Abstract
Background
Around 40% of people with bipolar disorder (BD) are non-adherent to medication leading to relapse, hospitalisation and increased suicide risk. Limited progress in addressing non-adherence may be partly attributable to insufficient understanding of the modifiable determinants of adherence that require targeting in interventions. We synthesised the modifiable determinants of adherence in BD and map them to the theoretical domains framework (TDF).
Method
We searched CINAHL, Cochrane Library, Embase, LILACS, Medline, PsychINFO and PubMed until February 2020. We included studies reporting modifiable determinants of adherence in BD. Two reviewers independently screened studies, assessed quality, extracted modifiable determinants and mapped them to TDF.
Results
We included 57 studies involving 32 894 participants. Determinants reported by patients spanned 11 of the 14 TDF domains compared to six domains represented by clinician/researcher. The TDF domains most commonly represented (% and example) in studies were: ‘Environmental context and resources’ (63%, e.g. experiencing side effects), ‘Beliefs about consequences’ (63%, e.g. beliefs about medication effects), ‘Knowledge’ (40%, e.g. knowledge about disorder), ‘Social influences’ (33%, e.g. support from family/clinicians), ‘Memory, attention and decision processes’ (33%, e.g. forgetfulness), ‘Emotion’ (21%, e.g. fear of addiction) and ‘Intentions’ (21%, e.g. wanting alternative treatment). ‘Intentions’, ‘Memory, attention and decision processes’ and ‘Emotion’ domains were only reported by patients but not clinicians.
Conclusions
Clinicians may be underappreciating the full range of modifiable determinants of adherence and thus not providing adherence support reflective of patients' needs. Reporting of modifiable determinants in behavioural terms facilitates developing theory-based interventions to address non-adherence in BD.
Key words: Adherence, barriers and facilitators, bipolar disorder, compliance, theoretical Domains Framework
Background
Bipolar disorder (BD) is generally a recurrent, lifelong mental health condition with a high risk of disability and excess mortality (Grande, Berk, Birmaher, & Vieta, 2016; Vazquez, Holtzman, Lolich, Ketter, & Baldessarini, 2015). The worldwide lifetime prevalence of the BD is estimated at 1% (Rowland & Marwaha, 2018). BD usually requires long-term medication but an estimated 40% of people are non-adherent to medication leading to relapse, functional impairment and suicidality (Gonzalez-Pinto et al., 2006; Lingam & Scott, 2002; Strakowski et al., 1998; Velligan et al., 2009). Medication non-adherence increases the probability of hospitalisation by at least five times (Scott & Pope, 2002).
Efforts to improve medication adherence have had marginal effects (Easthall, Taylor, & Bhattacharya, 2019; Nieuwlaat et al., 2014). This may be due to limited understanding of the modifiable determinants of medication adherence and existing support focussing on a narrow range of adherence determinants. We define modifiable determinants as ‘any determinants (barriers or facilitators) of medication adherence that can be modified by the patient, carer, or the prescriber within a short timeframe (days or weeks) to improve adherence’. We define a barrier as ‘a circumstance that prevents the patient from taking their medication as prescribed’, whereas a facilitator is ‘a circumstance that makes the process easy or easier’ (Oxford English dictionary online: Oxford university press, 2017). Some evidence syntheses report determinants of adherence to mental health treatment but they do not clearly distinguish between those that are modifiable, such as knowledge regarding how to take medication and non-modifiable such as age and gender. Such distinction is vital to allow adherence interventions to target modifiable determinants.
Furthermore, any differences between the perspective of clinicians and patients on determinants of medication adherence require exploration. Clinicians are the treatment experts but patients are the experts of their lived experience. Their goals, priorities and knowledge of the situation may differ. Thus, clinicians and patients may see the determinants of medication adherence differently (Devine, Edwards, & Feldman, 2018; Velligan et al., 2009). Exploring such differences will help design adherence support based on the patient's needs.
A recent systematic review by Garcia et al. provides an overview of barriers to medication adherence in BD and schizophrenia (Garcia et al., 2016). However, the study limited on determinants of adherence to antipsychotics (one group of medication to manage BD). Other common medications for BD are known as mood stabilisers which includes lithium. The omission of adherence determinants to lithium and other mood stabilisers is significant since lithium is recognised as the first-line gold standard long-term therapy in BD [Grunze et al., 2013; National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE), 2014]. It is also noteworthy that the challenges to adhere to lithium may be different as lithium is a narrow therapeutic index drug and thus require a regular blood test, some dietary restrictions and has significant interactions with other medications [National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE), 2014]. Furthermore, the review does not delineate modifiable from non-modifiable determinants which lack specific behaviour change techniques (BCTs) (Michie, Johnston, Francis, & Hardeman, 2008).
Additionally, the lack of behavioural theory underpinning the evidence synthesis in medication adherence in BD is evident. Thus, a systematic review of modifiable determinants of all treatment option in BD underpinned by theoretical framework is needed. Further details regarding the rationale for this systematic review are provided in the published protocol (Prajapati et al., 2019).
This systematic review aimed to identify modifiable determinants of medication adherence in BD reported in the literature and map them to the theoretical domains framework (TDF).
This study is a part of the Collaborative Medication Adherence in Bipolar disorder (C-MAB) project funded by Health Education England/National Institute for Health Research UK. The C-MAB project aims to develop a medication adherence tool for people with BD. The project advisory board includes stakeholders, patients, carers, clinicians, health psychologist and experts in behavioural medicine.
Method
The study was registered with PROSPERO, registration number: CRD42018096306.
The protocol with detailed methods for this systematic review is published elsewhere (Prajapati et al., 2019), and a summary of the methods is provided below.
We searched CINAHL, Cochrane Library, Embase, LILACS, Medline, PsychINFO and PubMed from database inception to October 2018 using the search terms ‘Treatment Adherence and Compliance’, ‘Bipolar Disorder’ and ‘Psychotropic Drugs’. We updated the search in February 2020. The detailed search strategy is available in online Supplementary file.
We included primary, qualitative and quantitative studies published in the English language and studies explicitly reporting modifiable determinants of medication adherence in BD in adults. We excluded reviews, intervention studies to improve adherence, case reports, clinical guidelines or general disease management articles, studies involving short-term treatment of acute agitation or treatment other than medication such as psychotherapy.
Two reviewers (AP, DB, FS, GM, JW and SS) independently screened the study abstracts and full-texts and carried out the quality assessment. Disagreements were resolved through discussion and referral to a third reviewer for arbitration if necessary. A range of quality assessment tools (Center for Evidence Based Management, 2014; Critical Appraisal Skills Programme, 2018; National Institute of Health, 2014) was used according to the study designs (Frambach, van der Vleuten, & Durning, 2013).
We used Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses (PRISMA) (Moher, Liberati, Tetzlaff, Altman, & The PRISMA Group, 2009) checklist for data extraction and reporting. The completed PRISMA checklist is available in online Supplementary file 2.
Underpinning theoretical framework
We used framework analysis with the TDF as an a priori framework, to map modifiable determinants of medication adherence to their relevant TDF domain. The use of a theoretical framework provides a broad lens through which to capture the literature identified modifiable determinants. The TDF is a comprehensive framework capturing 33 theories and 84 theoretical constructs related to behaviour change (Atkins et al., 2017). Atkins et al. report the definition of each TDF domain and construct within each domain (Atkins et al., 2017). TDF was developed as a consensus framework by experts in health service research and behaviour science (Michie et al., 2005). The TDF offers the additional advantage that each of its 14 domains is coupled with BCTs (Michie et al., 2008). Thus, mapping modifiable determinants of adherence to the TDF offers a significant utility for intervention development.
Two independent reviewers (AP, AD, DB and SS), with experience in using the TDF, extracted modifiable determinants and coded them to the TDF domains using Nvivo 12 (QSR International Pty Ltd, 2018). For example, the extracted text ‘lack of awareness that medication needed to be taken regularly led to non-adherence’ in the study was coded to the TDF domain ‘Knowledge’. In addition to the 14 TDF domains, we also created another domain called ‘Others’ for any modifiable determinant not suitable to map to those 14 domains. Agreement between two reviewers in mapping modifiable determinants to the same TDF domain was calculated in SPSS version 25 using Cohen's kappa.
We grouped the modifiable determinants into overarching themes (Gale, Heath, Cameron, Rashid, & Redwood, 2013). We also coded whether the modifiable determinants were barriers or facilitators and whether it was reported by patients, clinicians, carers or any other third parties.
