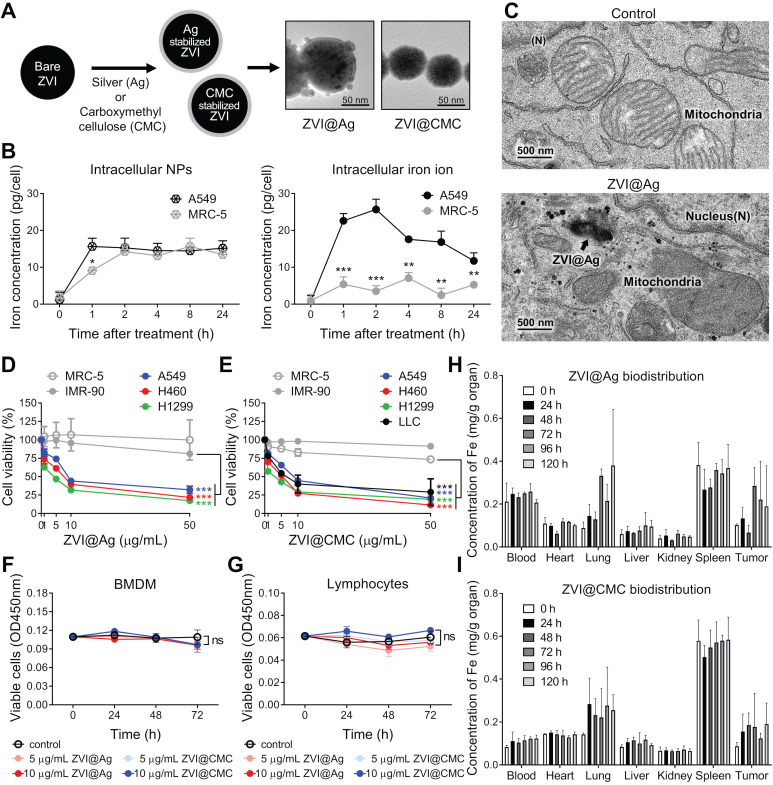
Figure 1.
Morphological and biological characterization of ZVI-NPs in cancer-specific cytotoxicity. A, TEM images showing the round shape morphology and surface coating of both types of NPs. Scale bar: 50 nm. B, Intracellular concentrations of ZVI@CMC NPs (left) and iron ions (right) were determined in A549 and MRC-5 cells after treatment with ZVI@CMC NPs (10 mg/mL) for 1, 2, 4, 8, or 24 h. C, TEM images showing the presence of ZVI@Ag (arrow) and the mitochondria with damaged cristae 24 h after NPs (10 μg/mL) treatment. D and E, MTT assay showing both ZVI@Ag NPs (D) and ZVI@CMC NPs (E) dose-dependently inhibited cell viability in lung cancer cells H460, A549 and H1299 without affecting lung fibroblast cells MRC-5 and IMR-90 after 48 h of treatment. F and G, Both ZVI@Ag NPs or ZVI@CMC NPs did not inhibit cell viability of ex vivo isolated BMDMs (F) and splenic lymphocytes (G) in the test concentrations (5 and 10 μg/mL) in the 72 h of treatment period. H and I, Biodistribution of ZVI@Ag NPs (H) or ZVI@CMC NPs (I) in major organs in nude mice given i.v. injection of a single dose (50 mg/kg). The iron concentrations in tissue samples were quantified at indicated time (n = 5 per group). Data were mean ± s.e.m. (n = 3 for cell-based assays). ns: non-significant; *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.