Abstract
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) greatly suffers from the weak NIR-absorption, oxygen dependence and poor stability of photosensitizers (PSs). Herein, inspired by natural bacteriochlorin, we develop a bacteriochlorin analogue, tetrafluorophenyl bacteriochlorin (FBC), by one-step reduction of tetrafluorophenyl porphyrin (TFPP). FBC can realize deep tissue penetration, benefitting from the strong NIR absorption. The reactive oxygen species (ROS) generation capacity of FBC can retain around 60% with a 1.0 cm-thick pork skin as the barrier. Besides, FBC could not only produce oxygen-dependent 1O2, but also generate less oxygen-dependent O2−˙ and ˙OH to achieve excellent PDT even in hypoxic tumors. Moreover, FBC exhibits an ultra-high stability and it is almost unchanged even under visible light at room temperature for 15 months. Interestingly, the high reactivity of the fluorophenyl group makes it easy for FBC to produce FBC derivatives. A biocompatible FBC nanogel could be directly formed by blending FBC with SH–PEG–SH. The FBC nanogel displays excellent photodynamic efficacy in vitro and in vivo. Thus, FBC would be a promising PS for the clinical PDT of deep tumors.
A hypoxia-tolerant photosensitizer FBC-based nanoplatform with strong NIR absorbance and ultra-high stability was facilely prepared for PDT of deep tumors.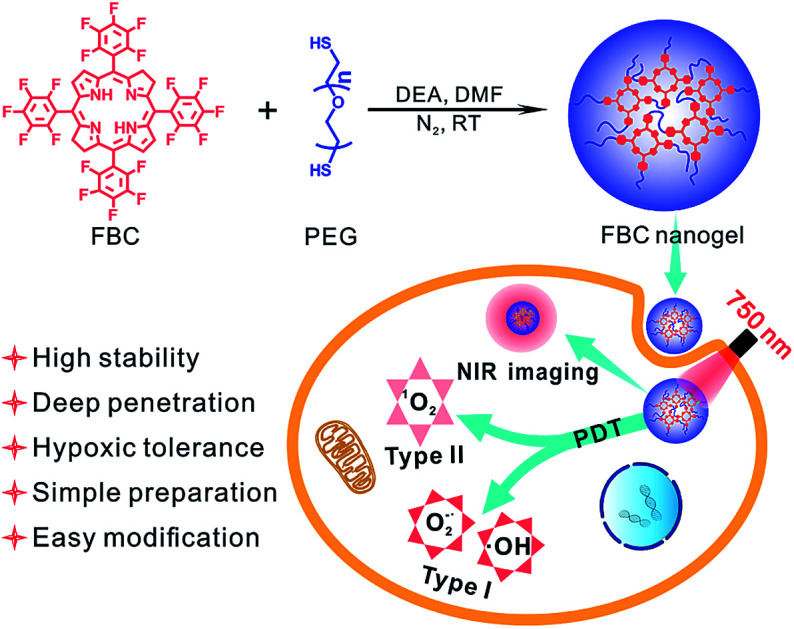
Introduction
Photodynamic therapy (PDT) is an attractive approach for tumor inhibition due to its advantages of being non-invasive, and having weak adverse effects and spatiotemporal control.1,2 However, the clinical utility of PDT is greatly limited by the inadequate NIR absorption, oxygen dependence and poor stability of conventional photosensitizers (PSs) such as photofin, verteporfin and padeliporfin. Short wavelength light absorbed by PSs cannot reach deep tissue due to absorption of skin and subcutaneous adipose tissue, resulting in lower photoconversion, serious tissue damage and limited clinical application of PDT in deep tumors.3 To address this issue, some strategies such as the two-photon excitation (TPE) technique4,5 and upconversion nanoparticles (UCNPs)6,7 had been introduced for the therapy of deep tumors, but their complex equipment and their low conversion efficiency will bring about new problems for clinical applications.8,9 Thus, PSs with strong NIR (700–1000 nm) absorption, which display deeper tissue penetration and minimized photodamage, have attracted intense research efforts for eradicating tumors in deep sites.10–12 Moreover, PDT efficacy also greatly suffers from the hypoxic environment of solid tumors, since conventional PSs consume oxygen to produce reactive oxygen species (ROS) for inhibiting tumor growth (type II mechanism). A great number of contributions have been recently dedicated to defeating the hypoxia of tumors by increasing oxygen concentration,13,14 including in situ oxygen production at tumor sites via catalytic reactions15–17 and oxygen delivery into tumors.18,19 Besides the elevation of oxygen concentration, exploiting photosensitizers that produce ROS through a less oxygen-dependent mechanism (type I mechanism) is a prospective approach to overcome the limitations of hypoxia.20,21 Additionally, some PSs are unstable towards oxygen and light. The photobleaching of PSs significantly reduces the efficacy of PDT, hindering the clinical application of PDT.22–25 Therefore, to achieve clinical treatment of deep tumors, it is urgent to develop highly stable, less oxygen-dependent PSs with strong NIR absorption for enhancing PDT efficacy.
