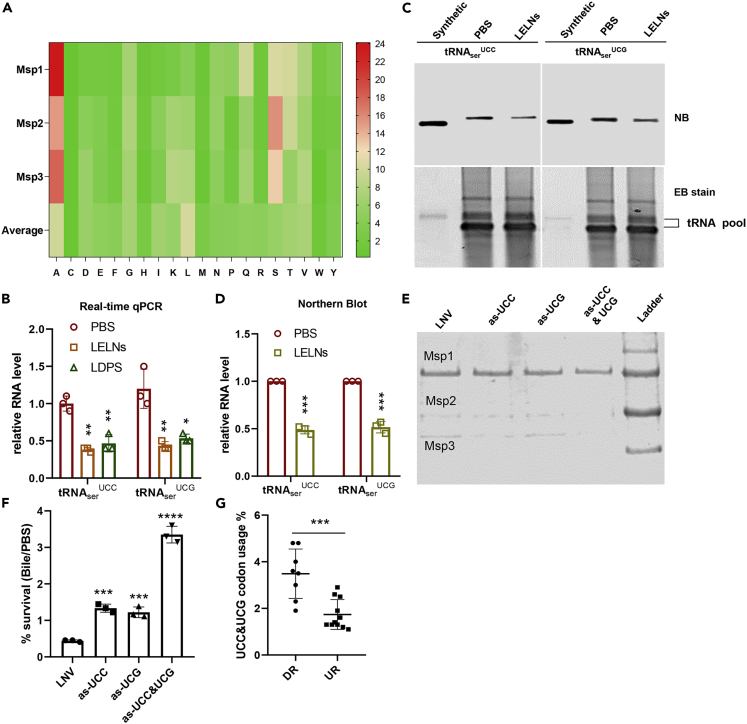
Figure 3.
Preferential utility of serine tRNA contributes to LELNs-mediated downregulation of LGG Msps
(A) Amino acid composition analysis of Msp1, Msp2, and Msp3. Average amino acid composition in whole LGG proteome was used as a control. Amino acid composition analyses were conducted using BioEdit software.
(B–D) Real-time qPCR (B) and northern blot (NB) analysis (C and D) of relative serine tRNA levels in LGG. PBS treatment served as a control, synthetic tRNA prepared by in vitro transcription was used as a positive control, and ethidium bromide (EB) stain was used as the loading control. Northern blots were quantified using ImageJ software.
(E and F) SDS-PAGE analysis of secretory proteins in the cultured broth and bile resistance tests of tRNAserUCC and tRNAserUCG knockdown strains; protein from 200 μL LGG culture supernatant were loaded on the SDS-PAGE gel. as-UCC and as-UCG indicate knockdown of either tRNAserUCC or tRNAserUCG, respectively, and as-UCC&UCG indicates knockdown of both tRNAserUCC and tRNAserUCG. LNV without RNA inclusion was used as a control. Samples were collected at 6 h (supernatant for SDS-PAGE) or 12 h (bacteria for bile resistance test) after adding antisense RNA.
(G) UCC and UCG codon usage analysis in top downregulated (DR) and upregulated (UR) genes in Table S3 due to LELNs treatment; codon usage analysis was conducted using an online codon usage tool in Sequence Manipulation Suite (Stothard, 2000). The data are presented as values with standard deviation (mean ± SD). The significance is shown as ∗p ≤ 0.05; ∗∗p ≤ 0.01; ∗∗∗p ≤ 0.001; ∗∗∗∗p ≤ 0.0001 and p > 0.05 was considered not significant (n.s.).