Fig. 3.
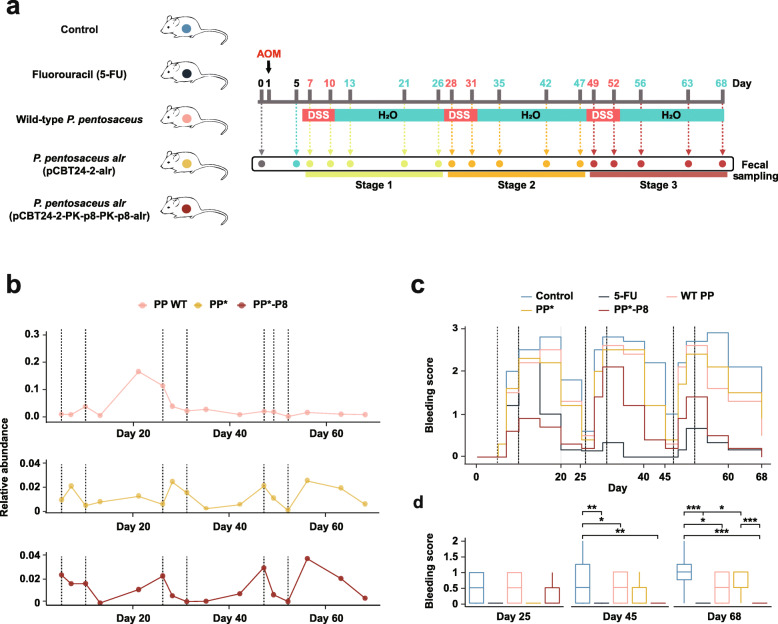
AOM/DSS-induced mouse model of colitis-associated colon carcinogenesis. a The experimental scheme for tumor induction by azoxymethane (AOM) and dextran sodium sulfate (DSS). Mice (n = 10 in each group) were intraperitoneally injected with 12.5 mg/kg body weight AOM on day 1 and on day 5; they were given water containing 2% w/v DSS for 5 days, followed by regular water for 16 days, which was repeated three times during the 68-day treatment. Treatment groups: untreated control (0.9% saline, oral), fluorouracil (5-FU; 40 mg/kg body weight, intraperitoneal, twice a week), wild-type P. pentosaceus (PP WT; 1 × 1010 CFU/head, oral, five times a week), P. pentosaceus alr (pCBT24-2-alr) (PP*; 1 × 1010 CFU/head, oral, five times a week), and P. pentosaceus alr (pCBT24-2-PK-p8-PK-p8-alr) (PP*-P8; 1 × 1010 CFU/head, oral, five times a week). Schedules for fecal sampling are indicated with arrows. b Temporal dynamics of the PP*-P8 population in relative abundance during the experimental period. Dashed lines represent the DSS treatment episodes. c Bleeding scores were assessed every 5 days by hemoccult testing and visible signs. Dashed lines represent the DSS treatment episodes. d Comparison of bleeding scores in days 25, 45, and 68, the last days of each stage. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001