Abstract
The transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1 (TRPV1) is a transmembrane protein that can be activated by various physical and chemical stimuli and is associated with pain transduction. In recent years, TRPV1 was discovered to play essential roles in cancer tumorigenesis and development, as TRPV1 expression levels are altered in numerous cancer cell types. Several investigations have discovered direct associations between TRPV1 and cancer cell proliferation, cell death, and metastasis. Furthermore, about two dozen TRPV1 agonists/antagonists are under clinical trial, as TRPV1 is a potential drug target for treating various diseases. Hence, more researchers are focusing on the effects of TRPV1 agonists or antagonists on cancer tumorigenesis and development. However, both agonists and antagonists may reveal anti-cancer effects, and the effect may function via or be independent of TRPV1. In this review, we provide an overview of the impact of TRPV1 on cancer cell proliferation, cell death, and metastasis, as well as on cancer therapy and the tumor microenvironment, and consider the implications of using TRPV1 agonists and antagonists for future research and potential therapeutic approaches.
Keywords: TRPV1, proliferation, cell death, metastasis, therapy, microenvironment.
Introduction
Cancer is increasingly recognized as a serious public health concern worldwide; however, the mechanisms of tumorigenesis and development are complex and not well understood. The transformation from normal cells to cancer cells is caused by numerous alterations in various signaling pathways, which lead to enhanced cell proliferation, inhibition of programmed cell death, migration, and invasion.
Many proteins in cancer cells exhibit enhanced or reduced expression levels compared with the levels in normal cells, and these proteins play important roles in tumorigenesis and development. The recently identified transient receptor potential (TRP) channels are subject to expression changes in cancer cells 1, 2. So far, the most studied members of the family have been TRPC1, TRPV6, TRPM1, and TRPM8 3. However, in the previous two decades, researchers have shown an increased interest in TRP subfamily V member 1 (V1), as it appears to play multiple roles in cancer 4, 5. Alterations in both the expression and activity of TRPV1 are associated with tumorigenesis and therapy. The activation of the cation channel TRPV1 by heat and small molecules permeabilizes cells to allow Ca2+ and Na+ influx 6. A considerable amount of literature has been published on the effects of TRPV1 agonists and antagonists on tumorigenesis and development.
In this review, we summarize the observations reported to date of the changes in TRPV1 expression and channel activity associated with cancers and the effects of these alterations on cancer cell proliferation, death, and metastasis, and the tumor microenvironment. We further discuss the therapeutic potential of targeting TRPV1 in cancer cells. To comprehensively understand the effects of TRPV1 activation on proliferation, cell death, metastasis, and therapy, we provide tables detailing the investigations reviewed so far regarding relevant drug applications, drug concentrations, tissue/cell types, and their effects on the treatment of tumors.
What is TRPV1
The human TRPV1 protein is encoded by the TRPV1 gene located on chromosome 17p13. TRPV1 belongs to the transient receptor potential channel vanilloid subfamily and is also known as the capsaicin receptor and vanilloid receptor 1 (VR1). TRPV1 predominantly forms a homotetramer, with each subunit consisting of six transmembrane segments, a pore-forming loop between the fifth and sixth transmembrane domains, and cytoplasmic C- and N-terminal domains 7-10. Initially, TRPV1 was found to be expressed prominently in small-to-medium-sized neurons of the dorsal root, trigeminal, and vagal ganglia 8, 11, and was discovered to be involved in pain transduction 12. Later, TRPV1 expression was reported in non-neuronal system cells, such as arteriolar smooth muscle cells 13, 14 and the bladder urothelium 15. TRPV1 is a nonselective cation channel that can be activated by different physical and chemical stimuli, including temperatures over 43°C, acidic conditions (pH <6), and vanilloids 8, 9, 16. The activation of TRPV1 induces the cellular influx of Ca2+ and Na+ ions 17-19, and the excess intracellular Ca2+ and Na+ leads to cell death 20. Numerous putative endogenous and exogenous agonists and antagonists of TRPV1 have been identified and summarized (Table 1). Because TRPV1 is a promising therapeutic target in many human diseases and conditions 21, 22, about two dozen TRPV1 agonists/antagonists are being used in clinical trials, many of which are concerned with pain and inflammation 23, 24.
Table 1.
Endogenous and exogenous ligands of TRPV1.