Besides, most traditional PSs are hydrophobic conjugated macrocycle compounds, and they often could not produce high PDT efficiency due to their fatal disadvantages including poor solubility, the aggregation-caused quenching (ACQ) effect and inappropriate selectivity.26–28 To enhance PDT efficiency, many strategies have been explored to enrich PSs at tumor sites.29–31 For example, a series of nano-carriers have been developed to load and deliver hydrophobic PSs.32–34 Nevertheless, some irreparable deficiencies of nano-carriers such as low loading efficiency, non-repeatability, drug leakage and carrier-induced toxicity severely limit the development of their large-scale applications.35,36 Recently, nanogels have received great attention for delivering and enriching drugs into tumors upon incorporating hydrophobic drugs into the gel network,37,38 since they not only possess many promising hydrogel features such as high drug-loading efficiency, water-solubility, and biocompatibility for delivery of hydrophobic drugs, but also exhibit size in the nanoscale range for accumulation of drugs at tumor sites by the enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect. Given that hydrophobic PSs are incorporated into nanogel networks to form PS-based nanogels, except for the above advantageous properties of nanogels, the ACQ effect of PSs could be inhibited effectively since PS units are fixed on network knots to prevent aggregation.39
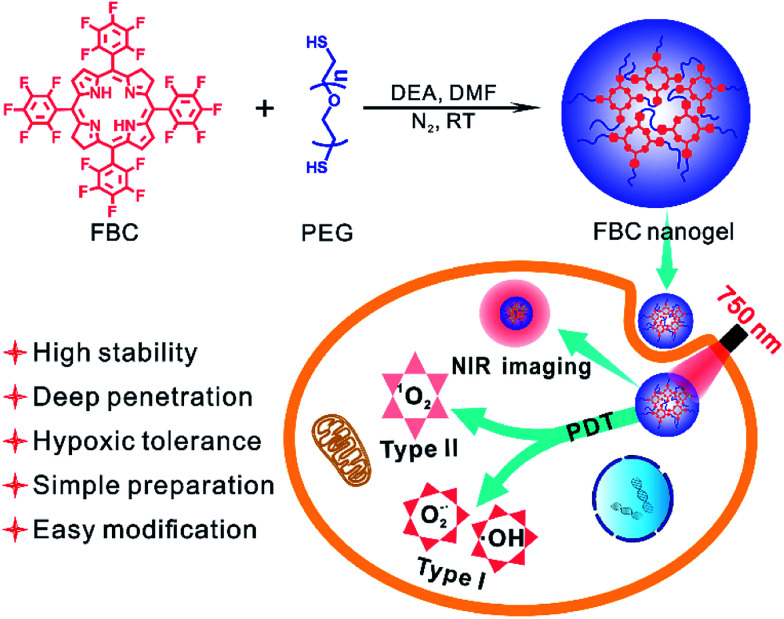
Inspired by the strong NIR absorption of natural bacteriochlorin, we developed a bacteriochlorin-based photosensitizer tetrafluorophenyl bacteriochlorin (FBC) by one-step reduction of tetrafluorophenyl porphyrin (TFPP). FBC could be further utilized to prepare a hydrophilic FBC nanogel by directly mixing with HS-terminated telechelic poly(ethylene glycol) (HS-PEG-SH), due to the high reactivity of the p-F atom of fluorophenyl in FBC. The FBC nanogel as a novel nano-photosensitizer possesses the following advantages (Scheme 1): (i) strong NIR absorption of FBC at 750 nm endows the FBC nanogel with deep tissue permeability, realizing the possibility of PDT against deep tumors. (ii) FBC could not only produce oxygen-dependent singlet oxygen (type II), but also generate less oxygen-dependent ROS (type I), achieving excellent PDT even in hypoxic tumors. (iii) FBC has an ultra-high stability under visible light at room temperature, showing the potential for clinical applications. (iv) FBC could be facilely obtained by two-step reactions from the original reactive agents pentafluorobenzaldehyde and pyrrole, providing an opportunity as a novel commercial photosensitizer. (v) The p-F atom of fluorophenyl in FBC is highly reactive, making it easy to prepare FBC derivatives. (vi) The formation of the FBC nanogel improves the PDT efficacy due to the high drug loading efficiency, biocompatibility and reduced ACQ effect of PSs. Consequently, the FBC-based nanophotosensitizer would be a promising candidate for NIR-mediated PDT against hypoxic tumors at deep sites.
Scheme 1. Illustration of the FBC nanogel synthesis and the mechanism of the PDT performance of the FBC nanogel.
Results and discussion
Synthesis of FBC
Bacteriochlorins extracted from bacteria have presented great promising application in PDT, since they exhibit a strong absorption in the near-infrared region. But, the difficult preparation, low yield and poor stability of bacteriochlorins limited their applications.25,40 Inspired by the structure of bacteriochlorins, an analogue of bacteriochlorin, FBC, was synthesized via one-step diimide reduction of TFPP. TFPP could be directly obtained using the original reactive agents pentafluorobenzaldehyde and pyrrole, according to previous studies.41,42 As shown in Scheme S1 (ESI†), TFPP was carefully mixed with p-toluenesulfonyl hydrazide (TSH) by grinding, and then the mixture was heated under vacuum to produce FBC after 2 h of vacuuming. FBC was characterized with 1H-NMR and 19F-NMR spectra (Fig. S1–S5, ESI†). Compared to that of to TFPP, a new peak at 4 ppm appeared in Fig. S4 (ESI†), indicating that TFPP was reduced to FBC. Additionally, the successful synthesis of FBC was also confirmed by mass spectrometry (Fig. S3 and S6, ESI†).
