Abstract
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is the metabolic disorder that appears during pregnancy. The current investigation aimed to identify central differentially expressed genes (DEGs) in GDM. The transcription profiling by array data (E-MTAB-6418) was obtained from the ArrayExpress database. The DEGs between GDM samples and non-GDM samples were analyzed. Functional enrichment analysis were performed using ToppGene. Then we constructed the protein–protein interaction (PPI) network of DEGs by the Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes database (STRING) and module analysis was performed. Subsequently, we constructed the miRNA–hub gene network and TF–hub gene regulatory network. The validation of hub genes was performed through receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC). Finally, the candidate small molecules as potential drugs to treat GDM were predicted by using molecular docking. Through transcription profiling by array data, a total of 869 DEGs were detected including 439 up-regulated and 430 down-regulated genes. Functional enrichment analysis showed these DEGs were mainly enriched in reproduction, cell adhesion, cell surface interactions at the vascular wall and extracellular matrix organization. Ten genes, HSP90AA1, EGFR, RPS13, RBX1, PAK1, FYN, ABL1, SMAD3, STAT3 and PRKCA were associated with GDM, according to ROC analysis. Finally, the most significant small molecules were predicted based on molecular docking. This investigation identified hub genes, signal pathways and therapeutic agents, which might help us, enhance our understanding of the mechanisms of GDM and find some novel therapeutic agents for GDM.
Keywords: bioinformatics analysis, differentially expressed genes, gestational diabetes mellitus, novel biomarkers, small drug molecules
Introduction
Gestational diabetes mellitus (GDM) is the metabolic disorder diagnosed during pregnancy, affecting 2–5% of pregnant women worldwide [1,2]. Risk factors of GDM include obesity, previous occurrence of diabetes, family history of type 2 diabetes, preeclampsia, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases and genetic factors [3]. At third trimester of pregnancy, blood glucose levels are drastically elevated [4]. Moreover, the elevated glucose level in pregnancy is closely linked with detrimental consequences in the newborn babies includes fetal hyperglycemia and cardiovascular disease [5]. Therefore, it is essential to examine the factual molecular targets included in occurrence and advancement of GDM, in order to make an improvement to the diagnosis, prognosis and treatment of GDM.
The molecular mechanisms of GDM initiation and development remain unclear. It is therefore essential to identify new genes and pathways that are linked with GDM progression and patient prognosis, which might not only help to explicate the underlying molecular mechanisms associated, but also to discover new diagnostic molecular markers and therapeutic targets. Transcription profiling by array can rapidly detect gene expression on a global basis and are particularly useful in screening for differentially expressed genes (DEGs) [6]. Gene chips allow the analysis of gene expression in a high-throughput way with great sensitivity, specificity and repeatability. A symbolic amount of data have been produced via the use of gene chips and the majority of such gene expression datasets have been uploaded and stored in public databases includes ArrayExpress database and NCBI‐Gene Expression Omnibus (NCBI‐GEO) database. Previous investigation concerning GDM transcription profiling by array have found hundreds of DEGs [7,8]. The availability of bioinformatics analysis based on high-throughput technology enabled the investigation of altered gene expression and the interaction between genes in GDM, to provide novel insights for further in-depth investigations.
In the current investigation, public transcription profiling by array data of E-MTAB-6418 from ArrayExpress database was downloaded. A total of 38 patients with GDM and 70 non-GDM candidates data in E-MTAB-6418 were available. DEGs between patients with GDM and non-GDM candidates were filtered and obtained using bioconductor package limma in R software. Gene Ontology (GO) and REACTOME pathway enrichment analyses of the DEGs were performed. The functions of the DEGs were further assessed by PPI network and module analyses to identify the hub genes in GDM. Subsequently, miRNA–hub gene regulatory network and TF–hub gene regulatory network were constructed and analyzed to find out the hub genes, miRNAs and TFs in GDM. Further, hub genes were validated by receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analysis and RT-PCR. Finally, a molecular docking study was performed for prediction of small drug molecules. Collectively, the findings of the current investigation highlighted hub genes and pathways that might contribute to the pathology of GDM. These might provide a basis for the advancement of future diagnostic, prognostic and therapeutic targets for GDM.
Materials and methods
Transcription profiling by array data information
The mRNA expression profile E-MTAB-6418 [9] based on A-MEXP-2072—Illumina HumanHT-12_V4_0_R2_15002873_B was downloaded from the ArrayExpress database (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/) [10], which included 38 patients with GDM and 70 non-GDM candidates.
Identification of DEGs
To obtain DEGs between GDM and non-GDM samples. After limma package in R analysis [11], results including adjusted P-values (adj. P. Val) and log FC were provided. Cut-off criterion was set as adj. P. Val <0.05, |log FC| > 1.158 for up-regulated genes and |log FC| < −0.83 for down-regulated genes. A list of candidate DEGs was obtained via the above methods.
Gene ontology and pathway enrichment of DEGs analysis
Gene ontology (GO) analysis (http://geneontology.org/) [12] and REACTOME (https://reactome.org/) [13] pathway enrichment analysis were both integrated in the ToppGene (ToppFun) (https://toppgene.cchmc.org/enrichment.jsp) [14] program. Therefore, ToppGene was capable of providing comprehensive annotations for functional and pathway interpretations. In this experiment, DEGs were uploaded on to ToppGene in order to perform related GO and REACTOME pathway enrichment analyses. The cut-off criterion was set as P<0.05.
PPI network establishment and modules selection
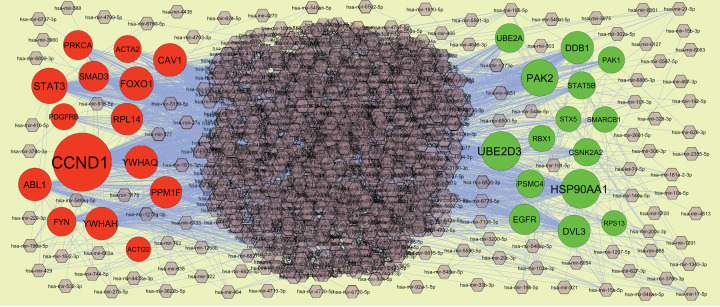
Search Tool for the Retrieval of Interacting Genes StringDB interactome (https://string-db.org/) is a database of known and predicted protein–protein interactions (PPIs) [15]. All candidate DEGs were posted into the STRING website, with a confidence score of ≥0.4 set as the cut-off criterion for PPI network construction. Then, Cytoscape (version 3.8.2, http://www.cytoscape.org/) [16] software was utilized to construct protein interaction relationship network. The Network Analyzer plugin was performed to scale node degree [17], betweenness centrality [18], stress centrality [19] and closeness centrality [20] of the PPI network. Significant modules in the visible PPI network were screened using the PEWCC1 (http://apps.cytoscape.org/apps/PEWCC1) [21] plugin. Degree cutoff = 2, node score cutoff = 0.2, k-core = 2 and max depth = 100 were set as the cut-off criterion. Three highest degree modules were extracted, and the potential mechanisms of each module were investigated with ToppGene. A degree of ≥10 was set as the filter criterion. Hub genes with high degree were selected as the potential key genes and biomarkers.
miRNA–hub gene regulatory network construction
The miRNet database (https://www.mirnet.ca/) [22] is an open-source platform mainly focusing on miRNA–target interactions. miRNet utilizes 14 established miRNA–target prediction databases, including TarBase, miRTarBase, miRecords, miRanda, miR2Disease, HMDD, PhenomiR, SM2miR, PharmacomiR, EpimiR, starBase, TransmiR, ADmiRE and TAM 2.0. In the present study, miRNAs were considered the targeted miRNAs of hub genes. Subsequently, the network of the hub genes and their targeted miRNAs was visualized by Cytoscape software.
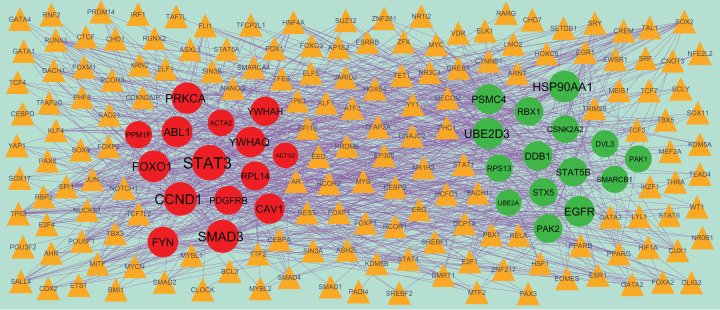
TF–hub gene regulatory network construction
The NetworkAnalyst database (https://www.networkanalyst.ca/) [23] is an open-source platform mainly focusing on TF–target interactions. NetworkAnalyst utilizes three established TF–target prediction databases, including ENCODE, JASPAR, ChEA. In the present study, TFs were considered the targeted TFs of hub genes based on ChEA database. Subsequently, the network of the hub genes and their targeted TFs was visualized by Cytoscape software.
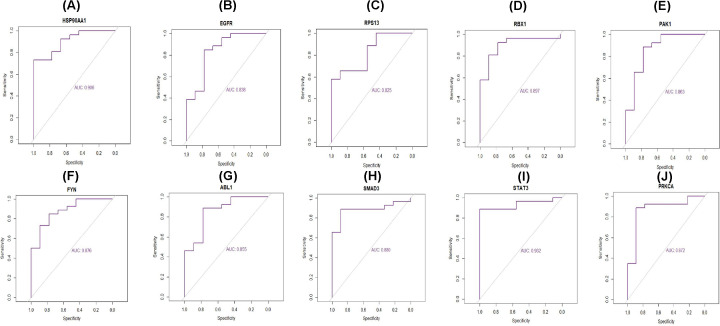
Receiver operating characteristic curve analysis
The receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) was constructed by predicting the probability of a diagnosis being of high or low integrated score of significant hub gene expression in GDM. Area under curve (AUC) analysis was operated to calculate the diagnostic ability by using the statistical package pROC in R software [24].
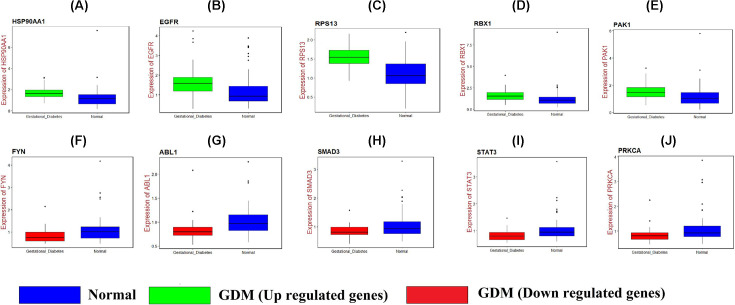
RT-PCR analysis
The HTR8/SVneo (ATCC CRL3271) cell line procured from ATCC. For normal HTR8/SVneo (ATCC CRL3271) cell line was grown in RPMI-1640 medium added with 10% fetal bovine serum, containing 5.5 mM glucose, and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. This cell line was incubated at 37°C in a 5% CO2 in humidified cell culture incubator. Similarly, for GDM HTR8/SVneo (ATCC CRL3271) cell line was grown in RPMI-1640 medium added with 10% fetal bovine serum, containing 5.5 mM glucose, and 1% penicillin/streptomycin. This cell line was incubated at 37°C in a 5% CO2 in humidified cell culture incubator for 24 h, then stimulated with various concentrations 40 mM of d-glucose for 6 h. TRIzol (cat. no. 9109; Takara Bio, Inc.) was used to isolate total RNA from HTR8/SVneo cell line and HTR8/SVneo cell line treated with glucose according to the manufacturer’s instructions. TRI Reagent (Sigma, U.S.A.). was used to isolate total RNA from each tissue sample according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Then, total RNA was reverse transcribed into cDNAs using the FastQuant RT kit (with gDNase; Tiangen Biotech Co., Ltd.). RT-PCR was performed to measure the levels of cDNAs using a QuantStudio 7 Flex real-time PCR system (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, U.S.A.). RT-PCR procedure was performed as follows: pre-denaturation at 95°C for 30 s for 1 cycle followed by 40 cycles of 95°C for 5 s and 60°C for 20 s. The relative expression level of the hub genes was calculated following comparative CT method [25]. β-actin was used to normalize the mRNA expression level. The primer sequences are listed in Table 1.
Table 1. The sequences of primers for quantitative RT-PCR.
| Genes | Forward primers | Reverse primers |
|---|---|---|
| HSP90AA1 | AGGAGGTTGAGACGTTCGC | AGAGTTCGATCTTGTTTGTTCGG |
| EGFR | AGGCACGAGTAACAAGCTCAC | ATGAGGACATAACCAGCCACC |
| RPS13 | TCCCAGTCGGCTTTACCCTAT | CAGGATTACACCGATCTGTGAAG |
| RBX1 | TTGTGGTTGATAACTGTGCCAT | GACGCCTGGTTAGCTTGACAT |
| PAK1 | CAGCCCCTCCGATGAGAAATA | CAAAACCGACATGAATTGTGTGT |
| FYN | ATGGGCTGTGTGCAATGTAAG | GAAGCTGGGGTAGTGCTGAG |
| ABL1 | AAGCCGCTCGTTGGAACTC | AGACCCGGAGCTTTTCACCT |
| SMAD3 | TGGACGCAGGTTCTCCAAAC | CCGGCTCGCAGTAGGTAAC |
| STAT3 | CAGCAGCTTGACACACGGTA | AAACACCAAAGTGGCATGTGA |
| PRKCA | GTCCACAAGAGGTGCCATGAA | AAGGTGGGGCTTCCGTAAGT |
Molecular docking experiments
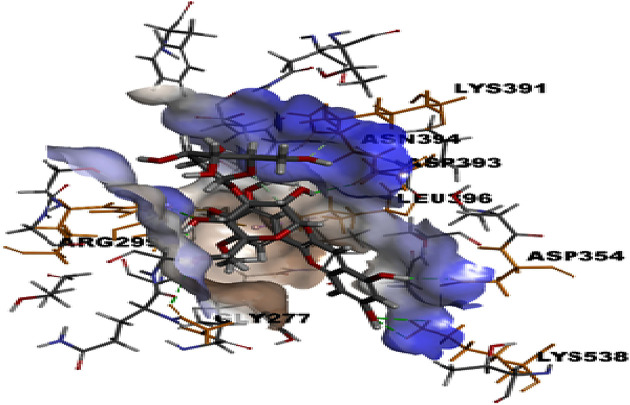
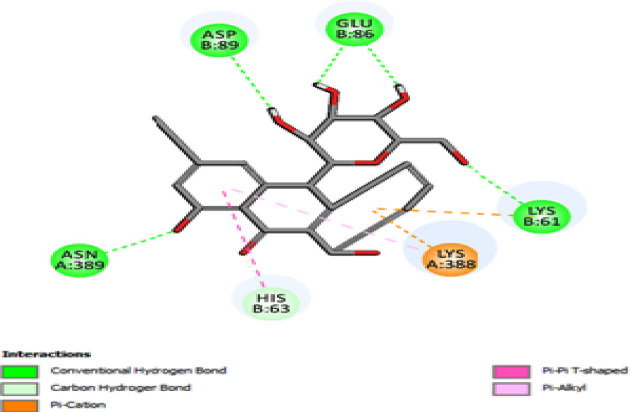
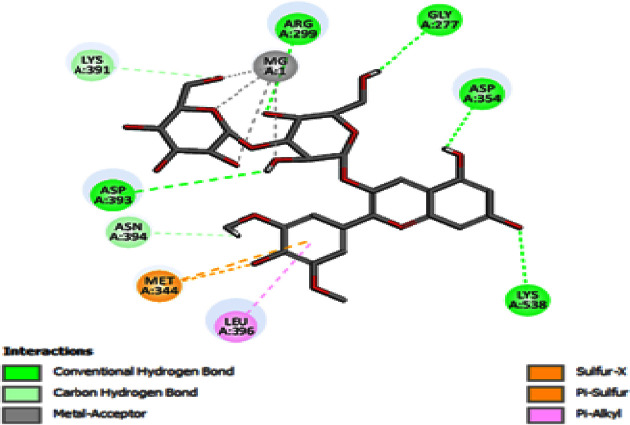
Molecular docking was used to find biologically active hits among the designed ligands. Using perpetual software module BIOVIA Discovery Studio (Perpetual), Surflex-Docking docking studies were conducted on active constituents. The lowest binding energy conformation was presumed to form a stable complex within the active site of the overexpressed proteins. The 2D structures were sketched using Chemdraw software, imported and saved into sdf. format using Open Babelfree software. The protein structure was processed after introduction of the protein, the co-crystallized ligand and all the water molecules were excluded from the crystal structure; more hydrogen was added and refined the side chain. The present study employed CDOCKER, a grid-based molecular docking approach that utilizes the CHARMm force field. A higher number indicates a stronger bond. The CDOCKER score is expressed as a negative number (–CDOCKER ENERGY). The H-bonds, van der Waals and electrostatic interactions between the target protein and the ligand were used to measure the CDOCKER energy. The modeled protein’s binding site was determined using the template protein’s crystal data and proteins which did not co-crystallize ligand generated binding site automatically. To make it easier for ligands to interact with amino acids, the binding site sphere center was set at 9 Å radius. Furthermore, using smart minimizer algorithm, CHARMm force field was applied followed by energy minimization to define local minima (lowest energy conformation) of the modeled over expressed proteins with an energy gradient of 0.1 kcal mol−1.Å−1, respectively. The energy minimized receptor protein and the set of 44 natural molecules which was reported as effective in diabetes mellitus and the well-known commonly used allopathic drugs, Metformin and Glyburide, were used as standard and to compare the binding interactions with natural molecules on overexpressed proteins in gestational diabetes. The binding site sphere radius set at X = 29.50, Y = −31.38 and Z = −38.79 were submitted to the CDOCKER parameter and also calculated binding energy. The X-ray co-crystallized structures were extracted from Protein Data Bank of PDB code of 4UV7, 5NJX, 3Q4Z and 3FNI of overexpressed genes of Epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), Heat shock protein 90 α family class A member 1 (HSP90AA1), P21 RAC1 activated kinase 1 (PAK1) and Ring-box 1 (RBX1), respectively, in gestational diabetes were selected for docking studies [26–29]. The best position was inserted into the molecular area between the protein and the ligand. The 2D and 3D interaction of amino acid molecules was achieved using the free online Discovery Studio Visualizer.
Results
Identification of DEGs
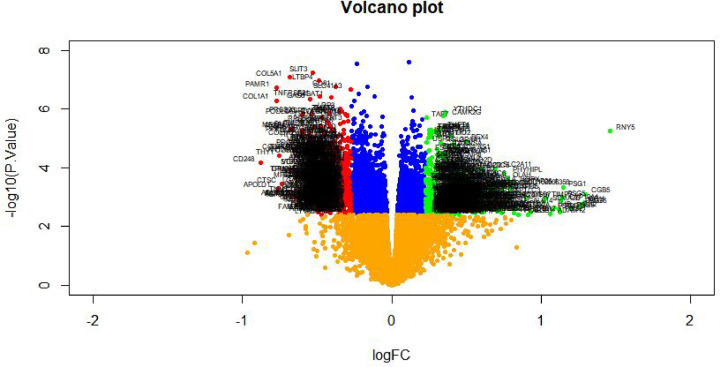
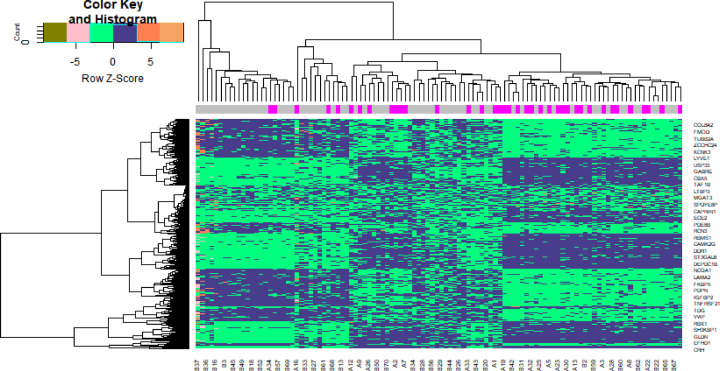
Transcription profiling by array datasets was obtained from the ArrayExpress database containing GDM and non-GDM samples; E-MTAB-6418. Then, the R package named ‘limma’ was processed for analysis with adjusted P<0.05, |log FC| > 1.158 for up-regulated genes and |log FC| < −0.83 for down-regulated genes. All DEGs were displayed in volcano maps (Figure 1). A total of 869 genes were finally obtained including 439 up-regulated and 430 down-regulated genes in the GDM samples compared with the non-GDM samples and are listed in Table 2. Top 869 genes in this dataset were displayed in the heatmap (Figure 2).
Figure 1. Volcano plot of DEGs.
Genes with a significant change of more than two-fold were selected. Green dot represented up-regulated significant genes and red dot represented down-regulated significant genes.
Table 2. The statistical metrics for key DEGs.
| IlluminaID | GeneSymbol | logFC | pValue | adj.P.Val | tvalue | Regulation | GeneName |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ILMN_3246433 | RNY5 | 1.462757 | 5.68E-06 | 0.002906 | 4.775349 | Up | RNA, Ro60-associated Y5 |
| ILMN_1691647 | CGB5 | 1.297516 | 0.000781 | 0.021869 | 3.457767 | Up | chorionic gonadotropin subunit β 5 |
| ILMN_1668035 | CRH | 1.29002 | 0.001459 | 0.029715 | 3.266769 | Up | corticotropin releasing hormone |
| ILMN_1716238 | PSG6 | 1.284052 | 0.00171 | 0.032189 | 3.217109 | Up | pregnancy specific β-1-glycoprotein 6 |
| ILMN_1772768 | PSG7 | 1.257768 | 0.001767 | 0.032784 | 3.206816 | Up | pregnancy specific β-1-glycoprotein 7 (gene/pseudogene) |
| ILMN_2413473 | GH2 | 1.248351 | 0.002276 | 0.037103 | 3.126124 | Up | growth hormone 2 |
| ILMN_1801776 | PSG9 | 1.204077 | 0.002468 | 0.038662 | 3.100092 | Up | pregnancy specific β-1-glycoprotein 9 |
| ILMN_1798000 | PSG1 | 1.147959 | 0.000469 | 0.017456 | 3.608336 | Up | pregnancy specific β-1-glycoprotein 1 |
| ILMN_1728734 | PSG5 | 1.143624 | 0.000969 | 0.024168 | 3.392528 | Up | pregnancy specific β-1-glycoprotein 5 |
| ILMN_2387860 | CYP19A1 | 1.130568 | 0.00132 | 0.028092 | 3.297762 | Up | cytochrome P450 family 19 subfamily A member 1 |
| ILMN_1764483 | PSG2 | 1.123521 | 0.003218 | 0.044644 | 3.013539 | Up | pregnancy specific β-1-glycoprotein 2 |
| ILMN_1706911 | PSG11 | 1.115865 | 0.002642 | 0.040078 | 3.07808 | Up | pregnancy specific β-1-glycoprotein 11 |
| ILMN_1765187 | LHB | 1.086528 | 0.002327 | 0.037529 | 3.118995 | Up | luteinizing hormone subunit β |
| ILMN_1693397 | PSG4 | 1.079921 | 0.002644 | 0.040091 | 3.077764 | Up | pregnancy specific β-1-glycoprotein 4 |
| ILMN_1785393 | ADAM12 | 1.058143 | 0.003796 | 0.048669 | 2.958837 | Up | ADAM metallopeptidase domain 12 |
| ILMN_1749078 | TIMP2 | 1.029031 | 0.001077 | 0.025325 | 3.360515 | Up | TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 2 |
| ILMN_2406299 | SEMA3B | 1.019814 | 0.001424 | 0.029234 | 3.274226 | Up | semaphorin 3B |
| ILMN_1691937 | CSH2 | 0.93195 | 0.003208 | 0.044568 | 3.014577 | Up | chorionic somatomammotropin hormone 2 |
| ILMN_2044645 | CGB1 | 0.914238 | 0.003818 | 0.048801 | 2.956891 | Up | chorionic gonadotropin subunit β 1 |
| ILMN_2083578 | CGB7 | 0.902725 | 0.001095 | 0.025576 | 3.355412 | Up | chorionic gonadotropin subunit β 7 |
| ILMN_1754207 | PLAC1 | 0.846799 | 0.003832 | 0.048867 | 2.955674 | Up | placenta enriched 1 |
| ILMN_1698318 | LGALS14 | 0.831948 | 0.001715 | 0.032189 | 3.216166 | Up | galectin 14 |
| ILMN_2068104 | TFPI2 | 0.817524 | 0.003376 | 0.04562 | 2.997767 | Up | tissue factor pathway inhibitor 2 |
| ILMN_2316236 | HOPX | 0.817388 | 0.000335 | 0.014808 | 3.70535 | Up | HOP homeobox |
| ILMN_1789638 | MFSD2A | 0.815456 | 0.002488 | 0.038799 | 3.097506 | Up | major facilitator superfamily domain containing 2A |
| ILMN_1786908 | KRTAP26-1 | 0.796216 | 0.00037 | 0.01533 | 3.677008 | Up | keratin associated protein 26-1 |
| ILMN_1659597 | LOC100506358 | 0.792699 | 0.000395 | 0.015895 | 3.658029 | Up | uncharacterized LOC100506358 |
| ILMN_2118663 | ERV3-1 | 0.791098 | 0.001056 | 0.025169 | 3.366462 | Up | endogenous retrovirus group 3 member 1, envelope |
| ILMN_1712066 | EXPH5 | 0.790876 | 0.000584 | 0.01904 | 3.543961 | Up | exophilin 5 |
| ILMN_1674696 | OLAH | 0.774415 | 0.00023 | 0.012505 | 3.811374 | Up | oleoyl-ACP hydrolase |
| ILMN_2233454 | SPTLC3 | 0.771167 | 0.000748 | 0.021335 | 3.470437 | Up | serine palmitoyltransferase long chain base subunit 3 |
| ILMN_1693530 | PSG3 | 0.760751 | 0.002195 | 0.036289 | 3.137778 | Up | pregnancy specific β-1-glycoprotein 3 |
| ILMN_1784824 | LINC01118 | 0.760468 | 0.001118 | 0.025812 | 3.349058 | Up | long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1118 |
| ILMN_1813350 | HSD11B2 | 0.758705 | 0.002101 | 0.035634 | 3.151814 | Up | hydroxysteroid 11-β dehydrogenase 2 |
| ILMN_2352921 | BPGM | 0.755678 | 0.000432 | 0.016748 | 3.631747 | Up | bisphosphoglyceratemutase |
| ILMN_1678710 | PHYHIPL | 0.750771 | 0.000149 | 0.010164 | 3.932405 | Up | phytanoyl-CoA 2-hydroxylase interacting protein like |
| ILMN_1794842 | LGALS13 | 0.737107 | 0.002229 | 0.036621 | 3.132873 | Up | galectin 13 |
| ILMN_2188862 | GDF15 | 0.733888 | 0.003343 | 0.045512 | 3.000989 | Up | growth differentiation factor 15 |
| ILMN_1702858 | ADHFE1 | 0.733838 | 0.000566 | 0.018799 | 3.553236 | Up | alcohol dehydrogenase iron containing 1 |
| ILMN_2187746 | EMX2 | 0.724034 | 0.002408 | 0.038098 | 3.108039 | Up | empty spiracles homeobox 2 |
| ILMN_1780693 | HSD3B1 | 0.713165 | 0.003003 | 0.043117 | 3.03634 | Up | hydroxy-δ-5-steroid dehydrogenase, 3 β- and steroid δ-isomerase 1 |
| ILMN_1814737 | LNPEP | 0.699558 | 0.001327 | 0.028154 | 3.296246 | Up | leucyl and cystinylaminopeptidase |
| ILMN_1807277 | IFI30 | 0.696224 | 0.000433 | 0.01676 | 3.631088 | Up | IFI30 lysosomalthiolreductase |
| ILMN_1756443 | INHA | 0.693534 | 0.000602 | 0.019237 | 3.535224 | Up | inhibin subunit α |
| ILMN_1748090 | SLC2A11 | 0.691618 | 0.000104 | 0.008561 | 4.029682 | Up | solute carrier family 2 member 11 |
| ILMN_1774287 | CFB | 0.689441 | 0.002619 | 0.039846 | 3.080829 | Up | complement factor B |
| ILMN_1768662 | UCK2 | 0.666106 | 0.00056 | 0.018724 | 3.556095 | Up | uridine-cytidine kinase 2 |
| ILMN_1720540 | INSL4 | 0.662317 | 0.001009 | 0.024621 | 3.380194 | Up | insulin like 4 |
| ILMN_1797744 | TPPP3 | 0.660409 | 0.000586 | 0.019062 | 3.543117 | Up | tubulin polymerization promoting protein family member 3 |
| ILMN_1680139 | MAFF | 0.655013 | 0.001413 | 0.02907 | 3.276627 | Up | MAF bZIP transcription factor F |
| ILMN_2368188 | TRPV6 | 0.647442 | 0.001158 | 0.02618 | 3.338062 | Up | transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 6 |
| ILMN_1740466 | TENT5A | 0.645318 | 0.000443 | 0.016957 | 3.624672 | Up | terminal nucleotidyltransferase 5A |
| ILMN_1800412 | BMP1 | 0.634772 | 0.000459 | 0.017315 | 3.614562 | Up | bone morphogenetic protein 1 |
| ILMN_1727633 | NECTIN3 | 0.633198 | 0.002322 | 0.037503 | 3.11981 | Up | nectin cell adhesion molecule 3 |
| ILMN_1664855 | PPP1R14C | 0.629794 | 0.001066 | 0.025246 | 3.363473 | Up | protein phosphatase 1 regulatory inhibitor subunit 14C |
| ILMN_1695562 | ZNF471 | 0.623497 | 0.000993 | 0.024402 | 3.38509 | Up | zinc finger protein 471 |
| ILMN_1714586 | VGLL3 | 0.618471 | 0.001854 | 0.033507 | 3.191522 | Up | vestigial like family member 3 |
| ILMN_1744949 | RHOBTB3 | 0.61326 | 0.001612 | 0.031272 | 3.235567 | Up | Rho related BTB domain containing 3 |
| ILMN_1703284 | SPIRE2 | 0.612933 | 0.00328 | 0.045007 | 3.007246 | Up | spire type actin nucleation factor 2 |
| ILMN_1704376 | GLDN | 0.605249 | 0.002329 | 0.037531 | 3.118817 | Up | gliomedin |
| ILMN_2415421 | SLC30A2 | 0.602925 | 0.002569 | 0.039356 | 3.087159 | Up | solute carrier family 30 member 2 |
| ILMN_1757406 | H1-2 | 0.598625 | 0.001243 | 0.027166 | 3.316284 | Up | H1.2 linker histone, cluster member |
| ILMN_1651496 | H2BC5 | 0.597413 | 0.000105 | 0.008597 | 4.027633 | Up | H2B clustered histone 5 |
| ILMN_1773125 | ENTPD1 | 0.596924 | 0.003282 | 0.045007 | 3.007041 | Up | ectonucleoside triphosphate diphosphohydrolase 1 |
| ILMN_1790228 | FURIN | 0.595716 | 0.001344 | 0.028402 | 3.292157 | Up | furin, paired basic amino acid cleaving enzyme |
| ILMN_1741143 | TXK | 0.593669 | 0.001359 | 0.028533 | 3.288903 | Up | TXK tyrosine kinase |
| ILMN_1787750 | CD200 | 0.592992 | 0.001168 | 0.02622 | 3.335461 | Up | CD200 molecule |
| ILMN_1795106 | PSG8 | 0.59239 | 0.002853 | 0.041916 | 3.053083 | Up | pregnancy specific β-1-glycoprotein 8 |
| ILMN_1672908 | TWIST1 | 0.585791 | 0.002193 | 0.036269 | 3.138064 | Up | twist family bHLH transcription factor 1 |
| ILMN_1787691 | CITED4 | 0.583851 | 0.000456 | 0.017275 | 3.616082 | Up | Cbp/p300 interacting transactivator with Glu/Asp rich carboxy-terminal domain 4 |
| ILMN_1740917 | SCNN1B | 0.580064 | 0.00208 | 0.035516 | 3.155039 | Up | sodium channel epithelial 1 β subunit |
| ILMN_1681248 | TCHH | 0.579544 | 0.000868 | 0.023007 | 3.42568 | Up | trichohyalin |
| ILMN_1713397 | NCCRP1 | 0.577054 | 0.001607 | 0.031251 | 3.236641 | Up | NCCRP1, F-box associated domain containing |
| ILMN_1771019 | MTMR4 | 0.575772 | 0.000998 | 0.024462 | 3.383725 | Up | myotubularin related protein 4 |
| ILMN_1792689 | H2AC6 | 0.572844 | 0.000198 | 0.011571 | 3.853384 | Up | H2A clustered histone 6 |
| ILMN_1732071 | H2BC21 | 0.571255 | 0.000494 | 0.01788 | 3.593188 | Up | H2B clustered histone 21 |
| ILMN_1777934 | MORN3 | 0.570881 | 0.000392 | 0.015793 | 3.660351 | Up | MORN repeat containing 3 |
| ILMN_1754126 | SH2D5 | 0.567064 | 0.000548 | 0.018452 | 3.562897 | Up | SH2 domain containing 5 |
| ILMN_1768820 | CYP11A1 | 0.562921 | 0.002281 | 0.037107 | 3.125417 | Up | cytochrome P450 family 11 subfamily A member 1 |
| ILMN_1721842 | RYBP | 0.560609 | 0.001133 | 0.026002 | 3.344898 | Up | RING1 and YY1 binding protein |
| ILMN_2323172 | CSF3R | 0.55608 | 0.002173 | 0.03615 | 3.140995 | Up | colony stimulating factor 3 receptor |
| ILMN_1693789 | ALPP | 0.554751 | 0.003332 | 0.045427 | 3.002056 | Up | alkaline phosphatase, placental |
| ILMN_2129015 | AFF1 | 0.5529 | 0.003097 | 0.043799 | 3.026214 | Up | AF4/FMR2 family member 1 |
| ILMN_1807652 | STRA6 | 0.548925 | 0.001375 | 0.028697 | 3.285192 | Up | stimulated by retinoic acid 6 |
| ILMN_1746517 | KYNU | 0.547309 | 0.002021 | 0.035003 | 3.164234 | Up | kynureninase |
| ILMN_1793695 | ITIH5 | 0.543721 | 0.002744 | 0.041015 | 3.065788 | Up | inter-α-trypsin inhibitor heavy chain 5 |
| ILMN_1814600 | DEPDC1B | 0.542445 | 0.001287 | 0.027725 | 3.305687 | Up | DEP domain containing 1B |
| ILMN_1708340 | DAPK1 | 0.541376 | 0.003167 | 0.04426 | 3.018827 | Up | death associated protein kinase 1 |
| ILMN_2204545 | ST3GAL4 | 0.537233 | 0.001733 | 0.032379 | 3.212881 | Up | ST3 β-galactoside α-2,3-sialyltransferase 4 |
| ILMN_1794239 | ODAPH | 0.533324 | 0.000498 | 0.017895 | 3.590399 | Up | odontogenesis associated phosphoprotein |
| ILMN_2315780 | TACC2 | 0.532522 | 0.000106 | 0.00868 | 4.024113 | Up | transforming acidic coiled-coil containing protein 2 |
| ILMN_2309446 | RBBP6 | 0.528104 | 0.000254 | 0.013135 | 3.783862 | Up | RB binding protein 6, ubiquitin ligase |
| ILMN_1791545 | KRT23 | 0.527971 | 0.000209 | 0.011919 | 3.838417 | Up | keratin 23 |
| ILMN_1798458 | KAZN | 0.51384 | 0.001255 | 0.027297 | 3.313396 | Up | kazrin, periplakin interacting protein |
| ILMN_1777683 | ADAMTSL4 | 0.513545 | 0.00031 | 0.014326 | 3.727088 | Up | ADAMTS like 4 |
| ILMN_1811593 | NIPAL1 | 0.509377 | 0.000573 | 0.018927 | 3.549631 | Up | NIPA like domain containing 1 |
| ILMN_3236821 | HSPB1 | 0.507177 | 0.000829 | 0.022503 | 3.439718 | Up | heat shock protein family B (small) member 1 |
| ILMN_1774229 | SLC7A4 | 0.504867 | 0.003047 | 0.043409 | 3.031496 | Up | solute carrier family 7 member 4 |
| ILMN_1795838 | C4orf19 | 0.503581 | 0.000615 | 0.019397 | 3.528742 | Up | chromosome 4 open reading frame 19 |
| ILMN_1689004 | TNFRSF12A | 0.50273 | 0.000813 | 0.022284 | 3.44546 | Up | TNF receptor superfamily member 12A |
| ILMN_1702105 | EFS | 0.502312 | 0.001688 | 0.032021 | 3.221088 | Up | embryonal Fyn-associated substrate |
| ILMN_1725831 | TINCR | 0.502082 | 0.001143 | 0.026058 | 3.342141 | Up | TINCR ubiquitin domain containing |
| ILMN_1726597 | RIPOR2 | 0.501684 | 0.000791 | 0.022033 | 3.453621 | Up | RHO family interacting cell polarization regulator 2 |
| ILMN_1746618 | PAQR7 | 0.498553 | 0.000293 | 0.014028 | 3.743357 | Up | progestin and adipoQ receptor family member 7 |
| ILMN_2351638 | BEX4 | 0.49812 | 1.22E-05 | 0.003404 | 4.586051 | Up | brain expressed X-linked 4 |
| ILMN_1762207 | SGSM1 | 0.495004 | 0.000544 | 0.018404 | 3.565008 | Up | small G protein signaling modulator 1 |
| ILMN_1802690 | GULP1 | 0.492328 | 0.002712 | 0.040738 | 3.069508 | Up | GULP PTB domain containing engulfment adaptor 1 |
| ILMN_1679041 | SLC3A2 | 0.486676 | 0.001058 | 0.025186 | 3.365946 | Up | solute carrier family 3 member 2 |
| ILMN_1728677 | CREB5 | 0.486008 | 0.000136 | 0.009772 | 3.957019 | Up | cAMP responsive element binding protein 5 |
| ILMN_2390609 | ANK3 | 0.481205 | 0.001627 | 0.031404 | 3.232619 | Up | ankyrin 3 |
| ILMN_1740170 | CHCHD10 | 0.479287 | 0.002374 | 0.03792 | 3.11261 | Up | coiled-coil-helix-coiled-coil-helix domain containing 10 |