| Ligands | Ref. |
|---|---|
| Endogenous agonists: | |
| Anandamide | 25 |
| N-arachidonoyldopamine | 26 |
| N-oleoyldopamine | 27 |
| R(+)-methanandamide | 25 |
| 12- and 15-hydroperoxyeicosatetraenoic acid | 28 |
| 5- and 15-hydroxyeicosatetraenoic acid | 28 |
| Leukotriene B4 | 28 |
| 9- and 13-hydroxy-octadecadienoic acid | 12 |
| 9- and 13-oxo-octadecadienoic acid | 12 |
| Oleoylethanolamide | 29 |
| Palmitoylethanolamide | 30 |
| Lysophosphatidic acid | 31 |
| Oxytocin | 32 |
| Exogenous agonists | |
| 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate | 33 |
| 4α-phorbol-12,13-didecanoate | 34 |
| Ornithoctonus huwena toxin ['double-knot' toxin (DkTx)] | 35 |
| Capsaicin | 8 |
| Piperine | 36 |
| Resiniferatoxin | 37 |
| Gingerol | 38 |
| Evodiamine | 39 |
| Cannabidiol | 40 |
| Cannabigerol | 41 |
| Polygodial | 42 |
| Vanillotoxin | 43 |
| MD-652 | 44 |
| Linopirdine | 45 |
| Endogenous antagonists | |
| Resolvin D2 | 46 |
| Noradrenaline | 47 |
| Exogenous antagonists | |
| Capsazepine | 48 |
| Iodo-resiniferatoxin | 49 |
| Hypericum perforatum | 50 |
| JNJ-17203212 | 51 |
| BCTC | 52 |
| Thapsigargin | 53 |
| Yohimbine | 54 |
| JYL 1421 | 55 |
| Caffeic acid | 56 |
| Asivatrep | 57 |
| SB-366791 | 58 |
| A-1165442 | 59 |
| AMG 9810 | 60 |
| AG489, AG505 | 61 |
| ABT-102, AMG-517, AZD-1386, DWP-05195, GRC-6211, JTS-653, MK-2295, PHE377, SB-705498 | 62, 63 |
Expression of TRPV1 in cancers
TRPV1 expression has been reported to be higher in human primary brain tumors than tumor-free brains. Furthermore, its expression positively correlates with the grading of tumors 64. Compared with in a normal pancreas, TRPV1 mRNA expression is significantly upregulated in human pancreatic cancer and chronic pancreatitis 65. Elevated TRPV1 expression has also been verified in squamous cell carcinoma of the human tongue, prostate carcinoma, and breast cancer 66-68. All the above published work indicated that TRPV1 expression is upregulated in cancers.
TRPV1 regulates proliferation
TRPV1 channel activation increases the intracellular Ca2+ concentration, and Ca2+ signaling plays an essential role in cancer cell proliferation, regulation, and survival 69. A few studies have investigated the associations between changes in TRPV1 protein expression and the regulation of cancer cell proliferation. The majority of studies focused on the effects of TRPV1 agonists or antagonists on cell proliferation; however, some of these chemicals regulate proliferation independently of TRPV1 because they either play roles in cells without TRPV1 expression or affect other receptors. In this section, we describe the roles and underlying mechanisms of the TRPV1 gene and the effects of TRPV1 agonists and antagonists, both independently of and dependent on TRPV1 and other receptors, on proliferation (Table 2).
Table 2.
Role of TRPV1 in Proliferation.
| Drug | Dose (μM) | Duration (h) | Tissue/Cell Type | Mechanism | Outcomes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Human colorectal cancer HCT116 cells | Overexpression of TRPV1 suppressed EGFR phosphorylation at Y1068 | Proliferation ↓ | 70 | |||
| Trpv1 knockout mice | TRPV1 knockout increased constitutive EGFR Y1068 phosphorylation and PCNA, c-Fos and c-Myc expression levels | Proliferation ↑ | 70 | |||
| Human colorectal cancer HCT116 cells | TRPV1 activation activates calpain and PTP1B, which dephosphorylates EGFR | Proliferation ↓ | 70 | |||
| Human melanoma A2058 and A375 cells | Overexpression of TRPV1 activated p53 and, subsequently, upregulated its downstream target genes p21, PUMA, and mdm2 to induce apoptosis | Proliferation ↓ | 71 | |||
| Human pancreatic cancer cell line, PANC-1 | Overexpression of TRPV1 downregulates EGFR levels by inducing EGFR ubiquitination and degradation | Proliferation ↓ | 72 | |||
| Human skin A431 cells | Overexpression of TRPV1 promotes EGFR ubiquitylation and lysosomal degradation | Proliferation ↓ | 73 | |||
| Capsaicin | 100 | 24 | Human urothelial cancer RT4 cells | Induced cell cycle arrest in G0/G1 phase and apoptosis by activating p53 to upregulate Fas/CD95 in TRPV1-overexpressing cells | Proliferation ↓ | 74 |
| Capsaicin | 50-400 | 24-48 | Human renal carcinoma 786-O cells | Activated p38 and JNK MAPK pathways to induce apoptosis | Proliferation ↓ | 75 |
| Capsaicin | 0.1-20 | 48 | Human prostate tumor androgen-responsive LNCaP cells | Activated PI3K and p44/42 MAPK pathways to suppress ceramide production and increased androgen receptor expression | Proliferation ↑ | 76 |
| Capsaicin | 15 | 96-120 | Human ESCC cell lines Eca109 | Proliferation ↑ | 77 | |
| Capsaicin | 100 | 24 | Human hepatocellular carcinoma PLC/PRF/5 cells | Induced apoptosis by increasing the phosphorylation level of ERK and attenuating STAT3 phosphorylation | Proliferation ↓ | 81 |
| Capsaicin | 20 | 36 | Human prostate tumor androgen-resistant PC-3 cells | Induced apoptosis by producing ROS originating from the mitochondria and decreasing perturbations in the inner transmembrane potential (△Ψm) independently of TRPV1 | Proliferation ↓ | 82 |
| Capsaicin | 100 | 24-72 | Human pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor BON and QGP-1 cells | Disrupted mitochondrial membrane potential and suppressed ATP synthesis to induce apoptosis | Proliferation ↓ | 83 |
| Capsaicin | 75 | 24/48 | Human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE2 and SUNE1 cells | Inhibited MKK3-induced p38 activation | Proliferation ↓ | 84 |
| Capsaicin | 3 | 48/96 | Human breast carcinoma cell line MCF-7 cells | Proliferation ↑ | 90 | |