Results
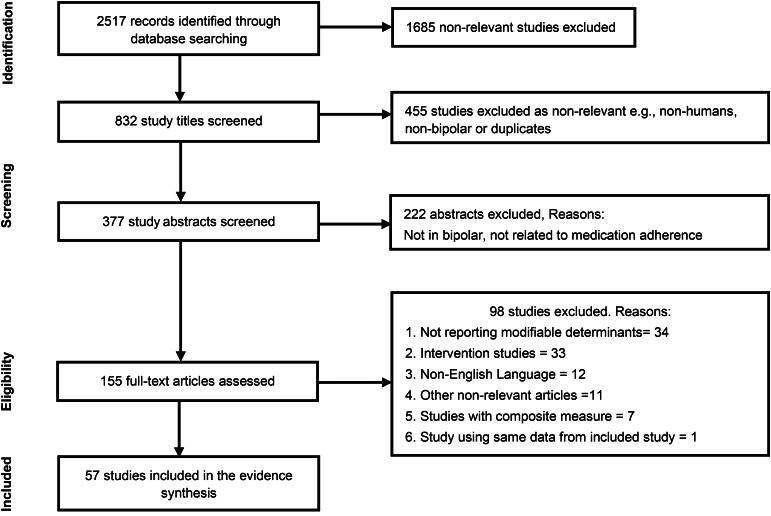
From the 2517 studies retrieved, we included 57, comprising 32 894 patients and clinicians. Figure 1 provides the screening process, number of retrieved studies, number of studies included and excluded during title screening, abstract screening and full text screening as well as the reasons for exclusion. The primary reasons for exclusion at full-text screening were failure to report modifiable determinants or reporting an intervention to address adherence.
Fig. 1.
PRISMA flow diagram.
PRISMA = Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses.
Study characteristics
Summary characteristics such as study design, participant details and, country in which the included study was conducted are presented in Table 1. Fifty studies explored determinants from the perspective of patients and two (Vieta et al., 2012; Younas, Bradley, Holmes, Sud, & Maidment, 2016) from clinicians' perspective. Three studies included both patient and clinician perspectives (Baldessarini, Perry, & Pike, 2008; Maczka, Siwek, Skalski, Grabski, & Dudek, 2010; Pope & Scott, 2003). Further two studies were from the researcher's perspective (Gianfrancesco, Sajatovic, Tafesse, & Wang, 2009; Greene et al., 2018). However, none of the studies included carers. Most of the included studies collected data via surveys or interviews. The majority (79%) of the studies were conducted in the USA and Europe. A majority of the studies (64%) were focused purely on BD. Of the 57 included studies, 33% (Arvilommi et al., 2014; Baldessarini et al., 2008; Bauer et al., 2013; Fleck, Corey, Strakowski, & Keck, 2005; Grover, Ghosh, Sarkar, Chakrabarti, & Avasthi, 2014; Hajda et al., 2015; Johnson et al., 2007; Jonsdottir et al., 2013; Jose, Bhaduri, & Mathew, 2003; Manwani et al., 2007; Nagesh, Kishore, & Raveesh, 2016; Pope & Scott, 2003; Ralat, Depp, & Bernal, 2018; Roe, Goldblatt, Baloush-Klienman, Swarbrick, & Davidson, 2009; Scott & Pope, 2002; Stentzel et al., 2018; Vieta et al., 2012) explicitly focused on exploring barriers to adherence. Table 2 describes the quality of the included studies. The majority (65%) of the studies was of moderate quality, 19% were of high quality and 16% were of low quality.
Table 1.
Summary of included studies
| Study details | Study design | Study included | Study aims | No. of participants | Country | Non-adherence rate |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Agyapong, Nwankwo, Bangaru, and Kirrane (2009) | Cross-sectional survey | BD, schizophrenia, depression | Assessment of associated factors that might influence compliance | 409 | Ireland | Not reported |
| Arvilommi et al. (2014) | Structured Clinical Interviews | BD only | Explored barriers of adherence: to investigate reasons were for treatment discontinuation | 168 | Finland | Not reported |
| Averous, Charbonnier, Lagouanelle-Simeoni, Dany, and Prosperi (2018) | Face to face interview | BD only | To explore associations between illness perceptions and adherence | 38 | France | Not reported |
| Baldessarini et al. (2008) | Survey | BD only | Explored barriers of adherence: risk factors to guide clinical prediction of nonadherence | 429 patients + 131 psychiatrists | USA | 33.8% |
| Bates, Whitehead, Bolge, and Kim (2010) | Web-based cross-sectional survey | BD only | To identify and describe correlates of medication adherence | 1052 | USA | 49.5% |
| Bauer et al. (2013) | Naturalistic study where patient recorded their medication taking in self-reporting software | BD only | Explored barriers of adherence: to investigate regularity in the daily mood stabiliser dosage taken by patient and factors associated with irregularity | 206 | Germany | Not reported |
| Belzeaux et al. (2013) | Cross-sectional survey and interviews | BD only | To explore adherence behaviour and characterise the sociodemographic and clinical factors associated with adherence | 382 | France | 25% of patients exhibited clear poor adherence |
| Bener, Dafeeah, and Salem (2013) | Survey | BD, schizophrenia, depression, anxiety and others | To examine the extent of compliance and non-compliance and examine the factors that affect compliance. | 564 | Qatar | 41.8% |
| Clatworthy et al. (2007) | Semi-structured interviews | BD only | To explore in-depth beliefs about BD and its treatment that are associated with adherence to medication prescribed for BD | 16 | UK | 8 reported non-adherence in the past and 5 reported current non-adherence |
| Clatworthy et al. (2009) | Questionnaire survey | BD only | The utility of the necessity concerns framework for understanding patient attitudes towards and levels of adherence | 223 | UK | 30% |
| Col, Caykoylu, Karakas, and Ugurlu (2014) | Semi-structured interviews | BD only | To determine the factors affecting treatment compliance | 78 | Turkey | 42.3% |
| Copeland et al. (2008) | Cross-sectional survey | BD only | To determine the association of insight and adherence | 435 | USA | 27% had poor adherence based on missed dose and 46% had poor adherence based on Moriskey |
| Correard et al. (2017) | Cross-sectional observational | BD only | To investigate influence of age and neuropsychological functioning on adherence | 353 | France | 47.3% |
| Darling et al. (2008) | Survey/interview | BD only | The influence of family and health stress, level of coping and internal health locus of control upon the life contentment of adherent and non-adherent individuals | 100 | USA | Not applicable as purposive sampling to include 50 adherent and 50 non-adherent patients |
| De Las, Penate, and Sanz (2014) | Survey | Bipolar, depression and dysthymia | To identify potential modelling factors influencing adherence | 145 | Spain | 46.2% |
| De Las, Penate, and Cabrera (2016) | Survey | BD, schizophrenia, depression and others | To examine the role of perceived health control variables in psychiatric patients' adherence to prescribed treatment. | 966 | Spain | A quarter of patients self-reported a high level of adherence; 46.8% medium adherence and 28.2% a low adherence |
| Deegan (2005) | Interviews | BD, schizophrenia, major depression, and others | To understand how people with psychiatric disorders demonstrate the capacity for resilience in the ways they use or do not use psychiatric medications | 29 | USA | Not reported |
| Fleck et al. (2005) | Interviews | BD only | Explored barriers of adherence: to examine rates, self-perceived reasons and attitudes associated with non-adherence | 50 | USA | 45% African American and 50% Whites totally non-adherent |
| Gianfrancesco et al. (2009) | Retrospective analysis of database | BD only | The study investigated monotherapy v. polypharmacy | 3626 | USA | Variable (depending on the medication and combination of medication) |
| Greene et al. (2018) | Retrospective analyses from database | Bipolar and schizophrenia (here we included only bipolar) | To compare differences in medication adherence and discontinuation between those who initiated a long acting injection and those who changed from one oral antipsychotic monotherapy to another | 11 344 | USA | 61.1% in LAIs group and 78.5% in oral group |
| Greenhouse, Meyer, and Johnson (2000) | Survey | BD only | This report hypothesised that acceptance coping would correlate positively, and denial coping would correlate inversely with adherence | 32 | USA | 75% of participants reported perfect adherence during the previous week |
| Grover et al. (2014) | Survey and semi structured interview with the patient and spouse/partner | BD only | Explored barriers of adherence: to evaluate the prevalence of sexual dysfunction in patients with BD receiving lithium and to study the correlates of sexual dysfunction | 100 | India | Varied (used BARS, MAQ) 84% took the prescribed doses of medications |
| Hajda et al. (2015) | Survey | BD only | Explored barriers of adherence: to determine the relationship between current adherence, medication discontinuing in the past and self-stigma | 33 | Czech Republic | Nineteen (57.6%) patients discontinued medication at least once in the past |
| Hibdye, Bekan, Dessalegne, Debero, and Sintayehu (2015) | Survey | BD only | Explored barriers of adherence: to assess the prevalence and factors associated with medication non-adherence among patients with BDs | 410 | Ethiopia | 51.2% |
| Hou, Cleak, and Peveler (2010) | Survey | BD only | To investigate the impact of treatment and illness beliefs on medication adherence | 35 | UK | 54.3% (probably non-adherent) |
