Abstract
Fish allergy is a life-long food allergy whose prevalence is affected by many demographic factors. Currently, there is no cure for fish allergy, which can only be managed by strict avoidance of fish in the diet. According to the WHO/IUIS Allergen Nomenclature Sub-Committee, 12 fish proteins are recognized as allergens. Different processing (thermal and non-thermal) techniques are applied to fish and fishery products to reduce microorganisms, extend shelf life, and alter organoleptic/nutritional properties. In this concise review, the development of a consistent terminology for studying food protein immunogenicity, antigenicity, and allergenicity is proposed. It also summarizes that food processing may lead to a decrease, no change, or even increase in fish antigenicity and allergenicity due to the change of protein solubility, protein denaturation, and the modification of linear or conformational epitopes. Recent studies investigated the effect of processing on fish antigenicity/allergenicity and were mainly conducted on commonly consumed fish species and major fish allergens using in vitro methods. Future research areas such as novel fish species/allergens and ex vivo/in vivo evaluation methods would convey a comprehensive view of the relationship between processing and fish allergy.
Keywords: fish allergy, parvalbumin, antigenicity, allergenicity, immunogenicity, linear epitope, conformational epitope, processing, immunoglobulin G (IgG), immunoglobulin E (IgE), calcium-binding protein
1. Introduction
Food allergy is an adverse immune response to food, which can be classified into immunoglobulin (Ig) E-mediated and non-IgE mediated [1]. In IgE-mediated food allergy, IgEs bind to the food allergens, leading to the granulation of immune effector cells, releasing histamine and other inflammatory mediators [2]. Food allergy can be diagnosed using clinical disorders, physical examination such as serum total/specific IgE measurement, a skin prick test (SPT), and oral food challenge (OFC) [3,4]. It is reported that food allergy affects around 2.5% of the worldwide population, and its prevalence is increasing over time [5]. In the U.S., at least 10% of adults and 8% of children [6] have a food allergy. Some prevention strategies such as ingestion of potential allergens during pregnancy [7], consumption of prebiotics/probiotics/symbiotics/bacterial lysates [8], and vitamin D supplementation [9] are suggested. However, there is no treatment for food allergy, except for peanut allergy, which can be alleviated by oral immunotherapy with PALFORZIA (Aimmune Therapeutics, Inc., Brisbane, CA, USA) [10].
According to the World Allergy Organization (WAO), peanuts, tree nuts, finned fish, shellfish, milk, egg, wheat, soy, and sesame are the foods causing the most significant allergic reactions [11]. Among them, the estimated prevalence of finned fish allergy worldwide and in the U.S. is 0.3% [12] and 0.3–0.9% [13,14], respectively. Fish allergy usually persists throughout life, and its prevalence is unlikely to decrease or become stable [15]. The symptoms of fish allergy vary from mild to severe and may even lead to death. As an immunoglobulin (Ig) E-mediated food allergy, fish allergy is an adverse response when IgE binds to the ingested fish allergens [1]. According to the WHO/IUIS Allergen Nomenclature Sub-Committee [16], many fish proteins, including beta parvalbumin, beta enolase, aldolase A, tropomyosin, collagen alpha, creatine kinase, triosephosphate isomerase, pyruvate kinase, beta-prime-component of vitellogenin, PKM-like L-lactate dehydrogenase, glucose 6-phosphate isomerase, and glyceraldehyde3-phosphate dehydrogenase, have been recognized as food allergens. It should be noted that due to the variety of fish species from different regions and under-investigated fish species, more fish allergens from different species are continuously being submitted to the WHO/IUIS [17,18]. Among the currently reported fish allergens, parvalbumin IgE epitopes have been reported from many species such as cod [19,20,21], Pacific mackerel [22], Atlantic salmon [23], and Asian seabass [24]. IgE epitopes from other fish allergens are seldom reported. Many studies pointed out the clinical importance of characterizing other important fish allergens [18,25,26]. Fish and fishery products undergo different food processing techniques to inactivate pathogenic microorganisms, destroy toxins, and improve the taste. It is well known that protein structure and functional properties can be changed during different processing methods. For example, treatment such as drying, heating, and smoking leads to protein denaturation and protein solubility impairment [27]. Fish protein hydrolysates from chemical or enzymatic hydrolysis contain shorter peptides or amino acids that are easily absorbed [28]. Food processing techniques could lead to a decrease, no change, or even increase in fish antigenicity and allergenicity. Generally, both in vitro and in vivo methods are used to evaluate the effect of food processing on the properties of fish proteins. For in vitro methods, gel electrophoresis is used to study the soluble proteins’ conformation, stability, and interaction. Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs) and immunoblots are applied to study fish proteins’ antigenicity and allergenicity. For example, de Jongh et al. [29] used gel electrophoresis to study parvalbumin glycation and its digestion stability. Kubota et al. [30] applied ELISA and Western blotting to demonstrate the weakened thermostability of Pacific mackerel parvalbumin. For in vivo methods, SPT [31] and OFC [32] were used to illustrate patients’ immune responses to fish collagen.
In this concise review, three aspects of fish allergy (terminology of immunogenicity, antigenicity, and allergenicity; the epitopes of fish allergens; and effect of food processing on fish antigenicity/allergenicity) are elaborated.
2. Immunogenicity, Antigenicity, and Allergenicity
When studying the effect of food processing on allergens, terms such as immunogenicity, antigenicity, and allergenicity are often used interchangeably. Immunogenicity is the ability of a substance to induce a cellular or humoral immune response under a given set of conditions [33]. Immunogenicity is described in terms of the following three aspects: (1) the ability to defend the immune system; (2) the ability to keep the immune system steady; (3) the ability to kill or to remove abnormally mutated cells [34]. Antigenicity is defined as “the capacity to combine specifically with antibodies or T-cell receptor/major histocompatibility complex (MHC)” [33]. It is the ability to induce an immunological response [34]. From our perspective, protein antigenicity can be described from in vitro experiments such as Western blots and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays (ELISAs). Both immunoglobulin (Ig) G or IgE can be used for in vitro antigenicity studies. For IgG, either a monoclonal antibody (mAb) that binds to the same epitope of the protein or a polyclonal antibody (pAb) that binds to multiple epitopes of the same protein is applied. For example, frying increased anti-shrimp tropomyosin mAb immunoreactivity [35], while glycated parvalbumin showed a decrease in antigenicity using pAb [36]. As for IgE, pooled human sera [37] or individual serum containing IgE [38] are also reported. Protein immunogenicity can be characterized in vitro by analyzing its ability to produce T and B cell responses during the allergic sensitization phase [39]. For example, Ilchmann et al. [40] reported an activation and proliferation of T cells after glycation of ovalbumin. Cooking crustacean shellfish did not change T cell proliferative or cytokine reactivity in allergic patients’ peripheral blood mononuclear cells [41].
According to the WAO, allergy is a hypersensitivity reaction initiated by a specific immunologic mechanism [1]. Food allergy is an adverse immunologic response to food proteins [42]. To the best of our knowledge, no official definition was given for food allergenicity. The authors specify their individual descriptions in each publication. For example, according to the European Food Safety Authority (EFSA), allergenicity is “the ability of an antigen to induce an abnormal immune response, which is an overreaction and different from a normal immune response in that it does not result in a protective/prophylaxis effect but instead causes physiological function disorder or tissue damage” [34]. Deifl and Bohle [43] defined it as “the property of being able to induce a type 2 T helper (Th2) response and subsequent production of allergen-specific IgE antibodies.” Allergenicity could also be considered as “specifically bind IgE using sera from individuals with clear allergies to the source of the gene/protein and further that the protein causes basophil activation or histamine release, skin test reactivity or challenge test reactivity using subjects allergic to the source” [44] or “the ability of an antigen to induce an abnormal immune response, which is an overreaction and different from a normal immune response in that it does not result in a protective/prophylaxis effect but instead causes physiological function disorder or tissue damage” [45]. The term “food protein allergenicity” should be used carefully because it emphasizes the development of adverse reactions in skin, respiratory, digestive, and circulatory organs. Food protein allergenicity should be described using in vitro and in vivo methods according to the WHO/IUIS allergen submission requirement [46]. First, in vitro IgE tests such as ImmunoCAP, ELISA, and immunoblotting could show what the body is reacting to [47]. A basophil activation test is a replacement to measure the markers on the surface of basophils following stimulation with the allergen [48]. Second, a skin prick test or an in vivo allergen challenge test could also be applied. As an example, Faeste et al. [49] applied specific serum IgE determination, a skin prick test, and an open food challenge to illustrate the allergenicity of fenugreek proteins. Overall, to avoid confusion and improve multidisciplinary communication, accurate and consistent terminology and the recommended methods for studying food protein immunogenicity, antigenicity, and allergenicity should be developed.
3. Fish Allergy and Allergens
3.1. Fish Allergy Prevalence
Fish allergy usually has the following characteristics. First, fish allergy can happen due to ingestion, skin contact, or even inhalation exposure in the occupational environment [50] and is typically a life-long illness [51]. In this review, only ingested fish allergy will be discussed. The prevalence of fish allergy is summarized in Table 1. Fish allergy prevalence is affected by demographic factors such as region, age, gender, and ethnicity. Generally, Asians, adults, and females have a higher chance of developing fish allergies than those in Western countries, children, and males, respectively. Second, cross-reactivity in fish allergy is more common compared to other food allergies, such as wheat and egg. A person with fish allergy has a 50% possibility of being allergic to more than one fish [52]. It is suggested that patients who have fish allergies should avoid all types of fish in their diet [53]. In addition, fish allergic patients were also reported to be allergic to shellfish [54], chicken [55], and frogs [56] due to protein (such as parvalbumin and collagen) cross-reactivity. Third, fish allergy is one of the leading causes of food anaphylaxis [57]. It was found that fish accounted for 9% of deaths from anaphylaxis [58]. Pitsio et al. [59] first reported two cases of anaphylaxis during the SPT using commercial fish extracts.
Table 1.
