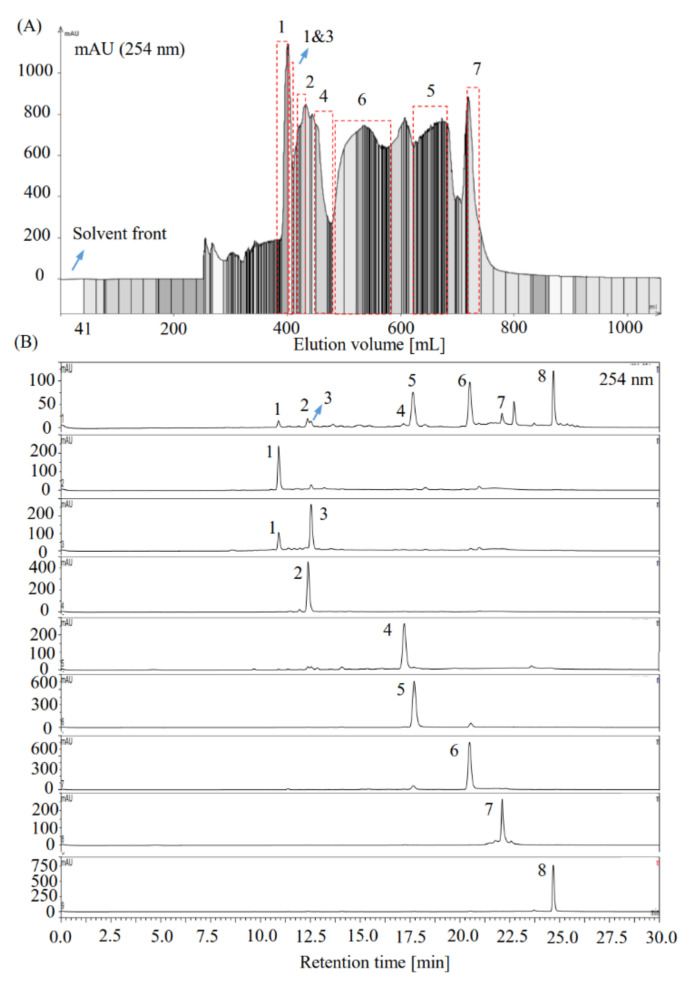
Figure 3.
Chromatograms of pH-zone-refining CCC separation and HPLC detection of the target compounds from the 70% MeOH extract of V. rigida root. (A) pH-zone-refining CCC separation of the target compounds 1–7 from the extract using solvent system EtOAc/n-BuOH/H2O (2:3:5, v/v). The upper phase of EtOAc/n-BuOH/H2O (2:3:5, v/v) was acidified using formic acid (208 mM) as the stationary phase, whereas the lower phase of EtOAc/n-BuOH/H2O (2:3:5, v/v) was basified using ammonia (30 mM) as the mobile phase. Revolution speed: 800 rpm; mobile phase flow rate: 4 mL/min; UV detection wavelength 254 nm. (B) HPLC chromatograms (254 nm) of the 70% MeOH extract of V. rigida root and the compounds separated from it by pH-zone-refining CCC. Notably, compound 8 was obtained by its natural crystallization in the remaining stationary phase collected after separation.