Sun et al. (1) question the Late Pleistocene chronologies of five hominin sites from southern China, including Fuyan Cave with 47 Homo sapiens teeth (2), and suggest they belong to the Holocene. Here we question the validity of their study, based on the uncertain origin and taxonomical identification of the two “human” specimens from Fuyan (FY-HT-1 and FY-HT-2) and the quality standards of their ancient DNA (aDNA) and 14C analysis.
-
1)
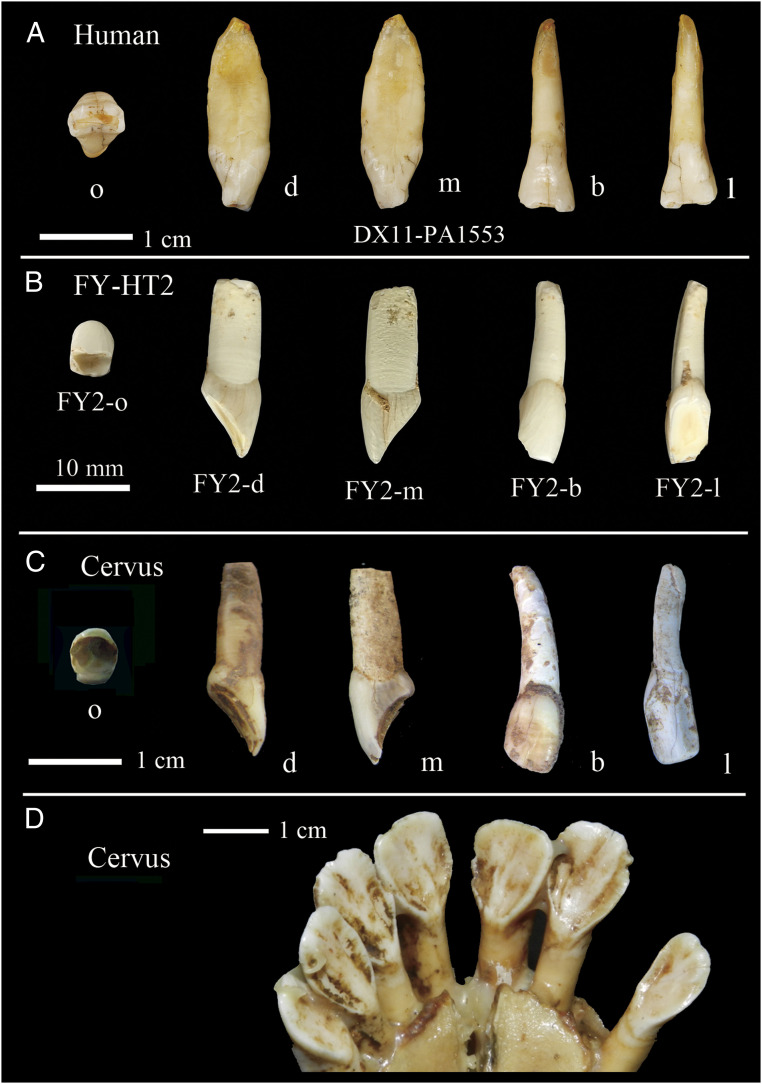
FY-HT-1 and FY-HT-2 were collected by Sun and colleagues in 2019 without supervision of the key team members leading the Fuyan excavations. They allege that both specimens belong to the same sample we studied (2), because they are “clearly AMH [anatomically modern human] and fit metrically and morphologically within the range of earlier finds from the site” (1). However, they do not provide any morphometric data to sustain this claim, nor precise information about the purportedly in situ position of the teeth. Critically, we confirm that FY-HT-2 is not human but belongs to an herbivore (Fig. 1): Wear is predominantly lingual instead of incisal; there are not visible interproximal wear facets despite the degree of incisal/lingual wear; the crown is high and narrow; and the inclination of the root with regard to the crown is typical of some herbivores (e.g., deer). Grievously, despite its nonhuman nature, they claim to have obtained human aDNA that “falls within the variation of present-day Eurasian lineages.” Obviously, these results question the rigor and quality of their study.
