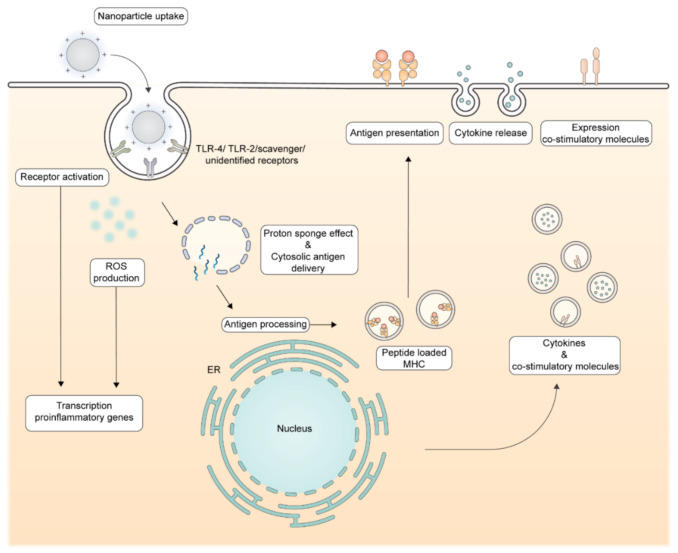
Figure 4.
Molecular immune-stimulating mechanisms by cationic nanoparticles. Upon uptake, cationic nanoparticles can have immune-stimulating properties via the induction of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and receptor activation, such as the TLR-4. These pathways result in the transcription of pro-inflammatory genes, resulting in translation of proinflammatory cytokines and co-stimulatory molecules. The proton–sponge effect results in cytosolic antigen delivery, enabling the polypeptide antigen to enter the antigen processing machinery. Proteasome and peptidase mediated processing will deliver oligopeptides to be presented in MHC molecules which will be transported to the cell surface. An increase in cytosolic antigen delivery combined with the immune-stimulating properties of cationic nanoparticles results in efficient priming of antigen-specific T-cells.