Abstract
Background
Osteopetrosis is a rare inherited bone disorder affected individual by osteoclast disfunction and increasing bone density. Surgery was taken for histological examination of the specimen and evidence of malignancy was not found. Finally, X-ray and gene detection lead to the diagnosis.
Case presentation
We report a 10-year-old girl with two years history of pus rhinorrhea, nasal obstruction and smelly nose. She was diagnosed and treated as sinusitis. But the symptoms were recurrent. Ten months ago, she was afflicted with persistent swelling and broken skin on the right cheek. All the laboratory findings showed normal. During surgery, we resected the right gingiva, the right nasal mucosa and the right facial tissue for biopsies. Histological examination showed proliferation of granulation tissue in chronic inflammatory mucosa. X-rays showed generalized sclerosis. Genetic analysis strongly supported a novel mutation of TNFRSF11A gene which caused osteoporosis. We found a novel mutation of the c.1196C > G (p.S399X) in exon 9 of TNFRSF11A. The TNFRSF11A gene encodes RANK, which is fundamental for osteoclast formation.
Conclusion
Osteopetrosis is a rare genetic bone disease characterized by increased bone density because of bone resorption failure. Diagnosis is based on X-ray and gene analyze. Osteoclasts are bone-related cells derived from hematopoietic cell lines. Since osteoclasts arise from a hematopoietic progenitor cell of the monocytic lineage, the defect can be corrected by hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT). Better understanding of this pathological situation and pathogenesis is so important to plan appropriate immunotherapy to benefit.
Keywords: TNFRSF11A gene, Osteopetrosis, Autosomal recessive
Background
Osteopetrosis is a rare inherited bone disorder characterized by osteoclast disfunction and increasing bone density [1]. It was first reported by a German radiologist named Albers-Schönberg in 1904.It was also called “Albers-Schönberg disease” or “marble disease”. This disease is caused by abnormal bone remodeling and resulted in osteoclast disorder. Osteoclasts are bone-related cells derived from hematopoietic cell lines. Increase in bone density leads to limitation of bone marrow cavity, resulted in hematopoietic failure and anemia or pancytopenia, followed by hepatosplenomegaly and frontal bone eminence. Expanding bone will have a negative impact on the patient's movement, and lead to blindness, deafness, even facial paralysis and dysphagia [2].
According to the basis of mode of inheritance, osteopetrosis is generally classified into autosomal recessive osteopetrosis (ARO), autosomal dominant osteopetrosis (ADO) and X-linked [3–6]. ARO is now documented to affect 1 in 250 000 live births, ADO is with an incidence of approximately 1 in 20,000 births [7, 8]. Osteopetrosis exhibits high phenotypic and genotypic diversity, patients with different mutation can be symptomatic or asymptomatic, with symptoms various from mild to severe. Due to clinical manifestation, the disease can be divided into three types: mild, intermediate and severe types. The severe type has increased bone density and frequent fractures. To the contrary, as for the mild group, some of which have normal life expectancy [9].
Infantile malignant osteopetrosis is the most several type of autosomal recessive osteopetrosis. It is usually detected during infancy or early childhood due to whole body bone sclerosis, short stature, macrocephaly, tooth deformities, hepatosplenomegaly, severe anemia, and persistent fracture [10]. Although approximately 30% of the etiology of human osteopetrosis remain genetically unrecognized, but so far, at least 20 genes mutation including TCIRG1, CLCN7, SNX10, OSTM1, PLEKHM1, CAII, FERMT3,RANKL, RANK( TNFRSF11), SLC29A3, TRAF6,LRRK1,MITF, NEMO, RELA,CSF1R,C16ORF57,CTSK,Kindlin-3,CalDAG-GEFI, have been reported to associated with human osteopetrosis [3–6]. TCIRG1 is the most common one. Here we present a case of a pediatric female, who carried a homozygous gene mutation in TNFRSF11A.
Case presentation
A 10-year-old girl was referred by her doctor with the chief complains of pus rhinorrhea, nasal obstruction and smelly nose for two years. Ten months ago, she was afflicted with persistent swelling and broken skin on the right cheek. Physical examination showed that smelly purulent secretion of abscess along with soft tissues below right medial canthus. Poor nasal ventilation, secretion occupied middle meatus and total meatus. Several teeth did not erupt and were still sub-gingival. So it was difficult to distinguish primary and permanent teeth (Fig. 1). #84,85 root malformations and alveolar bone osteonecrosis were seen (Fig. 2). Oral hygiene was poor; rampant caries and gingivitis were present.
