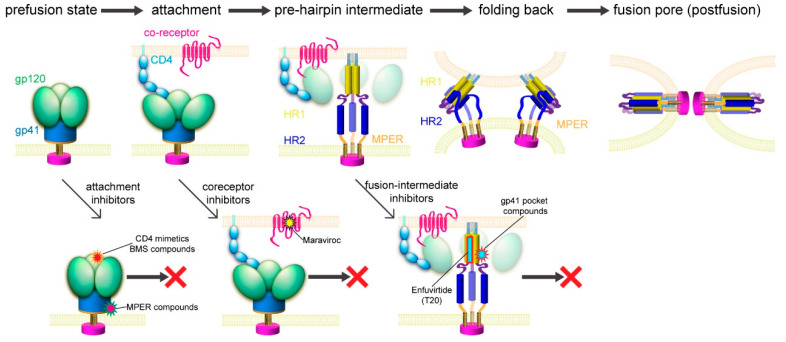
Figure 3.
HIV-1 membrane fusion and its inhibition. Top, membrane fusion likely proceeds stepwise as follows. (1) Binding of gp120 to CD4 and a coreceptor allows viral attachment and triggers structural changes in Env. (2) Dissociation of gp120 and insertion of the fusion peptide of gp41 into the target cell membrane leads to the prehairpin intermediate [95]. (3) HR2 folds back onto the inner core of HR1 and brings the two membranes together. (4) A hemifusion stalk forms and resolves into a fusion pore [96]. Bottom, opportunities for fusion inhibitors, including attachment inhibitors targeting the CD4 binding site and the MPER; coreceptor inhibitors; and fusion-intermediate inhibitors.