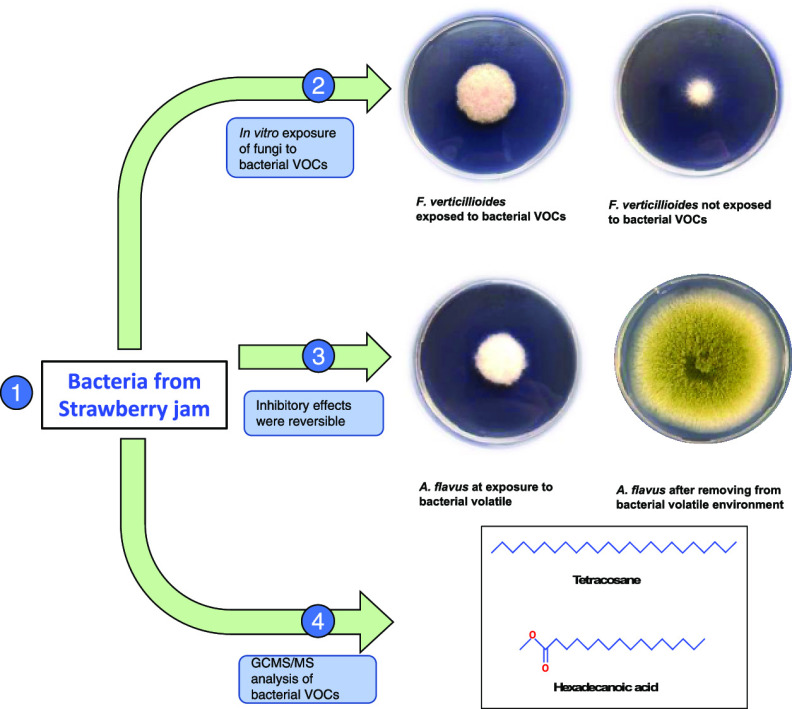
Abstract
Mycotoxins are secondary metabolites of some fungal species and represent important contaminants of food and feed. This study aimed to explore the biological control activity of Bacillus megaterium BM344-1 volatile organic compounds (VOCs) on the growth and mycotoxin production of single representatives of the toxigenic species Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus carbonarius, Penicillium verrucosum, and Fusarium verticillioides. In vitro co-incubation experiments indicated the P. verrucosum isolate as the most sensitive one, with a growth inhibition ratio of 66.7%, followed by A. flavus (29.4%) and F. verticillioides (18.2%). Exposure of A. flavus, P. verrucosum, and F. verticillioides to BM344-1 VOCs resulted in complete inhibition of aflatoxins (AFB1, AFG1, and AFG2), ochratoxin A, and fumonisin B1 (FB1) synthesis on artificial media, respectively. In vivo experiments on maize kernels showed 51% inhibition of fungal growth on ears simultaneously infected with A. flavus spores and exposed to BM344-1 volatiles. Likewise, AF synthesis by A. flavus was significantly (p < 0.05) inhibited (25.34 ± 6.72 μg/kg) by bacterial volatiles as compared to that in control maize ears (91.81 ± 29.10 μg/kg). Gas chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry-based analysis of headspace volatiles revealed hexadecanoic acid methyl ester (palmitic acid) and tetracosane as bioactive compounds in the BM344-1 volatilome. Bacterial volatiles have promising potential to control the growth and mycotoxin synthesis of toxigenic fungi and may present valuable aid in the efforts to warrant food and feed safety.
1. Introduction
Mycotoxins are important contaminants of agriculture and food industries and are mainly produced by some species of Aspergillus, Penicillium, and Fusarium. After the first discovery of aflatoxin (AF) in 1960s, there has been a tremendous effort to dissect mycotoxin nature, toxicity, and mycotoxigenic species.1 At present, the list of known mycotoxins covers over 400 compounds,2 including toxins produced by Aspergillus and Penicillium (such as AFs, ochratoxins, patulin, etc.) and Fusarium (e.g., zearalenone, fumonisins, deoxynivalenol, and T-2/HT-2). AFB1 produced by Aspergillus flavus, Aspergillus parasiticus, and Aspergillus nomius is widely known for its hepatotoxicity3 and has been classified as a group 1A human carcinogen.4 Ochratoxin A (OTA), a nephrotoxic metabolite, is found in many food commodities and is synthesized by some Aspergillus (Aspergillus carbonarius, Aspergillus ochraceous, Aspergillus westerdijkiae, Aspergillus niger, etc.) and Penicillium (such as Penicillium verrucosum and Penicillium nordicum) species.5 Fumonisins (FB1 and FB2) are among the most important mycotoxins produced by Fusarium species (Fusarium verticillioides and Fusarium proliferatum) and induce neurotoxic effects on the exposed animal and human.6
Pre- and post-harvest contamination of food crops with toxigenic fungi and the accumulation of their toxins remain ever challenging for food and feed regulatory authorities.7 Agricultural husbandry practices such as crop rotation, proper sowing and harvesting timing, insect and pest control, grading and segregation of products, proper irrigation and the use of effective fungicides result in significant control of fungal infection and mycotoxin accumulation.8,9 However, persistence of fungicide residues in food10 and emerging fungicide-resistant fungal populations11 are major concerns associated with chemical fungicides. Likewise, some physical control methods in spite of having significant potential to degrade mycotoxins may affect the quality of cereal-derived food and feed. UV irradiation of toxin-contaminated food not only has limited applicability but also compromises the nutritional and organoleptic characteristic of food.12
Over the recent past, several efforts have been devoted to define alternate and safer strategies to minimize the impact of mycotoxins and to control fungal infection in crops. Microbial control by living and inactivated yeasts and bacterial cells, their diffusible and volatile compounds, and enzymes are being explored for their antagonistic potential against fungi.13,14
In our previous studies, we have reported yeast15−18 and bacterial19−21 cultures possessing strong antifungal potential against toxigenic fungi. This study was designed to investigate in vitro as well as in vivo effects of Bacillus megaterium (BM344-1) against the growth and toxin production potential of toxigenic isolates of A. flavus, P. verrucosum, and F. verticillioides. Additionally, the chemical nature of the BM344-1 volatilome was investigated to identify the bioactive molecule (s) in the bacterial volatilome.