| ILMN_1813139 | ANKDD1A | 0.477831 | 0.000338 | 0.014847 | 3.702751 | Up | ankyrin repeat and death domain containing 1A |
| ILMN_2194448 | STT3B | 0.477537 | 0.00228 | 0.037103 | 3.125635 | Up | STT3 oligosaccharyltransferase complex catalytic subunit B |
| ILMN_2079991 | ERVW-1 | 0.468734 | 0.000211 | 0.01196 | 3.835811 | Up | endogenous retrovirus group W member 1, envelope |
| ILMN_1684034 | STAT5B | 0.466134 | 0.000495 | 0.01788 | 3.59265 | Up | signal transducer and activator of transcription 5B |
| ILMN_1796423 | CLIC3 | 0.465597 | 0.001265 | 0.027404 | 3.31097 | Up | chloride intracellular channel 3 |
| ILMN_3280402 | GLRX | 0.464843 | 0.000542 | 0.018404 | 3.56612 | Up | glutaredoxin |
| ILMN_1753931 | CDO1 | 0.464443 | 0.000182 | 0.011037 | 3.877815 | Up | cysteine dioxygenase type 1 |
| ILMN_2065690 | GRAMD2B | 0.464402 | 0.000499 | 0.017901 | 3.589918 | Up | GRAM domain containing 2B |
| ILMN_1752510 | FAM13A | 0.463446 | 0.000335 | 0.014808 | 3.705566 | Up | family with sequence similarity 13 member A |
| ILMN_2384857 | DHRS2 | 0.460744 | 0.001634 | 0.031474 | 3.23133 | Up | dehydrogenase/reductase 2 |
| ILMN_1720771 | STX11 | 0.459749 | 0.002149 | 0.035892 | 3.144568 | Up | syntaxin 11 |
| ILMN_1807563 | FKBP2 | 0.457573 | 0.000724 | 0.02097 | 3.480237 | Up | FKBP prolylisomerase 2 |
| ILMN_1669557 | CRYBG2 | 0.4569 | 0.001328 | 0.028154 | 3.296056 | Up | crystallin β-γ domain containing 2 |
| ILMN_1699206 | FHDC1 | 0.455751 | 0.00209 | 0.035562 | 3.153528 | Up | FH2 domain containing 1 |
| ILMN_1806149 | C16orf74 | 0.455006 | 0.000426 | 0.016582 | 3.636053 | Up | chromosome 16 open reading frame 74 |
| ILMN_1751120 | H4C8 | 0.45076 | 0.000764 | 0.021605 | 3.464112 | Up | H4 clustered histone 8 |
| ILMN_1740604 | RAB11FIP5 | 0.450629 | 0.003974 | 0.049778 | 2.943476 | Up | RAB11 family interacting protein 5 |
| ILMN_3195497 | ADIRF-AS1 | 0.448015 | 0.002142 | 0.035854 | 3.145598 | Up | ADIRF antisense RNA 1 |
| ILMN_1813625 | TRIM25 | 0.445493 | 0.000114 | 0.00893 | 4.005574 | Up | tripartite motif containing 25 |
| ILMN_1753515 | SRR | 0.44366 | 0.003251 | 0.044884 | 3.010168 | Up | serine racemase |
| ILMN_1772627 | NSG1 | 0.441643 | 0.001427 | 0.029273 | 3.273602 | Up | neuronal vesicle trafficking associated 1 |
| ILMN_2364700 | ENSA | 0.441237 | 1.88E-05 | 0.004187 | 4.477906 | Up | endosulfine α |
| ILMN_1674243 | TFRC | 0.43767 | 0.003549 | 0.046989 | 2.981226 | Up | transferrin receptor |
| ILMN_1779448 | EFHD1 | 0.435614 | 0.003381 | 0.045635 | 2.997287 | Up | EF-hand domain family member D1 |
| ILMN_1798975 | EGFR | 0.434921 | 0.002718 | 0.040787 | 3.068785 | Up | epidermal growth factor receptor |
| ILMN_1802053 | ZNF91 | 0.433844 | 0.000914 | 0.023507 | 3.410338 | Up | zinc finger protein 91 |
| ILMN_1797557 | PLEKHA6 | 0.43335 | 0.003538 | 0.046906 | 2.982198 | Up | pleckstrin homology domain containing A6 |
| ILMN_1814333 | SERPINI1 | 0.433318 | 0.00355 | 0.046989 | 2.981082 | Up | serpin family I member 1 |
| ILMN_1683211 | NCAN | 0.430909 | 0.002311 | 0.037392 | 3.121301 | Up | neurocan |
| ILMN_2142353 | GRTP1 | 0.430742 | 0.001078 | 0.025332 | 3.360135 | Up | growth hormone regulated TBC protein 1 |
| ILMN_1809477 | CARHSP1 | 0.428795 | 0.001041 | 0.024977 | 3.370793 | Up | calcium regulated heat stable protein 1 |
| ILMN_1767365 | PAK1 | 0.427899 | 0.000143 | 0.009932 | 3.94428 | Up | p21 (RAC1) activated kinase 1 |
| ILMN_1759792 | CLIP4 | 0.427572 | 0.000478 | 0.017642 | 3.60267 | Up | CAP-Gly domain containing linker protein family member 4 |
| ILMN_2143685 | CLDN7 | 0.426872 | 0.000634 | 0.019679 | 3.519853 | Up | claudin 7 |
| ILMN_2074860 | RN7SK | 0.425278 | 0.000506 | 0.017919 | 3.586106 | Up | RNA component of 7SK nuclear ribonucleoprotein |
| ILMN_1742538 | PCDHGC4 | 0.422624 | 0.00088 | 0.023184 | 3.421715 | Up | protocadherin γ subfamily C, 4 |
| ILMN_1689817 | LCOR | 0.419011 | 0.001391 | 0.028854 | 3.281687 | Up | ligand dependent nuclear receptor corepressor |
| ILMN_1667994 | AMD1 | 0.418735 | 0.00061 | 0.019374 | 3.531034 | Up | adenosylmethionine decarboxylase 1 |
| ILMN_1683598 | ACSL4 | 0.416616 | 0.003954 | 0.04961 | 2.945175 | Up | acyl-CoA synthetase long chain family member 4 |
| ILMN_1796206 | KMT2C | 0.415266 | 8.27E-05 | 0.007525 | 4.092148 | Up | lysine methyltransferase 2C |
| ILMN_1729417 | GNE | 0.413507 | 0.001169 | 0.02622 | 3.335407 | Up | glucosamine (UDP-N-acetyl)-2-epimerase/N-acetylmannosamine kinase |
| ILMN_1778956 | STS | 0.411932 | 0.000347 | 0.014977 | 3.695049 | Up | steroid sulfatase |
| ILMN_2405254 | GRB7 | 0.408773 | 0.00026 | 0.013186 | 3.777315 | Up | growth factor receptor bound protein 7 |
| ILMN_1813314 | H2BC12 | 0.408761 | 0.002651 | 0.04015 | 3.076962 | Up | H2B clustered histone 12 |
| ILMN_2346339 | FOLR1 | 0.407865 | 0.000266 | 0.013333 | 3.771078 | Up | folate receptor α |
| ILMN_1747112 | GPAA1 | 0.407772 | 1.5E-05 | 0.003692 | 4.534163 | Up | glycosylphosphatidylinositol anchor attachment 1 |
| ILMN_1736863 | TMEM140 | 0.40612 | 0.000597 | 0.019237 | 3.537542 | Up | transmembrane protein 140 |
| ILMN_3226388 | PSG10P | 0.399644 | 0.00336 | 0.045553 | 2.999338 | Up | pregnancy specific β-1-glycoprotein 10, pseudogene |
| ILMN_1769092 | EVA1B | 0.398688 | 0.002925 | 0.042546 | 3.044952 | Up | eva-1 homolog B |
| ILMN_1654322 | ATP1B3 | 0.398471 | 0.00148 | 0.029861 | 3.262353 | Up | ATPase Na+/K+ transporting subunit β 3 |
| ILMN_1699674 | ZNF703 | 0.397878 | 0.003462 | 0.046339 | 2.989443 | Up | zinc finger protein 703 |
| ILMN_2159730 | GABRB1 | 0.396679 | 0.000663 | 0.020103 | 3.506538 | Up | γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor β1 subunit |
| ILMN_2342437 | KLHL5 | 0.395369 | 0.003031 | 0.043318 | 3.033257 | Up | kelch like family member 5 |
| ILMN_1704472 | EID2 | 0.394584 | 8.47E-06 | 0.00295 | 4.677314 | Up | EP300 interacting inhibitor of differentiation 2 |
| ILMN_2374865 | ATF3 | 0.394537 | 0.001939 | 0.034245 | 3.177337 | Up | activating transcription factor 3 |
| ILMN_1652540 | RELL2 | 0.39244 | 0.00081 | 0.022284 | 3.446717 | Up | RELT like 2 |
| ILMN_1697642 | BCAP29 | 0.391558 | 0.000201 | 0.011654 | 3.849685 | Up | B cell receptor associated protein 29 |
| ILMN_2382974 | CCDC7 | 0.391544 | 0.000891 | 0.023304 | 3.4178 | Up | coiled-coil domain containing 7 |
| ILMN_1742260 | ITPRID2 | 0.39091 | 0.000176 | 0.010925 | 3.886377 | Up | ITPR interacting domain containing 2 |
| ILMN_2060145 | GRHL2 | 0.389706 | 0.000397 | 0.015954 | 3.656341 | Up | grainyhead like transcription factor 2 |
| ILMN_2195821 | CREBRF | 0.389024 | 0.000261 | 0.013186 | 3.77657 | Up | CREB3 regulatory factor |
| ILMN_1746676 | CLDN8 | 0.388757 | 0.002765 | 0.041192 | 3.063276 | Up | claudin 8 |
| ILMN_1700583 | ZNF750 | 0.388452 | 0.000505 | 0.017918 | 3.586783 | Up | zinc finger protein 750 |
| ILMN_1655913 | NUCB2 | 0.386679 | 0.002616 | 0.039837 | 3.081247 | Up | nucleobindin 2 |
| ILMN_1701393 | TBX3 | 0.381209 | 1.9E-05 | 0.004198 | 4.474884 | Up | T-box transcription factor 3 |
| ILMN_1769201 | ELF3 | 0.380808 | 0.002808 | 0.041529 | 3.058207 | Up | E74 like ETS transcription factor 3 |
| ILMN_1791280 | HSPB8 | 0.380526 | 0.002023 | 0.03504 | 3.163783 | Up | heat shock protein family B (small) member 8 |
| ILMN_2149292 | TMEM40 | 0.378498 | 0.000676 | 0.020287 | 3.500728 | Up | transmembrane protein 40 |
| ILMN_1707088 | DENND2D | 0.37794 | 7.09E-05 | 0.007061 | 4.133296 | Up | DENN domain containing 2D |
| ILMN_2179778 | PHLDB2 | 0.377513 | 0.000242 | 0.012762 | 3.797837 | Up | pleckstrin homology like domain family B member 2 |
| ILMN_1801216 | S100P | 0.375994 | 0.00042 | 0.016421 | 3.640526 | Up | S100 calcium binding protein P |
| ILMN_1699254 | PLEKHH1 | 0.374597 | 0.000398 | 0.015954 | 3.656068 | Up | pleckstrin homology, MyTH4 and FERM domain containing H1 |
| ILMN_1710954 | FBXL19-AS1 | 0.37328 | 0.000271 | 0.013483 | 3.765506 | Up | FBXL19 antisense RNA 1 |
| ILMN_2376502 | RHOBTB1 | 0.372696 | 0.001027 | 0.024813 | 3.374907 | Up | Rho related BTB domain containing 1 |
| ILMN_1673455 | RASAL2 | 0.372204 | 6.16E-05 | 0.006575 | 4.170741 | Up | RAS protein activator like 2 |
| ILMN_3194638 | EVA1A | 0.371837 | 0.001826 | 0.033257 | 3.196396 | Up | eva-1 homolog A, regulator of programmed cell death |
| ILMN_1710284 | HES1 | 0.370834 | 0.000842 | 0.022673 | 3.435074 | Up | hes family bHLH transcription factor 1 |
| ILMN_2064655 | CXorf40A | 0.369875 | 3.68E-05 | 0.005267 | 4.305465 | Up | chromosome X open reading frame 40A |
| ILMN_2373566 | PJA1 | 0.365283 | 0.001767 | 0.032784 | 3.206709 | Up | praja ring finger ubiquitin ligase 1 |
| ILMN_1779648 | H2AW | 0.365117 | 0.002673 | 0.040354 | 3.074252 | Up | H2A.W histone |
| ILMN_2333107 | TLE5 | 0.363987 | 0.003586 | 0.047223 | 2.977803 | Up | TLE family member 5, transcriptional modulator |
| ILMN_1722025 | CPEB4 | 0.363264 | 0.000601 | 0.019237 | 3.535255 | Up | cytoplasmic polyadenylation element binding protein 4 |
| ILMN_1670263 | CNST | 0.362857 | 0.001654 | 0.031635 | 3.227556 | Up | consortin, connexin sorting protein |
| ILMN_2214678 | MXD1 | 0.36052 | 0.003377 | 0.04562 | 2.997692 | Up | MAX dimerization protein 1 |
| ILMN_2324202 | GABRE | 0.359786 | 0.001796 | 0.032966 | 3.20158 | Up | γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor epsilon subunit |
| ILMN_2049727 | OSER1 | 0.358697 | 0.000322 | 0.014545 | 3.716924 | Up | oxidative stress responsive serine rich 1 |
| ILMN_1704377 | USP27X | 0.35826 | 0.00113 | 0.025976 | 3.34568 | Up | ubiquitin specific peptidase 27 X-linked |
| ILMN_3233388 | RELL1 | 0.357964 | 0.002177 | 0.036172 | 3.1404 | Up | RELT like 1 |
| ILMN_1670878 | YTHDC1 | 0.357534 | 1.29E-06 | 0.001955 | 5.128971 | Up | YTH domain containing 1 |
| ILMN_1815445 | IDS | 0.356888 | 0.002505 | 0.038937 | 3.095289 | Up | iduronate 2-sulfatase |
| ILMN_1775448 | PFN2 | 0.353131 | 0.000871 | 0.023045 | 3.424684 | Up | profilin 2 |
| ILMN_1657423 | SPG21 | 0.353073 | 0.000213 | 0.011986 | 3.833747 | Up | SPG21 abhydrolase domain containing, maspardin |
| ILMN_2162799 | AHR | 0.353025 | 0.002516 | 0.039016 | 3.093903 | Up | aryl hydrocarbon receptor |
| ILMN_1698323 | PLEKHB2 | 0.352741 | 0.00209 | 0.035562 | 3.153476 | Up | pleckstrin homology domain containing B2 |
| ILMN_1725718 | ZSCAN4 | 0.352414 | 0.000589 | 0.019114 | 3.541628 | Up | zinc finger and SCAN domain containing 4 |
| ILMN_2414325 | TNFAIP8 | 0.351941 | 4.64E-05 | 0.005784 | 4.245233 | Up | TNF α induced protein 8 |
| ILMN_1656291 | TSKS | 0.350101 | 3.27E-05 | 0.005189 | 4.336503 | Up | testis specific serine kinase substrate |
| ILMN_3245236 | FBRS | 0.349549 | 0.002921 | 0.042546 | 3.045346 | Up | fibrosin |
| ILMN_3243972 | SNORA70B | 0.349376 | 0.00036 | 0.015127 | 3.684829 | Up | small nucleolar RNA, H/ACA box 70B |
| ILMN_1687519 | SNAP23 | 0.349045 | 0.000691 | 0.020442 | 3.494035 | Up | synaptosome associated protein 23 |
| ILMN_3307729 | CXXC5 | 0.347435 | 0.003855 | 0.04893 | 2.953691 | Up | CXXC finger protein 5 |
| ILMN_2359601 | CAMK2G | 0.346831 | 1.67E-06 | 0.001955 | 5.068099 | Up | calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II γ |
| ILMN_2358541 | RBMS1 | 0.346578 | 0.001495 | 0.030009 | 3.259102 | Up | RNA binding motif single stranded interacting protein 1 |
| ILMN_1812262 | DDR1 | 0.345856 | 0.001274 | 0.027548 | 3.308776 | Up | discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 1 |
| ILMN_1655702 | ABHD5 | 0.34552 | 0.000199 | 0.011583 | 3.852742 | Up | abhydrolase domain containing 5 |
| ILMN_1730294 | INO80C | 0.345306 | 0.000584 | 0.01904 | 3.543858 | Up | INO80 complex subunit C |
| ILMN_1729095 | PDZD2 | 0.34383 | 0.000816 | 0.022314 | 3.444388 | Up | PDZ domain containing 2 |
| ILMN_1775405 | ARL4A | 0.3433 | 0.000509 | 0.017937 | 3.584468 | Up | ADP ribosylation factor like GTPase 4A |
| ILMN_1680937 | H2BC4 | 0.342683 | 0.003302 | 0.045124 | 3.005054 | Up | H2B clustered histone 4 |
| ILMN_1689578 | TLR3 | 0.342449 | 0.002261 | 0.036968 | 3.128251 | Up | toll like receptor 3 |
| ILMN_2278335 | AKR1B15 | 0.342114 | 0.001891 | 0.033788 | 3.185343 | Up | aldo-ketoreductase family 1 member B15 |
| ILMN_1721922 | NAB2 | 0.340891 | 0.00057 | 0.018862 | 3.551119 | Up | NGFI-A binding protein 2 |
| ILMN_1691237 | CAP2 | 0.339551 | 0.00234 | 0.037639 | 3.117244 | Up | cyclase associated actin cytoskeleton regulatory protein 2 |
| ILMN_2395389 | PSMC4 | 0.336399 | 0.000477 | 0.017642 | 3.602967 | Up | proteasome 26S subunit, ATPase 4 |
| ILMN_2173919 | MYO9A | 0.33636 | 0.003286 | 0.045007 | 3.006655 | Up | myosin IXA |
| ILMN_1661809 | PRRG4 | 0.336227 | 0.00211 | 0.035643 | 3.150489 | Up | proline rich and Gla domain 4 |
| ILMN_2307455 | UBE2A | 0.334363 | 0.001495 | 0.030009 | 3.259139 | Up | ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 A |
| ILMN_3307700 | SPCS3 | 0.333342 | 0.002825 | 0.041676 | 3.056249 | Up | signal peptidase complex subunit 3 |
| ILMN_1654370 | TESK2 | 0.333053 | 3.57E-05 | 0.005231 | 4.313565 | Up | testis associated actin remodelling kinase 2 |
| ILMN_1742824 | SPATA13 | 0.331307 | 0.000114 | 0.008925 | 4.006357 | Up | spermatogenesis associated 13 |
| ILMN_1688755 | AAK1 | 0.329844 | 7.89E-05 | 0.007387 | 4.104652 | Up | AP2 associated kinase 1 |
| ILMN_1781374 | TUFT1 | 0.328884 | 4.48E-06 | 0.002802 | 4.832739 | Up | tuftelin 1 |
| ILMN_2124386 | RGL2 | 0.327869 | 1.43E-05 | 0.003559 | 4.547271 | Up | ral guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator like 2 |
| ILMN_1803939 | YIPF6 | 0.327011 | 0.000892 | 0.023304 | 3.417647 | Up | Yip1 domain family member 6 |
| ILMN_2170949 | SNX10 | 0.326909 | 0.002527 | 0.039088 | 3.092476 | Up | sorting nexin 10 |
| ILMN_1775304 | DNAJB1 | 0.326714 | 0.001071 | 0.025282 | 3.362025 | Up | DnaJ heat shock protein family (Hsp40) member B1 |
| ILMN_1657515 | RPS6KA5 | 0.32621 | 0.003592 | 0.047263 | 2.977249 | Up | ribosomal protein S6 kinase A5 |
| ILMN_1690826 | TNKS1BP1 | 0.321786 | 0.001116 | 0.025804 | 3.349443 | Up | tankyrase 1 binding protein 1 |
| ILMN_1814002 | TEAD3 | 0.320268 | 7.41E-05 | 0.007229 | 4.121364 | Up | TEA domain transcription factor 3 |
| ILMN_1768958 | RASGRP1 | 0.31925 | 0.003686 | 0.047951 | 2.968625 | Up | RAS guanyl releasing protein 1 |
| ILMN_2077623 | RRAS2 | 0.319214 | 0.001037 | 0.024918 | 3.371789 | Up | RAS related 2 |
| ILMN_1693014 | CEBPB | 0.318883 | 0.002995 | 0.043063 | 3.037146 | Up | CCAAT enhancer binding protein β |
| ILMN_3235340 | ACER2 | 0.318499 | 3.54E-05 | 0.005231 | 4.315633 | Up | alkaline ceramidase 2 |
| ILMN_2403458 | SMARCB1 | 0.318053 | 0.002694 | 0.040563 | 3.071724 | Up | SWI/SNF related, matrix associated, actin dependent regulator of chromatin, subfamily b, member 1 |
| ILMN_1805395 | LTBP3 | 0.317611 | 0.000756 | 0.021442 | 3.467486 | Up | latent transforming growth factor β binding protein 3 |
| ILMN_1804148 | TMED4 | 0.317228 | 0.001133 | 0.026002 | 3.344761 | Up | transmembrane p24 trafficking protein 4 |
| ILMN_1702447 | IGF2BP2 | 0.316952 | 0.000692 | 0.020442 | 3.493585 | Up | insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 2 |
| ILMN_1717195 | MBD2 | 0.316258 | 0.000121 | 0.009233 | 3.98994 | Up | methyl-CpG binding domain protein 2 |
| ILMN_1747451 | PLCXD1 | 0.316197 | 3.44E-05 | 0.005189 | 4.323024 | Up | phosphatidylinositol specific phospholipase C X domain containing 1 |
| ILMN_1777439 | TCL6 | 0.313824 | 4.13E-05 | 0.005607 | 4.275901 | Up | T cell leukemia/lymphoma 6 |
| ILMN_2358457 | ATF4 | 0.312963 | 5E-06 | 0.002879 | 4.806336 | Up | activating transcription factor 4 |
| ILMN_1694233 | ACYP1 | 0.312484 | 8.05E-06 | 0.00295 | 4.689698 | Up | acylphosphatase 1 |
| ILMN_1675937 | ANKRD9 | 0.312142 | 0.000113 | 0.008909 | 4.008887 | Up | ankyrin repeat domain 9 |
| ILMN_1670304 | FAM156A | 0.311579 | 0.002344 | 0.03767 | 3.116659 | Up | family with sequence similarity 156 member A |
| ILMN_1717234 | CAST | 0.310235 | 0.000968 | 0.024163 | 3.392908 | Up | calpastatin |
| ILMN_1710136 | PUDP | 0.309696 | 0.000391 | 0.015793 | 3.661101 | Up | pseudouridine 5′-phosphatase |
| ILMN_1750969 | FAM120AOS | 0.309171 | 0.001969 | 0.034468 | 3.172477 | Up | family with sequence similarity 120A opposite strand |
| ILMN_1717046 | MOB3B | 0.309072 | 0.001014 | 0.024678 | 3.378711 | Up | MOB kinase activator 3B |
| ILMN_1684042 | BET1 | 0.307537 | 0.000168 | 0.010659 | 3.898957 | Up | Bet1 golgi vesicular membrane trafficking protein |
| ILMN_1664303 | HTATIP2 | 0.306236 | 0.00063 | 0.019629 | 3.521367 | Up | HIV-1 Tat interactive protein 2 |
| ILMN_3263225 | CRIM1-DT | 0.305254 | 0.000552 | 0.018547 | 3.560684 | Up | CRIM1 divergent transcript |
| ILMN_1763127 | ACKR2 | 0.305224 | 0.001928 | 0.03416 | 3.179209 | Up | atypical chemokine receptor 2 |
| ILMN_1708611 | RDX | 0.30478 | 0.001592 | 0.031099 | 3.239468 | Up | radixin |
| ILMN_2190414 | ZNF83 | 0.304639 | 0.003774 | 0.048525 | 2.960719 | Up | zinc finger protein 83 |
| ILMN_3184978 | ST8SIA6-AS1 | 0.304228 | 3.46E-05 | 0.005189 | 4.321517 | Up | ST8SIA6 antisense RNA 1 |
| ILMN_1746494 | FNTA | 0.303227 | 2.43E-05 | 0.00477 | 4.412621 | Up | farnesyltransferase, CAAX box, α |
| ILMN_3238854 | RGPD8 | 0.302737 | 0.000139 | 0.00984 | 3.950626 | Up | RANBP2 like and GRIP domain containing 8 |
| ILMN_2322498 | RORA | 0.302665 | 5.91E-05 | 0.006473 | 4.181545 | Up | RAR related orphan receptor A |
| ILMN_2181892 | BEX2 | 0.301932 | 0.000691 | 0.020442 | 3.494243 | Up | brain expressed X-linked 2 |
| ILMN_1716988 | OPN3 | 0.300318 | 0.002185 | 0.036205 | 3.139321 | Up | opsin 3 |
| ILMN_1780382 | SPCS2P4 | 0.299459 | 0.003743 | 0.048256 | 2.963549 | Up | signal peptidase complex subunit 2 pseudogene 4 |
| ILMN_1782685 | DDB1 | 0.298269 | 0.003647 | 0.047663 | 2.972203 | Up | damage specific DNA binding protein 1 |
| ILMN_1801020 | ADK | 0.298209 | 0.000201 | 0.011664 | 3.849125 | Up | adenosine kinase |
| ILMN_1653793 | PDPK1 | 0.297954 | 0.002793 | 0.041395 | 3.059925 | Up | 3-phosphoinositide dependent protein kinase 1 |
| ILMN_1805225 | LPCAT3 | 0.296395 | 6.38E-06 | 0.00295 | 4.746876 | Up | lysophosphatidylcholineacyltransferase 3 |
| ILMN_1741371 | PGAP6 | 0.296064 | 0.003279 | 0.045007 | 3.007377 | Up | post-glycosylphosphatidylinositol attachment to proteins 6 |
| ILMN_2187718 | COX17 | 0.295972 | 0.000244 | 0.01284 | 3.795442 | Up | cytochrome c oxidase copper chaperone COX17 |
| ILMN_2263466 | ACADVL | 0.295932 | 0.000784 | 0.021918 | 3.456584 | Up | acyl-CoA dehydrogenase very long chain |
| ILMN_1687947 | H2BC6 | 0.295728 | 0.000669 | 0.020173 | 3.503643 | Up | H2B clustered histone 6 |
| ILMN_1723843 | CSNK2A2 | 0.294128 | 0.002683 | 0.040473 | 3.073056 | Up | casein kinase 2 α 2 |
| ILMN_1662578 | C1GALT1 | 0.294084 | 0.00014 | 0.00984 | 3.949908 | Up | core 1 synthase, glycoprotein-N-acetylgalactosamine 3-β-galactosyltransferase 1 |
| ILMN_1807423 | IGF2BP3 | 0.293802 | 0.000826 | 0.02247 | 3.440691 | Up | insulin like growth factor 2 mRNA binding protein 3 |
| ILMN_3204734 | STAG3L5P-PVRIG2P-PILRB | 0.293124 | 0.003136 | 0.044111 | 3.022076 | Up | STAG3L5P-PVRIG2P-PILRB readthrough |
| ILMN_1754145 | CAPRIN1 | 0.293108 | 0.00032 | 0.014545 | 3.71836 | Up | cell cycle associated protein 1 |
| ILMN_1730794 | SERTAD4 | 0.292851 | 9.6E-05 | 0.008175 | 4.051978 | Up | SERTA domain containing 4 |
| ILMN_2394250 | PLEKHA1 | 0.291747 | 0.002354 | 0.03774 | 3.115333 | Up | pleckstrin homology domain containing A1 |
| ILMN_2078389 | SLC4A2 | 0.291257 | 0.001113 | 0.025759 | 3.35042 | Up | solute carrier family 4 member 2 |
| ILMN_2220403 | GINM1 | 0.290762 | 0.000493 | 0.01788 | 3.593513 | Up | glycoprotein integral membrane 1 |
| ILMN_1710027 | PNMT | 0.290062 | 0.0003 | 0.014133 | 3.736366 | Up | phenylethanolamine N-methyltransferase |
| ILMN_1734478 | PIP5K1B | 0.289858 | 5.33E-06 | 0.002879 | 4.790836 | Up | phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase type 1 β |
| ILMN_1758034 | ETFDH | 0.288994 | 0.000644 | 0.019798 | 3.514851 | Up | electron transfer flavoprotein dehydrogenase |
| ILMN_1666713 | LYPLA1 | 0.287789 | 0.00059 | 0.019114 | 3.541151 | Up | lysophospholipase 1 |
| ILMN_1797964 | ARL6IP6 | 0.287061 | 0.000378 | 0.015488 | 3.670358 | Up | ADP ribosylation factor like GTPase 6 interacting protein 6 |
| ILMN_3290211 | PIGH | 0.286739 | 0.00285 | 0.041916 | 3.053413 | Up | phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class H |
| ILMN_1687546 | HSP90AA1 | 0.286692 | 0.000957 | 0.02406 | 3.396413 | Up | heat shock protein 90 α family class A member 1 |
| ILMN_1719344 | NRBF2 | 0.286671 | 0.002233 | 0.036626 | 3.132293 | Up | nuclear receptor binding factor 2 |
| ILMN_1734655 | ATG9B | 0.286517 | 0.000583 | 0.01904 | 3.544278 | Up | autophagy related 9B |
| ILMN_1711408 | ANXA4 | 0.286403 | 0.002191 | 0.036239 | 3.138437 | Up | annexin A4 |
| ILMN_1811178 | SCAPER | 0.286258 | 0.002028 | 0.035067 | 3.163085 | Up | S-phase cyclin A associated protein in the ER |
| ILMN_1669281 | CLN3 | 0.285791 | 0.000543 | 0.018404 | 3.565093 | Up | CLN3 lysosomal/endosomaltransmembrane protein, battenin |
| ILMN_1686985 | MTM1 | 0.284755 | 0.00147 | 0.029797 | 3.264326 | Up | myotubularin 1 |
| ILMN_1781560 | ST3GAL6 | 0.284681 | 0.000826 | 0.02247 | 3.440705 | Up | ST3 β-galactoside α-2,3-sialyltransferase 6 |
| ILMN_1734229 | SPPL2A | 0.283933 | 0.001105 | 0.025674 | 3.352613 | Up | signal peptide peptidase like 2A |
| ILMN_2094166 | CHMP5 | 0.282317 | 0.002279 | 0.037103 | 3.125771 | Up | charged multivesicular body protein 5 |
| ILMN_1773849 | ATP6V0C | 0.282222 | 0.000886 | 0.023276 | 3.419682 | Up | ATPase H+ transporting V0 subunit c |
| ILMN_1739876 | RAB3GAP1 | 0.281181 | 0.001209 | 0.026753 | 3.324924 | Up | RAB3 GTPase activating protein catalytic subunit 1 |
| ILMN_1797594 | NFAT5 | 0.28094 | 0.002689 | 0.040538 | 3.072332 | Up | nuclear factor of activated T cells 5 |
| ILMN_1734542 | OVGP1 | 0.280116 | 0.00204 | 0.035106 | 3.161242 | Up | oviductal glycoprotein 1 |
| ILMN_1665982 | AKTIP | 0.277649 | 0.001862 | 0.03357 | 3.190258 | Up | AKT interacting protein |
| ILMN_1679268 | PELI1 | 0.277477 | 0.001777 | 0.032803 | 3.204955 | Up | pellino E3 ubiquitin protein ligase 1 |
| ILMN_3249846 | LIMS3-LOC440895 | 0.276865 | 0.001178 | 0.026374 | 3.333032 | Up | LIMS3-LOC440895 readthrough |
| ILMN_2323526 | WAC | 0.276545 | 0.000268 | 0.013383 | 3.769114 | Up | WW domain containing adaptor with coiled-coil |
| ILMN_1748077 | DDX59 | 0.275827 | 0.00214 | 0.035854 | 3.145909 | Up | DEAD-box helicase 59 |
| ILMN_1782444 | YIPF4 | 0.275515 | 0.001307 | 0.027959 | 3.300882 | Up | Yip1 domain family member 4 |
| ILMN_2339284 | CHD2 | 0.27514 | 0.000192 | 0.011354 | 3.862717 | Up | chromodomain helicase DNA binding protein 2 |
| ILMN_1706342 | ZNF746 | 0.274797 | 0.001538 | 0.03037 | 3.250211 | Up | zinc finger protein 746 |
| ILMN_3215367 | PPP4R2 | 0.274625 | 0.000744 | 0.021279 | 3.472213 | Up | protein phosphatase 4 regulatory subunit 2 |
| ILMN_1687279 | DHPS | 0.274317 | 0.000812 | 0.022284 | 3.445971 | Up | deoxyhypusine synthase |
| ILMN_1685678 | EEF1B2 | 0.273865 | 0.001055 | 0.025169 | 3.366614 | Up | eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1 β 2 |
| ILMN_1690066 | TIGD2 | 0.273626 | 0.000317 | 0.014515 | 3.720901 | Up | tigger transposable element derived 2 |
| ILMN_1736752 | COMTD1 | 0.273513 | 0.001712 | 0.032189 | 3.216644 | Up | catechol-O-methyltransferase domain containing 1 |
| ILMN_2387090 | CGGBP1 | 0.273351 | 0.000341 | 0.01488 | 3.699974 | Up | CGG triplet repeat binding protein 1 |
| ILMN_2194627 | GMCL1 | 0.273232 | 0.000277 | 0.013644 | 3.759819 | Up | germ cell-less 1, spermatogenesis associated |
| ILMN_3241234 | S100A11 | 0.273188 | 0.000851 | 0.022765 | 3.431703 | Up | S100 calcium binding protein A11 |
| ILMN_1678454 | CASP4 | 0.27189 | 0.00153 | 0.030267 | 3.25192 | Up | caspase 4 |
| ILMN_1705907 | NUP153 | 0.271384 | 0.000255 | 0.013135 | 3.782266 | Up | nucleoporin 153 |
| ILMN_2106265 | GDPD1 | 0.271243 | 0.003428 | 0.046055 | 2.992682 | Up | glycerophosphodiesterphosphodiesterase domain containing 1 |
| ILMN_1699357 | SLC22A5 | 0.270646 | 0.003156 | 0.044202 | 3.019938 | Up | solute carrier family 22 member 5 |
| ILMN_3282768 | PPP1R14B | 0.270021 | 0.001182 | 0.026432 | 3.331779 | Up | protein phosphatase 1 regulatory inhibitor subunit 14B |
| ILMN_1784655 | TLCD1 | 0.269664 | 0.001698 | 0.03211 | 3.219351 | Up | TLC domain containing 1 |
| ILMN_1809344 | BTBD10 | 0.269367 | 0.003946 | 0.049535 | 2.945897 | Up | BTB domain containing 10 |
| ILMN_1651268 | BORCS5 | 0.268841 | 0.000523 | 0.0181 | 3.576152 | Up | BLOC-1 related complex subunit 5 |
| ILMN_1676385 | PAK2 | 0.268282 | 0.000156 | 0.010361 | 3.920545 | Up | p21 (RAC1) activated kinase 2 |
| ILMN_1658337 | AKIRIN1 | 0.268214 | 0.003147 | 0.04417 | 3.020957 | Up | akirin 1 |
| ILMN_2137464 | DVL3 | 0.267864 | 0.0012 | 0.026647 | 3.327306 | Up | dishevelled segment polarity protein 3 |
| ILMN_1721833 | IER5 | 0.26766 | 0.003092 | 0.043799 | 3.026706 | Up | immediate early response 5 |
| ILMN_1781431 | GLCCI1 | 0.267281 | 8.05E-05 | 0.007462 | 4.099378 | Up | glucocorticoid induced 1 |
| ILMN_1808824 | NEBL | 0.266945 | 0.001597 | 0.031164 | 3.238616 | Up | nebulette |
| ILMN_1813028 | CBX5 | 0.266695 | 4.39E-05 | 0.005755 | 4.259566 | Up | chromobox 5 |
| ILMN_1717745 | TIAL1 | 0.266333 | 6.37E-06 | 0.00295 | 4.747368 | Up | TIA1 cytotoxic granule associated RNA binding protein like 1 |
| ILMN_1695110 | BCAT2 | 0.266237 | 0.002867 | 0.042043 | 3.051398 | Up | branched chain amino acid transaminase 2 |
| ILMN_1735052 | ULK1 | 0.266063 | 0.002947 | 0.042626 | 3.042442 | Up | unc-51 like autophagy activating kinase 1 |
| ILMN_1666670 | RBX1 | 0.265833 | 9.11E-06 | 0.003026 | 4.659225 | Up | ring-box 1 |
| ILMN_1801476 | CDS1 | 0.265788 | 0.002179 | 0.036176 | 3.140131 | Up | CDP-diacylglycerol synthase 1 |
| ILMN_1707350 | TUSC1 | 0.265484 | 0.002186 | 0.036205 | 3.139179 | Up | tumor suppressor candidate 1 |
| ILMN_1671265 | ING2 | 0.264936 | 0.000146 | 0.010103 | 3.937352 | Up | inhibitor of growth family member 2 |
| ILMN_1776297 | GOLGA4 | 0.262744 | 0.001009 | 0.024621 | 3.380238 | Up | golgin A4 |
| ILMN_1717063 | FBXO9 | 0.262663 | 5.06E-06 | 0.002879 | 4.803593 | Up | F-box protein 9 |
| ILMN_1791826 | RAB25 | 0.262537 | 0.003142 | 0.04417 | 3.021403 | Up | RAB25, member RAS oncogene family |
| ILMN_1704550 | AZIN1 | 0.262282 | 0.002375 | 0.03792 | 3.112496 | Up | antizyme inhibitor 1 |
| ILMN_1660111 | UCHL3 | 0.262244 | 4.55E-05 | 0.005773 | 4.250481 | Up | ubiquitin C-terminal hydrolase L3 |
| ILMN_1709043 | PLGRKT | 0.26194 | 0.001065 | 0.025246 | 3.363896 | Up | plasminogen receptor with a C-terminal lysine |
| ILMN_1695961 | CLK3 | 0.261157 | 6.84E-05 | 0.006944 | 4.142743 | Up | CDC like kinase 3 |
| ILMN_3197097 | TSTD1 | 0.260702 | 0.000162 | 0.010401 | 3.909022 | Up | thiosulfate sulfurtransferase like domain containing 1 |
| ILMN_1792497 | AGFG1 | 0.259601 | 0.000823 | 0.022397 | 3.442009 | Up | ArfGAP with FG repeats 1 |
| ILMN_1684346 | TNFAIP8L1 | 0.259593 | 0.001641 | 0.031522 | 3.229929 | Up | TNF α induced protein 8 like 1 |
| ILMN_1737475 | ABHD11 | 0.259331 | 0.002117 | 0.035667 | 3.149412 | Up | abhydrolase domain containing 11 |
| ILMN_1682147 | HOOK2 | 0.258381 | 0.000116 | 0.009 | 4.000611 | Up | hook microtubule tethering protein 2 |
| ILMN_1736154 | LZTS3 | 0.257357 | 0.000288 | 0.013983 | 3.747905 | Up | leucine zipper tumor suppressor family member 3 |
| ILMN_2328776 | STK26 | 0.257332 | 0.003144 | 0.04417 | 3.021189 | Up | serine/threonine kinase 26 |
| ILMN_3246900 | LINC01278 | 0.255848 | 0.002475 | 0.03872 | 3.09914 | Up | long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1278 |