Penetration ability of FBC
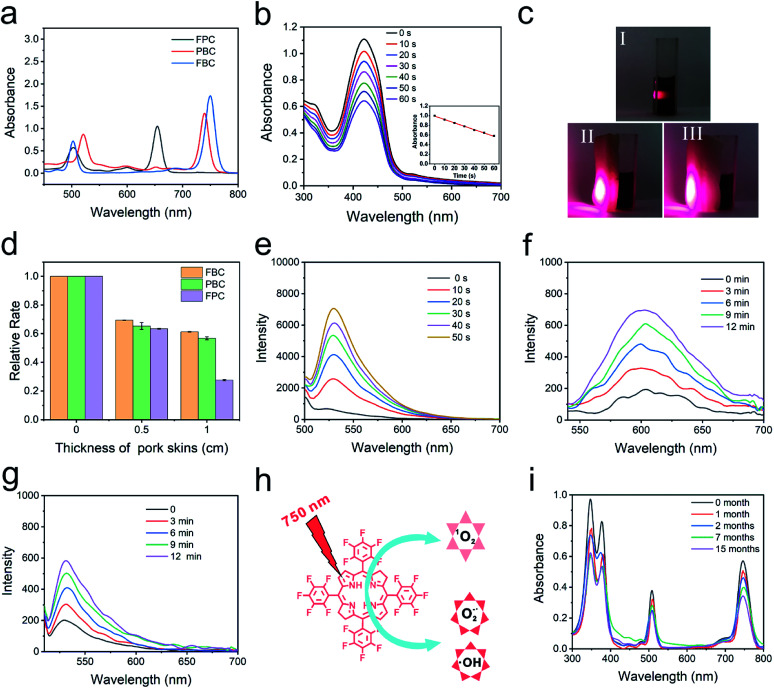
The photophysical features of FBC were determined by UV-vis spectroscopy and fluorescence spectroscopy, as shown in Fig. 1a and S7 (ESI†). It can be observed that a strong absorbance and emission peak separately appeared at 750 nm (ε = 8.23 × 104 L mol−1 cm−1) and 760 nm (fluorescence quantum yield: 0.011), indicating that FBC could possess deep tissue penetrability. To confirm the deep penetration ability of FBC, tetrafluorophenyl chlorin (FPC) and tetraphenyl bacteriochlorin (PBC) with different absorption wavelengths were selected as the references (Fig. S8, ESI†). FPC and PBC were synthesized according to the previous literature41,43 and the maximum absorbance wavelengths were 660 nm and 730 nm, respectively. The penetration ability was evaluated using 1,3-diphenylisobenzofuran (DPBF) as a probe by detecting the generation of ROS under light irradiation. DPBF can irreversibly react with ROS, leading to the decrease of the absorbance with the increase of illumination time (Fig. 1b). To mimic the penetration of light more accurately into tissues, pork skins with different thicknesses were utilized as barriers to evaluate the penetration ability of light with different wavelengths (Fig. 1c). As shown in Fig. 1d and S9–S11 (ESI†), it was observed that the degradation rate of DPBF with three solutions clearly decreased with pork skins. There is no significant difference between them with a 0.5 cm pork skin, since the absorbed light of three solutions all have good penetrating abilities to thin tissue. But the degradation rate of DPBF for FBC can still retain more than 60% with a 1.0 cm thick pork skin barrier, compared with the 27% retention for FPC. Thus, FBC has a remarkable penetration capability, which is beneficial to the treatment of deep tumors.
Fig. 1. Characterization of FBC. (a) UV-vis absorbance spectra of FPC, PBC and FBC. (b) UV-vis spectra of DPBF with increasing illumination time. The inset image shows the intensity changes at the maximum absorbance wavelength. (c) Photographs of FBC under laser irradiation with or without a barrier ((I) without a barrier; (II) with a 0.5 cm thick pork skin; (III) with a 1.0 cm thick pork skin). The degradation rates of DPBF in FPC (655 nm), PBC (730 nm) and FBC (750 nm) under laser irradiation (50 mW cm−2) with or without different thicknesses of pork skins (d). Fluorescence spectra of (e) SOSG, (f) DHE and (g) HPF for 1O2, O2−˙ and ˙OH detection with increasing illumination time (750 nm, 50 mW cm−2), respectively. (h) Schematic of ROS production. (i) The UV-vis absorbance spectra of FBC at different times.
ROS production of FBC
The mechanism of ROS production of FBC under 750 nm light irradiation was further studied by using probes of ROS including singlet oxygen (1O2), superoxide ions (O2−˙) and hydroxyl radicals (˙OH).44–46 First, Singlet Oxygen Sensor Green (SOSG) was used as a 1O2 probe to detect generated 1O2 (Fig. 1e), and the fluorescence emission of SOSG incubated with FBC increased gradually with the increase of the illumination time, which confirmed that the 1O2 could be produced by FBC under light irradiation. The singlet oxygen quantum yield is 0.496, using tetraphenyl porphyrin (TPP) as the standard (Fig. S12, ESI†).47 Then, dihydroethidium (DHE) as an O2−˙ fluorescent probe was employed to determine the generation of O2−˙, where DHE can be dehydrogenated by O2−˙ and emit red fluorescence at 610 nm. As shown in Fig. 1f, the fluorescence intensity increased significantly with the extension of illumination time, suggesting that O2−˙ could be effectively produced by FBC. In addition, the ˙OH production potential of FBC was also demonstrated using fluorescence emission spectra using hydroxyphenyl fluorescein (HPF) as an indicator (Fig. 1g). The gradual increase of the fluorescence intensity of HPF revealed that FBC could successfully induce the formation of highly toxic ˙OH. These consequences demonstrated that FBC can not only generate 1O2 through a type II reaction, but also produce O2−˙ and ˙OH through a type I reaction. However, FPC almost did not result in the generation of O2−˙ and PBC could only generate modest O2−˙ as depicted in Fig. S13 and S14 (ESI†), respectively. Therefore, FBC would achieve excellent PDT even in hypoxic tumors.
Stability evaluation of FBC
In addition, stability is also a crucial parameter for an excellent photosensitizer. To evaluate the stability, FPC, PBC and FBC solutions were irradiated at 660, 730, and 750 nm, respectively, and the stability of the samples was detected by UV-vis spectroscopy. As shown in Fig. S15 (ESI†), there is no significant change for FPC and FBC solutions with increase of light irradiation, except for the obvious decrease of the absorption intensity of PBC solution, revealing that FPC and FBC have superior light stability. Much more visual results could be seen from their photographs taken before and after laser irradiation, as displayed in Fig. S16 (ESI†). More importantly, FBC in the mixed solution (VDMF/Vwater, 1/99) was further evaluated under visible light at room temperature for more than one year (Fig. 1i). The strong characteristic absorbance peak of FBC could be well retained even after 15 months, which further confirms the excellent stability of FBC. Therefore, hypoxia-tolerant FBC with remarkable penetration capability and excellent stability would present promising clinical application for NIR-mediated PDT of deep tumors.