2. Results and Discussion
2.1. Optimum Conditions for the Efficient Production of Bacterial Antifungal Volatiles
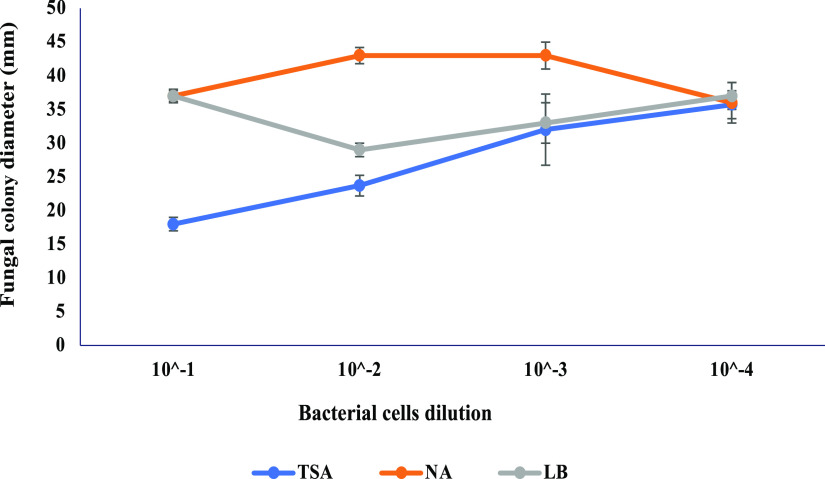
Lipophilicity, low polarity, high vapor pressure, and low molecular weight are the main characteristics of microbial volatile organic compounds (VOCs) that are gaining momentum for their potential application against fungal contamination of food and feed commodities.22,23 The precise mode of action of VOCs is not yet well understood and probably varies with the chemical nature of molecules and their microbial sources.24 However, interference with the fungal metabolic pathways by alteration in the expression of key genes is generally an accepted mechanism of their antifungal activity.15,16 Three media [tryptic soy agar (TSA), Luria-Bertani (LB), and nutrient agar (NA)] and four bacterial cell dilutions (10–1, 10–2, 10–3, and 10–4) were preliminarily tested to explore the appropriate requirements for an efficient antagonistic activity of BM344-1 against Aspergillus carbonarius AC82. The volatiles produced by BM 344-1 on TSA at 10–1 dilution showed the highest inhibitory effect on a colony size of A. carbonarius as measured at day 7 of co-incubation (Figure 1). The composition of growth media, particularly protein- and sugar-contents, plays a key role in the bacterial volatilome. On protein-rich media, Lysobacter sp. produced bioactive compounds such as pyrrole, decanal, and pyrazines as compared to inactive compounds on sugar-rich media.25 In the present study, the antagonistic activity of BM344-1 was linked to protein richness with the highest inhibitory efficacy measured on TSA (15 g of pancreatic casein and 5 g of soy peptone in 1 L), followed by that on LB (10 g of tryptone, 5 g of yeast extract), and the least on NA (5 g of peptone and 2 g of yeast extract). In the study of Bruce et al.,26 VOCs produced by bacterial cultures on TSA showed a complete inhibition of fungal growth, whereas inhibition was minimal when bacteria were grown on other media. In fact, amino acids acting as components of antagonistic volatiles are found in particular high-protein media compared to others.
Figure 1.
Effect of the type of growth media and bacterial cell dilution on the antifungal activity of B. megaterium BM344-1. Bacterial cells at dilutions 10–1, 10–2, 10–3, and 10–4 were spread inoculated on three types of media (TSA, LB agar, and NA) and sealed with fungal inoculated plates.
