To the editor:
The immunologic response following several varieties of vaccination has been described as a potential trigger for the development of both de novo as well as recurrent minimal change disease (MCD).1 There have been emerging cases, including that described by D’Agati et al., of MCD shortly after vaccination with the BNT162b2 vaccine (Pfizer-BioNTech).2 , 3 We report, to the best of the authors’ knowledge, the first case of MCD presenting as nephrotic syndrome following the Moderna mRNA-1273 severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) vaccine.
The patient, a 63-year-old woman, had a medical history that was significant only for hypertension and tobacco dependence. She had no prior history of renal disease. In April 2021, she presented to our hospital with a 4-week history of progressive anasarca, fatigue, periorbital edema, and dyspnea. The patient relayed that the edema and development of foamy urine appeared abruptly and occurred less than a week after having received the first (and only) dose of the Moderna mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine (lot 006B21A). Vaccination was confirmed by cross-referencing her outpatient pharmacy, which administered the dose. Unfortunately, anti-S protein antibody titer is not available to report.
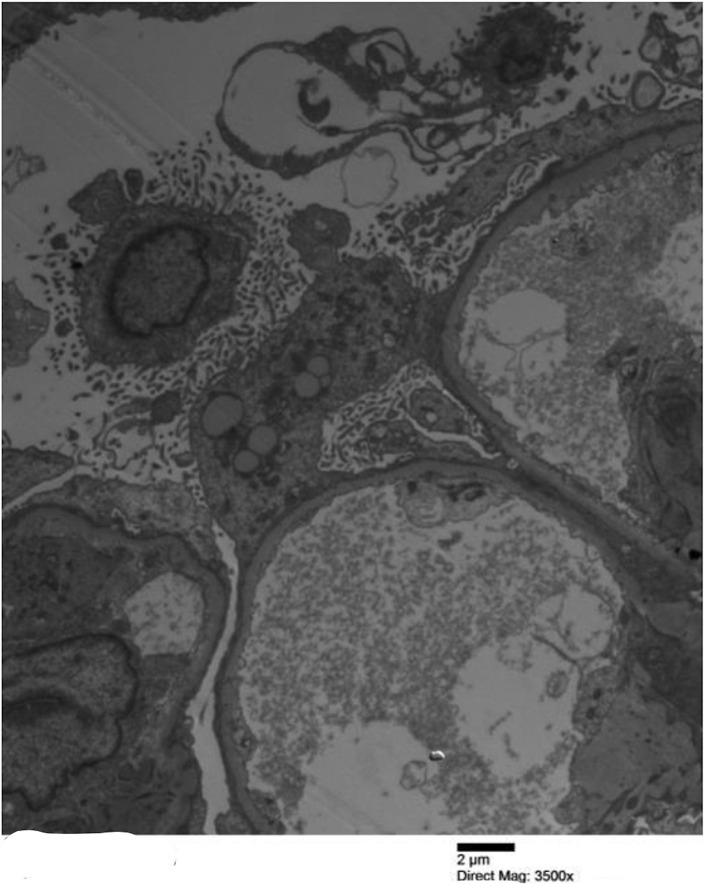
Clinical and diagnostic evaluation also revealed newly uncontrolled hypertension (181/82 mm Hg) as well as mild acute kidney injury (serum creatinine 1.48 mg/dl; baseline was 0.7 mg/dl). Hypoalbuminemia (0.7 g/dl), urinalysis with 3+ proteinuria (without microscopic hematuria), and hyperlipidemia (triglycerides, 221 mg/dl; total cholesterol, 450 mg/dl) were noted. Nephrotic syndrome was confirmed as the 24-hour urine collection revealed 13.4 g proteinuria. Renal biopsy was promptly performed. Pathology confirmed MCD, with mild acute tubular injury, although a focal acute interstitial nephritis was also present. Four of 69 sampled glomeruli were globally sclerosed. There was 10% tubulointerstitial fibrosis. The sampled glomeruli were found to have 100% foot process effacement (Figure 1 ).
Figure 1.
Electron micrograph featuring glomerular capillary loop with diffuse podocyte effacement. Bar = 2 μm. Original magnification ×3500. To optimize viewing of this image, please see the online version of this article at www.kidney-international.org.
Treatment with conservative measures, including valsartan, 80 mg orally twice a day, for renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system inhibition was initiated along with a loop diuretic. She was also given pulse methyl-prednisolone, 500 mg i.v. for 3 days, followed by 1 mg/kg prednisone orally. On the basis of other case reports and our experience with MCD, we anticipate a prompt response to these measures.4 We have recommended the patient forgo the second scheduled dose of the Moderna mRNA-1273 SARS-CoV-2 vaccine. In addition, the authors believe further rechallenges or boosters of this particular vaccine in this patient would be unwise until this potential relationship is more clear.
Acknowledgments
Written informed consent was obtained from the patient for publication of this case report and any accompanying images. A copy of the written consent is available for review by the editor-in-chief of this journal.
Author Contributions
Author contributions were evenly divided, and included but not limited to patient care, research, writing the article, and subsequent revisions.
References
- 1.Gutiérrez S., Dotto B., Petiti J.P. Minimal change disease following influenza vaccination and acute renal failure: just a coincidence? Nefrologia. 2012;32:414–415. doi: 10.3265/Nefrologia.pre2012.Feb.11370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Lebedev L., Sapojnikov M., Wechsler A. Minimal change disease following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. Am J Kidney Dis. 2021;78:142–145. doi: 10.1053/j.ajkd.2021.03.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.D'Agati V.D., Kudose S., Bomback A.S. Minimal change disease and acute kidney injury following the Pfizer-BioNTech COVID-19 vaccine. Kidney Int. 2021;100:461–463. doi: 10.1016/j.kint.2021.04.035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Vivarelli M., Massella L., Ruggiero B. Minimal change disease. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2017;12:332–345. doi: 10.2215/CJN.05000516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]