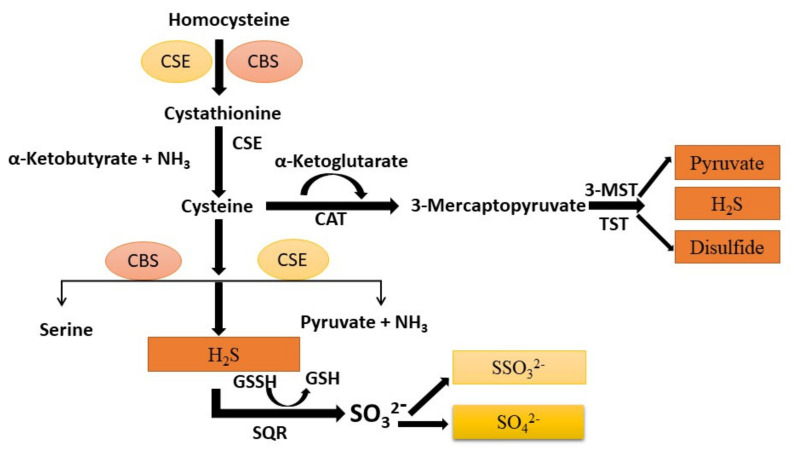
Figure 2.
Illustration of vascular synthesis of H2S formed by a catalytic process in several enzymes (CSE, CBS, and 3-MSPT) in the lung. Cysteine is generated from homocysteine through transculturation pathways intervened by CBS and CSE. H2S forms from homocysteine and cysteine via CBS and CSE. 3-MSPT forms 3-MST-cysteine persulfide (MST-SSH) using mercapto pyruvate, which is formed from cysteine via CAT. H2S is formed from MST-SSH via a non-enzymatic reaction. H2S is oxidized via sulfide oxidation to form thiosulfate and sulfate. H2S is produced from thiosulfate through a non-enzymatic reaction through reductants via the catalytic activity of thiosulfate sulfurtransferase or 3-MST. H2S: hydrogen sulfide; SQR: sulfide-quinone reductase; CBS: cystathionine beta-synthase; CSE: cystathionine γ-lyase; 3-MPST: 3-mercaptopyravute sulfurtransferase; TST: thiosulfate sulfurtransferase; CAT: cysteine aminotransferase; GSSH: glutathione.