2.2. Antagonistic Spectrum of B. megaterium BM344-1 Volatiles against A. flavus, F. verticillioides, and P. verrucosum
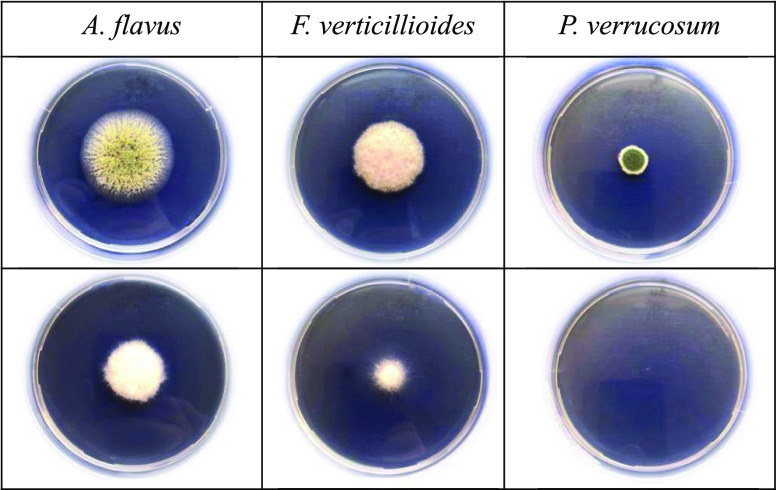
Exposure of different mycotoxigenic fungi to BM344-1 volatiles resulted in a significant decrease in the colony diameter as compared to that of unexposed control fungi. P. verrucosum showed the highest sensitivity to bacterial volatiles, followed by A. flavus and F. verticillioides. The growth inhibition ratios (%) calculated with comparison to control fungi were 66.7, 29.4, and 18.2% for P. verrucosum, A. flavus, and F. verticillioides, respectively (Figure 2). The higher sensitivity of P. verrucosum compared to that of A. flavus to bacterial volatiles was previously observed by Ul Hassan et al.(19) Exposure of P. verrucosum and A. flavus to Bacillus licheniformis volatiles (the major antagonistic compound was 3-methyl-1-butanol) resulted in 53 and 49% reduction in the colony diameter when compared to that of the unexposed control, respectively. In line with this study, Zeidan et al.(17) found that the highest sensitivity is of Penicillium, followed by that of Aspergillus, and the least by Fusarium to yeast VOCs. The observed differences in fungal colony diameters among the three fungi (each from different genus) in response to bacterial volatiles may be associated with their cell wall structure. The cell wall composition of fungi varies according to their microenvironmental stressors and plays a significant role in the fungal resistance.27,28 Antagonistic Bacillus volatiles (such as those of Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus amyloliquefaciens, Bacillus cereus, and B. megaterium) against phytopathogenic and toxigenic Aspergillus and Penicillium spp. have been reported by several authors.29−31
Figure 2.
Spectrum of antifungal activities of Bacillus megaterium BM344-1 against toxigenic Aspergillus, Fusarium, and Penicillium fungi. The fungi in the second row are the control (unexposed to bacterial volatiles), while those in the third row showing significant effects on colony size and sporulation are exposed to B. megaterium BM344-1 volatiles for 3 days.
2.3. Reversibility in BM344-1-Induced Fungal Growth Inhibition
After removal from the bacterial volatile environment, all three fungi showed normal growth and sporulation, suggesting that microbial volatiles effects were transient and the presence of antagonistic bacteria or their VOCs is needed for consistent inhibition. In a study by Wheatley et al.,32 similar reversibility to physiological growth and sporulation was observed in fungi after removal from the bacterial environment. In a similar study, after removal from the VOC environment, Fiori et al.(33) observed the reversibility of sporulation in A. carbonarius which was completely inhibited upon exposure to yeast volatiles.
B. licheniformis BL350-2 producing 3-methyl-1-butanol as a bioactive compound caused significant growth inhibition in Aspergillus westerdijkiae BA1 (62%), A. carbonarius MG7 (60%), P. verrucosum MC12 (53%), Aspergillus niger MC05 (50%), A. flavus CM5 (49%), A. parasiticus SB01 (47%), and Aspergillus ochraceus MD1 (44%), which showed complete reversal upon removing the fungi from the bacterial VOC environment.19
2.4. Inhibitory Effect of B. megaterium BM344-1 on Mycotoxin Synthesis
Exposure to BM344-1 volatiles not only inhibited the vegetative growth but also affected the mycotoxin biosynthesis potential of toxigenic fungi (Table 1). At day 7 of co-incubation, A. flavus showed a significant reduction in AFB2 synthesis, while the production of other classes of AFs (AFB1, AFG1, and AFG2) was totally inhibited. Similarly, OTA synthesis by P. verrucosum and FB1 by F. verticillioides were also completely inhibited by bacterial volatiles. F. verticillioides exposed to BM344-1 was able to synthesize FB2, but the concentration of this mycotoxin in the medium was significantly lower than that of unexposed control fungi.
Table 1. Effect of B. megaterium BM344-1 Volatiles on the Mycotoxin Biosynthesis by Different Toxigenic Fungia.
| fungi | mycotoxin (μg/kg) | control | VOCs-exposed |
|---|---|---|---|
| A. flavus | AFB1 | 199.44 ± 16.40a | n.d* |
| AFB2 | 84.82 ± 11.00a | 13.91 ± 2.45b | |
| AFG1 | 37.26 ± 4.50a | n.d | |
| AFG2 | 14.21 ± 2.12a | n.d | |
| P. verrucosum | OTA | 84.80 ± 9.50a | n.d |
| F. verticillioides | FB1 | 1.04 ± 0.07a | n.d |
| FB2 | 11.85 ± 2.36a | 1.62 ± 0.01b |
Effect of B. megaterium BM344-1 volatiles on mycotoxin production of A. flavus, P. verrucosum, and F. verticillioides. Mycotoxin production of the control (fungi not exposed to BM344-1 volatiles) and VOCs-exposed fungi are shown as mean ± SD obtained from three replicates. Different superscript letters on values in rows indicate the significant difference at p ≤ 0.05. *Not detected (below the limit of detection of the analytical system).
