Abstract
Ongoing training in the area of basic life support aims to encourage and sustain the willingness to act in out-of-hospital cardiac arrest situations among first aiders. The contribution of witnesses and first aiders has diminished rapidly, as suspicion associated with the COVID-19 pandemic has risen. In this paper, we present teaching methods from the medical education field to create a new teaching-learning process for sustaining the prehospital involvement of first aiders and encourage new first aiders. The most important benefit—improving outcomes—can be achieved by introducing a variety of teaching-learning methods and formative assessments that provide participants with immediate feedback to help them move forward in the basic life support course. The new reality of web-based learning that has been introduced by the pandemic requires an innovative approach to traditional training that involves techniques and methods that have been proven to be useful in other fields.
Keywords: COVID-19, web-based training, basic life support, formative assessment, out-of-hospital cardiac arrest, web-based learning, web-based education, first aid, medical education, life support, transition, outcome, formative
Introduction
Due to public health concerns in the wake of 2020, which were caused by the novel COVID-19, face-to-face contact in medical training was promptly substituted with remote teaching. The teaching-learning process was moved to the houses of participants through a variety of learning management systems and videoconferencing services [1]. Similarly, all hands-on resuscitation training in the form of in-person, hands-on sessions was stopped [2]. Nevertheless, the European Resuscitation Council (ERC) as well as the International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR), in their educational update in April 2020 on teaching during a pandemic, highlighted the importance of sustaining sudden cardiac arrest training in some form, despite the modified conditions for knowledge transfer. The ILCOR and national societies underlined the significance of continuing education to improve resuscitation knowledge, certain skills, and, most importantly, patient-centered care to sustain and encourage the willingness to act during out-of-hospital cardiac arrest (OHCA) situations [3,4]. Complementary basic life support (BLS) teaching methods involving computer-based and video-based e-learning or the gamification approach have been proven to be useful in the area of BLS [5,6]. However, the cost-effectiveness and standardization of the training delivered via these educational methods should also be considered [7,8].
The long-term retention of BLS competencies is essential and outweighs skills performance during teaching sessions, according to published evidence [9,10]. Such pieces of evidence have opened a new door in the era of BLS training. Additionally, as BLS training is conducted in each health care professional undergraduate medical curriculum, there have been additional demands for finalizing modules that were planned for educational months, which changed due to the COVID-19 pandemic. The Polish Ministry of Health, together with the Ministry of Education, suspended face-to-face education from March 12, 2020, onward [11]. Therefore, the opportunity for launching a web-based BLS course arose (e-BLS) in response to new conditions.
To expand people’s knowledge about distant and web-based possibilities for learning in the area of BLS, we present a proposal for a newly designed e-learning course about BLS competencies. This course was developed to (1) enable participants to understand and cultivate the necessary competencies in each of the OHCA domains and (2) promote the implementation of the steps required for helping people in need of BLS. The course design entails a novel teaching methodology that has been extensively researched in the medical education field.
Methods
The Goal Of Training and Its Objectives
A multimodal, participant-centered, interactive, web-based course for addressing the unique challenges of sudden cardiac arrest that a layperson may face daily was developed. The overarching goals of the course are to (1) enable participants to understand and cultivate the necessary competencies in each of the OHCA domains and (2) promote the implementation of the steps required for helping people in need of BLS. Specific objectives were determined by analyzing the ERC guidelines update for the COVID-19 pandemic. This was done to set up BLS course learning objectives and the needs assessment of the participants (Table 1).
Table 1.
Objectives, instructional methods, and implementation strategies for each basic life support (BLS) competency session.
| Session topic (number of sessions; time of each session) | Objectives | Instructional design and implementation |
| Safety (2; 45 minutes) |
|
|
| BLS (3; 45 minutes) |
|
|
| AEDb (3; 45 minutes) |
|
|
| pBLSc and FBAOd (3; 45 minutes) |
|
|
| Special circumstances leading to sudden cardiac arrest, such as anaphylaxis, heart attacks, strokes, diabetes, drowning, hypothermia, burns, and seizures (3; 45 minutes) |
|
|
| Review (4; 45 minutes) |
|
|
aCPR: cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
bAED: automated external defibrillator.
cpBLS: pediatric basic life support.
dFBAO: foreign body airway obstruction.