| ILMN_1702407 | SPIN1 | 0.255702 | 0.001221 | 0.026874 | 3.322 | Up | spindlin 1 |
| ILMN_2344956 | ACP1 | 0.255631 | 0.001788 | 0.032895 | 3.202956 | Up | acid phosphatase 1 |
| ILMN_1685415 | HBP1 | 0.25552 | 0.00362 | 0.04748 | 2.974605 | Up | HMG-box transcription factor 1 |
| ILMN_2399264 | SEPTIN6 | 0.25419 | 0.000112 | 0.008891 | 4.010048 | Up | septin 6 |
| ILMN_2055523 | CSGALNACT1 | 0.253386 | 0.002808 | 0.041529 | 3.058213 | Up | chondroitin sulfate N-acetylgalactosaminyltransferase 1 |
| ILMN_3279712 | SMS | 0.252553 | 0.001715 | 0.032189 | 3.216153 | Up | spermine synthase |
| ILMN_1701514 | TRAF3IP2 | 0.252377 | 0.003172 | 0.044294 | 3.018317 | Up | TRAF3 interacting protein 2 |
| ILMN_3227529 | RPS13 | 0.252336 | 0.000401 | 0.01601 | 3.65339 | Up | ribosomal protein S13 |
| ILMN_1680397 | CXCR2 | 0.251961 | 0.000716 | 0.020858 | 3.483454 | Up | C-X-C motif chemokine receptor 2 |
| ILMN_1661142 | TMF1 | 0.251932 | 0.000831 | 0.02251 | 3.439126 | Up | TATA element modulatory factor 1 |
| ILMN_2228044 | TBC1D23 | 0.251655 | 5.18E-06 | 0.002879 | 4.797583 | Up | TBC1 domain family member 23 |
| ILMN_2352326 | COASY | 0.25148 | 0.003205 | 0.044541 | 3.014949 | Up | Coenzyme A synthase |
| ILMN_1753457 | PKP3 | 0.251362 | 0.000802 | 0.02216 | 3.449557 | Up | plakophilin 3 |
| ILMN_2081673 | INSL6 | 0.250409 | 6.77E-06 | 0.00295 | 4.732468 | Up | insulin like 6 |
| ILMN_1743396 | ACOX3 | 0.250377 | 0.001149 | 0.026102 | 3.340671 | Up | acyl-CoA oxidase 3, pristanoyl |
| ILMN_1711786 | NFE2 | 0.250104 | 0.001205 | 0.026691 | 3.326009 | Up | nuclear factor, erythroid 2 |
| ILMN_3289090 | CAPZA1 | 0.24988 | 0.001472 | 0.029809 | 3.263922 | Up | capping actin protein of muscle Z-line subunit α 1 |
| ILMN_2151056 | BORCS7 | 0.249315 | 0.000261 | 0.013186 | 3.776529 | Up | BLOC-1 related complex subunit 7 |
| ILMN_1716195 | H2BC8 | 0.248687 | 0.00072 | 0.020871 | 3.481999 | Up | H2B clustered histone 8 |
| ILMN_2366864 | JUP | 0.248584 | 0.003341 | 0.045507 | 3.001191 | Up | junction plakoglobin |
| ILMN_1709026 | PXDC1 | 0.248166 | 0.00183 | 0.033266 | 3.19572 | Up | PX domain containing 1 |
| ILMN_1690894 | HSP90B3P | 0.248104 | 0.001371 | 0.028675 | 3.2861 | Up | heat shock protein 90 β family member 3, pseudogene |
| ILMN_1662880 | LINC01554 | 0.248026 | 0.000163 | 0.010418 | 3.908142 | Up | long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1554 |
| ILMN_1664560 | DYRK1A | 0.248006 | 0.003816 | 0.048801 | 2.957108 | Up | dual specificity tyrosine phosphorylation regulated kinase 1A |
| ILMN_3241665 | SERTAD4-AS1 | 0.247969 | 2.49E-05 | 0.004816 | 4.406676 | Up | SERTAD4 antisense RNA 1 |
| ILMN_2347541 | NIN | 0.24778 | 0.002743 | 0.041015 | 3.065875 | Up | ninein |
| ILMN_3185198 | ACTR3C | 0.247744 | 0.000969 | 0.024168 | 3.392602 | Up | actin related protein 3C |
| ILMN_2274420 | SPTLC1 | 0.247643 | 0.001511 | 0.030094 | 3.255789 | Up | serine palmitoyltransferase long chain base subunit 1 |
| ILMN_2356654 | LGALS8 | 0.247618 | 0.000254 | 0.013135 | 3.783998 | Up | galectin 8 |
| ILMN_1711792 | GPBP1 | 0.246944 | 0.000145 | 0.010064 | 3.939077 | Up | GC-rich promoter binding protein 1 |
| ILMN_1785765 | TM9SF2 | 0.246663 | 0.003558 | 0.047012 | 2.980358 | Up | transmembrane 9 superfamily member 2 |
| ILMN_1739967 | TBK1 | 0.246267 | 0.000318 | 0.01452 | 3.72025 | Up | TANK binding kinase 1 |
| ILMN_1737005 | SMG9 | 0.245801 | 9.57E-06 | 0.003088 | 4.647172 | Up | SMG9 nonsense mediated mRNA decay factor |
| ILMN_3243514 | PP12613 | 0.245456 | 5.23E-05 | 0.006073 | 4.213967 | Up | uncharacterized LOC100192379 |
| ILMN_2113938 | TOR1AIP2 | 0.245454 | 0.001286 | 0.027708 | 3.306016 | Up | torsin 1A interacting protein 2 |
| ILMN_1669905 | DCP2 | 0.24544 | 0.001721 | 0.032249 | 3.215129 | Up | decapping mRNA 2 |
| ILMN_1667977 | TAF1B | 0.245081 | 0.000116 | 0.009 | 4.001937 | Up | TATA-box binding protein associated factor, RNA polymerase I subunit B |
| ILMN_1765212 | LARP1B | 0.244844 | 0.001587 | 0.031031 | 3.240414 | Up | La ribonucleoprotein 1B |
| ILMN_2275248 | ECE2 | 0.244549 | 0.000156 | 0.010362 | 3.919402 | Up | endothelin converting enzyme 2 |
| ILMN_1697864 | CXorf38 | 0.243864 | 7.18E-05 | 0.007104 | 4.130027 | Up | chromosome X open reading frame 38 |
| ILMN_1771286 | PDE4DIP | 0.242808 | 0.001603 | 0.031243 | 3.237261 | Up | phosphodiesterase 4D interacting protein |
| ILMN_1804064 | ESRRG | 0.242656 | 2.74E-05 | 0.004869 | 4.381513 | Up | estrogen related receptor γ |
| ILMN_1808860 | STX5 | 0.241476 | 0.001945 | 0.034306 | 3.176409 | Up | syntaxin 5 |
| ILMN_2359345 | NET1 | 0.241323 | 0.001147 | 0.026081 | 3.341062 | Up | neuroepithelial cell transforming 1 |
| ILMN_2324157 | UBA3 | 0.24102 | 0.000534 | 0.018273 | 3.570218 | Up | ubiquitin like modifier activating enzyme 3 |
| ILMN_1778803 | ZFAND6 | 0.239907 | 0.002388 | 0.037999 | 3.110718 | Up | zinc finger AN1-type containing 6 |
| ILMN_1810782 | SH3KBP1 | 0.239001 | 0.003315 | 0.045247 | 3.003739 | Up | SH3 domain containing kinase binding protein 1 |
| ILMN_1666258 | AMFR | 0.238013 | 0.002066 | 0.035418 | 3.157186 | Up | autocrine motility factor receptor |
| ILMN_1776154 | COG3 | 0.237721 | 0.001616 | 0.031301 | 3.234779 | Up | component of oligomericgolgi complex 3 |
| ILMN_2387553 | PSMA3 | 0.237489 | 0.000128 | 0.009505 | 3.973908 | Up | proteasome 20S subunit α 3 |
| ILMN_1730630 | CXorf56 | 0.236626 | 0.002038 | 0.035103 | 3.1615 | Up | chromosome X open reading frame 56 |
| ILMN_1673380 | GNG12 | 0.236565 | 0.003033 | 0.04332 | 3.033043 | Up | G protein subunit γ 12 |
| ILMN_3247111 | LRRC69 | 0.233635 | 0.000701 | 0.020587 | 3.489939 | Up | leucine rich repeat containing 69 |
| ILMN_1757956 | PCGF1 | 0.23308 | 0.000729 | 0.021012 | 3.478289 | Up | polycomb group ring finger 1 |
| ILMN_1759460 | TAF7 | 0.232964 | 1.99E-06 | 0.002078 | 5.027658 | Up | TATA-box binding protein associated factor 7 |
| ILMN_1747241 | IWS1 | 0.232787 | 0.00339 | 0.045729 | 2.996419 | Up | interacts with SUPT6H, CTD assembly factor 1 |
| ILMN_1676763 | PIPSL | 0.232594 | 0.000323 | 0.014545 | 3.715885 | Up | PIP5K1A and PSMD4 like (pseudogene) |
| ILMN_1813148 | TOM1 | 0.23244 | 0.002966 | 0.04284 | 3.040312 | Up | target of myb1 membrane trafficking protein |
| ILMN_3240721 | TDG | 0.231924 | 0.000256 | 0.013135 | 3.782108 | Up | thymine DNA glycosylase |
| ILMN_1682919 | PAFAH2 | 0.231731 | 0.002527 | 0.039088 | 3.09253 | Up | platelet activating factor acetylhydrolase 2 |
| ILMN_2306077 | USP33 | 0.231641 | 1.33E-05 | 0.00347 | 4.564689 | Up | ubiquitin specific peptidase 33 |
| ILMN_2413572 | MARK2 | 0.231373 | 0.003901 | 0.049215 | 2.94973 | Up | microtubule affinity regulating kinase 2 |
| ILMN_2320853 | UBE2D3 | 0.230668 | 0.001111 | 0.025736 | 3.351016 | Up | ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 D3 |
| ILMN_1760256 | RBM22 | 0.230632 | 0.001806 | 0.033086 | 3.199833 | Up | RNA binding motif protein 22 |
| ILMN_1658743 | CCNDBP1 | 0.229972 | 9.97E-05 | 0.008353 | 4.04187 | Up | cyclin D1 binding protein 1 |
| ILMN_1717294 | PTPN3 | 0.229265 | 0.002347 | 0.037683 | 3.116328 | Up | protein tyrosine phosphatase non-receptor type 3 |
| ILMN_2101920 | HNRNPH1 | 0.229246 | 0.000147 | 0.010107 | 3.93673 | Up | heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein H1 |
| ILMN_1736234 | CHTOP | 0.228517 | 0.001144 | 0.026058 | 3.341855 | Up | chromatin target of PRMT1 |
| ILMN_1700384 | KIAA1522 | 0.228516 | 0.000577 | 0.018974 | 3.547666 | Up | KIAA1522 |
| ILMN_1719237 | SPDYE8P | 0.228465 | 0.00384 | 0.048887 | 2.954952 | Up | speedy/RINGO cell cycle regulator family member E8, pseudogene |
| ILMN_1701724 | GET4 | 0.228197 | 0.000247 | 0.012906 | 3.79222 | Up | guided entry of tail-anchored proteins factor 4 |
| ILMN_1785852 | NABP1 | 0.227819 | 0.002071 | 0.035437 | 3.156321 | Up | nucleic acid binding protein 1 |
| ILMN_1755649 | SLC16A5 | 0.227432 | 0.001462 | 0.029722 | 3.266055 | Up | solute carrier family 16 member 5 |
| ILMN_1742118 | RNASE12 | 0.226586 | 0.000101 | 0.008365 | 4.039673 | Up | ribonuclease A family member 12 (inactive) |
| ILMN_1701169 | HP1BP3 | 0.226445 | 0.000651 | 0.019899 | 3.512006 | Up | heterochromatin protein 1 binding protein 3 |
| ILMN_1754179 | AP1G2 | 0.226367 | 0.000599 | 0.019237 | 3.536286 | Up | adaptor related protein complex 1 subunit γ 2 |
| ILMN_2396813 | BABAM1 | 0.226351 | 0.000283 | 0.013823 | 3.753519 | Up | BRISC and BRCA1 A complex member 1 |
| ILMN_1726589 | CD248 | −0.87731 | 6.86E-05 | 0.006945 | −4.14215 | Down | CD248 molecule |
| ILMN_1658356 | PAMR1 | −0.77303 | 1.88E-07 | 0.000867 | −5.57122 | Down | peptidase domain containing associated with muscle regeneration 1 |
| ILMN_1701308 | COL1A1 | −0.77213 | 5.05E-07 | 0.001127 | −5.34677 | Down | collagen type I α 1 chain |
| ILMN_1723522 | APOLD1 | −0.75887 | 0.00051 | 0.017953 | −3.58362 | Down | apolipoprotein L domain containing 1 |
| ILMN_1779875 | THY1 | −0.75181 | 3.89E-05 | 0.005414 | −4.29148 | Down | Thy-1 cell surface antigen |
| ILMN_1696347 | CTSC | −0.73439 | 0.000361 | 0.015151 | −3.68404 | Down | cathepsin C |
| ILMN_1706505 | COL5A1 | −0.68289 | 8.23E-08 | 0.000792 | −5.75462 | Down | collagen type V α 1 chain |
| ILMN_3237946 | PXDN | −0.68073 | 4.96E-06 | 0.002879 | −4.80838 | Down | peroxidasin |
| ILMN_1673639 | ABI3BP | −0.67199 | 0.000934 | 0.023743 | −3.40373 | Down | ABI family member 3 binding protein |
| ILMN_1766914 | MFAP4 | −0.66612 | 4.35E-06 | 0.002772 | −4.84032 | Down | microfibril associated protein 4 |
| ILMN_1795325 | ACTG2 | −0.65224 | 0.000984 | 0.024307 | −3.38785 | Down | actin γ 2, smooth muscle |
| ILMN_1757604 | TPM2 | −0.65 | 0.00014 | 0.00984 | −3.94965 | Down | tropomyosin 2 |
| ILMN_1706643 | COL6A3 | −0.64553 | 2.54E-05 | 0.004833 | −4.40149 | Down | collagen type VI α 3 chain |
| ILMN_1725193 | IGFBP2 | −0.63091 | 0.001035 | 0.024881 | −3.3724 | Down | insulin like growth factor binding protein 2 |
| ILMN_1720231 | TNNT3 | −0.61868 | 0.000693 | 0.020442 | −3.49345 | Down | troponin T3, fast skeletal type |
| ILMN_2104356 | COL1A2 | −0.60473 | 8.52E-06 | 0.00295 | −4.67573 | Down | collagen type I α 2 chain |
| ILMN_1773079 | COL3A1 | −0.6033 | 5.14E-06 | 0.002879 | −4.79969 | Down | collagen type III α 1 chain |
| ILMN_1707070 | PCOLCE | −0.59908 | 1.55E-06 | 0.001955 | −5.0867 | Down | procollagen C-endopeptidase enhancer |
| ILMN_1797776 | PRSS23 | −0.59791 | 1.36E-06 | 0.001955 | −5.11653 | Down | serine protease 23 |
| ILMN_2390919 | FBLN2 | −0.59331 | 6.9E-06 | 0.00295 | −4.72775 | Down | fibulin 2 |
| ILMN_1712046 | CPXM1 | −0.59179 | 0.000142 | 0.009889 | −3.94586 | Down | carboxypeptidase X, M14 family member 1 |
| ILMN_1670379 | ANTXR1 | −0.59159 | 3.06E-05 | 0.005173 | −4.35299 | Down | ANTXR cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| ILMN_1743445 | FAM107A | −0.58708 | 0.001007 | 0.02461 | −3.38091 | Down | family with sequence similarity 107 member A |
| ILMN_1697268 | EMILIN2 | −0.58178 | 2.61E-05 | 0.004833 | −4.39456 | Down | elastin microfibrilinterfacer 2 |
| ILMN_1756071 | MFGE8 | −0.58136 | 0.00023 | 0.012505 | −3.81152 | Down | milk fat globule-EGF factor 8 protein |
| ILMN_2115125 | CCN2 | −0.56274 | 0.00135 | 0.028444 | −3.29078 | Down | cellular communication network factor 2 |
| ILMN_1700690 | VAT1 | −0.55561 | 1.38E-05 | 0.003478 | −4.55564 | Down | vesicle amine transport 1 |
| ILMN_1761968 | PPP1R14A | −0.55382 | 6.36E-06 | 0.00295 | −4.74771 | Down | protein phosphatase 1 regulatory inhibitor subunit 14A |
| ILMN_1783909 | COL6A2 | −0.55352 | 3.46E-05 | 0.005189 | −4.32174 | Down | collagen type VI α 2 chain |
| ILMN_2384056 | GPER1 | −0.55173 | 0.001275 | 0.027557 | −3.30852 | Down | G protein-coupled estrogen receptor 1 |
| ILMN_1688642 | LAMC3 | −0.54794 | 0.000167 | 0.010606 | −3.90071 | Down | laminin subunit γ 3 |
| ILMN_1779558 | GAS6 | −0.54545 | 4.6E-07 | 0.001127 | −5.36823 | Down | growth arrest specific 6 |
| ILMN_1800787 | RFTN1 | −0.54246 | 9.71E-06 | 0.003091 | −4.6434 | Down | raftlin, lipid raft linker 1 |
| ILMN_1665909 | LASP1 | −0.53453 | 1.44E-06 | 0.001955 | −5.10383 | Down | LIM and SH3 protein 1 |
| ILMN_1811313 | SLIT3 | −0.53304 | 5.6E-08 | 0.000792 | −5.83956 | Down | slit guidance ligand 3 |
| ILMN_1793476 | CAVIN3 | −0.5317 | 2.2E-05 | 0.004675 | −4.43772 | Down | caveolae associated protein 3 |
| ILMN_2307903 | VCAM1 | −0.53139 | 8.12E-05 | 0.007511 | −4.09693 | Down | vascular cell adhesion molecule 1 |
| ILMN_1656560 | PARM1 | −0.53103 | 0.00016 | 0.010366 | −3.91255 | Down | prostate androgen-regulated mucin-like protein 1 |
| ILMN_1672611 | CDH11 | −0.52302 | 0.000212 | 0.011964 | −3.83473 | Down | cadherin 11 |
| ILMN_1765557 | OLFML2B | −0.52097 | 4.2E-06 | 0.00273 | −4.84868 | Down | olfactomedin like 2B |
| ILMN_1815057 | PDGFRB | −0.52016 | 1.82E-05 | 0.004138 | −4.48559 | Down | platelet derived growth factor receptor β |
| ILMN_1736178 | AEBP1 | −0.5199 | 3.33E-05 | 0.005189 | −4.33169 | Down | AE binding protein 1 |
| ILMN_1748124 | TSC22D3 | −0.51824 | 0.000928 | 0.02368 | −3.40564 | Down | TSC22 domain family member 3 |
| ILMN_1723978 | LGALS1 | −0.51718 | 0.000364 | 0.015227 | −3.68144 | Down | galectin 1 |
| ILMN_1738147 | NES | −0.51576 | 8.77E-06 | 0.003014 | −4.6686 | Down | nestin |
| ILMN_2301722 | PDE8B | −0.51488 | 2.73E-05 | 0.004869 | −4.38289 | Down | phosphodiesterase 8B |
| ILMN_1687301 | VCAN | −0.51483 | 0.000221 | 0.012223 | −3.82288 | Down | versican |
| ILMN_1778523 | KLF9 | −0.50597 | 5.25E-05 | 0.006073 | −4.21296 | Down | Kruppel like factor 9 |
| ILMN_2062468 | IGFBP7 | −0.50184 | 0.000947 | 0.023893 | −3.3994 | Down | insulin like growth factor binding protein 7 |
| ILMN_1748323 | CXCL14 | −0.49871 | 0.000454 | 0.017215 | −3.61778 | Down | C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 14 |
| ILMN_1751326 | FAM162B | −0.49815 | 0.00278 | 0.041278 | −3.06149 | Down | family with sequence similarity 162 member B |
| ILMN_2373791 | ENPP2 | −0.49776 | 6.94E-05 | 0.006958 | −4.13908 | Down | ectonucleotidepyrophosphatase/phosphodiesterase 2 |
| ILMN_1752968 | LAMB2 | −0.49708 | 0.000303 | 0.014156 | −3.73363 | Down | laminin subunit β 2 |
| ILMN_1654324 | HEYL | −0.49611 | 0.000102 | 0.008419 | −4.03652 | Down | hes related family bHLH transcription factor with YRPW motif like |
| ILMN_1667295 | VASN | −0.49482 | 1.16E-05 | 0.003364 | −4.5987 | Down | vasorin |
| ILMN_1812618 | ARAP3 | −0.49404 | 0.003139 | 0.044148 | −3.0217 | Down | ArfGAP with RhoGAP domain, ankyrin repeat and PH domain 3 |
| ILMN_1661599 | DDIT4 | −0.49301 | 0.002513 | 0.039003 | −3.09422 | Down | DNA damage inducible transcript 4 |
| ILMN_1713496 | ST3GAL5 | −0.492 | 8.48E-05 | 0.007599 | −4.08534 | Down | ST3 β-galactoside α-2,3-sialyltransferase 5 |
| ILMN_1665865 | IGFBP4 | −0.49057 | 0.002826 | 0.041676 | −3.05613 | Down | insulin like growth factor binding protein 4 |
| ILMN_1687652 | TGFB3 | −0.48958 | 0.002071 | 0.035437 | −3.15638 | Down | transforming growth factor β 3 |
| ILMN_1801616 | EMP1 | −0.48942 | 0.000266 | 0.013333 | −3.77097 | Down | epithelial membrane protein 1 |
| ILMN_1733259 | TMIGD3 | −0.48909 | 0.00024 | 0.012746 | −3.79958 | Down | transmembrane and immunoglobulin domain containing 3 |
| ILMN_1670490 | PDPN | −0.48881 | 0.000138 | 0.009821 | −3.95297 | Down | podoplanin |
| ILMN_1665219 | LTBP4 | −0.4882 | 1.05E-07 | 0.000838 | −5.70174 | Down | latent transforming growth factor β binding protein 4 |
| ILMN_1738578 | FILIP1L | −0.48742 | 0.000178 | 0.010961 | −3.88315 | Down | filamin A interacting protein 1 like |
| ILMN_1654109 | EGFLAM | −0.48718 | 0.000239 | 0.012746 | −3.80108 | Down | EGF like, fibronectin type III and laminin G domains |
| ILMN_1796734 | SPARC | −0.48641 | 1.76E-05 | 0.004057 | −4.49427 | Down | secreted protein acidic and cysteine rich |
| ILMN_1675797 | EPDR1 | −0.48638 | 0.002889 | 0.0423 | −3.04891 | Down | ependymin related 1 |
| ILMN_1752755 | VWF | −0.48403 | 0.000698 | 0.02056 | −3.491 | Down | von Willebrand factor |
| ILMN_1743836 | MXRA7 | −0.48256 | 0.000135 | 0.009758 | −3.9585 | Down | matrix remodeling associated 7 |
| ILMN_1732151 | COL6A1 | −0.48252 | 0.000537 | 0.018298 | −3.56848 | Down | collagen type VI α 1 chain |
| ILMN_1699695 | TNFRSF21 | −0.48252 | 3.82E-07 | 0.001058 | −5.41081 | Down | TNF receptor superfamily member 21 |
| ILMN_1671703 | ACTA2 | −0.48127 | 0.001006 | 0.024602 | −3.3812 | Down | actin α 2, smooth muscle |
| ILMN_1777190 | CFD | −0.48004 | 0.001794 | 0.032947 | −3.20188 | Down | complement factor D |
| ILMN_1785646 | PMP22 | −0.47862 | 1.24E-05 | 0.003412 | −4.58237 | Down | peripheral myelin protein 22 |
| ILMN_1795166 | PTH1R | −0.47706 | 1.22E-05 | 0.003404 | −4.58718 | Down | parathyroid hormone 1 receptor |
| ILMN_1779182 | TMEM98 | −0.47485 | 3.81E-06 | 0.002678 | −4.87203 | Down | transmembrane protein 98 |
| ILMN_3248591 | LTBP2 | −0.47272 | 3.28E-05 | 0.005189 | −4.33519 | Down | latent transforming growth factor β binding protein 2 |
| ILMN_1672503 | DPYSL2 | −0.47143 | 5.37E-06 | 0.002879 | −4.78877 | Down | dihydropyrimidinase like 2 |
| ILMN_2223941 | FBLN5 | −0.47095 | 1.94E-06 | 0.002072 | −5.03358 | Down | fibulin 5 |
| ILMN_1688480 | CCND1 | −0.46977 | 0.000483 | 0.017744 | −3.59964 | Down | cyclin D1 |
| ILMN_1808114 | LYVE1 | −0.46936 | 0.003925 | 0.049436 | −2.9477 | Down | lymphatic vessel endothelial hyaluronan receptor 1 |
| ILMN_2087692 | CYBRD1 | −0.46894 | 2.69E-05 | 0.004861 | −4.38626 | Down | cytochrome b reductase 1 |
| ILMN_1808707 | FSCN1 | −0.46767 | 3.69E-05 | 0.005267 | −4.30499 | Down | fascin actin-bundling protein 1 |
| ILMN_1660808 | WFDC1 | −0.46665 | 0.000163 | 0.010418 | −3.90783 | Down | WAP four-disulfide core domain 1 |
| ILMN_2337655 | WARS1 | −0.4653 | 4.87E-05 | 0.005873 | −4.23248 | Down | tryptophanyl-tRNAsynthetase 1 |
| ILMN_2347145 | DCN | −0.46414 | 8.34E-05 | 0.007533 | −4.08985 | Down | decorin |
| ILMN_1694840 | MATN2 | −0.46405 | 0.000542 | 0.018404 | −3.56578 | Down | matrilin 2 |
| ILMN_1729117 | COL5A2 | −0.46318 | 0.000177 | 0.010947 | −3.88468 | Down | collagen type V α 2 chain |
| ILMN_1681983 | RSPO3 | −0.46314 | 0.000248 | 0.012955 | −3.79059 | Down | R-spondin 3 |
| ILMN_3246401 | AIF1L | −0.46241 | 0.000187 | 0.011245 | −3.86955 | Down | allograft inflammatory factor 1 like |
| ILMN_1778668 | TAGLN | −0.46167 | 0.001483 | 0.029912 | −3.26159 | Down | transgelin |
| ILMN_1700183 | APLNR | −0.46027 | 0.000159 | 0.010362 | −3.91414 | Down | apelin receptor |
| ILMN_2413158 | PODXL | −0.45912 | 0.000113 | 0.008916 | −4.0078 | Down | podocalyxin like |
| ILMN_1701877 | AXL | −0.45803 | 3.57E-05 | 0.005231 | −4.31359 | Down | AXL receptor tyrosine kinase |
| ILMN_1676893 | ADCY3 | −0.45717 | 5.23E-05 | 0.006073 | −4.21395 | Down | adenylatecyclase 3 |
| ILMN_1660086 | MYH11 | −0.45693 | 0.00135 | 0.028444 | −3.29091 | Down | myosin heavy chain 11 |
| ILMN_1781149 | INMT | −0.45264 | 0.000222 | 0.012233 | −3.82134 | Down | indolethylamine N-methyltransferase |
| ILMN_1671928 | PROS1 | −0.45214 | 5.66E-05 | 0.006347 | −4.19283 | Down | protein S |
| ILMN_2377900 | MAP1B | −0.45172 | 0.000292 | 0.014028 | −3.74419 | Down | microtubule associated protein 1B |
| ILMN_1691127 | VTN | −0.45044 | 5.91E-06 | 0.002933 | −4.76576 | Down | vitronectin |
| ILMN_1701441 | LPAR1 | −0.45043 | 2.49E-05 | 0.004816 | −4.40602 | Down | lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 |
| ILMN_1734190 | TCEAL3 | −0.45031 | 0.000148 | 0.010152 | −3.93406 | Down | transcription elongation factor A like 3 |
| ILMN_1696749 | LMNA | −0.44963 | 7.46E-06 | 0.00295 | −4.70841 | Down | lamin A/C |
| ILMN_3236825 | RAPGEF5 | −0.4488 | 0.00152 | 0.030129 | −3.25398 | Down | Rap guanine nucleotide exchange factor 5 |
| ILMN_1791890 | SPON1 | −0.44793 | 0.000369 | 0.01532 | −3.67762 | Down | spondin 1 |
| ILMN_1656951 | APCDD1 | −0.44608 | 5.84E-05 | 0.006463 | −4.18452 | Down | APC down-regulated 1 |
| ILMN_1723480 | BST2 | −0.44433 | 3.39E-05 | 0.005189 | −4.32664 | Down | bone marrow stromal cell antigen 2 |
| ILMN_1651429 | SELENOM | −0.44235 | 0.000729 | 0.021012 | −3.47803 | Down | selenoprotein M |
| ILMN_1758164 | STC1 | −0.44235 | 5.34E-05 | 0.006098 | −4.20849 | Down | stanniocalcin 1 |
| ILMN_1728197 | CLDN5 | −0.44196 | 0.002297 | 0.037268 | −3.1232 | Down | claudin 5 |
| ILMN_1663866 | TGFBI | −0.44055 | 0.000185 | 0.011135 | −3.87297 | Down | transforming growth factor β induced |
| ILMN_2057479 | EGFL6 | −0.44039 | 0.002923 | 0.042546 | −3.04508 | Down | EGF like domain multiple 6 |
| ILMN_1784863 | CD36 | −0.43914 | 0.001443 | 0.029457 | −3.27014 | Down | CD36 molecule |
| ILMN_1789492 | ZDHHC8 | −0.43853 | 1.97E-05 | 0.004301 | −4.4659 | Down | zinc finger DHHC-type containing 8 |
| ILMN_1790689 | CRISPLD2 | −0.43782 | 0.000578 | 0.018974 | −3.54695 | Down | cysteine rich secretory protein LCCL domain containing 2 |
| ILMN_1795442 | LAMA4 | −0.43771 | 8.57E-05 | 0.007637 | −4.08249 | Down | laminin subunit α 4 |
| ILMN_1702501 | RPS6KA2 | −0.43678 | 2.81E-06 | 0.002369 | −4.94542 | Down | ribosomal protein S6 kinase A2 |
| ILMN_1671106 | GJA4 | −0.43644 | 0.000331 | 0.014708 | −3.70883 | Down | gap junction protein α 4 |
| ILMN_1692058 | NDN | −0.43561 | 2.4E-05 | 0.004755 | −4.41545 | Down | necdin, MAGE family member |
| ILMN_1668629 | C4orf48 | −0.43536 | 3.2E-05 | 0.005189 | −4.34205 | Down | chromosome 4 open reading frame 48 |
| ILMN_1697448 | TXNIP | −0.43462 | 4.43E-05 | 0.005755 | −4.25718 | Down | thioredoxin interacting protein |
| ILMN_1798360 | ACKR3 | −0.43355 | 0.000768 | 0.021647 | −3.46258 | Down | atypical chemokine receptor 3 |
| ILMN_1671565 | RNASET2 | −0.43033 | 0.000961 | 0.024096 | −3.39507 | Down | ribonuclease T2 |
| ILMN_1676449 | SLIT2 | −0.42992 | 0.000142 | 0.009889 | −3.94603 | Down | slit guidance ligand 2 |
| ILMN_1687978 | PHLDA1 | −0.42734 | 1.82E-05 | 0.004138 | −4.48565 | Down | pleckstrin homology like domain family A member 1 |
| ILMN_1715991 | CAVIN2 | −0.42665 | 0.001128 | 0.025959 | −3.34614 | Down | caveolae associated protein 2 |
| ILMN_2067656 | CCND2 | −0.42587 | 0.000216 | 0.012027 | −3.82966 | Down | cyclin D2 |
| ILMN_1680037 | RIPOR1 | −0.42581 | 3.23E-06 | 0.002557 | −4.91159 | Down | RHO family interacting cell polarization regulator 1 |
| ILMN_1669409 | VSIG4 | −0.42564 | 0.000387 | 0.015721 | −3.66386 | Down | V-set and immunoglobulin domain containing 4 |
| ILMN_1673566 | ADAMTS1 | −0.42513 | 0.000988 | 0.024354 | −3.3866 | Down | ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 1 |
| ILMN_1709486 | SRPX | −0.42497 | 0.000723 | 0.020945 | −3.48076 | Down | sushi repeat containing protein X-linked |
| ILMN_2308849 | MYADM | −0.42477 | 0.00028 | 0.013713 | −3.75666 | Down | myeloid associated differentiation marker |
| ILMN_1742534 | COL4A5 | −0.42458 | 3.49E-05 | 0.005194 | −4.31961 | Down | collagen type IV α 5 chain |
| ILMN_1662419 | COX7A1 | −0.42139 | 0.001898 | 0.033868 | −3.1842 | Down | cytochrome c oxidase subunit 7A1 |
| ILMN_1666894 | CSPG4 | −0.42081 | 0.000309 | 0.014326 | −3.72785 | Down | chondroitin sulfate proteoglycan 4 |
| ILMN_1681679 | TSPO | −0.41878 | 0.000143 | 0.009968 | −3.9429 | Down | translocator protein |
| ILMN_2410929 | PAPSS2 | −0.41817 | 0.000199 | 0.011586 | −3.85207 | Down | 3′-phosphoadenosine 5′-phosphosulfate synthase 2 |
| ILMN_1675936 | HIGD1B | −0.41805 | 0.002299 | 0.037268 | −3.12291 | Down | HIG1 hypoxia inducible domain family member 1B |
| ILMN_1800697 | LDB2 | −0.41769 | 0.000812 | 0.022284 | −3.44608 | Down | LIM domain binding 2 |
| ILMN_1695959 | EVA1C | −0.41726 | 1.48E-06 | 0.001955 | −5.09704 | Down | eva-1 homolog C |
| ILMN_1815700 | WNT3A | −0.41588 | 0.000685 | 0.020354 | −3.49693 | Down | Wnt family member 3A |
| ILMN_1672878 | ABR | −0.41554 | 1.42E-06 | 0.001955 | −5.1066 | Down | ABR activator of RhoGEF and GTPase |
| ILMN_1653203 | EFEMP2 | −0.41486 | 1.59E-05 | 0.003762 | −4.52062 | Down | EGF containing fibulin extracellular matrix protein 2 |
| ILMN_1705442 | CMTM3 | −0.41405 | 3.33E-05 | 0.005189 | −4.33163 | Down | CKLF like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing 3 |
| ILMN_1678353 | FARP1 | −0.41327 | 3.99E-06 | 0.002688 | −4.86121 | Down | FERM, ARH/RhoGEF and pleckstrin domain protein 1 |
| ILMN_1745963 | FOLR2 | −0.4129 | 0.002926 | 0.042546 | −3.04483 | Down | folate receptor β |
| ILMN_2189027 | LIPG | −0.41278 | 0.002567 | 0.039356 | −3.08744 | Down | lipase G, endothelial type |
| ILMN_1673352 | IFITM2 | −0.41277 | 1.45E-05 | 0.003584 | −4.54291 | Down | interferon induced transmembrane protein 2 |
| ILMN_1814327 | AGTR1 | −0.4127 | 0.003348 | 0.045512 | −3.00053 | Down | angiotensin II receptor type 1 |
| ILMN_1727532 | OLFML3 | −0.41123 | 0.000299 | 0.014133 | −3.73746 | Down | olfactomedin like 3 |
| ILMN_1764964 | IFNGR2 | −0.41058 | 0.000123 | 0.009352 | −3.98429 | Down | interferon γ receptor 2 |
| ILMN_1756573 | NDUFA4L2 | −0.40838 | 0.001643 | 0.031536 | −3.22967 | Down | NDUFA4 mitochondrial complex associated like 2 |
| ILMN_1653466 | HES4 | −0.40777 | 0.000111 | 0.008868 | −4.013 | Down | hes family bHLH transcription factor 4 |
| ILMN_2396875 | IGFBP3 | −0.40708 | 0.001143 | 0.026058 | −3.34212 | Down | insulin like growth factor binding protein 3 |
| ILMN_2038775 | TUBB2A | −0.40565 | 0.001946 | 0.03431 | −3.17614 | Down | tubulin β 2A class IIa |
| ILMN_1812031 | PALM | −0.40551 | 1.37E-05 | 0.003478 | −4.55698 | Down | paralemmin |
| ILMN_1709307 | GPSM1 | −0.4053 | 3.66E-05 | 0.005267 | −4.30712 | Down | G protein signaling modulator 1 |
| ILMN_3246214 | B4GAT1 | −0.40496 | 3.87E-07 | 0.001058 | −5.40781 | Down | β-1,4-glucuronyltransferase 1 |
| ILMN_1802411 | ITGA1 | −0.4038 | 3.16E-05 | 0.005189 | −4.34541 | Down | integrin subunit α 1 |
| ILMN_1714861 | CD68 | −0.40235 | 0.001299 | 0.027871 | −3.30268 | Down | CD68 molecule |
| ILMN_1666819 | PHLDB1 | −0.40159 | 2.35E-05 | 0.004738 | −4.42152 | Down | pleckstrin homology like domain family B member 1 |
| ILMN_1723481 | CHST3 | −0.40156 | 5.39E-06 | 0.002879 | −4.78828 | Down | carbohydrate sulfotransferase 3 |
| ILMN_1724994 | COL4A2 | −0.40135 | 0.000401 | 0.01601 | −3.65332 | Down | collagen type IV α 2 chain |
| ILMN_1768483 | KCNK3 | −0.40133 | 4.77E-05 | 0.005826 | −4.23792 | Down | potassium two pore domain channel subfamily K member 3 |
| ILMN_1717934 | SYT11 | −0.40115 | 2.98E-05 | 0.005073 | −4.35983 | Down | synaptotagmin 11 |
| ILMN_1812968 | SOX18 | −0.40033 | 0.000526 | 0.018141 | −3.57485 | Down | SRY-box transcription factor 18 |
| ILMN_2173611 | MT1E | −0.39988 | 0.000353 | 0.015039 | −3.69035 | Down | metallothionein 1E |
| ILMN_1668283 | HYAL2 | −0.39864 | 0.000646 | 0.019821 | −3.51392 | Down | hyaluronidase 2 |
| ILMN_1757440 | DIPK1B | −0.39796 | 0.00033 | 0.014704 | −3.70918 | Down | divergent protein kinase domain 1B |
| ILMN_1773059 | ADGRA2 | −0.39739 | 0.000911 | 0.023503 | −3.41136 | Down | adhesion G protein-coupled receptor A2 |
| ILMN_1795429 | VCL | −0.39693 | 0.000348 | 0.014991 | −3.69401 | Down | vinculin |
| ILMN_1789733 | CLIP3 | −0.39665 | 1.53E-05 | 0.00373 | −4.53031 | Down | CAP-Gly domain containing linker protein 3 |
| ILMN_1675062 | MYL9 | −0.39519 | 0.001559 | 0.030619 | −3.24612 | Down | myosin light chain 9 |
| ILMN_1711566 | TIMP1 | −0.39465 | 0.001568 | 0.030761 | −3.24426 | Down | TIMP metallopeptidase inhibitor 1 |
| ILMN_1682781 | TEAD2 | −0.39462 | 2.27E-05 | 0.004675 | −4.42977 | Down | TEA domain transcription factor 2 |
| ILMN_1806733 | COL18A1 | −0.39225 | 0.000595 | 0.019227 | −3.53859 | Down | collagen type XVIII α 1 chain |
| ILMN_1769091 | PRCP | −0.39168 | 0.000281 | 0.013751 | −3.75557 | Down | prolylcarboxypeptidase |