Synthesis of the FBC nanogel
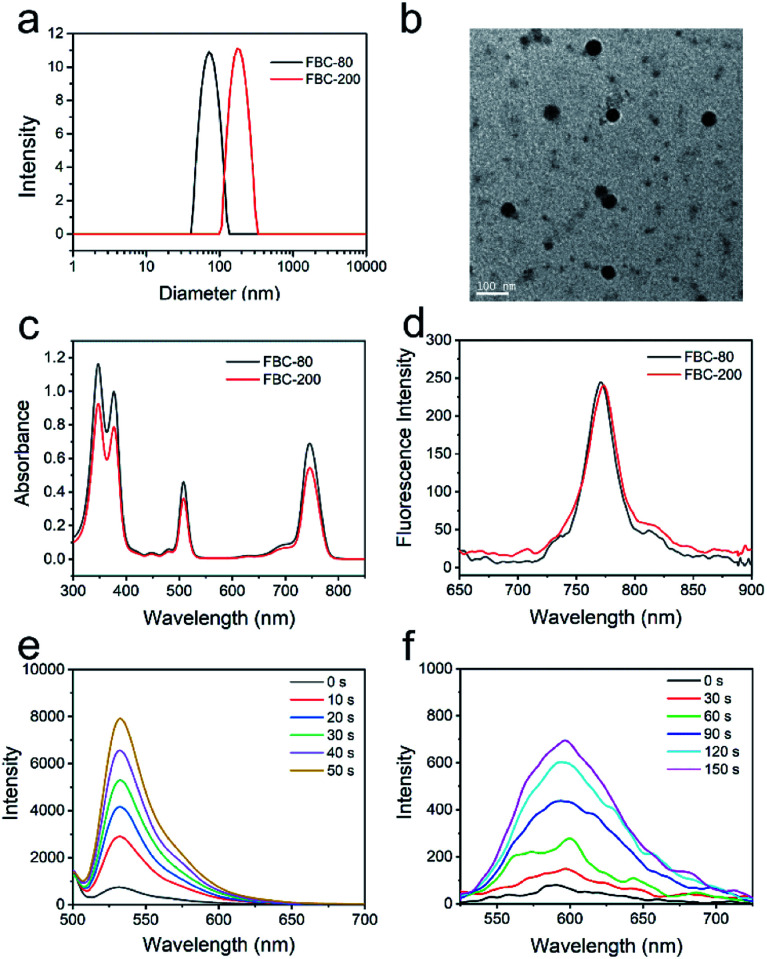
Encouraged by the hypoxia tolerance, excellent stability and penetration ability, FBC was further reacted with SH-PEG-SH to form cross-linked FBC nanogels for improving the hydrophilicity and biocompatibility. The reaction could be simply carried out by stirring at room temperature due to the high reactivity of fluorophenyl groups of FBC and strong nucleophilicity of sulfhydryl groups.48,49 The particle size of FBC nanogels could be tuned with the concentrations of reactants, which was determined by dynamic light scattering (DLS), and it can be found that the size of FBC nanogels increased with increasing the concentration (Fig. S17, ESI†). Therefore, we prepared two kinds of FBC nanogels with different sizes by varying the concentrations of reactants. FBC nanogels were characterized by DLS and transmission electron microscopy (TEM), respectively. As shown in Fig. 2a, the hydrodynamic sizes of two kinds of FBC nanogels measured by DLS were about 80 nm and 200 nm, and they were termed FBC-80 and FBC-200, respectively. The FBC-80 and FBC-200 observed by TEM all showed a spherical morphology with homogeneous sizes of 50 nm and 180 nm, respectively (Fig. 2b and S18, ESI†), which were smaller than those obtained by DLS, probably resulting from the shrinkage of the hydration of PEG chains in TEM measurements. 1H-NMR and 19F-NMR spectra were also utilized to determine the formation of FBC nanogels (Fig. S19–S22, ESI†). By comparing the integration area of the signal at 3.64 ppm (protons of SH-PEG-SH) to that of 8.1 ppm (protons of FBC) from the 1H-NMR spectra of FBC nanogels, FBC nanogels were formed using a 2 : 1 molar ratio of SH-PEG-SH and FBC. Moreover, the 19F-NMR spectrum also showed that the characteristic peak of p-F completely disappeared in that of FBC nanogels, indicating that the p-F atoms were all replaced by the sulfhydryl groups of SH-PEG-SH. The photophysical properties of FBC nanogels were determined by utilizing UV-vis and fluorescence spectra as depicted in Fig. 2c and d. Both FBC nanogels have similar UV-vis absorbance and fluorescence emission behaviors to the small molecular FBC, indicating that the formation of nanogels has no impact on the photophysical properties of FBC. Then, the ROS (1O2, O2−˙ and ˙OH) generation of FBC nanogels was also assessed using the corresponding probes under 750 nm light irradiation (Fig. 2d, e and S23, ESI†). The result is similar to that of FBC, suggesting that the formation of nanogels did not affect the ROS production capability of FBC. In addition, FBC nanogels could reduce the ACQ effect of PSs (Fig. S24 and S25, ESI†) and have excellent stability under physiological conditions (Fig. S26–S29, ESI†). Thus, the FBC nanogels should be suitable for NIR-mediated hypoxia-tolerant PDT.
Fig. 2. Characterization of FBC-80 and FBC-200. (a) Average hydrodynamic sizes of FBC-80 and FBC-200. (b) TEM images of FBC-80. UV-Vis absorbance spectrum (c) and fluorescence emission spectrum (d) of FBC-80 and FBC-200. Fluorescence spectrum of SOSG (e) and DHE (f) for 1O2, O2−˙ detection with the increasing illumination time.
