Abstract
A 34‐year‐old woman presented due to progressive painful swelling around the nail of the right index finger. Onychectomy and drainage of the abscess of the affected finger were performed as the inflammation was progressive despite the previous antibiotic therapy. The microbiological culture revealed a ciprofloxacin‐susceptible Citrobacter braakii.
Keywords: Citrobacter braakii, green nail syndrome, onychectomy, onycholysis
Green nail syndrome (GNS) is a rare condition, usually caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. A case of GNS caused by Citrobacter braakii has not been reported in the literature so far.

1. CASE DESCRIPTION
A 34‐year‐old woman presented in our emergency department due to progressive painful swelling around the nail of the right index finger, that had first appeared 30 days prior to the referral. The symptoms occurred immediately after a finger injury. Approximately 2 weeks after the trauma, the patient noticed a greenish discoloration of the nail plate of the affected finger. An empirical antibiotic therapy with amoxicillin/clavulanic acid had been unsuccessful.
On examination, the patient's vital signs were unremarkable. A distal onycholysis and a greenish discoloration of the entire nail plate of the right index finger, as well as a purulent proximal nail fold were seen (Figure 1).
FIGURE 1.
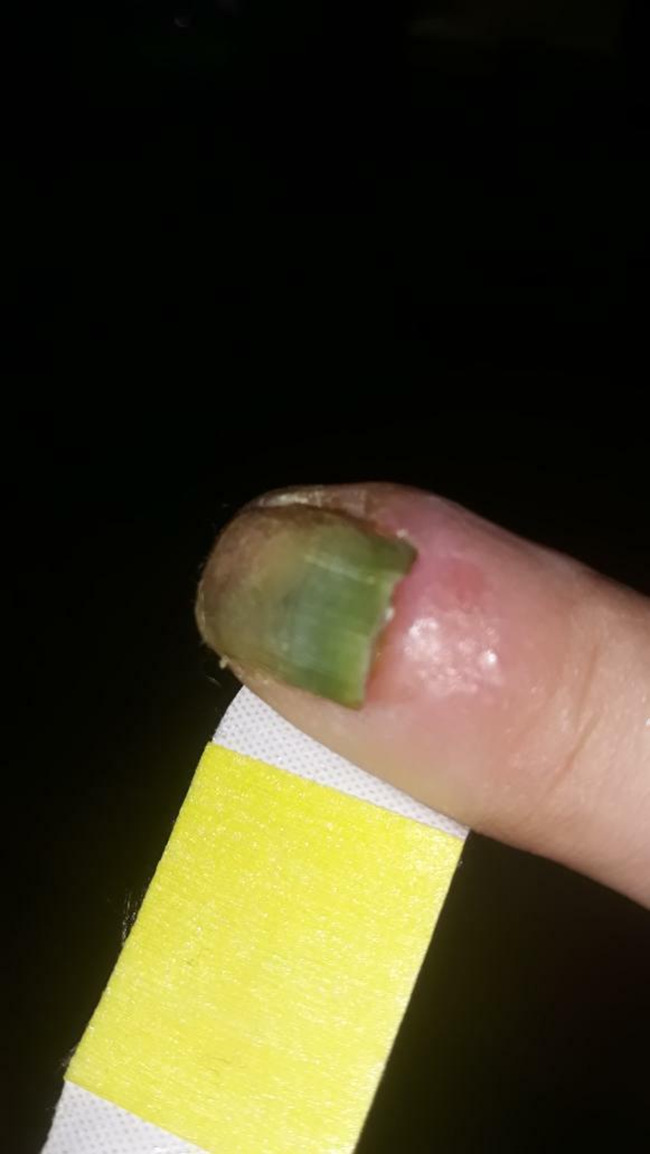
Green nail syndrome in a 34‐y‐old young woman: A distal onycholysis and a greenish discoloration of the entire nail plate of the right index finger, as well as a purulent proximal nail fold
Onychectomy and drainage of the abscess of the affected finger were performed as the inflammation was progressive despite the previous antibiotic therapy. The microbiological culture revealed a ciprofloxacin‐susceptible Citrobacter braakii infection, and a postoperative antibiotic therapy with ciprofloxacin was, therefore, prescribed. In the 5‐day follow‐up, the patient was symptom‐free and the inflammatory markers (WBC, CRP) were within the normal range.
Green nail syndrome (GNS) is a rare condition, usually caused by Pseudomonas aeruginosa. 1 However, other pathogens, such as the rare gram‐negative bacillus C braakii, can also be involved in the pathogenesis of this condition. 2
CONFLICT OF INTEREST
None declared.
AUTHOR CONTRIBUTIONS
FM, LT, EL, KT, FI, CK, NP, and K‐MP: contributed to the clinical data collection and prepared the case report. FM and K‐MP: contributed to the design of the case report presentation and performed the final revision of the manuscript.
PATIENT CONSENT FOR PUBLICATION
A written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report.
Mulita F, Tchabashvili L, Liolis E, et al. Green nail syndrome caused by Citrobacter braakii . Clin Case Rep. 2021;9:e04203. 10.1002/ccr3.4203
DATA AVAILABILITY STATEMENT
Data are available on request from the authors.
REFERENCES
- 1. Schwartz RA, Reynoso‐Vasquez N, Kapila R. Chloronychia: the goldman‐fox syndrome ‐ implications for patients and healthcare workers. Indian J Dermatol. 2020;65(1):1‐4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2. Oyeka M, Antony S Citrobacter braakii bacteremia: case report and review of the literature. Infect Disord Drug Targets. 2017;17(1):59‐63. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Data are available on request from the authors.