| Cannabidiol | 10 | 48 | Human breast carcinoma cell line MBA-MD-231 cells | Induced apoptosis via activation of CB2 and TRPV1 to elevate reactive oxygen species | Proliferation ↓ | 78 |
| Cannabidiol | 10 | 24 | Human colon adenocarcinoma cell line Caco-2 cells | Reduced the phosphorylation level of Akt, which was dependent on TRPV1 and CB1 | Proliferation ↓ | 79 |
| Noradrenaline | 100 | 24 | Human prostate tumor androgen-resistant PC-3 cells | Activated both alpha 1D-AR and TRPV1 and, subsequently, elicited the PLC/PKC/ERK pathways | Proliferation ↑ | 80 |
| Cannabigerol | 10 | 24 | Human colon adenocarcinoma cell line Caco-2 cells | Stimulated ROS generation, increased CHOP expression level, and promoted apoptosis | Proliferation ↓ | 85 |
| AEA | 10 | 24-72 | The murine neuroblastoma cell line N1E-115 | Seemed to occur via a lipid raft-dependent mechanism | Proliferation ↓ | 86 |
TRPV1 expression suppresses cell proliferation
The overexpression of TRPV1 in intestinal epithelial HCT116 cells suppressed the phosphorylation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) at Y1068, a receptor that is associated with a variety of pro-proliferative signaling pathways 70. According to the results of in vitro studies, the depletion of Trpv1 in mice led to the constitutive phosphorylation of EGFR at Y1068 and subsequently increased the expression of the oncogenes c-Fos and c-Myc, indicating that TRPV1 is a negative regulator in intestinal tumorigenesis 70. The proliferation of human melanoma A2058 and A375 cells was inhibited after TRPV1 overexpression, as the overexpression induced apoptosis via the calcineurin-ATF3-p53 pathway in these cells 71. It was reported that TRPV1 overexpression prevented the proliferation of human pancreatic cancer PANC-1 cells and human skin carcinoma A431 cells by promoting EGFR ubiquitination and degradation 72, 73. The evidence presented thus far supports the hypothesis that TRPV1 acts to suppress cancer cell proliferation.
TRPV1 agonist capsaicin affects cell proliferation dependent on TRPV1
Ligand-induced autophosphorylation of the EGFR results in phospholipase C (PLC) activation, which cleaves phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2) into diacylglycerol (DAG) and inositol triphosphate (IP3). Then IP3 triggers TRPV1 and Ca2+ influx, which activates calpain and subsequently protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B (PTP1B). PTP1B then dephosphorylates EGFR to inhibit intestinal epithelial HCT116 cell proliferation 70. Amantini et al. found that the capsaicin-induced arrest of the cell cycle in the G0/G1 phase and apoptosis mediated by the ATM-p53 and ATM-Fas/CD95 pathways inhibited the proliferation of human urothelial cancer RT4 cells but not that of TCCSUP, J82, or EJ urothelial cancer cell lines, as TRPV1 showed high expression levels in RT4 cells 74. Furthermore, this antiproliferation effect was completely rescued by capsazepine and SB366791, two antagonists of TRPV1 74. Another study illustrated the capsaicin suppression of human renal carcinoma 786-O cell proliferation, which was also reversed by capsazepine treatment 75. Additionally, capsaicin induced apoptosis by activating the p38 and JNK/MAPK pathways, suppressing proliferation 75. However, the opposite effect of capsaicin on proliferation has also been reported. For example, Malagarie-Cazenave et al. discovered that capsaicin promoted human prostate tumor androgen-responsive LNCaP cell growth by activating the PI3K and p44/42 MAPK pathways to suppress ceramide production as well as increasing androgen receptor (AR) expression 76. The proliferative effect of capsaicin on LNCaP cells was reversed by the TRPV1 antagonists 5-iodo-resiniferatoxin (I-RTX), capsazepine, and SB366791 76. In a similar study, Huang et al. demonstrated that capsaicin treatment promoted the proliferation of human esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) Eca109 cells, and the effect was abolished by the TRPV1 receptor antagonist AMG9810 77. The information detailed in Table 2 indicates that the effect of capsaicin on proliferation is dependent on its concentration: low-dose capsaicin promotes cancer cell proliferation, whereas high-dose capsaicin prevents proliferation.
Some agonists affect cell proliferation via both TRPV1 and other receptors
Some pharmacological regulators activate not only TRPV1 but also other reporters to affect cancer cell proliferation. For instance, cannabidiol prevented the proliferation of human breast cancer MBA-MD-231 cells through the activation of cannabinoid receptor type 2 (CB2) and TRPV1 to elevate intracellular Ca2+ and ROS generation and induce apoptosis 78. The respective CB2 and TRPV1 antagonists SR144528 and I-RTX partially rescued the antiproliferation effect of cannabidiol 78. Similarly, Aviello et al. suggested that cannabidiol reduces the phosphorylation levels of Akt to prevent human colon adenocarcinoma Caco-2 cells growth. This effect was counteracted by the CB1 receptor antagonists rimonabant and AM251 and the TRPV1 receptor antagonist capsazepine 79. Noradrenaline has been shown to induce Ca2+ flux by activating alpha 1D-AR and TRPV1 and, subsequently, eliciting the extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1/2 (ERK1/2), PLC, and PKC pathways to promote the proliferation of human prostate tumor PC-3 cells. This effect was completely reversed by alpha 1D-AR/TRPV1 double-knockdown or treatment with a combination of clopenphendioxan and capsazepine 80.