Fig. 1.
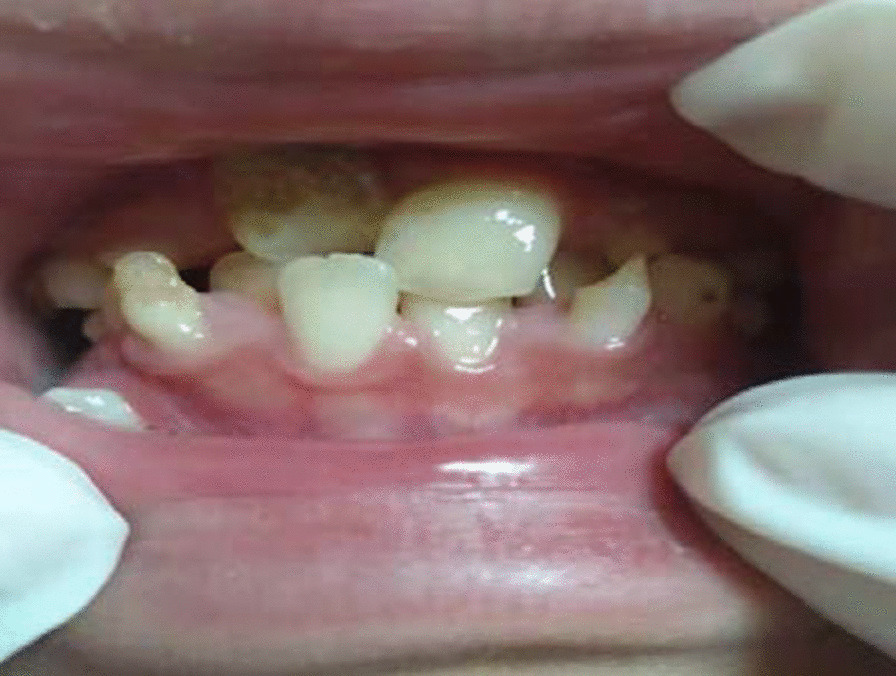
Intraoral front view- mixed dentition and caries
Fig. 2.
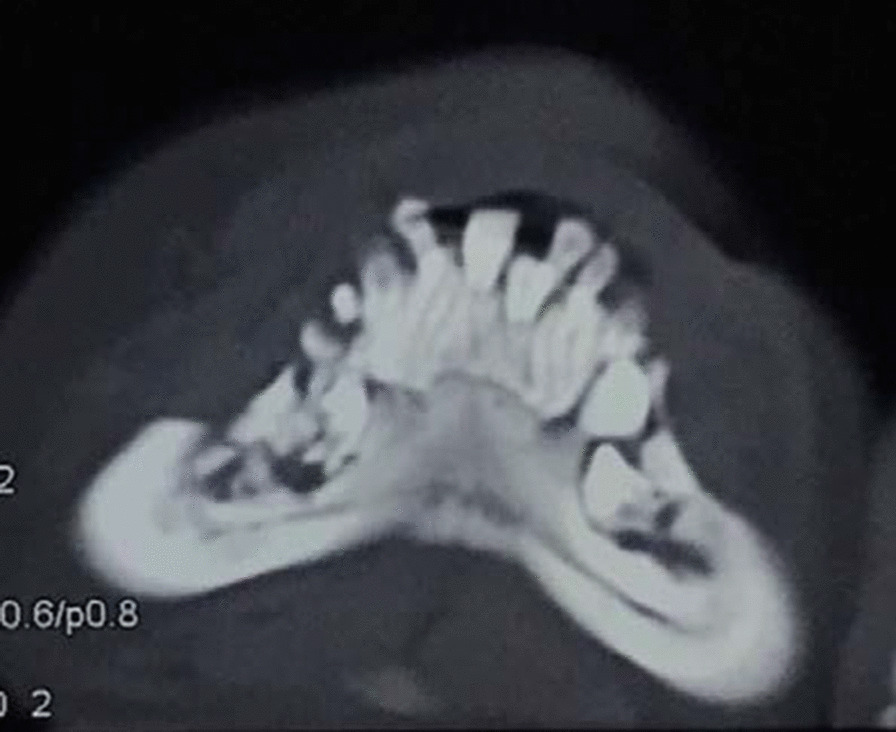
Destruction of maxillary alveolar bone
The girl stayed as an inpatient for 24 days. In hospital, antibiotic of amoxicillin and clavulanate potassium (800 mg per 8 h) was using for 7 days and the skin of her cheek began to heal. For evaluation the cause of the disease, laboratory tests; computer tomography (CT) of sinusitis and surgery was taken. All the laboratory findings showed normal. CT of and paranasal sinus shows bone destruction of right maxillary sinus wall and right nasal bone, and maxillary sinus and anterior part of nasal cavity are filled with more soft tissue density (Fig. 3). On day 8, surgery was carried out under general anesthesia. During surgery, we resected the right gingiva, the right nasal mucosa and the right facial tissue for biopsies. Histological examination showed proliferation of granulation tissue in chronic inflammatory mucosa. Evidence of malignancy was not observed.