| ILMN_1691376 | JAG1 | −0.39137 | 0.000108 | 0.008727 | −4.02057 | Down | jagged canonical Notch ligand 1 |
| ILMN_1808238 | RBPMS2 | −0.39047 | 2.27E-05 | 0.004675 | −4.43015 | Down | RNA binding protein, mRNA processing factor 2 |
| ILMN_1684391 | PLOD1 | −0.38987 | 5.67E-06 | 0.002906 | −4.77593 | Down | procollagen-lysine,2-oxoglutarate 5-dioxygenase 1 |
| ILMN_1755657 | RASIP1 | −0.38985 | 0.00111 | 0.025736 | −3.35121 | Down | Ras interacting protein 1 |
| ILMN_1754795 | FAT1 | −0.38928 | 0.000803 | 0.02216 | −3.44913 | Down | FAT atypical cadherin 1 |
| ILMN_1723684 | ACKR1 | −0.38904 | 0.000258 | 0.013173 | −3.77982 | Down | atypical chemokine receptor 1 (Duffy blood group) |
| ILMN_1763640 | NCKAP5L | −0.38828 | 4.47E-05 | 0.005755 | −4.25481 | Down | NCK associated protein 5 like |
| ILMN_2066151 | TEK | −0.38809 | 0.001131 | 0.025976 | −3.34543 | Down | TEK receptor tyrosine kinase |
| ILMN_1730995 | AFAP1L2 | −0.38806 | 6.29E-05 | 0.006657 | −4.16513 | Down | actin filament associated protein 1 like 2 |
| ILMN_1676846 | ABCE1 | −0.38772 | 0.002141 | 0.035854 | −3.14571 | Down | ATP binding cassette subfamily E member 1 |
| ILMN_2306540 | PDE9A | −0.38716 | 0.000255 | 0.013135 | −3.78258 | Down | phosphodiesterase 9A |
| ILMN_1756920 | ADAM15 | −0.38698 | 2.31E-05 | 0.004723 | −4.4258 | Down | ADAM metallopeptidase domain 15 |
| ILMN_1667460 | SULF2 | −0.38575 | 0.000356 | 0.015084 | −3.68742 | Down | sulfatase 2 |
| ILMN_1778681 | EBF1 | −0.38542 | 0.000387 | 0.015721 | −3.66397 | Down | EBF transcription factor 1 |
| ILMN_1810852 | LAMC1 | −0.38297 | 0.000107 | 0.008689 | −4.02291 | Down | laminin subunit γ 1 |
| ILMN_1723123 | FGFR3 | −0.38138 | 0.000151 | 0.010247 | −3.92785 | Down | fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 |
| ILMN_1741632 | RAB3IL1 | −0.381 | 1.3E-05 | 0.003464 | −4.57014 | Down | RAB3A interacting protein like 1 |
| ILMN_2230025 | PDLIM3 | −0.381 | 0.000642 | 0.019792 | −3.51588 | Down | PDZ and LIM domain 3 |
| ILMN_1772612 | ANGPTL2 | −0.37902 | 2.69E-05 | 0.004861 | −4.38663 | Down | angiopoietin like 2 |
| ILMN_1810844 | RARRES2 | −0.37881 | 0.000884 | 0.023267 | −3.42025 | Down | retinoic acid receptor responder 2 |
| ILMN_1738816 | FOXO1 | −0.37837 | 0.000525 | 0.018141 | −3.57509 | Down | forkhead box O1 |
| ILMN_1689953 | CD81 | −0.37702 | 1.74E-07 | 0.000867 | −5.58795 | Down | CD81 molecule |
| ILMN_1651950 | TPST1 | −0.37597 | 3.72E-05 | 0.005297 | −4.30272 | Down | tyrosylproteinsulfotransferase 1 |
| ILMN_1692731 | TTYH3 | −0.37535 | 3.37E-05 | 0.005189 | −4.32847 | Down | tweety family member 3 |
| ILMN_1658835 | CAV2 | −0.37448 | 0.001154 | 0.026156 | −3.33932 | Down | caveolin 2 |
| ILMN_1680453 | ITM2C | −0.37416 | 0.000588 | 0.019112 | −3.54215 | Down | integral membrane protein 2C |
| ILMN_1702835 | SH3BGRL | −0.37249 | 0.000342 | 0.01488 | −3.69952 | Down | SH3 domain binding glutamate rich protein like |
| ILMN_1732923 | SIPA1L2 | −0.37207 | 0.000758 | 0.021475 | −3.46637 | Down | signal induced proliferation associated 1 like 2 |
| ILMN_1797009 | F3 | −0.37136 | 0.00032 | 0.014545 | −3.71818 | Down | coagulation factor III, tissue factor |
| ILMN_1738263 | PIGU | −0.37121 | 0.00019 | 0.011345 | −3.86457 | Down | phosphatidylinositol glycan anchor biosynthesis class U |
| ILMN_1739946 | VKORC1 | −0.3684 | 0.000138 | 0.009805 | −3.95412 | Down | vitamin K epoxide reductase complex subunit 1 |
| ILMN_1803312 | DIMT1 | −0.36765 | 2.11E-05 | 0.004531 | −4.44861 | Down | DIMT1 rRNAmethyltransferase and ribosome maturation factor |
| ILMN_2089752 | ALKAL2 | −0.3669 | 0.003884 | 0.049065 | −2.95119 | Down | ALK and LTK ligand 2 |
| ILMN_1729563 | UGDH | −0.36578 | 0.00195 | 0.034354 | −3.1755 | Down | UDP-glucose 6-dehydrogenase |
| ILMN_1695290 | FERMT2 | −0.36562 | 8.34E-06 | 0.00295 | −4.68113 | Down | fermitin family member 2 |
| ILMN_1748473 | GIMAP4 | −0.3654 | 0.000178 | 0.010961 | −3.88275 | Down | GTPase, IMAP family member 4 |
| ILMN_3242038 | GPX8 | −0.36483 | 0.000302 | 0.014133 | −3.73508 | Down | glutathione peroxidase 8 (putative) |
| ILMN_1781256 | LEFTY2 | −0.36409 | 0.001663 | 0.031713 | −3.2258 | Down | left-right determination factor 2 |
| ILMN_1718607 | TSPAN4 | −0.36243 | 0.000121 | 0.009241 | −3.98826 | Down | tetraspanin 4 |
| ILMN_1653028 | COL4A1 | −0.36243 | 0.000251 | 0.013046 | −3.78705 | Down | collagen type IV α 1 chain |
| ILMN_1806403 | RASL12 | −0.3617 | 0.000182 | 0.011037 | −3.87729 | Down | RAS like family 12 |
| ILMN_1770338 | TM4SF1 | −0.36154 | 0.002035 | 0.035083 | −3.16202 | Down | transmembrane 4 L six family member 1 |
| ILMN_1757552 | CAVIN1 | −0.36036 | 1.87E-05 | 0.004187 | −4.47961 | Down | caveolae associated protein 1 |
| ILMN_2148944 | ADCY4 | −0.36032 | 0.002039 | 0.035103 | −3.16139 | Down | adenylatecyclase 4 |
| ILMN_2346997 | RAB23 | −0.36006 | 4.72E-05 | 0.005816 | −4.241 | Down | RAB23, member RAS oncogene family |
| ILMN_1803429 | CD44 | −0.35802 | 0.001453 | 0.029623 | −3.268 | Down | CD44 molecule (Indian blood group) |
| ILMN_1757845 | SPIRE1 | −0.35788 | 0.000136 | 0.009769 | −3.9577 | Down | spire type actin nucleation factor 1 |
| ILMN_2063168 | MALL | −0.35738 | 0.000348 | 0.014991 | −3.69453 | Down | mal, T cell differentiation protein like |
| ILMN_1794492 | HOXC6 | −0.35691 | 2.08E-05 | 0.004478 | −4.45271 | Down | homeobox C6 |
| ILMN_2089073 | ATP9A | −0.35669 | 0.000323 | 0.014545 | −3.71549 | Down | ATPase phospholipid transporting 9A (putative) |
| ILMN_1676897 | HSPA12B | −0.35655 | 0.001255 | 0.027297 | −3.31351 | Down | heat shock protein family A (Hsp70) member 12B |
| ILMN_1720158 | ETS2 | −0.35607 | 1.88E-05 | 0.004187 | −4.47844 | Down | ETS proto-oncogene 2, transcription factor |
| ILMN_1767448 | LHFPL6 | −0.35579 | 0.000815 | 0.022307 | −3.44483 | Down | LHFPL tetraspan subfamily member 6 |
| ILMN_3238560 | IFI27L2 | −0.35573 | 2.7E-05 | 0.004861 | −4.38599 | Down | interferon α inducible protein 27 like 2 |
| ILMN_1784871 | FASN | −0.35492 | 1.19E-06 | 0.001926 | −5.14833 | Down | fatty acid synthase |
| ILMN_1680874 | TUBB2B | −0.35438 | 2.27E-05 | 0.004675 | −4.42951 | Down | tubulin β 2B class IIb |
| ILMN_2081682 | SMAP2 | −0.35276 | 6.18E-05 | 0.006575 | −4.16954 | Down | small ArfGAP2 |
| ILMN_1774982 | CDC42EP5 | −0.35271 | 4.66E-05 | 0.005784 | −4.24433 | Down | CDC42 effector protein 5 |
| ILMN_1788019 | LAMA2 | −0.35245 | 0.00276 | 0.041163 | −3.0638 | Down | laminin subunit α 2 |
| ILMN_1783276 | NEXN | −0.35153 | 0.000177 | 0.010947 | −3.88438 | Down | nexilin F-actin binding protein |
| ILMN_1676088 | MSRB3 | −0.35012 | 0.000365 | 0.015248 | −3.68065 | Down | methionine sulfoxidereductase B3 |
| ILMN_1795183 | RNASE1 | −0.34959 | 0.003183 | 0.044326 | −3.01723 | Down | ribonuclease A family member 1, pancreatic |
| ILMN_1704537 | PHGDH | −0.34957 | 8.55E-05 | 0.007633 | −4.08329 | Down | phosphoglycerate dehydrogenase |
| ILMN_1805543 | ADAMTS9 | −0.34922 | 0.001219 | 0.026853 | −3.32252 | Down | ADAM metallopeptidase with thrombospondin type 1 motif 9 |
| ILMN_2127605 | LRP3 | −0.3484 | 9.59E-07 | 0.001775 | −5.19866 | Down | LDL receptor related protein 3 |
| ILMN_2410523 | DDR2 | −0.34789 | 0.000108 | 0.008756 | −4.019 | Down | discoidin domain receptor tyrosine kinase 2 |
| ILMN_2389876 | TGFB1I1 | −0.34786 | 0.000225 | 0.012343 | −3.81789 | Down | transforming growth factor β 1 induced transcript 1 |
| ILMN_3241758 | POTEF | −0.34764 | 0.001247 | 0.027181 | −3.31554 | Down | POTE ankyrin domain family member F |
| ILMN_1770454 | AGRN | −0.34742 | 0.00053 | 0.018229 | −3.57218 | Down | agrin |
| ILMN_1752249 | PIEZO1 | −0.34641 | 0.000798 | 0.022091 | −3.45127 | Down | piezo type mechanosensitive ion channel component 1 |
| ILMN_1663080 | LFNG | −0.34636 | 5.26E-05 | 0.006073 | −4.21211 | Down | LFNG O-fucosylpeptide 3-β-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase |
| ILMN_1672389 | CRYZ | −0.3461 | 0.000537 | 0.018298 | −3.56835 | Down | crystallin zeta |
| ILMN_1776724 | LYPD6 | −0.34584 | 1.34E-05 | 0.00347 | −4.56326 | Down | LY6/PLAUR domain containing 6 |
| ILMN_1777397 | MSX1 | −0.34534 | 0.000377 | 0.015431 | −3.67168 | Down | mshhomeobox 1 |
| ILMN_1783593 | CCL13 | −0.34534 | 0.001155 | 0.026177 | −3.33892 | Down | C-C motif chemokine ligand 13 |
| ILMN_2398159 | DKK3 | −0.34528 | 0.003364 | 0.045581 | −2.99896 | Down | dickkopf WNT signaling pathway inhibitor 3 |
| ILMN_1743367 | FZD4 | −0.34522 | 0.000443 | 0.016957 | −3.62449 | Down | frizzled class receptor 4 |
| ILMN_2186061 | PFKFB3 | −0.34512 | 0.000537 | 0.018294 | −3.56884 | Down | 6-phosphofructo-2-kinase/fructose-2,6-biphosphatase 3 |
| ILMN_1662340 | ZNF358 | −0.34471 | 3.09E-06 | 0.002517 | −4.9227 | Down | zinc finger protein 358 |
| ILMN_1778991 | NFIB | −0.34285 | 0.001613 | 0.031272 | −3.23532 | Down | nuclear factor I B |
| ILMN_1812926 | ANTXR2 | −0.3415 | 5.68E-05 | 0.006347 | −4.19218 | Down | ANTXR cell adhesion molecule 2 |
| ILMN_1657632 | TMEM35B | −0.33999 | 8.22E-05 | 0.007511 | −4.09378 | Down | transmembrane protein 35B |
| ILMN_1778226 | EXTL3 | −0.33995 | 0.001652 | 0.03162 | −3.22796 | Down | exostosin like glycosyltransferase 3 |
| ILMN_1782938 | SLC16A10 | −0.33976 | 0.002898 | 0.042362 | −3.04796 | Down | solute carrier family 16 member 10 |
| ILMN_2193325 | MMP23B | −0.33959 | 0.000713 | 0.020805 | −3.48474 | Down | matrix metallopeptidase 23B |
| ILMN_1739496 | PRRX1 | −0.33948 | 0.000146 | 0.010103 | −3.93722 | Down | paired related homeobox 1 |
| ILMN_1865764 | ZMAT3 | −0.33777 | 1.18E-06 | 0.001926 | −5.14964 | Down | zinc finger matrin-type 3 |
| ILMN_1794863 | CAMK2N1 | −0.33759 | 0.001093 | 0.025566 | −3.35581 | Down | calcium/calmodulin dependent protein kinase II inhibitor 1 |
| ILMN_1735877 | EFEMP1 | −0.33701 | 0.003 | 0.043103 | −3.03665 | Down | EGF containing fibulin extracellular matrix protein 1 |
| ILMN_2120247 | SLC2A10 | −0.33689 | 0.001012 | 0.02466 | −3.37924 | Down | solute carrier family 2 member 10 |
| ILMN_1803423 | ARHGEF6 | −0.33673 | 0.001997 | 0.034749 | −3.16805 | Down | Rac/Cdc42 guanine nucleotide exchange factor 6 |
| ILMN_2201533 | TMEM256 | −0.3363 | 9.84E-05 | 0.008273 | −4.04548 | Down | transmembrane protein 256 |
| ILMN_1698934 | CMTM7 | −0.33562 | 6.8E-05 | 0.006927 | −4.14452 | Down | CKLF like MARVEL transmembrane domain containing 7 |
| ILMN_1697409 | TNFRSF14 | −0.33559 | 0.000266 | 0.013333 | −3.77075 | Down | TNF receptor superfamily member 14 |
| ILMN_1778240 | GFOD1 | −0.33518 | 0.00062 | 0.019425 | −3.52642 | Down | glucose-fructose oxidoreductase domain containing 1 |
| ILMN_1743373 | DLL1 | −0.3346 | 0.000177 | 0.010936 | −3.88539 | Down | δ like canonical Notch ligand 1 |
| ILMN_2216582 | LYL1 | −0.3343 | 0.000484 | 0.017744 | −3.59922 | Down | LYL1 basic helix-loop-helix family member |
| ILMN_1765641 | SEMA3A | −0.33427 | 0.000485 | 0.017744 | −3.59859 | Down | semaphorin 3A |
| ILMN_1890614 | INKA2 | −0.33389 | 7.18E-06 | 0.00295 | −4.71805 | Down | inka box actin regulator 2 |
| ILMN_2095133 | SPTAN1 | −0.33345 | 7.54E-05 | 0.007229 | −4.11685 | Down | spectrin α, non-erythrocytic 1 |
| ILMN_1783681 | MRPL34 | −0.33294 | 0.001535 | 0.030319 | −3.25087 | Down | mitochondrial ribosomal protein L34 |
| ILMN_1705302 | FCGRT | −0.33153 | 0.00135 | 0.028444 | −3.29084 | Down | Fc fragment of IgG receptor and transporter |
| ILMN_1682738 | SMAD3 | −0.33045 | 6.58E-05 | 0.006811 | −4.15297 | Down | SMAD family member 3 |
| ILMN_2059535 | PPM1F | −0.3304 | 0.001065 | 0.025246 | −3.36391 | Down | protein phosphatase, Mg2+/Mn2+ dependent 1F |
| ILMN_1790953 | TBCB | −0.3301 | 2.21E-05 | 0.004675 | −4.43726 | Down | tubulin folding cofactor B |
| ILMN_1764788 | TNFRSF1B | −0.32976 | 0.003169 | 0.044269 | −3.0186 | Down | TNF receptor superfamily member 1B |
| ILMN_1754660 | ZCCHC24 | −0.32898 | 0.000101 | 0.008387 | −4.03815 | Down | zinc finger CCHC-type containing 24 |
| ILMN_2252309 | DPP7 | −0.32892 | 0.001126 | 0.025921 | −3.34674 | Down | dipeptidyl peptidase 7 |
| ILMN_1674160 | BIN1 | −0.32855 | 0.000214 | 0.012004 | −3.83144 | Down | bridging integrator 1 |
| ILMN_1675656 | PPFIBP2 | −0.32771 | 0.00043 | 0.016689 | −3.63326 | Down | PPFIA binding protein 2 |
| ILMN_1728512 | YWHAH | −0.32748 | 6.04E-05 | 0.006541 | −4.17595 | Down | tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein eta |
| ILMN_1789171 | EEF2K | −0.32709 | 1.05E-05 | 0.003154 | −4.62387 | Down | eukaryotic elongation factor 2 kinase |
| ILMN_1680973 | FOXF1 | −0.3269 | 0.000111 | 0.008868 | −4.01194 | Down | forkhead box F1 |
| ILMN_1805750 | IFITM3 | −0.3253 | 0.000765 | 0.021605 | −3.46392 | Down | interferon induced transmembrane protein 3 |
| ILMN_2298365 | PPP2R2B | −0.3252 | 0.000614 | 0.019397 | −3.52901 | Down | protein phosphatase 2 regulatory subunit Bβ |
| ILMN_1814194 | TCF4 | −0.32479 | 0.00114 | 0.026051 | −3.34287 | Down | transcription factor 4 |
| ILMN_1769520 | UBE2L6 | −0.32451 | 0.001765 | 0.032784 | −3.20703 | Down | ubiquitin conjugating enzyme E2 L6 |
| ILMN_1730487 | CALD1 | −0.32449 | 0.000631 | 0.019631 | −3.52115 | Down | caldesmon 1 |
| ILMN_1804929 | OXTR | −0.32448 | 0.000803 | 0.02216 | −3.44941 | Down | oxytocin receptor |
| ILMN_2174127 | DCBLD2 | −0.32399 | 6.83E-06 | 0.00295 | −4.73008 | Down | discoidin, CUB and LCCL domain containing 2 |
| ILMN_1703477 | ARHGEF2 | −0.32314 | 7.85E-05 | 0.007364 | −4.10614 | Down | Rho/Rac guanine nucleotide exchange factor 2 |
| ILMN_1804277 | SPRED1 | −0.32305 | 0.002215 | 0.036485 | −3.13485 | Down | sprouty related EVH1 domain containing 1 |
| ILMN_1712075 | SYNM | −0.32231 | 0.002466 | 0.038662 | −3.10033 | Down | synemin |
| ILMN_1770290 | CNN2 | −0.3223 | 0.000584 | 0.01904 | −3.54398 | Down | calponin 2 |
| ILMN_2064725 | METTL7B | −0.32199 | 0.000739 | 0.021238 | −3.474 | Down | methyltransferase like 7B |
| ILMN_2343097 | NCALD | −0.32174 | 5.26E-06 | 0.002879 | −4.7939 | Down | neurocalcin δ |
| ILMN_1676515 | IMPDH1 | −0.32151 | 2.8E-06 | 0.002369 | −4.94609 | Down | inosine monophosphate dehydrogenase 1 |
| ILMN_1685540 | SHROOM3 | −0.32144 | 9.41E-05 | 0.008052 | −4.05753 | Down | shroom family member 3 |
| ILMN_1839019 | LPP | −0.32071 | 0.000295 | 0.01409 | −3.74125 | Down | LIM domain containing preferred translocation partner in lipoma |
| ILMN_1747223 | FRYL | −0.32039 | 0.000312 | 0.014386 | −3.72536 | Down | FRY like transcription coactivator |
| ILMN_1779735 | LAMTOR4 | −0.32032 | 0.001384 | 0.028811 | −3.28315 | Down | late endosomal/lysosomal adaptor, MAPK and MTOR activator 4 |
| ILMN_2316386 | GPBAR1 | −0.31949 | 0.000134 | 0.009736 | −3.96066 | Down | G protein-coupled bile acid receptor 1 |
| ILMN_1810559 | RHOQ | −0.31922 | 9.79E-05 | 0.008252 | −4.04665 | Down | ras homolog family member Q |
| ILMN_1804498 | BRAT1 | −0.31861 | 0.000157 | 0.010362 | −3.91859 | Down | BRCA1 associated ATM activator 1 |
| ILMN_1785618 | SMTN | −0.31794 | 0.000103 | 0.008513 | −4.03259 | Down | smoothelin |
| ILMN_1778444 | FKBP5 | −0.31765 | 0.003284 | 0.045007 | −3.00692 | Down | FKBP prolylisomerase 5 |
| ILMN_1704154 | TNFRSF19 | −0.31706 | 0.000322 | 0.014545 | −3.71667 | Down | TNF receptor superfamily member 19 |
| ILMN_2104141 | FGD5 | −0.317 | 0.000237 | 0.012746 | −3.80302 | Down | FYVE, RhoGEF and PH domain containing 5 |
| ILMN_2149226 | CAV1 | −0.31687 | 0.002907 | 0.042449 | −3.04697 | Down | caveolin 1 |
| ILMN_1654398 | RGL1 | −0.31678 | 0.000409 | 0.016197 | −3.64795 | Down | ral guanine nucleotide dissociation stimulator like 1 |
| ILMN_3307892 | PARVA | −0.31677 | 1.15E-05 | 0.003353 | −4.60138 | Down | parvin α |
| ILMN_3241262 | PABPC4L | −0.3167 | 0.001528 | 0.030233 | −3.2524 | Down | poly(A) binding protein cytoplasmic 4 like |
| ILMN_1730229 | CGNL1 | −0.31553 | 0.000937 | 0.02378 | −3.40267 | Down | cingulin like 1 |
| ILMN_1779071 | FEZ1 | −0.31546 | 3.78E-05 | 0.005357 | −4.29902 | Down | fasciculation and elongation protein zeta 1 |
| ILMN_1775330 | CCDC9B | −0.31511 | 8.78E-05 | 0.007748 | −4.07615 | Down | coiled-coil domain containing 9B |
| ILMN_1701204 | VEGFC | −0.31459 | 0.000186 | 0.011194 | −3.87116 | Down | vascular endothelial growth factor C |
| ILMN_1777881 | TSPAN17 | −0.31456 | 4.57E-05 | 0.005773 | −4.24941 | Down | tetraspanin 17 |
| ILMN_1677200 | CYFIP2 | −0.31396 | 0.0005 | 0.017901 | −3.58965 | Down | cytoplasmic FMR1 interacting protein 2 |
| ILMN_2056032 | CD99 | −0.3134 | 0.001609 | 0.031251 | −3.23623 | Down | CD99 molecule (Xg blood group) |
| ILMN_1752591 | LEPROTL1 | −0.3128 | 0.001734 | 0.032382 | −3.21268 | Down | leptin receptor overlapping transcript like 1 |
| ILMN_1757338 | PLSCR4 | −0.31123 | 0.000327 | 0.014624 | −3.7118 | Down | phospholipid scramblase 4 |
| ILMN_3245564 | ARHGAP44 | −0.3111 | 4.92E-05 | 0.005917 | −4.22987 | Down | Rho GTPase activating protein 44 |
| ILMN_1699980 | TSPAN18 | −0.31001 | 0.000286 | 0.013944 | −3.74989 | Down | tetraspanin 18 |
| ILMN_3232894 | CNRIP1 | −0.30921 | 0.00187 | 0.033574 | −3.18876 | Down | cannabinoid receptor interacting protein 1 |
| ILMN_1771800 | PRKCA | −0.30913 | 3.17E-05 | 0.005189 | −4.34465 | Down | protein kinase C α |
| ILMN_2397954 | PARP3 | −0.30902 | 1.52E-06 | 0.001955 | −5.09076 | Down | poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase family member 3 |
| ILMN_1808777 | EHD2 | −0.30827 | 0.0001 | 0.008353 | −4.04098 | Down | EH domain containing 2 |
| ILMN_1758128 | CYGB | −0.30813 | 3.22E-05 | 0.005189 | −4.34001 | Down | cytoglobin |
| ILMN_1668514 | PIP5K1C | −0.30797 | 0.000323 | 0.014545 | −3.71537 | Down | phosphatidylinositol-4-phosphate 5-kinase type 1 γ |
| ILMN_3236344 | BMS1P4 | −0.30771 | 0.000204 | 0.011804 | −3.84512 | Down | BMS1 pseudogene 4 |
| ILMN_1708743 | NT5DC2 | −0.30746 | 7.44E-05 | 0.007229 | −4.12035 | Down | 5′-nucleotidase domain containing 2 |
| ILMN_1760493 | LIMS2 | −0.30721 | 0.000139 | 0.00984 | −3.95143 | Down | LIM zinc finger domain containing 2 |
| ILMN_1736670 | PPP1R3C | −0.30647 | 0.001626 | 0.031392 | −3.23287 | Down | protein phosphatase 1 regulatory subunit 3C |
| ILMN_1671295 | CCDC3 | −0.3059 | 0.001513 | 0.030094 | −3.25547 | Down | coiled-coil domain containing 3 |
| ILMN_2102330 | COL8A2 | −0.3057 | 0.000112 | 0.008882 | −4.01107 | Down | collagen type VIII α 2 chain |
| ILMN_2359945 | CES1 | −0.30559 | 0.00016 | 0.010366 | −3.91273 | Down | carboxylesterase 1 |
| ILMN_1780057 | RENBP | −0.3052 | 0.000155 | 0.010361 | −3.92141 | Down | renin binding protein |
| ILMN_1658847 | NRARP | −0.30411 | 0.000766 | 0.021608 | −3.46347 | Down | NOTCH regulated ankyrin repeat protein |
| ILMN_1718303 | NECTIN2 | −0.30407 | 0.000344 | 0.014909 | −3.69776 | Down | nectin cell adhesion molecule 2 |
| ILMN_1764410 | GUCD1 | −0.30401 | 0.001226 | 0.026935 | −3.3206 | Down | guanylylcyclase domain containing 1 |
| ILMN_1691717 | RHBDF2 | −0.30355 | 0.000467 | 0.017456 | −3.60933 | Down | rhomboid 5 homolog 2 |
| ILMN_1766675 | CDH6 | −0.30348 | 5.65E-05 | 0.006347 | −4.19354 | Down | cadherin 6 |
| ILMN_1752046 | SH2B3 | −0.30284 | 0.003129 | 0.044068 | −3.02278 | Down | SH2B adaptor protein 3 |
| ILMN_1656300 | GFRA2 | −0.30283 | 0.000222 | 0.012233 | −3.82121 | Down | GDNF family receptor α 2 |
| ILMN_2148459 | B2M | −0.30266 | 0.003487 | 0.046567 | −2.98705 | Down | β-2-microglobulin |
| ILMN_1795639 | MGMT | −0.30229 | 0.000215 | 0.012004 | −3.83117 | Down | O-6-methylguanine-DNA methyltransferase |
| ILMN_1687335 | FLNA | −0.30213 | 0.00045 | 0.017125 | −3.62022 | Down | filamin A |
| ILMN_2049536 | TRPV2 | −0.30191 | 5E-05 | 0.005957 | −4.22548 | Down | transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 2 |
| ILMN_1668721 | CCND3 | −0.30153 | 0.003431 | 0.046061 | −2.99245 | Down | cyclin D3 |
| ILMN_1801226 | DOCK6 | −0.30138 | 0.000109 | 0.008759 | −4.01846 | Down | dedicator of cytokinesis 6 |
| ILMN_3238196 | CYTH4 | −0.30118 | 0.001775 | 0.0328 | −3.20526 | Down | cytohesin 4 |
| ILMN_1760667 | POLR3GL | −0.30114 | 0.000115 | 0.009 | −4.00214 | Down | RNA polymerase III subunit G like |
| ILMN_2367707 | PKN1 | −0.30078 | 1.76E-05 | 0.004057 | −4.49419 | Down | protein kinase N1 |
| ILMN_1756439 | SCRN1 | −0.30064 | 2.03E-05 | 0.004408 | −4.45788 | Down | secernin 1 |
| ILMN_1746704 | TRIM8 | −0.30043 | 1.71E-06 | 0.001955 | −5.06366 | Down | tripartite motif containing 8 |
| ILMN_1727043 | COLGALT1 | −0.30041 | 1.61E-06 | 0.001955 | −5.0774 | Down | collagen β(1-O)galactosyltransferase 1 |
| ILMN_1789639 | FMOD | −0.29998 | 0.000703 | 0.020621 | −3.48914 | Down | fibromodulin |
| ILMN_1759513 | RND3 | −0.2987 | 0.00056 | 0.018724 | −3.5563 | Down | Rho family GTPase 3 |
| ILMN_2339294 | LILRB5 | −0.29854 | 0.000286 | 0.013933 | −3.75069 | Down | leukocyte immunoglobulin like receptor B5 |
| ILMN_2205896 | MEIS3P1 | −0.29849 | 3.51E-05 | 0.005215 | −4.31774 | Down | Meishomeobox 3 pseudogene 1 |
| ILMN_1677404 | RAP2A | −0.29848 | 1.01E-05 | 0.003119 | −4.63287 | Down | RAP2A, member of RAS oncogene family |
| ILMN_1716678 | NPC2 | −0.29813 | 0.000259 | 0.013173 | −3.77819 | Down | NPC intracellular cholesterol transporter 2 |
| ILMN_1686555 | FYN | −0.29766 | 6.74E-05 | 0.006914 | −4.14687 | Down | FYN proto-oncogene, Src family tyrosine kinase |
| ILMN_1853824 | MGAT3 | −0.29749 | 0.000891 | 0.023304 | −3.4178 | Down | β-1,4-mannosyl-glycoprotein 4-β-N-acetylglucosaminyltransferase |
| ILMN_1661264 | SHMT2 | −0.29747 | 0.000466 | 0.017456 | −3.61015 | Down | serine hydroxymethyltransferase 2 |
| ILMN_1748206 | CCM2L | −0.29721 | 0.001703 | 0.032137 | −3.21833 | Down | CCM2 like scaffold protein |
| ILMN_1724480 | AXIN2 | −0.29689 | 0.000111 | 0.008868 | −4.01392 | Down | axin 2 |
| ILMN_1776157 | SEPTIN4 | −0.29638 | 0.000337 | 0.014847 | −3.70339 | Down | septin 4 |
| ILMN_1775734 | SH2D3C | −0.29607 | 0.001157 | 0.02618 | −3.33856 | Down | SH2 domain containing 3C |
| ILMN_1761159 | ESYT1 | −0.29576 | 9.88E-06 | 0.003091 | −4.63908 | Down | extended synaptotagmin 1 |
| ILMN_1770824 | ARHGAP4 | −0.29525 | 0.000371 | 0.015365 | −3.67562 | Down | Rho GTPase activating protein 4 |
| ILMN_1713732 | ABL1 | −0.29499 | 1.21E-05 | 0.003404 | −4.58941 | Down | ABL proto-oncogene 1, non-receptor tyrosine kinase |
| ILMN_1687440 | HIPK2 | −0.2942 | 0.001881 | 0.033734 | −3.1869 | Down | homeodomain interacting protein kinase 2 |
| ILMN_1694539 | MAP3K6 | −0.29418 | 7.48E-05 | 0.007229 | −4.11899 | Down | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinasekinase 6 |
| ILMN_2381697 | P4HA2 | −0.29305 | 0.000174 | 0.010872 | −3.88914 | Down | prolyl 4-hydroxylase subunit α 2 |
| ILMN_1803348 | EHBP1 | −0.29305 | 0.000173 | 0.010825 | −3.89106 | Down | EH domain binding protein 1 |
| ILMN_1776464 | PARP4 | −0.29295 | 4.71E-05 | 0.005816 | −4.24138 | Down | poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase family member 4 |
| ILMN_1671404 | SVIL | −0.29228 | 0.00024 | 0.012746 | −3.79968 | Down | supervillin |
| ILMN_1769118 | SEPTIN9 | −0.29218 | 0.000231 | 0.012551 | −3.81002 | Down | septin 9 |
| ILMN_2315789 | PTPRD | −0.292 | 0.000226 | 0.012397 | −3.81635 | Down | protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type D |
| ILMN_2401978 | STAT3 | −0.29197 | 2.58E-06 | 0.002346 | −4.96523 | Down | signal transducer and activator of transcription 3 |
| ILMN_1785424 | ABLIM1 | −0.29182 | 0.002923 | 0.042546 | −3.04516 | Down | actin binding LIM protein 1 |
| ILMN_2082585 | SNAI2 | −0.29137 | 0.000937 | 0.02378 | −3.40282 | Down | snail family transcriptional repressor 2 |
| ILMN_1809850 | RCN3 | −0.2896 | 0.000133 | 0.009736 | −3.96254 | Down | reticulocalbin 3 |
| ILMN_3246065 | CCDC151 | −0.28935 | 0.000122 | 0.009241 | −3.98798 | Down | coiled-coil domain containing 151 |
| ILMN_1745806 | PEMT | −0.28934 | 0.000161 | 0.010372 | −3.91073 | Down | phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase |
| ILMN_1791226 | NXN | −0.28912 | 6.77E-05 | 0.006914 | −4.14567 | Down | nucleoredoxin |
| ILMN_1758315 | SLC9A9 | −0.28902 | 0.000259 | 0.013173 | −3.77817 | Down | solute carrier family 9 member A9 |
| ILMN_1661194 | CLDN14 | −0.28826 | 0.000466 | 0.017456 | −3.61005 | Down | claudin 14 |
| ILMN_3225591 | RPL14 | −0.28806 | 0.000665 | 0.020117 | −3.50549 | Down | ribosomal protein L14 |
| ILMN_2232712 | MYO10 | −0.28774 | 0.001061 | 0.02524 | −3.36484 | Down | myosin X |
| ILMN_1913060 | CMKLR1 | −0.28763 | 0.00032 | 0.014545 | −3.71847 | Down | chemerin chemokine-like receptor 1 |
| ILMN_1789502 | GPC4 | −0.28702 | 0.001807 | 0.033091 | −3.19966 | Down | glypican 4 |
| ILMN_2047599 | TMEM50B | −0.28576 | 0.001003 | 0.024564 | −3.38214 | Down | transmembrane protein 50B |
| ILMN_1719543 | MAF | −0.28566 | 0.000438 | 0.016832 | −3.62816 | Down | MAF bZIP transcription factor |
| ILMN_1748625 | TCEAL4 | −0.2856 | 0.000494 | 0.01788 | −3.59303 | Down | transcription elongation factor A like 4 |
| ILMN_1670134 | FADS1 | −0.28515 | 0.000296 | 0.01409 | −3.74097 | Down | fatty acid desaturase 1 |
| ILMN_1660871 | NEK6 | −0.28507 | 0.000893 | 0.023304 | −3.41739 | Down | NIMA related kinase 6 |
| ILMN_1674385 | YWHAQ | −0.28455 | 2.86E-05 | 0.004971 | −4.37044 | Down | tyrosine 3-monooxygenase/tryptophan 5-monooxygenase activation protein theta |
| ILMN_1681515 | CRLF1 | −0.2833 | 0.002663 | 0.04025 | −3.07546 | Down | cytokine receptor like factor 1 |
| ILMN_1782086 | AOC3 | −0.28296 | 0.000461 | 0.01734 | −3.61347 | Down | amine oxidase copper containing 3 |
| ILMN_1768110 | MAP3K20 | −0.28275 | 0.00124 | 0.027121 | −3.31715 | Down | mitogen-activated protein kinase kinasekinase 20 |
| ILMN_1733538 | RGS10 | −0.28222 | 0.001065 | 0.025246 | −3.36393 | Down | regulator of G protein signaling 10 |
| ILMN_2185884 | DHRS4 | −0.28207 | 0.001328 | 0.028154 | −3.29599 | Down | dehydrogenase/reductase 4 |
| ILMN_2381899 | OPTN | −0.28193 | 0.000301 | 0.014133 | −3.73615 | Down | optineurin |
| ILMN_3202024 | FTL | −0.28175 | 0.00324 | 0.044809 | −3.01128 | Down | ferritin light chain |
| ILMN_1815500 | ITPR3 | −0.28174 | 0.002482 | 0.038752 | −3.09823 | Down | inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate receptor type 3 |
| ILMN_1684554 | COL16A1 | −0.28149 | 0.001102 | 0.025658 | −3.35341 | Down | collagen type XVI α 1 chain |
| ILMN_1709590 | PGM5 | −0.28126 | 0.000681 | 0.020348 | −3.49848 | Down | phosphoglucomutase 5 |
| ILMN_1669033 | NCOA1 | −0.28125 | 2.76E-05 | 0.00487 | −4.37959 | Down | nuclear receptor coactivator 1 |
| ILMN_1913678 | IRAK3 | −0.28034 | 0.002099 | 0.035634 | −3.15202 | Down | interleukin 1 receptor associated kinase 3 |
| ILMN_1815745 | SOX4 | −0.27903 | 4.4E-05 | 0.005755 | −4.25887 | Down | SRY-box transcription factor 4 |
| ILMN_3236858 | NYNRIN | −0.2784 | 4.66E-05 | 0.005784 | −4.24391 | Down | NYN domain and retroviral integrase containing |
| ILMN_1800634 | NME4 | −0.27818 | 0.000791 | 0.022033 | −3.4539 | Down | NME/NM23 nucleoside diphosphate kinase 4 |
| ILMN_1714170 | SPSB1 | −0.27787 | 0.001682 | 0.031939 | −3.22231 | Down | splA/ryanodine receptor domain and SOCS box containing 1 |
| ILMN_1698725 | FRMD3 | −0.27757 | 0.002954 | 0.042707 | −3.04173 | Down | FERM domain containing 3 |
| ILMN_1695946 | TRNP1 | −0.27716 | 1.26E-05 | 0.003423 | −4.57872 | Down | TMF1 regulated nuclear protein 1 |
| ILMN_1654065 | ATOH8 | −0.27686 | 0.001152 | 0.02613 | −3.33982 | Down | atonal bHLH transcription factor 8 |
| ILMN_1739885 | SLC41A3 | −0.27657 | 2.16E-07 | 0.000867 | −5.53926 | Down | solute carrier family 41 member 3 |
| ILMN_1693826 | HAVCR2 | −0.27451 | 0.003493 | 0.046607 | −2.98647 | Down | hepatitis A virus cellular receptor 2 |
| ILMN_1775931 | EPHA3 | −0.27402 | 0.002521 | 0.039049 | −3.09318 | Down | EPH receptor A3 |
| ILMN_1659206 | RARA | −0.27351 | 0.00249 | 0.038808 | −3.09718 | Down | retinoic acid receptor α |
Figure 2. Heat map of DEGs.