TRPV1 agonists affect cell proliferation independently of TRPV1
Several research groups have reported TRPV1 agonists affecting cell proliferation in a TRPV1-independent manner. These agonists perform proliferation functions through two mechanisms. Firstly, the chemicals contribute to antiproliferation; for example, in the study carried out by Zhang et al., capsaicin induced apoptosis by increasing ERK phosphorylation and alleviating STAT3 phosphorylation, thus inhibiting the proliferation of a hepatocellular carcinoma cell line (PLC/PRF/5) cells. This was independent of TRPV1 81 because no TRPV1 expression was detected in PLC/PRF/5 or the other hepatocellular carcinoma cell lines (HuH7 and HepG2) 81. Capsaicin suppressed prostate cancer androgen-resistant PC-3 cell proliferation by inducing apoptosis via the production of ROS by the mitochondria and a decrease in perturbations in the inner transmembrane potential (△Ψm), which could not be reversed by capsazepine treatment, indicating TRPV1 was not involved 82. Capsaicin reduced the proliferation of human pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor BON and QGP-1 cells by disrupting the mitochondrial membrane potential and suppressing ATP synthesis to induce apoptosis, which was unaffected by a reduction in TRPV1 expression levels 83. Recently, we found that capsaicin inhibited cell proliferation in nasopharyngeal carcinoma (NPC) CNE2 and SUNE1 cells by directly targeting p38, leading to MKK3-p38 axis blockage, in a TRPV1-independent manner 84.
Secondly, the chemicals play vital roles in proliferation by activating receptors other rather than TRPV1. For example, cannabigerol, an agonist of TRPV1, prevented human Caco-2 cells growth by increasing CHOP mRNA levels and ROS production to stimulate apoptosis 85. This effect was alleviated in TRPM8-knockdown cells but not in cells treated with the TRPV1 antagonist ruthenium red 85. N-arachidonoylethanolamine (anandamide, AEA) inhibited the proliferation of murine neuroblastoma N1E-115 cells, and proliferation was rescued by a lipid raft disruptor, methyl-b-cyclodextrin, but not by the TRPV1 antagonist capsazepine 86.
TRPV1 regulates cell death
Studies have demonstrated that pathological changes in or the pharmacological regulation of TRPV1 expression levels affect cell death. As mentioned in the previous section, TRPV1 overexpression or agonist treatment induces apoptosis, preventing cancer cell proliferation. Therefore, in this section, we focus on the roles of TRPV1 in cell death and provide a summary of the information (Table 3).
Table 3.
Role of TRPV1 in Cell Death.
| Drug | Dose (μM) | Duration (h) | Tissue/cell type | Mechanism | Outcomes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capsaicin | 3 | 48/96 | Human breast carcinoma cell line MCF-7 cells | Activated exogenous TRPV1 and, subsequently, upregulated c-Fos and necrotic marker RIP3 | Necrosis | 90 |
| Capsaicin | 150 | 24 | Human osteosarcoma G292 cells | Activated endoplasmic reticulum TRPV1 and induced cytochrome C release | Apoptosis | 92 |
| Capsaicin | 10 | 72 | Human breast cancer MCF-7 cells | Stimulated ROS production and mitochondrial membrane depolarization | Apoptosis | 93 |
| Capsaicin | 150 | 48 | Human breast cancer SUM149PT cells | Activated TRPV1 | Apoptosis Necrosis |
68 |
| Capsaicin | 100 | 72 | Human Methylcholanthrene-induced fibrosarcoma Meth A cells | Decreased Fas-associated factor1 (FAF1) expression level | Apoptosis | 97 |
| Capsaicin | 50 | 36 | Human small cell lung cancer H69, DMS 114, DMS 53, and H82 cells | Activated TRPV6 and, subsequently, induced calpain-1 and calpain-2 activation | Apoptosis | 98 |
| Capsaicin | 50 | 1/6/24 | Human gastric cancer AGS cells | Disrupted mitochondrial integrity, activated JNK and, thus, led to TRPV6-mediated p53 stabilization | Apoptosis | 99 |
| Capsaicin | 37.5/75 | 24/48 | Human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE2 and SUNE1 cells | Inhibited p38 phosphorylation mediated by MKK3 | Apoptosis | 84 |
| Capsaicin | 150 | 24 | Human oral squamous cell carcinoma HSC3, SCC4 and SCC25 cells | Cell death | 102 | |
| Arachidonyl ethanolamide | 30 | 48 | Human uterine cervix cancer C299, Caski, and HeLa cells | Activated TRPV1 | Apoptosis | 91 |
| Anandamide/ cannabidiol | 50/25 | 48 | Human endometrial cancer Ishikawa cells | Activated TRPV1 to increase intracellular calcium levels | Apoptosis | 94 |
| Anandamide | 10 | 24 | Human cutaneous melanoma A375 cells | A complex mechanism comprising CB1 activation, COX-2, and LOX-derived product synthesis | Apoptosis | 95 |
| Anandamide | 20 | 4 | The murine squamous carcinoma cell line JWF2 and human colorectal cancer cell line, HCA-7 Colony 29 | Induced oxidative stress and ER-stress apoptosis | Apoptosis | 96 |