Intracellular uptake and photoactivity
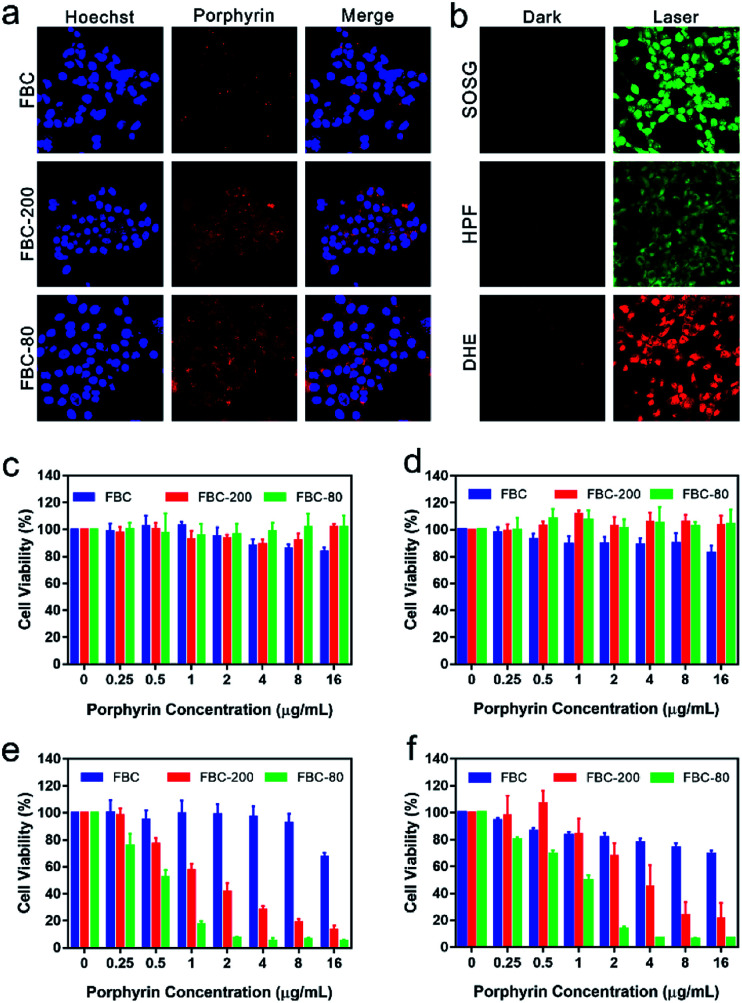
To evaluate the intracellular uptake of FBC nanogels, 4T1 cell lines were respectively co-incubated with FBC, FBC-80 and FBC-200 for 24 h. The cellular uptake of the samples was observed by confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM), where the nucleus was stained using Hoechst (blue fluorescence) and the samples were located through the red fluorescence produced by FBC itself. As shown in Fig. 3a, it can be observed that the red fluorescence appeared around the blue fluorescence, indicating that the samples were taken by the cells. Compared with those of FBC, the groups of FBC nanogels showed stronger fluorescence intensity, illustrating that more nanogels have been taken up by cells than the small molecular FBC.
Fig. 3. In vitro PDT efficacy of FBC-80 and FBC-200. (a) Confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM) images of 4T1 cells treated with FBC, FBC-200 and FBC-80 for 24 h. (b) CLSM images of 1O2, ˙OH and O2−˙ in FBC nanogels-treated 4T1 cells using SOSG, HPF and DHE as detection probes, respectively. Cell viability of 4T1 cells treated with FBC, FBC-200 and FBC-80 without a laser in normoxic (c) and hypoxic (d) environments. Cell viability of 4T1 cells treated with FBC, FBC-200 and FBC-80 with a laser in normoxic (e) and hypoxic (f) environments.
To confirm the photodynamic performance of FBC nanogels against cancer cells, the intracellular ROS generation of FBC nanogels was evaluated as well (Fig. 3b). SOSG was used as a probe to detect the 1O2, since it can be oxidized to produce green fluorescence by 1O2. As demonstrated by CLSM in Fig. 3b, strong green fluorescence could be observed under laser irradiation, indicating that FBC nanogels can produce massive 1O2 after 750 nm laser irradiation. In addition, HPF and DHE as specific ROS probes were separately employed to detect ˙OH and O2−˙, which were generally produced through a less oxygen-dependent type I process of PDT. The bright fluorescence images of HPF and DHE are shown in Fig. 3b, meaning that a large amount of ˙OH and O2−˙ was produced with light irradiation. Thus, FBC nanogels can be used as a potential nanophotosensitizer especially for a hypoxic environment.
Encouraged by the excellent cellular uptake and ROS production capability of FBC nanogels, the phototherapeutic effect of FBC was investigated by in vitro cytotoxicity assays. FBC, FBC-200 and FBC-80 with different concentrations were co-cultured with 4T1 cells, respectively. Cell viability was tested by a standard MTT assay in normal and hypoxic environments, respectively. As shown in Fig. 3c and d, the cells treated with the three samples all maintain a high cell survival rate under dark conditions. Moreover, FBC nanogels both showed higher cell viability compared with FBC, indicating that the introduction of hydrophilic PEG moieties endowed FBC nanogels with an excellent biocompatibility. The photodynamic efficiency was determined by using a 750 nm light source to irradiate cells for 15 min at a power density of 100 mW cm−2 (Fig. 3e and f). The viability of cells in all groups showed a concentration-related decrease whenever under normal and hypoxic conditions, indicating that FBC can produce ROS to cause cell death under illumination. Compared with those treated with FBC, cells treated with FBC-200 and FBC-80 showed a significantly lower survival rate, suggesting that FBC nanogels have a superior photodynamic therapeutic effect. This result may be attributed to the enhanced internalization of FBC nanogels. In addition, we found that FBC-80 nanogels had the most efficient inhibition to cancer cells both under normal and hypoxic conditions, which could be resulting from the weak aggregation of FBC in FBC-80 nanogels compared with FBC-200 nanogels.