Participants: Target Group
The course aims to provide an introduction to BLS and strengthen the elements of the chain of survival. No professional BLS experience is required. However, the course can also be treated as a refresher course for maintaining participants’ motivation to assist in OHCA situations and providing an update on BLS training to health professionals. Therefore, the target population includes students of medical faculties (medicine, dentistry, nursing, midwifery, biomedicine, paramedics, public health, and dieticians), first aiders with initial first aid knowledge, lay rescuers who are enrolled in a first aid course, and health care providers who want to refresh their knowledge.
The e-learning modules have been embedded in the curriculum of students in all medical faculties of the local medical university, as first aid is obligatory in all curricula. The decision trees and the Script Concordance Test (SCT) have been prepared in Polish and English language for Polish and foreign students. The course is planned for 20 teaching hours and takes place in an academic environment.
To target other professional groups and voluntary first aiders, a massive, open, web-based course will be established to enable their participation and access to the proposed activities.
Evaluation
The course will be assessed on the basis of participants’ achievements on the final, summative, multiple-choice question test; the SCT; and decision trees as well as data from an anonymous survey based on the Utrecht Seminar Evaluation questionnaire by Spruijt et el [18]. The authors made the tool available upon our request.
Learning Management Systems and Videoconferencing Services
Based on the advice of experienced researchers, two platforms that are well known to participants were chosen to host the course—Zoom (Zoom Video Communications Inc; Figure 1) and Moodle (Figures 2 and 3)—to alleviate uncertainty and distrust among the students [19]. Zoom enabled live meetings with participants for discussing a given topic, whereas Moodle, a web-based guiding platform, was used to store all of the information on the course meetings and requirements and the organization, all of the materials and resources assigned to topics, and the links to the formative tasks described in this paper. To adjust to web-based classes, participants received detailed instructions on the use of both platforms. The decision trees’ software constituted another university software; however, links to each task appeared on Moodle and were assigned to a given subject (BLS, BLS/automated external defibrillator [AED], or pediatric BLS), and detailed instructions on how to access the task as well as the rules of engagement were provided.
Figure 1.
An anonymized screen shot from an individual Zoom meeting.
Figure 2.
A general overview of an introductory Moodle course website.
Figure 3.
A screenshot of another course on Moodle and a decision tree for instruction. AED: automated external defibrillator; PEA: pulseless electrical activity; VF: ventricular fibrillation; VT: ventricular tachycardia.
The educational game for engaging with BLS/AED drills was also located on a different server. A freely available resource was used [20]. Elements of the game were scored, and participants posted their obtained results on the Moodle forum.
Another type of software that was used during the course was a newly developed testing system—the Testing Centre for Medical Exams (Centrum Medycznych Egzaminów Testowych [CMET]) [21]. The final summative assignment was held on CMET. The CMET used the following 3-level system for constructing the summative assessment (multiple-choice questions): (1) teachers input the questions into the system; (2) specialists in the area reviewed the questions; and (3) the course coordinator accepted, edited, or sent back the questions (with comments) to their primary creator. This was done to ensure the quality of the provided tasks and generate a more complex task (Figures 4 and 5).
Figure 4.
A screenshot of a login page to the CMET website. CMET: Centrum Medycznych Egzaminów Testowych.
Figure 5.
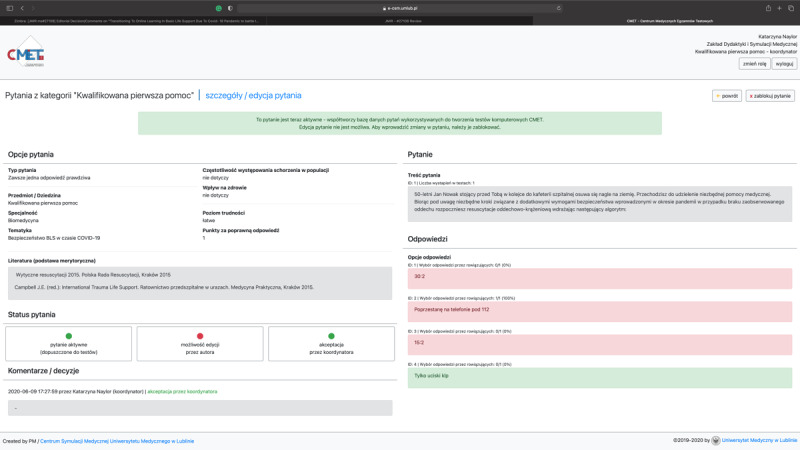
A screenshot of a coordinator account page for a single question on the CMET website. CMET: Centrum Medycznych Egzaminów Testowych.
