Abstract
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) can have profound impact on the function of the pituitary gland. We have performed an electronic literature search using the following database: PubMed, Medline, Scopus, and Google Scholar. These databases were searched using the keywords HIV, pituitary glands, cancer, pituitary apoplexy, and infertility. HIV can cause hypopituitarism and also can lead to diabetes insipidus. The impact can be slow and insidious, and diagnosis depends on high index of clinical suspicion. The effect on anterior pituitary gland can be associated with growth hormone deficiency, hypothyroidism, adrenal insufficiency, premature menopause, erectile dysfunction, and infertility. HIV can cause pituitary apoplexy, and this should be treated as an endocrine emergency. Importantly, HIV can be associated with pituitary lymphoma and pituitary cancer. Therefore, joined management between HIV physicians, clinical biochemists and endocrinologists may help in establishing pituitary dysfunction.
Keywords: HIV, pituitary gland, apoplexy, diabetes insipidus
Introduction
Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) is an RNA (ribonucleic acid) retrovirus with a prevalence of 37.9 million cases worldwide 1 and can lead to the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS) if left unchecked. Due to these widespread effects, HIV may present differently in different patients. If there is a suspicion that a patient is infected with HIV, they will be investigated using the serological HIV antibody and p24 antigen tests. 2 Combined anti-retroviral therapy (cART) is the mainstay of HIV treatment 3 and is divided into six subclasses of medications. These medications can also have side effects on the patient such as the lipodystrophy syndrome and increased risk of myocardial infarction. 4
HIV has become a well-managed disease with the use of cART, where it is now the long-term complications such as cardiovascular disease that are forming the majority of deaths in HIV patients. 5 With this, other complications such as pituitary function dysfunction are becoming more prevalent. The pituitary gland is made up of two lobes, the anterior and posterior separated by the intermediate lobe. 6 It is named the “master gland” due to its widespread hormonal function, providing essential homeostasis for the body. 7 The anterior pituitary is responsible for the release of growth hormone (GH), prolactin, follicle stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinizing hormone (LH), thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH), and adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH), while the posterior lobe releases oxytocin and antidiuretic hormone (ADH). 6 Therefore, with its widespread functions, HIV can affect this gland in multiple ways, and this will be discussed in this review. In addition, we have also included sections about HIV’s role in pituitary apoplexy and pituitary cancer.
Methodology
This research project was conducted as a review article. The authors searched on the literature using the following database: pub Med, Medline, Scopus, and Google scholar. These databases were searched using the keywords: HIV, pituitary, pituitary cancer, hypopituitarism, apoplexy, and diabetes insipidus. The authors searched also using combination of the following terms ([HIV] AND [pituitary] AND [hypopituitarism]) OR ([cancer] AND [apoplexy] AND [diabetes insipidus]). The search based on studies published in English language from November 1981 to January 2020, the abstracts, and the articles were then screened. Articles were scanned and read; further relevant references in the reference lists are also included and data were extracted.
HIV and the Anterior Pituitary Lobe
The anterior pituitary as an organ helps to mediate multiple physiological processes within the body such as growth, metabolism, blood pressure balance, lactation, and reproduction. 8 Its centralized role allows it to be involved in many homeostatic processes 7 which means when there is an infection like HIV that affects the anterior pituitary, there are multiple physiological changes seen within the body.
Generally speaking, HIV has been proven to be linked to hypopituitarism. 9 There are several mechanisms stated to cause hypopituitarism such as infection (e.g., Toxoplasmosis 10 ), neoplastic, or even iatrogenic through cART. 11 Therefore, it has been recommended to have radiological imaging as a diagnostic tool when suspecting hypopituitarism in an HIV patient 9 to differentiate between different pituitary causes. As well as these causes of hypopituitarism, there has been evidence to prove that the secondary organ failure caused by HIV such as in adrenal insufficiency 12 and hypothyroidism, 13 may lead to an increase in pituitary activity, however the mechanism for this is still unknown.
GH deficiency has been well-documented within HIV patients. 14 The possible cause of this can be due to reduced release 15 and reduced response to stimuli by somatotropic cells. Deficiency in other hormones such as ghrelin has also been shown to cause this GH deficiency. 16 These changes are suggested to be due to HIV alone rather than a secondary cause such as opportunistic infection that may occur in the immunocompromised patients. This can lead to different symptoms within both adults and children who have HIV. In children, it can lead to a failure to thrive 17 which can also be caused by GH insensitivity. Within adolescents, this decrease in GH has shown to cause an increase in insulin and adiposity. 18 This decrease in GH and increase in adiposity lead to HIV lipodystrophy. Adversely, within advanced HIV (where there is wasting), GH levels are shown to have increased 19 which may be due to a GH resistance. In the future, therapies aiming to increase GH might help to prevent metabolic syndrome or cardiovascular diseases 20 that are prevalent within patients with HIV, thus improving prognosis for HIV patients.
