An 85-year-old man with microscopic polyangiitis and diabetes presented with a 2-week history of painful, rapidly progressive ulcers on his left leg. A physical examination revealed skin ulcers with a purulent base and an irregular edge (Picture 1, 2). Antimicrobial agents and high-dose corticosteroid therapy were initiated for exacerbation of vasculitis. A histopathological examination of a skin biopsy specimen revealed inflammatory cell infiltration with neutrophils from the dermis to the subcutaneous adipose tissue. In addition, we observed yeast with thick capsules that showed positive results on Grocott staining, which characterizes Cryptococcus neoformans infection (Picture 3). Antifungal treatment was initiated; however, his condition worsened rapidly, necessitating admission to the intensive-care unit. Subsequently, he was diagnosed with disseminated cryptococcosis based on an examination of cultures of cerebrospinal fluid, urine, and pus from ulcers. He ultimately died of Pseudomonas aeruginosa sepsis.
Picture 1.
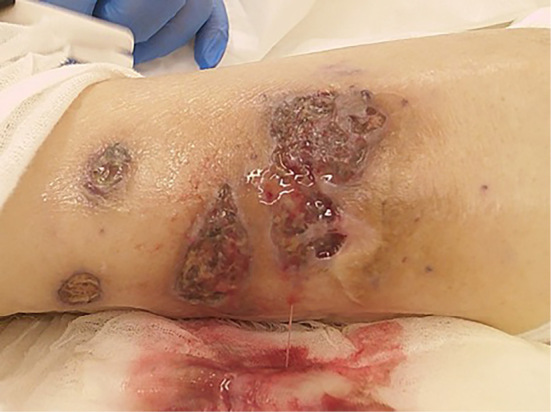
Picture 2.
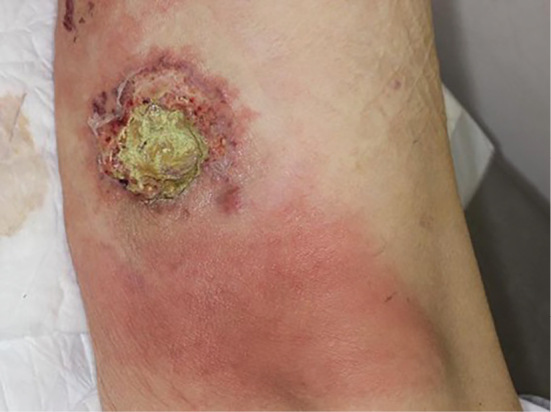
Picture 3.
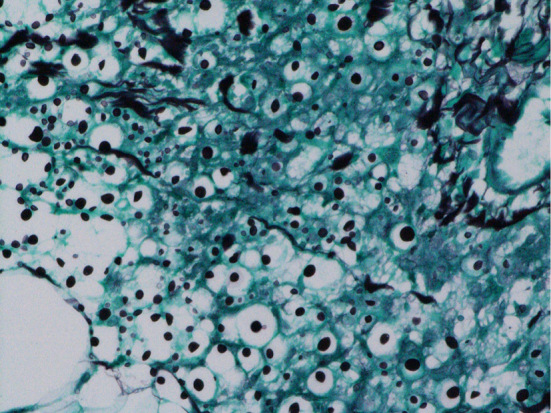
The authors state that they have no Conflict of Interest (COI).


