Fig. 6. Sex differences.
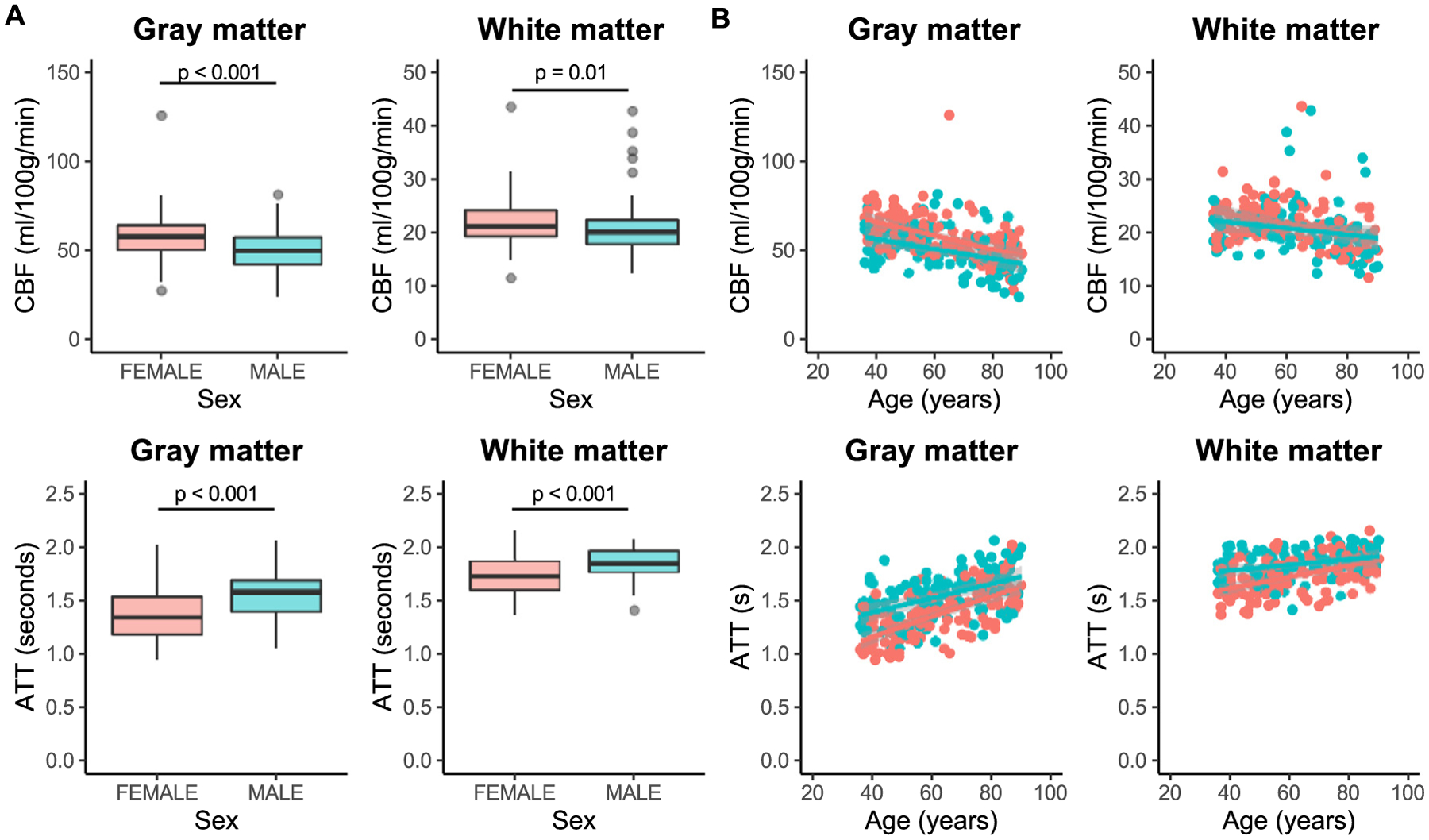
Differences in cerebral blood flow (CBF) and arterial arrival time (ATT) between males (blue) and females (red) are shown here. Gray matter CBF (p < 0.001) is higher in females compared with males. White matter CBF (p = 0.01) was slightly lower in males, but this was not significant after accounting for age (A; top). ATT in both gray and white matter is longer (p < 0.001) in males than in females (A; bottom). Relationships between age and hemodynamics are similar in males and females, with sex differences in CBF and ATT reducing with increasing age (B).