| MRS1477 | 2 | 72 | Human breast cancer MCF-7 cells | Stimulated ROS production and mitochondrial membrane depolarization | Apoptosis | 93 |
| R(+)-methanandamide (MA) | 10 | 24-72 | Human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells | Increased COX-2 expression and activity | Apoptosis | 100 |
| Resiniferatoxin | 20 | 24 | Human bladder cancer T24 and 5637 cells | Induced mitochondrial dysfunction | Necrosis | 101 |
| Capsazepine | 30 | 24 | Human oral squamous cell carcinoma HSC3, SCC4 and SCC25 cells | Stimulated ROS production | Apoptosis | 102 |
TRPV1 expression affects cell death
In 2018, Yang et al. published a paper in which they described the overexpression of TRPV1 inducing a pro-apoptotic effect mediated by p53 activation 71. In 2016, Pecze and co-workers demonstrated that the ectopic expression of TRPV1 in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells led to apoptosis 87. The overexpression of fibulin‐5, a multifunctional extracellular matrix (ECM) protein encoded by the FBLN5 gene, induced apoptosis in human colorectal cancer HT‐29 and SW480 cells by enhancing the phosphorylation of p38 and ERK and alleviating the level of p‐Akt by downregulating TRPV1 88. These studies indicate that TRPV1 can promote or inhibit cell death in a cancer- or tissue-specific manner.
TRPV1 agonists affect cell death dependent on TRPV1
Apoptotic or necrotic cell death can be triggered by calcium influx 89. A large body of evidence shows the Ca2+-channel-activating function of TRPV1 evoked by its agonists is responsible for these chemically induced cell deaths. The overexpression of TRPV1 in human breast cancer MCF-7 cells has been reported to have no effect on cell numbers; however, the increased expression of exogenous TRPV1 meant that necrosis was more effectively induced by the capsaicin activation of TRPV1 and the subsequent upregulation of c-Fos and the necrotic marker RIP3 90. Arachidonyl ethanolamide induced apoptosis in human uterine cervix cancer C299, Caski, and HeLa cells, and this was reversed by capsazepine 91. Capsaicin induced apoptosis in human osteosarcoma G292 cells by activating endoplasmic reticulum TRPV1, which led to cytochrome C release 92. TRPV1 agonists, capsaicin and MRS1477, stimulated ROS production and mitochondrial membrane depolarization to induce apoptosis, which was blocked by capsazepine 93. In human endometrial cancer Ishikawa cells, AEA and cannabidiol caused apoptosis by activating TRPV1 to increase intracellular Ca2+ levels 94. Capsaicin also induced apoptotic and necrotic cell death in human breast cancer SUM149PT cells, and the reduction in cell viability mediated by capsaicin was diminished by capsazepine treatment 68. Taken together, it appears agonists of TRPV1, such as capsaicin, arachidonyl ethanolamide, MRS1477, AEA and cannabidiol, induce cell death by activating TRPV1 channels.
TRPV1 agonists and antagonists affect cell death independently of TRPV1
In contrast, several studies have revealed that certain TRPV1 pharmacological regulators trigger cell death independently of TRPV1. For example, the induction of apoptosis in human cutaneous melanoma A375 cells by the TRPV1-activator AEA was completely counteracted by methyl-β-cyclodextrin, a membrane cholesterol depletory, but not by capsazepine 95. A similar effect was observed in non-melanoma skin cancer and colorectal cancer 96. Capsaicin treatment induced apoptosis in methylcholanthrene-induced fibrosarcoma Meth A cells, and this could not be inhibited by the antagonists capsazepine and I-RTX 97. Capsaicin induced apoptosis in human small cell lung cancer H69, DMS 114, DMS 53, and H82 cells by activating TRPV6 and, subsequently, inducing calpain-1 and calpain-2 activity. However, this pro-apoptotic effect was not abolished by the TRPV1 antagonist SB366791 98. Another report showed capsaicin-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer AGS cells was mediated by TRPV6 rather than TRPV1 99. Our recent results also indicate that capsaicin promoted apoptosis in NPC CNE2 and SUNE1 cells by inhibiting MKK3-induced p38 activation in a TRPV1-independent manner 84. R(+)-methanandamide (MA) treatment increased COX-2 and PPARγ activity and induced the apoptosis of human cervical carcinoma HeLa cells, an effect that was unaltered by capsazepine 100. The promotion of necrosis by resiniferatoxin was associated with mitochondrial dysfunction and was not reversed by I-RTX 101. Furthermore, Gonzales et al. illustrated that both capsaicin and capsazepine induce cell death independently of TRPV1 in oral squamous cell carcinoma HSC3, SCC4, and SCC25 cells 102.