Fig. 3.
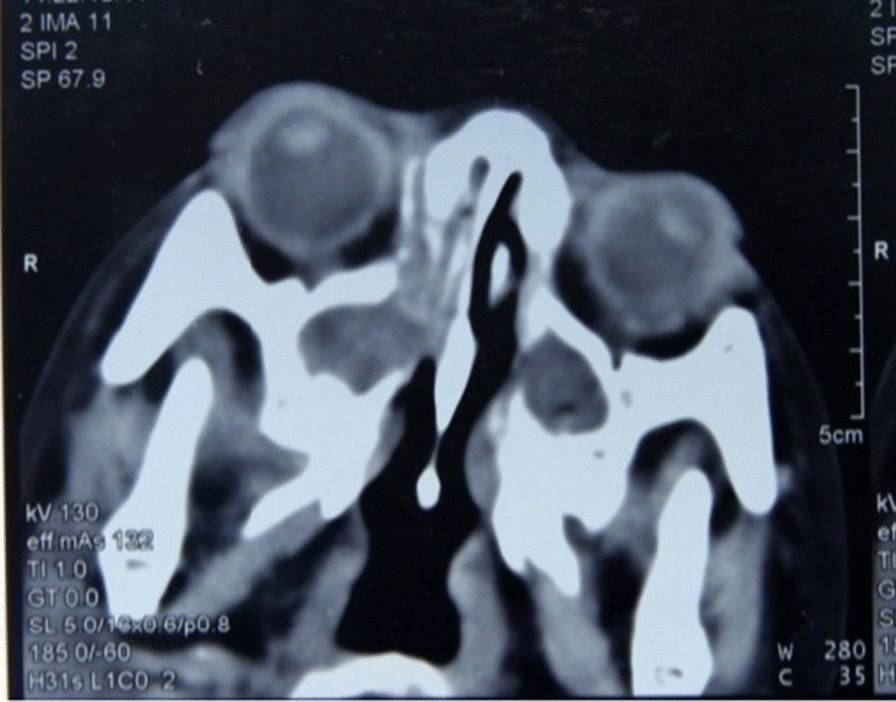
Paranasal sinusitis
All the examination results could not lead to diagnosis. After the hospital consultation, we suspected the diagnosis of osteopetrosis. X-rays of hands, legs, chest and skull was taken place on day 15. Radiographs showed multiple bony abnormalities involving the skull, vertebrae and limb. X-rays showed generalized sclerosis, for example: thickening and increasing Cranial plate, narrowing diploic vein, Sella turcica, increased vertebral bone density in cliff, smaller pituitary fossa, and costochondral junction widening. A typical form of “sandwich” vertebra was noted. Longitudinal striation of the long bones, extreme metaphyseal flaring, reduced bone vascularity and dense bone structure was simply found (Fig. 4).
Fig. 4.