Prevalence of fish allergy.
| Target | Method | Prevalence (%) | Comment | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 5529 households | Telephone survey | 0.4 | Adults have a higher prevalence than children Females have a higher prevalence than males |
[62] |
| 574 adults (>18 yr) | Telephone survey | 0.8 | [63] | |
| 38,480 U.S. children | Telephone survey | 0.5 | [6] | |
| 20,686 U.S. participants | Self-report survey | 0.45 | Adults have a higher prevalence than children | [14] |
| 7218 U.S. households (>18 yr) | Telephone survey | 0.9 | Finfish allergy is likely to be developed in adulthood | [13] |
| 11,434 children in the Philippines (14–16 yr) | Questionnaire survey | 2.9 | Females have a higher prevalence than males | [64] |
| 6498 children in Singapore (14–16 yr) | Questionnaire survey | 0.26 | Females have a higher prevalence than males | |
| 2304 children in Bangkok (14–16 yr) | Questionnaire survey | 0.29 | Females have a higher prevalence than males | |
| 9667 individuals in Canada | Telephone survey | 0.61 | Cod and salmon are most reported allergenic species | [65] |
| 3500 children in Turkey (6–9 yr) | Questionnaire | 3.5 | [66] | |
| Skin prick test | 5.6 | |||
| DBPCFC † | 4.5 | Only one child was positive in the DBPCFC | ||
| 9184 children in low-income clinic (0–21 yr) | Medical records | 0.4 | Fish is the second species group that easily causes anaphylaxis | [67] |
| 30,018 individuals in Taiwan, China | Questionnaire | 19 | Mostly occurred in children between 4-18 yr | [68] |
| 430 children in Poland with asthma | DBPCFC | 0.3 | The prevalence of fish allergy in Poland was relatively low | [69] |
| 22 Chinese patients with fish allergy | DBPCFC | 71.4 | 17.8% of patients were allergic to both carp and salmon | [70] |
DBPCFC †: Double-blind placebo-controlled food challenge.
Most of the fish allergy prevalence studies used a self-reported questionnaire-based method or telephone survey. Other methods such as an SPT, serum IgE measurement, and the gold standard DBPCFC criterion are seldom reported (Table 1). There are some adverse reactions such as scombroid fish poisoning [60] and fish parasite Anisakis simplex allergy [61] that are similar to the symptoms of fish allergy, which may lead to deviation of the prevalence.
3.2. Fish Allergens
According to the WHO/IUIS Allergen Nomenclature Sub-Committee [16], fish proteins including beta parvalbumin, beta enolase, aldolase A, tropomyosin, collagen alpha, creatine kinase, triosephosphate isomerase, pyruvate kinase, beta-prime-component of vitellogenin, PKM-like L-lactate dehydrogenase, glucose 6-phosphate isomerase, and glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase have been recognized as food allergens. Many review articles have been published on the structure and physicochemical characterization of fish allergens [51,71,72,73]. The reported fish allergen IgE-binding epitopes are summarized in Table 2. The epitopes are usually mapped using synthetic peptides, while this method cannot generate conformational epitopes. It is noted that the IgE-binding epitopes for fish allergens other than parvalbumin are seldom reported. For fish parvalbumin, both linear and conformational IgE epitopes from different species have been recognized (Table 2). Its IgE epitopes were mainly found in EF-hand motifs which are capable of binding with calcium and magnesium ions [74]. Despite the relatively low amino acid similarity among fish and other vertebrate animals, the high resemblance (~90%) in CD and EF domains, i.e., metal-binding sites, is noticed. This is probably why fish allergic patients can develop symptoms to more than one fish species or even other vertebrate animals, such as frogs and chicken.
Table 2.
Reported IgE epitopes of fish allergens from publications.
| Species | Protein | UniProtKB Accession Number | Method | Amino Acid | Reported IgE Epitope | Comment | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gadus morhua (Baltic cod) | Parvalbumin beta | P02622 | Epitope mapping | 33–44 | VGLDAFSADELK | Located on the junction between AB and CD domains Located on the junction between CD and EF domains Located on the calcium-binding loop of EF domain |
[20] |
| 49–64 | IADEDKEGFIEEDELK | ||||||
| 65–74 | LFLIAFAADL | ||||||
| 88–96 | AGDSDGDGK | ||||||
| Generation of mimotopes using phage display to mimic epitopes | 23 | S | The IgE binding epitopes are partially in accordance with previously defined peptides The identified IgE binding epitopes are conformational |
[19] | |||
| 25–29 | NHKAF | ||||||
| 33–37 | VGLTS | ||||||
| 77–79 | LTG | ||||||
| 87 | K | ||||||
| 89–92 | GDSD | ||||||
| 94 | D | ||||||
| Gadus morhua (Atlantic cod) | Parvalbumin beta | Q90YK9 | Epitope mapping Indirect non-competitive ELISA |
95–109 | GDGKIGVDEFGAMIKA | Corresponding to EF domain | [21] |
| Parvalbumin beta | D3GME4 | Indirect non-competitive ELISA | 21-40 | AGSFDHKKFFKACGLSGKST | It is a specific IgE epitope of Sco j 1 | [22] | |
| Salmo salar (Atlantic salmon) | Parvalbumin beta 2 | Q91483 | Peptide-based microarray immunoassay | No IgE epitopes were found | [75] | ||
| Parvalbumin beta 1 | Q91482 | Peptide-based microarray immunoassay | 1–18 | MACAHLCKEADIKTALEA | Located in the AB domain Located in the AB domain; also reported in Baltic cod Located between CD and EF domains; also reported in Baltic cod |
||
| 28–45 | KTFFHTIGFASKSADDVK | ||||||
| 61–85 | VEELKLFLQNFCPKARELTDA | ||||||
| Asian seabass | Parvalbumin beta 1 | Q5IRB2 | Indirect non-competitive ELISA | 17–25 | AACQAADSF | Both IgE binding regions are very similar to the identified regions from cod and carp | [24] |
| 106–109 | LVKV | ||||||
| Salmo salar (Atlantic salmon) | Tropomyosin alpha-1 chain | Q91472 | Epitope mapping | 43–57 | LVALQKKLKGTEDEL | Both peptides were found in flathead gray mullet and Mozambique tilapia | [76] |
| 235–252 | AETRAEFAERSVAKLEKT |
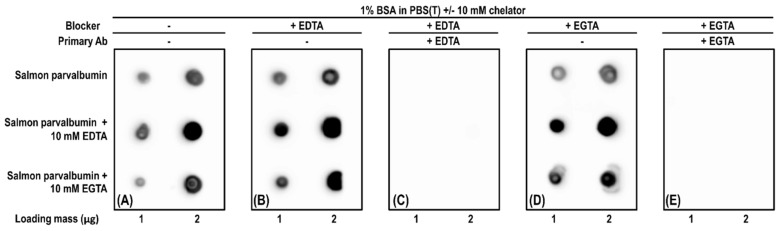
Calcium ions play an important role in parvalbumin IgE-binding properties due to its ability to keep parvalbumin’s conformation. Many studies showed a decrease in the IgE-binding ability after calcium depletion using ELISA and Western blots (Table 3). To study the effect of calcium on parvalbumin–antibody interactions, chelators such as ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA) or ethylene glycol-bis(β-aminoethyl ether)-N,N,N’,N’-tetraacetic acid (EGTA) are often added. However, there are two concerns. First, it is crucial to verify if the calcium ion has been removed completely. It is commonly accepted that EGTA has a higher affinity to calcium ion than EDTA. Methods such as fluorescence spectrum determination using Quin 2 [30] or conformation analysis using circular dichroism [77] should be applied. Second, chelators are not recommended to coexist with both the target protein and antibody due to their interference with antibody–antigen interactions. For example, we used a commercial mouse anti-parvalbumin mAb (PARV19, Millipore Sigma, P3088), which has a calcium-dependent epitope [78], to illustrate as follows. From the dot blot (Figure 1), three major findings were obtained. First, salmon parvalbumin immunoreactivity increased when 10 mM EDTA or 10 mM EGTA was incubated with purified salmon parvalbumin (Figure 1A), which matched our previous findings [23]. Additionally, Gajewski and Hsieh [79] reported an increase in mAb PARV19 immunoreactivity with calcium-depleted fish protein extracts. Second, when chelators were only added to the blocker, immunoreactive parvalbumin was still visible, and its dot intensity was not different from the one blocked without chelators (Figure 1A,B,D). It is also noticed that neither EDTA nor EGTA could affect the immunoreactivity. Third, when EDTA and EGTA were also added to the primary antibody buffer, which contained mAb PARV19, the parvalbumin dots disappeared (Figure 1C,E). From this research, it was found that chelators such as EDTA and EGTA not only chelate calcium ions but also may affect the antibody–target interaction. Any false positive/negative detection results should be carefully evaluated when chelators are added in the presence of antibodies.
Table 3.
Effect of calcium ion on parvalbumin antigenicity.
| Sample | Method | Chelator in Blocker | Antibody | Chelator in Antibody Buffer | Major Result | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Frog muscle protein extracts | Western blot | No | Human sera | 5 mM EGTA | A decrease in IgE binding | [56] |
| No | mAb PARV19 | 5 mM EGTA | No IgG binding | |||
| Pacific mackerel protein extracts | Western blot | No | Rabbit anti-Pacific mackerel parvalbumin antiserum | 5 mM EDTA | Same IgG binding | [30] |
| No | mAb PARV19 | 5 mM EGTA | No IgG binding | |||
| Scamp, sunfish, ocean perch, mullet, striped bass, catfish, pompano, red grouper, cobia, sheephead, tilapia, red snapper, basa, tra, amberjack, wahoo, Alaskan halibut, and yellowfin tuna protein extracts in coating buffer containing 10 mM EGTA | Indirect non-competitive ELISA | No | mAb PARV19 | No | An increase in IgG binding | [79] |
| No | mAb3E1 | No | An increase in IgG binding | |||
| Salmon and mullet protein extracts in water | Western blot | 10 mM EDTA | mAb PARV19 | 10 mM EDTA | No IgG binding | [23] |
| 10 mM EDTA | mAb3E1 | 10 mM EDTA | IgG binding was not affected | |||
| Salmon and mullet protein extracts in 5 mM EDTA in water | Western blot | No | mAb PARV19 | No | IgG binding was enhanced | |
| No | mAb3E1 | No | IgG binding was enhanced | |||
| Pacific mackerel parvalbumin | Indirect non-competitive ELISA | Unknown | Human sera | 5 mM EGTA | Reduced IgE binding for 100% of patients | [80] |
| Cod, tuna, carp, salmon, and eel protein extracts | Western blot | No | Human sera | 5 mM EGTA | More than 50% IgE binding reduction was observed in 64.2% of patients | [81] |
| Carp parvalbumin | Western blot | Unknown | Human sera | 5 mM EGTA | 100% of patients showed IgE binding reduction to a different extent | [77] |
| Unknown | Anti-parvalbumin mAb | 5 mM EGTA | 18% IgG binding reduction | |||
| Recombinant carp parvalbumin | Western blot | Unknown | Human sera | 5 mM EGTA | 100% of patients showed IgE binding reduction to a different extent | [82] |
Figure 1.