| Inder, Lacey, and Crowe (2019) | Interviews | BD only | Analysis of medication adherence | 36 | New Zealand | NA |
| Johnson et al. (2007) | Survey | BD only | Explored barriers of adherence: to investigate factors associated with nonadherence and to assess the effect of patient preference on hypothetical medications | 469 | USA | 23% always adherent, 37% usually adherent, 23% occasionally adherent, 17% rarely adherent |
| Jonsdottir et al. (2013) | Interviews | Bipolar and schizophrenia | Explored barriers of adherence: to investigate potential risk factors for medication nonadherence | 255 | Norway | 13% Nonadherent, 31% partial adherent |
| Jose et al. (2003) | Survey | BD only | Explored barriers of adherence: to identify the reason for non-compliance | 96 | India | Not applicable (purposive sampling) |
| Kamaradova et al. (2016) | Survey | Bipolar, schizophrenia, depression, anxiety disorder and others | Explored barriers of adherence: to examine associations between self-stigma and adherence to treatment and discontinuation of medication in patients from various diagnostic groups | 332 | Czech Republic | 124 patients (37.35%) admitted they had discontinued their medication previously |
| Keck et al. (1996) | Cohort study – patients evaluated at admission and followed up at 6 months | BD only | To identify clinical factors associated with maintenance antipsychotic treatment in patients with BD | 77 | USA | Varied, 41–68% |
| Keck, McElroy, Strakowski, Bourne, and West (1997) | Interviews | BD only | To assess patients' compliance with pharmacotherapy | 140 | USA | 51% |
| Kraemer et al. (2013) | Observational study | BD only | To assess the duration of time on different mood stabilising medications and retention rates in standard clinical care | 761 | Germany | 28.4% |
| Kutzelnigg et al. (2014) | Observational study | BD only | To determine factors associated with better compliance and to assess compliance between patients stabilised on olanzapine monotherapy and those stabilised on combination therapy | 657 | Austria, Romania, Hungary, Korea, Taiwan and Mexico | High levels of compliance (⩾80%) were observed in 67% of patients at baseline, increasing to 80% in study completers |
| Maczka et al. (2010) | Survey | Psychiatrists and patients with BD | An analysis and comparison of patients' and psychiatrists' beliefs regarding the most important aspects of BD treatment. | 100 psychiatrists and 100 remitted patients | Poland | Not applicable |
| Manwani et al. (2007) | Structured Interviews | BD only | Explored barriers of adherence: to examine patterns and reasons of non-adherence | 115 | USA | 17.5% in non-substance users, 34.5% in substance users |
| Morselli and Elgie (2003) | Survey | People with bipolar and non-bipolar (unipolar depression, or dysthymia or atypical depression) | To gain a better understanding of what it is like to live with BD | 1732 | Austria, Finland, France, Hungary, Holland, Italy, Portugal, Russia, Spain, Sweden and UK | 47% |
| Nagesh et al. (2016) | An interviewer-assisted questionnaire-based study | Acute and transient psychotic disorder, borderline personality disorder, major depressive disorder, BD | Explored barriers of adherence: to assess the level of patients' adherence to psychotropic medications and to explore factors associated with non-adherence to medication | 156 | India | Adherence rate varied from low adherence (24.4%) through medium (34%) to high adherence (41.7%) among participants |
| Novick et al. (2017) | Post hoc analysis of 1-year observational study | Bipolar and schizophrenia | To explore non adherence with oro-dispersible v. standard normal tablet of olanzapine | 903 | France, Germany, Greece | Only reported average MARS scores |
| Perron, Zeber, Kilbourne, and Bauer (2009) | Survey | Bipolar, cyclothymia or schizoaffective disorder-bipolar subtype | To examine concurrent and predictive associations between provider support and adherence, access to care and health related quality of life | 433 | USA | Not reported |
| Pope and Scott (2003) | Survey | Patients with BD and their treating clinicians | Explored barriers of adherence: likely reasons for non-adherence identified by patients, the most common concerns of adherent and non- adherent subjects and the similarities and differences between clinicians' perceptions and patient concerns | 72 patients taking lithium and 41 psychiatrists treating them | UK | 46% |
| Ralat et al. (2018) | Focus group | BD only | Explored barriers of adherence: to identify patients' perspectives on the reasons for nonadherence to psychiatric medication | 22 | Puerto Rico | 68% of participants reported nonadherence during the week of recruitment |
| Roe et al. (2009) | Semi-structured interviews | Bipolar and schizophrenia | Explored barriers of adherence: to explore why and how people with a serious mental illness choose to stop taking prescribed medication | 7 | Israel | Not applicable |
| Rosa et al. (2007) | Survey | BD only | To determine plasma and red blood cell lithium concentrations in bipolar patients at the same time as estimating attitudes and knowledge about lithium treatment in adherence scales | 106 | Brazil | 33.06% based on MARS >7 14.4% based on plasma lithium |
| Rosenblat et al. (2018) | Survey | Bipolar depression and Major depressive disorder | Explore factors that impact treatment decisions | 896 | Canada | Bipolar depression and Major depressive disorder |
| Sajatovic, Bauer, Kilbourne, Vertrees, and Williford (2006) | Interview and self-report | BD only | Evaluated factors related to adherence | 184 | USA | 38.6% |
| Sajatovic et al. (2009) | Interviews | BD only | This cross-sectional analysis examined clinical and subjective variables in relation to adherence | 140 | USA | 19.3% |
| Sajatovic et al. (2011) | Interview plus quantitative assessments, adherence behaviour and treatment attitudes | BD only | This mixed-method analysis evaluated factors related to adherence among 20 poorly adherent community mental health clinic patients with BD | 20 | USA | Not applicable |
| Scott and Pope (2002) | Structured clinical interviews | BD (n = 78) and major depressive disorder (n = 20) | Explored barriers of adherence: to explore the prevalence and predictors of nonadherence with mood stabilisers | 98 | UK | Variable (47% had been non-adherent within last 2 years) |
| Sharma et al. (2012) | Survey | BD, schizophrenia and depression | This study examined the rates of medication non-adherence, associated disease, illness, treatment and physician-related factors of compliance | 400 | India | 40.2% |
| Stentzel et al. (2018) | Interviews | BD, schizophrenia, schizotypal and delusional disorder, depression | Explored barriers of adherence: to examine potential determinants of non-adherence for patients with severe mental disorders | 127 | Germany | 54% of the participants reported some kind of non-adherence |
| Teter et al. (2011) | Interviews | BD only | The study examined the impact of substance use disorder history with regards to medication-taking behaviours and attitudes | 54 | USA | Not reported |
| Vargas-Huicochea, Huicochea, Berlanga, and Fresan (2014) | Semi-structured interviews | BD only | To characterise the patients' perceptions and to give information that can help identify some of the factors involved in the treatment nonadherence | 50 | Mexico | Not reported |
| Vieta et al. (2012) | Survey | Psychiatrist treating bipolar patients | Explored barriers of adherence: to canvas the opinions of psychiatrists treating patients with BD and ascertain their perceptions of potential reasons for partial and non-adherence | 2448 | Austria, France, Germany, Italy, Spain, Switzerland, Turkey and UK | Psychiatrists estimated that 57% of their patients were partially or non-adherent |
| Weiss et al. (1998) | Structured interviews | Coexisting BD and substance use disorder | The study examined the pattern of medication compliance and reasons for non-compliance | 44 | USA | Variable and dependent on individual medication |
| Younas et al. (2016) | Interviews | Mental health pharmacists | To explore the views and experiences of UK mental health pharmacists regarding the use of shared decision making in antipsychotic prescribing in people with serious mental illness | 13 | UK | Not applicable |
| Zeber et al. (2008) | Survey | BD, cyclothymia, or schizoaffective disorder-bipolar subtype | The study examined the association between adherence and therapeutic environment perceptions among veterans with BD | 435 | USA | 27% |
Table 2.