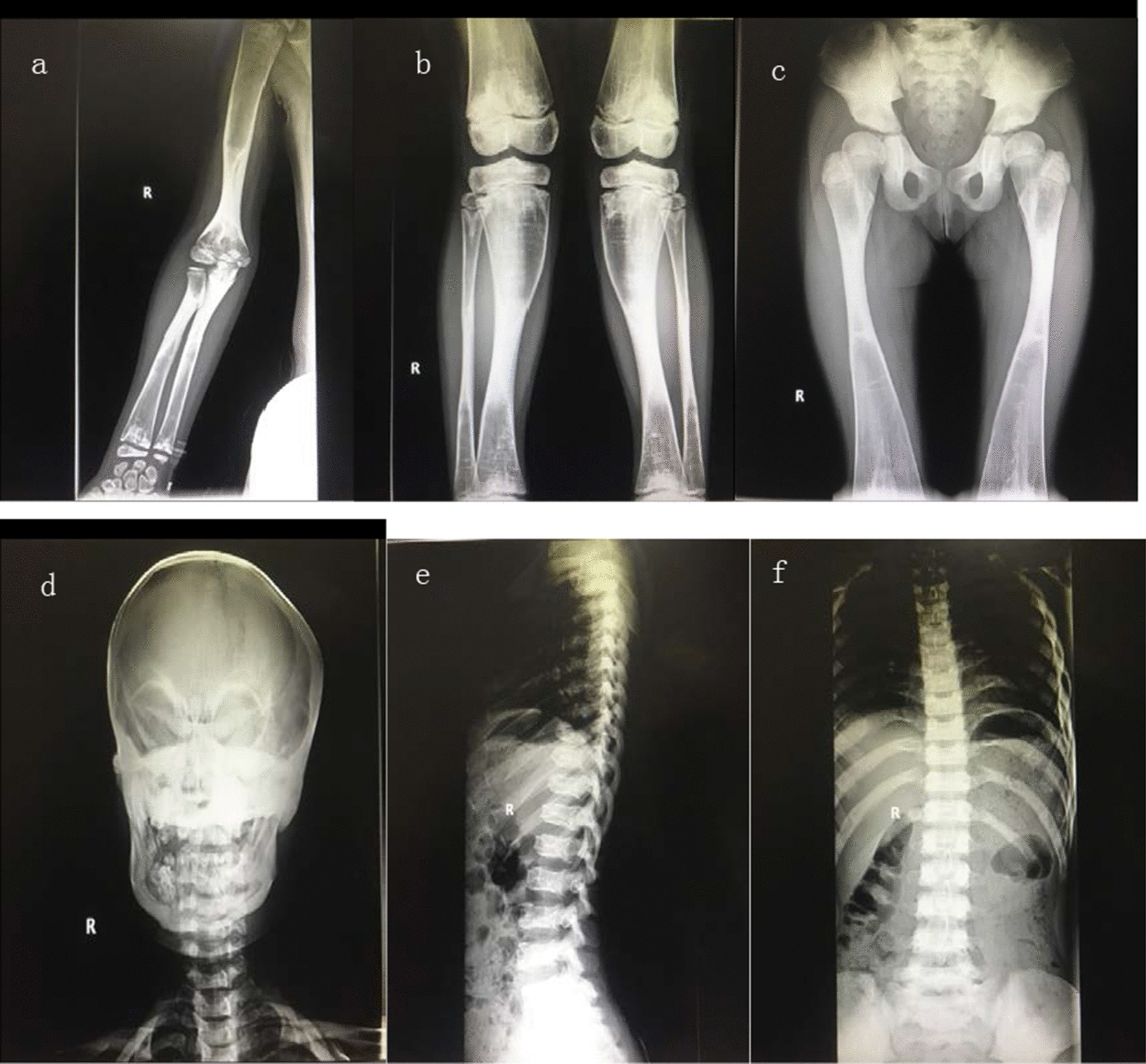
a–c The structure of limb bones is deformed. Extreme metaphyseal flaring, reduced bone vascularity and dense bone structure is found. d Skull radiograph showing typical wolf carnival appearance. e, f Front-Lateral Chest radiograph showing diffuse sclerotic vertebra and costochondral junction widening
After informed consent, Peripheral blood samples (3 ml) from the proband, sister and both parents were collected into graded negative pressure vacuum ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid (EDTA)anticoagulant tubes. Genomic deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) from all available family members were obtained for Sanger sequencing. The whole‐exome sequencing and Sanger sequencing were performed by Beijing Mygenostics Co, Ltd were taken place. Targeted gene panel sequencing was performed to check for the presence of pathogenic variants of multiple associated genes responsible for osteopetrosis.