Effect of chelator on antibody-antigen interaction using dot blot. (A,E) Dot blot using mAb PARV19 (monoclonal anti-parvalbumin antibody, Sigma-Aldrich, P3088). (B,C) and (D,E) membranes were blocked using 1% (g/mL) BSA (bovine serum albumin) in PBS (10 mM phosphate-buffered saline, pH 7.2) containing 10 mM EDTA or 10 mM EGTA, respectively. (C,E) membranes were incubated with PARV19 diluted in 1% BSA in PBST (0.05% (mL/mL) Tween 20 in PBS) containing 10 mM EDTA or 10 mM EGTA, respectively.
4. Effect of Processing on Fish Allergens
Fish are more perishable than other high-protein animal meat due to the high concentration of nonprotein nitrogenous compounds present [83]. Food processing is directed to (1) avoid spoilage and decrease foodborne diseases; (2) increase food tastes and nutritional values; (3) improve transportation stability; and (4) produce convenient food [84]. Both thermal and non-thermal processing techniques are applied to fish products to increase shelf life and enhance sensory properties (Table 4). After processing, fish protein structure [85], stability [86], and antigenicity/allergenicity [87] can be altered.
Table 4.
Summary of food processing techniques on fish products from selected publications.
| Food Processing Technique | Property | Impact on Fishery Products | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cooking | Different strategies such as boiling, steaming, microwaving, baking, roasting, frying, and grilling are applied | Improve taste and flavor; affect texture and nutrition value; induce protein denaturation | [27] |
| Canning | Add food in jars and process in a pressure canner | Extend shelf life; induce flavor, texture, and nutrition loss | [27] |
| Hot smoking | Apply the smoke from burning materials such as wood at a temperature around 70–80 °C | Reduce moisture and microorganisms; impart desirable flavor | [95] |
| Drying | Remove water or other solvents by evaporation | Reduce moisture and microorganisms; induce protein denaturation; alter fish texture and color | [96] |
| Fermenting | Apply microorganisms to convert carbohydrates into different products | Extend shelf life; impart organoleptic and nutritional characteristics | [97] |
| Salting | Apply dry edible salt | Reduce moisture and microorganisms; induce lipid and protein degradation; alter fish texture and color | [98] |
| Cold smoking | Smoking of the product up to 33 °C | Less efficient in microbial reduction; alter texture, color, and flavor | [95] |
| High-pressure processing | Apply pressure between 200–800 MPa at a mild temperature of 5 to 35 °C | Inactivate microorganisms; induce protein denaturation; increase lipid oxidation; decrease water-holding capacity | [99,100,101] |
| Ultrasound | Apply an ultrasound frequency from 20 kHz to 10 MHz | Reduce microbials; affect color | [102,103] |
| Pulsed light | Apply short duration, high-peak power pulsed light of wide spectra (100–1100 nm) | Reduce microbials; affect color and texture; reduce lipid oxidation | [104,105] |
| Pulsed electric fields | Induce electroporation phenomena between two electrodes, leading to a non-invasive tissue structure modification | Improve water-holding capacity; tenderize texture; extraction of fishery by-products | [106] |
| Cold plasma | Apply energetic, reactive gases such as argon, helium | Reduce microbials; alter moisture content and lipid oxidation | [107,108] |
| Ozone | Works as a powerful oxidant and does not leave residues in foods | Reduce microbials; extend shelf life | [109] |
Table 5 summarizes the effect of food processing on fish antigenicity/allergenicity. Overall, three major conclusions can be driven. First, fish antigenicity/allergenicity is affected by a number of factors (matrix, detection method, antibody). The antigenicity/allergenicity of the same protein exhibits differences in different matrices. Griesmeier et al. [88] reported IgE binding to heated (100 °C/10 min) whiff proteins even after in vitro pepsin digestion for 120 min while the IgE binding to heated whiff parvalbumin monomer disappeared after a 5 s digestion. Keshavarz et al. [23] noticed parvalbumin was almost undetectable in heated (100 °C/8 min) salmon protein extracts, while purified salmon parvalbumin was thermostable and soluble after the same heat treatment.
Table 5.
Effect of processing on fish protein solubility, antigenicity, and allergenicity.
| Fish Matrix | Processing Method | Method | Antibody | Major Results | Explanation | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pacific mackerel protein extracts | 60, 80, 100, 120, 140 °C for 5, 10, 15, 20, 25, 30 min | Western blot | mAb PARV-19 | Parvalbumin band decreased as a function of heating temperature and time | The reduction was caused by heat-induced conformational change due to the release of calcium | [30] |
| Indirect non-competitive ELISA | Human IgE | IgE reactivity decreased as a function of heating temperature and time; a complete loss of IgE reactivity at 140 °C | ||||
| Hilsa, pomfret, bhetki, and mackerel | 90 °C for 10 min | Indirect non-competitive ELISA | Human IgE | A decrease in IgE reactivity was observed in pomfret, hilsa, and mackerel while an increase in IgE reactivity was seen in bhetki | Boiling removed many polypeptide bands | [110] |
| Skin prick test | Patients exhibited different reactions to boiled fish | |||||
| Fry with mustard oil for 5 min | Indirect non-competitive ELISA | Human IgE | A decrease in IgE reactivity was observed in pomfret, hilsa, and mackerel while an increase in IgE reactivity was seen in bhetki | Frying removed many polypeptide bands and caused protein denaturation to form high molecular weight proteins | ||
| Skin prick test | Patients exhibited different reactions to boiled fish | |||||
| Snapper, silver bream, yellowtail kingfish, barramundi, bluefin tuna, slimy mackerel, orange roughy, tiger flathead, Atlantic salmon, rainbow trout, carp, pilchard, rock ling, Atlantic cod, | 95 °C for 15 min | Western blot | mAb PARV-19 | Parvalbumin from heated fish was still immunodetectable. Especially for yellowfin tuna, a stronger and more intense parvalbumin band was observed compared to unheated extracts | Heat processing affected antibody–antigen interaction differently for each species | [111] |
| gummy shark, sparsely spotted stingaree, blacktip shark, and elephant shark | 95 °C for 15 min | Western blot | mAb PARV-19 | Except for elephant shark, immunoreactive parvalbumin was not visible | ||
| Purified cod parvalbumin | 80 °C for 30 min | Indirect non-competitive ELISA | Human IgE | IgE binding was not affected | Heat-induced secondary structure and calcium-binding ability changes were not enough to reduce antigenicity | [112] |
| 80 °C, 300 MPa for 30 min | IgE binding was not affected | |||||
| Bhetki and mackerel fish extracts | 90 °C, 10 min then pepsin digested | Indirect non-competitive ELISA | No significant difference in IgE level was observed | [113] | ||
| Western blot | Additional immunoreactive protein bands were observed | Thermal processing generated new allergenic epitopes that were pepsin stable | ||||
| Fry in mustard oil for 5 min then pepsin digested | Western blot | Increased IgE binding proteins were observed | Structural changes may offer some protection from enzymatic digestion | |||
| Surimi | 100 °C for 10, 15, and 20 min | Indirect non-competitive ELISA and indirect competitive ELISA |
Anti-fish tropomyosin mAb | IgG binding decreased after 10 min and remained constant for 15 and 20 min | High temperature and long processing time decreased extractable protein concentration, destroyed epitopes, and affected antibody–antigen interaction | [114] |
| Steam at 100 °C for 10, 15, and 20 min | IgG binding decreased after 10 min and remained constant for 15 and 20 min | |||||
| Bake at 149 °C for 10, 20, and 30 min | IgG binding decreased as a function of baking temperature | |||||
| Microwave on high power for 0.5, 1, and 1.5 min | IgG binding decreased as a function of microwaving temperature | |||||
| Fry in canola oil for 0.5, 1, and 1.5 min | IgG binding decreased after 10 min and remained constant for 15 and 20 min | |||||
| Purified cod parvalbumin | Glycation with D-glucose (60 °C for 5 h) and in vitro digestion | SDS-PAGE | All parvalbumin was digested after 30 min | Reduced aggregation during processing allowed a better protein degradation by pepsin | [115] | |
| Fish protein hydrolysates | Glycation with ribose at 121 °C for 30, 60, and 90 min | Histamine release using RBL-2H3 cells | Histamine release in RBL-2H3 cells was reduced | Glycated fish protein hydrolysates reduced NO synthesis | [116] | |
| Purified great snakehead parvalbumin | 90 °C for 1, 2, 3 h | SDS-PAGE | The parvalbumin band intensity decreased as a function of heating time but was visible after 3 h heating | Parvalbumin maintained its typical structural properties after experiencing extensive thermal stroke | [117] | |
| Purified sardine parvalbumin | 70, 80, and 90 °C for 30, 60, and 120 min | Indirect non-competitive ELISA and dot blot | Rabbit anti-parvalbumin antibody | IgG binding to parvalbumin diminished 65% after 90 °C heating for 30 min | Heating was responsible for the reduction of antibody binding to purified sardine parvalbumin | [93] |
| Human IgE | 90% of patients showed reduced IgE binding, while 10% patients showed increased IgE binding | |||||
| Monkfish, Atlantic salmon, trout, pink ling, jewfish, pumpkin head trevally, swordfish, northern sand flathead, red gurnard, tiger flathead, and mosaic leatherjacket | 100 °C for 45 min | Western blot | Anti-carp mAb Anti-cod mAb |
Reduced IgG binding | [118] | |
| Pilchard, cod, dory, bright redfish, sea mullet, pink ling, barramundi, blue threadfin, cobia, crimson snapper, flame snapper, grunter bream, jewfish, pink snapper, pumpkin head trevally, sweetlip emperor, saddletail snapper, striped snapper, yellowfin bream, yellowtail scad, northern sand flathead, and red gurnard | 100 °C for 45 min | Western blot | Anti-carp mAb Anti-cod mAb |
Consistent IgG binding as the raw protein extracts | ||
| Coral trout, eastern school whiting, grass emperor, sand whiting, Spanish mackerel, yellowfin tuna, and tiger flathead | 100 °C for 45 min | Western blot | Anti-carp mAb Anti-cod mAb |
Increased IgG binding |
||
| Purified sardine parvalbumin | 90 °C for 1 h then pepsin digested for 30, 60, 120 min at pH 2, 37 °C | Indirect non-competitive ELISA and dot blot | Rabbit anti-parvalbumin antibody | Decreased IgG binding | Pepsin hydrolysis decreased the binding of IgG | |