Quality of included studies
| High quality (n = 11) | Moderate quality (n = 37) | Low quality (n = 9) |
|---|---|---|
| Belzeaux et al. (2013) Clatworthy et al. (2009) Copeland et al. (2008) Deegan (2005) De Las et al. (2016) Hou et al. (2010) Kamaradova et al. (2016) Sajatovic et al. (2006) Sajatovic et al. (2009) Sajatovic et al. (2011) Vargas-Huicochea et al. (2014) |
Agyapong et al. (2009) Arvilommi et al. (2014) Averous et al. (2018) Baldessarini et al. (2008) Bates et al. (2010) Bauer et al. (2013) Clatworthy et al. (2007) Col et al. (2014) Darling et al. (2008) De Las et al. (2014) Fleck et al. (2005) Gianfrancesco et al. (2009) Greene et al. (2018) Grover et al. (2014) Hibdye et al. (2015) Inder et al. (2019) Johnson et al. (2007) Jonsdottir et al. (2013) Keck et al. (1996) Kraemer et al. (2013) Kutzelnigg et al. (2014) Maczka et al. (2010) Manwani et al. (2007) Morselli and Elgie (2003) Nagesh et al. (2016) Novick et al. (2017) Pope and Scott (2003) Ralat et al. (2018) Roe et al. (2009) Rosenblat et al. (2018) Scott and Pope (2002) Stentzel et al. (2018) Teter et al. (2011) Vieta et al. (2012) Weiss et al. (1998) Younas et al. (2016) Zeber et al. (2008) |
Bener et al. (2013) Correard et al. (2017) Greenhouse et al. (2000) Hajda et al. (2015) Jose et al. (2003) Keck et al. (1997) Perron et al. (2009) Rosa et al. (2007) Sharma et al. (2012) |
Reported modifiable determinants of medication adherence
We extracted 290 modifiable determinants, which were grouped into 33 themes and mapped to 11 TDF domains. Inter-rater reliability for mapping the modifiable determinants to the TDF domains was 76% (Cohen's kappa 0.71), indicating substantial agreement between the reviewers (Landis & Koch, 1977). Cohen's kappa was calculated using SPSS 25.0 (IBM Corporation, 2017). Examples of the modifiable determinants, themes of determinants and TDF domains to which they were mapped are reported in Table 3.
Table 3.
TDF domains, themes of determinants and examples of determinants (barriers and facilitators)
| TDF domain (no. of studies reporting the domain) | Themes | Examples of determinants of medication adherence | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Barriers | Facilitators | ||
| Environmental context and resources (n = 36) | Side effects of medicationa |
|
|
| Medication formulation and treatment regimen |
|
|
|
| Ineffective medicationsa |
|
||
| Cost of medication |
|
|
|
| Irregular routinea |
|
||
| Access to health care providers |
|
||
| Belief about consequences (n = 36) | Belief about the necessity of medication either during treatment initiation or maintenance phasea |
|
|
| Belief about the positive or negative effects of medicationsa |
|
|
|
| Doubt about the effectiveness of medication |
|
||
| Belief that it is unnatural to take psychotropic medications |
|
||
| To avoid punishment/trouble |
|
||
| Knowledge (n = 23) | Knowledge about BD and its treatmenta |
|
|
| Understanding how and when to take medication |
|
||
| Social influences (n = 19) | Personal support by the care provider |
|
|
| Feeling stigma |
|
||
| Support or opposition from family, friends, relatives to diagnosis and treatmenta |
|
|
|
| Memory, attention and decision process (n = 19) | Forgetfulness/carelessness |
|
|
| Medication taking routine |
|
· Attaching medication taking to other routine behaviours (e.g. taking medication after cleaning teeth) | |
| Emotion (n = 12) | Fear of addiction or side effect of medication |
|
|
| Feeling threatened |
|
||
| Feeling of not being able to fulfil a social role |
|
||
| Negative feeling with medication prescribing and administration process |
|
||
| Intentions (n = 12) | Denial of illness or illness severity |
|
|
| Acceptance or denial of the need for treatment |
|
|
|
| Intentional non-adherence |
|
||
| Social, professional role and identity (n = 9) | Listening and shared decision makinga |
|
|
| Relationship with the prescriber |
|
||
| Being in control of the treatment regime |
|
||
| Belief about capabilities (n = 6) | Belief in self and controla |
|
|
| Conflicting belief between clinician and patient |
|
||
| Goals (n = 3) | Different priorities over medication taking |
|
|
| Desire to experience manic symptoms |
|
||
| Skills (n = 2) | Provision of training to manage BD |
|
|
| Optimism (n = 0) | No determinants mapped to this domain | ||
| Reinforcement (n = 0) | No determinants mapped to this domain | ||
| Behavioural regulation (n = 0) | No determinants mapped to this domain | ||
Clinicians only reported these themes of determinants.
Some facilitators were reported as the opposite of barriers. For example, ‘cost of medication’ was identified as a barrier in the ‘Environmental context and resources’ domain, for which ‘medication being free of charge’ represented the corresponding facilitator. In other cases, facilitators were occasionally worded as BCTs. For example, forgetfulness represented a barrier in the ‘memory, attention, and decision processes’ domain, for which the corresponding facilitators were reminders and formulating routines; these were classified in the BCT category of ‘prompts and cues’ which may successfully modify behaviour by addressing determinants in this TDF domain (Johnston et al., 2020).
The TDF domains represented in the greatest number of studies were ‘Environmental context and resources’ (63% of studies) and ‘Beliefs about consequences’ (63% of studies). Experience of side effects (49% of studies) and the nature of the medication, e.g. tablet, injection and dose frequency (22% of studies) were the main determinants mapped to the former; acting as barriers when unacceptable and facilitators when acceptable to patients. Beliefs about the likely positive/negative outcomes arising from adhering (36% of studies) and a belief that the medication is not needed (25% of studies) were the main determinants mapped to the latter.
Other TDF domains (and corresponding themes of determinants) reported in 20% or more studies, among all studies, were ‘Knowledge’ (whether the patient had sufficient knowledge about BD or its treatment); ‘Social influences’ (support or opposition from family, friends, relatives, clinicians regarding adherence); ‘Emotion’ (fear of addiction to or side effect from medication); ‘Memory, attention, and decision process’ (forgetfulness/carelessness with medication taking) and ‘Intentions’ (denial of illness or need for treatment).
Modifiable determinants were most frequently reported in the context of barriers rather than facilitators. However, unlike most other TDF domains, for ‘social influences’, facilitators and barriers were reported with similar frequency. This trend was also observed for ‘Social/Professional Role and identity’. Modifiable determinants related to ‘Goals’ and ‘Skills’ were infrequently reported. No determinants were mapped to the TDF domains of ‘Optimism’, ‘Reinforcement’ and ‘Behavioural regulation’.
Determinants from the perspectives of patients and clinicians
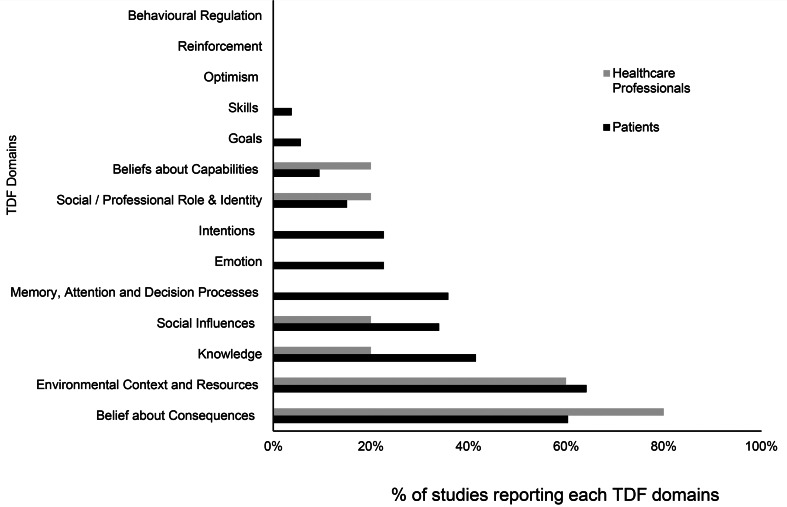
Figure 2 illustrates the TDF domains reported in patient studies compared to clinician studies. ‘Beliefs about consequences’ and ‘Environmental context and resources’ were the two most frequently reported TDF domains in both patient studies as well as clinicians studies. There were, however, noticeable differences in the range and nature of determinants reported by patients relative to clinicians. Determinants reported by clinicians were mapped to only six TDF domains compared to 11 TDF domains covered by patient studies. Only patient studies reported determinants which were mapped to the TDF domains ‘Intention’, ‘Memory, attention and decision process’ and ‘Emotion’. These domains included determinants such as denial of the illness or need for treatment, forgetfulness/carelessness and fear of addiction to or side effect of medication respectively (see Table 3 for more details).
Fig. 2.
Comparison of TDF domains reported by patients and clinicians. No. of patients only studies = 50; no. of clinicians only studies = 2; no. of studies including patients and clinicians = 3. Two studies exploring researchers' perspectives were not included in this graph.
Furthermore, ‘Goals’ and ‘Skills’ domains were reported in patient studies, albeit infrequently. An example of determinants in these two domains includes different priorities over medication taking and provision of training to manage BD, as shown in Table 3.
Clinicians reported modifiable determinants of adherence themed around lack of knowledge about medication, shared decision making, belief in self and perceived control, belief that medication is not needed, belief about positive or negative effects of medication, side effects, ineffective medication and irregular routine.
Two studies reported determinants from the researcher perspective (Gianfrancesco et al., 2009; Greene et al., 2018) namely medication formulations (such as tablets and injections) and the number of medications, both of which were mapped to ‘Environmental context and resources’ domain.
Discussion
Synthesis of the literature through the theoretical lens of the TDF has enabled us to identify that negative emotions evoked by medication taking and intentional non-adherence make a notable contribution to non-adherent behaviour. In contrast to the focus of existing interventions on practical barriers to adherence (MacDonald, 2017; Torres-Robles et al., 2018), clinicians should additionally address negative emotions and lack of intentions.