The inhibition/reduction in mycotoxin synthesis by toxigenic fungi in the bacterial19,30 or yeast15−18 VOCs-saturated environment could be associated with changes in the expression of biosynthetic-cluster genes,15 protein profiles,16,34 or altered enzymatic activities of the target fungi.32 The volatiles synthesized by B. megaterium KU143 resulted in the inhibition of AF accumulation on stored rice grains colonized by A. flavus.30
2.5. Biological Control Activity of B. megaterium BM-344-1 against A. flavus Growth and AF Synthesis on Maize Kernels
In vivo exposure of A. flavus-infected maize ears to BM3441-1 volatiles showed a significant inhibition of fungal growth as well as AF synthesis (Table 2). In the control maize ears (without BM344-1 VOCs), the spread of A. flavus, measured as number of kernels with visible fungal growth, was significantly higher (22.5 ± 0.7 kernels) compared to that in the ears infected with fungi and exposed to bacterial VOCs (11 ± 1 ears), showing 51% inhibition in the fungal growth as a consequence to bacterial VOC exposure. In line with the present study, Mannaa et al. (2017)30 reported a significant decrease in the A. flavus population on un-hulled rice grains exposed to B. megaterium KU143 volatiles. The VOCs (3-methyl-1-butanol as compound) produced by B. licheniformis showed a similar inhibitory effect on the growth of A. flavus on infected maize ears.19
Table 2. In Vivo Antifungal Activity of B. megaterium BM344-1 Volatiles on Infected Maize Earsa.
| treatment | no. of infected kernels (growth inhibition ratio) | AF (μg/kg) |
|---|---|---|
| control (exposed to BM344-1) | 0 | n.d* |
| BM344-1 +A. flavus | 11 ± 1.0b (51%) | 25.34 ± 6.72b |
| TSA +A. flavus | 22 ± 0.0a(2%) | 99.85 ± 36.21a |
| A. flavus | 22.5 ± 0.7a(0%) | 91.81 ± 29.10a |
Surface-disinfected maize ears were inoculated with A. flavus spores and exposed to B. megaterium BM344-1 volatiles. The values in each column represent the mean ± SD of three replicates, and the different superscript letter indicates the significant difference at p ≤ 0.05. *n.d = not detected.
In line with the fungal growth, the levels of AFs in the VOCs-exposed A. flavus-contaminated maize ears were significantly (p ≤ 0.05) lower [25.34 ± 6.72 ± standard deviation (SD)] than that in the unexposed maize ears (91.81 ± 29.10). TSA alone showed no effect on fungal growth and its mycotoxin production ability (Table 2). These in vivo results are in line with the in vitro antagonistic activity of BM344-1 against mycotoxin synthesis potential of A. carbonarius, P. verrucosum, and F. verticillioides (Section 4.4). Inhibition of AF synthesis by A. flavus on exposure to volatiles emitted by B. megaterium KU143 and B. licheniformis 350-2 on un-hulled rice and maize ears has been reported by Mannaa and Kim31 and Ul Hassan et al.,19 respectively. However, in the present study, it is unclear if the observed reduced mycotoxin synthesis is associated with fungal growth slowdown or with specific mechanisms such as effects on the expression of genes involved in mycotoxin biosynthesis15 or alteration in the enzymatic activities.32
2.6. GC–MSMS Analysis of BM344-1 Volatiles
Bacterial volatiles analysis performed by gas chromatography–mass spectrometry (GC–MS) revealed the presence of hexadecanoic acid methyl ester (palmitic acid) and tetracosane. Both these compounds are well-known microbial volatiles holding strong antagonistic activities against toxigenic as well as phytopathogenic fungi (Figure 3).33−35
Figure 3.
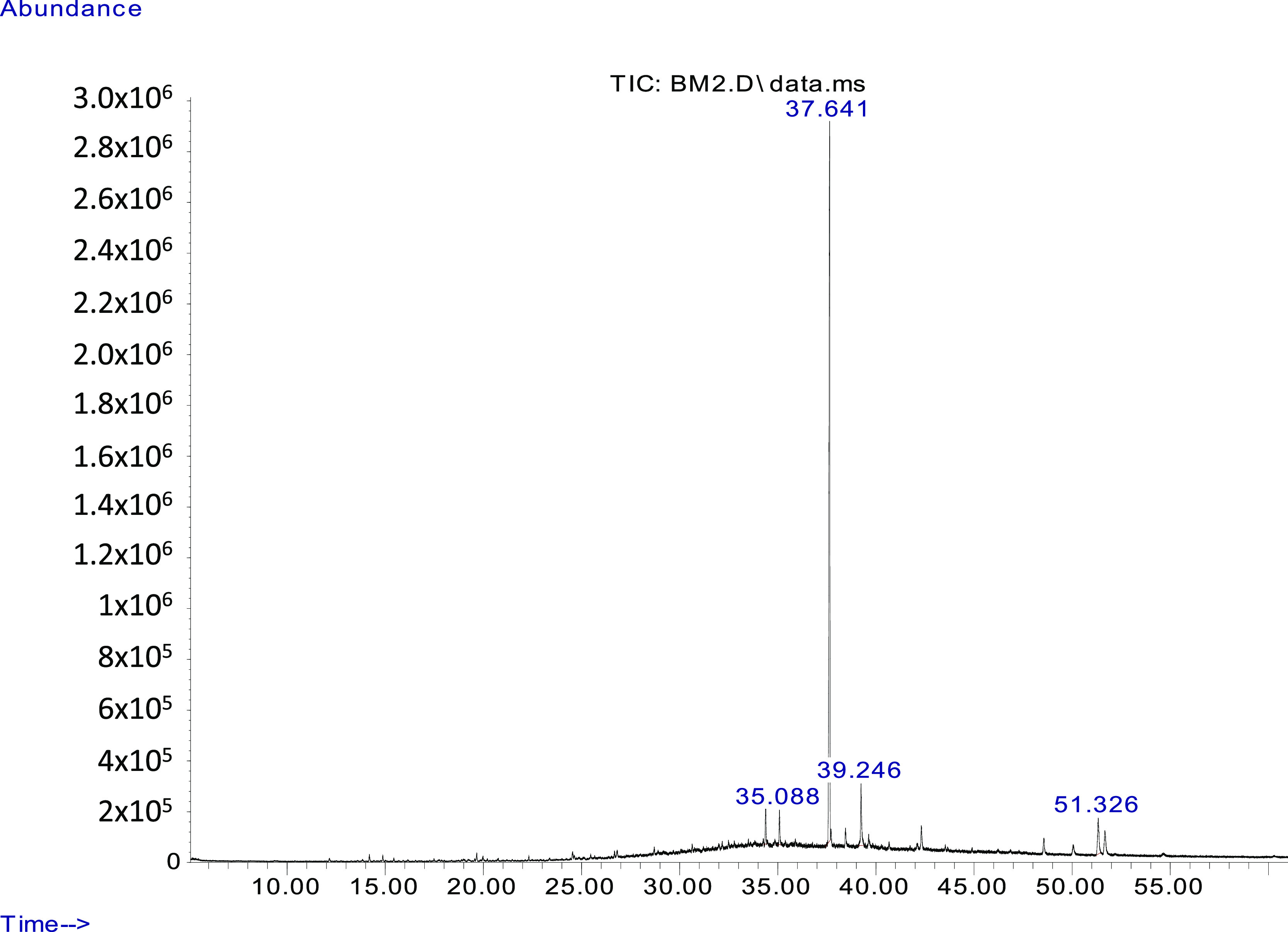