Before the final assignment, the participants receive access to a practice test to confirm their login details and familiarize themselves with the system’s construction. During the test, each student is individually timed during their attempt and receives immediate feedback on the questions alongside their results after they finalize their attempt.
Discussion
Content and Facilitation
The implemented assessment points support learning and correspond with the implemented content. Our assessments points focus on formative assessment; they are not used as a tool for passing judgment and making pass-fail decisions but as a tool for assisting with and supporting learning [22]. Formative assessments are also known as assessments for learning or learning-oriented assessments. Such assessments aim to provide feedback on understanding and help participants move forward in the course (Table 1).
Novel Assessment Formats That Promote Knowledge Acquisition
Learning is promoted through the formative tasks in the outlined BLS web-based course. Participants need to be consciously analyzing and applying gathered “intel” on a given subject in order to benefit from the experience. All of the proposed types of formative assessments in our course aim to produce feedback on performance to advance the learning of participants [23].
The American Heart Association (AHA) has implemented a video-based approach (a teaching approach centered on using videos) that allows AHA course participants to practice BLS techniques while watching videos (ie, practice-while-watching method) during AHA courses. The AHA also provides the option of an e-learning module, in which participants familiarize themselves with the content of videos and textual content before participating in hands-on sessions [24]. Additionally, the ERC has focused on implementing the Peyton approach (ie, a 4-step method) during their hands-on sessions [25]. Therefore, the focus of BLS courses was placed on face-to-face training, and web-based materials were only used to prepare for face-to-face meetings.
The SCT
The SCT as an assessment method for evaluating clinical reasoning that has several advantages in BLS training. Students tackle a genuine case to demonstrate their ability to incorporate new data into the information on the provided scenario [16,17]. They can compare their reasoning and conduct related discussions, thereby allowing them to learn from each other. This is especially important in emergency situations and OHCA situations, in which quick and timely decisions are required. Additionally, the SCT goes beyond pure fact checking; it requires logical thinking and knowledge application based on procedural knowledge (Multimedia Appendix 1).
Decision Trees
Decision trees are based on the assumption that machine learning algorithms are helpful in the medicine field, as errors can have a dire consequence. Decision trees have been used in the decision-making process in clinical settings [13,26]. Nevertheless, the existing system allows first aiders to tackle the complexities and uncertainties of OHCA. Existing decision tress allow for the implementation of knowledge at the more critical level of the Millers pyramid in BLS competency training (Multimedia Appendix 2; Figure 6).
Figure 6.
A screenshot of a login website for accessing the decision trees.
Gamification
The BLS/AED game was designed to complement BLS teaching and refresh skills in a unique, enjoyable way [6]. The game presents an OHCA scenario by using simple graphics and takes players to a virtual environment where they make choices based on the steps of the BLS/AED algorithm (Multimedia Appendix 2). The game is educational and is a unique medium for knowledge transmission; such games have been proven to promote active learning, help with solving clinical problems, and help learners gain experience in a risk-free environment [6]. At the end of the game, the participants of our course will receive feedback on their performance, and they will have an opportunity to undergo another attempt (Multimedia Appendix 3).
Conclusions
There is a large variety of web-based first responder and BLS courses. Although the new reality resulting from a pandemic and teaching and learning during a pandemic can have difficulties, they also create new possibilities. Enabling continuous BLS training with appropriate tools, including a variety of didactic methods and assessment formats, can facilitate an uninterrupted process of learning for battling the fear of out-of-hospital resuscitation during the COVID-19 pandemic. However, the modifications in distant BLS learning are at an early stage, and there is a need for robust research that determines (1) their association with participant outcomes; (2) their impact on OHCA; and (3) whether such methodologically diverse learning is cost-effective. Addressing these issues will provide further insight into the role and effectiveness of new technologies and their potential impact on acquiring and sustaining BLS competencies.
Possible Implications for Practice
First, during the pandemic, the OHCA and BLS curricula require more care for nurturing and supporting competencies in the area of public health. Second, an integrated web-based program requires the combination of modern technology and formative assessments that are dedicated to developing critical thinking and decision-making skills that encourage people to take action in OHCA situations. Third, appropriate modern resources are an integral part of creating modern curricula for BLS that encourage people to take action in OHCA situations.