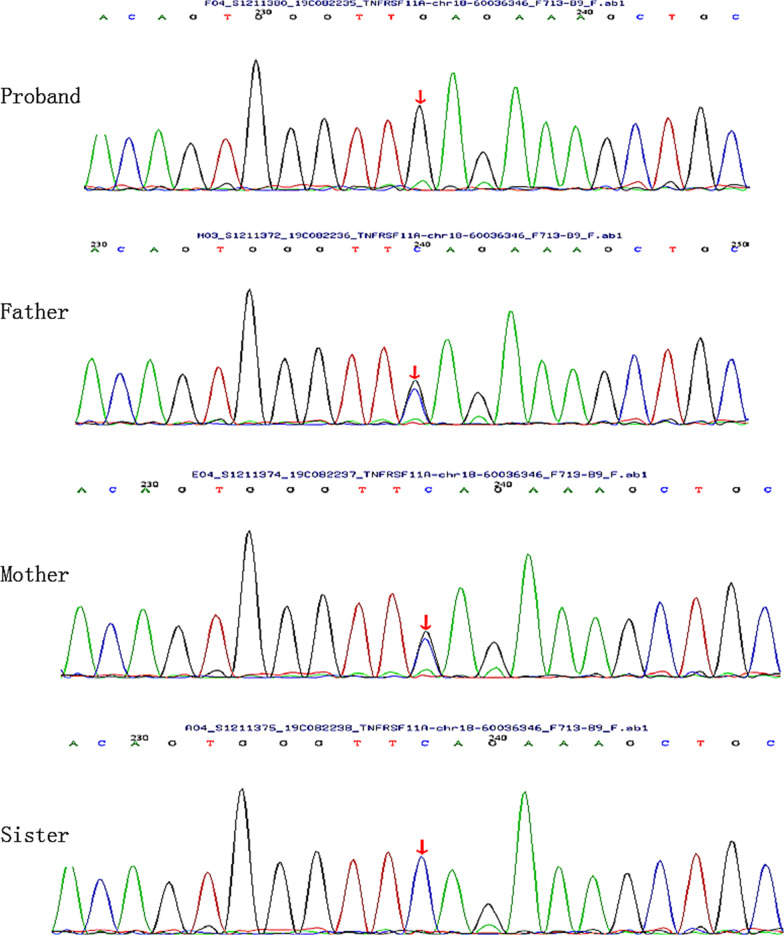
The results of whole‐exome sequencing revealed homozygous nonsense mutation c.1196C > G (p.S399X) in exon 9 of the TNFRSF11A gene in the proband. It was a novel mutation which was not previously reported in a patient with osteopetrosis. Sanger sequencing was applied to confirm the presence of this identified variant, and the same heterozygous variant was found in both the patient’s father and mother (Fig. 5). However, the parents denied having any complaints including osteomyelitis, history of fracture, visual impairment and hearing loss.
Fig. 5.
A homozygous nonsense mutation of the c.1196C > G (p.S399X) of the TNFRSF11A gene was identified in the proband and marked with arrow. The same heterozygous variant was found in both the patient’s father and mother. The sister is normal
Discussion and conclusion
In this case, the child went to the otolaryngology department with the onset of nasal symptoms as the main-complain. After systemic X-ray examination with characteristic imaging changes and genetic test, the patient was diagnosed of osteopetrosis. This is the first case of pediatric osteopetrosis in China with a mutation in TNFRSF11A gene. The molecular analysis of the patient led to the identification of a novel mutations in the TNFRSF11A gene: a nonsense mutations c.1196C > G (p.S399X) in exon 9.Mutations in the human TNFRSF11A gene which leading to osteopetrosis was first reported by Sobacchi [11]. Monogenic mutations of TNFRSF11A has previously been fully documented as the cause of human autosomal recessive osteopetrosis [12–14]. It caused amino acid substitutions at moderately conserved position and supporting the diagnosis of autosomal recessive osteopetrosis type 7 [15].
TNFRSF11A(RANK) gene belongs to the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily and located on chromosome 18 (18q21.33), which encoding a receptor with 616 amino acids [16]. The RANK gene codes for the functional receptor for RANKL. The mutated residues seem to be highly conserved in evolution, so it could be considered that amino acid substitutions at these positions might change the folding of the outer domain thus the interaction with RANKL. RANKL, RANK and TNFRSF11 affect the differentiation of osteoclasts, resulting in a decrease in the number of osteoclasts, while the remaining genes all cause osteoclast dysfunction [17].
