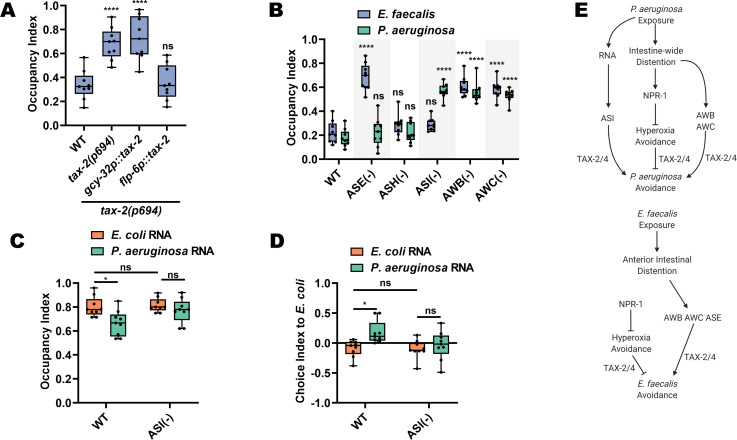
Figure 5. ASE, AWB, and AWC neurons mediate avoidance of E. faecalis.
(A) Occupancy index on E. faecalis at 4 hr for WT, tax-2(p694) and animals with tax-2 expression in ASE neurons (flp-6p::tax-2) or AQR, PQR, or URX neurons (gcy-32p::tax-2) in the tax-2(p694) background. One-way ANOVA with subsequent comparison to wild-type (WT) animals was performed. (B) Occupancy index of WT animals and animals with ablated neurons on E. faecalis at 4 hr and P. aeruginosa at 24 hr. Ablation of sensory neurons either by mutation (che-1(p680) = ASE(−)) or by caspase expression (sra-6p::mCasp-1=ASH(−); gpa-4p::TU#813 + gcy-27p::TU#814 = ASI(−); str-1p::mCasp-1 = AWB(−); ceh-36p::TU#813 + ceh-36p::TU#814 = AWC(−)). Two-way ANOVA with subsequent comparisons to WT groups for each respective bacterium were performed. (C) Occupancy index at 1 hr for WT and ASI(−) animals on P. aeruginosa lawns. Animals were trained on E. coli OP50 lawns supplemented with either E. coli or P. aeruginosa RNA for 24 hr. Two-way ANOVA with subsequent comparison with WT control groups was performed. (D) Choice index after 1 hr for WT and ASI(−) animals choosing between E. coli and P. aeruginosa lawns. Two-way ANOVA with subsequent comparison with WT control groups was performed. Choice Index = (number of animals on E. coli – number of animals on P. aeruginosa)/(number of animals on E. coli + number of animals on P. aeruginosa). (E) Model for avoidance of P. aeruginosa (top) and E. faecalis (bottom) Avoidance of P. aeruginosa depends on both an ASI neuron-mediated bacterial sRNA pathway along with intestine-wide distention. The latter requires the NPR-1-dependent hyperoxia avoidance pathway along with AWB and AWC olfactory neurons. Avoidance of E. faecalis also depends on intestinal distention, though this is confined to the anterior intestine. This anterior intestinal distention-induced avoidance also requires AWB and AWC olfactory neurons, but also requires ASE chemosensory neurons. NPR-1-dependent hyperoxia avoidance opposes E. faecalis avoidance and depends on functional TAX-2/4.