Prolactin is also produced by anterior pituitary and its levels were shown to be altered with HIV infection. Prolactin levels are shown to be increased within patients with HIV. 21 This has repercussions on both the reproductive and the immune system. In the immune system, the increase in prolactin leads to immune system cell activity and it is theorized that prolactin levels could predicate prognosis and allow for new types of therapeutic management. Within the reproductive system, this increase in prolactin may in certain cases cause galactorrhea and gynecomastia and can be related to cART therapy 22 as well.
Importantly, HIV can induce different changes in the thyroid function. For instance, TSH levels are shown to be both high and low with HIV patients. High TSH presents with hypothyroidism 13 and subclinical hypothyroidism; however, the mechanism that causes this increase in TSH is unknown. 23 This trend in high TSH can correlate with CD4 level, thus the presence of worsening thyroid dysfunction could be used as an indication of progression of HIV. 24 Low TSH, which is less prevalent in HIV compared with high TSH, 25 is seen within hyperthyroidism. This has been stated to be caused by both HIV directly and cART therapy as a side effect. It must also be remembered that opportunistic infections in HIV may also lead to sick euthyroid syndrome which can also be a secondary cause of a decrease in TSH. The clinical implications of these changes within TSH levels (and subsequently Thyroxine T4 and T3) can be far reaching within the body and means that management of HIV must include thyroid function tests to help to reduce the likelihood of these adverse effects.
As stated earlier, HIV is a known cause of adrenal insufficiency, which would lead to an increase in ACTH. There are different theories of how this occurs within late and early stage HIV. In the early stages, the high ACTH may be due to corticotrophin releasing hormone production by interleukin-1, whereas in later stages it can be due to a glucocorticoid resistance. 26 This can also lead to electrolyte imbalances due to its effects on aldosterone 27 which can be further exacerbated by HIV’s effect on the posterior pituitary (which we speak about below).
As with some of other hormones, both a high and low level of FSH and LH can be observed. An increase in FSH and LH is commonly seen 28 due to the well documented primary hypogonadism caused by HIV. This increase in FSH can be further exacerbated by being on cART. A low FSH and LH can also be observed in primary hypogonadism. 28 Again, this endocrine abnormality can also occur due to secondary causes within HIV such as neoplasms and infections to the hypothalamus. Summary of the effect of HIV in the anterior pituitary gland hormones can be seen in Table 1 .
Table 1. A summary of the effect of HIV on the function of the anterior part of the pituitary gland.
| Hormone/Condition | Main effect of HIV on hormone/condition |
|---|---|
| Abbreviations: ACTH, adrenocorticotropic hormone; FSH, follicle stimulating hormone; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; LH, luteinizing hormone, TSH, thyroid stimulating hormone. | |
| Growth hormone | Reduction in hormone levels. 14 |
| Prolactin | Increase in hormone levels. 22 |
| ACTH | Increase in hormone levels. 28 |
| Thyroid hormones | Increase and decrease of TSH depending on secondary factors. Increase and decrease in T4 and T3 levels depending on secondary factors. 25,28 |
| FSH and LH | Increase in FSH and LH. 62 |
| Estrogen | Decrease in hormone levels. 63 |
| Testosterone | Decrease in hormone levels. 39 |
| Menopause | Women may reach menopause at earlier ages 62 and have worse symptoms. 64 |
| Erectile dysfunction | Higher risk of erectile dysfunction in HIV-seropositive men. 65 |
| Impact on fertility | Fertility rates are lower in both women 66 and men. 67 |
HIV and the Posterior Pituitary Lobe
The posterior pituitary gland secretes ADH, that regulates plasma osmolality and water balance, and oxytocin plays a role in the uterine contractions during birth and milk-ejection in response to suckling in breastfeeding women. 29
Anti-diuretic Hormone Function
Hyponatremia is a common electrolyte abnormality found in HIV patients. This can be caused by syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion (SIADH), which has been associated with mortality and morbidity in HIV patients. This syndrome is due to excessive ADH release from the posterior pituitary that results in increased renal reabsorption, causing this electrolyte abnormality. Opportunistic infections of the respiratory system that are seen in HIV can induce SIADH. The mechanism behind this is unclear, but it is shown that the resulting hypoxemia and hypercapnia, can stimulate the nonosmotic release of ADH from the posterior pituitary. Alongside this, cortisol has an inhibitory effect on ADH release. Therefore, as HIV is associated with adrenal insufficiency as discussed earlier in this article, leading to low cortisol levels, this can be another possible mechanism by which increased ADH levels and hyponatremia are seen in the HIV population. SIADH can be treated with fluid restriction in most cases, and mineralocorticoid replacement if the cause is cortisol insufficiency. 30 A further retrospective cohort study, investigated whether hyponatremia due to ADH dysfunction should be used as a marker for disease severity in HIV-positive patients. They concluded it was associated with a lower CD4 cell count, a higher prevalence of AIDS and increased hospitalization rates, arguing that monitoring this could improve patient outcomes. 31 Therefore, screening and treatment of underlying cause of SIADH in individuals living with HIV is essential. Importantly, HIV can also be associated with ADH deficiency (central diabetes insipidus). For instance, in post-mortems of HIV-encephalitic patients compared with HIV-negative controls, 52% of them showed a decrease of ADH immunoreactive neurons compared with their controls and this was thought to explain the lower ADH levels released from the posterior pituitary gland. 32 Peripheral diabetes insipidus can be due to the damage of the collecting ducts in the kidney or due to resistance to the action of ADH. Table 2 provides summary of different studies that explain the two types of diabetes insipidus
Table 2. Different studies showing the different types of diabetes insipidus with HIV.