Limitations
One of the limitations of our research may be that a lot of time is required to complete all of the formative activities. An increase in the amount of time devoted to a given training course puts an additional burden on course participants. However, well-thought-out activities that mirror real-life situations should encourage participants to spend more time in tackling such activities.
Abbreviations
- AED
automated external defibrillator
- AHA
American Heart Association
- BLS
basic life support
- CMET
Centrum Medycznych Egzaminów Testowych
- ERC
European Resuscitation Council
- ILCOR
International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation
- OHCA
out-of-hospital cardiac arrest
Appendix
The proposed Script Concordance Test.
A recording of an exemplary decision tree used during the course.
A recording of the game used during the course. Audio commentary in English is provided.
Footnotes
Conflicts of Interest: None declared.
References
- 1.Schlegel E. Designing online courses: 12 tips for health professions educators. MedEdPublish. 2020;9(1):117. doi: 10.15694/mep.2020.000117.1. https://www.mededpublish.org/manuscripts/3013. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nolan JP, Monsieurs KG, Bossaert L, Böttiger BW, Greif R, Lott C, Madar J, Olasveengen TM, Roehr CC, Semeraro F, Soar J, Van de Voorde P, Zideman DA, Perkins GD, European Resuscitation Council COVID-Guideline Writing Groups European Resuscitation Council COVID-19 guidelines executive summary. Resuscitation. 2020 Aug;153:45–55. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2020.06.001. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32525022. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.European Resuscitation Council COVID-19 Guidelines. European Resuscitation Council. 2020. Apr 24, [2020-05-17]. https://www.spci.pt/media/covid-19/European_Resuscitation_Council_COVID-19_Guidelines.pdf.
- 4.Scquizzato T, Olasveengen TM, Ristagno G, Semeraro F. The other side of novel coronavirus outbreak: Fear of performing cardiopulmonary resuscitation. Resuscitation. 2020 May;150:92–93. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2020.03.019. http://europepmc.org/abstract/MED/32259607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.García-Suárez M, Méndez-Martínez C, Martínez-Isasi S, Gómez-Salgado J, Fernández-García D. Basic life support training methods for health science students: A systematic review. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2019 Mar 03;16(5):768. doi: 10.3390/ijerph16050768. https://www.mdpi.com/resolver?pii=ijerph16050768. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Boada I, Rodriguez-Benitez A, Garcia-Gonzalez JM, Olivet J, Carreras V, Sbert M. Using a serious game to complement CPR instruction in a nurse faculty. Comput Methods Programs Biomed. 2015 Nov;122(2):282–291. doi: 10.1016/j.cmpb.2015.08.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Tobase L, Peres HHC, Gianotto-Oliveira R, Smith N, Polastri TF, Timerman S. The effects of an online basic life support course on undergraduate nursing students' learning. Int J Med Educ. 2017 Aug 25;8:309–313. doi: 10.5116/ijme.5985.cbce. https://www.ijme.net/pmid/28850944. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Napp A, Kosan J, Hoffend C, Häge A, Breitfeld P, Doehn C, Daubmann A, Kubitz J, Beck S. Implementation of basic life support training for school children: Online education for potential instructors? Results of a cluster randomised, controlled, non-inferiority trial. Resuscitation. 2020 Jul;152:141–148. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2020.04.041. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Pedersen TH, Kasper N, Roman H, Egloff M, Marx D, Abegglen S, Greif R. Self-learning basic life support: A randomised controlled trial on learning conditions. Resuscitation. 2018 May;126:147–153. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2018.02.031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Finn JC, Bhanji F, Lockey A, Monsieurs K, Frengley R, Iwami T, Lang E, Ma MHM, Mancini ME, McNeil MA, Greif R, Billi JE, Nadkarni VM, Bigham B, Education‚ Implementation‚ Teams Chapter Collaborators Part 8: Education, implementation, and teams: 2015 International Consensus on Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation and Emergency Cardiovascular Care Science with Treatment Recommendations. Resuscitation. 2015 Oct;95:e203–e224. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2015.07.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Rozporządzenie Ministra Edukacji Narodowej z dnia 11 marca 2020 r. w sprawie czasowego ograniczenia funkcjonowania jednostek systemu oświaty w związku z zapobieganiem, przeciwdziałaniem i zwalczaniem COVID-19. Strona główna Sejmu Rzeczpospolitej Polskiej. [2021-05-07]. https://isap.sejm.gov.pl/isap.nsf/download.xsp/WDU20200000410/O/D20200410.pdf.