TRPV1 regulates cancer metastasis
Metastasis, which is one of the major causes of cancer-related deaths, requires two early events: migration and invasion 103. Recently, calcium signaling was found to be closely related to carcinogenesis and metastasis 104-106, yet only a few reports mention the role of TRPV1 in cancer cell metastasis. As TRPV1 serves as the main Ca2+-influx channel, it is reasonable to suggest that TRPV1 could act as an enhancer or inhibitor of migration and invasion in a tissue- or cell-specific manner.
TRPV1 agonists and antagonists affect cell migration dependent on TRPV1
Few published reports describe the direct impact of altering TRPV1 expression on cancer cell metastasis. Most of the studies using agonists or antagonists showed an ambiguous effect of TRPV1 channel activity on migration. On the one hand, Vriens et al. and Waning et al. reported that the activation of TRPV1 can be evoked by hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and causes the influx of Ca2+ into HepG2 cells following capsaicin treatment, leading to increased cell migration 107, 108. Another investigation into the pro-migration role of TRPV1 conducted on lymphatic endothelial cells by Nakanishi et al. found TRPV1 functioned as a pH sensor and was activated by an acidic environment, upregulating the expression of IL-8, and therefore promoting cell migration and invasion 109. On the other hand, Ramer et al. reported the activation of TRPV1 by MA did not affect cervix adenocarcinoma (HeLa) cell migration but inhibited cell invasion 110. In addition, a recent study by Xu et al. focusing on the function of capsaicin in papillary thyroid carcinoma BCPAP cells showed that capsaicin inhibited cell migration in a TRPV1-dependent manner 111. It is interesting that the activation of TRPV1 can lead to both cell death and increased migration. One possible explanation is that the concentrations of most of the agonists used in the pro-apoptosis/necrosis studies were at micromolar levels, and the treatment duration was usually 24 hours. In contrast, the concentrations of agonists used in the pro-migration studies were at nanomolar levels, or the treatment was provided over a short period (Tables 3 and 4). Although the exact mechanism is unclear, one suggestion is that the treatments differentially altered the levels of Ca2+ influx, which led to opposing effects.
Table 4.
Role of TRPV1 in Metastasis.
| Drug | Dose | Duration | Tissue/cell type | Mechanism | Outcomes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capsaicin | 10 μM | 400 s | Hepatoblastoma HepG2 cell | HGF evoked TRPV1 channel activity, causing Ca2+ influx | Migration ↑ | 107 |
| Capsaicin | 100 nM | 5 h | HGF pretreated hepatoblastoma HepG2 (20 ng/mL for 24 h) cells | HGF evoked TRPV1 channel activity, causing Ca2+ influx | Migration ↑ | 108 |
| Capsaicin | 25/50/100 μM | 24/48 h | Human papillary thyroid carcinoma BCPAP cells | Capsaicin downregulated Tiwst1, Snail1, MMP2, and MMP9 and upregulated E-cadherin | Migration ↓ Invasion ↓ |
111 |
| Capsaicin | 100 μM | 24 h | Urothelial cancer 5637 cells (null-TRPV1) | Capsaicin treatment induced more aggressive gene expression, e.g., MMP1, MMP9, and S100A4 | invasion ↑ | 115 |
| Capsaicin | 25/37.5/75 μM | 48 h | Human nasopharyngeal carcinoma CNE2 and SUNE1 cells | Capsaicin directly targeted p38 and blocked the MKK3-p38 axis | Migration ↓ Invasion ↓ |
84 |
| 4α-PDD | 1 μM | 5 h | HGF pretreated hepatoblastoma HepG2 ( 20 ng/mL for 24 h) cells | HGF evoked TRPV1 channel activity, causing Ca2+ influx | Migration ↑ | 108 |
| Primary human adult dermal LECs (HDLECs) incubated with pH-6.4 starvation medium | Acidic environment elicited TRPV1 activation, which upregulated IL-8 expression | Migration ↑ | 109 | |||
| MA | 10 μM | 72 h | Cervix adenocarcinoma HeLa cells | MA elicited TRPV1 activation and upregulated TIMP-1 expression via MAPK pathway, causing decrease in MMP2 | Invasion ↓ | 110 |
| Cannabidiol | 3 μM | 72 h | Human lung cancer A549, H358, and H460 cells | CBD elicited TRPV1 activation, upregulated ICAM1 expression via phosphorylating p42/44, and subsequently upregulated TIMP-1 | Migration ↓ Invasion ↓ |
114 |
| AM404 | 5/15/25 μM | 24 h | Neuroblastoma cells SK-N-SH | AM404 inhibited NFAT transcriptional activity, thus, downregulating MMP1, MMP2, and MMP7 | Migration ↓ Invasion ↓ |
116 |
| Bortezomib | 10 nM | 24 h | Osteosarcoma HOS cell | Inhibited TRPV1 degradation | Invasion ↓ | 117 |
TRPV1 affects cell invasion
Unlike its effect on migration, the effect of TRPV1 on cancer cell invasion has been relatively well characterized and studied, and TRPV1 is believed to function as an invasion repressor. In 2005, Lazzeri et al. showed TRPV1 protein expression levels in urothelial cancer (UC) progressively decreased over progressive cancer metastasis stages 112. In the same vein, Kalogris et al. found this reduction to be not only translational but also transcriptional in UC. They also showed TRPV1 expression was positively related to survival rate, suggesting TRPV1 could be used as a factor for estimating the prognosis 113.