| Central diabetes insipidus (main finding of the study) references | Peripheral diabetes insipidus (main finding of the study) references |
|---|---|
| Abbreviations: ACTH, adrenocorticotropic hormone; HIV, human immunodeficiency virus; HPT, hypothalamus-pituitary-thyroid. | |
| Contributions of HIV infection in the hypothalamus and substance abuse/use to HPT dysregulation. Langford et al, 2011 32 |
Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus as the first manifestation of ectopic ACTH syndrome in an HIV infected patient Fiorot Costalonga et al, 2016 68 |
| Diabetes Insipidus as a complication of cryptococcal meningitis in an HIV-infected patient Juffermans et al, 2002 69 |
Latrogenic nephrogenic diabetes insipidus Singh, 2003 60 |
| Diabetes insipidus and hypopituitarism in HIV: an unexpected cause. Tavares Bello et al, 2017 5 |
Fanconi syndrome and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus associated with didanosine therapy in HIV infection: a case report and literature review D'Ythurbide et al, 2007 61 |
Oxytocin
A study that looked at the hypothalamus in patients with AIDS compared with HIV-negative controls, concluded that there was a 40% less oxytocin-expressing neurons in the AIDS participants. 33 Furthermore, in the same study that looked at post-mortem HIV encephalitic patients that noted a decrease in ADH, a bigger decrease in oxytocin was also observed. They documented sparse oxytocin immunoreactivity that decreased oxytocin levels. 32 However, there has been a lack of studies on how HIV affects oxytocin directly at the posterior pituitary. It has been suggested that oxytocin forms a part of the neuroendocrine stress response alongside the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. A study tried to utilize this to investigate how oxytocin, cortisol, and noradrenaline were affected in HIV-positive ethnic minority women. This took into account sociodemographic characteristics and stress measures that included their stress perception. It concluded that at low levels of oxytocin, there was an inverse association between CD4+ cell count, but at high levels it was a positive association. 34 Therefore, the study was inconclusive. Moreover, if we consider the physiological function of oxytocin for breastfeeding and parturition, 35 no remarkable changes were reported in these physiological functions in women living with HIV. Research is more focused on defining the risk of mother-to-child transmission for HIV-positive women on cART. 36 Current NICE guidance suggests that women on cART with a viral load < 400 copies per mL, or women with any antiretroviral therapy with < 50 copies per mL can have vaginal deliveries as HIV transmission risk is the same as caesarean sections. 37 Hence it is established these physiological functions are not hindered by HIV infection, with the emphasis in the literature being on transmission. It suggests that oxytocin levels are still being produced at an adequate level in those living with HIV, to counteract the arguments made when HIV affects the hypothalamic level. However, further research is needed to assess the interaction between oxytocin and HIV.
HIV and Pituitary Apoplexy
Pituitary apoplexy is a hemorrhage or infarction of the pituitary gland, most commonly occurring in the presence of a pituitary tumor. 38 It can present with headaches, vomiting, visual abnormalities and hypopituitarism. These symptoms can occur directly (as said previously due to a tumor) or due to secondary infections that may mimic pituitary apoplexy. 39
There have been many reported cases within literature to demonstrate this. For example, a B cell lymphoma presented with symptoms of pituitary apoplexy. 40 The pathophysiology behind this indicates that tumors, such as the previously mentioned lymphoma, tend to invade the suprasellar region above the pituitary leading to interruption of the blood flow into the pituitary. This therefore leads to infarctions leading to apoplexy. This invasion can also compress the optic chiasm leading to visual defects. It is also important to remember that pituitary apoplexy may further exacerbate symptoms of previous hypopituitarism by causing hormonal abnormalities such as GHs deficiency. 41
Due to the immunosuppressant nature of HIV, a patient may be at risk of infections which can also cause pituitary apoplexy. For instance, tuberculosis (TB) can also infect the pituitary and result in hypopituitarism. Other infections that present with these symptoms are meningitis and cytomegalovirus. 42 It is also possible for infections and tumors affecting the pituitary, 42 to present together within an HIV patient leading to both pathologies causing infarcts, which could then cause a patient to have symptoms of apoplexy. Interestingly, one study suggested that the increase in incidence of AIDS may cause an increase in pituitary TB, 41 which may then lead to increase in pituitary apoplexy cases in AIDS patients.
