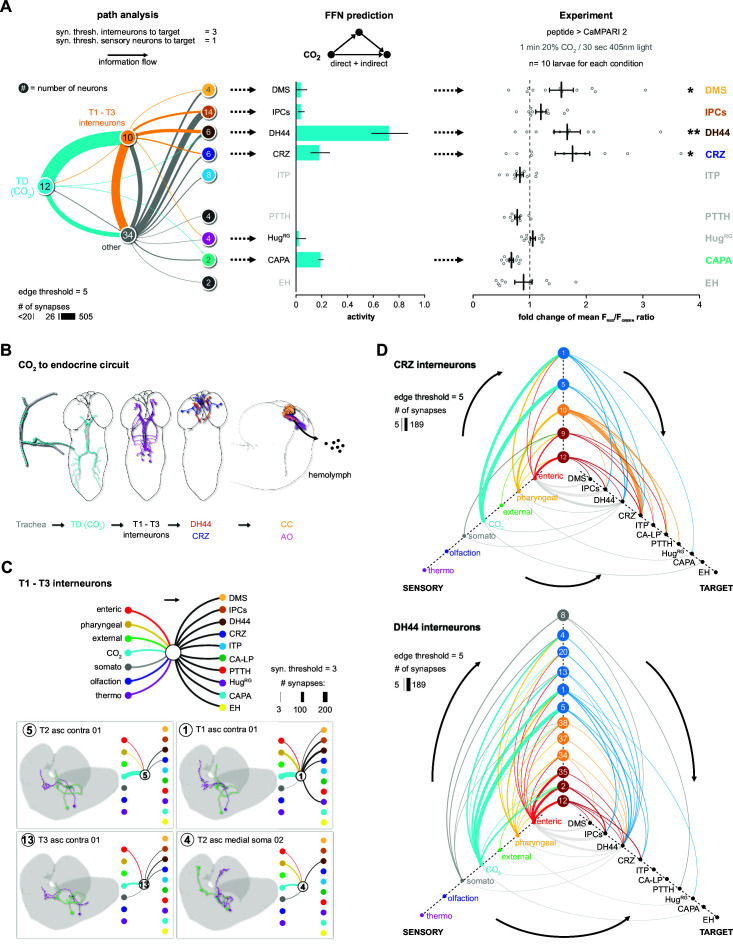
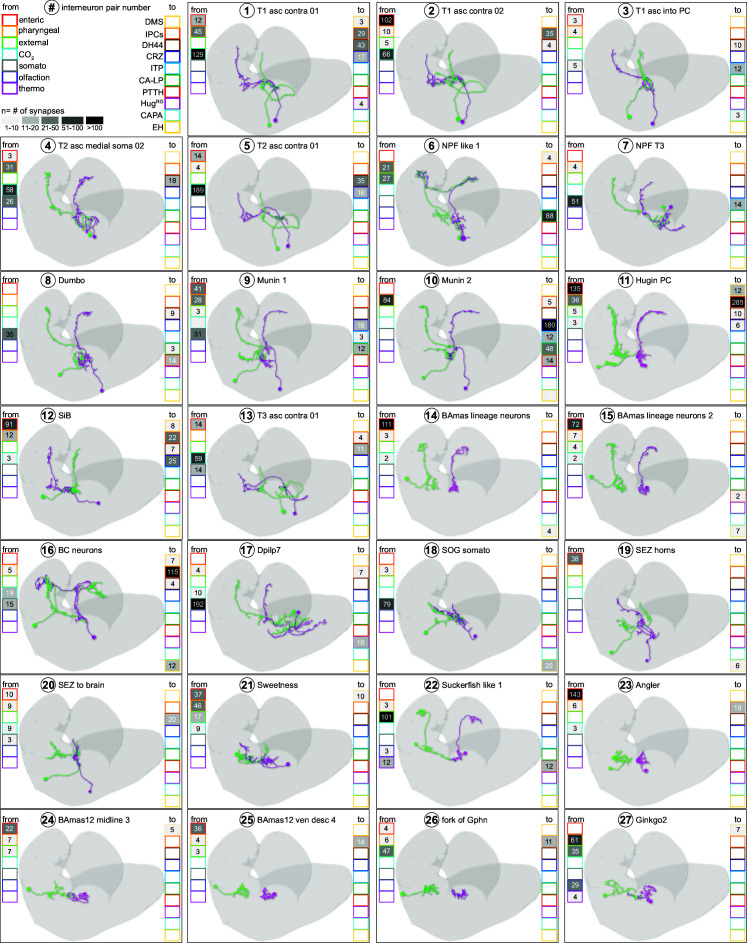
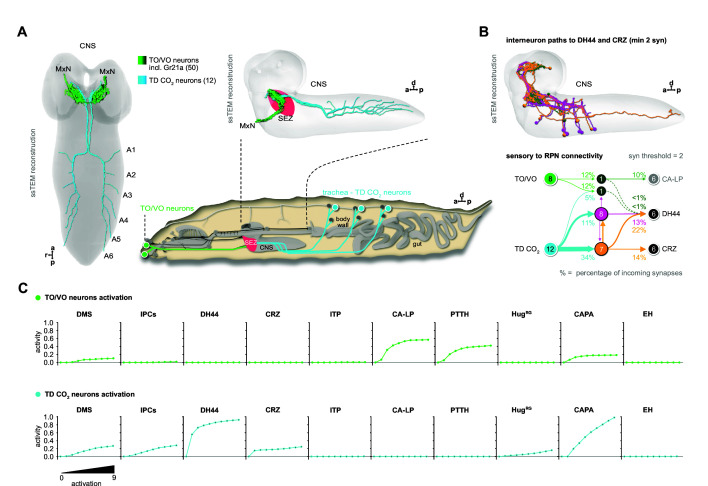
Figure 5. CO2-dependent pathway from TD neurons to RPNs.
(A) Comparison of underlying connectivity of TD (CO2) neurons via interneurons to the RPNs, with the predicted outcome of mean activity (with an activation factor of 2; when more than 5% of presynaptic neurons are active, interneurons become activated up to an activity of 50%) of RPNs, and the outcome of CaMPARI-2 CO2 experiments. FFN diffusion model reliably shows modulation of the RPNs. Please note that the circled numbers in the path analysis refer to the total number of neurons, not neuron identification number. (B) Using the combination of connectivity, prediction, and functional imaging experiments, a new sensory to endocrine neural circuit can be derived. TD (CO2) neurons at the trachea respond to CO2 levels and communicate predominantly via a core set of thoracic interneurons to DH44 and CRZ, which show release sites in the CC and AO. (C) Connectivity of the single thoracic interneurons (hemilateral pairs) to presynaptic sensory origins and to the distinct postsynaptic RPN groups. Thoracic interneurons receive additionally other sensory modalities apart from TD (CO2) neurons and target different combinations of RPNs. (D) CRZ interneurons: hive plot showing the polysynaptic pathways from all sensory origins to all RPN target groups using the interneurons (synaptic threshold = 3) that target CRZ. Main sensory origins are enteric, pharyngeal, and CO2. DH44 interneurons: TD (CO2) represent the most dominant polysynaptic path from sensory origins to DH44. Note that monosynaptic connections from sensory neurons to RPNs are shown in gray. AO: aorta; CA-LP: corpus allatum innervating neurosecretory neurons of the lateral protocerebrum; CaMPARI-2: calcium-modulated photoactivatable ratiometric integrator 2; CAPA: capability neurons; CC: corpora cardiaca; CO2: carbon dioxide; CRZ: corazonin neurons; DH44: diuretic hormone 44 neurons; DMS: Drosophila myosuppressin neurons; EH: eclosion hormone neurons; FFN: feed forward network; HugRG: hugin neurons innervating ring gland; IPCs: insulin-producing cells; ITP: ion transport peptide neurons; PTTH: prothoracicotropic hormone neurons; RPNs: ring gland projection neurons; ssTEM: serial section transmission electron microscope; TD: tracheal dendritic neurons.