Evidence suggests TRPV1 may regulate the ECM, which plays a critical role in cell metastasis 12, 13 and, thus, the regulation of cell invasiveness. Ramer et al. demonstrated that the TRPV1 agonist MA can inhibit cell invasion in HeLa cells by inducing the expression of tissue inhibitor of MMPs (TIMP)-1 and, thereby, downregulating MMP2, in a TRPV1 dependent manner 110. In a later study, the same group found that intercellular adhesion molecule-1 (ICAM1) was upregulated by cannabidiol-elicited TRPV1-activation-mediated p42/44 activation in lung cancer cell lines A549, H358, and H460, subsequently inhibiting cell invasion 114. Additionally, Xu et al. showed capsaicin-elicited TRPV1 activation downregulated Twist1, Snail1, MMP2, and MMP9 expression and upregulated E-cadherin expression, thereby inhibiting cell invasion by papillary thyroid carcinoma BCPAP cells 111.
TRPV1 agonists and antagonists affect cell migration independently of TRPV1
Investigations into TRPV1 commonly focus on the effects of treatment with agonists, e.g., capsaicin and cannabinoids, or antagonists such as capsazepine and AM404. However, the effects on metastasis either from TRPV1 activity alteration or the actions of agonists and antagonists should be interpreted with caution because of the reports of TRPV1 agonists and antagonists regulating cell migration and invasion in a TRPV1-independent manner. For instance, Caprodossi et al. found capsaicin promoted the more aggressive expression of genes, such as MMP1, MMP9, and S100A, and the invasiveness of null-TRPV1 urothelial cancer 5637 cells 115. Whereas, in NPC, we found capsaicin inhibited cell mobility by blocking MKK3-induced p38 activation in a TRPV1-independent manner 84. Caballero et al. reported AM404, an antagonist of TRPV1 and CB1, inhibited NFAT transcriptional activity and, thus, downregulated MMP1, MMP2, and MMP7 in neuroblastoma SK-N-SH cells via a mechanism unrelated to TRPV1 116. Furthermore, a recent investigation conducted by Punzo et al. reported JWH133 and resiniferatoxin enhanced the antiproliferation, anti-invasion, and apoptosis effects of bortezomib (BTX), a selective, reversible proteasome inhibitor, in osteosarcoma cells. However, this report does not include direct evidence to show if the synergism was exerted by BTX-mediated TRPV1 upregulation or if the TRPV1 upregulation was an unrelated effect of BTX 117.
TRPV1 affects cancer therapy
TRPV1 agonists and antagonists affect cancer therapy dependent on TRPV1
To date, there has been some evidence associating TRPV1 expression with the efficiency of radiotherapy and chemotherapy, and several investigators have published the impact of TRPV1 agonists and antagonists on these treatments. In 2016, Nishino et al. reported that pretreatment with the TRPV1 channel inhibitors capsazepine, SB366791, AMG9810, and BCTC suppressed repair of γ-ray-induced-DNA-damage in human lung cancer A549 cells, indicating TRPV1 antagonists may serve as radiosensitizers, enhancing the efficacy of radiation therapy 118. Although there is no strong evidence that these chemicals impact the effectiveness of radiotherapy through TRPV1, Masumoto et al. demonstrated that depletion of TRPV1 suppressed the degree of DNA damage induced by γ-irradiation and UVB irradiation 119. Therefore, it is likely TRPV1 is involved in DNA-damage responses induced by radiotherapy. However, not all the effects and mechanisms have been clarified.
There are many pharmacological regulators of TRPV1, and several studies have focused on the roles of TRPV1 agonists/antagonists in chemotherapy (Table 5). The toxicity of cisplatin on breast cancer MCF-7 cells was found to be increased by TRPV1-channel activation by alpha-lipoic acid (ALA), the effect of which was reversed by the TRPV1 blocker capsazepine 120. Capsaicin increased the antiproliferative effects of pirarubicin, a major drug used in urinary bladder instillation chemotherapy, and the effect was reversed by capsazepine treatment 121. In human breast cancer MCF-7 cells, doxorubicin treatment activated TRPV1, resulting in increased intracellular Ca2+, which was reversed by the TRPV1 antagonist melatonin. Furthermore, a combination of doxorubicin and melatonin treatment led to higher apoptosis levels than doxorubicin treatment 122. TRPV1 was also activated by 5-fluorouracil, inducing apoptosis; however, 5-fluorouracil toxicity was downregulated by the TRPV1-channel inhibitor Hypericum perforatum in breast cancer MCF-7 cells 123. The TRPV1 agonist resiniferatoxin enhanced the antiproliferation effect of BTX in human osteosarcoma HOS cell lines by aggravating apoptosis 117. The above-described cases indicate that TRPV1 agonists and chemotherapeutic agents may have synergic effects in cancer therapy. Nevertheless, the roles of TRPV1 antagonists in cancer therapy are controversial.
Table 5.