GC–MSMS chromatograph of detected compounds in B. megaterium BM344-1 headspace volatiles. On the x-axis, there is retention time in min, and on the y-axis, there is retention time in abundance of compounds. The compound detected at 35.08 min is tetracosane and that at 39.24 min is hexadecanoic acid methyl ester. The peaks in chromatographs from BM344-1-inoculated headspace volatiles were compared with those of the control (media without bacterial inoculation). The peaks detected at 37.64 and 52.32 min were found in both the control and bacterial inoculated headspace volatiles, probably indicating the compounds emitted by the media.
The absence of these compounds in the control flasks [tryptic soy broth (TSB) without bacteria] suggests that both the fungal growth and mycotoxin synthesis inhibition were due to single or synergistic/additive interaction of the two compounds (Table 3). Hexadecanoic acid was the major compound in the microbial VOC mix of Bacillus atrophaeus HAB-536 inhibiting Colletotrichum gloeosporioides(35) and seaweeds suppressing Aspergillus, Penicillium, and Fusarium.37 Likewise, tetracosane was the major constituent of antifungal volatiles produced by Chaetomium globosum.38
Table 3. GC–MS Analysis of B. megaterium BM344-1 Headspace Volatilesa.
| S. no. | name | retention time (min) | peak area (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | hexadecanoic acid methyl ester | 39.24 | 8.18 |
| 2 | tetracosane | 35.08 | 3.41 |
Detected volatile compounds with a peak area of less than 1.5% are not listed in this table. The compounds detected in B. megaterium BM344-1 headspace volatiles as well as in the control flasks (containing TSA only) are also excluded.
3. Conclusions
The volatiles produced by B. megaterium BM344-1 have shown high potential against the growth and mycotoxin biosynthesis in three representative isolates of A. flavus, P. verrucosum, and F. verticillioides. The antifungal activity of BM344-1 was enhanced by increasing the protein content in the growth medium. During in vitro co-incubation experiments, P. verrucosum showed the highest sensitivity, with a growth inhibition ratio of 66.7%, followed by A. flavus (29.4%) and F. verticillioides (18.2%). Exposure of A. flavus, P. verrucosum, and F. verticillioides to BM344-1 VOCs resulted in complete inhibition of AFs (AFB1, AFG1, and AFG2), OTA, and fumonisin B1 (FB1) synthesis on artificial media, respectively. Under in vivo testing on maize ears, BM344-1 showed significant inhibition of A. flavus growth and AF synthesis on infected kernels. The headspace analysis of bacterial volatiles indicated hexadecanoic acid methyl ester (palmitic acid) and tetracosane as bioactive compounds. These results suggest potential application of bacterial culture for the preservation of food commodities.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Microbial Cultures and Growth Media
B. megaterium BM344-1 was isolated from strawberry jam (imported from Turkey) marketed in Qatar and identified by its protein spectrum using matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization time-of-flight.19A. flavus CECT 2687 was obtained from the culture collection center, University de Valencia Spain; A. carbonarius AC82, F. verticillioides FV04, and P. verrucosum PV11 were isolated from animal feed.22 TSA was prepared by adding 15 g of pancreatic casein, 5 g of soy peptone, 5 g of sodium chloride, and 15 g of agar in 1 L of distilled water. LB agar for Bacillus sp. was prepared by mixing 15 g of agar, 10 g of tryptone, 5 g of yeast extract and 5 g of NaCl in 1 L of distilled water. NA was prepared by adding peptone (5 g), meat extract (1 g), yeast extract (2 g), sodium chloride (5 g), and agar (15 g) in 1 L of distilled water.