| Human IgE | All IgE-binding capacity was eliminated completely | |||||
| Whiting protein extracts | Soak in vinegar for 30 min and then heat at 100 °C for 5 min | Indirect non-competitive ELISA and Western blot | Anti-fish tropomyosin mAb | IgG-binding capacity decreased significantly regardless of different types of vinegar | Acidic pH changed the immunoreactivity and detectability of whiting | [119] |
| Whiting, cod, and red grouper protein extracts | Soak in vinegar for different periods (<1 min, 15 min, 30 min, and 60 min) and then heat at 100 °C for 5 min | Indirect non-competitive ELISA and Western blot | Anti-fish tropomyosin mAb | Whiting: IgG immunoreactivity decreased significantly after 15 min treatment; cod and grouper: IgG immunoreactivity decreased significantly even within 1 min treatment | Acid pH either altered tropomyosin conformation or lowered its solubility | |
| Whiting, cod, and red grouper protein extracts | 100 °C for 5, 15, 30, and 60 min | Western blot | Human IgE | Prolonged vinegar cooking time significantly reduced the IgE immunoreactivity | Acid pH-induced protein denaturation | |
| Cod protein extracts | In vitro digestion at pH 1.25–5 | Western blot | Human IgE | When pH ≤ 2.5, all proteins lost IgE-binding capability within 1 min; when 2.5 < pH ≤ 5, IgE immunoreactivity was still observed after 1 h digestion | Gastric pH could digest and degrade cod proteins. Those patients with abnormal gastric pH may be exposed to an increased allergenicity | [120] |
| RAST inhibition | Human IgE | Digested cod proteins inhibited IgE binding as a function of time | ||||
| Histamine release assay | Histamine release was only observed at high concentration of digests | |||||
| Whiff protein extracts | 100 °C for 10 min | Western blot | Human IgE | More IgE-reactive bands were observed | [88] | |
| Whiff protein extracts | 100 °C for 10 min and then in vitro gastric digestion | Western blot | Human IgE | IgE bound to fragmented proteins even after 120 min; IgE binding to 24 kDa, 34 kDa, and 130 kDa proteins was weakened | Heating-induced protein degradation | |
| Purified whiff parvalbumin | 100 °C for 10 min and then in vitro gastric digestion | Western blot | Human IgE | Immunoreactive parvalbumin monomer disappeared after 5 s digestion while its dimer was visible after 120 min | Heating generated dimers that were partially stable towards gastric digestion | |
| Purified Alaska pollock parvalbumin | Glycation with glucose, fructose, ribose, lactose, and galactose at 60 °C, 65% for 1 h | Indirect competitive ELISA |
Rabbit antisera | Glycation with glucose and fructose enhanced both IgG and IgE binding, while glycation with ribose, lactose, and galactose decreased both IgG and IgE binding | Glycation changed protein conformation, which affected the specific recognition of antigen and antibody | [121] |
| Human IgE | ||||||
| Glass carp purified parvalbumin | Glycation with maltose | Indirect competitive ELISA | Rabbit anti-PV sera | Reduced IgG binding | Heat treatment was the major cause for decreased immunoreactivity | [36] |
| Human IgE | Suppressed IgE binding | Heat treatment and Maillard reaction led to the structural change of parvalbumin | ||||
| Recombinant silver cap parvalbumin | Glycation with glucose at 60 °C for 72 h | Dot blot | Human IgE | Decreased IgE binding | Glycation sites were partially located at IgE-binding epitopes | [122] |
| Rat basophilic leukemia assay | Reduced histamine release and secretion of IL-4 and TNF-α. | |||||
| Tuna | Canning | Double-blind placebo-controlled food challenge | All patients did not show sensitization and adverse reaction after consumption | Canning led to the formation of a homogenous mixture of different molecular weight fragments | [123] | |
| Immunoblot and indirect competitive ELISA | Human IgE | All sera showed minimal to absent IgE binding | ||||
| Salmon | Canning | Double-blind placebo-controlled food challenge | All patients did not show an adverse reaction after consumption | Canning led to a remarkable loss of definable protein bands on SDS-PAGE | ||
| Immunoblot and indirect competitive ELISA | Human IgE | Minimal IgE binding | ||||
| Haddock and rainbow trout | Hot smoking at 80–100 °C | Indirect competitive ELISA | Human IgE | 83.3% of patients showed increased IgE binding | Novel bands at around 65 kDa were observed on SDS-PAGE | [38] |
| Tuna | Canning at high temperature (116–121 °C) and pressure for up to 14 h | Indirect competitive ELISA | Human IgE | All patients showed decreased IgE binding | No parvalbumin band was visible on the SDS-PAGE | |
| Atlantic cod | Drying | Indirect competitive ELISA | Human IgE | All patients showed increased IgE binding | Several novel bands from 70 to > 188 kDa were observed on SDS-PAGE | [38] |
| Atlantic cod | Dried cod soaked in a pH 11–12 lye solution and subsequently in cold water | Indirect competitive ELISA | Human IgE | All patients showed reduced IgE binding | Parvalbumin band intensity on SDS-PAGE was reduced 48% | |
| Atlantic cod | Cod dried after salting | Indirect competitive ELISA | Human IgE | 58.3% of patients showed decreased IgE binding, while 33.3% patients showed increased IgE binding | Several novel bands from 70 to > 188 kDa were observed on SDS-PAGE | |
| Atlantic salmon | Cured in a mixture of sugar, spices, and salt | Indirect competitive ELISA | Human IgE | 80% of patients showed reduced IgE binding, while 20% of patients showed 65 times more IgE binding | Parvalbumin band intensity on SDS-PAGE was reduced by 34% | |
| Atlantic salmon | Cold smoking at 20–30 °C after being cured for a day | Indirect competitive ELISA | Human IgE | 80% of patients showed increased IgE binding | Novel bands at around 30 kDa were observed on SDS-PAGE | |
| Rainbow trout | Salted trout undergoes controlled enzymatic fermentation | Indirect competitive ELISA | Human IgE | 81.8% of patients showed decreased IgE binding, while 18.2% patients showed 30 times more IgE binding | Parvalbumin band intensity on SDS-PAGE was reduced by 40% | |
| Herring | Pickled herrings are prepared in an acetic acid–salt brine | Indirect competitive ELISA | Human IgE | 87.5% of patients showed decreased IgE binding | Few bands < 62 kDa were observed, and parvalbumin band intensity decreased on SDS-PAGE | |
| Salmon | Hydrolysis | Indirect competitive ELISA | Human IgE | Three patients showed more IgE binding | Absence of discernible bands and weak bands up to around 50 kDa | |
| Blue whiting | Hydrolysis | Indirect competitive ELISA | Human IgE | Two patients showed decreased IgE binding, while one patient showed more IgE binding | Absence of discernible bands and weak bands up to around 50 kDa | |
| Carp, catfish, chub mackerel, sardine, chinook salmon, albacore tuna, and mahi-mahi | Stored at −20 °C | Indirect non-competitive ELISA | IgG | A decrease in parvalbumin immunoreactivity was observed after 112-day storage, but parvalbumin was still considered stable at frozen stages | Less freeze-induced protein denaturation was observed in intact muscle. Frozen storage mainly altered myofibrillar proteins instead of sarcoplasmic proteins | [124] |
| Food-grade cod gelatin | Histamine release assay | 10% of patients showed histamine release | ||||
| Skin prick test | 23.3% of patients showed positive results | |||||
| Double-blind placebo-controlled food challenge | None of the patients showed allergic symptoms to 3.61 g fish gelatin | [125] | ||||
| Yellowfin tuna gelatin | Western blot | Human IgE | 3% of patients showed IgE binding | The manufacturing process eliminated the fish allergens | [32] | |
| Double-blind placebo-controlled food challenge | None of the patients showed allergic symptoms to 5 g fish gelatin |
Indirect ELISAs and Western blots are the methods that are commonly used to study the effect of processing on fish allergens. These methods mainly investigated the binding between antibodies and processed proteins that may lead to a modified capacity to elicit an allergic reaction [89]. The reliability of the results is dependent on the extractability of fish allergens and the selection of antibodies. First, both ELISAs and Western blots rely on the extractable fish proteins, whose amount is affected by the extraction condition. Generally, the processed fish proteins are extracted using water or phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), which may not represent the total amount of allergens. Like other animal muscle proteins, fish proteins are classified as myofibrillar, sarcoplasmic, and stromal proteins, and the specific composition is species dependent [90]. Different extraction strategies should be conducted against different proteins’ properties to ensure their extractability. It is reported that a larger amount of IgE-reactive bands was observed from oyster when it was extracted using high-salt buffers or high-pH buffers [91]. The addition of 5 mM EDTA in the extraction solution increased salmon parvalbumin extractability significantly [23]. Water non-extractable parvalbumin from heated (100 °C/8 min) salmon was further extractable by adding a surfactant (SDS) and reducing agent (β-mercaptoethanol) [23]. Ma et al. [92] compared the parvalbumin extractability using 12 different buffers and noted that the reducing agent (dithiothreitol) enhanced extraction efficacy and led to higher stability and functionality of the protein extracts. Meanwhile, the antibody used affects the results. When IgGs are used as the detection antibody, this usually involves immunoreactivity changes of one single protein. When human IgEs are used, this reflects the total antigenicity/allergenicity. During the evaluation of the same product, IgGs and IgEs can lead to the same or different detection results. For example, decreased IgG and IgE immunoreactivities were observed after glycation parvalbumin with maltose [36] while a reduction in IgG binding and an increase in IgE binding were observed in heated (100 °C/10 min) sardine parvalbumin [93]. Despite the wide applications of immunoblots and ELISAs, few reports that focus on the ability of fish proteins to induce allergic sensitization have been published. In vitro experiments such as histamine release tests, mediator release tests, T cell polarization assays, cytokine production and proliferation [94], and in vivo tests such as skin prick tests and oral food challenges are all recommended.