Legend on the top left indicates log fold change of genes (A1– A38, GDM; B1–B70, GDM).
Gene ontology and pathway enrichment of DEGs analysis
To clarify the major functions of these DEGs, we first explored the associated biological processes and REACTOME pathways. The top highly enriched GO terms were divided into three categories: biological process (BP), cellular component (CC) and molecular function (MF) and are listed in Table 3. The most enriched GO terms in BP was reproduction, macromolecule catabolic process, cell adhesion and localization of cell, that in CC was nuclear outer membrane–endoplasmic reticulum membrane network, Golgi apparatus, supramolecular complex and cell junction, and that in MF had identical protein binding, molecular function regulator, signaling receptor binding and molecular function regulator. In the REACTOME pathway enrichment analysis, the DEGs were mostly enriched in cell surface interactions at the vascular wall, epigenetic regulation of gene expression, extracellular matrix organization and axon guidance and are listed in Table 4.
Table 3. The enriched GO terms of the up- and down-regulated DEGs.
| GO ID | CATEGORY | GO Name | P Value | FDR B and H | FDR B and Y | Bonferroni | Gene count | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up-regulated genes | ||||||||
| GO:0000003 | BP | reproduction | 1.54E-05 | 1.92E-02 | 1.75E-01 | 7.69E-02 | 59 | CEBPB, GRHL2, ACSL4, S100A11, KMT2C, UBE2A, TESK2, AGFG1, AHR, HES1, MAFF, HSD11B2, PAQR7, RHOBTB3, NECTIN3, CRH, SLC4A2, STS, CSNK2A2, SLC22A5, GABRB1, PLAC1, SPIRE2, PSG1, PSG2, ING2, PSG3, INHA, PSG4, PSG5, PSG6, PSG7, PSG9, CYP11A1, PSG11, CYP19A1, YTHDC1, SEPTIN6, STAT5B, CREBRF, NFE2, SPIN1, STRA6, MBD2, DDR1, TBX3, CAST, CGB7, TEAD3, LHB, GMCL1, OVGP1, TIAL1, EGFR, INSL6, LNPEP, TLR3, TMF1, PLEKHA1 |
| GO:0009057 | BP | macromolecule catabolic process | 5.89E-04 | 1.28E-01 | 1.00E+00 | 1.00E+00 | 48 | CARHSP1, RPS13, WAC, UBE2A, UBE2D3, CLN3, UCHL3, LYPLA1, HSPB1, HSP90AA1, AMFR, DCP2, IDS, AZIN1, IGF2BP3, IGF2BP2, GET4, CSNK2A2, MTM1, NCAN, TNKS1BP1, USP33, TRIM25, PSMA3, PSMC4, DDB1, CREBRF, PTPN3, STX5, FBXO9, SMG9, PJA1, USP27X, RBX1, RBBP6, CAST, RDX, PELI1, NCCRP1, STT3B, RYBP, OVGP1, EGFR, TIMP2, LNPEP, PKP3, FURIN, TMF1 |
| GO:0042175 | CC | nuclear outer membrane- endoplasmic reticulum membrane network | 1.06E-03 | 1.69E-01 | 1.00E+00 | 6.75E-01 | 38 | SPTLC3, CDS1, BET1, ACSL4, SPCS3, PIGH, EVA1A, CLN3, HSD3B1, ULK1, HSD11B2, FKBP2, AMFR, FOLR1, SPTLC1, RAB3GAP1, STS, NSG1, GDPD1, GPAA1, CYP19A1, STX5, BCAP29, NUP153, TOR1AIP2, CAMK2G, NUCB2, CASP4, TMED4, STT3B, RASGRP1, MFSD2A, SPPL2A, EGFR, LPCAT3, FURIN, TLR3, PAFAH2 |
| GO:0005794 | CC | Golgi apparatus | 1.36E-02 | 3.09E-01 | 1.00E+00 | 1.00E+00 | 46 | SGSM1, CNST, BET1, SPG21, ST3GAL6, CLN3, AMFR, ANK3, FOLR1, GDF15, YIPF4, RHOBTB3, ST3GAL4, RAB3GAP1, STS, NCAN, NSG1, PDE4DIP, RAB11FIP5, FHDC1, TBC1D23, STX11, CSGALNACT1, ECE2, USP33, ACER2, ATP6V0C, ING2, STK26, C1GALT1, COG3, BMP1, STX5, AP1G2, TAF7, GOLGA4, YIPF6, NUCB2, TMED4, LHB, RASGRP1, EGFR, FURIN, TLR3, TMF1, ELF3 |
| GO:0042802 | MF | identical protein binding | 4.89E-03 | 2.96E-01 | 1.00E+00 | 1.00E+00 | 59 | CEBPB, IER5, TWIST1, S100A11, S100P, H2BC8, H2BC6, H2BC4, TLE5, CLK3, AHR, UCK2, TRPV6, HES1, HOOK2, ULK1, HSPB1, CAP2, HSP90AA1, AMFR, GDF15, ANXA4, SRR, CLDN7, NECTIN3, CGGBP1, TBK1, GRAMD2B, ATF3, RIPOR2, STK26, NAB2, DAPK1, BMP1, JUP, DHPS, SMG9, KYNU, HSPB8, NUP153, YIPF6, CAMK2G, DYRK1A, GRB7, RDX, UBA3, TDG, CLDN8, TFRC, GMCL1, RASGRP1, SPPL2A, EGFR, CBX5, ENTPD1, TLR3, PAK1, PAK2, SPATA13 |
| GO:0098772 | MF | molecular function regulator | 1.03E-02 | 2.96E-01 | 1.00E+00 | 1.00E+00 | 55 | SGSM1, NET1, PDPK1, DENND2D, SERPINI1, AGFG1, TNFAIP8, HSPB1, RASAL2, HSP90AA1, DNAJB1, FNTA, GDF15, ANXA4, CRH, AZIN1, RAB3GAP1, CSH2, PPP4R2, ATP1B3, DEPDC1B, RIPOR2, INHA, MYO9A, INSL4, GH2, BMP1, PTPN3, CGB1, SEMA3B, RGL2, TOR1AIP2, RGPD8, PPP1R14C, TFPI2, FBRS, CAST, CGB7, COX17, PPP1R14B, ITIH5, LHB, RASGRP1, EEF1B2, GRTP1, FAM13A, EGFR, INSL6, TIMP2, FURIN, TLR3, PAK2, MARK2, ENSA, SPATA13 |
| Down-regulated genes | ||||||||
| GO:0007155 | BP | cell adhesion | 4.46E-28 | 8.58E-25 | 7.92E-24 | 2.57E-24 | 104 | CLDN14, ABL1, ENPP2, VSIG4, EMILIN2, LAMC3, PGM5, NRARP, FZD4, SLIT2, MFAP4, MFGE8, FAT1, FBLN2, MYL9, CD99, SPON1, JAG1, GPC4, ANTXR1, SRPX, VCAM1, VCL, FOXF1, COL1A1, PMP22, VEGFC, COL3A1, COL5A1, COL6A1, COL6A2, FLNA, COL6A3, COL8A2, FBLN5, VTN, VWF, COL16A1, ABI3BP, PODXL, FOLR2, EGFL6, CYFIP2, LIMS2, PDPN, RND3, IGFBP2, CCM2L, IGFBP7, FEZ1, PPM1F, VCAN, PARVA, SNAI2, AOC3, PRKCA, CCN2, EGFLAM, EPDR1, FYN, NEXN, MYADM, MYO10, AXL, ADAM15, PIEZO1, TNFRSF14, GAS6, ITGA1, TNFRSF21, LYVE1, PTPRD, ADAMTS9, ACKR3, WNT3A, NECTIN2, FERMT2, RARA, SH2B3, DDR2, LAMA2, LAMA4, LAMB2, LAMC1, CAV1, TEK, DLL1, PIP5K1C, LGALS1, TGFB1I1, TGFBI, HAVCR2, COL18A1, THY1, FAM107A, CD36, LPP, CD44, CD81, CLDN5, CDH6, CDH11, SMAD3, EPHA3 |
| GO:0051674 | BP | localization of cell | 2.02E-23 | 1.67E-20 | 1.54E-19 | 1.17E-19 | 111 | ABL1, ABR, MAP1B, APCDD1, PDGFRB, ENPP2, MATN2, ACTA2, CYGB, TMIGD3, SOX18, LAMC3, F3, ADCY3, SEMA3A, SLIT2, FAT1, MGAT3, EFEMP1, CD99, JAG1, AGTR1, GPC4, CCL13, CMKLR1, CNN2, VCAM1, VCL, FOXF1, COL1A1, COL1A2, PMP22, VEGFC, COL3A1, COL5A1, FLNA, DDIT4, VTN, ADAMTS1, PODXL, FOLR2, CXCL14, ADGRA2, PDPN, RND3, ARHGAP4, IGFBP3, PRCP, PPM1F, VCAN, CSPG4, SLIT3, PARVA, SNAI2, AOC3, PRKCA, PKN1, CCN2, EGFLAM, CAVIN1, FSCN1, FYN, NEXN, HYAL2, PROS1, MYADM, SPARC, MYO10, AXL, ADAM15, TNFRSF14, GAS6, TUBB2B, NDN, ITGA1, DCN, STAT3, STC1, ADAMTS9, BST2, ACKR3, TSPO, RIPOR1, BRAT1, RAP2A, RARRES2, CD248, GPER1, DDR2, LAMA2, LAMA4, LAMB2, LAMC1, CAV1, TEK, PIP5K1C, LPAR1, LDB2, COL18A1, ARAP3, THY1, LMNA, FAM107A, TIMP1, ATOH8, CD44, SPRED1, CD81, ARHGEF2, SMAD3, EPHA3 |
| GO:0099080 | CC | supramolecular complex | 3.08E-13 | 1.81E-11 | 1.24E-10 | 1.63E-10 | 77 | TPM2, CYBRD1, MAP1B, ACTA2, ACTG2, TUBB2A, PGM5, TBCB, MFAP4, PARP4, FAT1, MYL9, PEMT, ANTXR1, CCDC151, CNN2, VCAM1, VCL, COL1A1, COL1A2, COL3A1, COL4A1, COL4A2, COL4A5, COL5A1, COL5A2, COL6A1, FLNA, COL6A3, BIN1, SHROOM3, FBLN5, SEPTIN4, PODXL, NCKAP5L, ADGRA2, SMTN, PDPN, ARHGAP4, FEZ1, PARVA, AOC3, FSCN1, FYN, NEXN, HYAL2, NES, MYH11, NEK6, MYO10, SEPTIN9, SPTAN1, TUBB2B, AIF1L, DCN, PTH1R, ITPR3, PDLIM3, SVIL, FERMT2, DPYSL2, CALD1, GPER1, SYNM, TEK, RHOQ, ABLIM1, OXTR, LMNA, FAM107A, FARP1, CD36, LPP, CD44, PALM, ARHGEF2, TNNT3 |
| GO:0030054 | CC | cell junction | 3.95E-13 | 2.09E-11 | 1.43E-10 | 2.09E-10 | 71 | CLDN14, MAP1B, PDGFRB, PGM5, FZD4, FAT1, CAMK2N1, CD99, JAG1, FGFR3, CNN2, ARHGEF6, VCL, PMP22, FLNA, SHROOM3, PODXL, YWHAH, CYFIP2, LIMS2, PDPN, RND3, CSPG4, PARVA, PRKCA, EGFLAM, FSCN1, NEXN, RAB23, MYADM, LYPD6, ADAM15, SPTAN1, B2M, CCND1, AIF1L, ITGA1, RASIP1, GJA4, PDLIM3, SYT11, ARHGAP44, SVIL, NECTIN2, YWHAQ, FERMT2, GPER1, SYNM, DDR2, LASP1, CAV1, CAV2, TEK, DLL1, PIP5K1C, TGFB1I1, HAVCR2, OXTR, THY1, FAM107A, FARP1, LPP, CD44, TSPAN4, CD81, CLDN5, CGNL1, ARHGEF2, AGRN, CDH6, CDH11 |
| GO:0005102 | MF | signaling receptor binding | 6.59E-08 | 6.11E-06 | 4.59E-05 | 6.72E-05 | 75 | CMTM3, ABL1, CRLF1, PDGFRB, ETS2, SEMA3A, SLIT2, MFGE8, EFEMP1, JAG1, AGTR1, CCL13, LTBP4, VCAM1, VEGFC, COL3A1, COL5A1, FLNA, FBLN5, VTN, VWF, COL16A1, CNRIP1, CXCL14, ALKAL2, YWHAH, EGFL6, PDPN, IGFBP2, IGFBP4, SLIT3, NCOA1, PRKCA, PKN1, CCN2, FYN, DKK3, HYAL2, NES, ADAM15, B2M, GAS6, ITGA1, STAT3, STC1, PXDN, PTPRD, WNT3A, PLSCR4, RARA, RARRES2, SH2B3, SH2D3C, LAMA2, LAMA4, LAMB2, CAV1, CAV2, DLL1, TGFB1I1, TGFB3, LEFTY2, TGFBI, RSPO3, ANGPTL2, THY1, TIMP1, CD36, CD44, TSPAN4, PALM, SPRED1, CD81, CMTM7, SMAD3 |
| GO:0098772 | MF | molecular function regulator | 2.41E-05 | 1.12E-03 | 8.38E-03 | 2.46E-02 | 69 | CMTM3, CRLF1, ABR, CTSC, PPP1R14A, SEMA3A, SLIT2, CAMK2N1, EFEMP1, JAG1, CCL13, SIPA1L2, DOCK6, SMAP2, ARHGEF6, VEGFC, FLNA, COL6A3, WARS1, CXCL14, ALKAL2, YWHAH, PPP1R3C, TXNIP, ARHGAP4, PPP2R2B, IGFBP3, LAMTOR4, CCN2, GPSM1, DKK3, HYAL2, CYTH4, PROS1, LYPD6, RAPGEF5, GAS6, CCND1, INKA2, STC1, RGL1, AFAP1L2, PXDN, BST2, WNT3A, ARHGAP44, RIPOR1, FGD5, RAB3IL1, RARA, SH2D3C, WFDC1, RENBP, CAV1, RGS10, CCND2, CCND3, TGFB3, LEFTY2, ARAP3, THY1, TIMP1, ABCE1, FARP1, SPRED1, ARHGEF2, CMTM7, AGRN, PCOLCE |
BP, CC and MF.
Table 4. The enriched pathway terms of the up- and down-regulated DEGs.
| Pathway ID | Pathway Name | P-value | FDR B& H | FDR B&Y | Bonferroni | Gene Count | Gene |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up-regulated genes | |||||||
| 1269373 | Cell surface interactions at the vascular wall | 2.86E-05 | 4.73E-03 | 3.47E-02 | 2.46E-02 | 13 | PSG8, SLC3A2, ATP1B3, PSG1, PSG2, PSG3, PSG4, PSG5, PSG6, PSG7, PSG9, PSG11, GRB7 |
| 1269734 | Epigenetic regulation of gene expression | 8.47E-04 | 2.18E-02 | 1.60E-01 | 7.28E-01 | 11 | H2AC6, H2BC8, H2BC6, H2BC4, H2BC21, H4C8, H2BC12, MBD2, TAF1B, TDG, H2BC5 |
| 1270001 | Metabolism of lipids and lipoproteins | 1.33E-03 | 2.87E-02 | 2.10E-01 | 1.00E+00 | 33 | OLAH, SPTLC3, CDS1, ACADVL, ACOX3, ACSL4, AHR, PIP5K1B, HSD3B1, TNFAIP8, HSD11B2, SH3KBP1, SPTLC1, TNFAIP8L1, PLEKHA6, STS, CSNK2A2, MTM1, ACER2, GDPD1, CYP11A1, CYP19A1, BMP1, TEAD3, LHB, MFSD2A, MTMR4, ABHD5, LPCAT3, FURIN, AKR1B15, PLEKHA1, RORA |
| 1268701 | Post-translational protein modification | 3.57E-03 | 6.02E-02 | 4.41E-01 | 1.00E+00 | 38 | BET1, WAC, H2AC6, H2BC8, UBE2A, H2BC6, H2BC4, UBE2D3, H2BC21, ST3GAL6, PIGH, UCHL3, ADAMTSL4, H2BC12, AMFR, ANK3, FOLR1, ST3GAL4, STS, BABAM1, USP33, TRIM25, GPAA1, INO80C, PSMA3, PSMC4, C1GALT1, COG3, H2AW, STX5, DHPS, NUP153, RAB25, GNE, TDG, LHB, FURIN, H2BC5 |
| 1268677 | Metabolism of proteins | 1.06E-02 | 1.30E-01 | 9.49E-01 | 1.00E+00 | 52 | ACADVL, BET1, RPS13, WAC, H2AC6, SPCS3, H2BC8, UBE2A, H2BC6, H2BC4, UBE2D3, H2BC21, ST3GAL6, PIGH, H4C8, UCHL3, ADAMTSL4, H2BC12, AMFR, ANK3, FOLR1, DCP2, ST3GAL4, STS, BABAM1, CSNK2A2, ATF3, ATF4, CGB5, USP33, CHCHD10, TRIM25, GPAA1, INO80C, INHA, PSMA3, PSMC4, C1GALT1, COG3, H2AW, STX5, GNG12, DHPS, NUP153, RAB25, GNE, COX17, TDG, LHB, EEF1B2, FURIN, H2BC5 |
| 1270302 | Developmental Biology | 1.79E-02 | 1.92E-01 | 1.00E+00 | 1.00E+00 | 36 | CEBPB, RPS6KA5, PFN2, KMT2C, H2AC6, H2BC8, H2BC6, H2BC4, H2BC21, H4C8, HES1, H2BC12, RASAL2, CAP2, HSP90AA1, ANK3, KRT23, CSNK2A2, NCAN, PSMA3, PSMC4, JUP, KAZN, KRTAP26-1, RBX1, CAMK2G, GRB7, RDX, RASGRP1, TCHH, EGFR, PKP3, FURIN, PAK1, PAK2, H2BC5 |
| Down-regulated genes | |||||||
| 1270244 | Extracellular matrix organization | 1.93E-23 | 1.40E-20 | 1.00E-19 | 1.40E-20 | 46 | LAMC3, MFAP4, FBLN2, EFEMP1, PLOD1, LTBP4, VCAM1, COL1A1, COL1A2, COL3A1, COL4A1, COL4A2, COL4A5, COL5A1, COL5A2, COL6A1, COL6A2, COL6A3, COL8A2, FBLN5, VTN, FMOD, COL16A1, ADAMTS1, EFEMP2, VCAN, PRKCA, SPARC, ADAM15, ITGA1, DCN, ADAMTS9, P4HA2, DDR2, LAMA2, LAMA4, LAMB2, LAMC1, COLGALT1, TGFB3, COL18A1, TIMP1, CD44, LTBP2, AGRN, PCOLCE |
| 1270303 | Axon guidance | 3.15E-05 | 1.35E-03 | 9.67E-03 | 2.29E-02 | 31 | ABL1, PDGFRB, RPS6KA2, SEMA3A, SLIT2, MYL9, FGFR3, VCL, COL4A1, COL4A2, COL4A5, COL6A1, COL6A2, COL6A3, VWF, SLIT3, PRKCA, FYN, MYH11, MYO10, SPTAN1, ITGA1, GFRA2, DPYSL2, LAMC1, TEK, PIP5K1C, ABLIM1, SPRED1, AGRN, EPHA3 |
| 1269478 | Signaling by PDGF | 2.76E-04 | 7.15E-03 | 5.13E-02 | 2.00E-01 | 22 | PDGFRB, ADCY3, FGFR3, VCL, COL4A1, COL4A2, FOXO1, COL4A5, COL6A1, COL6A2, COL6A3, ADCY4, VWF, PRKCA, FYN, SPTAN1, GFRA2, STAT3, ITPR3, TEK, PIP5K1C, SPRED1 |
| 1269340 | Hemostasis | 1.83E-03 | 3.51E-02 | 2.51E-01 | 1.00E+00 | 29 | ABL1, PDE9A, F3, EHD2, CD99, DOCK6, VCL, VEGFC, FLNA, VWF, PDPN, PRCP, PRKCA, FYN, PROS1, SPARC, GAS6, ITGA1, ITPR3, CFD, RARRES2, SH2B3, CAV1, TEK, TGFB3, LEFTY2, TIMP1, CD36, CD44 |
| 1270302 | Developmental Biology | 6.14E-03 | 8.76E-02 | 6.28E-01 | 1.00E+00 | 41 | ABL1, PDGFRB, RPS6KA2, SEMA3A, SLIT2, MYL9, FGFR3, VCL, COL4A1, COL4A2, FOXO1, COL4A5, COL6A1, COL6A2, COL6A3, VWF, SLIT3, NCOA1, PRKCA, FYN, MYH11, MYO10, SPTAN1, ITGA1, GFRA2, STAT3, TCF4, DPYSL2, RARA, LAMC1, EBF1, TEK, PIP5K1C, CCND3, LEFTY2, ABLIM1, CD36, SPRED1, AGRN, SMAD3, EPHA3 |
| 1269310 | Cytokine Signaling in Immune system | 6.57E-03 | 9.18E-02 | 6.58E-01 | 1.00E+00 | 31 | CRLF1, UBE2L6, PDGFRB, IFITM3, FGFR3, VCAM1, VCL, COL1A2, FOXO1, VWF, IFITM2, IFNGR2, FSCN1, FYN, SPTAN1, B2M, TNFRSF14, CCND1, NDN, GFRA2, STAT3, BST2, TRIM8, TEK, HAVCR2, TIMP1, CD36, CD44, SPRED1, IRAK3, TNFRSF1B |
PPI network establishment and modules selection
By using the STRING database, the PPI network of DEGs was established and consisted of 4687 nodes and 11236 edges (Figure 3). A total of ten hub genes were selected for key biomarker identification and are listed in Table 5. They consisted of five up-regulated genes (HSP90AA1, EGFR, RPS13, RBX1 and PAK1) and five down-regulated genes (FYN, ABL1, SMAD3, STAT3 and PRKCA). Then PEWCC1 was used to find clusters in the network. Four modules were calculated according to k-core = 2. Among them, module 1 contained 16 nodes and 32 edges, with the highest score (Figure 4A) and module 2 contained 16 nodes and 34 edges (Figure 4B). We performed the functional analysis for the top 2 modules. In functional enrichment analysis, the DEGs of module 1 were mostly enriched in post-translational protein modification, developmental biology and macromolecule catabolic process; the DEGs of module 2 in supramolecular complex and localization of cell.
Figure 3. PPI network of DEGs.
The PPI network of DEGs was constructed using Cytoscape. Up-regulated genes are marked in green; down-regulated genes are marked in red.