In vivo imaging and biodistribution, photodynamic therapy and bio-safety
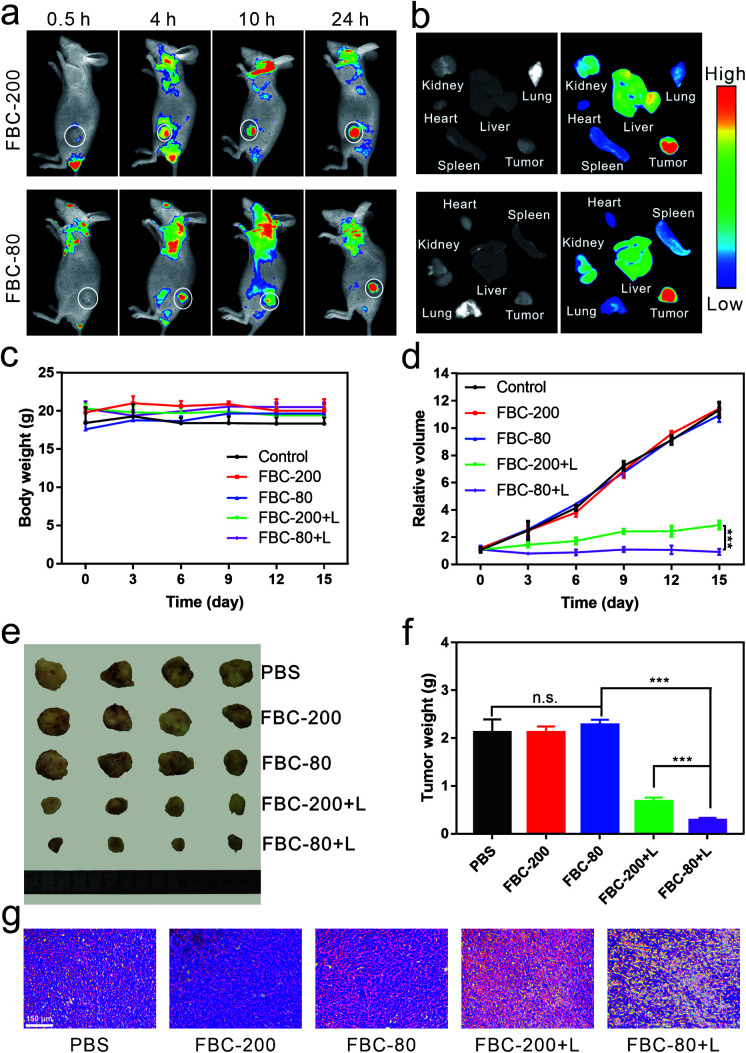
In order to demonstrate the accumulation of FBC nanogels at the tumor site, a 4T1 tumor xenograft mouse model was chosen. Since FBC nanogels have a fluorescence emission in the near infrared region, the accumulation of FBC nanogels at the tumor site could be monitored in label-free methods by detecting the fluorescence of FBC itself. FBC nanogels were injected into tumor-bearing mice through the tail vein, and then the fluorescence images of nanogels were observed at 0.5 h, 4 h, 10 h, and 24 h post-injection. As shown in Fig. 4a, b and S30–S33 (ESI†), FBC-80 and FBC-200 both showed a strong fluorescence signal at the tumor site after 24 h, indicating that the nanogels could successfully accumulate into the tumor through the EPR effect. Subsequently, the in vivo anti-tumor therapeutic effect of FBC nanogels was studied. When the volume of the tumor xenograft in mice reached 100 mm3, the mice were divided into five groups and injected with a 200 μL solution of different agents (n = 4 for each group): (1) PBS, (2) FBC-80, (3) FBC-200, (4) FBC-80+L and (5) FBC-200+L (porphyrin concentration at 1 mg kg−1). At 24 h post injection, tumors of FBC-80+L and FBC-200+L groups were treated with 750 nm laser irradiation (200 mW cm−2) for 10 min, respectively. In the period of treatment, the body weights of the mice and the volumes of the tumors were recorded every three days (Fig. 4c and d). There is no significant weight loss for all mice as shown in Fig. 4c, indicating that the FBC nanogels are biocompatible. The curves of relative tumor volume are shown in Fig. 4d. Compared with those in the control groups, the tumor growths in FBC-80+L and FBC-200+L groups were observed to be significantly suppressed after 15 days. In addition, the FBC-80+L group has better tumor suppression than the FBC-200+L group, indicating that FBC nanogels with a small particle size have a better photodynamic effect.50 In order to further confirm the photodynamic therapeutic effect, the mice were sacrificed on the 15th day. The photograph of the tumors is displayed in Fig. 4e. The weights of the tumors are measured and recorded in Fig. 4f. From Fig. 4e and f, it can be seen that in the cases of treatment with FBC nanogels under light irradiation, the sizes and weights of the tumors changed significantly, which is consistent with Fig. 4d. These results confirm that FBC nanogels show excellent phototherapy against tumors. Among them, the FBC-80+L group had the most significant tumor suppressive effect, indicating that the photodynamic therapy of FBC nanogels with a small particle size was the most effective among these groups.51–53 Additionally, according to qualitative histological examinations (Fig. 4g), the most significant tumor necrosis was observed for the FBC-80+L group, which further confirmed the excellent photodynamic effect of FBC-80 in inhibiting tumor growth. Besides, hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) staining of the major organ tissues is shown in Fig. S34 (ESI†). No obvious tissue damage was found in all organ tissues, revealing that the FBC nanogels are biocompatible.
Fig. 4. In vivo PDT efficacy against 4T1 tumors. (a) Real-time fluorescence images of 4T1 tumor bearing mice after intravenous injection with FBC-200 and FBC-80. (b) Ex vivo fluorescence images of major organs and tumors 24 h post i.v. injection. (c) Body weight. (d) Relative tumor volume. (e) Photographs of tumors. (f) Tumor weight. (g) H&E staining of tumors (n = 4, mean ± s.d., **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).