Second, processing may lead to a decreased, unchanged, or even increased antigenicity and allergenicity. For example, the IgG immunoreactivity decreased when fish was processed into surimi [114]. Oral food challenge results showed that none of the 30 fish allergic patients developed allergic symptoms after the ingestion of fish gelatin [125]. This is because different food processing techniques cause (1) breaking of linear epitopes into small fragments; (2) changing its conformation to destroy conformational epitopes; (3) changing its conformation or exposure of the neoepitopes; and (4) masking of epitopes due to molecule attachment. Generally, linear epitopes are considered more stable than conformation epitopes. Heating, such as boiling, canning, and frying, might change protein solubility due to denaturation and protein aggregation as a function of temperature and time. As Kuehn et al. [126] reported, parvalbumin content in commercially thermally processed (smoked and canned) and laboratory-cooked (100 °C/10 or 20 min) fish decreased up to 60% and 25%, respectively, compared to unheated fish. Additionally, Wang [119] found a significant reduction of soluble protein concentration after treating whiting with vinegar. Hou [114] noticed a decrease in protein concentration after processing fish into surimi. Hydrolysis could reduce allergenicity/antigenicity but could also expose preexisting epitopes or create neoepitopes [127]. For example, trypsin hydrolysis generated two polypeptide fragments from cod that are allergenic [128]. Glycation, as another food processing method, could also increase or protein allergenicity [129]. After glycation, the digestibility and allergenicity of carp parvalbumin increased and decreased, respectively, due to glucose attachment to IgE epitopes [122]. The effect of glycation on parvalbumin allergenicity is also dependent on sugar structure, protein concentration, and glycation condition [121]. Non-thermal processing such as high hydrostatic pressure (HHP) could alter the secondary and tertiary structure of parvalbumin, which could effectively reduce its antigenicity [130]. It should be noted that a decrease in allergenicity in some fish allergic patients does not guarantee this function in other patients. Many studies reported different reactions to the same processed fish from different patients [32,38,93,124].
Third, current research on the effect of food processing on fish antigenicity and allergenicity has some limitations. Most of the studies used in vitro methods, such as Western blots and ELISAs, to study the effect of food processing on fish antigenicity and allergenicity. When using food allergic patient sera to evaluate IgE-binding capacity, it is important to consider the usage of pooled or individual patient sera. Pooled sera could rule out inter-individual differences, but they only reflect an average IgE reactivity [89]. When individual sera are used, the number of individuals should be taken into consideration. According to the WHO/IUIS, at least five sera of patients allergic to the respective allergen source should be used in allergenicity tests [46]. Those in vitro tests could not truly represent the fish allergenicity after human consumption. Few studies have applied skin prick tests, which may give false positive/negative results due to the different exposure routes. As for the ex vivo basophil activation test (BAT), the detection sensitivity also decreases over time [131]. In addition, recent studies have primarily focused on the major fish allergen, i.e., parvalbumin. Other major fish allergens, such as beta enolase, creatine kinase, and collagen, have not been fully studied. It is possible to generate new allergens from processing-induced protein–protein interaction. Some researchers have recently pointed out the urgency and necessity of further characterizing other fish allergens. For example, the first case of anaphylaxis due to the ingestion of gummy candy containing fish collagen was reported [132,133]. Kalic et al. [26] further proposed the relevance of investigating fish collagen. Additionally, Ruethers et al. [25] reported that fish tropomyosin, as a novel major fish allergen, is underestimated at the current stage.
5. Conclusions
Due to the fact that the production and consumption of fish have been increasing in recent years, the prevalence of fish allergy among different regions is also increasing. Currently, there is no cure for fish allergy, which can only be managed by strict avoidance of fish in the diet. The effect of food processing on fish proteins’ antigenicity and allergenicity is summarized in this concise review article. It is found that processing could alter a fish protein’s solubility and conformation and lead to an enhanced, impaired, or unchanged antigenicity and allergenicity. There are some limitations in recent studies. First, terminologies such as immunogenicity, antigenicity, and allergenicity are used interchangeably by different researchers. Second, due to the various fish species, recent research has mainly focused on the commonly consumed species. Moreover, among the 12 WHO/IUIS recognized fish allergens, parvalbumin is studied the most, whose antigenicity and allergenicity are mainly dependent on the existence of calcium. As for other fish allergens, although their antigenicity and allergenicity have been reported from different fish species, the characterization is not comprehensive. Third, current antigenicity/allergenicity evaluation methods are mainly conducted in vitro, which may not reflect the real immune response in reality. Future research can be conducted on (1) the development of official methods for evaluating proteins antigenicity, allergenicity, and immunogenicity; (2) the evaluation of other major fish allergens such as tropomyosin and collagen; (3) the investigation of food processing of less commonly consumed fish species.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Q.R.; methodology, Q.R. and X.J.; data curation, X.J.; writing—original draft preparation, X.J.; writing—review and editing, X.J. and Q.R.; supervision, Q.R.; project administration, Q.R.; funding acquisition, Q.R. Both authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Institute of Food and Agriculture, U.S. Department of Agriculture, grant number 2018-70001-28759 and 2020-67017-33236.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Footnotes
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Johansson S., Bieber T., Dahl R., Friedmann P.S., Lanier B.Q., Lockey R.F., Motala C., Martell J.A.O., Platts-Mills T.A., Ring J. Revised nomenclature for allergy for global use: Report of the Nomenclature Review Committee of the World Allergy Organization, October 2003. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004;113:832–836. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2003.12.591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Stone K.D., Prussin C., Metcalfe D.D. IgE, mast cells, basophils, and eosinophils. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010;125:S73–S80. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.11.017. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Yu W., Freeland D.M.H., Nadeau K.C. Food allergy: Immune mechanisms, diagnosis and immunotherapy. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2016;16:751–765. doi: 10.1038/nri.2016.111. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Raposo A., Perez E., Faria C.T.D., Carrascosa C. Allergen management as a key issue in food safety. In: Rai V.R., Bai J.A., editors. Food Safety and Protection. CRC Press Taylor & Francis Group; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2017. pp. 157–195. [Google Scholar]
- 5.Alessandro F., Fierro V. World Allergy Organization: Food Allergy. [(accessed on 16 April 2021)]; Available online: https://www.worldallergy.org/education-and-programs/education/allergic-disease-resource-center/professionals/food-allergy#:~:text=Food%20allergy%20is%20described%20as,from%201%25%20to%2010%25.
- 6.Gupta R.S., Springston E.E., Warrier M.R., Smith B., Kumar R., Pongracic J., Holl J.L. The Prevalence, Severity, and Distribution of Childhood Food Allergy in the United States. Pediatrics. 2011;128:e9–e17. doi: 10.1542/peds.2011-0204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Maslova E., Granström C., Hansen S., Petersen S.B., Strøm M., Willett W.C., Olsen S.F. Peanut and tree nut consumption during pregnancy and allergic disease in children—Should mothers decrease their intake? Longitudinal evidence from the Danish National Birth Cohort. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012;130:724–732. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.05.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Jensen M.P., Meldrum S., Taylor A.L., Dunstan J.A., Prescott S.L. Early probiotic supplementation for allergy prevention: Long-term outcomes. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2012;130:1209–1211.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2012.07.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Vassallo M.F., Camargo C.A. Potential mechanisms for the hypothesized link between sunshine, vitamin D, and food allergy in children. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010;126:217–222. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.06.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.USFDA FDA Approves First Drug for Treatment of Peanut Allergy for Children. [(accessed on 16 April 2021)]; Available online: https://www.fda.gov/news-events/press-announcements/fda-approves-first-drug-treatment-peanut-allergy-children.
- 11.El-Ghoneimy D., Lamia D., Cesar G., Sakura S. World Allergy Organization Food Allergy Information Sheet. [(accessed on 16 April 2021)]; Available online: https://www.worldallergy.org/UserFiles/file/WAO-2019-Food-Allergy-Information-Sheet.pdf.
- 12.Rona R.J., Keil T., Summers C., Gislason D., Zuidmeer L., Sodergren E., Sigurdardottir S.T., Lindner T., Goldhahn K., Dahlstrom J., et al. The prevalence of food allergy: A meta-analysis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007;120:638–646. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.05.026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Gupta R.S., Warren C.M., Smith B.M., Jiang J., Blumenstock J.A., Davis M.M., Schleimer R.P., Nadeau K.C. Prevalence and Severity of Food Allergies Among US Adults. JAMA Netw. Open. 2019;2:e185630. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.5630. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.McGowan E.C., Keet C.A. Prevalence of self-reported food allergy in the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (NHANES) 2007–2010. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2013;132:1216–1219.e5. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2013.07.018. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Tang M.L.K., Mullins R.J. Food allergy: Is prevalence increasing? Intern. Med. J. 2017;47:256–261. doi: 10.1111/imj.13362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.WHO/IUIS Allergen Nomenclature Sub-Committee Allergen Nomenclature. [(accessed on 16 April 2021)]; Available online: http://www.allergen.org/index.php.