Table 5. Topology table for up- and down-regulated genes.
| Regulation | Node | Degree | Betweenness | Stress | Closeness |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up | HSP90AA1 | 655 | 0.22721 | 81351654 | 0.412863 |
| Up | EGFR | 324 | 0.081831 | 21358048 | 0.396682 |
| Up | RPS13 | 176 | 0.040553 | 21024400 | 0.332742 |
| Up | RBX1 | 132 | 0.02978 | 9542636 | 0.3408 |
| Up | PAK1 | 115 | 0.016755 | 4561194 | 0.37158 |
| Up | CSNK2A2 | 112 | 0.026157 | 6172590 | 0.354758 |
| Up | PAK2 | 107 | 0.012051 | 4334042 | 0.349858 |
| Up | DDB1 | 105 | 0.024917 | 6240978 | 0.340602 |
| Up | PSMC4 | 101 | 0.019368 | 3810802 | 0.348739 |
| Up | DVL3 | 99 | 0.017256 | 5360158 | 0.344762 |
| Up | UBE2D3 | 96 | 0.018158 | 6872298 | 0.333975 |
| Up | SMARCB1 | 90 | 0.021042 | 7085456 | 0.333215 |
| Up | STAT5B | 89 | 0.005633 | 1782886 | 0.349937 |
| Up | STX5 | 86 | 0.021729 | 5783250 | 0.327692 |
| Up | UBE2A | 86 | 0.01665 | 6800442 | 0.330652 |
| Up | NUP153 | 81 | 0.019493 | 3839268 | 0.33388 |
| Up | JUP | 79 | 0.012614 | 3875882 | 0.320148 |
| Up | PSMA3 | 78 | 0.009276 | 2735940 | 0.330535 |
| Up | SH3KBP1 | 76 | 0.011315 | 2648130 | 0.345321 |
| Up | HSPB1 | 69 | 0.012593 | 3676246 | 0.34167 |
| Up | BET1 | 67 | 0.013941 | 4543480 | 0.325711 |
| Up | AMFR | 66 | 0.018899 | 2411936 | 0.345907 |
| Up | RRAS2 | 64 | 0.00438 | 2166928 | 0.301914 |
| Up | MARK2 | 63 | 0.012107 | 3287228 | 0.338315 |
| Up | CBX5 | 62 | 0.015481 | 3171408 | 0.327807 |
| Up | CEBPB | 62 | 0.007601 | 2245984 | 0.350172 |
| Up | PDPK1 | 62 | 0.005919 | 1612918 | 0.342169 |
| Up | HNRNPH1 | 59 | 0.013608 | 2423406 | 0.335625 |
| Up | DNAJB1 | 58 | 0.00611 | 1362926 | 0.344205 |
| Up | ATF3 | 57 | 0.005226 | 1555506 | 0.352755 |
| Up | SPATA13 | 56 | 0.00717 | 2217896 | 0.295759 |
| Up | FURIN | 55 | 0.017306 | 2333572 | 0.332317 |
| Up | RHOBTB1 | 54 | 0.005265 | 891404 | 0.309798 |
| Up | SNAP23 | 52 | 0.010301 | 2133980 | 0.326551 |
| Up | STX11 | 49 | 0.006356 | 1012388 | 0.276999 |
| Up | TBK1 | 48 | 0.00946 | 1612462 | 0.346521 |
| Up | RAB25 | 48 | 0.00796 | 4209932 | 0.282579 |
| Up | ING2 | 42 | 0.006848 | 2338492 | 0.325236 |
| Up | ULK1 | 42 | 0.007643 | 7120856 | 0.274292 |
| Up | UCHL3 | 42 | 0.007629 | 1994146 | 0.325779 |
| Up | PFN2 | 41 | 0.004889 | 1200798 | 0.329235 |
| Up | CAP2 | 40 | 0.002011 | 661156 | 0.288156 |
| Up | UBA3 | 40 | 0.005749 | 1625200 | 0.326187 |
| Up | DYRK1A | 40 | 0.004394 | 1121650 | 0.309634 |
| Up | RBM22 | 39 | 0.01146 | 1346380 | 0.322616 |
| Up | TXK | 38 | 0.001513 | 482866 | 0.300558 |
| Up | TAF7 | 38 | 0.010147 | 1476134 | 0.322972 |
| Up | CAMK2G | 38 | 0.007152 | 1050770 | 0.341969 |
| Up | ATF4 | 37 | 0.006742 | 1255258 | 0.328036 |
| Up | TLR3 | 36 | 0.004686 | 1054636 | 0.305217 |
| Up | MYO9A | 36 | 8.05E-04 | 406980 | 0.28752 |
| Up | BABAM1 | 36 | 0.008431 | 1423346 | 0.324044 |
| Up | STK26 | 36 | 0.008804 | 1319200 | 0.323842 |
| Up | ACTR3C | 35 | 0.002617 | 659206 | 0.282732 |
| Up | CREB5 | 35 | 0.001154 | 566084 | 0.298035 |
| Up | NET1 | 33 | 0.003076 | 787876 | 0.327189 |
| Up | EEF1B2 | 32 | 0.00465 | 1484558 | 0.32501 |
| Up | AHR | 32 | 0.003156 | 847220 | 0.347858 |
| Up | PIP5K1B | 31 | 0.00183 | 957308 | 0.326391 |
| Up | CLN3 | 31 | 0.007159 | 992822 | 0.323485 |
| Up | HES1 | 30 | 0.0035 | 796872 | 0.300115 |
| Up | RBBP6 | 29 | 0.008094 | 1087968 | 0.324089 |
| Up | AP1G2 | 29 | 0.008892 | 933344 | 0.321377 |
| Up | RDX | 29 | 0.003378 | 953914 | 0.325146 |
| Up | RGPD8 | 28 | 0.002967 | 626564 | 0.32295 |
| Up | HSD3B1 | 28 | 0.009418 | 6545696 | 0.230497 |
| Up | COG3 | 27 | 0.00261 | 458374 | 0.24988 |
| Up | ATP6V0C | 27 | 0.008472 | 953284 | 0.320959 |
| Up | TFRC | 27 | 0.004398 | 847110 | 0.329004 |
| Up | TIAL1 | 27 | 0.005954 | 1083682 | 0.323485 |
| Up | DCP2 | 27 | 0.007451 | 4215608 | 0.243872 |
| Up | CAPZA1 | 26 | 0.002869 | 626878 | 0.325191 |
| Up | FKBP2 | 25 | 0.003414 | 683462 | 0.282255 |
| Up | TWIST1 | 24 | 0.001372 | 488874 | 0.298643 |
| Up | TIMP2 | 24 | 0.001662 | 741652 | 0.250924 |
| Up | SPTLC1 | 24 | 0.008272 | 878220 | 0.320827 |
| Up | DAPK1 | 24 | 0.003354 | 582304 | 0.3437 |
| Up | STT3B | 23 | 0.005888 | 688678 | 0.320805 |
| Up | RBMS1 | 23 | 0.005223 | 803708 | 0.322772 |
| Up | ANK3 | 21 | 0.004965 | 565126 | 0.321819 |
| Up | TDG | 21 | 0.00124 | 515588 | 0.326346 |
| Up | CHMP5 | 20 | 0.00503 | 681262 | 0.320915 |
| Up | MBD2 | 20 | 0.003168 | 3223460 | 0.265195 |
| Up | TRIM25 | 20 | 0.002013 | 463938 | 0.326073 |
| Up | TEAD3 | 20 | 0.001225 | 501618 | 0.323954 |
| Up | SLC3A2 | 20 | 0.005187 | 569152 | 0.332435 |
| Up | BMP1 | 19 | 0.00311 | 565522 | 0.259095 |
| Up | RHOBTB3 | 19 | 0.002152 | 346198 | 0.322439 |
| Up | CHD2 | 19 | 0.00121 | 998828 | 0.256894 |
| Up | RYBP | 19 | 0.002415 | 541940 | 0.322572 |
| Up | GLRX | 18 | 0.00459 | 583470 | 0.320959 |
| Up | KMT2C | 18 | 0.003676 | 553422 | 0.285019 |
| Up | YTHDC1 | 18 | 0.003349 | 530960 | 0.33407 |
| Up | GRB7 | 18 | 5.17E-04 | 151894 | 0.294958 |
| Up | IWS1 | 17 | 0.004258 | 1715034 | 0.236798 |
| Up | TRAF3IP2 | 17 | 0.001901 | 398464 | 0.324246 |
| Up | CSF3R | 17 | 0.001832 | 324530 | 0.329027 |
| Up | AFF1 | 17 | 0.003482 | 1512904 | 0.247805 |
| Up | INO80C | 17 | 0.003498 | 441732 | 0.321245 |
| Up | CASP4 | 17 | 0.002253 | 931980 | 0.263822 |
| Up | YIPF6 | 17 | 0.003441 | 5013996 | 0.201367 |
| Up | PCGF1 | 16 | 0.003259 | 409788 | 0.320827 |
| Up | CXCR2 | 16 | 0.003899 | 2017434 | 0.253558 |
| Up | ELF3 | 16 | 6.72E-04 | 203260 | 0.333452 |
| Up | USP33 | 16 | 0.002932 | 430028 | 0.322927 |
| Up | AGFG1 | 15 | 0.003227 | 435804 | 0.321443 |
| Up | LNPEP | 14 | 7.10E-04 | 211470 | 0.322483 |
| Up | RORA | 14 | 0.001493 | 299584 | 0.282187 |
| Up | LARP1B | 14 | 0.004683 | 546700 | 0.321708 |
| Up | ACSL4 | 14 | 0.005208 | 423594 | 0.320388 |
| Up | ESRRG | 14 | 0.001317 | 573474 | 0.244687 |
| Up | MXD1 | 13 | 6.21E-04 | 548286 | 0.273427 |
| Up | GET4 | 13 | 0.001988 | 297146 | 0.321113 |
| Up | NFE2 | 13 | 0.001758 | 361494 | 0.277475 |
| Up | SCNN1B | 13 | 0.001794 | 293352 | 0.321863 |
| Up | TBX3 | 11 | 0.00107 | 660104 | 0.254826 |
| Up | TAF1B | 11 | 0.00167 | 339720 | 0.323106 |
| Up | ADK | 11 | 0.003862 | 318638 | 0.320257 |
| Up | CLK3 | 11 | 0.001752 | 276054 | 0.272997 |
| Up | PELI1 | 10 | 0.001025 | 246998 | 0.322195 |
| Up | PHYHIPL | 2 | 1.23E-05 | 3410 | 0.238801 |
| Up | MAFF | 2 | 8.27E-06 | 5370 | 0.260986 |
| Up | TESK2 | 2 | 1.97E-05 | 2606 | 0.259425 |
| Up | MTMR4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.259138 |
| Up | ZFAND6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.230519 |
| Up | ACP1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.27858 |
| Up | EFS | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.27858 |
| Up | RAB11FIP5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.220331 |
| Up | CYP11A1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.187328 |
| Up | ADAM12 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.230951 |
| Up | FBXO9 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.25419 |
| Up | HSPB8 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.254674 |
| Up | CCNDBP1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.256234 |
| Up | LTBP3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.217731 |
| Up | FNTA | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.246424 |
| Up | ACOX3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.24266 |
| Up | PJA1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.24372 |
| Up | SERTAD4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.247308 |
| Up | EID2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.259138 |
| Up | AKTIP | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.254951 |
| Up | SPTLC3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.242911 |
| Up | SGSM1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.246424 |
| Up | LRRC69 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.292236 |
| Down | FYN | 305 | 0.060673 | 15146282 | 0.386124 |
| Down | ABL1 | 256 | 0.044808 | 14298188 | 0.385806 |
| Down | SMAD3 | 209 | 0.042609 | 22810928 | 0.349754 |
| Down | STAT3 | 202 | 0.037341 | 10226766 | 0.378422 |
| Down | PRKCA | 182 | 0.041662 | 11865040 | 0.377234 |
| Down | ACTA2 | 161 | 0.02569 | 7462512 | 0.366351 |
| Down | YWHAH | 149 | 0.028069 | 10474112 | 0.350015 |
| Down | ACTG2 | 131 | 0.011051 | 3779892 | 0.354141 |
| Down | RPL14 | 127 | 0.022838 | 13966136 | 0.331377 |
| Down | PDGFRB | 123 | 0.013902 | 4225738 | 0.358778 |
| Down | CCND1 | 119 | 0.017659 | 8841110 | 0.344483 |
| Down | PPM1F | 119 | 0.016265 | 6535610 | 0.32041 |
| Down | CAV1 | 113 | 0.018938 | 4593828 | 0.368628 |
| Down | YWHAQ | 101 | 0.013637 | 4845932 | 0.355674 |
| Down | FOXO1 | 96 | 0.015104 | 5652522 | 0.349128 |
| Down | WNT3A | 95 | 0.013629 | 4052094 | 0.299674 |
| Down | RHOQ | 92 | 0.016733 | 3678142 | 0.331471 |
| Down | TUBB2A | 91 | 0.012587 | 3886552 | 0.334213 |
| Down | FGFR3 | 83 | 0.010949 | 3642512 | 0.326755 |
| Down | RARA | 81 | 0.013223 | 4465300 | 0.341869 |
| Down | MYH11 | 72 | 0.01194 | 3062450 | 0.35249 |
| Down | HIPK2 | 72 | 0.01135 | 3565432 | 0.339639 |
| Down | HSPA12B | 68 | 0.003037 | 744544 | 0.301991 |
| Down | RPS6KA2 | 68 | 0.005549 | 2522498 | 0.317738 |
| Down | TEK | 66 | 0.004665 | 1653094 | 0.338168 |
| Down | NCOA1 | 65 | 0.008395 | 3153458 | 0.31475 |
| Down | VCL | 63 | 0.009681 | 2780132 | 0.338217 |
| Down | TUBB2B | 62 | 0.00676 | 1694194 | 0.343977 |
| Down | PPP2R2B | 62 | 0.010479 | 4191976 | 0.328542 |
| Down | TPM2 | 62 | 0.006776 | 1763750 | 0.334428 |
| Down | SPTAN1 | 62 | 0.011399 | 2596256 | 0.334046 |
| Down | MYL9 | 60 | 0.008098 | 2479906 | 0.335361 |
| Down | DIMT1 | 58 | 0.008481 | 2242228 | 0.327326 |
| Down | TCF4 | 54 | 0.009445 | 2760706 | 0.330629 |
| Down | MRPL34 | 52 | 0.006656 | 17810170 | 0.236106 |
| Down | CCND3 | 51 | 0.003239 | 1601134 | 0.295927 |
| Down | LMNA | 47 | 0.00911 | 2401846 | 0.338682 |
| Down | PKN1 | 46 | 0.003592 | 1349794 | 0.299559 |
| Down | CD44 | 46 | 0.010187 | 2270300 | 0.349493 |
| Down | DCN | 45 | 0.007594 | 1930616 | 0.322283 |
| Down | ADCY3 | 45 | 0.008618 | 1694556 | 0.33133 |
| Down | TGFB1I1 | 45 | 0.003137 | 931752 | 0.325349 |
| Down | EPHA3 | 44 | 0.002379 | 661600 | 0.318884 |
| Down | FZD4 | 43 | 0.005096 | 1738748 | 0.327006 |
| Down | RND3 | 42 | 0.006152 | 1123788 | 0.333832 |
| Down | ADCY4 | 41 | 0.001819 | 672196 | 0.287785 |
| Down | ETS2 | 41 | 0.004246 | 1834106 | 0.329559 |
| Down | RAP2A | 40 | 0.007351 | 1433240 | 0.326983 |
| Down | CCND2 | 40 | 0.002601 | 1155154 | 0.334046 |
| Down | AXIN2 | 39 | 0.00394 | 1203884 | 0.333618 |
| Down | OPTN | 37 | 0.00695 | 1707428 | 0.328289 |
| Down | UBE2L6 | 37 | 0.005601 | 1462120 | 0.327189 |
| Down | PIP5K1C | 37 | 0.002815 | 1263578 | 0.334714 |
| Down | MAP1B | 34 | 0.007029 | 1488054 | 0.325371 |
| Down | AXL | 34 | 0.002374 | 729250 | 0.345881 |
| Down | IRAK3 | 33 | 8.12E-04 | 865022 | 0.277229 |
| Down | FLNA | 33 | 0.004649 | 1087030 | 0.310146 |
| Down | COL1A1 | 32 | 0.008312 | 1395294 | 0.32942 |
| Down | DLL1 | 31 | 0.006383 | 1006300 | 0.324583 |
| Down | JAG1 | 29 | 0.005281 | 874336 | 0.325033 |
| Down | PDE9A | 29 | 0.003164 | 644058 | 0.281577 |
| Down | AGTR1 | 28 | 0.004101 | 926250 | 0.304088 |
| Down | TNNT3 | 27 | 1.64E-04 | 89708 | 0.268585 |
| Down | MYO10 | 27 | 0.002183 | 551478 | 0.325892 |
| Down | GPC4 | 26 | 0.001618 | 1207760 | 0.258652 |
| Down | IGFBP3 | 26 | 0.004163 | 894182 | 0.300288 |
| Down | ABCE1 | 25 | 0.007191 | 831802 | 0.321973 |
| Down | TIMP1 | 23 | 0.006574 | 950444 | 0.322905 |
| Down | VTN | 23 | 0.005502 | 970948 | 0.284138 |
| Down | ARAP3 | 23 | 8.48E-04 | 298776 | 0.326642 |
| Down | COL1A2 | 23 | 0.001462 | 373484 | 0.28554 |
| Down | B2M | 23 | 0.00758 | 619198 | 0.322505 |
| Down | TBCB | 22 | 0.002726 | 428028 | 0.322705 |
| Down | VASN | 22 | 0.003962 | 582444 | 0.343574 |
| Down | LGALS1 | 21 | 0.004371 | 578082 | 0.333903 |
| Down | CD81 | 21 | 0.005039 | 710796 | 0.323708 |
| Down | VCAM1 | 21 | 0.003333 | 2717522 | 0.2699 |
| Down | THY1 | 21 | 0.003795 | 675432 | 0.288956 |
| Down | PHGDH | 21 | 0.004117 | 689964 | 0.323999 |
| Down | ITPR3 | 21 | 0.003472 | 727920 | 0.327326 |
| Down | TGFB3 | 20 | 0.002631 | 725004 | 0.278316 |
| Down | BIN1 | 20 | 0.002083 | 351704 | 0.291835 |
| Down | LPAR1 | 20 | 0.001469 | 1296676 | 0.242258 |
| Down | MSX1 | 20 | 0.003633 | 648486 | 0.289134 |
| Down | SLIT2 | 20 | 0.001084 | 281232 | 0.291273 |
| Down | SHMT2 | 19 | 0.005637 | 547666 | 0.32215 |
| Down | COL4A1 | 19 | 0.001742 | 983934 | 0.257813 |
| Down | RAB3IL1 | 19 | 0.002314 | 1857444 | 0.231054 |
| Down | SPARC | 17 | 0.002023 | 197820 | 0.275923 |
| Down | VCAN | 17 | 0.003487 | 561304 | 0.267405 |
| Down | LDB2 | 17 | 0.003396 | 1291388 | 0.254812 |
| Down | DPYSL2 | 17 | 0.003321 | 506826 | 0.325869 |
| Down | MAF | 17 | 0.001088 | 288082 | 0.289456 |
| Down | PARVA | 16 | 0.003041 | 421786 | 0.323731 |
| Down | TNFRSF1B | 16 | 0.001419 | 325188 | 0.32382 |
| Down | FBLN2 | 16 | 0.001835 | 589690 | 0.249987 |
| Down | EEF2K | 15 | 0.001411 | 364288 | 0.323083 |
| Down | TEAD2 | 15 | 7.99E-04 | 352390 | 0.324066 |
| Down | TAGLN | 15 | 0.001241 | 205764 | 0.280381 |
| Down | FASN | 15 | 0.001757 | 367956 | 0.322084 |
| Down | CD36 | 15 | 0.002116 | 386412 | 0.294661 |
| Down | NDN | 15 | 0.003831 | 473694 | 0.322239 |
| Down | ADAM15 | 15 | 0.001982 | 294010 | 0.331283 |
| Down | ARHGEF2 | 15 | 9.41E-04 | 262426 | 0.330396 |
| Down | PEMT | 14 | 0.005116 | 629532 | 0.293664 |
| Down | VWF | 14 | 0.001828 | 345586 | 0.275097 |
| Down | OXTR | 14 | 0.001359 | 1221820 | 0.23325 |
| Down | FRYL | 14 | 0.001994 | 332012 | 0.321598 |
| Down | AGRN | 14 | 0.001733 | 263834 | 0.326482 |
| Down | LFNG | 13 | 0.001654 | 331212 | 0.264357 |
| Down | ARHGEF6 | 13 | 0.001032 | 179796 | 0.326573 |
| Down | TSC22D3 | 13 | 1.34E-04 | 119696 | 0.32391 |
| Down | IMPDH1 | 13 | 0.002712 | 390200 | 0.321554 |
| Down | NME4 | 12 | 0.003215 | 901430 | 0.228485 |
| Down | EHD2 | 12 | 0.003128 | 309602 | 0.320717 |
| Down | RGL1 | 12 | 5.53E-04 | 670384 | 0.247308 |
| Down | COL18A1 | 12 | 0.001098 | 309928 | 0.266008 |
| Down | ADGRA2 | 12 | 8.13E-04 | 196338 | 0.301583 |
| Down | FMOD | 11 | 2.68E-04 | 98450 | 0.300385 |
| Down | SLIT3 | 10 | 6.95E-05 | 22762 | 0.24207 |
| Down | COL5A1 | 3 | 4.31E-05 | 14682 | 0.244636 |
| Down | TGFBI | 3 | 8.62E-06 | 14986 | 0.248607 |
| Down | RASIP1 | 2 | 1.64E-06 | 1660 | 0.251732 |
| Down | CAV2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.285836 |
| Down | PCOLCE | 2 | 3.25E-05 | 6584 | 0.246761 |
| Down | COL4A2 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.208517 |
| Down | SVIL | 2 | 0 | 0 | 0.262801 |
| Down | SMTN | 2 | 7.00E-06 | 2536 | 0.261073 |
| Down | COL4A5 | 2 | 7.45E-06 | 6672 | 0.244776 |
| Down | FSCN1 | 2 | 2.41E-06 | 2090 | 0.268585 |
| Down | ADAMTS1 | 2 | 5.19E-05 | 3268 | 0.250857 |
| Down | CTSC | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.244559 |
| Down | FEZ1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.21526 |
| Down | MALL | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.269357 |
| Down | LYL1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.248489 |
| Down | SEMA3A | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.27858 |
| Down | ENPP2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.195022 |
| Down | BST2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.24757 |
| Down | F3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.236738 |
| Down | COL16A1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.204978 |
| Down | ANGPTL2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.252724 |
| Down | NCALD | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.250508 |
| Down | RASL12 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.228262 |
| Down | PPP1R14A | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.273923 |
| Down | FCGRT | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.243872 |
| Down | CNN2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.268139 |
| Down | EHBP1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.242848 |
| Down | COL3A1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.216264 |
| Down | DDIT4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.25408 |
| Down | ITM2C | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.249441 |
| Down | GAS6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.257007 |
| Down | FERMT2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.252751 |
| Down | RAPGEF5 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.246424 |
| Down | APCDD1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.230588 |
| Down | MMP23B | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.200599 |
| Down | PTPRD | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.274549 |
| Down | RSPO3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.249441 |
| Down | COL6A1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.243745 |
| Down | DDR2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.247805 |
| Down | NEK6 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.244776 |
| Down | COL5A2 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.205788 |
| Down | TSPAN4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.244559 |
| Down | IFITM3 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.27858 |
| Down | HES4 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.261875 |
| Down | FAT1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.242521 |
Figure 4. Modules of isolated form PPI of DEGs.
(A) The most significant module was obtained from PPI network with 16 nodes and 32 edges for up-regulated genes. (B) The most significant module was obtained from PPI network with 16 nodes and 34 edges for down-regulated genes. Up-regulated genes are marked in green; down-regulated genes are marked in red.
MiRNA–hub gene regulatory network construction
miRNet database was applied to screen the targeted miRNAs of the hub genes. Cytoscape software was used to construct the miRNA–hub gene network. As illustrated in Figure 5, the interaction network consists of 307 hub genes and 2280 miRNAs. The hub genes and miRNAs in the network were ranked by their degree of connectivity using Network Analyzer and are listed in Table 6. Based on the expression trend of hub genes in GDM, we found that UBE2D3 was the predicted target of hsa-mir-6127, HSP90AA1 was the predicted target of hsa-let-7d-5p, PAK2 was the predicted target of hsa-mir-8063, DDB1 was the predicted target of hsa-mir-329-3p, DVL3 was the predicted target of hsa-mir-1207-5p, FYN was the predicted target of hsa-mir-4651, ABL1 was the predicted target of hsa-mir-410-5p, SMAD3 was the predicted target of hsa-mir-222-3p, STAT3 was the predicted target of hsa-mir-29c-3p and PRKCA was the predicted target of hsa-mir-663a.
Figure 5. MiRNA–hub gene regulatory network.
The light purple color diamond nodes represent the key miRNAs; up-regulated genes are marked in green; down-regulated genes are marked in red.
Table 6. miRNA–hub gene and TF–hub gene interactions.
| Regulation | Hub Genes | Degree | MicroRNA | Regulation | Hub Genes | Degree | TF |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Up | UBE2D3 | 189 | hsa-mir-6127 | Up | HSP90AA1 | 45 | E2F1 |
| Up | HSP90AA1 | 188 | hsa-let-7d-5p | Up | UBE2D3 | 43 | HCFC1 |
| Up | PAK2 | 158 | hsa-mir-8063 | Up | EGFR | 39 | SRY |
| Up | DDB1 | 108 | hsa-mir-329-3p | Up | PSMC4 | 34 | ZFX |
| Up | DVL3 | 104 | hsa-mir-1207-5p | Up | DDB1 | 32 | RUNX1 |
| Up | EGFR | 83 | hsa-mir-181a-2-3p | Up | STAT5B | 28 | ESR1 |
| Up | UBE2A | 60 | hsa-mir-5700 | Up | PAK2 | 27 | REST |
| Up | PSMC4 | 47 | hsa-mir-665 | Up | RBX1 | 27 | YY1 |
| Up | CSNK2A2 | 45 | hsa-mir-30d-3p | Up | STX5 | 24 | SREBF2 |
| Up | STAT5B | 42 | hsa-mir-1343-3p | Up | CSNK2A2 | 21 | SIN3A |
| Up | PAK1 | 31 | hsa-mir-629-3p | Up | RPS13 | 19 | ASH2L |
| Up | RBX1 | 29 | hsa-mir-4513 | Up | SMARCB1 | 18 | EGR1 |
| Up | SMARCB1 | 21 | hsa-mir-192-5p | Up | DVL3 | 17 | TTF2 |
| Up | STX5 | 15 | hsa-mir-146a-5p | Up | PAK1 | 16 | TP63 |
| Up | RPS13 | 10 | hsa-mir-15b-3p | Up | UBE2A | 11 | TRIM28 |
| Down | CCND1 | 396 | hsa-mir-4651 | Down | STAT3 | 67 | SPI1 |
| Down | STAT3 | 148 | hsa-mir-410-5p | Down | CCND1 | 56 | MYBL2 |
| Down | FOXO1 | 124 | hsa-mir-222-3p | Down | SMAD3 | 53 | SUZ12 |
| Down | CAV1 | 115 | hsa-mir-29c-3p | Down | FOXO1 | 44 | TBX3 |
| Down | ABL1 | 112 | hsa-mir-663a | Down | PRKCA | 43 | YAP1 |
| Down | YWHAH | 112 | hsa-mir-577 | Down | ABL1 | 40 | TEAD4 |
| Down | YWHAQ | 111 | hsa-mir-16-2-3p | Down | FYN | 39 | CEBPD |
| Down | RPL14 | 99 | hsa-mir-3960 | Down | YWHAQ | 38 | SOX9 |
| Down | PPM1F | 99 | hsa-mir-638 | Down | CAV1 | 36 | BMI1 |
| Down | SMAD3 | 78 | hsa-mir-744-5p | Down | YWHAH | 31 | RCOR3 |
| Down | PRKCA | 67 | hsa-mir-6727-3p | Down | RPL14 | 29 | LMO2 |
| Down | FYN | 61 | hsa-mir-429 | Down | PDGFRB | 28 | TAL1 |
| Down | ACTA2 | 42 | hsa-mir-376c-3p | Down | PPM1F | 18 | FOXP1 |
| Down | PDGFRB | 28 | hsa-mir-101-3p | Down | ACTA2 | 14 | E2F4 |
| Down | ACTG2 | 10 | hsa-mir-103a-3p | Down | ACTG2 | 8 | CUX1 |
TF–hub gene regulatory network construction
NetworkAnalyst database was applied to screen the targeted TFs of the hub genes. Cytoscape software was used to construct the TF–hub gene network. As illustrated in Figure 6, the interaction network consists of 306 hub genes and 195 TFs. The hub genes and TFs in the network were ranked by their degree of connectivity using Network Analyzer and are listed in Table 6. Based on the expression trend of hub genes in GDM, we found that HSP90AA1 was the predicted target of E2F1, UBE2D3 was the predicted target of HCFC1, EGFR was the predicted target of SRY, PSMC4 was the predicted target of ZFX, DDB1 was the predicted target of RUNX1, STAT3 was the predicted target of SPI1, CCND1 was the predicted target of MYBL2, SMAD3 was the predicted target of SUZ12, FOXO1 was the predicted target of TBX3 and PRKCA was the predicted target of YAP1.
Figure 6. TF–hub gene regulatory network.
The yellow color triangle nodes represent the key TFs; up-regulated genes are marked in green; down-regulated genes are marked in red.
ROC curve analysis
ROC curve analysis was implemented to evaluate the capacity of hub genes to distinguish GDM and non-GDM in E-MTAB-6418, HSP90AA1, EGFR, RPS13, RBX1, PAK1, FYN, ABL1, SMAD3, STAT3 and PRKCA, exhibiting better diagnostic efficiency for GDM and non-GDM, and the combined diagnosis of these ten hub genes was more effective. The AUC index for the ten hub gene scores were 0.906, 0.838, 0.825, 0.897, 0.863, 0.876, 0.855, 0.880, 0.932 and 0.872, and are shown in Figure 7.
Figure 7. ROC curve validated the sensitivity, specificity of hub genes as a predictive biomarker for GDM prognosis.
(A) HSP90AA1, (B) EGFR, (C) RPS13, (D) RBX1, (E) PAK1, (F) FYN, (G) ABL1, (H) SMAD3, (I) STAT3, (J) PRKCA.
RT-PCR analysis
To further verify the expression level of hub genes in GDM, RT-PCR was performed to calculate the mRNA levels of the ten hub genes identified in the present study (HSP90AA1, EGFR, RPS13, RBX1, PAK1, FYN, ABL1, SMAD3, STAT3 and PRKCA) in GDM. As illustrated in Figure 8, the expressions of HSP90AA1, EGFR, RPS13, RBX1, PAK1 were significantly up-regulated in GDM samples compared with normal, while FYN, ABL1, SMAD3, STAT3 and PRKCA were significantly down-regulated in GDM samples compared with normal. The present RT-PCR results were in-line with the aforementioned bioinformatics analysis, suggesting that these hub genes might be linked to the molecular mechanism underlying GDM.
Figure 8. Validation of hub genes by RT- PCR.
(A) HSP90AA1, (B) EGFR, (C) RPS13, (D) RBX1, (E) PAK1, (F) FYN, (G) ABL1, (H) SMAD3, (I) STAT3, (J) PRKCA.
Molecular docking experiments
In the recent findings, the docking study was performed using Biovia Discovery Studio perpetual software to analyze the binding pattern of the natural plant products such as herbs have the ability to lower blood glucose levels and ameliorate diabetes with decreased adverse side effects. The natural well-known phytoconstituents which decreases the blood sugar level are Malvidin 3-laminaribioside (MLR), Ferulic acid (FRA), Inosporone (INO), Allicin (ALL), Liriodenin (LIR), Azadirachitin (AZA), Sulforaphane, Cajanin (CAJ), Carvone (CAR), Capsaicin (CAP), Terpineol (TER), Phellandrene (PHE), Terpene (TPN), Ellagic acid (ELA), Leucodelphinidin, O-methyltylophorinidine (OMT), Gymnemic acid, β-Carotene (BCR), Leucocyanidin (LEC), Syringin (SYR), Ginsenoside (GNS), Phyllanthin (PHY), Punicalagin (PUC), Punicalin (PUN), Arjunic acid (AJA), Arjunetin (ARJ), Arabic acid (ARA), Arjungenin (ARG), Gingerol (GIN), Shogaol, Aloe emodin (ALE), Arabic acid (ARA), Aloin (ALO), Charantin (CHR), Cinnamic acid (CIN), Curcumin (CUR), Euginol (EUG), Gymnemagenin (GMG), Gymnestrogenin (GYM), Hydroxylucin (HYD), Methoxy hydroxyl chalcoli (MHC), Myricetin (MYR), Nimbine (NIM), Quercetin (QUE), Vicine (VIC) and Shagoal (SHA) are shown in Figure 9. The molecules were constructed based on the natural plant products containing these chemical constituents which play vital role in reducing type 2 diabetes mellitus. The traditional plant products are used in conjunction with allopathic drug to reduce the dose of the allopathic drugs and/or to increase the efficacy of allopathic drugs. Some common and most prominent antidiabetic plants and active principles were selected from their phytochemicals for docking studies in the present research to identify the active natural molecule to avoid the use of allopathic drugs in gestational diabetes and the blood sugar level is controlled by altering the diet. For docking experiments well-known and most commonly used two allopathic drugs such as Glyburide (GLY), Metformin (MET) in gestational diabetes are used as standard and to compare the binding interaction of natural phytoconstituents with allopathic drugs. A total of common 44 in that 42 natural active constituents, few from each of flavonoids, saponins, tannins and glycosides etc., present in plant extracts responsible for antidiabetic function and 2 allopathic drugs were chosen for docking studies on overexpressed proteins and the structures are depicted in Figure 1, respectively. The one protein from each overexpressed gene in gestational type 2 diabetes mellitus such as EGFR, HSP90AA1, PAK1 and RBX1 and their X-ray crystallographic structure and co-crystallized PDB code and their PDB codes 4UV7, 5NJX, 3Q4Z and 3FNI, respectively were constructed for docking. The docking on natural active constituents was conducted to classify the potential molecule and their binding affinity to proteins. A higher number of negative number -CDOCKER energy and binding energy indicates a stronger binding interactions with proteins, few constituents obtained with a greater -CDOCKER energy and binding energy respectively with particular proteins. Docking experiments were carried out on a total of 42 constituents from plant products, few constituents obtained excellent -CDOCKER energy and binding energy. Out of 44 molecules, few of the molecules obtained -CDOCKER interaction energy of more than 40 and majority with more than 30 and less than 40, few molecules obtained optimum -CDOCKER interaction energy of less than 30, respectively. the molecules with -CDOCKER interaction energy of 40 and above are said to have good interaction with proteins and stable. The natural constituents of the molecules GLY, GNS, GYM, MLR, PUC and ALO, GLY, MLRand ALE, ALO, BCR, CAP, CHR, ELA, LUR, GIN, GLY, GMG, GNS, GYM, LEC, LIR, MLR, MYR, NIM, OMP, PHY, PUC, PUN, QUE, SHE,VI C obtained a -CDOCKER interaction energy of more than 40 with protein of PDB codes 5NJX and 3FNI and 3Q4Z, respectively. The natural constituents obtained -CDOCKER interaction energy of less than 40 and more than 30 are ALO, ARJ, BCR, CHR, CUR, PHY, PUN and BCR, CAJ, CAP, CUR, GIN, LEC, MYR, OMP, QUE, VIC and AJA, ARA, ARG, CAJ, FRA, HYD, MHC and GNS, PHY, PUC, PUN with 5NJX and 3FNI and 3Q4Z and 4UV7. The constituents obtained less than 30 and more than 20 are AJA, ALE, ARG, CAJ, CAP, GIN, GMG, GYM, HYD, LEC, MHC, MLR, MYR, NIM, OMP, QUE, VIC and AJA, ALE, ALL, ARG, AJA,CHR, CIN, EUG, FRA, GMG, GNS, GYM, LIR, MHC, NIM, PUC and ALL, CIN, EUG, MET, TER and ALA, ALE, ALO, ARJ, BCR, CAJ, CHR, ELA, FRA, GIN, GMG, LEC, MLR, MYR, OMP, QUE, SHA with 5NJX and 3FNI and 3Q4Z and 4UV7. Following the molecules obtained less than 20 -CDOCKER interaction energy are ALL, ARA, CAR, CHR, CIN, EUG, FRA, LIR, MET, PHE, TER, TPN and ARJ, ARA, CAR, HYD, MET, PHE, TPN and CAR, PHE, TPN and AJA, ALL, ARG, CAR, CIN, EUG, GYM, HYD, LIR, MET, MHC, NIM, PHE, TER, TPN, VIC with protein 5NJX and 3FNI and 3Q4Z and 4UV7, respectively, the binding energy, -CDOCKER energy and -CDOCKER interaction energy are depicted in Table 7. The two molecules such as ALO and MAL (Figures 10 and 11), their interaction with amino acids of proteins with 3D structures for 3FN1 (Figure 12) and 3Q4Z (Figure 13), while 2D structures for 3FN1 (Figure 14) and 3Q4Z (Figure 15).
Figure 9. Chemical structures of phytoconstituents.