To investigate apoplexy relating to HIV, there are two concurrent pathways of investigation. One is to do general investigations that would occur with each case of apoplexy and the other is to investigate the specific cause of the apoplexy. The gold standard for general investigation would be magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) 43 (computed tomography should be done if MRI not possible). This should be in conjunction with bloods tests 43 to check for any endocrine and biochemical derangement that may present. Specific investigations would be related to the cause of the apoplexy itself and would need clinical judgment to facilitate which investigations to order. For example, TB screening tests or polymerase chain reaction for TB and cytomegalovirus, respectively.
In patient’s management with pituitary apoplexy, there can be either surgical or medical interventions. However, first the patient must be stabilized immediately and given steroid therapy (such as hydrocortisone). 44 The decision to which type of intervention to take should be done promptly in a multidisciplinary team (MDT) format which will ideally comprise of the appropriate specialists. If there is no indication for surgery, a conservative medial management should be taken. If there is a severe deterioration of visual acuity or severe visual field defects, 44 a surgical approach should be taken. In regard to HIV patient with pituitary apoplexy, the appropriate HIV team within the hospital should be involved within the patient’s MDT (no benefit of cART, in HIV patient with pituitary apoplexy). Regular follow-up with the appropriate teams would be necessary after discharge.
HIV, Cancers, and Pituitary Function
HIV is regarded as a risk factor for several cancers, including AIDS defining cancers such as Kaposi’s sarcoma, invasive cervical cancer, primary central nervous system lymphomas, and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. While this risk has decreased due to the advances in cART, 45 several studies have been undertaken to explore the relationship between HIV and cancers affecting the pituitary gland.
HIV-associated cancers have been documented to affect pituitary gland functions to produce a variety of presentations. For instance, a case report showed that the presence of polydipsia, polyuria, and severe dehydration in HIV patient was found to be due to advanced primary CNS lymphoma (PCNSL) of diffuse large B cell type. 5 Primary CNS lymphoma is otherwise a rare intracranial neoplasm, especially that of primary pituitary origin. 46 Importantly, poorly managed HIV due to lack of compliance with cART and immunodeficiency are the main risk for PCNSL. 47
Importantly, in narrative review it was concluded that pituitary dysfunction in HIV patients is likely due to primary lymphoma of the pituitary gland. It concluded that endocrine dysfunction was one of the most common presenting features as reported in 50% of the cases, alongside headaches and visual symptoms. 48 Lymphoma in HIV can have different presentations. For instance, a female had a history of infertility for 5 years and more recently amenorrhea, galactorrhea, and neurological disorders. An endocrinological evaluation showed low levels of FSH and LH, with otherwise normal hormonal levels. After diagnostic workup stereotactic biopsy was performed to reveal the underlying pituitary lymphoma. 49 Furthermore, it has been shown that different hormones of the pituitary gland can be affected by these neoplasms, where a case of primary pituitary T-cell lymphoma in a 47-year-old male caused low levels of ACTH and FSH to be extremely low (LH was undetectable). 50 Hence, as endocrine dysfunction is a common presentation of this cancer in immunocompetent individuals, whose risk of getting this malignancy is lower than HIV-positive patients; it is always important to think of this as a differential in the HIV population that are showing hormonal changes.
Despite the fact that brain lesions associated with HIV are PCNSL and toxoplasmosis, 51 the prevalence in non-AIDS defining intracranial malignancies such as glioblastoma multiforme (GBM) has risen in the HIV population. 52 A case report showed an immunocompetent 62-year-old male with malignant glioma. He presented with nausea and vomiting, decreased, blurred, and double vision along with headache. On endocrinological evaluation, his ACTH levels were low with everything else within normal limits. The tumor compressed the optic chiasm explaining the visual symptoms the man presented with. In general, it is reported in the literature that these tumors present with signs of headache, intracranial focal lesions, and a reduction in pituitary hormones. 53 In an article studying these tumors specifically in HIV patients, it concluded that there is an increased incidence of GBM compared with the general population. In 21 cases that Hall and Short 54 looked over, the mean CD4 count at GBM presentation was 400/mm 3 (moderately immunosuppressed), and they had a median HIV diagnosis of 3 years. It was shown that in HIV-patients this tumor occurs at an earlier age and was concluded the management to be the same as non-HIV GBM patients with surgery, chemotherapy, and radiotherapy, alongside cART. This is because survival is dictated by the tumor, not the HIV-status. Therefore, in individuals living with HIV and presented with neurological and endocrinological signs who has good adherence to cART, it is important that intracranial lesions are included in the differential diagnosis, as it is not just AIDS-defining tumors that are now being seen.
