Figure 1.
Interaction between HDL and S. pneumoniae molecules PLY and NanA reduces PLY-mediated cytolysis and leads to HDL modification ex vivo
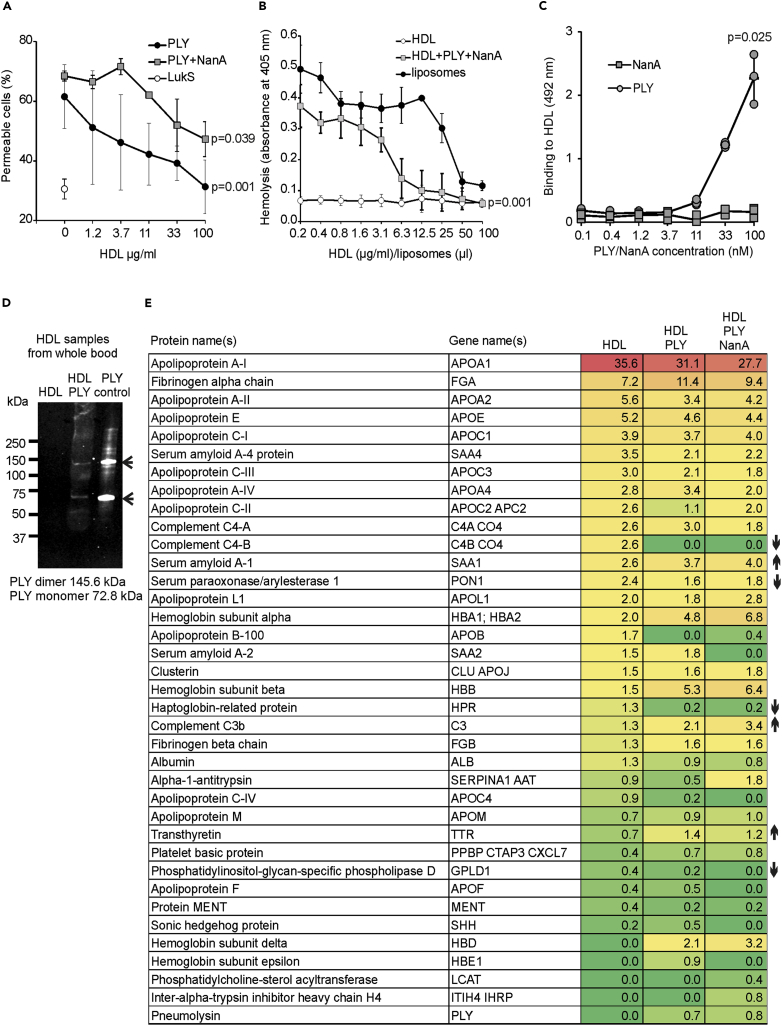
(A) THP-1 cells incubated with increasing concentrations of HDL-2 with or without 100 nM PLY or 100 nM PLY and 800 nM NanA. LukS was used as a negative control for cell lysis. Permeability is shown as the percentage of cells staining positive for 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole in flow cytometry. See also Figures S1A and S1B.
(B) Human red blood cells incubated with 10 nM PLY and 800 nM NanA. The effect of HDL-2 on the lytic activity of PLY was tested by the addition of increasing concentrations of HDL-2. Cholesterol-mediated inhibition was analyzed with increasing concentrations of liposomes. A sample with only HDL-2 was used as a negative control.
(C) Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay indicating binding of PLY to HDL-2. See also Figures S1C and S1D.
(D) Western blot of total HDL samples, isolated from plasma, incubated with (HDL + PLY) or without PLY (HDL). PLY control shows the size of the PLY monomer and dimer in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE).
(E) Total HDL samples isolated from ex vivo experiment analyzed by MS/MS. See also Table S1. Numbers are shown as the percentage of peptide spectrum matches (PSMs) of all identified proteins with a score of >10 or PSMs >4 in the HDL sample. Increase or reduction in the protein content in plasma-isolated HDL samples from the blood incubated with PLY and NanA compared to the sample without microbial molecules is marked with arrows. The detected statistically significant differences (p < 0.05) between highest and lowest ([A] and [B]) HDL or (C) PLY concentrations were calculated using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Dunnett's non-parametric multiple comparison test. Error bars indicate standard deviation (SD) values calculated from three repeated experiments.