Table 7. Docking results of designed molecules on overexpressed proteins.
| Sl. No/Code | EGFR | HSP90AA1 | PAK1 | RBX1 | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PDB: 4UV7 | PDB:5NJX | PDB: 3Q4Z | PDB: 3FN1 | |||||||||
| Binding Energy | −Cdocker Energy | − Cdocker Interaction Energy | Binding Energy | −Cdocker Energy | − Cdocker Interaction Energy | Binding Energy | −Cdocker Energy | − Cdocker Interaction Energy | Binding Energy | −Cdocker Energy | − Cdocker Interaction Energy | |
| AJA | −56.02 | −10.57 | 18.17 | −77.05 | −6.93 | 21.66 | −196.65 | 13.03 | 43.86 | −113.94 | 5.61 | 37.90 |
| ALE | −22.04 | −17.45 | 10.55 | −16.93 | −16.44 | 12.00 | −58.34 | −2.81 | 24.49 | −24.28 | −9.71 | 18.84 |
| ALO | −6.22 | −25.19 | 8.57 | −2.69 | −24.11 | 9.65 | −4.41 | −19.09 | 14.60 | −11.36 | −18.02 | 15.96 |
| ARA | −50.94 | −28.62 | 19.50 | −57.53 | −18.31 | 26.43 | −159.25 | 8.76 | 57.02 | −83.85 | −16.52 | 33.54 |
| ARJ | −43.98 | 17.23 | 28.38 | −39.56 | 18.14 | 25.73 | −119.99 | 33.00 | 43.82 | −39.87 | 26.58 | 31.46 |
| ARG | −49.90 | 20.57 | 23.74 | −61.58 | 22.29 | 25.37 | −151.03 | 40.87 | 47.08 | −7.21 | −116.32 | 22.65 |
| ANA | −65.59 | −68.87 | 32.04 | −89.71 | −66.11 | 51.76 | −245.05 | −79.05 | 83.86 | −61.60 | 21.05 | 41.01 |
| ALL | −118.34 | −47.02 | 34.21 | −168.97 | −50.42 | 39.91 | −139.90 | −23.49 | 62.54 | −18.62 | −15.64 | 14.90 |
| CAR | −86.83 | 19.53 | 35.26 | −45.09 | 19.64 | 36.45 | −131.24 | 37.17 | 58.34 | −48.59 | −55.20 | 21.22 |
| CAJ | −6.67 | −21.05 | 9.42 | −6.26 | −20.34 | 10.30 | −9.30 | −16.06 | 13.09 | −47.54 | 28.64 | 30.02 |
| CAP | −35.79 | −58.29 | 19.06 | −42.81 | −50.54 | 28.01 | −172.32 | −28.95 | 57.88 | −6.63 | −25.87 | 30.85 |
| CAV | −65.69 | 22.19 | 25.24 | −53.63 | 25.00 | 27.33 | −136.49 | 43.84 | 47.47 | −46.65 | 19.83 | 28.55 |
| CHA | −4.05 | −30.55 | 21.32 | −35.08 | −30.24 | 21.35 | −107.73 | −7.42 | 44.11 | −27.07 | 13.28 | 14.79 |
| CHL | −14.17 | 8.84 | 17.63 | −49.92 | 15.28 | 24.60 | −81.41 | 27.24 | 34.82 | −80.66 | −26.20 | 43.47 |
| CIN | −50.02 | 12.60 | 14.67 | −27.06 | 11.55 | 13.70 | −92.97 | 18.99 | 21.39 | −29.49 | −17.74 | 24.17 |
| CUR | −61.32 | −38.90 | 27.73 | −64.69 | −22.71 | 40.68 | −276.18 | 16.00 | 87.65 | −61.40 | 18.48 | 32.45 |
| ELL | −40.77 | −22.62 | 18.69 | −34.20 | −24.49 | 16.72 | −137.67 | 1.59 | 41.48 | −73.55 | 20.96 | 35.11 |
| EUG | −71.25 | 14.65 | 28.33 | −71.08 | 13.46 | 27.19 | −149.04 | 30.21 | 46.83 | −40.14 | −27.96 | 25.52 |
| FER | −84.22 | 11.92 | 24.50 | −38.93 | 14.41 | 25.46 | −157.42 | 32.92 | 48.59 | −74.77 | −97.25 | 24.35 |
| GIN | −26.63 | −36.38 | 14.98 | −51.74 | −30.08 | 21.65 | −135.45 | −15.24 | 39.95 | −47.21 | 14.33 | 17.68 |
| GNS | −36.67 | 10.71 | 17.53 | −41.60 | 12.11 | 20.48 | −132.64 | 26.84 | 30.74 | −84.78 | −82.04 | 29.12 |
| GYM | −41.53 | −84.64 | 23.43 | −52.36 | −79.44 | 27.80 | −110.88 | −55.77 | 55.03 | −78.34 | −164.85 | 26.81 |
| GYA | −75.68 | −162.34 | 32.37 | −86.27 | −145.33 | 40.68 | −160.78 | −122.08 | 67.89 | −75.89 | 20.89 | 41.44 |
| GMT | −4.26 | −99.21 | 17.86 | −72.64 | −91.68 | 25.64 | −109.57 | −79.81 | 40.10 | −47.57 | 30.04 | 32.56 |
| HYD | −68.08 | 19.53 | 34.12 | −125.59 | 23.82 | 41.37 | −158.25 | 41.54 | 59.92 | −20.94 | 20.67 | 23.23 |
| INO | −50.91 | 24.87 | 26.12 | −43.89 | 24.42 | 27.14 | −87.39 | 39.52 | 44.59 | −28.20 | 15.41 | 23.15 |
| LEU | −38.73 | 18.54 | 21.60 | −26.25 | 15.39 | 18.10 | −122.22 | 27.38 | 32.75 | −48.37 | 26.66 | 39.62 |
| LEP | −16.17 | 7.13 | 15.51 | −21.35 | 8.09 | 16.21 | −62.06 | 19.28 | 25.76 | −31.27 | 18.48 | 20.64 |
| LIR | −53.70 | 9.95 | 22.56 | −84.07 | 18.36 | 27.30 | −142.76 | 31.85 | 41.89 | −29.11 | −73.02 | 27.80 |
| MAL | −58.66 | 21.70 | 30.45 | −34.92 | 23.71 | 32.09 | −138.59 | 36.48 | 50.57 | −24.50 | −15.13 | 18.76 |
| MHC | −28.62 | 13.37 | 15.74 | −32.04 | 13.89 | 16.17 | −33.87 | 21.61 | 22.73 | −40.19 | −77.90 | 31.36 |
| MYR | −22.60 | −74.73 | 29.54 | −51.69 | −68.66 | 31.40 | −94.78 | −45.63 | 63.61 | −48.31 | 20.69 | 36.63 |
| NIM | −17.29 | −20.00 | 11.23 | −22.94 | −18.68 | 12.75 | −39.38 | −11.59 | 19.23 | −73.77 | 21.14 | 30.96 |
| MPO | −26.31 | −85.18 | 28.60 | −27.95 | −81.28 | 30.13 | −62.20 | −67.23 | 48.83 | −49.69 | −107.43 | 17.79 |
| PHE | −52.17 | 12.68 | 21.80 | −59.98 | 17.35 | 28.95 | −140.57 | 34.70 | 49.40 | −51.52 | −95.45 | 20.50 |
| PUN | −23.27 | −121.88 | 26.67 | −62.56 | 19.02 | 28.47 | −100.15 | 27.33 | 36.00 | −6.35 | 3.83 | 17.39 |
| PUC | −22.94 | −98.54 | 23.93 | −110.98 | −114.66 | 31.90 | −147.91 | −67.17 | 73.20 | −25.35 | −112.29 | 24.27 |
| QUE | −25.04 | −95.41 | 19.39 | −29.38 | −88.29 | 31.16 | −182.08 | −73.82 | 62.28 | −119.62 | 14.22 | 41.65 |
| SHA | −62.78 | 4.01 | 17.60 | −97.71 | −87.07 | 28.88 | −133.51 | −71.22 | 39.42 | −38.98 | 22.34 | 28.18 |
| SYR | −42.02 | −112.72 | 18.53 | −57.33 | 0.94 | 14.08 | −111.64 | 16.61 | 30.08 | −28.67 | 15.86 | 22.42 |
| TER | −48.17 | 3.01 | 26.96 | −45.14 | −109.25 | 24.75 | −88.49 | −99.19 | 31.30 | −55.95 | 20.86 | 33.04 |
| TPN | −48.96 | 17.76 | 22.80 | −58.53 | 5.58 | 30.24 | −151.71 | 24.04 | 55.75 | −38.43 | 15.22 | 28.09 |
| VIC | −49.26 | 11.32 | 17.70 | −60.62 | 17.96 | 23.33 | −150.32 | 32.32 | 43.25 | −15.63 | 21.72 | 55.13 |
| GLY | −49.25 | 15.93 | 28.98 | −46.36 | 9.39 | 14.16 | −83.17 | 23.57 | 29.57 | −25.71 | 18.79 | 28.22 |
| MET | −35.21 | 18.35 | 32.89 | −25.62 | 34.77 | 17.74 | −196.65 | 13.03 | 43.86 | −61.04 | 27.56 | 32.39 |
Figure 10. Structure of ALO.
Figure 11. Structure of MAL.
Figure 12. 3D binding of ALO with 3FN1.
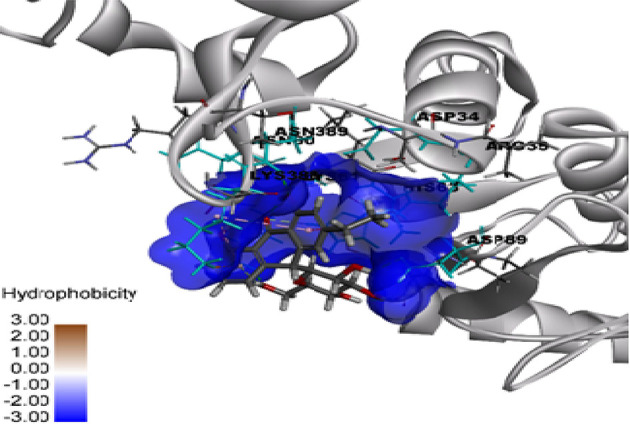
Figure 13. 3D binding of MAL with 3Q4Z.
Figure 14. 2D binding of ALO with 3FN1.
Figure 15. 2D binding of MAL with 3Q4Z.
Discussion
GDM is a metabolic disorder that can be caused by various factors, including genetics and the endocrine system. It is essential to understand the molecular mechanisms underlying GDM in order to find and advance more valid diagnostic and therapeutic strategies. Gene chip technology is generally used to reveal the expression levels of numerous genes within the human genome and might help in the recognition of target genes of interest for diagnosing or treating GDM.
In our study, a total of 869 DEGs were screened, including 439 up-regulated genes and 430 down-regulated genes. The CGB5 was associated with pregnancy success and might be a possible genetic marker for pregnancy success [30]. Studies have reported that corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) [31], PSG1 [32] and CYP19A1 [33] are directly related to the development preeclampsia. CD248 has become an attractive target for hypertension [34], but this gene might be novel target for GDM. A previous study showed that COL1A1 [35] was expressed in type 2 diabetes mellitus, but this gene might be novel target for GDM. In a recent study, ABI3BP could facilitate the progression of cardiovascular diseases [36], but this gene might be novel target for GDM. In previous studies, there was a large amount of evidence that MFAP4 [37] directly or indirectly affects the occurrence and development of type 1 diabetes mellitus, but this gene might be novel target for GDM.
Potential pathways were obtained after GO and pathway enrichment analysis. Evidence suggests that CEBPB (CCAAT enhancer binding protein β) [38], ACSL4 [39], MBD2 [40], ULK1 [41], NUCB2 [42], TWIST1 [43], HOOK2 [44], CLDN7 [45], TBK1 [46], YIPF6 [47], TFRC (transferrin receptor) [48], ENPP2 [49], SLIT2 [50], MFGE8 [51], FAT1 [52], GPC4 [53], COL6A3 [54], EGFL6 [55], AOC3 [56], CCN2 [57], LYVE1 [58], RARA (retinoic acid receptor α) [59], COL18A1 [60], THY1 [61], CD36 [62], PEMT (phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase) [63], AIF1L [64], OXTR (oxytocin receptor) [65], LMNA (lamin A/C) [66], CXCL14 [67], DKK3 [68], ANGPTL2 [69] and CMTM7 [70] might be regarded as genetic factors in humans due to their involvement in obesity, but these genes might be novel target for GDM. Expression sites of AHR (aryl hydrocarbon receptor) [71], STS (steroid sulfatase) [72], PLAC1 [73], CYP11A1 [74], PSG11 [75], STAT5B [76], TLR3 [77], FOLR1 [78], HSPB1 [79], HSP90AA1 [80], ANXA4 [81], ATF3 [82], DAPK1 [83], ENTPD1 [84], ABL1 [85], VSIG4 [86], CD99 [87], VWF (von Willebrand factor) [88], PODXL (podocalyxin like) [89], PDPN (podoplanin) [90], RND3 [91], VCAN (versican) [92], AXL (AXL receptor tyrosine kinase) [93], PIEZO1 [94], GAS6 [93], LAMA4 [95], CAV1 [96], DLL1 [97], CD44 [98], CD81 [99], SMAD3 [100], NES (nestin) [101], DCN (decorin) [102], AGTR1 [103], SLIT3 [104], B2M [105], STAT3 [106], STC1 [107], ADAMTS1 [108], HSD11B2 [109] and HSD3B1 [110] in preeclampsia were specific, but these genes might be novel target for GDM. Increasing evidence indicates that the development of type 2 diabetes mellitus, due to the dysregulation of genes, such as CSNK2A2 [111], NFE2 [112], CAMK2G [113], RASGRP1 [114], S100P [115], SRR (serine racemase) [116], DHPS (deoxyhypusine synthase) [117], DYRK1A [118], JAG1 [119], COL3A1 [120], VTN (vitronectin) [121], WNT3A [122], ACTA2 [123], SEMA3A [124], RARRES2 [125], CAV2 [126] and SPRED1 [127], but these genes might be novel target for GDM. In a previous report, Santiago et al. [128], Auburger et al. [129], Qu et al. [130], Śnit et al. [131] and Hjortebjerg et al. [132] reported that SLC22A5, SH2B3, ITPR3, CALD1 and IGFBP4 served important roles in type 1 diabetes mellitus, but these genes might be novel target for GDM. Krishnan et al. [133], Hu et al. [134], Martins et al. [135], Prieto-Sánchez et al. [136], Sugulle et al. [137], Zhao et al. [138], Siddiqui et al. [139], Han et al. [140], Lappas et al. [141], Wang et al. [142], Artunc-Ulkumen et al. [143], Blois et al. [144], Vacínová et al. [145] and Vilmi-Kerälä et al. [146] demonstrated that the expression of CREBRF (CREB3 regulatory factor), STRA6, EGFR, MFSD2A, GDF15, PAK1, VCAM1, IGFBP2, IGFBP7, PRKCA (protein kinase C α), ADAMTS9, LGALS1, BIN1 are susceptibility for GDM, but further analysis of the function remains to be seen. Aquila et al. [147], Chen et al. [148], Xie et al. [149], Zhang et al. [150], Aspit et al. [151], Akadam-Teker et al. [152], Jiang et al. [153], Cetinkaya et al. [154], Grond-Ginsbach et al. [155], Dong et al. [156], Chardon et al. [157], Chen et al. [158], Yamada et al. [159], Hu et al. [160], Bobik and Kalinina [161], Schwanekamp et al. [162], Liu et al. [163], Schroer et al. [164], Raza et al. [165], Yang et al. [166], Azuaje et al. [167], Durbin et al. [168], Chowdhury et al. [169], Wang et al. [170], Li et al. [171], Lv et al. [172], Bertoli-Avella et al. [173], Grossman et al. [174], Andenæs et al. [175] and Chen et al. [176] demonstrated that expression of HES1, SPIN1, TBX3, EVA1A, CAP2, BMP1, HSPB8, RDX (radixin), COL5A1, LIMS2, PARVA (parvin α), EGFLAM (EGF like, fibronectin type III and laminin G domains), NEXN (nexilin F-actin binding protein), TNFRSF14, TGFBI (transforming growth factor β induced), HAVCR2, CDH11, COL4A1, COL4A2, COL5A2, SHROOM3, HYAL2, PDLIM3, ETS2, PLSCR4, TGFB3, COL6A2 and LTBP2 have previously been detected in cardiovascular diseases as well, but these genes might be novel target for GDM. Flamant et al. [177], Wan et al. [178], Zhang et al. [179], Vallvé et al. [180], Heximer and Husain [181], Selvarajah et al. [182], Jain et al. [183], Sun et al. [184], Satomi-Kobayashi et al. [185], Jiang et al. [186], Waghulde et al. [187] and Dahal et al. [188] reported that DDR1, CAST (calpastatin), KYNU (kynureninase), FBLN2, SPON1, VEGFC (vascular endothelial growth factor C), FLNA (filamin A), SNAI2, MYADM (myeloid associated differentiation marker), NECTIN2 and SMTN (smoothelin), GPER1, PDGFRB (platelet-derived growth factor receptor β) are important genetic factors related to hypertension, but these genes might be novel target for GDM. This investigation demonstrated that the pathogenesis of GDM has genetic heterogeneity. These candidate genes might play a pathogenic role through different signaling pathways, and different gene alteration might lead to different system damage in GDM. The genetic pathogenesis of GDM will become a more research hotspot again.
From the PPI network and modules diagram, it can be observed that hub genes were the key nodes of the PPI network and modules, with the highest node degree, betweenness, stress and closeness value. RPS13, RBX1, FYN, UBE2A, TUBB2A and TBCB were the novel biomarkers for the progression of GDM.
From the miRNA–hub gene network construction and TF–hub gene network diagram, it can be observed that hub genes, miRNAs and TFs are the key nodes with the highest degree value. CCND1 has been shown to be involved in the pathogenesis of obesity [189], but this gene might be novel target for GDM. Other studies which shown that FOXO1 [190], hsa-mir-1207-5p [191], hsa-mir-4651 [191], hsa-mir-222-3p [192] and E2F1 [193] are involved in GDM evolution. Hsa-let-7d-5p [194], hsa-mir-29c-3p [195] and SRY (sex-determining region Y) [196] have been reported to be associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus, but these genes might be novel target for GDM. Expression of hsa-mir-663a [197] and TBX3 [198] were consistent in cardiovascular diseases, but these genes might be novel target for GDM. Several reports have demonstrated that RUNX1 [199] and YAP1 [200] have active roles in preeclampsia, but these genes might be novel target for GDM. UBE2D3, PAK2, DDB1, DVL3, PSMC4, hsa-mir-6127, hsa-mir-8063, hsa-mir-329-3p, hsa-mir-410-5p, HCFC1, ZFX (zinc finger protein, X-linked), SPI1, MYBL2 and SUZ12 were the novel biomarkers for the progression of GDM.
The molecule GLY, MLR obtained a good -CDOCKER interaction energy with 5NJX, 3FNI and 3Q4Z the -CDOCKER interaction energy of GLY is 41.37, 59.92, 41.44 and for MLR is 40.68, 87.65, 43.47 with 5NJX, 3FNI and 3Q4Z, respectively. The two molecules such as ALO and MAL its interaction with amino acids are 2′ hydroxyl group formed hydrogen bond interaction with ASP-89 and 3′, 4′ hydroxyl groups formed hydrogen bond interaction with GLU-86. Following 6′ hydroxyl group formed hydrogen bond interaction with LYS-61. The C-13 hydroxyl formed hydrogen bond interaction with ASP-389 and ring C electrons formed π–π t-shaped interactions with HIS-63 and π–alkyl interaction with LYS-388. Ring A electrons formed π–carbon interaction with LYS-388 and LYS61, respectively. The ring C electrons and 4′ hydroxyl group of molecule MLR formed sulphur oxygen interaction with MET-344 and ring C electrons formed π–alkyl interaction with LEU-396. The ring A 5 and 6 hydroxyl group formed hydrogen bond interaction with ASP-354 and LYS-538. Ring D 3″ and 6″ hydroxyl group formed hydrogen bond interaction with ASP-393 and GLY-277, 3″ hydroxyl group formed pi-alkyl interaction with Mg ion. Ring D 5″ hydroxyl group formed hydrogen bond interaction with ARG-299. Ring E 6′″ alkyl hydroxyl formed Carbon hydrogen interaction with LYS-391 and ring E oxygen, 3′″ hydroxyl group and 6′″ alkyl hydroxyl formed π–alkyl interaction with Mg ions, respectively.
We conducted a comprehensive bioinformatics analysis on transcription profiling of GDM. Hub genes and pathways were identified to provide more detailed molecular mechanisms for the process of GDM and shed light on potential therapeutic targets. Nevertheless, further experiments are needed to further validate the identified hub genes and pathways.
Acknowledgements
We thank Marian C. Aldhous, Tommy’s Centre for Fetal and Maternal Health, Medical Research Council Centre for Reproductive Health, Queen’s Medical Research Institute, University of Edinburgh, Edinburgh, U.K., very much, the author who deposited their profiling by high-throughput sequencing dataset E-MTAB-6418, into the public ArrayExpress database.
Abbreviations
- adj. P. val
adjusted P value
- AUC
area under the curve
- BP
biological process
- CC
cellular component
- CEBPB
CCAAT enhancer binding protein beta
- CRH
corticotropin releasing hormone
- DEG
differentially expressed gene
- EGFR
epidermal growth factor receptor
- GDM
gestational diabetes mellitus
- GEO
Gene Expression Omnibus
- GO
Gene Ontology
- HSP90AA1
heat shock protein 90 alpha family Class A member 1
- MF
molecular function
- PAK1
p21 (RAC1) activated kinase 1
Data Availability
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are available in the ArrayExpress database (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/) repository [(E-MTAB-6418) https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/experiments/E-MTAB-6418/?array=A-MEXP-2072].
Competing Interests
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Funding
The authors declare that there are no sources of funding to be acknowledged.
Author Contribution
V.A.: Methodology and validation. V.R.: Formal analysis and validation. B.V.: Writing original draft, and review and editing. A.T.: Formal analysis and validation. C.V.: Software and investigation. S.K.: Supervision and resources.
Ethics Approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
References
- 1.Alfadhli E.M. (2015) Gestational diabetes mellitus. Saudi Med. J. 36, 399–406 10.15537/smj.2015.4.10307 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lambrinoudaki I., Vlachou S.A. and Creatsas G. (2010) Genetics in gestational diabetes mellitus: association with incidence, severity, pregnancy outcome and response to treatment. Curr. Diabetes Rev. 6, 393–399 10.2174/157339910793499155 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Chen P., Wang S., Ji J., Ge A., Chen C., Zhu Y.et al. (2015) Risk factors and management of gestational diabetes. Cell Biochem. Biophys. 71, 689–694 10.1007/s12013-014-0248-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Tieu J., McPhee A.J., Crowther C.A., Middleton P. and Shepherd E. (2017) Screening for gestational diabetes mellitus based on different risk profiles and settings for improving maternal and infant health. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 8, CD007222 10.1002/14651858.CD007222.pub4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Farrar D., Simmonds M., Bryant M., Sheldon T.A., Tuffnell D., Golder S.et al. (2016) Hyperglycaemia and risk of adverse perinatal outcomes: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 354, i4694 10.1136/bmj.i4694 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Zhu N., Hou J., Wu Y., Li G., Liu J., Ma G.et al. (2018) Identification of key genes in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis based on bioinformatics analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 97, e10997 10.1097/MD.0000000000010997 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Liu Y., Wang Y., Wang Y., Lv Y., Zhang Y. and Wang H. (2020) Gene expression changes in arterial and venous endothelial cells exposed to gestational diabetes mellitus. Gynecol. Endocrinol. 36, 791–795 10.1080/09513590.2020.1712696 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Zhang Q., He M., Wang J., Liu S., Cheng H. and Cheng Y. (2015) Predicting of disease genes for gestational diabetes mellitus based on network and functional consistency. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 186, 91–96 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2014.12.016 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Chiswick C.A., Reynolds R.M., Denison F.C., Drake A.J., Forbes S., Newby D.E.et al. (2016) Does Metformin Reduce hhjExcess Birthweight in Offspring of Obese Pregnant Women? A Randomised Controlled Trial of Efficacy, Exploration of Mechanisms and Evaluation of Other Pregnancy Complications, NIHR Journals Library, Southampton (U.K.) [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kolesnikov N., Hastings E., Keays M., Melnichuk O., Tang Y.A., Williams E.et al. (2015) ArrayExpress update–simplifying data submissions. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, D1113–D1116 10.1093/nar/gku1057 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Ritchie M.E., Phipson B., Wu D., Hu Y., Law C.W., Shi W.et al. (2015) limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 43, e47 10.1093/nar/gkv007 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Thomas P.D. (2017) The gene ontology and the meaning of biological function. Methods Mol. Biol. 1446, 15–24 10.1007/978-1-4939-3743-1_2 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Fabregat A., Jupe S., Matthews L., Sidiropoulos K., Gillespie M., Garapati P.et al. (2018) The Reactome Pathway Knowledgebase. Nucleic Acids Res. 46, D649–D655 10.1093/nar/gkx1132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Chen J., Bardes E.E., Aronow B.J. and Jegga A.G. (2009) ToppGene Suite for gene list enrichment analysis and candidate gene prioritization. Nucleic Acids Res. 37, W305–W311 10.1093/nar/gkp427 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Szklarczyk D., Morris J.H., Cook H., Kuhn M., Wyder S., Simonovic M.et al. (2017) The STRING database in 2017: quality-controlled protein-protein association networks, made broadly accessible. Nucleic Acids Res. 45, D362–D368 10.1093/nar/gkw937 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Shannon P., Markiel A., Ozier O., Baliga N.S., Wang J.T., Ramage D.et al. (2003) Cytoscape: a software environment for integrated models of biomolecular interaction networks. Genome Res. 13, 2498–2504 10.1101/gr.1239303 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Przulj N., Wigle D.A. and Jurisica I. (2004) Functional topology in a network of protein interactions. Bioinformatics 20, 340–348 10.1093/bioinformatics/btg415 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Nguyen T.P., Liu W.C. and Jordán F. (2011) Inferring pleiotropy by network analysis: linked diseases in the human PPI network. BMC Syst. Biol. 5, 179 10.1186/1752-0509-5-179 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Shi Z. and Zhang B. (2011) Fast network centrality analysis using GPUs. BMC Bioinformatics 12, 149 10.1186/1471-2105-12-149 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Fadhal E., Gamieldien J. and Mwambene E.C. (2014) Protein interaction networks as metric spaces: a novel perspective on distribution of hubs. BMC Syst. Biol. 8, 6 10.1186/1752-0509-8-6 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Zaki N., Efimov D. and Berengueres J. (2013) Protein complex detection using interaction reliability assessment and weighted clustering coefficient. BMC Bioinformatics 14, 163 10.1186/1471-2105-14-163 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Fan Y. and Xia J. (2018) miRNet-functional analysis and visual exploration of miRNA-target interactions in a network context. Methods Mol. Biol. 1819, 215–233 10.1007/978-1-4939-8618-7_10 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Zhou G., Soufan O., Ewald J., Hancock R.E.W., Basu N. and Xia J. (2019) NetworkAnalyst 3.0: a visual analytics platform for comprehensive gene expression profiling and meta-analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 47, W234–W241 10.1093/nar/gkz240 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Robin X., Turck N., Hainard A., Tiberti N., Lisacek F., Sanchez J.C.et al. (2011) pROC: an open-source package for R and S+ to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics 12, 77 10.1186/1471-2105-12-77 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Livak K.J. and Schmittgen T.D. (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods 25, 402–408 10.1006/meth.2001.1262 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Wierzchowski M., Dutkiewicz Z., Gielara-Korzańska A., Korzański A., Teubert A., Teżyk A.et al. (2017) Synthesis, biological evaluation and docking studies of trans-stilbene methylthio derivatives as cytochromes P450 family 1 inhibitors. Chem. Biol. Drug Des. 90, 1226–1236 10.1111/cbdd.13042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.O’Boyle N.M., Banck M., James C.A., Morley C., Vandermeersch T. and Hutchison G.R. (2011) Open Babel: an open chemical toolbox. J. Cheminform. 3, 33 10.1186/1758-2946-3-33 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Petchi R.R., Vijaya C. and Parasuraman S. (2014) Antidiabetic activity of polyherbal formulation in streptozotocin - nicotinamide induced diabetic wistar rats. J. Trad. Complement. Med. 4, 108–117 10.4103/2225-4110.126174 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Gupta R.C., Chang D., Nammi S., Bensoussan A., Bilinski K. and Roufogalis B.D. (2017) Interactions between antidiabetic drugs and herbs: an overview of mechanisms of action and clinical implications. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 9, 59 10.1186/s13098-017-0254-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Uusküla L., Rull K., Nagirnaja L. and Laan M. (2011) Methylation allelic polymorphism (MAP) in chorionic gonadotropin beta5 (CGB5) and its association with pregnancy success. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 96, E199–E207 10.1210/jc.2010-1647 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Purwosunu Y., Sekizawa A., Farina A., Wibowo N., Okazaki S., Nakamura M.et al. (2007) Cell-free mRNA concentrations of CRH, PLAC1, and selectin-P are increased in the plasma of pregnant women with preeclampsia. Prenat. Diagn. 27, 772–777 10.1002/pd.1780 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Temur M., Serpim G., Tuzluoğlu S., Taşgöz F.N., Şahin E. and Üstünyurt E. (2020) Comparison of serum human pregnancy-specific beta-1-glycoprotein 1 levels in pregnant women with or without preeclampsia. J. Obstet. Gynaecol. 40, 1074–1078 10.1080/01443615.2019.1679734 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Shimodaira M., Nakayama T., Sato I., Sato N., Izawa N., Mizutani Y.et al. (2012) Estrogen synthesis genes CYP19A1, HSD3B1, and HSD3B2 in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Endocrine 42, 700–707 10.1007/s12020-012-9699-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Xu T., Shao L., Wang A., Liang R., Lin Y., Wang G.et al. (2020) CD248 as a novel therapeutic target in pulmonary arterial hypertension. Clin. Transl. Med. 10, e175 10.1002/ctm2.175 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar] [Retracted]
- 35.Lin G., Wan X., Liu D., Wen Y., Yang C. and Zhao C. (2021) COL1A1 as a potential new biomarker and therapeutic target for type 2 diabetes. Pharmacol. Res. 165, 105436 10.1016/j.phrs.2021.105436 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Delfín D.A., DeAguero J.L. and McKown E.N. (2019) The extracellular matrix protein ABI3BP in cardiovascular health and disease. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 6, 23 10.3389/fcvm.2019.00023 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Blindbæk S.L., Schlosser A., Green A., Holmskov U., Sorensen G.L. and Grauslund J. (2017) Association between microfibrillar-associated protein 4 (MFAP4) and micro- and macrovascular complications in long-term type 1 diabetes mellitus. Acta Diabetol. 54, 367–372 10.1007/s00592-016-0953-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Bennett C.E., Nsengimana J., Bostock J.A., Cymbalista C., Futers T.S., Knight B.L.et al. (2010) CCAAT/enhancer binding protein alpha, beta and delta gene variants: associations with obesity related phenotypes in the Leeds Family Study. Diabetes Vasc. Dis. Res. 7, 195–203 10.1177/1479164110366274 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Killion E.A., Reeves A.R., El Azzouny M.A., Yan Q.W., Surujon D., Griffin J.D.et al. (2018) A role for long-chain acyl-CoA synthetase-4 (ACSL4) in diet-induced phospholipid remodeling and obesity-associated adipocyte dysfunction. Mol. Metab. 9, 43–56 10.1016/j.molmet.2018.01.012 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Cheng J., Song J., He X., Zhang M., Hu S., Zhang S.et al. (2016) Loss of Mbd2 protects mice against high-fat diet-induced obesity and insulin resistance by regulating the homeostasis of energy storage and expenditure. Diabetes 65, 3384–3395 10.2337/db16-0151 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.An M., Ryu D.R., Won Park J., Ha Choi J., Park E.M., Eun Lee K.et al. (2017) U.K. prevents cardiac dysfunction in obesity through autophagy-meditated regulation of lipid metabolism. Cardiovasc. Res. 113, 1137–1147 10.1093/cvr/cvx064 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Hofmann T., Weibert E., Ahnis A., Obbarius A., Elbelt U., Rose M.et al. (2017) Alterations of circulating NUCB2/nesfatin-1 during short term therapeutic improvement of anxiety in obese inpatients. Psychoneuroendocrinology 79, 107–115 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2017.02.021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Ma W., Lu S., Sun T., Wang X., Ma Y., Zhang X.et al. (2014) Twist 1 regulates the expression of PPARγ during hormone-induced 3T3-L1 preadipocyte differentiation: a possible role in obesity and associated diseases. Lipids Health Dis. 13, 132 10.1186/1476-511X-13-132 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Rodríguez-Rodero S., Menéndez-Torre E., Fernández-Bayón G., Morales-Sánchez P., Sanz L., Turienzo E.et al. (2017) Altered intragenic DNA methylation of HOOK2 gene in adipose tissue from individuals with obesity and type 2 diabetes. PLoS ONE 12, e0189153 10.1371/journal.pone.0189153 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Belalcazar L.M., Papandonatos G.D., McCaffery J.M., Peter I., Pajewski N.M., Erar B.et al. (2015) A common variant in the CLDN7/ELP5 locus predicts adiponectin change with lifestyle intervention and improved fitness in obese individuals with diabetes. Physiol. Genomics 47, 215–224 10.1152/physiolgenomics.00109.2014 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Reilly S.M., Chiang S.H., Decker S.J., Chang L., Uhm M., Larsen M.J.et al. (2013) An inhibitor of the protein kinases TBK1 and IKK-ɛ improves obesity-related metabolic dysfunctions in mice. Nat. Med. 19, 313–321 10.1038/nm.3082 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Wang L., Mazagova M., Pan C., Yang S., Brandl K., Liu J.et al. (2019) YIPF6 controls sorting of FGF21 into COPII vesicles and promotes obesity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 116, 15184–15193 10.1073/pnas.1904360116 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Garcia-Valdes L., Campoy C., Hayes H., Florido J., Rusanova I., Miranda M.T.et al. (2015) The impact of maternal obesity on iron status, placental transferrin receptor expression and hepcidin expression in human pregnancy. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 39, 571–578 10.1038/ijo.2015.3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Reeves V.L., Trybula J.S., Wills R.C., Goodpaster B.H., Dubé J.J., Kienesberger P.C.et al. (2015) Serum Autotaxin/ENPP2 correlates with insulin resistance in older humans with obesity. Obesity (Silver Spring) 23, 2371–2376 10.1002/oby.21232 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Lim R. and Lappas M. (2015) Slit2 exerts anti-inflammatory actions in human placenta and is decreased with maternal obesity. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 73, 66–78 10.1111/aji.12334 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Khalifeh-Soltani A., McKleroy W., Sakuma S., Cheung Y.Y., Tharp K., Qiu Y.et al. (2014) Mfge8 promotes obesity by mediating the uptake of dietary fats and serum fatty acids. Nat. Med. 20, 175–183 10.1038/nm.3450 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Bidu C., Escoula Q., Bellenger S., Spor A., Galan M., Geissler A.et al. (2018) The transplantation of ω3 PUFA-altered gut microbiota of fat-1 mice to wild-type littermates prevents obesity and associated metabolic disorders. Diabetes 67, 1512–1523 10.2337/db17-1488 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Leelalertlauw C., Korwutthikulrangsri M., Mahachoklertwattana P., Chanprasertyothin S., Khlairit P., Pongratanakul S.et al. (2017) Serum glypican 4 level in obese children and its relation to degree of obesity. Clin. Endocrinol. 87, 689–695 10.1111/cen.13435 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.McCulloch L.J., Rawling T.J., Sjöholm K., Franck N., Dankel S.N., Price E.J.et al. (2015) COL6A3 is regulated by leptin in human adipose tissue and reduced in obesity. Endocrinology 156, 134–146 10.1210/en.2014-1042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Oberauer R., Rist W., Lenter M.C., Hamilton B.S. and Neubauer H. (2010) EGFL6 is increasingly expressed in human obesity and promotes proliferation of adipose tissue-derived stromal vascular cells. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 343, 257–269 10.1007/s11010-010-0521-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Jargaud V., Bour S., Tercé F., Collet X., Valet P., Bouloumié A.et al. (2021) Obesity of mice lacking VAP-1/SSAO by Aoc3 gene deletion is reproduced in mice expressing a mutated vascular adhesion protein-1 (VAP-1) devoid of amine oxidase activity. J. Physiol. Biochem. 77, 141–154 10.1007/s13105-020-00756-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Tan J.T., McLennan S.V., Williams P.F., Rezaeizadeh A., Lo L.W., Bonner J.G.et al. (2013) Connective tissue growth factor/CCN-2 is upregulated in epididymal and subcutaneous fat depots in a dietary-induced obesity model. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 304, E1291–E1302 10.1152/ajpendo.00654.2012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Michurina S.V., Ishchenko I.Y., Arkhipov S.A., Klimontov V.V., Rachkovskaya L.N., Konenkov V.I.et al. (2016) Effects of melatonin, aluminum oxide, and polymethylsiloxane complex on the expression of LYVE-1 in the liver of mice with obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Bull. Exp. Biol. Med. 162, 269–272 10.1007/s10517-016-3592-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Redonnet A., Bonilla S., Noël-Suberville C., Pallet V., Dabadie H., Gin H.et al. (2002) Relationship between peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma and retinoic acid receptor alpha gene expression in obese human adipose tissue. Int. J. Obes. Relat. Metab. Disord. 26, 920–927 10.1038/sj.ijo.0802025 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Errera F.I., Canani L.H., Yeh E., Kague E., Armelin-Corrêa L.M., Suzuki O.T.et al. (2008) COL18A1 is highly expressed during human adipocyte differentiation and the SNP c.1136C > T in its “frizzled” motif is associated with obesity in diabetes type 2 patients. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 80, 167–177 10.1590/S0001-37652008000100012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Paine A., Woeller C.F., Zhang H., de la Luz Garcia-Hernandez M., Huertas N., Xing L.et al. (2018) Thy1 is a positive regulator of osteoblast differentiation and modulates bone homeostasis in obese mice. FASEB J. 32, 3174–3183 10.1096/fj.201701379R [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Wu R.X., Dong Y.Y., Yang P.W., Wang L., Deng Y.H., Zhang H.W.et al. (2019) CD36- and obesity-associated granulosa cells dysfunction. Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 31, 993–1001 10.1071/RD18292 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Gao X., van der Veen J.N., Zhu L., Chaba T., Ordoñez M., Lingrell S.et al. (2015) Vagus nerve contributes to the development of steatohepatitis and obesity in phosphatidylethanolamine N-methyltransferase deficient mice. J. Hepatol. 62, 913–920 10.1016/j.jhep.2014.11.026 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Parikh D., Riascos-Bernal D.F., Egaña-Gorroño L., Jayakumar S., Almonte V., Chinnasamy P.et al. (2020) Allograft inflammatory factor-1-like is not essential for age dependent weight gain or HFD-induced obesity and glucose insensitivity. Sci. Rep. 10, 3594 10.1038/s41598-020-60433-4 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Bush N.R., Allison A.L., Miller A.L., Deardorff J., Adler N.E. and Boyce W.T. (2017) Socioeconomic disparities in childhood obesity risk: association with an oxytocin receptor polymorphism. JAMA Pediatr. 171, 61–67 10.1001/jamapediatrics.2016.2332 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kim Y., Bayona P.W., Kim M., Chang J., Hong S., Park Y.et al. (2018) Macrophage lamin A/C regulates inflammation and the development of obesity-induced insulin resistance. Front. Immunol. 9, 696 10.3389/fimmu.2018.00696 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Cereijo R., Quesada-López T., Gavaldà-Navarro A., Tarascó J., Pellitero S., Reyes M.et al. (2021) The chemokine CXCL14 is negatively associated with obesity and concomitant type-2 diabetes in humans. Int. J. Obes. (Lond.) 10.1038/s41366-020-00732-y [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Xie L., Wang P.X., Zhang P., Zhang X.J., Zhao G.N., Wang A.et al. (2016) DKK3 expression in hepatocytes defines susceptibility to liver steatosis and obesity. J. Hepatol. 65, 113–124 10.1016/j.jhep.2016.03.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Tabata M., Kadomatsu T., Fukuhara S., Miyata K., Ito Y., Endo M.et al. (2009) Angiopoietin-like protein 2 promotes chronic adipose tissue inflammation and obesity-related systemic insulin resistance. Cell Metab. 10, 178–188 10.1016/j.cmet.2009.08.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Zhu Q., Xue K., Guo H.W., Deng F.F. and Yang Y.H. (2020) Interaction of the CMTM7 rs347134 polymorphism with dietary patterns and the risk of obesity in Han Chinese male children. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 17, 1515 10.3390/ijerph17051515 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Wang K., Zhou Q., He Q., Tong G., Zhao Z. and Duan T. (2011) The possible role of AhR in the protective effects of cigarette smoke on preeclampsia. Med. Hypotheses 77, 872–874 10.1016/j.mehy.2011.07.061 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Gratton A.M., Ye L., Brownfoot F.C., Hannan N.J., Whitehead C., Cannon P.et al. (2016) Steroid sulfatase is increased in the placentas and whole blood of women with early-onset preeclampsia. Placenta 48, 72–79 10.1016/j.placenta.2016.10.008 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Wan L., Sun D., Xie J., Du M., Wang P., Wang M.et al. (2019) Declined placental PLAC1 expression is involved in preeclampsia. Medicine (Baltimore) 98, e17676 10.1097/MD.0000000000017676 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Pan T., He G., Chen M., Bao C., Chen Y., Liu G.et al. (2017) Abnormal CYP11A1 gene expression induces excessive autophagy, contributing to the pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Oncotarget 8, 89824–89836 10.18632/oncotarget.21158 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Zhao L., Triche E.W., Walsh K.M., Bracken M.B., Saftlas A.F., Hoh J.et al. (2012) Genome-wide association study identifies a maternal copy-number deletion in PSG11 enriched among preeclampsia patients. BMC Pregn. Childb. 