Combined Anti-retroviral Therapy and Pituitary Function
The antiretroviral medication can also have negative impact in the pituitary function. For instance, nevirapine, ritonavir, or abacavir sulfate appeared not to influence GH level. 55 Furthermore, nelfinavir (protease inhibitor) was shown to sensitize pituitary adenoma cells to ionizing radiation but no impact on prolactin secretion. 56 However, in certain cases with galactorrhea and gynecomastia, this was attributed to an increase in prolactin related to a cART. 22 Treatment with cART therapy can be associated with both low or high TSH 24 25 . Administration of cART for 2 years appeared to have no impact on the free testosterone. 57 While other studies suggested restoration of sexual function after administration of antiretroviral medication. 58 59 In certain patient cART can be associated with high FSH. 28 The effect of cART on the posterior pituitary lobe can be seen in terms of possible association in some patients with diabetes inspidious, 60 61 but majority of women on cART still can have normal vaginal delivery without need for synthetic oxytocin. 37 Overall, antiretroviral medication is well tolerated in majority of individuals with HIV, but clinicians need to be aware that certain patients may respond in different ways in particular in relation to pituitary functions.
Conclusion
HIV can have complex impact on the function of the pituitary gland (summary can be seen in Fig. 1 ). There are many potential direct and indirect effects of HIV on pituitary function and this needs to be addressed, monitored, and managed in proper clinical settings. Effective multidisciplinary collaboration between clinical biochemists, HIV physicians, and endocrinologists will lead to better management of patients and better future research in this field.
Fig. 1.
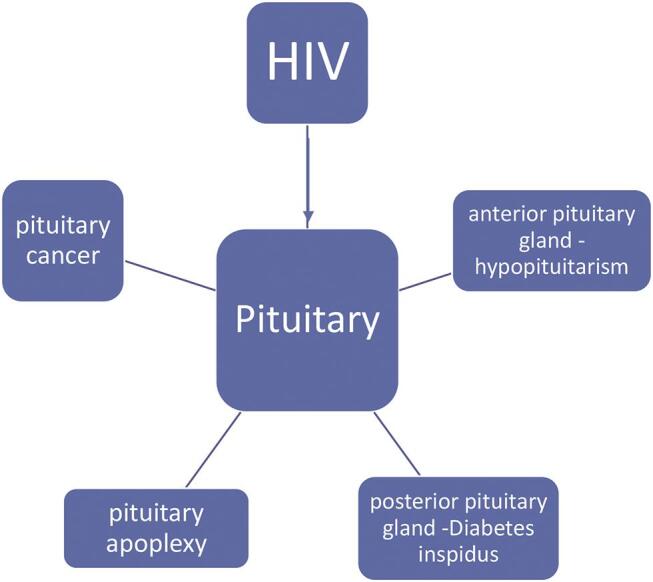
The complex impact of HIV on the pituitary gland. HIV, human immunodeficiency virus.
Funding Statement
Funding None.
Footnotes
Authors’ ContributionsConflict of Interest All authors contributed equally in this review.
None declared.
References
- 1.World Health Organization. n.d. Data and Statistics. Available at: https://www.who.int/hiv/data/en/. Accessed April 25, 2020
- 2.Cks.nice.org.uk. 2018. HIV Infection and AIDS—NICE CKS. Available at: https://cks.nice.org.uk/hiv-infection-and-aids#!diagnosisAdditional:3. Accessed April 25, 2020
- 3.Arts E, Hazuda D. 2012. HIV-1 antiretroviral drug therapy. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3312400/#. Accessed April 25, 2020 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 4.Filardi P P, Paolillo S, Marciano C et al. Cardiovascular effects of antiretroviral drugs: clinical review. Cardiovasc Hematol Disord Drug Targets. 2008;8(04):238–244. doi: 10.2174/187152908786786232. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Tavares Bello C, Sousa Santos F, Sequeira Duarte J, Vasconcelos C. Diabetes insipidus and hypopituitarism in HIV: an unexpected cause. Endocrinol Diabetes Metab Case Rep. 2017;2017:17–24. doi: 10.1530/EDM-17-0024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Sayed S, Fahmy M, Schwartz J. 2019. Physiology, pituitary gland. . Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459247/. Accessed April 24, 2020
- 7.Amar A P, Weiss M H. Pituitary anatomy and physiology. Neurosurg Clin N Am. 2003;14(01):11–23, v. doi: 10.1016/s1042-3680(02)00017-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Téblick A, Langouche L, Van den Berghe G. Anterior pituitary function in critical illness. Endocr Connect. 2019;8(08):R131–R143. doi: 10.1530/EC-19-0318. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Harbeck B, Klose S, Buchfelder M, Brabant G, Lehnert H. Hypopituitarism in a HIV affected patient. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2011;119(10):633–635. doi: 10.1055/s-0031-1284366. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Hamdeh S, Abbas A, Fraker J, Lambrecht J E. Intracranial toxoplasmosis presenting as panhypopituitarism in an immunocompromised patient. Am J Emerg Med. 2015;33(12):18480–184800. doi: 10.1016/j.ajem.2015.04.071. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Zirilli L, Orlando G, Diazzi C et al. Hypopituitarism and HIV-infection: a new comorbidity in the HAART era? J Endocrinol Invest. 2008;31 09:33–38. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Membreno L, Irony I, Dere W, Klein R, Biglieri E G, Cobb E. Adrenocortical function in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1987;65(03):482–487. doi: 10.1210/jcem-65-3-482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Beltran S, Lescure F X, Desailloud R et al. Thyroid and VIH Group. Increased prevalence of hypothyroidism among human immunodeficiency virus-infected patients: a need for screening. Clin Infect Dis. 2003;37(04):579–583. doi: 10.1086/376626. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Rietschel P, Hadigan C, Corcoran C et al. Assessment of growth hormone dynamics in human immunodeficiency virus-related lipodystrophy. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2001;86(02):504–510. doi: 10.1210/jcem.86.2.7175. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Rochira V, Guaraldi G. Growth hormone deficiency and human immunodeficiency virus. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;31(01):91–111. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2017.02.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Koutkia P, Meininger G, Canavan B, Breu J, Grinspoon S. Metabolic regulation of growth hormone by free fatty acids, somatostatin, and ghrelin in HIV-lipodystrophy. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2004;286(02):E296–E303. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00335.2003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Myhre J A, Chadwick E G, Yogev R. Failure to thrive in HIV-infected children: incidence, prevalence, and clinical correlates. Pediatr AIDS HIV Infect. 1996;7(02):83–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Viganò A, Mora S, Brambilla P et al. Impaired growth hormone secretion correlates with visceral adiposity in highly active antiretroviral treated HIV-infected adolescents. AIDS. 2003;17(10):1435–1441. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200307040-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Jain S, Desai N, Bhangoo A. Pathophysiology of GHRH-growth hormone-IGF1 axis in HIV/AIDS. Rev Endocr Metab Disord. 2013;14(02):113–118. doi: 10.1007/s11154-013-9245-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Triant V A. Cardiovascular disease and HIV infection. Curr HIV/AIDS Rep. 2013;10(03):199–206. doi: 10.1007/s11904-013-0168-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Graef A S, Gonzalez S S, Baca V R et al. High serum prolactin levels in asymptomatic HIV-infected patients and in patients with acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Clin Immunol Immunopathol. 1994;72(03):390–393. doi: 10.1006/clin.1994.1157. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Mira J A, Lozano F, Santos J et al. Grupo Andaluz para el Estudio de las Enfermedades Infecciosas. Gynaecomastia in HIV-infected men on highly active antiretroviral therapy: association with efavirenz and didanosine treatment. Antivir Ther. 2004;9(04):511–517. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Wilson L D, Truong M P, Barber A R, Aoki T T. Anterior pituitary and pituitary-dependent target organ function in men infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. Metabolism. 1996;45(06):738–746. doi: 10.1016/s0026-0495(96)90140-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Thongam S, Keithelakpam S, Singh T Y, Singh R L, Singh A M, Ranabir S. Thyroid dysfunction in human immunodeficiency virus-infected children and its correlation with CD4(+) T lymphocyte count. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2015;19(02):272–276. doi: 10.4103/2230-8210.149321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Madge S, Smith C J, Lampe F C et al. No association between HIV disease and its treatment and thyroid function. HIV Med. 2007;8(01):22–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1293.2007.00422.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Norbiato G, Galli M, Righini V, Moroni M. The syndrome of acquired glucocorticoid resistance in HIV infection. Baillieres Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994;8(04):777–787. doi: 10.1016/s0950-351x(05)80300-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Findling J W, Buggy B P, Gilson I H, Brummitt C F, Bernstein B M, Raff H. Longitudinal evaluation of adrenocortical function in patients infected with the human immunodeficiency virus. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 1994;79(04):1091–1096. doi: 10.1210/jcem.79.4.7962279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Bajaj S, Pathak Y, Varma S, Verma S. Metabolic status and hypogonadism in human immunodeficiency virus-infected males. Indian J Endocrinol Metab. 2017;21(05):684–687. doi: 10.4103/ijem.IJEM_127_17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Sayed S, Fahmy M, Schwartz J. 2019. Physiology, pituitary gland. Available at: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK459247/#_ncbi_dlg_citbx_NBK459247. Accessed April 19, 2020