- 17.Ruethers T., Raith M., Sharp M.F., Koeberl M., Stephen J.N., Nugraha R., Le T.T.K., Quirce S., Nguyen H.X.M., Kamath S.D., et al. Characterization of Ras k 1 a novel major allergen in Indian mackerel and identification of parvalbumin as the major fish allergen in 33 Asia-Pacific fish species. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2017;48:452–463. doi: 10.1111/cea.13069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Ruethers T., Taki A.C., Karnaneedi S., Nie S., Kalic T., Dai D., Daduang S., Leeming M., Williamson N.A., Breiteneder H., et al. Expanding the allergen repertoire of salmon and catfish. Allergy. 2020:1–11. doi: 10.1111/all.14574. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Untersmayr E., Szalai K., Riemer A.B., Hemmer W., Swoboda I., Hantusch B., Schöll I., Spitzauer S., Scheiner O., Jarisch R., et al. Mimotopes identify conformational epitopes on parvalbumin, the major fish allergen. Mol. Immunol. 2006;43:1454–1461. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2005.07.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Elsayed S., Apold J. Immunochemical Analysis of Cod Fish Allergen M: Locations of the Immunoglobulin Binding Sites as Demonstrated by the Native and Synthetic Peptides. Allergy. 1983;38:449–459. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.1983.tb02353.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Perez-Gordo M., Pastor-Vargas C., Lin J., Bardina L., Cases B., Ibáñez M.D., Vivanco F., Cuesta-Herranz J., Sampson H.A. Epitope mapping of the major allergen from Atlantic cod in Spanish population reveals different IgE-binding patterns. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2013;57:1283–1290. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.201200332. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Yoshida S., Ichimura A., Shiomi K. Elucidation of a major IgE epitope of Pacific mackerel parvalbumin. Food Chem. 2008;111:857–861. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2008.04.062. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Keshavarz B., Jiang X., Hsieh Y.-H.P., Rao Q. Matrix effect on food allergen detection—A case study of fish parvalbumin. Food Chem. 2019;274:526–534. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.08.138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Sharp M.F., Taki A.C., Ruethers T., Stephen J.N., Daly N.L., Lopata A.L., Kamath S.D. IgE and IgG4 epitopes revealed on the major fish allergen Lat c 1. Mol. Immunol. 2021;131:155–163. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2020.12.033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Ruethers T., Kamath S., Taki A., Le T., Karnaneedi S., Nugraha R., Cao T., Nie S., Williamson N., Mehr S., et al. Tropomyosin Is A Novel Major Fish Allergen Of Unrecognized Importance. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020;145:AB226. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2019.12.187. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kalic T., Kamath S.D., Ruethers T., Taki A.C., Nugraha R., Le T.T., Humeniuk P., Williamson N.A., Hira D., Rolland J.M., et al. Collagen—An Important Fish Allergen for Improved Diagnosis. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020;8:3084–3092.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.04.063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Abraha B., Admassu H., Mahmud A., Tsighe N., Shui X.W., Fang Y. Effect of processing methods on nutritional and physico-chemical composition of fish: A review. MOJ Food Process. Technol. 2018;6:1. doi: 10.15406/mojfpt.2018.06.00191. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Wisuthiphaet N., Kongruang S., Chamcheun C. Production of Fish Protein Hydrolysates by Acid and Enzymatic Hydrolysis. J. Med. Bioeng. 2015;4:466–470. doi: 10.12720/jomb.4.6.466-470. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 29.De Jongh H.H.J., Robles C.L., Timmerman E., Nordlee J.A., Lee P.-W., Baumert J.L., Hamilton R.G., Taylor S.L., Koppelman S.J. Digestibility and IgE-Binding of Glycosylated Codfish Parvalbumin. BioMed Res. Int. 2013;2013:1–10. doi: 10.1155/2013/756789. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Kubota H., Kobayashi A., Kobayashi Y., Shiomi K., Hamada-Sato N. Reduction in IgE reactivity of Pacific mackerel parvalbumin by heat treatment. Food Chem. 2016;206:78–84. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2016.03.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kobayashi Y., Kuriyama T., Nakagawara R., Aihara M., Hamada-Sato N. Allergy to fish collagen: Thermostability of collagen and IgE reactivity of patients’ sera with extracts of 11 species of bony and cartilaginous fish. Allergol. Int. 2016;65:450–458. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2016.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.André F., Cavagna S., André C. Gelatin Prepared from Tuna Skin: A Risk Factor for Fish Allergy or Sensitization? Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2003;130:17–24. doi: 10.1159/000068370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Punt J., Stranford S.A., Jones P.P., Owen J.A. Kuby Immunology. W. H. Freeman and Company; New York, NY, USA: 2007. [Google Scholar]
- 34.Parenti M.D., Santoro A., Del Rio A., Franceschi C. Literature review in support of adjuvanticity/immunogenicity assessment of proteins. EFSA Support. Publ. 2019;16:1551. doi: 10.2903/sp.efsa.2019.EN-1551. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Faisal M., Vasiljevic T., Donkor O.N. Effects of selected processing treatments on antigenicity of banana prawn (Fenneropenaeus merguiensis) tropomyosin. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2018;54:183–193. doi: 10.1111/ijfs.13922. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Li Z., Jiang M., You J., Luo Y., Feng L. Impact of Maillard reaction conditions on the antigenicity of parvalbumin, the major allergen in grass carp. Food Agric. Immunol. 2013;25:486–497. doi: 10.1080/09540105.2013.838943. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Song Y.-S., Frias J., Martinez-Villaluenga C., Vidal-Valdeverde C., de Mejia E.G. Immunoreactivity reduction of soybean meal by fermentation, effect on amino acid composition and antigenicity of commercial soy products. Food Chem. 2008;108:571–581. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2007.11.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Sletten G., Van Do T., Lindvik H., Egaas E., Florvaag E. Effects of Industrial Processing on the Immunogenicity of Commonly Ingested Fish Species. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2010;151:223–236. doi: 10.1159/000242360. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Teodorowicz M., Van Neerven J., Savelkoul H. Food Processing: The Influence of the Maillard Reaction on Immunogenicity and Allergenicity of Food Proteins. Nutrients. 2017;9:835. doi: 10.3390/nu9080835. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Ilchmann A., Burgdorf S., Scheurer S., Waibler Z., Nagai R., Wellner A., Yamamoto Y., Yamamoto H., Henle T., Kurts C., et al. Glycation of a food allergen by the Maillard reaction enhances its T-cell immunogenicity: Role of macrophage scavenger receptor class A type I and II. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010;125:175–183.e11. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.08.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Abramovitch J.B., Lopata A.L., O’Hehir R.E., Rolland J.M. Effect of thermal processing on T cell reactivity of shellfish allergens—Discordance with IgE reactivity. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e0173549. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0173549. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Waserman S., Watson W. Food allergy. Allergy Asthma Clin. Immunol. 2011;7:S7. doi: 10.1186/1710-1492-7-S1-S7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Deifl S., Bohle B. Factors influencing the allergenicity and adjuvanticity of allergens. Immunotherapy. 2011;3:881–893. doi: 10.2217/imt.11.69. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Mari A. When does a protein become an allergen? Searching for a dynamic definition based on most advanced technology tools. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2008;38:1089–1094. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.03011.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Zhang J., Tao A. Antigenicity, Immunogenicity, Allergenicity. Transl. Bioinform. 2015;8:175–186. doi: 10.1007/978-94-017-7444-4_11. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 46.WHO/IUIS Allergen Nomenclature Sub-Committee New Allergen Submission Form. [(accessed on 16 April 2021)]; Available online: http://www.allergen.org/submission.php.
- 47.CDC Laboratory Procedure Manual: Specific IgE/total IgE. [(accessed on 16 April 2021)]; Available online: https://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/nhanes/nhanes_05_06/al_ige_d_met_specific_ige_total_ige.pdf.