12, 61 10.1186/1471-2393-12-61 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Li W., Geng L., Liu X., Gui W. and Qi H. (2019) Recombinant adiponectin alleviates abortion in mice by regulating Th17/Treg imbalance via p38MAPK-STAT5 pathway. Biol. Reprod. 100, 1008–1017 10.1093/biolre/ioy251 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Gierman L.M., Silva G.B., Pervaiz Z., Rakner J.J., Mundal S.B., Thaning A.J.et al. (2021) TLR3 expression by maternal and fetal cells at the maternal-fetal interface in normal and preeclamptic pregnancies. J. Leukoc. Biol. 109, 173–183 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Piñuñuri R., Castaño-Moreno E., Llanos M.N. and Ronco A.M. (2020) Epigenetic regulation of folate receptor-α (FOLR1) in human placenta of preterm newborns. Placenta 94, 20–25 10.1016/j.placenta.2020.03.009 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.White B.G., Williams S.J., Highmore K. and Macphee D.J. (2005) Small heat shock protein 27 (Hsp27) expression is highly induced in rat myometrium during late pregnancy and labour. Reproduction 129, 115–126 10.1530/rep.1.00426 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Torres-Salazar Q., Martínez-López Y., Reyes-Romero M., Pérez-Morales R., Sifuentes-Álvarez A. and Salvador-Moysén J. (2020) Differential methylation in promoter regions of the genes NR3C1 and HSP90AA1, involved in the regulation, and bioavailability of cortisol in leukocytes of women with preeclampsia. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 7, 206 10.3389/fmed.2020.00206 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Xu Y., Sui L., Qiu B., Yin X., Liu J. and Zhang X. (2019) ANXA4 promotes trophoblast invasion via the PI3K/Akt/eNOS pathway in preeclampsia. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 316, C481–C491 10.1152/ajpcell.00404.2018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Kaitu’u-Lino T.J., Brownfoot F.C., Hastie R., Chand A., Cannon P., Deo M.et al. (2017) Activating transcription factor 3 is reduced in preeclamptic placentas and negatively regulates sFlt-1 (soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase 1), soluble endoglin, and proinflammatory cytokines in placenta. Hypertension 70, 1014–1024 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.09548 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Yung C., MacDonald T.M., Walker S.P., Cannon P., Harper A., Pritchard N.et al. (2019) Death associated protein kinase 1 (DAPK-1) is increased in preeclampsia. Placenta 88, 1–7 10.1016/j.placenta.2019.09.010 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Zhu L., Lv R., Kong L. and Li X. (2018) Reduced methylation downregulates CD39/ENTPD1 and ZDHHC14 to suppress trophoblast cell proliferation and invasion: Implications in preeclampsia. Pregn. Hypertens. 14, 59–67 10.1016/j.preghy.2018.03.012 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Griesshammer M., Sadjadian P. and Wille K. (2018) Contemporary management of patients with BCR-ABL1-negative myeloproliferative neoplasms during pregnancy. Expert Rev. Hematol. 11, 697–706 10.1080/17474086.2018.1506325 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Textoris J., Ivorra D., Ben Amara A., Sabatier F., Ménard J.P., Heckenroth H.et al. (2013) Evaluation of current and new biomarkers in severe preeclampsia: a microarray approach reveals the VSIG4 gene as a potential blood biomarker. PLoS ONE 8, e82638 10.1371/journal.pone.0082638 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Kelemu T., Erlandsson L., Seifu D., Abebe M., Teklu S., Storry J.R.et al. (2020) Association of maternal regulatory single nucleotide polymorphic CD99 genotype with preeclampsia in pregnancies carrying male fetuses in Ethiopian women. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 5837 10.3390/ijms21165837 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Aref S. and Goda H. (2013) Increased VWF antigen levels and decreased ADAMTS13 activity in preeclampsia. Hematology 18, 237–241 10.1179/1607845412Y.0000000070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Martineau T., Boutin M., Côté A.M., Maranda B., Bichet D.G. and Auray-Blais C. (2019) Tandem mass spectrometry analysis of urinary podocalyxin and podocin in the investigation of podocyturia in women with preeclampsia and Fabry disease patients. Clin. Chim. Acta 495, 67–75 10.1016/j.cca.2019.03.1615 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Onyangunga O., Moodley J., Odun-Ayo F. and Naicker T. (2018) Immunohistochemical localization of podoplanin in the placentas of HIV-positive preeclamptic women. Turk. J. Med. Sci. 48, 916–924 10.3906/sag-1706-88 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Li L., Zhang X., Hong S.L., Chen Y. and Ren G.H. (2018) Long non-coding HOTTIP regulates preeclampsia by inhibiting RND3. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 22, 3277–3285 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Gogiel T., Galewska Z., Romanowicz L., Jaworski S. and Bańkowski E. (2007) Pre-eclampsia-associated alterations in decorin, biglycan and versican of the umbilical cord vein wall. Eur. J. Obstet. Gynecol. Reprod. Biol. 134, 51–56 10.1016/j.ejogrb.2006.10.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Hirschi K.M., Tsai K.Y.F., Davis T., Clark J.C., Knowlton M.N., Bikman B.T.et al. (2020) Growth arrest-specific protein-6/AXL signaling induces preeclampsia in rats†. Biol. Reprod. 102, 199–210 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Arishe O.O., Ebeigbe A.B. and Webb R.C. (2020) Mechanotransduction and uterine blood flow in preeclampsia: the role of mechanosensing Piezo 1 ion channels. Am. J. Hypertens. 33, 1–9 10.1093/ajh/hpz158 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Ji Y., Zhou L., Wang G., Qiao Y., Tian Y. and Feng Y. (2019) Role of LAMA4 gene in regulating extravillous trophoblasts in pathogenesis of preeclampsia. Med. Sci. Monit. 25, 9630–9636 10.12659/MSM.917402 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Du F., Zhang Y., Xu Q., Teng Y., Tao M., Chen A.F.et al. (2020) Preeclampsia serum increases CAV1 expression and cell permeability of human renal glomerular endothelial cells via down-regulating miR-199a-5p, miR-199b-5p, miR-204. Placenta 99, 141–151 10.1016/j.placenta.2020.07.011 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Shimanuki Y., Mitomi H., Fukumura Y., Makino S., Itakura A., Yao T.et al. (2015) Alteration of Delta-like ligand 1 and Notch 1 receptor in various placental disorders with special reference to early onset preeclampsia. Hum. Pathol. 46, 1129–1137 10.1016/j.humpath.2015.03.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Todd N., McNally R., Alqudah A., Jerotic D., Suvakov S., Obradovic D.et al. (2021) Role of a novel angiogenesis FKBPL-CD44 pathway in preeclampsia risk stratification and mesenchymal stem cell treatment. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 106, 26–41 10.1210/clinem/dgaa403 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Ding H., Dai Y., Lei Y., Wang Z., Liu D., Li R.et al. (2019) Upregulation of CD81 in trophoblasts induces an imbalance of Treg/Th17 cells by promoting IL-6 expression in preeclampsia. Cell Mol. Immunol. 16, 302–312 10.1038/s41423-018-0186-9 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Brkić J., Dunk C., Shan Y., O'Brien J.A., Lye P., Qayyum S.et al. (2020) Differential role of Smad2 and Smad3 in the acquisition of an endovascular trophoblast-like phenotype and preeclampsia. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne) 11, 436 10.3389/fendo.2020.00436 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Yang X., Ding Y., Yang M., Yu L., Hu Y. and Deng Y. (2018) Nestin improves preeclampsia-like symptoms by inhibiting activity of cyclin-dependent kinase 5. Kidney Blood Press. Res. 43, 616–627 10.1159/000489146 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Lala P.K. and Nandi P. (2016) Mechanisms of trophoblast migration, endometrial angiogenesis in preeclampsia: The role of decorin. Cell Adh. Migr. 10, 111–125 10.1080/19336918.2015.1106669 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Zhao L., Dewan A.T. and Bracken M.B. (2012) Association of maternal AGTR1 polymorphisms and preeclampsia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 25, 2676–2680 10.3109/14767058.2012.708370 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Lim R., Barker G. and Lappas M. (2014) SLIT3 is increased in supracervical human foetal membranes and in labouring myometrium and regulates pro-inflammatory mediators. Am. J. Reprod. Immunol. 71, 297–311 10.1111/aji.12181 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Kristensen K., Wide-Swensson D., Schmidt C., Blirup-Jensen S., Lindström V., Strevens H.et al. (2007) Cystatin C, beta-2-microglobulin and beta-trace protein in pre-eclampsia. Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 86, 921–926 10.1080/00016340701318133 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Tang J., Wang D., Lu J. and Zhou X. (2021) MiR-125b participates in the occurrence of preeclampsia by regulating the migration and invasion of extravillous trophoblastic cells through STAT3 signaling pathway. J. Recept. Signal Transduct. Res. 41, 202–208 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Abid N., Embola J., Tryfonos Z., Bercher J., Ashton S.V., Khalil A.et al. (2020) Regulation of stanniocalcin-1 secretion by BeWo cells and first trimester human placental tissue from normal pregnancies and those at increased risk of developing preeclampsia. FASEB J. 34, 6086–6098 10.1096/fj.201902426R [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Namlı Kalem M., Kalem Z., Yüce T. and Soylemez F. (2018) ADAMTS 1, 4, 12, and 13 levels in maternal blood, cord blood, and placenta in preeclampsia. Hypertens. Pregn. 37, 9–17 10.1080/10641955.2017.1397690 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Majchrzak-Celińska A., Kosicka K., Paczkowska J., Główka F.K., Bręborowicz G.H., Krzyścin M.et al. (2017) HSD11B2, RUNX3, and LINE-1 methylation in placental DNA of hypertensive disorders of pregnancy patients. Reprod. Sci. 24, 1520–1531 10.1177/1933719117692043 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Shimodaira M., Nakayama T., Sato I., Sato N., Izawa N., Mizutani Y.et al. (2012) Estrogen synthesis genes CYP19A1, HSD3B1, and HSD3B2 in hypertensive disorders of pregnancy. Endocrine 42, 700–707 10.1007/s12020-012-9699-7 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Saxena R., Bjonnes A., Prescott J., Dib P., Natt P., Lane J.et al. (2014) Genome-wide association study identifies variants in casein kinase II (CSNK2A2) to be associated with leukocyte telomere length in a Punjabi Sikh diabetic cohort. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 7, 287–295 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.113.000412 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Yang W., Wang J., Chen Z., Chen J., Meng Y., Chen L.et al. (2017) NFE2 induces miR-423-5p to promote gluconeogenesis and hyperglycemia by repressing the hepatic FAM3A-ATP-Akt pathway. Diabetes 66, 1819–1832 10.2337/db16-1172 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Gloyn A.L., Desai M., Clark A., Levy J.C., Holman R.R., Frayling T.M.et al. (2002) Human calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II gamma gene (CAMK2G): cloning, genomic structure and detection of variants in subjects with type II diabetes. Diabetologia 45, 580–583 10.1007/s00125-002-0779-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Li J.Y., Tao F., Wu X.X., Tan Y.Z., He L. and Lu H. (2015) Common RASGRP1 gene variants that confer risk of type 2 diabetes. Genet. Test Mol. Biomarkers 19, 439–443 10.1089/gtmb.2015.0005 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Afarideh M., Zaker Esteghamati V., Ganji M., Heidari B., Esteghamati S., Lavasani S.et al. (2019) Associations of serum S100B and S100P with the presence and classification of diabetic peripheral neuropathy in adults with type 2 diabetes: a case-cohort study. Can. J. Diabetes 43, 336.e2–344.e2 10.1016/j.jcjd.2019.01.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Zhang S., Xiao J., Ren Q., Han X., Tang Y., Yang W.et al. (2014) Association of serine racemase gene variants with type 2 diabetes in the Chinese Han population. J. Diabetes Investig. 5, 286–289 10.1111/jdi.12145 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Robbins R.D., Tersey S.A., Ogihara T., Gupta D., Farb T.B., Ficorilli J.et al. (2010) Inhibition of deoxyhypusine synthase enhances islet {beta} cell function and survival in the setting of endoplasmic reticulum stress and type 2 diabetes. J. Biol. Chem. 285, 39943–39952 10.1074/jbc.M110.170142 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Belgardt B.F. and Lammert E. (2016) DYRK1A: a promising drug target for islet transplant-based diabetes therapies. Diabetes 65, 1496–1498 10.2337/dbi16-0013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Yoon C.H., Choi Y.E., Cha Y.R., Koh S.J., Choi J.I., Kim T.W.et al. (2016) Diabetes-induced jagged1 overexpression in endothelial cells causes retinal capillary regression in a murine model of diabetes mellitus: insights into diabetic retinopathy. Circulation 134, 233–247 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.014411 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Gaikwad A.B., Gupta J. and Tikoo K. (2010) Epigenetic changes and alteration of Fbn1 and Col3A1 gene expression under hyperglycaemic and hyperinsulinaemic conditions. Biochem. J. 432, 333–341 10.1042/BJ20100414 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Alessi M.C., Nicaud V., Scroyen I., Lange C., Saut N., Fumeron F.et al. (2011) Association of vitronectin and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 levels with the risk of metabolic syndrome and type 2 diabetes mellitus. Results from the D.E.S.I.R. prospective cohort. Thromb. Haemost. 106, 416–422 10.1160/TH11-03-0179 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Yang Q., Wang W.W., Ma P., Ma Z.X., Hao M., Adelusi T.I.et al. (2017) Swimming training alleviated insulin resistance through Wnt3a/β-catenin signaling in type 2 diabetic rats. Iran J. Basic Med. Sci. 20, 1220–1226 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Fang H., Luo X., Wang Y., Liu N., Fu C., Wang H.et al. (2014) Correlation between single nucleotide polymorphisms of the ACTA2 gene and coronary artery stenosis in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus. Exp. Ther. Med. 7, 970–976 10.3892/etm.2014.1510 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Xu X., Fang K., Wang L., Liu X., Zhou Y. and Song Y. (2019) Local application of semaphorin 3A combined with adipose-derived stem cell sheet and anorganic bovine bone granules enhances bone regeneration in type 2 diabetes mellitus rats. Stem Cells Int. 2019, 2506463 10.1155/2019/2506463 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Zhao K., Ding W., Zhang Y., Ma K., Wang D., Hu C.et al. (2020) Variants in the RARRES2 gene are associated with serum chemerin and increase the risk of diabetic kidney disease in type 2 diabetes. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 165, 1574–1580 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.10.030 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Fisher E., Schreiber S., Joost H.G., Boeing H. and Döring F. (2011) A two-step association study identifies CAV2 rs2270188 single nucleotide polymorphism interaction with fat intake in type 2 diabetes risk. J. Nutr. 141, 177–181 10.3945/jn.110.124206 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Meng S., Cao J.T., Zhang B., Zhou Q., Shen C.X. and Wang C.Q. (2012) Downregulation of microRNA-126 in endothelial progenitor cells from diabetes patients, impairs their functional properties, via target gene Spred-1. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 53, 64–72 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.04.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Santiago J.L., Martínez A., de la Calle H., Fernández-Arquero M., Figueredo M.A., de la Concha E.G.et al. (2006) Evidence for the association of the SLC22A4 and SLC22A5 genes with type 1 diabetes: a case control study. BMC Med. Genet. 7, 54 10.1186/1471-2350-7-54 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Auburger G., Gispert S., Lahut S., Omür O., Damrath E., Heck M.et al. (2014) 12q24 locus association with type 1 diabetes: SH2B3 or ATXN2? World J. Diabetes 5, 316–327 10.4239/wjd.v5.i3.316 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Qu H.Q., Marchand L., Szymborski A., Grabs R. and Polychronakos C. (2008) The association between type 1 diabetes and the ITPR3 gene polymorphism due to linkage disequilibrium with HLA class II. Genes Immun. 9, 264–266 10.1038/gene.2008.12 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Śnit M., Nabrdalik K., Długaszek M., Gumprecht J., Trautsolt W., Górczyńska-Kosiorz S.et al. (2017) Association of rs 3807337 polymorphism of CALD1 gene with diabetic nephropathy occurrence in type 1 diabetes - preliminary results of a family-based study. Endokrynol. Pol. 68, 13–17 10.5603/EP.2017.0003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Hjortebjerg R., Tarnow L., Jorsal A., Parving H.H., Rossing P., Bjerre M.et al. (2015) IGFBP-4 fragments as markers of cardiovascular mortality in type 1 diabetes patients with and without nephropathy. J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 100, 3032–3040 10.1210/jc.2015-2196 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Krishnan M., Murphy R., Okesene-Gafa K.A.M., Ji M., Thompson J.M.D., Taylor R.S.et al. (2020) The Pacific-specific CREBRF rs373863828 allele protects against gestational diabetes mellitus in Māori and Pacific women with obesity. Diabetologia 63, 2169–2176 10.1007/s00125-020-05202-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Hu S., Yan J., You Y., Yang G., Zhou H., Li X.et al. (2019) Association of polymorphisms in STRA6 gene with gestational diabetes mellitus in a Chinese Han population. Medicine (Baltimore) 98, e14885 10.1097/MD.0000000000014885 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Martins R.S., Ahmed T., Farhat S., Shahid S. and Fatima S.S. (2019) Epidermal growth factor receptor rs17337023 polymorphism in hypertensive gestational diabetic women: a pilot study. World J. Diabetes 10, 396–402 10.4239/wjd.v10.i7.396 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Prieto-Sánchez M.T., Ruiz-Palacios M., Blanco-Carnero J.E., Pagan A., Hellmuth C., Uhl O.et al. (2017) Placental MFSD2a transporter is related to decreased DHA in cord blood of women with treated gestational diabetes. Clin. Nutr. 36, 513–521 10.1016/j.clnu.2016.01.014 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Sugulle M., Dechend R., Herse F., Weedon-Fekjaer M.S., Johnsen G.M., Brosnihan K.B.et al. (2009) Circulating and placental growth-differentiation factor 15 in preeclampsia and in pregnancy complicated by diabetes mellitus. Hypertension 54, 106–112 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.130583 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Zhao H. and Tao S. (2019) MiRNA-221 protects islet β cell function in gestational diabetes mellitus by targeting PAK1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 520, 218–224 10.1016/j.bbrc.2019.09.139 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Siddiqui K., George T.P., Nawaz S.S. and Joy S.S. (2019) VCAM-1, ICAM-1 and selectins in gestational diabetes mellitus and the risk for vascular disorders. Future Cardiol. 15, 339–346 10.2217/fca-2018-0042 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Han N., Fang H.Y., Jiang J.X. and Xu Q. (2020) Downregulation of microRNA-873 attenuates insulin resistance and myocardial injury in rats with gestational diabetes mellitus by upregulating IGFBP2. Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 318, E723–E735 10.1152/ajpendo.00555.2018 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Lappas M. (2015) Insulin-like growth factor-binding protein 1 and 7 concentrations are lower in obese pregnant women, women with gestational diabetes and their fetuses. J. Perinatol. 35, 32–38 10.1038/jp.2014.144 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Wang F., Xu C., Reece E.A., Li X., Wu Y., Harman C.et al. (2017) Protein kinase C-alpha suppresses autophagy and induces neural tube defects via miR-129-2 in diabetic pregnancy. Nat. Commun. 8, 15182 10.1038/ncomms15182 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Artunc-Ulkumen B., Ulucay S., Pala H.G. and Cam S. (2017) Maternal serum ADAMTS-9 levels in gestational diabetes: a pilot study. J. Matern. Fetal Neonatal Med. 30, 1442–1445 10.1080/14767058.2016.1219717 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Blois S.M., Gueuvoghlanian-Silva B.Y., Tirado-González I., Torloni M.R., Freitag N., Mattar R.et al. (2014) Getting too sweet: galectin-1 dysregulation in gestational diabetes mellitus. Mol. Hum. Reprod. 20, 644–649 10.1093/molehr/gau021 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Vacínová G., Vejražková D., Lukášová P., Lischková O., Dvořáková K., Rusina R.et al. (2017) Associations of polymorphisms in the candidate genes for Alzheimer’s disease BIN1, CLU, CR1 and PICALM with gestational diabetes and impaired glucose tolerance. Mol. Biol. Rep. 44, 227–231 10.1007/s11033-017-4100-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Vilmi-Kerälä T., Lauhio A., Tervahartiala T., Palomäki O., Uotila J., Sorsa T.et al. (2017) Subclinical inflammation associated with prolonged TIMP-1 upregulation and arterial stiffness after gestational diabetes mellitus: a hospital-based cohort study. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 16, 49 10.1186/s12933-017-0530-x [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Aquila G., Vieceli Dalla Sega F., Marracino L., Pavasini R., Cardelli L.S., Piredda A.et al. (2020) Ticagrelor increases SIRT1 and HES1 mRNA levels in peripheral blood cells from patients with stable coronary artery disease and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 21, 1576 10.3390/ijms21051576 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Chen Y., Wu S., Zhang X.S., Wang D.M. and Qian C.Y. (2019) MicroRNA-489 promotes cardiomyocyte apoptosis induced by myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through inhibiting SPIN1. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 23, 6683–6690 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Xie H., Zhang E., Hong N., Fu Q., Li F., Chen S.et al. (2018) Identification of TBX2 and TBX3 variants in patients with conotruncal heart defects by target sequencing. Hum. Genomics 12, 44 10.1186/s40246-018-0176-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Zhang S., Lin X., Li G., Shen X., Niu D., Lu G.et al. (2017) Knockout of Eva1a leads to rapid development of heart failure by impairing autophagy. Cell Death Dis. 8, e2586 10.1038/cddis.2017.17 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Aspit L., Levitas A., Etzion S., Krymko H., Slanovic L., Zarivach R.et al. (2019) CAP2 mutation leads to impaired actin dynamics and associates with supraventricular tachycardia and dilated cardiomyopathy. J. Med. Genet. 56, 228–235 10.1136/jmedgenet-2018-105498 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 152.Akadam-Teker B., Ozkara G., Kurnaz-Gomleksiz O., Bugra Z., Teker E., Ozturk O.et al. (2018) BMP1 5′UTR + 104 T/C gene variation: can be a predictive marker for serum HDL and apoprotein A1 levels in male patients with coronary heart disease. Mol. Biol. Rep. 45, 1269–1276 10.1007/s11033-018-4283-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Jiang B., Liu Y., Liang P., Li Y., Liu Z., Tong Z.et al. (2017) MicroRNA-126a-5p enhances myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury through suppressing Hspb8 expression. Oncotarget 8, 94172–94187 10.18632/oncotarget.21613 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Cetinkaya A., Berge B., Sen-Hild B., Troidl K., Gajawada P., Kubin N.et al. (2020) Radixin relocalization and nonmuscle α-Actinin expression are features of remodeling cardiomyocytes in adult patients with dilated cardiomyopathy. Dis. Markers 2020, 9356738 10.1155/2020/9356738 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Grond-Ginsbach C., Weber R., Haas J., Orberk E., Kunz S., Busse O.et al. (1999) Mutations in the COL5A1 coding sequence are not common in patients with spontaneous cervical artery dissections. Stroke 30, 1887–1890 10.1161/01.STR.30.9.1887 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Dong Y., Zhai W. and Xu Y. (2020) Bioinformatic gene analysis for potential biomarkers and therapeutic targets of diabetic nephropathy associated renal cell carcinoma. Transl. Androl. Urol. 9, 2555–2571 10.21037/tau-19-911 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Chardon J.W., Smith A.C., Woulfe J., Pena E., Rakhra K., Dennie C.et al. (2015) LIMS2 mutations are associated with a novel muscular dystrophy, severe cardiomyopathy and triangular tongues. Clin. Genet. 88, 558–564 10.1111/cge.12561 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Chen H., Huang X.N., Yan W., Chen K., Guo L., Tummalapali L.et al. (2005) Role of the integrin-linked kinase/PINCH1/alpha-parvin complex in cardiac myocyte hypertrophy. Lab. Invest. 85, 1342–1356 10.1038/labinvest.3700345 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Yamada Y., Sakuma J., Takeuchi I., Yasukochi Y., Kato K., Oguri M.et al. (2017) Identification of EGFLAM, SPATC1L and RNASE13 as novel susceptibility loci for aortic aneurysm in Japanese individuals by exome-wide association studies. Int. J. Mol. Med. 39, 1091–1100 10.3892/ijmm.2017.2927 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Hu Y.W., Guo F.X., Xu Y.J., Li P., Lu Z.F., McVey D.G.et al. (2019) Long noncoding RNA NEXN-AS1 mitigates atherosclerosis by regulating the actin-binding protein NEXN. J. Clin. Invest. 129, 1115–1128 10.1172/JCI98230 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Bobik A. and Kalinina N. (2001) Tumor necrosis factor receptor and ligand superfamily family members TNFRSF14 and LIGHT: new players in human atherogenesis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 21, 1873–1875 10.1161/atvb.21.12.1873 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Schwanekamp J.A., Lorts A., Sargent M.A., York A.J., Grimes K.M., Fischesser D.M.et al. (2017) TGFBI functions similar to periostin but is uniquely dispensable during cardiac injury. PLoS ONE 12, e0181945 10.1371/journal.pone.0181945 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Liu C., Zhang H., Chen Y., Wang S., Chen Z., Liu Z.et al. (2021) Identifying RBM47, HCK, CD53, TYROBP, and HAVCR2 as hub genes in advanced atherosclerotic plaques by network-based analysis and validation. Front. Genet. 11, 602908 10.3389/fgene.2020.602908 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Schroer A.K., Bersi M.R., Clark C.R., Zhang Q., Sanders L.H., Hatzopoulos A.K.et al. (2019) Cadherin-11 blockade reduces inflammation-driven fibrotic remodeling and improves outcomes after myocardial infarction. JCI Insight 4, e131545 10.1172/jci.insight.131545 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Raza S.T., Abbas S., Eba A., Karim F., Wani I.A., Rizvi S.et al. (2018) Association of COL4A1 (rs605143, rs565470) and CD14 (rs2569190) genes polymorphism with coronary artery disease. Mol. Cell. Biochem. 445, 117–122 10.1007/s11010-017-3257-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Yang W., Ng F.L., Chan K., Pu X., Poston R.N., Ren M.et al. (2016) Coronary-heart-disease-associated genetic variant at the COL4A1/COL4A2 locus affects COL4A1/COL4A2 expression, vascular cell survival, atherosclerotic plaque stability and risk of myocardial infarction. PLoS Genet. 12, e1006127 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006127 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Azuaje F., Zhang L., Jeanty C., Puhl S.L., Rodius S. and Wagner D.R. (2013) Analysis of a gene co-expression network establishes robust association between Col5a2 and ischemic heart disease. BMC Med. Genomics 6, 13 10.1186/1755-8794-6-13 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Durbin M.D., O'Kane J., Lorentz S., Firulli A.B. and Ware S.M. (2020) SHROOM3 is downstream of the planar cell polarity pathway and loss-of-function results in congenital heart defects. Dev. Biol. 464, 124–136 10.1016/j.ydbio.2020.05.013 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Chowdhury B., Xiang B., Liu M., Hemming R., Dolinsky V.W. and Triggs-Raine B. (2017) Hyaluronidase 2 deficiency causes increased mesenchymal cells, congenital heart defects, and heart failure. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 10, e001598 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.116.001598 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Wang D., Fang J., Lv J., Pan Z., Yin X., Cheng H.et al. (2019) Novel polymorphisms in PDLIM3 and PDLIM5 gene encoding Z-line proteins increase risk of idiopathic dilated cardiomyopathy. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 23, 7054–7062 10.1111/jcmm.14607 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Li J., Su H., Zhu Y., Cao Y. and Ma X. (2020) ETS2 and microRNA-155 regulate the pathogenesis of heart failure through targeting and regulating GPR18 expression. Exp. Ther. Med. 19, 3469–3478 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 172.Lv L., Li T., Li X., Xu C., Liu Q., Jiang H.et al. (2018) The lncRNA Plscr4 Controls Cardiac Hypertrophy by Regulating miR-214. Mol. Ther. Nucleic Acids 10, 387–397 10.1016/j.omtn.2017.12.018 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 173.Bertoli-Avella A.M., Gillis E., Morisaki H., Verhagen J.M.A., de Graaf B.M., van de Beek G.et al. (2015) Mutations in a TGF-β ligand, TGFB3, cause syndromic aortic aneurysms and dissections. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 65, 1324–1336 10.1016/j.jacc.2015.01.040 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 174.Grossman T.R., Gamliel A., Wessells R.J., Taghli-Lamallem O., Jepsen K., Ocorr K.et al. (2011) Over-expression of DSCAM and COL6A2 cooperatively generates congenital heart defects. PLoS Genet. 7, e1002344 10.1371/journal.pgen.1002344 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 175.Andenæs K., Lunde I.G., Mohammadzadeh N., Dahl C.P., Aronsen J.M., Strand M.E.et al. (2018) The extracellular matrix proteoglycan fibromodulin is upregulated in clinical and experimental heart failure and affects cardiac remodeling. PLoS ONE 13, e0201422 10.1371/journal.pone.0201422 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 176.Chen H.X., Yang Z.Y., Hou H.T., Wang J., Wang X.L., Yang Q.et al. (2020) Novel mutations of TCTN3/LTBP2 with cellular function changes in congenital heart disease associated with polydactyly. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 24, 13751–13762 10.1111/jcmm.15950 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 177.Flamant M., Placier S., Rodenas A., Curat C.A., Vogel W.F., Chatziantoniou C.et al. (2006) Discoidin domain receptor 1 null mice are protected against hypertension-induced renal disease. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 17, 3374–3381 10.1681/ASN.2006060677 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 178.Wan F., Letavernier E., Abid S., Houssaini A., Czibik G., Marcos E.et al. (2016) Extracellular Calpain/Calpastatin balance is involved in the progression of pulmonary hypertension. Am. J. Respir. Cell Mol. Biol. 55, 337–351 10.1165/rcmb.2015-0257OC [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 179.Zhang Y., Shen J., He X., Zhang K., Wu S., Xiao B.et al. (2011) A rare variant at the KYNU gene is associated with kynureninase activity and essential hypertension in the Han Chinese population. Circ. Cardiovasc. Genet. 4, 687–694 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.110.959064 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 180.Vallvé J.C., Serra N., Zalba G., Fortuño A., Beloqui O., Ferre R.et al. (2012) Two variants in the fibulin2 gene are associated with lower systolic blood pressure and decreased risk of hypertension. PLoS ONE 7, e43051 10.1371/journal.pone.0043051 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 181.Heximer S. and Husain M. (2007) A candidate hypertension gene: will SPON1 hold salt and water? Circ. Res. 100, 940–942 10.1161/01.RES.0000265134.57140.da [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 182.Selvarajah V., Mäki-Petäjä K.M., Pedro L., Bruggraber S.F.A., Burling K., Goodhart A.K.et al. (2017) Novel mechanism for buffering dietary salt in humans: effects of salt loading on skin sodium, vascular endothelial growth factor C, and blood pressure. Hypertension 70, 930–937 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.117.10003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 183.Jain M., Mann T.D., Stulić M., Rao S.P., Kirsch A., Pullirsch D.et al. (2018) RNA editing of Filamin A pre-mRNA regulates vascular contraction and diastolic blood pressure. EMBO J. 37, e94813 10.15252/embj.201694813 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 184.Sun L., Lin P., Chen Y., Yu H., Ren S., Wang J.et al. (2020) miR-182-3p/Myadm contribute to pulmonary artery hypertension vascular remodeling via a KLF4/p21-dependent mechanism. Theranostics 10, 5581–5599 10.7150/thno.44687 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 185.Satomi-Kobayashi S., Ueyama T., Mueller S., Toh R., Masano T., Sakoda T.et al. (2009) Deficiency of nectin-2 leads to cardiac fibrosis and dysfunction under chronic pressure overload. Hypertension 54, 825–831 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.109.130443 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 186.Jiang J., Nakayama T., Shimodaira M., Sato N., Aoi N., Sato M.et al. (2012) Haplotype of smoothelin gene associated with essential hypertension. Hereditas 149, 178–185 10.1111/j.1601-5223.2012.02242.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 187.Waghulde H., Cheng X., Galla S., Mell B., Cai J., Pruett-Miller S.M.et al. (2018) Attenuation of microbiotal dysbiosis and hypertension in a CRISPR/Cas9 gene ablation rat model of GPER1. Hypertension 72, 1125–1132 10.1161/HYPERTENSIONAHA.118.11175 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 188.Dahal B.K., Heuchel R., Pullamsetti S.S., Wilhelm J., Ghofrani H.A., Weissmann N.et al. (2011) Hypoxic pulmonary hypertension in mice with constitutively active platelet-derived growth factor receptor-β. Pulm. Circ. 1, 259–268 10.4103/2045-8932.83448 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 189.Thun G.A., Imboden M., Berger W., Rochat T. and Probst-Hensch N.M. (2013) The association of a variant in the cell cycle control gene CCND1 and obesity on the development of asthma in the Swiss SAPALDIA study. J. Asthma 50, 147–154 10.3109/02770903.2012.757776 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 190.Zhang T., Ji C. and Shi R. (2019) miR-142-3p promotes pancreatic β cell survival through targeting FOXO1 in gestational diabetes mellitus. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Pathol. 12, 1529–1538 [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 191.Wang H., She G., Zhou W., Liu K., Miao J. and Yu B. (2019) Expression profile of circular RNAs in placentas of women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Endocr. J. 66, 431–441 10.1507/endocrj.EJ18-0291 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 192.Pheiffer C., Dias S., Rheeder P. and Adam S. (2019) MicroRNA profiling in HIV-infected South African women with gestational diabetes mellitus. Mol. Diagn. Ther. 23, 499–505 10.1007/s40291-019-00404-2 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 193.Zhang C., Wang L., Chen J., Song F. and Guo Y. (2020) Differential expression of miR-136 in gestational diabetes mellitus mediates the high-glucose-induced trophoblast cell injury through targeting E2F1. Int. J. Genomics 2020, 3645371 10.1155/2020/3645371 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 194.Catanzaro G., Besharat Z.M., Chiacchiarini M., Abballe L., Sabato C., Vacca A.et al. (2018) Circulating microRNAs in elderly type 2 diabetic patients. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2018, 6872635 10.1155/2018/6872635 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 195.Demirsoy İ.H., Ertural D.Y., Balci Ş., Çınkır Ü., Sezer K., Tamer L.et al. (2018) Profiles of circulating MiRNAs following metformin treatment in patients with type 2 diabetes. J. Med. Biochem. 37, 499–506 10.2478/jomb-2018-0009 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 196.Kasimiotis H., Myers M.A., Argentaro A., Mertin S., Fida S., Ferraro T.et al. (2000) Sex-determining region Y-related protein SOX13 is a diabetes autoantigen expressed in pancreatic islets. Diabetes 49, 555–561 10.2337/diabetes.49.4.555 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 197.Wang H., Shi J., Li B., Zhou Q., Kong X. and Bei Y. (2017) MicroRNA expression signature in human calcific aortic valve disease. Biomed Res. Int. 2017, 4820275 10.1155/2017/4820275 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 198.Xie H., Zhang E., Hong N., Fu Q., Li F., Chen S.et al. (2018) Identification of TBX2 and TBX3 variants in patients with conotruncal heart defects by target sequencing. Hum. Genomics 12, 44 10.1186/s40246-018-0176-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 199.Lappas M. (2018) Runt-related transcription factor 1 (RUNX1) deficiency attenuates inflammation-induced pro-inflammatory and pro-labour mediators in myometrium. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 473, 61–71 10.1016/j.mce.2018.01.003 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 200.Liu R., Wei C., Ma Q. and Wang W. (2020) Hippo-YAP1 signaling pathway and severe preeclampsia (sPE) in the Chinese population. Pregn. Hypertens. 19, 1–10 10.1016/j.preghy.2019.11.002 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets supporting the conclusions of this article are available in the ArrayExpress database (https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/) repository [(E-MTAB-6418) https://www.ebi.ac.uk/arrayexpress/experiments/E-MTAB-6418/?array=A-MEXP-2072].