- 12.Coyne E, Frommolt V, Rands H, Kain V, Mitchell M. Simulation videos presented in a blended learning platform to improve Australian nursing students' knowledge of family assessment. Nurse Educ Today. 2018 Jul;66:96–102. doi: 10.1016/j.nedt.2018.04.012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Hu YJ, Ku TH, Jan RH, Wang K, Tseng YC, Yang SF. Decision tree-based learning to predict patient controlled analgesia consumption and readjustment. BMC Med Inform Decis Mak. 2012 Nov 14;12:131. doi: 10.1186/1472-6947-12-131. https://bmcmedinformdecismak.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1472-6947-12-131. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Staying Alive - AED locations. Staying Alive. [2020-06-20]. https://www.stayingalive.org/index.php?lang=en.
- 15.Gurbanov E. The challenge of grading in self and peer-assessment (undergraduate students’ and university teachers’ perspectives) Journal of Education in Black Sea Region. 2016 May 25;1(2):82–91. doi: 10.31578/jebs.v1i2.21. https://files.eric.ed.gov/fulltext/ED569122.pdf. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Lubarsky S, Charlin B, Cook DA, Chalk C, van der Vleuten CPM. Script concordance testing: a review of published validity evidence. Med Educ. 2011 Apr;45(4):329–338. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2923.2010.03863.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Naylor K, Torres K. Approaches to stimulate clinical reasoning in continuing medical education during the coronavirus disease 2019 pandemic. Kardiol Pol. 2020 Aug 25;78(7-8):770–772. doi: 10.33963/KP.15419. doi: 10.33963/KP.15419. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Spruijt A, Leppink J, Wolfhagen I, Scherpbier A, van Beukelen P, Jaarsma D. Investigating teaching performance in seminars; a questionnaire study with a multi-level approach. BMC Med Educ. 2014 Sep 24;14:203. doi: 10.1186/1472-6920-14-203. https://bmcmededuc.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/1472-6920-14-203. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Fawns T, Aitken G, Jones D. Online Learning as Embodied, Socially Meaningful Experience. Postdigital Science and Education. 2019 May 31;1:293–297. doi: 10.1007/s42438-019-00048-9. http://link.springer.com/10.1007/s42438-019-00048-9. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Profesjonalny program do organizowania szkoleń BHP online dla firm bhp i pracowników służby bhp! Szkolenia BHP. [2021-05-07]. https://www.szkolenia-bhp24.pl/
- 21.Centrum Medycznych Egzaminów Testowych. Centrum Medycznych Egzaminów Testowych. [2021-05-07]. https://e-csm.umlub.pl/cmet/
- 22.Biggs J. Enhancing teaching through constructive alignment. High Educ. 1996 Oct;32:347–364. doi: 10.1007/bf00138871. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Nicol DJ, Macfarlane-Dick D. Formative assessment and self-regulated learning: a model and seven principles of good feedback practice. High Educ (Dordr) 2006 Jan 24;31(2):199–218. doi: 10.1080/03075070600572090. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 24.American Heart Association . Heartsaver CPR AED Student Workbook. Dallas, Texas: American Heart Association; 2015. [Google Scholar]
- 25.Greif R, Lockey AS, Conaghan P, Lippert A, De Vries W, Monsieurs KG, Education and implementation of resuscitation section Collaborators; Collaborators European Resuscitation Council Guidelines for Resuscitation 2015: Section 10. Education and implementation of resuscitation. Resuscitation. 2015 Oct;95:288–301. doi: 10.1016/j.resuscitation.2015.07.032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Martínez REB, Ramírez NC, Mesa HGA, Suárez IR, Trejo MDCG, León PP, Morales SLB. Decision trees as a tool in the medical diagnosis. Revista Médica de la Universidad Veracruzana. 2009;9(2):19–24. https://www.medigraphic.com/pdfs/veracruzana/muv-2009/muv092c.pdf. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
The proposed Script Concordance Test.
A recording of an exemplary decision tree used during the course.
A recording of the game used during the course. Audio commentary in English is provided.