- 48.Santos A.F., Lack G. Basophil activation test: Food challenge in a test tube or specialist research tool? Clin. Transl. Allergy. 2016;6:1–9. doi: 10.1186/s13601-016-0098-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Fæste C.K., Namork E., Lindvik H. Allergenicity and antigenicity of fenugreek (Trigonella foenum-graecum) proteins in foods. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2009;123:187–194. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2008.09.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Wild L.G., Lehrer S.B. Fish and shellfish allergy. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2005;5:74–79. doi: 10.1007/s11882-005-0059-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Sharp M.F., Lopata A.L. Fish Allergy: In Review. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2013;46:258–271. doi: 10.1007/s12016-013-8363-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Sicherer S.H., Sampson H.A. Food allergy. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010;125:S116–S125. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2009.08.028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Helbling A., Haydel R., McCants M.L., Musmand J.J., El-Dahr J., Lehrer S.B. Fish allergy: Is cross-reactivity among fish species relevant? Double-blind placebo-controlled food challenge studies of fish allergic adults. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 1999;83:517–523. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)62862-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Borrego J.T., Cuevas J.M., García J.T. Reactividad cruzada entre pescados y mariscos. Allergol. Immunopathol. 2003;31:146–151. doi: 10.1016/S0301-0546(03)79282-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Kuehn A., Codreanu-Morel F., Lehners-Weber C., Doyen V., Gomez-André S.-A., Bienvenu F., Fischer J., Ballardini N., Van Hage M., Perotin J.-M., et al. Cross-reactivity to fish and chicken meat—A new clinical syndrome. Allergy. 2016;71:1772–1781. doi: 10.1111/all.12968. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Hilger C., Thill L., Grigioni F., Lehners C., Falagiani P., Ferrara A., Romano C., Stevens W., Hentges F. IgE antibodies of fish allergic patients cross-react with frog parvalbumin. Allergy. 2004;59:653–660. doi: 10.1111/j.1398-9995.2004.00436.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Ross M.P., Ferguson M., Street D., Klontz K., Schroeder T., Luccioli S. Analysis of food-allergic and anaphylactic events in the National Electronic Injury Surveillance System. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2008;121:166–171. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2007.10.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Bock S., Muñoz-Furlong A., Sampson H.A. Fatalities due to anaphylactic reactions to foods. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001;107:191–193. doi: 10.1067/mai.2001.112031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Pitsios C., Dimitriou A., Stefanaki E.C., Kontou-Fili K. Anaphylaxis during skin testing with food allergens in children. Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging. 2009;169:613–615. doi: 10.1007/s00431-009-1070-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Attaran R.R. Histamine fish poisoning: A common but frequently misdiagnosed condition. Emerg. Med. J. 2002;19:474–475. doi: 10.1136/emj.19.5.474. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Moneo I., Caballero M.L., Gómez F., Ortega E., Alonso M.J., Gómez-Aguado F. Isolation and characterization of a major allergen from the fish parasite Anisakis simplex. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2000;106:177–182. doi: 10.1067/mai.2000.106732. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Sicherer S.H., Muñoz-Furlong A., Sampson H.A. Prevalence of seafood allergy in the United States determined by a random telephone survey. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2004;114:159–165. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2004.04.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Verrill L., Bruns R., Luccioli S. Allergy and Asthma Proceedings. Volume 36. Oceanside Publications Inc.; Chichester, UK: 2015. Prevalence of self-reported food allergy in U.S. adults: 2001, 2006, and 2010; pp. 458–467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Connett G.J., Gerez I., Cabrera-Morales E.A., Yuenyongviwat A., Ngamphaiboon J., Chatchatee P., Sangsupawanich P., Soh S.-E., Yap G.-C., Shek L.P.-C., et al. A Population-Based Study of Fish Allergy in the Philippines, Singapore and Thailand. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012;159:384–390. doi: 10.1159/000338940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Ben-Shoshan M., Harrington D.W., Soller L., Fragapane J., Joseph L., Pierre Y.S., Godefroy S.B., Elliot S.J., Clarke A.E. A population-based study on peanut, tree nut, fish, shellfish, and sesame allergy prevalence in Canada. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2010;125:1327–1335. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2010.03.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Orhan F., Karakas T., Cakir M., Aksoy A., Baki A., Gedik Y. Prevalence of immunoglobulin E-mediated food allergy in 6–9-year-old urban schoolchildren in the eastern Black Sea region of Turkey. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2009;39:1027–1035. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2009.03263.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Taylor-Black S., Wang J. The prevalence and characteristics of food allergy in urban minority children. Ann. Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2012;109:431–437. doi: 10.1016/j.anai.2012.09.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Wu T.-C., Tsai T.-C., Huang C.-F., Chang F.-Y., Lin C.-C., Chu C.-H., Lau B.-H., Wu L., Peng H.-J., Tang R.-B. Prevalence of food allergy in Taiwan: A questionnaire-based survey. Intern. Med. J. 2012;42:1310–1315. doi: 10.1111/j.1445-5994.2012.02820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Krogulska A., Dynowski J., Funkowicz M., Małachowska B., Wąsowska-Królikowska K. Prevalence and Clinical Impact of IgE-Mediated Food Allergy in School Children With Asthma: A Double-Blind Placebo-Controlled Food Challenge Study. Allergy Asthma Immunol. Res. 2015;7:547–556. doi: 10.4168/aair.2015.7.6.547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.Leung A.S.Y., Leung N.Y.H., Wai C.Y.Y., Xu K.J.Y., Lam M.C.Y., Shum Y.Y., Lee T.H., Ho M.H.K., Duque J.S.D.R., Chua G.T., et al. Characteristics of Chinese fish-allergic patients: Findings from double-blind placebo-controlled food challenges. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020;8:2098–2100.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.jaip.2020.02.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Ruethers T., Taki A.C., Johnston E.B., Nugraha R., Le T.T., Kalic T., McLean T.R., Kamath S.D., Lopata A.L. Seafood allergy: A comprehensive review of fish and shellfish allergens. Mol. Immunol. 2018;100:28–57. doi: 10.1016/j.molimm.2018.04.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Fernandes T.J.R., Costa J., Oliveira M.B.P.P., Mafra I. An overview on fish and shellfish allergens and current methods of detection. Food Agric. Immunol. 2015;26:848–869. doi: 10.1080/09540105.2015.1039497. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 73.Klueber J., Schrama D., Rodrigues P., Dickel H., Kuehn A. Fish Allergy Management: From Component-Resolved Diagnosis to Unmet Diagnostic Needs. Curr. Treat. Options Allergy. 2019;6:322–337. doi: 10.1007/s40521-019-00235-w. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Stephen J.N., Sharp M.F., Ruethers T., Taki A., Campbell D.E., Lopata A.L. Allergenicity of bony and cartilaginous fish—Molecular and immunological properties. Clin. Exp. Allergy. 2017;47:300–312. doi: 10.1111/cea.12892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Perez-Gordo M., Lin J., Bardina L., Pastor-Vargas C., Cases B., Vivanco F., Cuesta-Herranz J., Sampson H.A. Epitope Mapping of Atlantic Salmon Major Allergen by Peptide Microarray Immunoassay. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2012;157:31–40. doi: 10.1159/000324677. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Keshavarz B., Rao Q., Jiang X., Hsieh Y.-H.P. Immunochemical analysis of pepsin-digested fish tropomyosin. Food Control. 2020;118:107427. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107427. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Bugajska-Schrette A., Grote M., Vangelista L., Valent P., Sperr W.R., Rumpold H., Pastore A., Reichelt R., Valenta R., Spitzauer S. Purification, biochemical, and immunological characterisation of a major food allergen: Different immunoglobulin E recognition of the apo- and calcium-bound forms of carp parvalbumin. Gut. 2000;46:661–669. doi: 10.1136/gut.46.5.661. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Sigma-Aldrich P3088: Monoclonal Anti-Parvalbumin Antibody Produced in Mouse. [(accessed on 16 April 2021)]; Available online: https://www.sigmaaldrich.com/catalog/product/sigma/p3088?lang=en®ion=US.
- 79.Gajewski K.G., Hsieh Y.-H.P. Monoclonal Antibody Specific to a Major Fish Allergen: Parvalbumin. J. Food Prot. 2009;72:818–825. doi: 10.4315/0362-028X-72.4.818. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Tomura S., Ishizaki S., Nagashima Y., Shiomi K. Reduction in the IgE reactivity of Pacific mackerel parvalbumin by mutations at Ca2+-binding sites. Fish. Sci. 2008;74:411–417. doi: 10.1111/j.1444-2906.2008.01538.x. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Bugajska-Schretter A., Elfman L., Fuchs T., Kapiotis S., Rumpold H., Valenta R., Spitzauer S. Parvalbumin, a cross-reactive fish allergen, contains IgE-binding epitopes sensitive to periodate treatment and Ca2+ depletion. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1998;101:67–74. doi: 10.1016/S0091-6749(98)70195-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Swoboda I., Bugajska-Schretter A., Verdino P., Keller W., Sperr W.R., Valent P., Valenta R., Spitzauer S. Recombinant Carp Parvalbumin, the Major Cross-Reactive Fish Allergen: A Tool for Diagnosis and Therapy of Fish Allergy. J. Immunol. 2002;168:4576–4584. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.168.9.4576. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Ashie I.N.A., Smith J.P., Simpson B.K., Haard N.F. Spoilage and shelf-life extension of fresh fish and shellfish. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 1996;36:87–121. doi: 10.1080/10408399609527720. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Knorr D., Watzke H. Food Processing at a Crossroad. Front. Nutr. 2019;6:85. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2019.00085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Mills E.N.C., Sancho A.I., Rigby N.M., Jenkins J.A., Mackie A.R. Impact of food processing on the structural and allergenic properties of food allergens. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009;53:963–969. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200800236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Sathe S.K., Teuber S.S., Roux K.H. Effects of food processing on the stability of food allergens. Biotechnol. Adv. 2005;23:423–429. doi: 10.1016/j.biotechadv.2005.05.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Sathe S.K., Sharma G.M. Effects of food processing on food allergens. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009;53:970–978. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200800194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Griesmeier U., Bublin M., Radauer C., Vázquez-Cortés S., Ma Y., Fernández-Rivas M., Breiteneder H. Physicochemical properties and thermal stability of Lep w 1, the major allergen of whiff. Mol. Nutr. Food Res. 2009;54:861–869. doi: 10.1002/mnfr.200900043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Verhoeckx K.C., Vissers Y.M., Baumert J.L., Faludi R., Feys M., Flanagan S., Herouet-Guicheney C., Holzhauser T., Shimojo R., van der Bolt N., et al. Food processing and allergenicity. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2015;80:223–240. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2015.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Kristinsson H.G., Lanier T.C., Halldorsdottir S.M., Geirsdottir M., Park J.W. Chapter 6 Fish protein isolate by pH shift. In: Park J.W., editor. Surimi and Surimi Seafood. CRC Press; Boca Raton, FL, USA: 2013. pp. 141–169. [Google Scholar]