-
2)
For the accelerator mass spectrometry (AMS) 14C dating, it is unclear whether there is any preprocess for the total organic carbon (TOC) measurement before adapting the procedures described in ref. 3, since the postdeposited carbonate is hard to eliminate with the normal acid−alkali−acid approach. It is also not clear what types of components, beside the collagen, are included in the TOC, since their C/N ratio is much higher [e.g., 46.2 in FY-HT-2 (1) vs. 2.9 to 3.6 (4) and 3.1 to 3.5 (5)] than that of collagen suitable for 14C dating (6). Furthermore, the percent of C in FY-HT-1 is about 2.3, much higher than in contemporary enamel (0.1 to 0.8%) (6). Overall, it seems that these samples have undergone postdepositional alteration and/or contamination, and their 14C dates are questionable. In addition, the authors do not discuss the Late Pleistocene fauna nor the >43 ka cal B.P. AMS 14C dating we obtained for it.
-
3)
Regarding FY-HT-1, we highlight the extremely good preservation of the root edges in contrast to the severe root alteration of the specimens in ref. 2. The possibility of two different taphonomic stories questions the association of all teeth to the same sample.
Fig. 1.
Morphological comparison of human and deer lower incisors. (A) H. sapiens lower incisor recovered at Fuyan Cave in 2012 and published in Liu et al. (2); o, occlusal; d, distal; m, mesial; b, buccal; and l, lingual. (B) FY-HT-2 tooth recovered by Sun et al. (1) at Fuyan in 2019 and alleged to be human (reprinted with permission from ref. 1); (C) o, d, m, b, and l views of Cervus lower incisors recovered at Fuyan Cave in 2012; and (D) lingual view of lower dentition from a recent Cervus (reprinted with permission from ref. 7). Note the intense lingual rather than incisal wear present in Cervus specimens as well as in FY-HT-2. Note also the shape similarities in root and crown shape and orientation in B−D.
Except for the dubious aDNA and 14C analyses of noncontextualized and likely contaminated samples, the U-Th dating of the speleothems and the optically stimulated luminescence of the sediments encasing the fossils confirm the Late Pleistocene ages of the Fuyan sample. Obtaining human aDNA from a nonhuman tooth brings into serious question the credibility of the study by Sun et al. (1). Our proposal of an early presence of H. sapiens in China (2) remains unchallenged.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Strategic Priority Research Program of Chinese Academy of Sciences (Grant XDB26000000) and the Young Talent Support Plan of Xi’an Jiaotong University (to Y.C.). M.M.-T. and J.M.B.d.C. receive funding from Ministerio de Ciencia, Innovación y Universidades (Grant PGC2018-093925-B-C31) and from The Leakey Foundation through the support of D. Crook (to M.M.-T.). We thank Prof. Wei Dong and Dr. Palmira Saladié for assisting in anatomical identification, and Prof. Peng Cheng for discussion on 14C dating.
Footnotes
The authors declare no competing interest.
References
- 1.Sun X.-f., et al., Ancient DNA and multimethod dating confirm the late arrival of anatomically modern humans in southern China. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 118, e2019158118 (2021). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Liu W., et al., The earliest unequivocally modern humans in southern China. Nature 526, 696–699 (2015). [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Xu X., et al., Modifying a sealed tube zinc reduction method for preparation of AMS graphite targets: Reducing background and attaining high precision. Nucl. Instrum. Methods Phys. Res. B 259, 320–329 (2007). [Google Scholar]
- 4.DeNiro M. J., Postmortem preservation and alteration of in vivo bone collagen isotope ratios in relation to palaeodietary reconstruction. Nature 317, 806–809 (1985). [Google Scholar]
- 5.van Klinken G. J., Bone collagen quality indicators for palaeodietary and radiocarbon measurements. J. Archaeol. Sci. 26, 687–695 (1999). [Google Scholar]
- 6.Dunbar E., Cook G. T., Naysmith P., Tripney B. G., Xu S., AMS 14C dating at the Scottish Universities Environmental Research Centre (SUERC) radiocarbon dating laboratory. Radiocarbon 58, 9–23 (2016). [Google Scholar]
- 7. M. A. O'Leary and S. Kaufman, MorphoBank: phylophenomics in the 'cloud'. Cladistics 27, 1–9 (2011). [DOI] [PubMed]