RANK-dependent ARO is confirmed to benefit from HSCT, although there is no long-term follow-up data. In the post-HSCT period, patients seem to be particularly prone to hypercalcemia, especially when HSCT surgery is older. These data increase the clinical and molecular heterogeneity of human ARO, further confirming the important role of accurate molecular diagnosis in therapy.
Until now, TNFRSF11A mutations have been observed in patients with the Paget’s disease of bone (PDB), primary ovarian insufficiency, recurrent fevers, familial expansile osteolysis, expansile skeletal hyperphosphatasia and autosomal recessive osteopetrosis [2, 16]. The TNFRSF11A gene encodes RANK, which is fundamental for osteoclast formation. This has been demonstrated before, which impacted osteoclasts maturation and have a severe defect in bone resorption and remodeling.
At present, there is no acceptable best therapy for osteopetrosis, as a result, symptomatic and supportive treatment was given to most patients [18]. HSCT is the only treatment that can offer cure to these patients according to reports, but not all the subtypes can benefit from HSCT (e.g. OSTM1 and some with CLCN7) [13]. Osteopetrosis can be diagnosed by typical x-ray manifestation. Typical bony abnormalities were illustrated, including generalized sclerosis, longitudinal striation of the long bones, extreme metaphyseal flaring or transverse lucent bands, “sandwich” vertebra, flask deformities, “bone-within-bone” appearance. Bone marrow biopsy showed shrinkage of bone marrow cavity, thickening of bone trabecula, reduction of bone marrow hematopoietic cells, and bone marrow fibrosis [9, 19].
The clinical manifestations included rhinitis, alveolar bone osteonecrosis, osteomyelitis of alveolar bone, bone destruction of right maxillary sinus, failure of tooth eruption, roots malformation, caries, optic nerve atrophy, compressive neuropathies, cranial nerve deficit [2]. The child exhibited most of the phenotypic who was diagnosed after two years. She is the first case of osteopetrosis in the family, her parents and old sister are with normal bone density. Her parents are close relatives.
Clinic examination of ear nose and throat (ENT) doctors combining the whole-body radiographic results can lead to early diagnosis of osteopetrosis. Vigorous physical activities should be avoided to prevent severe complications. Thus, routine ENT and dental examination should be applied to prevent sinusitis and osteomyelitis as well. The role of TNFRSF11A mutations in osteopetrosis has been revealed not long ago. Genetic analysis strongly supported the pathogenic role for this mutation. Better understanding of this pathological situation and pathogenesis is so important to plan appropriate immunotherapy to benefit. In summary, we report a novel mutation of TNFRSF11A gene in a Chinese girl with osteopetrosis. Analysis and reporting patients with mutation in this gene can be very helpful to obtain a better picture of the disease phenotype in TNFRSF11A-related osteopetrosis.
Acknowledgements
We appreciated Beijing Mygenostics Co, Ltd for genetic analysis of the manuscript.
Abbreviations
- HSCT
Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation
- ARO
Autosomal recessive osteopetrosis
- ADO
Autosomal dominant osteopetrosis
- EDTA
Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid
- DNA
Deoxyribonucleic acid
- CT
Computed tomography
- TNF
Tumor necrosis factor
- PDB
Paget’s disease of bone
- ENT
Ear nose and throat
Authors' contributions
XY: Writing. YXY: Literature search, data collection. HMJ: Surgical and medical practices, or processing, analysis or interpretation, and concept and design. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
There is no honorarium, grant, or other form of payment given to any of the authors/coauthors.
Availability of data and materials
Available at the request of the readers.
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The patient’s parents had given us a verbal permission to participate. When we decided to use patient data for reporting, the patient was discharged from hospital, her home was far away from the hospital, and the parents were unwilling to go to the hospital again to make a written commitment, so they gave verbal consent. The case was established and approved by the Human Ethics Committee of Chengdu Women's and Children's Central Hospital.
Consent for publication
Written informed consent for publication of the patient’s clinical details and/or clinical images was obtained directly from the patient’s parents.