In common with previous evidence syntheses, modifiable determinants were primarily barriers to adherence (Garcia et al., 2016; Velligan et al., 2009) with few reported facilitators. This may be an artefact of the included studies focussing on the challenges experienced by patients, rather than seeking to explore potential solutions. This hypothesis is supported by a third of the included studies explicitly seeking only barriers to medication adherence. For the few studies exploring facilitators, determinants that are not the opposite of barriers, such as wanting to keep the mood stable and not wanting to be hospitalised, have also been reported (Clatworthy, Parham, Horne, Bowskill, & Rank, 2007; Darling, Olmstead, Lund, & Fairclough, 2008). A strength of the present review is that we did not restrict the search to only adherence barriers; thus, we have identified a gap in the literature.
Current adherence interventions in BD focus mostly on education regarding medication and BD, cognitive therapy to address negative attitudes and beliefs, family therapy to encourage social support and technology to address forgetfulness (MacDonald, 2017; Torres-Robles et al., 2018). Furthermore, adherence support in the UK focusses on shared decision making regarding the choice of medication, side effects profile of medication, cost of medication and exploring patients beliefs [Care Quality Commission (CQC), 2018; National Institute of Healthand Care Excellence (NICE), 2009]. However, in this study, we found a broad range of other modifiable determinants that may be affecting medication adherence. This study provides clinicians with a comprehensive list of modifiable determinants of medication adherence, some of which are underappreciated by clinicians and unaddressed by existing adherence interventions.
Advantages of mapping modifiable determinants to the TDF
Mapping determinants to the TDF allows them to be linked to BCTs. Thus, this study provides a foundation for developing a complex adherence intervention tailored to patients' needs based on their predominant determinants of adherence. The most frequently reported TDF domains of ‘Beliefs about consequences’ and ‘Environmental context and resources’ indicate that working with the patient's belief system, medication acceptability and tolerability are vital to support medication adherence. However, other modifiable determinants, particularly in ‘Intentions’, ‘Memory, attention and decision process’ and ‘Emotion’ domains, presented in this study may be equally or more relevant to individual patients. Thus, identifying the modifiable determinants most pertinent to an individual patient is critical to providing patient-centred adherence support.
The most frequently reported domain ‘Environmental context and resources’ was primarily related to medication characteristics such as side effects, treatment regime, medication effectiveness or cost of medication, etc. This finding accords with previous studies (Garcia et al., 2016; Kikkert et al., 2006; Salzmann-Erikson & Sjodin, 2018; Velligan et al., 2009). Side effects were represented in the domains of both ‘Environmental context and resources’ and ‘Beliefs about consequences’. This was because patients reported non-adherence arising from both experiencing side effects and being concerned that side effects may result from taking the medication. Each requires a different BCT, for example, the former may be better addressed by ‘restructuring the physical environment,’ e.g. by changing medication with a lower propensity of a particular side effect that the patient is experiencing. In contrast, the latter aligns with BCTs such as ‘pros and cons,’ e.g. discussing the risk and benefit of taking and not taking the medication (The UCL Centre for Behaviour Change, 2019).
The dominance of ‘Beliefs about consequences’ on medication adherence in this review is supported by other studies using the TDF (Crayton et al., 2017; Easthall et al., 2019). Belief about the necessity or concerns of medication were frequently reported determinants of adherence within this domain. As often reported in clinical practice, many people stop taking their medication once they feel better believing they no longer need them. On the contrary, some people believe they do not need medication at the start of the treatment and thus do not initiate them. Therefore, BCTs such as ‘pros and cons’ may play a vital role in medication adherence (The UCL Centre for Behaviour Change, 2019).
The absence of determinants mapped to the TDF domains ‘Optimism’, ‘Reinforcement’ and ‘Behavioural regulation’ does not necessarily mean that these three domains are unimportant to medication adherence in BD. Previous studies may not have explored these specific domains. Some adherence intervention studies suggest ‘Reinforcement’ using financial incentives may improve adherence (Priebe, Bremner, Lauber, Henderson, & Burns, 2016). Similarly, optimism, as measured by the revised Life Orientation Test (Herzberg, Glaesmer, & Hoyer, 2006), was reported to lead to improved adherence in acute coronary syndrome (Millstein et al., 2016). Revised Life Orientation Test includes statements such as ‘Overall, I expect more good things happen to me than bad’, ‘In uncertain times, I usually expect the best’ (Herzberg et al., 2006). However, these may not be modifiable. Future study should explicitly investigate the extent to which these unrepresented domains are relevant to non-adherence in this population and whether they are modifiable in the context of medication adherence.
Although there was a significant overlap between determinants reported by clinicians and patients, there were also notable distinctions. These distinctions may explain the limited progress made by clinicians in identifying and addressing non-adherence (Hartung et al., 2017; Nieuwlaat et al., 2014). However, these distinctions may also have arisen due to the small number of studies exploring the clinician's perspective.
Clinician reported determinants mapped to less than half of the TDF domains, suggesting that clinicians may not be aware of the broad range of determinants affecting medication adherence or studies were not designed to elicit this information from clinicians. The influence of negative emotion evoked by taking medication and intentional non-adherence was the most notable omission from clinicians' perspectives. This incomplete picture may result in adherence support poorly reflecting patients' needs (Brown et al., 2017). This is evident from current adherence support being focused on a very limited number of determinants (MacDonald, 2017; National Institute of Healthand Care Excellence (NICE), 2009; Thompson, Kulkarni, & Sergejew, 2000; Torres-Robles et al. 2018).
Strengths and limitations
This study offers three novel aspects in the field of medication adherence research in BD. Firstly, the study focuses on potential adherence intervention targets by reporting only modifiable determinants. Secondly, as the application of theory is a core requirement for developing and implementing complex interventions, our use of a theoretical framework provides the foundations for developing future medication adherence interventions and their implementation. Finally, the comprehensive nature of a theoretical framework rather than an individual theory has enabled us to identify gaps in the literature.
Using the TDF as an a priori framework to organise modifiable determinants is a deductive approach. However, we did not constrain extraction of the determinants and mapping them to only the TDF domains as any determinants not aligned to the TDF would have been captured in the ‘Others’ category. The lack of detailed description of the determinants in some studies risked mapping them to incorrect TDF domains. For example, some studies described ‘hassle to acquire medication’ as a determinant of adherence. It could mean the patient has difficulty obtaining medication due to not knowing how to order their prescription or difficulty remembering to order a prescription or lack of transport/money/time to order prescription. Each interpretation would be mapped to a different TDF domain. Further qualitative study with patients will facilitate these further refinements in mapping.
We presented the modifiable determinants of adherence identified from a wide range of study designs. We recognise that the medium via which data are collected can influence the range of determinants captured. For example, interviews may elicit a greater range of determinants that are personal to the individual v. a structured survey of potentially relevant determinants (Lagard, Keegan, & Ward, 2003). This non-restrictive approach has contributed to identifying a list of modifiable determinants as comprehensively as possible which was one of the goals of this study.
Implications for practice
We provide theory and evidence-based modifiable determinants that influence a patient's ability to adhere to their prescribed medication. All these determinants should, therefore, be considered and potentially discussed with patients when initiating treatment and at every review. Currently, clinicians may not be providing adherence support tailored to patients' wide-ranging needs.
Implications for research
The application of a theoretical framework to the systematic review has enabled us to identify gaps in the literature where researchers have not sought to investigate the relevance of facilitators of adherence. Further research to explicitly capture the facilitators of adherence may help design future adherence interventions. The existing literature mostly represents the patient voice; absence of the carer voice is a notable gap given their role in supporting medication adherence in people with mental health problems (Deane, McAlpine, Byrne, Davis, & Mortimer, 2018). Future research exploring carers' views on modifiable determinants of medication adherence in BD is, therefore, needed.
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank members of the Collaborative Medication Adherence in Bipolar disorder (C-MAB) Research Advisory Board members for their support. We are also grateful to colleagues from NSFT and UEA libraries for help with the literature search and sourcing articles.
Author contributions
All authors contributed to the development of the protocol for this systematic review. AP led the literature search. AP, DB, GM, JW and SS screened the abstract and full text. AP, GM, JW and FS extracted data. AP, GM and FS quality assessed included studies. AP, AD, DB and SS extracted modifiable determinants and mapped to the TDF. AP and DB led manuscript preparation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Financial support
Asta Ratna Prajapati is funded by Health Education England (HEE)/National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) (Clinical Doctoral Research Fellowship) (NIHR reference number: ICA-CDRF-2017-03-054) for this research project. This paper presents independent research funded by the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR). The views expressed are those of the author(s) and not necessarily those of the NHS, the HEE/NIHR, or the Department of Health and Social Care.