4.2. Optimization and Investigation of B. megaterium BM344-1 for Its Antifungal Activities
In order to find appropriate conditions for the optimal production of antifungal volatiles, different dilutions of B. megaterium BM344-1 were preliminarily inoculated on three types of bacterial growth media. In each case, 100 μL of bacterial cell suspension [10–1 (∼2.5 × 107 cfu/mL), 10–2 (∼2.5 × 106 cfu/mL), 10–3 (∼2.5 × 105 cfu/mL), 10–4 (∼2.5 × 104 cfu/mL), and 10–5 (∼2.5 × 103 cfu/mL)] was plated on TSA, LB, and NA. Inoculated plates were incubated at 30 °C for 24 h. In an Eppendorf tube, fungal spores of A. carbonarius were prepared by transferring inocula from the freshly sporulating fungal colony to 1 mL of saline solution, amended with 0.05% Tween 80. A 10 μL aliquot of the spore suspension (adjusted at ×104) was inoculated at the center of PDA plates. The cover of the fungal inoculated plates was replaced with the base plate of bacterial inoculated plates. The two plates were sealed face-to-face with a double layer of Parafilm and then an additional layer of scotch tape. The sealed plates were incubated at 26 °C for 72 h before measuring the diameter of the fungal colonies and the extent of sporulation. Fungal growth inhibition was calculated as
C = colony diameter (mm) of control fungi. T = colony diameter (mm) of fungi exposed to bacterial volatiles.
After optimization, the spectrum of antifungal activities of BM344-1 was tested on three fungi (A. flavus, F. verticillioides, and P. verrucosum) representing different genera. In each case, 100 μL of 10–1 bacterial dilution was applied on TSA.
4.3. Reversibility of Bacterial VOC Effects on the Mycotoxigenic Fungi
To explore the reversibility of the effects of bacterial volatiles on fungal growth, at day 7 of exposure, a plug of ∼1 cm2 was removed from the margin of the fungal colony with a sterile blade and transferred to a new PDA plate. The inoculated plates were incubated at 26 °C to check the fungal growth and sporulation. The fungal colony diameter was monitored from 3 to 7 days on a daily basis and was compared with that of the control fungi that had not been exposed to VOCs.
4.4. Effect of the Bacterial VOCs on the Synthesis of Mycotoxins
Toxigenic cultures of A. flavus CECT 2687 and A. carbonarius AC82 were exposed to B. megaterium BM344-1 volatiles as described in Section 2.2. At day 7 of co-incubation, three plugs of the fungal culture were removed with a cork-borer (7 mm). After weighing, OTA and AF were extracted in organic solvents as described by Ul Hassan et al.(39) The extracts were analyzed for mycotoxin content using HPLC.
4.5. Effect of BM344-1 VOCs on the Growth of A. flavus on Maize Kernels
Yellow maize kernels (Foody’s, Thailand) were artificially infected with the toxigenic culture of A. flavus and exposed to B. megaterium BM344-1 VOCs to record their effect on fungal growth. For this purpose, kernels were purchased from the market, briefly sterilized in liquid bleach, and washed with sterilized distilled water. A loopful of fungal spores was taken from a 7 days-old colony of A. flavus in saline solution amended with Tween 80. A 10 μL (106 spores/mL) aliquot was spotted onto maize kernels. Infected kernels were placed in a Petri dish with nine holes (7 mm diameter) underneath to allow passage of bacterial volatiles emitted from a 24 h-old BM344-1 culture on TSA (placed at the bottom of a glass box). The lids were closed and completely sealed with Parafilm and incubated at 28 °C. Two A. flavus-inoculated controls were maintained, that is, kernels incubated in a glass box in the presence and absence of TSA agar plates (both in the absence of B. megaterium BM344-1).
The effect of BM344-1 volatiles on the growth of A. flavus was recorded as the fungal growth inhibition ratio (%) calculated by counting the number of maize kernels showing visible fungal growth at 7 dpi by using the formula as
C = Number of infected kernels in A. flavus-inoculated maize ear. T = Number of infected kernels in A. flavus-inoculated and BM344-1 volatiles-exposed maize ear.
4.6. Effect of BM344-1 Volatiles on AF Contamination on Maize Kernels
Maize ears were removed at the site of fungal inoculation from the treated kernels (Section 2.5) and thoroughly mixed. The AF contents of representative (2 g) samples were extracted in 10 mL of 70% methanol.19 Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) kits (RIDASCREEN Aflatoxin Total, Art no. R4701) obtained from R-Biopharm AG, Darmstadt, Germany, were used for AF analysis. An ELISA plate reader (Multiskan FC, Thermo Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA) installed with Skanlt software (Version 4.1. Thermo Scientific, MA, USA, 2015) was used to obtain the absorbance of ELISA plates wells. A calibration curve was generated by using absorbance data of known mycotoxins’ standards solutions, and the absorbance values of unknown samples were added to the calibration curve to calculate the amount of toxins in our samples. For this purpose, the software Z9996 RIDA-SOFT Win (R-Biopharm, Darmstadt, Germany) was used.
4.7. Analysis of BM344-1 Volatile Bioactive Compounds
Bacterial volatiles were captured on activated charcoal (AC) and analyzed by GC–MS/MS as described by Ul Hassan et al.,19 with little modification. Briefly, in 250 mL Erlenmeyer flasks, bacterial cell suspension was added to 100 mL of TSB media. Two valve rubber-corks were fitted to allow the passage of glass tubing. To the outer end of one tube, a volatile trap (glass Pasteur pipette filled with AC) was attached, while the other end was kept inside the flask at the neck level. The inner end of the second tube was placed ∼1 cm above the TSB level, and the outer end was sealed with Parafilm. Flasks were incubated at 30 °C in a shaking incubator for 72 h. A gentle stream of nitrogen gas was introduced into the flask through the open end of the second tube for the removal of headspace volatiles to be trapped on AC. Captured volatiles on AC were eluted in dichloromethane and analyzed by GC with the set parameters as described Ul Hassan et al.(19) The mass spectral libraries of Wiley and NIST were used to compare the obtained spectra of unknown compounds. The control flasks were maintained with TSB without adding bacterial cells.