Conclusions
In conclusion, we are inspired by the NIR absorption of natural bacteriochlorin to develop a novel bacteriochlorin-based photosensitizer FBC. In comparison to natural bacteriochlorin, FBC could be easily prepared by a two-step reaction from the original reactants pentafluorobenzaldehyde and pyrrole. Moreover, FBC exhibits an ultra-high stability even under visible light at room temperature for more than one year. FBC has strong NIR absorption at 750 nm, and its ROS generation capability can still retain around 60% with a 1.0 cm-thick pork skin as the barrier, which is significant for the treatment of deep tumors. FBC could not only produce oxygen-dependent 1O2, but also generate oxygen-independent ROS O2−˙ and OH˙, overcoming the bottleneck of PDT caused by tumor hypoxic microenvironments. Based on the promising properties of FBC, FBC nanogels were constructed by a simple crosslinking reaction with SH-PEG-SH. The formed FBC nanogels have a significant cumulative effect in the tumor site. Additionally, the FBC nanogels show a strong fluorescence emission in the NIR region, and thus distribution of drugs could be monitored using FBC itself. Finally, the excellent photodynamic efficacy of FBC nanogels has been revealed by in vitro and in vivo experiments. Therefore, FBC with superior properties would be a promising clinical photosensitizer for NIR-mediated hypoxia-tolerant PDT of deep tumors.
Ethical statement
All animal studies were conducted on male BALB/c nude mice (four to 5 weeks) in compliance with the National Institutes of Health Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of East China University of Science and Technology.
Conflicts of interest
There are no conflicts to declare.
Supplementary Material
Acknowledgments
This work was financially supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 21875063 and 22075079) and the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Municipality for the Shanghai International Cooperation Program (19440710600).
Electronic supplementary information (ESI) available. See DOI: 10.1039/d0sc05525e
References
- Wang Q. Dai Y. Xu J. Cai J. Niu X. Zhang L. Chen R. Shen Q. Huang W. Fan Q. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019;29:1901480. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201901480. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Teng K.-X. Niu L.-Y. Kang Y.-F. Yang Q.-Z. Chem. Sci. 2020;11:9703–9711. doi: 10.1039/D0SC01122C. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deng H. Lin L. Wang S. Yu G. Zhou Z. Liu Y. Niu G. Song J. Chen X. Adv. Mater. 2019;31:1903443. doi: 10.1002/adma.201903443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qiu K. Wang J. Song C. Wang L. Zhu H. Huang H. Huang J. Wang H. Ji L. Chao H. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces. 2017;9:18482–18492. doi: 10.1021/acsami.7b02977. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen Y. Shuhendler A. J. Ye D. Xu J. J. Chen H. Y. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2016;45:6725–6741. doi: 10.1039/C6CS00442C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu S. Zhu X. Zhang C. Huang W. Zhou Y. Yan D. Nat. Commun. 2018;9:2053. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-04318-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang M. Zhang Y. Ng M. Skripka A. Cheng T. Li X. Bhakoo K. K. Chang A. Y. Rosei F. Vetrone F. Chem. Sci. 2020;11:6653–6661. doi: 10.1039/D0SC01033B. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lan M. Zhao S. Liu W. Lee C. S. Zhang W. Wang P. Adv. Healthcare Mater. 2019;8:1900132. doi: 10.1002/adhm.201900132. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lifshits L. Roque III J. A. Konda P. Monro S. Cole H. D. von Dohlen D. Kim S. Deep G. Thummel R. P. Cameron C. G. Gujar S. McFarland S. A. Chem. Sci. 2020;11:11740–11762. doi: 10.1039/D0SC03875J. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. Cui D. Jiang Y. Huang J. Cheng P. Pu K. Adv. Mater. 2019;31:1905091. doi: 10.1002/adma.201905091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Y. Zhang X. H. Cheng D. B. Zhang Y. Liu Y. Ji L. Guo R. Chen H. Ren X. K. Chen Z. Qiao Z. Y. Wang H. ACS Nano. 2020;14:3640–3650. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c00118. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bu Y. Xu T. Zhu X. Zhang J. Wang L. Yu Z. Yu J. Wang A. Tian Y. Zhou H. Xie Y. Chem. Sci. 2020;11:10279–10286. doi: 10.1039/D0SC03093G. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao J. Duan L. Wang A. Fei J. Li J. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020;12:1583. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1583. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui D. Huang J. Zhen X. Li J. Jiang Y. Pu K. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019;58:5920–5924. doi: 10.1002/anie.201814730. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sahu A. Min K. Jeon J. Yang H. S. Tae G. J. Controlled Release. 2020;326:442–454. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.07.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- He S. Lu S. Liu S. Li T. Li J. Sun S. Liu M. Liang K. Fu X. Chen F. Meng G. Zhang L. Hai J. Wang B. Chem. Sci. 2020;11:8817–8827. doi: 10.1039/D0SC02387F. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ni K. Lan G. Song Y. Hao Z. Lin W. Chem. Sci. 2020;11:7641–7653. doi: 10.1039/D0SC01949F. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu D. R. Zhong L. Wang M. Y. Li H. H. Qu Y. Liu Q. Y. Han R. X. Yuan L. P. Shi K. Peng J. R. Qian Z. Y. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2019;29:1806199. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201806199. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Wang W. Cheng Y. Yu P. Wang H. Zhang Y. Xu H. Ye Q. Yuan A. Hu Y. Wu J. Nat. Commun. 2019;10:1580. doi: 10.1038/s41467-019-09389-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K. Yu Z. Meng X. Zhao W. Shi Z. Yang Z. Dong H. Zhang X. Adv. Sci. 2019;6:1900530. doi: 10.1002/advs.201900530. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan Q. Zhang R. Y. Zhuang Z. Y. Li Y. X. Huang Y. H. Wang Z. M. Zhang W. J. Hou J. Q. Tang B. Z. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2020;30:2002057. doi: 10.1002/adfm.202002057. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Luo T. Ni K. Culbert A. Lan G. Li Z. Jiang X. Kaufmann M. Lin W. