of DUSP6 by p38MAPK-MEF2 signaling. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:11349–11362. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku813. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Potthoff M.J., Olson E.N. MEF2: A central regulator of diverse developmental programs. Development. 2007;134:4131–4140. doi: 10.1242/dev.008367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Cardoso A.C., Pereira A.H.M., Ambrosio A.L.B., Consonni S.R., Rocha de Oliveira R., Bajgelman M.C., Dias S.M.G., Franchini K.G. FAK forms a complex with MEF2 to couple biomechanical signaling to transcription in cardiomyocytes. Structure. 2016;24:1301–1310. doi: 10.1016/j.str.2016.06.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Nadruz W., Corat M.A.F., Marin T.M., Guimarães Pereira G.A., Franchini K.G. Focal adhesion kinase mediates MEF2 and c-Jun activation by stretch: Role in the activation of the cardiac hypertrophic genetic program. Cardiovasc. Res. 2005;68:87–97. doi: 10.1016/j.cardiores.2005.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Peng X., Wu X., Druso J.E., Wei H., Park A.Y.J., Kraus M.S., Alcaraz A., Chen J., Chien S., Cerione R.A., Guan J.L. Cardiac developmental defects and eccentric right ventricular hypertrophy in cardiomyocyte focal adhesion kinase (FAK) conditional knockout mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2008;105:6638–6643. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0802319105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kim N.G., Gumbiner B.M. Adhesion to fibronectin regulates Hippo signaling via the FAK-Src-PI3K pathway. J. Cell Biol. 2015;210:503–515. doi: 10.1083/jcb.201501025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Park J.H., Shin J.E., Park H.W. The role of hippo pathway in cancer stem cell biology. Mol. Cells. 2018;41:83–92. doi: 10.14348/molcells.2018.2242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Huebsch N., Loskill P., Mandegar M.A., Marks N.C., Sheehan A.S., Ma Z., Mathur A., Nguyen T.N., Yoo J.C., Judge L.M., Spencer C.I., Chukka A.C., Russell C.R., So P.-L., Conklin B.R. Automated video-based analysis of contractility and calcium flux in human-induced pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes cultured over different spatial scales. Tissue Eng. Part C Methods. 2015;21:467–479. doi: 10.1089/ten.tec.2014.0283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Taniguchi K., Takeya R., Suetsugu S., Kan-o M., Narusawa M., Shiose A., Tominaga R., Sumimoto H. Mammalian formin Fhod3 regulates actin assembly and sarcomere organization in striated muscles. J. Biol. Chem. 2009;284:29873–29881. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.059303. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Ushijima T., Fujimoto N., Matsuyama S., Kan-O M., Kiyonari H., Shioi G., Kage Y., Yamasaki S., Takeya R., Sumimoto H. The actin-organizing formin protein Fhod3 is required for postnatal development and functional maintenance of the adult heart in mice. J. Biol. Chem. 2018;293:148–162. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M117.813931. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Fenix A.M., Neininger A.C., Taneja N., Hyde K., Visetsouk M.R., Garde R.J., Liu B., Nixon B.R., Manalo A.E., Becker J.R., Crawley S.W., Bader D.M., Tyska M.J., Liu Q., Gutzman J.H. Muscle-specific stress fibers give rise to sarcomeres in cardiomyocytes. Elife. 2018;7:1–33. doi: 10.7554/eLife.42144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Han P., Chang C.P. Myheart hits the core of chromatin. Cell Cycle. 2015;14:787–788. doi: 10.1080/15384101.2015.1010963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Wang Z., Zhang X., Ji Y., Zhang P., Yokota T., Ang Y.S., Li S., Cass A., Vondriska T.M. A long non-coding RNA defines an epigenetic checkpoint in cardiac hypertrophy. Nat. Med. 2017;22:1131–1139. doi: 10.1038/nm.4179. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Ballarino M., Cipriano A., Tita R., Santini T., Desideri F., Morlando M., Colantoni A., Carrieri C., Nicoletti C., Musarò A., Carroll D.O., Bozzoni I. Deficiency in the nuclear long noncoding RNA Charme causes myogenic defects and heart remodeling in mice. EMBO J. 2018;37:1–16. doi: 10.15252/embj.201899697. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Chang C.P., Han P. Epigenetic and lncRNA regulation of cardiac pathophysiology. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2016;1863:1767–1771. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Rashid F., Shah A., Shan G. Long non-coding RNAs in the cytoplasm. Genomics Proteomics Bioinformatics. 2016;14:73–80. doi: 10.1016/j.gpb.2016.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Torsoni A.S., Marin T.M., Velloso L.A., Franchini K.G. RhoA/ROCK signaling is critical to FAK activation by cyclic stretch in cardiac myocytes. Am. J. Physiol. Circ. Physiol. 2005;289:H1488–H1496. doi: 10.1152/ajpheart.00692.2004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Lian X., Hsiao C., Wilson G., Zhu K., Hazeltine L.B., Azarin S.M., Raval K.K., Zhang J., Kamp T.J., Palecek S.P. Robust cardiomyocyte differentiation from human pluripotent stem cells via temporal modulation of canonical Wnt signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2012;109:E1848–E1857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1200250109. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Nag S., Sommese R.F., Ujfalusi Z., Combs A., Langer S., Sutton S., Leinwand L.A., Geeves M.A., Ruppel K.M., Spudich J.A. Contractility parameters of human b-cardiac myosin with the hypertrophic cardiomyopathy mutation R403Q show loss of motor function. Sci. Adv. 2015;1:1–16. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1500511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Warren C.M., Greaser M.L. Method for cardiac myosin heavy chain separation by sodium dodecyl sulfate gel electrophoresis. Anal. Biochem. 2003;320:149–151. doi: 10.1016/s0003-2697(03)00350-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Data Availability Statement
The RNA-seq datasets generated for this study are available on NCBI GEO GSE157260 (MYH7b_sp overexpression) and GSE157217 (KD study).