- 30.Shu Z, Tian Z, Chen J et al. HIV/AIDS-related hyponatremia: an old but still serious problem. Ren Fail. 2018;40(01):68–74. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2017.1419975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Braconnier P, Delforge M, Garjau M, Wissing K M, De Wit S. Hyponatremia is a marker of disease severity in HIV-infected patients: a retrospective cohort study. BMC Infect Dis. 2017;17(01):98. doi: 10.1186/s12879-017-2191-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Langford D, Baron D, Joy J. Del Valle L, Shack J. Contributions of HIV infection in the hypothalamus and substance abuse/use to HPT dysregulation. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2011;36(05):710–719. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2010.10.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Purba J S, Hofman M A, Portegies P, Troost D, Swaab D F.Decreased number of oxytocin neurons in the paraventricular nucleus of the human hypothalamus in AIDS Brain 1993116(Pt 4)795–809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Fekete E M, Antoni M H, Lopez C et al. Stress buffering effects of oxytocin on HIV status in low-income ethnic minority women. Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2011;36(06):881–890. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2010.12.003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Lee H J, Macbeth A H, Pagani J H. Young WS III. Oxytocin: the great facilitator of life. Prog Neurobiol. 2009;88(02):127–151. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2009.04.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Bispo S, Chikhungu L, Rollins N, Siegfried N, Newell M L. Postnatal HIV transmission in breastfed infants of HIV-infected women on ART: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Int AIDS Soc. 2017;20(01):21251. doi: 10.7448/IAS.20.1.21251. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.2011. Caesarean section clinical guidance. NICE, p.14. Available at: https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/cg132/resources/caesarean-section-pdf-35109507009733. Accessed April 20, 2020
- 38.Ranabir S, Baruah M P.Pituitary apoplexy Indian J Endocrinol Metab 201115(suppl 3)S188–S196. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Wong N, Levy M, Stephenson I. Hypogonadism in the HIV-Infected Man. Curr Treat Options Infect Dis. 2017;9(01):104–116. doi: 10.1007/s40506-017-0110-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Quintero W olfe, S, Hood B, Barker J, Benveniste R J. Primary central nervous system lymphoma mimicking pituitary apoplexy: case report. Pituitary. 2009;12(01):76–79. doi: 10.1007/s11102-008-0084-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Rigolosi R S, Schwartz E, Glick S M. Occurrence of growth-hormone deficiency in acromegaly as a result of pituitary apoplexy. N Engl J Med. 1968;279(07):362–364. doi: 10.1056/NEJM196808152790707. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Sano T, Kovacs K, Scheithauer B W, Rosenblum M K, Petito C K, Greco C M. Pituitary pathology in acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 1989;113(09):1066–1070. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Rajasekaran S, Vanderpump M, Baldeweg S et al. UK guidelines for the management of pituitary apoplexy. Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 2011;74(01):9–20. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2265.2010.03913.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Baldeweg S E, Vanderpump M, Drake W et al. Society for Endocrinology Clinical Committee. Society for Endocrinology Endocrine Emergency Guidance: Emergency management of pituitary apoplexy in adult patients. Endocr Connect. 2016;5(05):G12–G15. doi: 10.1530/EC-16-0057. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Rubinstein P G, Aboulafia D M, Zloza A. Malignancies in HIV/AIDS: from epidemiology to therapeutic challenges. AIDS. 2014;28(04):453–465. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0000000000000071. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Kozáková D, Macháleková K, Brtko P, Szépe P, Vanuga P, Pura M. Primary B-cell pituitary lymphoma of the Burkitt type: case report of the rare clinic entity with typical clinical presentation. Cas Lek Cesk. 2008;147(11):569–573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Sierra del Rio M, Rousseau A, Soussain C, Ricard D, Hoang-Xuan K. Primary CNS lymphoma in immunocompetent patients. Oncologist. 2009;14(05):526–539. doi: 10.1634/theoncologist.2008-0236. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Rainsbury P, Mitchell-Innes A, Clifton N j, Khalil H. Primary lymphoma of the pituitary gland: an unusual cause of hemianopia in an immunocompetent patient. JRSM Short Rep. 2012;3(08):55. doi: 10.1258/shorts.2012.012067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Fadoukhair Z, Amzerin M, Ismaili N et al. Symptomatic hypopituitarism revealing primary suprasellar lymphoma. BMC Endocr Disord. 2010;10:19. doi: 10.1186/1472-6823-10-19. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Huang Y Y, Lin S F, Dunn P, Wai Y Y, Hsueh C, Tsai J S. Primary pituitary lymphoma presenting as hypophysitis. Endocr J. 2005;52(05):543–549. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.52.543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Chaudhry N S, Ahmad F U, Blieden C, Benveniste R J. Brainstem anaplastic glioma in patients with AIDS: a case report and review of the literature. BMJ Case Rep. 2013;2013:bcr2012008384. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2012-008384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Choy W, Lagman C, Lee S J, Bui T T, Safaee M, Yang I. Impact of human immunodeficiency virus in the pathogenesis and outcome of patients with glioblastoma multiforme. Brain Tumor Res Treat. 2016;4(02):77–86. doi: 10.14791/btrt.2016.4.2.77. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Anvari K, Samini F, Faraji M, Khooei A, Ghiasi T, Dehghan P. Pituitary glioblastoma: a case report. Iran J Cancer Prev. 2015;8(04):e3436. doi: 10.17795/ijcp-3436. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Hall JR, Short SC. Management of glioblastoma multiforme in HIV patients: a case series and review of published studies. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 2009;21(8):591–597 [DOI] [PubMed]
- 55.Brigante G, Riccetti L, Lazzaretti C et al. Abacavir, nevirapine, and ritonavir modulate intracellular calcium levels without affecting GHRH-mediated growth hormone secretion in somatotropic cells in vitro. Mol td Endocrinol. 2019;482:37–44. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2018.12.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Zeng J, See A P, Aziz K et al. Nelfinavir induces radiation sensitization in pituitary adenoma cells. Cancer Biol Ther. 2011;12(07):657–663. doi: 10.4161/cbt.12.7.17172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Wunder D M, Fux C A, Bersinger N A et al. Swiss HIV Cohort Study. Androgen and gonadotropin patterns differ in HIV-1-infected men who develop lipoatrophy during antiretroviral therapy: a case-control study. HIV Med. 2008;9(06):427–432. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-1293.2008.00578.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 58.Rochira V, Diazzi C, Santi D et al. Low testosterone is associated with poor health status in men with human immunodeficiency virus infection: a retrospective study. Andrology. 2015;3(02):298–308. doi: 10.1111/andr.310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Wanke C A, Silva M, Knox T A, Forrester J, Speigelman D, Gorbach S L. Weight loss and wasting remain common complications in individuals infected with human immunodeficiency virus in the era of highly active antiretroviral therapy. Clin Infect Dis. 2000;31(03):803–805. doi: 10.1086/314027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Singh G. Latrogenic nephrogenic diabetes insipidus. AIDS. 2003;17(09):1418. doi: 10.1097/00002030-200306130-00030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.D’Ythurbide G, Goujard C, Méchaï F, Blanc A, Charpentier B, Snanoudj R. Fanconi syndrome and nephrogenic diabetes insipidus associated with didanosine therapy in HIV infection: a case report and literature review. Nephrol Dial Transplant. 2007;22(12):3656–3659. doi: 10.1093/ndt/gfm467. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Imai K, Sutton M Y, Mdodo R.Del Rio C.HIV and menopause: a systematic review of the effects of HIV infection on age at menopause and the effects of menopause on response to antiretroviral therapy Obstet Gynecol Int 20132013340309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Karim R, Mack W J, Kono N et al. Gonadotropin and sex steroid levels in HIV-infected premenopausal women and their association with subclinical atherosclerosis in HIV-infected and -uninfected women in the women’s interagency HIV study (WIHS) J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2013;98(04):E610–E618. doi: 10.1210/jc.2012-3195. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Pebody R. Menopause and HIV; 2017. aidsmap.com. Available at: http://www.aidsmap.com/about-hiv/menopause-and-hiv. Accessed June 13, 2020
- 65.Romero-Velez G, Lisker-Cervantes A, Villeda-Sandoval C I et al. Erectile dysfunction among HIV patients undergoing highly active antiretroviral therapy: dyslipidemia as a main risk factor. Sex Med. 2014;2(01):24–30. doi: 10.1002/sm2.25. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Kongnyuy E J, Wiysonge C S. Association between fertility and HIV status: what implications for HIV estimates? BMC Public Health. 2008;8(01):309. doi: 10.1186/1471-2458-8-309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Kushnir V A, Lewis W. Human immunodeficiency virus/acquired immunodeficiency syndrome and infertility: emerging problems in the era of highly active antiretrovirals. Fertil Steril. 2011;96(03):546–553. doi: 10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.05.094. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Fiorot Costalonga E, Weberling Coelho Moreira A, Morais Borges F et al. Nephrogenic diabetes insipidus as the first manifestation of ectopic ACTH syndrome in a HIV infected patient. Int Arch Med. 2016;9:ISSN 1755–7682. [Google Scholar]
- 69.Juffermans N P, Verbon A, Van der Poll T. Diabetes insipidus as a complication of cryptococcal meningitis in an HIV-infected patient. Scand J Infect Dis. 2002;34(05):397–398. doi: 10.1080/00365540110080502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