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2020;142:7334–7339. doi: 10.1021/jacs.0c02129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wan Y. Lu G. Wei W. C. Huang Y. H. Li S. Chen J. X. Cui X. Xiao Y. F. Li X. Liu Y. Meng X. M. Wang P. Xie H. Y. Zhang J. Wong K. T. Lee C. S. ACS Nano. 2020;14:9917–9928. doi: 10.1021/acsnano.0c02767. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Panchenko P. A. Grin M. A. Fedorova O. A. Zakharko M. A. Pritmov D. A. Mironov A. F. Arkhipova A. N. Fedorov Y. V. Jonusauskas G. Yakubovskaya R. I. Morozova N. B. Ignatova A. A. Feofanov A. V. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2017;19:30195–30206. doi: 10.1039/C7CP04449F. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang Y. Y. Mroz P. Zhiyentayev T. Sharma S. K. Balasubramanian T. Ruzie C. Krayer M. Fan D. Borbas K. E. Yang E. Kee H. L. Kirmaier C. Diers J. R. Bocian D. F. Holten D. Lindsey J. S. Hamblin M. R. J. Med. Chem. 2010;53:4018–4027. doi: 10.1021/jm901908s. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roy I. Ohulchanskyy T. Y. Pudavar H. E. Bergey E. J. Oseroff A. R. Morgan J. Dougherty T. J. Prasad P. N. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003;125:7860–7865. doi: 10.1021/ja0343095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu W. Zhang J. Zhou Z. Zhang D. Zhang Y. Xu S. Zhu X. Adv. Mater. 2018;30:1800403. doi: 10.1002/adma.201800403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dong Y. Tu Y. Wang K. Xu C. Yuan Y. Wang J. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020;59:7168–7172. doi: 10.1002/anie.201913522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang M. Yang T. Mao C. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2019;58:14066–14080. doi: 10.1002/anie.201814098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang T. X. Zhang Z. Z. Yue Y. X. Hu X. Y. Huang F. Shi L. Liu Y. Guo D. S. Adv. Mater. 2020;32:1908435. doi: 10.1002/adma.201908435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang H. Li H. Cao Z. Du J. Yan L. Wang J. J. Controlled Release. 2020;324:47–54. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2020.04.046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang K. Meng X. Yang Z. Dong H. Zhang X. Biomaterials. 2020;258:120278. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2020.120278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cheng H. B. Zhang Y. M. Liu Y. Yoon J. Y. Chem. 2019;5:553–574. [Google Scholar]
- Gao P. Wang M. Chen Y. Pan W. Zhou P. Wan X. Li N. Tang B. Chem. Sci. 2020;11:6882–6888. doi: 10.1039/D0SC00847H. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li M. Sun X. Zhang N. Wang W. Yang Y. Jia H. Liu W. Adv. Sci. 2018;5:1800155. doi: 10.1002/advs.201800155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sztandera K. Gorzkiewicz M. Klajnert-Maculewicz B. WIREs Nanomed. Nanobiotechnol. 2020;12:1509. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1599. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L. H. Cai X. J. Zhu H. F. Li J. H. Shi D. X. Su D. F. Yue D. Gu Z. W. Adv. Funct. Mater. 2018;28:1804324. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201804324. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X. Chen X. Guo Y. Jia H. R. Jiang Y. W. Wu F. G. Nanoscale Horiz. 2020;5:481–487. doi: 10.1039/C9NH00643E. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu N. Liu H. Chen H. Wang G. Teng H. Chang Y. Colloids Surf., B. 2020;188:110753. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2019.110753. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu W. Gao Y. H. Liao P. Y. Chen D. Y. Sun N. N. Nguyen Thi P. A. Yan Y. J. Wu X. F. Chen Z. L. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018;160:146–156. doi: 10.1016/j.ejmech.2018.10.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z. Xue Y. Wu M. Yang G. Lan M. Zhang W. Biomacromolecules. 2019;20:4563–4573. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.9b01368. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z. Wu M. Xue Y. Chen C. Wurm F. R. Lan M. Zhang W. Chem. Commun. 2020;56:2415–2418. doi: 10.1039/D0CC00142B. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao H. Wang G. Xue Y. Yang G. Tian J. Liu F. Zhang W. ACS Macro Lett. 2019;8:616–622. doi: 10.1021/acsmacrolett.9b00320. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gollmer A. Arnbjerg J. Blaikie F. H. Pedersen B. W. Breitenbach T. Daasbjerg K. Glasius M. Ogilby P. R. Photochem. Photobiol. 2011;87:671–679. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.2011.00900.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peshavariya H. M. Dusting G. J. Selemidis S. Free Radical Res. 2007;41:699–712. doi: 10.1080/10715760701297354. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomizawa S. Imai H. Tsukada S. Simizu T. Honda F. Nakamura M. Nagano T. Urano Y. Matsuoka Y. Fukasaku N. Saito N. Neurosci. Res. 2005;53:304–313. doi: 10.1016/j.neures.2005.08.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Redmond R. W. Gamlin J. N. Photochem. Photobiol. 1999;70:391–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1999.tb08240.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerlich S. Eibenberger S. Tomandl M. Nimmrichter S. Hornberger K. Fagan P. J. Tuxen J. Mayor M. Arndt M. Nat. Commun. 2011;2:263. doi: 10.1038/ncomms1263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Day R. A. Estabrook D. A. Logan J. K. Sletten E. M. Chem. Commun. 2017;53:13043–13046. doi: 10.1039/C7CC07038A. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cai Y. Ni D. Cheng W. Ji C. Wang Y. Mullen K. Su Z. Liu Y. Chen C. Yin M. Angew. Chem., Int. Ed. 2020;59:14014–14018. doi: 10.1002/anie.202001107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang W. Kim B. Y. Rutka J. T. Chan W. C. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2008;3:145–150. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2008.30. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabral H. Matsumoto Y. Mizuno K. Chen Q. Murakami M. Kimura M. Terada Y. Kano M. R. Miyazono K. Uesaka M. Nishiyama N. Kataoka K. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2011;6:815–823. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2011.166. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chauhan V. P. Stylianopoulos T. Martin J. D. Popovic Z. Chen O. Kamoun W. S. Bawendi M. G. Fukumura D. Jain R. K. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2012;7:383–388. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2012.45. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.