Supplementary material
For supplementary material accompanying this paper visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291721001446.
click here to view supplementary material
Data
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, AP, upon a reasonable request.
Conflict of interest
None.
References
- Agyapong, V. I. O., Nwankwo, V., Bangaru, R., & Kirrane, R. (2009). Sources of patients' knowledge of the adverse effects of psychotropic medication and the perceived influence of adverse effects on compliance among service users attending community mental health services. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology, 29(6), 565–570. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvilommi, P., Suominen, K., Mantere, O., Valtonen, H., Isometsa, E., & Leppamaki, S. (2014). Predictors of adherence to psychopharmacological and psychosocial treatment in bipolar I or II disorders – An 18-month prospective study. Journal of Affective Disorders, 155(1), 110–117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkins, L., Francis, J., Islam, R., O'Connor, D., Patey, A., Ivers, N., … Michie, S. (2017). A guide to using the theoretical domains framework of behaviour change to investigate implementation problems. Implementation Science, 12, 77–95. doi: 10.1186/s13012-017-0605-9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Averous, P., Charbonnier, E., Lagouanelle-Simeoni, M. C., Dany, L., & Prosperi, A. (2018). Illness perceptions and adherence in bipolar disorder: An exploratory study. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 80, 109–115. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldessarini, R. J., Perry, R., & Pike, J. (2008). Factors associated with treatment nonadherence among US bipolar disorder patients. Human Psychopharmacology, 23(2), 95–105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bates, J. A., Whitehead, R., Bolge, S. C., & Kim, E. (2010). Correlates of medication adherence among patients with bipolar disorder: Results of the bipolar evaluation of satisfaction and tolerability (BEST) study: A nationwide cross-sectional study. Primary Care Companion to the Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 12(5), E1–E8. doi: 10.4088/PCC.09m00883yel. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer, M., Glenn, T., Alda, M., Sagduyu, K., Marsh, W., Grof, P., … Whybrow, & P. C. (2013). Regularity in daily mood stabilizer dosage taken by patients with bipolar disorder. Pharmacopsychiatry, 46(5), 163–168. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belzeaux, R., Correard, N., Azorin, J.-M., Etain, B., Loftus, J., Bellivier, F., … Boyer, L. (2013). Depressive residual symptoms are associated with lower adherence to medication in bipolar patients without substance use disorder: Results from the FACE-BD cohort. Journal of Affective Disorders, 151(3), 1009–1015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bener, A., Dafeeah, E. E., & Salem, M. O. (2013). A study of reasons of non-compliance of psychiatric treatment and patients' attitudes towards illness and treatment in Qatar. Issues in Mental Health Nursing, 34(4), 273–280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown, T., Twigg, M., Taylor, N., Easthall, C., Hartt, J., Budd, T., … Bhattacharya, D. (2017). Final report for the IMAB-Q study: Validation and feasibility testing of a novel questionnaire to identify barriers to medication adherence. London, UK. Retrieved May 5, 2020, from https://pharmacyresearchuk.org/wp-content/uploads/2017/01/IMAB-Q-validation-and-feasibility-testing-full-report.pdf.
- Care Quality Commission (CQC). (2018). NHS patient survey programme: 2018 community mental health survey, Statistical release, 30-34. Retrieved May 5, 2020, from https://www.cqc.org.uk/sites/default/files/20181122_cmh18_statisticalrelease.pdf.
- Center for Evidence Based Management. (2014). Critical Appraisal Checklists for a Qualitative Study. Retrieved May 10, 2020, from https://www.cebma.org.
- Clatworthy, J., Bowskill, R., Parham, R., Rank, T., Scott, J., & Horne, R. (2009). Understanding medication non-adherence in bipolar disorders using a necessity-concerns framework. Journal of Affective Disorders, 116(1), 51–55. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clatworthy, J., Parham, R., Horne, R., Bowskill, R., & Rank, T. (2007). Adherence to medication in bipolar disorder: A qualitative study exploring the role of patients' beliefs about the condition and its treatment. Bipolar Disorders, 9(6), 656–664. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Col, S. E., Caykoylu, A., Karakas, U. G., & Ugurlu, M. (2014). Factors affecting treatment compliance in patients with bipolar I disorder during prophylaxis: A study from Turkey. General Hospital Psychiatry, 36(2), 208–213. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Copeland, L. A., Zeber, J. E., Salloum, I. M., Pincus, H. A., Fine, M. J., & Kilbourne, A. M. (2008). Treatment adherence and illness insight in veterans with bipolar disorder. The Journal of Nervous and Mental Disease, 196(1), 16–21. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Correard, N., Consoloni, J.-L., Azorin, J.-M., Belzeaux, R., Raust, A., Etain, B., … Beetz, E. (2017). Neuropsychological functioning, age, and medication adherence in bipolar disorder. PLoS ONE, 12(9), e0184313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crayton, E., Fahey, M., Ashworth, M., Besser, S. J., Weinman, J., & Wright, A. J. (2017). Psychological determinants of medication adherence in stroke survivors: A systematic review of observational studies. Annals of Behavioral Medicine: A Publication of the Society of Behavioral Medicine, 51(6), 833–845. doi: 10.1007/s12160-017-9906-0 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP). (2018). 10 questions to help you make sense of qualitative research. CASP qual checkl. Oxford: UK. Retrieved May 5, 2020, from https://casp-uk.net/.
- Darling, C. A., Olmstead, S. B., Lund, V. E., & Fairclough, J. F. (2008). Bipolar disorder: Medication adherence and life contentment. Archives of Psychiatric Nursing, 22(3), 113–126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deane, F. P., McAlpine, E., Byrne, M. K., Davis, E. L., & Mortimer, C. (2018). Are carer attitudes toward medications related to self-reported medication adherence amongst people with mental illness? Psychiatry Research, 260, 158–163. doi: S0165-1781(17)30394-3 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deegan, P. E. (2005). The importance of personal medicine: A qualitative study of resilience in people with psychiatric disabilities. Scandinavian Journal of Public Health, 33, 29–35. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Las, C. C., Penate, W., & Cabrera, C. (2016). Perceived health control: A promising step forward in our understanding of treatment adherence in psychiatric care. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 77(10), e1233-e1239. doi: 10.4088/JCP.15m09769 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Las, C. C., Penate, W., & Sanz, E. J. (2014). Risk factors for non-adherence to antidepressant treatment in patients with mood disorders. European Journal of Clinical Pharmacology, 70(1), 89–98. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine, F., Edwards, T., & Feldman, S. R. (2018). Barriers to treatment: Describing them from a different perspective. Patient Preference and Adherence, 12, 129–133. doi: 10.2147/PPA.S147420 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Easthall, C., Taylor, N., & Bhattacharya, D. (2019). Barriers to medication adherence in patients prescribed medicines for the prevention of cardiovascular disease: A conceptual framework. The International Journal of Pharmacy Practice, 27(3), 223–231. doi: 10.1111/ijpp.12491 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fleck D.E., Corey K.B., Strakowski S.M., & Keck P.E Jr.. (2005). Factors associated with medication adherence in African American and white patients with bipolar disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 66(5), 646–652. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frambach, J. M., van der Vleuten, C. P., & Durning, S. J. (2013). AM last page. Quality criteria in qualitative and quantitative research. Academic Medicine: Journal of the Association of American Medical Colleges, 88(4), 552. doi: 10.1097/ACM.0b013e31828abf7f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gale, N. K., Heath, G., Cameron, E., Rashid, S., & Redwood, S. (2013). Using the framework method for the analysis of qualitative data in multi-disciplinary health research. BMC Medical Research Methodology, 13, 117–2288-13-117. doi: 10.1186/1471-2288-13-117. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, S., Martinez-Cengotitabengoa, M., Lopez-Zurbano, S., Zorrilla, I., Lopez, P., Vieta, E., & Gonzalez-Pinto, A. (2016). Adherence to antipsychotic medication in bipolar disorder and schizophrenic patients: A systematic review. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology, 36(4), 355–371. doi: 10.1097/JCP.0000000000000523 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gianfrancesco, F. D., Sajatovic, M., Tafesse, E., & Wang, R. H. (2009). Association between antipsychotic combination therapy and treatment adherence among individuals with bipolar disorder. Annals of Clinical Psychiatry, 21(1), 3–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez-Pinto, A., Mosquera, F., Alonso, M., Lopez, P., Ramirez, F., Vieta, E., & Baldessarini, R. J. (2006). Suicidal risk in bipolar I disorder patients and adherence to long-term lithium treatment. Bipolar Disorders, 8(5), 618–624. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grande, I., Berk, M., Birmaher, B., & Vieta, E. (2016). Bipolar disorder. Lancet (London, England), 387(10027), 1561–1572. