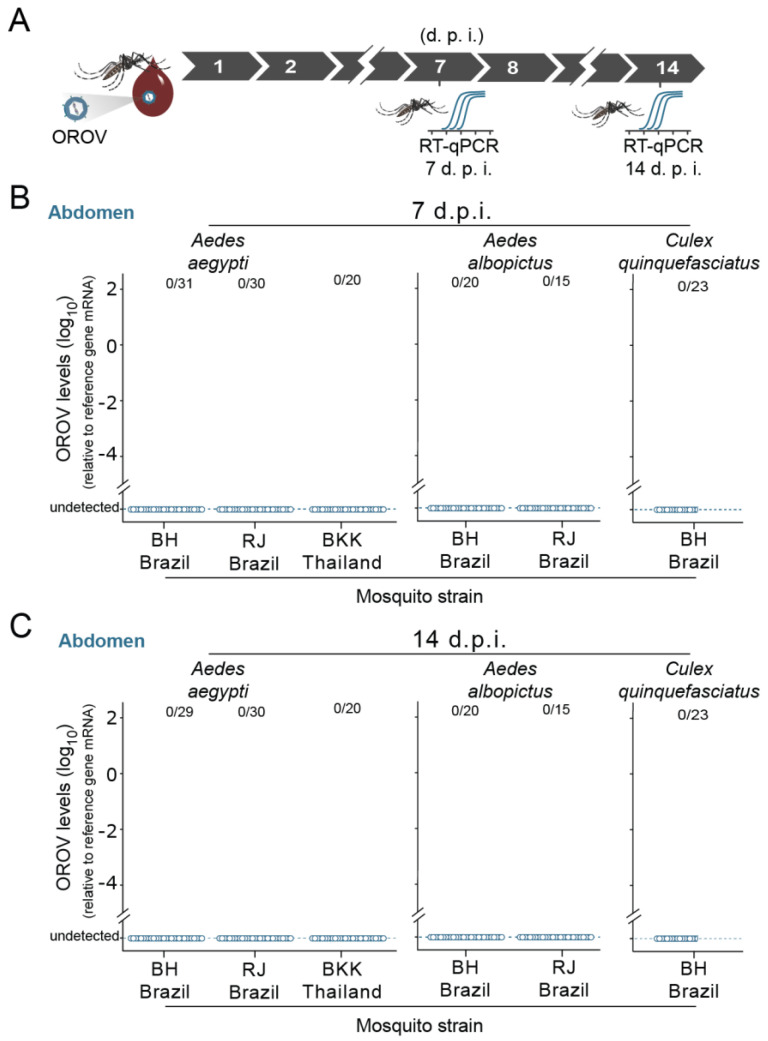
Figure 1.
Mosquitoes Ae. aegypti, Ae. albopictus, and Cx. quinquefasciatus are resistant to Oropouche orthobunyavirus (OROV) oral infection after an artificial blood meal. (A) Scheme of the experimental design using membrane blood-feeding system to orally infect mosquitoes. Mosquitoes were allowed to take blood meals in the membrane blood-feeding apparatus containing OROV-infected blood. Seven and 14 days after the blood meal, mosquitoes were collected and tested individually for the presence of OROV. (B) Seven days post feeding (d.p.f.) OROV RNA levels of mosquito abdomen on blood meal containing 6.7 × 107 p.f.u. mL−1 of OROV. RNA levels were quantified by quantitative real-time PCR (RT-qPCR). Three strains of Aedes aegypti were tested; that is, the BH strain; the RJ strain wild-caught population from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil); and the BKK strain. Two strains of Aedes albopictus were tested, the BH strain and the RJ strain (wild-caught population from Rio de Janeiro, Brazil). One strain of Culex quinquefasciatus was tested, the BH strain. (C) Fourteen d.p.f. OROV RNA levels of mosquito abdomen on blood meal containing 6.7 × 107 p.f.u. mL−1 of OROV. Each dot represents a sample (abdomen) from an individual mosquito.