4.8. Statistical Analysis
The effect of bacterial VOCs on fungal development (colony size) in vitro and on maize kernels was presented as the fungal growth inhibition (%) as compared to that of unexposed fungi calculated by the formula given in Section 2.2. The mean values of mycotoxin synthesis inhibition in VOCs-exposed fungi were compared with that of the control using Student’s “t-test”. The data for mycotoxin synthesis inhibition on maize kernels was subject to ANOVA, followed by post hoc multiple comparison by Duncan’s multiple range test at p ≤ 0.05. Statistical software IBM SPSS (IBM SPSS Version 25 for macOS; SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA) was used for these analyses.
Acknowledgments
This project was made possible by the NPRP grant # 8-392-4-003 from the Qatar National Research Fund (a member of Qatar Foundation). The findings achieved herein are solely the responsibility of the authors.
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
References
- Kensler T. W.; Roebuck B. D.; Wogan G. N.; Groopman J. D. Aflatoxin: A 50-Year Odyssey of mechanistic and translational toxicology. Toxicol. Sci. 2011, 120, S28–S48. 10.1093/toxsci/kfq283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Agriopoulou S.; Stamatelopoulou E.; Varzakas T. Advances in occurrence, importance, and mycotoxin control strategies: prevention and detoxification in foods. Foods 2020, 9, 137. 10.3390/foods9020137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotimi O. A.; Rotimi S. O.; Goodrich J. M.; Adelani I. B.; Agbonihale E.; Talabi G. Time-course effects of acute aflatoxin B1 exposure on hepatic mitochondrial lipids and oxidative stress in rats. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10, 467. 10.3389/fphar.2019.00467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostry V.; Malir F.; Toman J.; Grosse Y. Mycotoxins as human carcinogens—The IARC monographs classification. Mycotoxin Res. 2017, 33, 65–73. 10.1007/s12550-016-0265-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heussner A.; Bingle L. Comparative ochratoxin toxicity: A review of the available data. Toxins 2015, 7, 4253–4282. 10.3390/toxins7104253. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ji F.; He D.; Olaniran A. O.; Mokoena M. P.; Xu J.; Shi J. Occurrence, toxicity, production and detection of Fusarium mycotoxin: A review. Food Prod., Process. Nutr. 2019, 1, 6. 10.1186/s43014-019-0007-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Omotayo O. P.; Omotayo A. O.; Mwanza M.; Babalola O. O. Prevalence of mycotoxins and their consequences on human health. Toxicol. Res. 2019, 35, 1–7. 10.5487/tr.2019.35.1.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phokane S.; Flett B. C.; Ncube E.; Rheeder J. P.; Rose L. J. Agricultural practices and their potential role in mycotoxin contamination of maize and groundnut subsistence farming. S. Afr. J. Sci. 2019, 115, 1–6. 10.17159/sajs.2019/6221. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lagogianni C. S.; Tsitsigiannis D. I. Effective chemical management for prevention of aflatoxins in maize. Phytopathol. Mediterr. 2018, 57, 186–197. [Google Scholar]
- Carvalho F. P. Pesticides, environment, and food safety. Food Energy Secur. 2017, 6, 48–60. 10.1002/fes3.108. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Popiel D.; Dawidziuk A.; Koczyk G.; Mackowiak A.; Marcinkowska K. Multiple facets of response to fungicides—the influence of azole treatment on expression of key mycotoxin biosynthetic genes and candidate resistance factors in the control of resistant Fusarium strains. Eur. J. Plant Pathol. 2017, 147, 773–785. 10.1007/s10658-016-1042-3. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Calado T.; Venâncio A.; Abrunhosa L. Irradiation for mold and mycotoxin control: A Review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. Food Saf. 2014, 13, 1049–1061. 10.1111/1541-4337.12095. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Venkatesh N.; Keller N. P. Mycotoxins in conversation with bacteria and fungi. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 403. 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00403. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hathout A. S.; Aly S. E. Biological detoxification of mycotoxins: A review. Ann. Microbiol. 2014, 64, 905–919. 10.1007/s13213-014-0899-7. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Farbo M. G.; Urgeghe P. P.; Fiori S.; Marcello A.; Oggiano S.; Balmas V.; Ul Hassan Z.; Jaoua S.; Migheli Q. Effect of yeast volatile organic compounds on ochratoxin A-producing Aspergillus carbonarius and A. ochraceus. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2018, 284, 1–10. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2018.06.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilocca B.; Balmas V.; Ul Hassan Z.; Jaoua S.; Migheli Q. A proteomic investigation of Aspergillus carbonarius exposed to yeast volatilome or to its major component 2-phenylethanol reveals major shifts in fungal metabolism. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2019, 306, 108265. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2019.108265. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidan R.; Ul-Hassan Z.; Al-Thani R.; Balmas V.; Jaoua S. Application of low-fermenting yeast Lachancea thermotolerans for the control of toxigenic fungi Aspergillus parasiticus, Penicillium verrucosum and Fusarium graminearum and their mycotoxins. Toxins 2018, 10, 242. 10.3390/toxins10060242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alasmar R.; Ul-Hassan Z.; Zeidan R.; Al-Thani R.; Al-Shamary N.; Alnaimi H.; Migheli Q.; Jaoua S. Isolation of a novel Kluyveromyces marxianus strain QKM-4 and evidence of its volatilome production and binding potentialities in the biocontrol of toxigenic fungi and their mycotoxins. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 17637–17645. 