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)00241-X [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene, M., Yan, T., Chang, E., Broder, M. S., Hartry, A., & Touya, M. (2018). Medication adherence and discontinuation of long-acting injectable versus oral antipsychotics in patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Journal of Medical Economics, 21(2), 127–134. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenhouse, W. J., Meyer, B., & Johnson, S. L. (2000). Coping and medication adherence in bipolar disorder. Journal of Affective Disorders, 59(3), 237–241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grover, S., Ghosh, A., Sarkar, S., Chakrabarti, S., & Avasthi, A. (2014). Sexual dysfunction in clinically stable patients with bipolar disorder receiving lithium. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology, 34(4), 475–482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grunze, H., Vieta, E., Goodwin, G. M., Bowden, C., Licht, R. W., Moller, H. J., … WFSBP Task Force on Treatment Guidelines for Bipolar Disorders. (2013). The world federation of societies of biological psychiatry (WFSBP) guidelines for the biological treatment of bipolar disorders: Update 2012 on the long-term treatment of bipolar disorder. The World Journal of Biological Psychiatry, 14(3), 154–219. doi: 10.3109/15622975.2013.770551. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hajda, M., Kamaradova, D., Latalova, K., Prasko, J., Ociskova, M., Mainerova, B., … Tichackova, A. (2015). Self-stigma, treatment adherence, and medication discontinuation in patients with bipolar disorders in remission – A cross sectional study. Activitas Nervosa Superior Rediviva, 57(1), 6–11. [Google Scholar]
- Hartung, D., Low, A., Jindai, K., Mansoor, D., Judge, M., Mendelson, A., … Kondo, K. (2017). Interventions to improve pharmacological adherence among adults with psychotic spectrum disorders and bipolar disorder: A systematic review. Psychosomatics, 58(2), 101–112. doi: S0033-3182(16)30100-1 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzberg, P. Y., Glaesmer, H., & Hoyer, J. (2006). Separating optimism and pessimism: A robust psychometric analysis of the revised life orientation test (LOT-R). Psychological Assessment, 18(4), 433–438. doi: 10.1037/1040-3590.18.4.433 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibdye, G., Bekan, L., Dessalegne, Y., Debero, N., & Sintayehu, M. (2015). Prevalence of drug non adherence and associated factors among patients with bipolar disorder at outpatient unit of Amanuel Hospital, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, 2013. African Journal of Psychiatry (South Africa), 18, 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Hou, R., Cleak, V., & Peveler, R. (2010). Do treatment and illness beliefs influence adherence to medication in patients with bipolar affective disorder? A preliminary cross-sectional study. European Psychiatry, 25(4), 216–219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- IBM Corp. (2017). IBM SPSS statistics for windows. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp. [Google Scholar]
- Inder, M., Lacey, C., & Crowe, M. (2019). Participation in decision-making about medication: A qualitative analysis of medication adherence. International Journal of Mental Health Nursing, 28(1), 181–189. doi: 10.1111/inm.12516 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson, F. R., Ozdemir, S., Manjunath, R., Hauber, A. B., Burch, S. P., & Thompson, T. R. (2007). Factors that affect adherence to bipolar disorder treatments: A stated-preference approach. Medical Care, 45(6), 545–552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston, M., Carey, R. N., Connell Bohlen, L., Johnston, D. W., Rothman, A., de Bruin, M., … Michie, S. (2020). Linking behavior change techniques and mechanisms of action: Triangulation of findings from literature synthesis and expert consensus. Translational Behavioral Medicine, ibaa050, 1–17. doi: 10.1093/tbm/ibaa050 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonsdottir, H., Opjordsmoen, S., Birkenaes, A. B., Simonsen, C., Engh, J. A., Ringen, P. A., … Andreassen, O. A. (2013). Predictors of medication adherence in patients with schizophrenia and bipolar disorder. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 127(1), 23–33. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jose, T. T., Bhaduri, A., & Mathew, B. (2003). A study of the factors associated with compliance or non-compliance to lithium therapy among the patients with bipolar affective disorder. Nursing Journal of India, 94(1), 9–11. [Google Scholar]
- Kamaradova, D., Latalova, K., Prasko, J., Kubinek, R., Vrbova, K., Mainerova, B., … Holubova, M. (2016). Connection between self-stigma, adherence to treatment, and discontinuation of medication. Patient Preference and Adherence, 10, 1289–1298. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck, P. E., McElroy, S. L., Strakowski, S. M., Balistreri, T. M., Kizer, D. I., & West, S. A. (1996). Factors associated with maintenance antipsychotic treatment of patients with bipolar disorder. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 57(4), 147–151. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck, P. E., McElroy, S. L., Strakowski, S. M., Bourne, M. L., & West, S. A. (1997). Compliance with maintenance treatment in bipolar disorder. Psychopharmacology Bulletin, 33(1), 87–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkert, M. J., Schene, A. H., Koeter, M. W., Robson, D., Born, A., Helm, H., … Gray, R. J. (2006). Medication adherence in schizophrenia: Exploring patients', carers' and professionals' views. Schizophrenia Bulletin, 32(4), 786–794. doi: 10.1093/schbul/sbl011 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kraemer, S., Minarzyk, A., Eppendorfer, S., Henneges, C., Hundemer, H.-P., Wilhelm, S., & Grunze, H. (2013). Comparably high retention and low relapse rates in different subpopulations of bipolar patients in a German non-interventional study. BMC Psychiatry, 13, 193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kutzelnigg, A., Kasper, S., Kopeinig, M., Chen, C.-K., Fabian, A., Pujol-Luna, M. G., … Doby, D. (2014). Compliance as a stable function in the treatment course of bipolar disorder in patients stabilized on olanzapine: Results from a 24-month observational study. Clinical and Translational Imaging, 2(1), 1–14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagard, R., Keegan, J., & Ward, K. (2003). In-depth interviews. In Ritchie J., & Lewis J. (Eds.), Qualitative research practice: A guide for social science students and researchers (pp. 138–139). London, UK: Sage. [Google Scholar]
- Landis, J. R., & Koch, G. G. (1977). The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics, 33(1), 159–174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lingam, R., & Scott, J. (2002). Treatment non-adherence in affective disorders. Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica, 105(3), 164–172. doi: 10.1034/j.1600-0447.2002.1r084.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald, L. (2017) Medication adherence in bipolar disorder: Understanding patients’ perspectives to inform intervention development. PhD thesis, University College London, UK. 2017. Retrieved May 5, 2020. from https://discovery.ucl.ac.uk/id/eprint/1543201/1/MacDonald_LA_PhD_Thesis_2017.pdf. [Google Scholar]
- Maczka, G., Siwek, M., Skalski, M., Grabski, B., & Dudek, D. (2010). Patients' and doctors' attitudes towards bipolar disorder – Do we share our beliefs? Archives of Psychiatry and Psychotherapy, 12(2), 43–50. [Google Scholar]
- Manwani, S. G., Szilagyi, K. A., Griffin, M. L., Weiss, R. D., Hennen, J., & Zablotsky, B. (2007). Adherence to pharmacotherapy in bipolar disorder patients with and without co-occurring substance use disorders. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 68(8), 1172–1176. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie, S., Johnston, M., Abraham, C., Lawton, R., Parker, D., Walker, A., & ‘Psychological Theory’ Group. (2005). Making psychological theory useful for implementing evidence based practice: A consensus approach. Quality & Safety in Health Care, 14(1), 26–33. doi: 10.1136/qshc.2004.011155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michie, S., Johnston, M., Francis, J., & Hardeman, W. (2008). From theory to intervention: Mapping theoretically derived behavioural determinants to behaviour change techniques. Applied Psychology, 57(4), 660–680. [Google Scholar]
- Millstein, R. A., Celano, C. M., Beale, E. E., Beach, S. R., Suarez, L., Belcher, A. M., … Huffman, J. C. (2016). The effects of optimism and gratitude on adherence, functioning and mental health following an acute coronary syndrome. General Hospital Psychiatry, 43, 17–22. doi: 10.1016/j.genhosppsych.2016.08.006 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moher, D., Liberati, A., Tetzlaff, J., Altman, D. G., & The PRISMA Group. (2009). Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: The PRISMA statement. PLoS Medicine, 6(7), e1000097. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed1000097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morselli, P. L., & Elgie, R. (2003). GAMIAN-Europe*/BEAM survey I – Global analysis of a patient questionnaire circulated to 3450 members of 12 European advocacy groups operating in the field of mood disorders. Bipolar Disorders, 5(4), 265–278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagesh, H. N., Kishore, M. S., & Raveesh, B. N. (2016). Assessment of adherence to psychotropic medications in a psychiatric unit of district hospital. National Journal of Physiology, Pharmacy and Pharmacology, 6(6), 581–585. [Google Scholar]
- National Institute of Health. (2014). Quality assessment tool for observational cohort and cross sectional studies. Retrieved May 5, 2020, from https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/study-quality-assessment-tools.