Competing interests
No financial or non-financial benefits have been received or will be received from any party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Footnotes
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
References
- 1.Del FA, Capannolo M, Teti A. New mechanisms of osteopetrosis. IBMS Bonekey. 2009;6(1):16–28. doi: 10.1138/20090358. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Wu CC, Econs MJ, DiMeglio LA, Insogna KL, Levine MA, Orchard PJ, et al. Diagnosis and management of osteopetrosis: consensus guidelines from the osteopetrosis work group. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2017;102(9):3111–3123. doi: 10.1210/jc.2017-01127. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Sobacchi C, Schulz A, Coxon FP, et al. Osteopetrosis: genetics, treatment and new insights into osteoclast function. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2013;9(9):522–536. doi: 10.1038/nrendo.2013.137. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lorenzo J. The many ways of osteoclast activation. J Clin Invest. 2017;127(7):2530–2532. doi: 10.1172/JCI94606. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Mundy GR, Edwards JR. The osteoclast-not always guilty. Cell Metab. 2007;6(3):157–159. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2007.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Mansour A, Abou-Ezzi G, Sitnicka E, et al. Osteoclasts promote the formation of hematopoietic stem cell niches in the bone marrow. J Exp Med. 2012;209(3):537–549. doi: 10.1084/jem.20110994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Waguespack SG, Hui SL, DiMeglio LA, Econs MJ. Autosomal dominant osteopetrosis: clinical severity and natural history of 94 subjects with a chloride channel 7 gene mutation. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2007;92:771–778. doi: 10.1210/jc.2006-1986. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Bollerslev J, Henriksen K, Nielsen M, Brixen K, van Hul W. Autosomal dominant osteopetrosis revisited: lessons from recent studies. Eur J Endocrinol. 2013;169:R39–R57. doi: 10.1530/EJE-13-0136. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Stark Z, Savarirayan R. Osteopetrosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2009;4:5. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-4-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Kliegman R, Behrman R, Jenson H, Stanton B. Part 42. Section 3. Chapter 690. Disorders Involving Defective Bone Resorption. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. Philadelphia, PA, USA: Saunders. 2011;2432–3.
- 11.Sobacchi C,Villa A,Schulz A,Kornak U. In: Adam MP,Ar⁃ dinger HH,Pagon RA,Wallace SE,Bean LJH,Stephens K, Amemiya A,editors. CLCN7 ⁃ Related Osteopetrosis. GeneReviews® [Internet]. Seattle (WA): University of Wa Sobacchi, C., Frattini, A., Guerrini, M.M., Abinun, M., Pangra- zio, A., Susani, L., Bredius, R., Mancini, G., Cant, A., Bishop, N., et al. Osteoclast-poor human osteopetrosis due to mutations in the gene encoding RANKL. Nat. Genet. 2007;39, 960–962. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 12.Palagano E, Menale C, Sobacchi C, Villa A. Genetics of Ostropetrosis. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 2018;16(1):13–25. doi: 10.1007/s11914-018-0415-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Sobacchi C, Schulz A, Coxon FP, Villa A, Helfrich MH. Osteopetrosis: genetics, treatment and new insights into osteoclast function. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2013;9(9):522–36. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 14.Stark Z, Savarirayan R. Osteopetrosis. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2009;20(4):5. doi: 10.1186/1750-1172-4-5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Guerrini MM, Sobacchi C, Cassani B, Abinun M, Kilic SS, Pangrazio A, et al. Human osteoclast-poor osteopetrosis with hypogammaglobulinemia due to TNFRSF11A (RANK) mutations. Am J Hum Genet. 2008;83(1):64–76. doi: 10.1016/j.ajhg.2008.06.015. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Ono T, Hayashi M, Sasaki F, Nakashima T. RANKL biology: bone metabolism, the immune system, and beyond. Inflamm Regen. 2020;40:2. doi: 10.1186/s41232-019-0111-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Del Fattore A, Cappariello A, Teti A. Genetics, pathogenesis and complications of osteopetrosis. Bone. 2008;42(1):19–29. doi: 10.1016/j.bone.2007.08.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Bacon S, Crowley R. Developments in rare bone diseases and mineral disorders. Ther Adv Chronic Dis. 2018;9(1):51–60. doi: 10.1177/2040622317739538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Overholt KM, Rose MJ, Joshi S, Herman GE, Bajwa R, et al. Hematopoietic celltrans plantation fora child with OSTM1 osteopetrosis. Blood Adv. 2016;1(4):279–281. doi: 10.1182/bloodadvances.2016002345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
Available at the request of the readers.