10.1021/acsomega.0c02124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ul Hassan Z.; Al Thani R.; Alnaimi H.; Migheli Q.; Jaoua S. Investigation and application of Bacillus licheniformis volatile compounds for the biological control of toxigenic Aspergillus and Penicillium spp. ACS Omega 2019, 4, 17186–17193. 10.1021/acsomega.9b01638. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidan R.; Ul-Hassan Z.; Al-Thani R.; Migheli Q.; Jaoua S. In-vitro application of a Qatari Burkholderia cepacia strain (QBC03) in the biocontrol of mycotoxigenic fungi and in the reduction of ochratoxin A biosynthesis by Aspergillus carbonarius. Toxins 2019, 11, 700. 10.3390/toxins11120700. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higazy N. S.; Saleh A. E.; Ul Hassan Z.; Al Thani R.; Migheli Q.; Jaoua S. Investigation and application of Bacillus pumilus QBP344-3 in the control of Aspergillus carbonarius and ochratoxin A contamination. Food Control 2021, 119, 107464. 10.1016/j.foodcont.2020.107464. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Werner S.; Polle A.; Brinkmann N. Belowground communication: Impacts of volatile organic compounds (VOCs) from soil fungi on other soil-inhabiting organisms. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 100, 8651–8665. 10.1007/s00253-016-7792-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilocca B.; Cao A.; Migheli Q. Scent of a Killer: Microbial volatilome and its role in the biological control of plant pathogens. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 41. 10.3389/fmicb.2020.00041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulz-Bohm K.; Martín-Sánchez L.; Garbeva P. Microbial volatiles: small molecules with an important role in intra- and inter-kingdom interactions. Front. Microbiol. 2017, 8, 2484. 10.3389/fmicb.2017.02484. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lazazzara V.; Perazzolli M.; Pertot I.; Biasioli F.; Puopolo G.; Cappellin L. Growth media affect the volatilome and antimicrobial activity against Phytophthora infestans in four Lysobacter type strains. Microbiol. Res. 2017, 201, 52–62. 10.1016/j.micres.2017.04.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruce A.; Stewart D.; Verrall S.; Wheatley R. E. Effect of volatiles from bacteria and yeast on the growth and pigmentation of sapstain fungi. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 2003, 51, 101–108. 10.1016/s0964-8305(02)00088-4. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lima S. L.; Colombo A. L.; de Almeida Junior J. N. Fungal cell wall: Emerging antifungals and drug resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2573. 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Rubio R.; de Oliveira H. C.; Rivera J.; Trevijano-Contador N. The fungal cell wall: Candida, Cryptococcus, and Aspergillus species. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10, 2993. 10.3389/fmicb.2019.02993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaves-López C.; Serio A.; Gianotti A.; Sacchetti G.; Ndagijimana M.; Ciccarone C.; Stellarini A.; Corsetti A.; Paparella A. Diversity of food-borne Bacillus volatile compounds and influence on fungal growth. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2015, 119, 487–499. 10.1111/jam.12847. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannaa M.; Oh J. Y.; Kim K. D. Biocontrol activity of volatile-producing Bacillus megaterium and Pseudomonas protegens against Aspergillus flavus and aflatoxin production on stored rice grains. Mycobiology 2017, 45, 213–219. 10.5941/myco.2017.45.3.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannaa M.; Kim K. D. Biocontrol activity of volatile- producing Bacillus megaterium and Pseudomonas protegens against Aspergillus and Penicillium spp. Predominant in stored rice grains: Study II. Mycobiology 2018, 46, 52–63. 10.1080/12298093.2018.1454015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wheatley R. E. The consequences of volatile organic compound mediated bacterial and fungal interactions. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2002, 81, 357–364. 10.1023/a:1020592802234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fiori S.; Urgeghe P. P.; Hammami W.; Razzu S.; Jaoua S.; Migheli Q. Biocontrol activity of four non- and low-fermenting yeast strains against Aspergillus carbonarius and their ability to remove ochratoxin A from grape juice. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2014, 189, 45–50. 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2014.07.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Humphris S. N.; Bruce A.; Buultjens E.; Wheatley R. E. The effects of volatile microbial secondary metabolites on protein synthesis in Serpula lacrymans. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 2002, 210, 215–219. 10.1111/j.1574-6968.2002.tb11183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rajaofera M. J. N.; Wang Y.; Dahar G. Y.; Jin P.; Fan L.; Xu L.; Liu W.; Miao W. Volatile organic compounds of Bacillus atrophaeus HAB-5 inhibit the growth of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2019, 156, 170–176. 10.1016/j.pestbp.2019.02.019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abubakar M.; Majinda R. GC-MS analysis and preliminary antimicrobial activity of Albizia adianthifolia (Schumach) and Pterocarpus angolensis (DC). Medicines 2016, 3, 3. 10.3390/medicines3010003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohy El-Din E. S.; Mohyeldin M. Component analysis and antifungal activity of the compounds extracted from four brown seaweeds with different solvents at different seasons. J. Ocean Univ. China 2018, 17, 1178–1188. 10.1007/s11802-018-3538-2. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Kumar R.; Kundu A.; Dutta A.; Saha S. Profiling of volatile secondary metabolites of Chaetomium globosum for potential antifungal activity against soil borne fungi. J. Pharmacogn. Phytochem. 2020, 9, 922–9276. [Google Scholar]
- Ul Hassan Z.; Al-Thani R. F.; Migheli Q.; Jaoua S. Detection of toxigenic mycobiota and mycotoxins in cereal feed market. Food Control 2018, 84, 389–394. 10.1016/j.foodcont.2017.08.032. [DOI] [Google Scholar]