- National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE). (2009). Medicines adherence: Involving patients in decisions about prescribed medicines and supporting adherence. London: NICE. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- National Institute of Health and Care Excellence (NICE). (2014). Bipolar disorder: Assessment and management (clinical guideline, CG 185). London: nice. [Google Scholar]
- Nieuwlaat, R., Wilczynski, N., Navarro, T., Hobson, N., Jeffery, R., Keepanasseril, A., … Haynes, R. B. (2014). Interventions for enhancing medication adherence. The Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, 2014(11), CD000011. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD000011.pub4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novick, D., Montgomery, W., Treuer, T., Koyanagi, A., Aguado, J., Haro, J. M., et al. (2017). Comparison of clinical outcomes with orodispersible versus standard oral olanzapine tablets in nonadherent patients with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder. Patient Preference and Adherence, 11, 1019–1025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oxford English Dictionary online: Oxford university press. (2017). Retrieved March 2, 2017, from https://en.oxforddictionaries.com/definition/barrier.
- Perron, B. E., Zeber, J. E., Kilbourne, A. M., & Bauer, M. S. (2009). A brief measure of perceived clinician support by patients with bipolar spectrum disorders. Journal of Nervous & Mental Disease, 197(8), 574–579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pope, M., & Scott, J. (2003). Do clinicians understand why individuals stop taking lithium? Journal of Affective Disorders, 74(3), 287–291. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prajapati, A. R., Dima, A., Clark, A. B., Gant, C., Gibbons, C., Gorrod, R., … Bhattacharya, D. (2019). Mapping of modifiable barriers and facilitators of medication adherence in bipolar disorder to the theoretical domains framework: A systematic review protocol. BMJ Open, 9(2), e026980. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2018-026980 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priebe, S., Bremner, S. A., Lauber, C., Henderson, C., & Burns, T. (2016). Financial incentives to improve adherence to antipsychotic maintenance medication in non-adherent patients: A cluster randomised controlled trial. Health Technology Assessment, 20(70), 121–121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- QSR International Pty Ltd. (2018). Nvivo 12 for windows. NVivo qualitative data analysis software (computer software).
- Ralat, S. I., Depp, C. A., & Bernal, G. (2018). Reasons for nonadherence to psychiatric medication and cardiovascular risk factors treatment among Latino bipolar disorder patients living in Puerto Rico: A qualitative study. Community Mental Health Journal, 54(6), 707–716. doi: 10.1007/s10597-017-0202-z [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe, D., Goldblatt, H., Baloush-Klienman, V., Swarbrick, M., & Davidson, L. (2009). Why and how people decide to stop taking prescribed psychiatric medication: Exploring the subjective process of choice. Psychiatric Rehabilitation Journal, 33(1), 38–46. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa, A. R., Marco, M., Fachel, J. M. G., Kapczinski, F., Stein, A. T., & Barros, H. M. T. (2007). Correlation between drug treatment adherence and lithium treatment attitudes and knowledge by bipolar patients. Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology & Biological Psychiatry, 31(1), 217–224. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenblat, J. D., Simon, G. E., Sachs, G. S., Deetz, I., Doederlein, A., DePeralta, D., … McIntyre, R. S. (2018). Factors that impact treatment decisions: Results from an online survey of individuals with bipolar and unipolar depression. The Primary Care Companion for CNS Disorders, 20(6), 18m02340. doi: 10.4088/PCC.18m02340. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rowland, T. A., & Marwaha, S. (2018). Epidemiology and risk factors for bipolar disorder. Therapeutic Advances in Psychopharmacology, 8(9), 251–269. doi: 10.1177/2045125318769235 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajatovic, M., Bauer, M. S., Kilbourne, A. M., Vertrees, J. E., & Williford, W. (2006). Self-reported medication treatment adherence among veterans with bipolar disorder. Psychiatric Services (Washington, D.C.), 57(1), 56–62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajatovic, M., Ignacio, R. V., West, J. A., Cassidy, K. A., Safavi, R., Kilbourne, A. M., & Blow, F. C. (2009). Predictors of nonadherence among individuals with bipolar disorder receiving treatment in a community mental health clinic. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 50(2), 100–107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sajatovic, M., Levin, J., Fuentes-Casiano, E., Cassidy, K. A., Tatsuoka, C., & Jenkins, J. H. (2011). Illness experience and reasons for nonadherence among individuals with bipolar disorder who are poorly adherent with medication. Comprehensive Psychiatry, 52(3), 280–287. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Salzmann-Erikson, M., & Sjodin, M. (2018). A narrative meta-synthesis of how people with schizophrenia experience facilitators and barriers in using antipsychotic medication: Implications for healthcare professionals. International Journal of Nursing Studies, 85, 7–18. doi: S0020-7489(18)30115-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott, J., & Pope, M. (2002). Self-reported adherence to treatment with mood stabilizers, plasma levels, and psychiatric hospitalization. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 159(11), 1927–1929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, S., Kumar, N., Chakraborti, S., Sinha, S., Kumari, S., & Gajendragad, J. M. (2012). Prevalence and factors associated with medication compliance in Indian patients suffering from mental disorders. Tropical Doctor, 42(1), 28–31. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stentzel, U., van den, B. N., Schwaneberg, T., Radicke, F., Hoffmann, W., Schulze, L. N., … Langosch, J. M. (2018). Predictors of medication adherence among patients with severe psychiatric disorders: Findings from the baseline assessment of a randomized controlled trial (TECLA). BMC Psychiatry, 18(1), 155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strakowski, S. M., Keck, P. E., Jr, McElroy, S. L., West, S. A., Sax, K. W., Hawkins, J. M., … Bourne, M. L. (1998). Twelve-month outcome after a first hospitalization for affective psychosis. Archives of General Psychiatry, 55(1), 49–55. doi: 10.1001/archpsyc.55.1.49. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teter, C. J., Falone, A. E., Weiss, R. D., Bakaian, A. M., Tu, C., & Ongur, D. (2011). Medication adherence and attitudes in patients with bipolar disorder and current versus past substance use disorder. Psychiatry Research, 190(2), 253–258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, K., Kulkarni, J., & Sergejew, A. A. (2000). Reliability and validity of a new medication adherence rating scale (MARS) for the psychoses. Schizophrenia Research, 42(3), 241–247. doi: S0920-9964(99)00130-9 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torres-Robles, A., Wiecek, E., Tonin, F. S., Benrimoj, S. I., Fernandez-Llimos, F., & Garcia-Cardenas, V. (2018). Comparison of interventions to improve long-term medication adherence across different clinical conditions: A systematic review with network meta-analysis. Frontiers in Pharmacology, 9, 1454. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01454 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- The UCL Centre for Behaviour Change. (2019). The behaviour change taxonomy v1. Retrieved May 5, 2020, from https://www.bct-taxonomy.com/interventions.
- Vargas-Huicochea, I., Huicochea, L., Berlanga, C., & Fresan, A. (2014). Taking or not taking medications: Psychiatric treatment perceptions in patients diagnosed with bipolar disorder. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics, 39(6), 673–679. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vazquez, G. H., Holtzman, J. N., Lolich, M., Ketter, T. A., & Baldessarini, R. J. (2015). Recurrence rates in bipolar disorder: Systematic comparison of long-term prospective, naturalistic studies versus randomized controlled trials. European Neuropsychopharmacology: The Journal of the European College of Neuropsychopharmacology, 25(10), 1501–1512. doi: 10.1016/j.euroneuro.2015.07.013 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Velligan, D. I., Weiden, P. J., Sajatovic, M., Scott, J., Carpenter, D., Ross, R., … Expert Consensus Panel on Adherence Problems in Serious and Persistent Mental Illness. (2009). The expert consensus guideline series: Adherence problems in patients with serious and persistent mental illness. The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 70(Suppl 4), 1–46. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieta, E., Azorin, J. M., Bauer, M., Frangou, S., Perugi, G., Martinez, G., & Schreiner, A. (2012). Psychiatrists' perceptions of potential reasons for non- and partial adherence to medication: Results of a survey in bipolar disorder from eight European countries. Journal of Affective Disorders, 143(1–3), 125–130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss, R. D., Greenfield, S. F., Najavits, L. M., Soto, J. A., Wyner, D., Tohen, M., & Griffin, M. L. (1998). Medication compliance among patients with bipolar disorder and substance use disorder. Journal of Clinical Psychiatry, 59(4), 172–174. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Younas, M., Bradley, E., Holmes, N., Sud, D., & Maidment, I. D. (2016). Mental health pharmacists views on shared decision-making for antipsychotics in serious mental illness. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy, 38(5), 1191–1199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeber, J. E., Copeland, L. A., Good, C. B., Fine, M. J., Bauer, M. S., & Kilbourne, A. M. (2008). Therapeutic alliance perceptions and medication adherence in patients with bipolar disorder. Journal of Affective Disorders, 107(1–3), 53–62. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
For supplementary material accompanying this paper visit https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291721001446.
click here to view supplementary material
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author, AP, upon a reasonable request.