- 91.Nugraha R., Ruethers T., Johnston E., Rolland J., O’Hehir R., Kamath S., Lopata A. Effects of Extraction Buffer on the Solubility and Immunoreactivity of the Pacific Oyster Allergens. Foods. 2021;10:409. doi: 10.3390/foods10020409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Jiaju M., Ramesh P.T., Zhen-Xing L., Hong L. Optimisation of an extraction technique of fish allergens suitable for detection and diagnosis. Czech J. Food Sci. 2017;35:24–31. doi: 10.17221/578/2015-CJFS. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Mejrhit N., Azdad O., El Kabbaoui M., Ouahidi I., Tazi A., Aarab L. Sensitivity of Moroccans to sardine parvalbumin and effect of heating and enzymatic treatments. Food Agric. Immunol. 2017;28:1362–1373. doi: 10.1080/09540105.2017.1343804. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Vissers Y.M., Wichers H.J., Savelkoul H.F.J. Influence of food processing, digestion and the food matrix on allergenicity & cellular measures of allergenicity. In: Gao Z.-S., Zheng M., Gilissen L.J.W.J., Shen H.-H., Frewer L.J., editors. Multidisciplinary Approaches to Allergies. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 2012. pp. 203–227. [Google Scholar]
- 95.Arvanitoyannis I.S., Kotsanopoulos K.V. Smoking of Fish and Seafood: History, Methods and Effects on Physical, Nutritional and Microbiological Properties. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2011;5:831–853. doi: 10.1007/s11947-011-0690-8. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Van Nguyen M., Arason S., Eikevik T.M. Seafood Processing. Wiley; Hoboken, NJ, USA: 2013. Drying of Fish; pp. 161–175. [Google Scholar]
- 97.Zang J., Xu Y., Xia W., Regenstein J.M. Quality, functionality, and microbiology of fermented fish: A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2020;60:1228–1242. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2019.1565491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Jónsdóttir R., Sveinsdóttir K., Magnússon H., Arason S., Lauritzsen K., Thorarinsdottir K.A. Flavor and Quality Characteristics of Salted and Desalted Cod (Gadus morhua) Produced by Different Salting Methods. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2011;59:3893–3904. doi: 10.1021/jf104203p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.De Oliveira F.A., Neto O.C., dos Santos L.M.R., Ferreira E.H.R., Rosenthal A. Effect of high pressure on fish meat quality—A review. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 2017;66:1–19. doi: 10.1016/j.tifs.2017.04.014. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Hogan E., Kelly A.L., Sun D.-W. Emerging Technologies for Food Processing. Elsevier BV; Amsterdam, The Netherlands: 2005. High Pressure Processing of Foods: An Overview; pp. 3–32. [Google Scholar]
- 101.Rode T.M., Hovda M.B. High pressure processing extend the shelf life of fresh salmon, cod and mackerel. Food Control. 2016;70:242–248. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2016.05.045. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Rastogi N.K. Opportunities and Challenges in Application of Ultrasound in Food Processing. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2011;51:705–722. doi: 10.1080/10408391003770583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Pedrós-Garrido S., Condón-Abanto S., Beltrán J., Lyng J., Brunton N., Bolton D., Whyte P. Assessment of high intensity ultrasound for surface decontamination of salmon (S. salar), mackerel (S. scombrus), cod (G. morhua) and hake (M. merluccius) fillets, and its impact on fish quality. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2017;41:64–70. doi: 10.1016/j.ifset.2017.02.006. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Nicorescu I., Nguyen B., Chevalier S., Orange N. Effects of pulsed light on the organoleptic properties and shelf-life extension of pork and salmon. Food Control. 2014;44:138–145. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2014.03.052. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Zhao Y.-M., De Alba M., Sun D.-W., Tiwari B. Principles and recent applications of novel non-thermal processing technologies for the fish industry—A review. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. 2019;59:728–742. doi: 10.1080/10408398.2018.1495613. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Gómez B., Munekata P.E.S., Gavahian M., Barba F.J., Martí-Quijal F.J., Bolumar T., Campagnol P.C.B., Tomašević I., Lorenzo J.M. Application of pulsed electric fields in meat and fish processing industries: An overview. Food Res. Int. 2019;123:95–105. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.04.047. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 107.Alves Filho E.G., de Brito E.S., Rodrigues S. Chapter 8—Effects of cold plasma processing in food components. In: Bermudez-Aguirre D., editor. Advances in Cold Plasma Applications for Food Safety and Preservation. Academic Press; Cambridge, MA, USA: 2020. pp. 253–268. [Google Scholar]
- 108.Choi S., Puligundla P., Mok C. Effect of corona discharge plasma on microbial decontamination of dried squid shreds including physico-chemical and sensory evaluation. LWT. 2017;75:323–328. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2016.08.063. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Crowe K.M., Skonberg D., Bushway A., Baxter S. Application of ozone sprays as a strategy to improve the microbial safety and quality of salmon fillets. Food Control. 2012;25:464–468. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2011.11.021. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Chatterjee U., Mondal G., Chakraborti P., Patra H., Chatterjee B. Changes in the Allergenicity during Different Preparations of Pomfret, Hilsa, Bhetki and Mackerel Fish as Illustrated by Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay and Immunoblotting. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2006;141:1–10. doi: 10.1159/000094176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Saptarshi S.R., Sharp M.F., Kamath S.D., Lopata A.L. Antibody reactivity to the major fish allergen parvalbumin is determined by isoforms and impact of thermal processing. Food Chem. 2014;148:321–328. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2013.10.035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Somkuti J., Bublin M., Breiteneder H., Smeller L. Pressure–Temperature Stability, Ca2+ Binding, and Pressure–Temperature Phase Diagram of Cod Parvalbumin: Gad m 1. Biochemistry. 2012;51:5903–5911. doi: 10.1021/bi300403h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Mondal G., Chatterjee U., Samanta S., Chatterjee B.P. Role of pepsin in modifying the allergenicity of bhetki (Lates calcarifer) and mackerel (Rastrelliger kanagurta) fish. Indian J. Biochem. Biophys. 2007;44:94–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Hou C.M. Master’s Thesis. Florida State University; Tallahassee, FL, USA: 2011. Competitive Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Quantitative Detection of Fish Proteins in Heat-Processed Crab Meat. [Google Scholar]
- 115.De Jongh H.H., Taylor S.L., Koppelman S.J. Controlling the aggregation propensity and thereby digestibility of allergens by Maillardation as illustrated for cod fish parvalbumin. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 2011;111:204–211. doi: 10.1016/j.jbiosc.2010.09.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Yang S.-Y., Kim S.-W., Kim Y., Lee S.-H., Jeon H., Lee K.-W. Optimization of Maillard reaction with ribose for enhancing anti-allergy effect of fish protein hydrolysates using response surface methodology. Food Chem. 2015;176:420–425. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2014.12.090. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Arif S.H., Hasnain A.-u. A major cross-reactive fish allergen with exceptional stability. Parvalbumin. Afr. J. Food Sci. 2010;4:109–114. [Google Scholar]
- 118.Liang J., Taylor S.L., Baumert J., Lopata A.L., Lee N.A. Effects of thermal treatment on the immunoreactivity and quantification of parvalbumin from Southern hemisphere fish species with two anti-parvalbumin antibodies. Food Control. 2021;121:107675. doi: 10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107675. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Wang Y. Master’s Thesis. Florida State University; Tallahassee, FL, USA: 2013. Effects of Vinegar Treatment on Detectability and Allergenicity of Finfish. [Google Scholar]
- 120.Untersmayr E., Poulsen L.K., Platzer M.H., Pedersen M.H., Boltz-Nitulescu G., Skov P.S., Jensen-Jarolim E. The effects of gastric digestion on codfish allergenicity. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2005;115:377–382. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2004.10.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Zhang M., Tu Z., Liu J., Hu Y., Wang H., Mao J., Li J. The IgE/IgG binding capacity and structural changes of Alaska Pollock parvalbumin glycated with different reducing sugars. J. Food Biochem. 2021;45:e13539. doi: 10.1111/jfbc.13539. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Zhao Y.-J., Cai Q.-F., Jin T.-C., Zhang L.-J., Fei D.-X., Liu G.-M., Cao M.-J. Effect of Maillard reaction on the structural and immunological properties of recombinant silver carp parvalbumin. LWT. 2017;75:25–33. doi: 10.1016/j.lwt.2016.08.049. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Bernhisel-Broadbent J., Strause D., Sampson H.A. Fish hypersensitivity. II: Clinical relevance of altered fish allergenicity caused by various preparation methods. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 1992;90:622–629. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(92)90135-O. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Lee P.-W., Nordlee J.A., Koppelman S.J., Baumert J.L., Taylor S.L. Measuring parvalbumin levels in fish muscle tissue: Relevance of muscle locations and storage conditions. Food Chem. 2012;135:502–507. doi: 10.1016/j.foodchem.2012.05.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Hansen T.K., Poulsen L.K., Skov P.S., Hefle S.L., Hlywka J.J., Taylor S.L., Bindslev-Jensen U., Bindslev-Jensen C. A randomized, double-blinded, placebo-controlled oral challenge study to evaluate the allergenicity of commercial, food-grade fish gelatin. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2004;42:2037–2044. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2004.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Kuehn A., Scheuermann T., Hilger C., Hentges F. Important Variations in Parvalbumin Content in Common Fish Species: A Factor Possibly Contributing to Variable Allergenicity. Int. Arch. Allergy Immunol. 2010;153:359–366. doi: 10.1159/000316346. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Thomas K., Herouet-Guicheney C., Ladics G., Bannon G., Cockburn A., Crevel R., Fitzpatrick J., Mills C., Privalle L., Vieths S. Evaluating the effect of food processing on the potential human allergenicity of novel proteins: International workshop report. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2007;45:1116–1122. doi: 10.1016/j.fct.2006.12.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Elsayed S., Aas K., Sletten K., Johansson S. Tryptic cleavage of a homogeneous cod fish Allergen and isolation of two active polypeptide fragments. Immunochemistry. 1972;9:647–661. doi: 10.1016/0019-2791(72)90250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Rao Q., Jiang X., Li Y., Samiwala M., Labuza T.P. Can Glycation Reduce Food Allergenicity? J. Agric. Food Chem. 2018;66:4295–4299. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b00660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Zhang H., Liao H., Lu Y., Hu Y., Yang H., Cao S., Qi X. Effects of high hydrostatic pressure on the structural characteristics of parvalbumin of cultured large yellow croaker (Larimichthys crocea) J. Food Process. Preserv. 2020;44:14911. doi: 10.1111/jfpp.14911. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Ebo D.G., Bridts C.H., Mertens C.H., Sabato V. Principles, potential, and limitations of ex vivo basophil activation by flow cytometry in allergology: A narrative review. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021;147:1143–1153. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2020.10.027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 132.Ueno R., Takaoka Y., Shimojo N., Ohno F., Yamaguchi T., Matsunaga K., Kameda M. A case of pediatric anaphylaxis caused by gummy tablets containing fish collagen. Asia Pac. Allergy. 2020;10:e35. doi: 10.5415/apallergy.2020.10.e35. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Abe N., Ito T., Kobayashi T., Egusa C., Maeda T., Okubo Y., Tsuboi R. A case of anaphylaxis due to fish collagen in a gummy candy. Allergol. Int. 2020;69:146–147. doi: 10.1016/j.alit.2019.05.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.