Role of TRPV1 in Cancer Therapy.
| Drug | Dose (μM) | Duration (h) | Tissue/cell type | Mechanism | Outcomes | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Capsaicin | 100 | 24 | Human hepatocellular carcinoma PLC/PRF/5 cells | Induced apoptosis by increasing phosphorylation levels of ERK and attenuating STAT3 phosphorylation | Increased antitumor sensitivity of sorafenib | 81 |
| Capsaicin | 150 | 12 | Human bladder transitional cell carcinoma 5637 cells | Inhibited PCNA translocation to the nucleus | Increased antitumor efficacy of pirarubicin | 121 |
| Capsazepine | 10 | 6 | Human colorectal cancer HCT116 cells | Mediated induction of expression of death receptors DR4 and DR5 via ROS-JNK-CHOP pathway, downregulated the expression of cell survival proteins, and upregulated the expression of proapoptotic proteins | Increased antitumor activity of TRAIL | 125 |
| Capsazepine/SB366791/AMG9810/BCTC | 10 | 0.5 | Human lung cancer A549 cells | Enhanced cell death induced by γ-rays | 118 | |
| Alpha-lipoic acid | 50 | 24 | Human breast carcinoma cell line MCF-7 cells | Induced apoptosis via activation of TRPV1 | Increased antitumor sensitivity of cisplatin | 120 |
| Melatonin | 300 | 2 | Human breast carcinoma cell line MCF-7 cells | Increased apoptosis induced by doxorubicin | Increased antitumor sensitivity of doxorubicin | 122 |
| Hypericum perforatum | 300 | 24 | Human breast carcinoma cell line MCF-7 cells | Downregulated apoptosis induced by 5-fluorouracil | Decreased antitumor sensitivity of 5-fluorouracil | 123 |
TRPV1 agonists and antagonists affect therapy independently of TRPV1
Several reports show that TRPV1 agonists/antagonists alter the sensitivity of chemotherapeutic agents without stimulating TRPV1. For instance, sorafenib is the standard systemic chemotherapy drug for the treatment of advanced hepatocellular carcinoma 124; capsaicin enhanced the antitumor sensitivity of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma PLC/PRF/5 cells without obvious TRPV1 expression 81. Capsazepine amplified the antitumor activity of tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand (TRAIL) through multiple mechanisms, including promoting the expression of the death receptors DR4 and DR5 via the ROS-JNK-CHOP pathway; downregulating the expression of cell survival proteins cFLIP, survivin, Bcl-xL, Bcl-2, and cIAP-1; and upregulating the expression of proapoptotic proteins Bax and p53 125. However, these effects did not involve TRPV1 125.
TRPV1 regulates tumor microenvironment
Tumors are not just a simple collection of cancerous cells, rather they are a complex of tumor cells and their interactions with the surrounding cells, forming the tumor microenvironment (TME). Recent reviews have indicated TME is an important mediator in cancer progression and is mainly composed of (a) ECM, which provides structural and nutritional support for tumor development; (b) tumor vasculature, which carries oxygen and nutrients to tumor cells and a provides a “highway” for metastasis; (c) cancer-associated fibroblasts, which contribute to tumor proliferation and metastasis, as well as regulating the formation of ECM; and (d) the immune system, which plays a critical part in tumor-related inflammation 126-128. The contribution of the important intercellular and intracellular messengers, Ca2+ ions, to the TME has been reviewed elsewhere 105, 129-131. As TRPV1 is a major Ca2+ channel, we summarize the relationships between TRPV1 and TME in the following section.
TRPV1 and cancer-associated fibroblasts
The final outcome of cancer development is not only determined by autonomous cancer cell defects but also by interactions between cancer cells and the TME. Cancer-associated fibroblasts are major components of the tumor stroma, and evidence collated over many years indicates that fibroblasts are key players in cancer development 132, 133. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAF) can be recruited and activated by cancer-secreted growth factors, among which TGF-β is the main factor contributing to their activation 134-136.
Associations between TRPV1 and TGF-β in somatic cells have been reported for many years. For instance, Bodo et al. demonstrated that the activation of TRPV1 by capsaicin upregulated TGF-β2 mRNA and protein expression in human hair follicles through an unknown mechanism 137. This was supported by further studies, which showed expression of TGF-β1 was attenuated in a TRPV1-knock-out animal model 138-140. These findings hint at the possible regulation of TGF-β by TRPV1, yet currently, there is no evidence for correlation or interaction between TRPV1 and TGF-β in cancer. As fibroblasts act as important mediators for other TME components 132, 133, it would be interesting to further investigate the relationship between TRPV1 and TGF-β in cancer cells and cancer-related fibroblasts.
TRPV1 and ECM
ECM is mainly composed of the basement membrane, which primarily comprises collagen, and the interstitial matrix containing proteoglycans and fibrous proteins 141. Hence, TRPV1 is a transmembrane protein that functions as a temperature and pH sensor and a non-selective cation channel; it is unsurprising, therefore, that the ECM and TRPV1 are closely linked. According to previous research, several components of the ECM are able to modulate TRPV1 activity; for instance, extracellular hyaluronan (hyaluronic acid) reduced the excitation of the TRPV1 channel, thereby reducing the activity of peripheral nociceptors 142. Moreover, another ECM protein, fibulin-5, was reported to induce apoptosis in colorectal cancer cells by downregulating TRPV1 expression 88. However, TRPV1 is also capable of regulating ECM proteins, including the main regulators of collagen in ECM matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs), which are highly relevant to the metastatic processes of cancer cells 143, 144. In the immortalized somatic cell, TRPV1 was reported to directly mediate the expression of MMP-1 145, 146, and Huang et al. further elucidated that TRPV1 regulates MMP1 expression via the Ca2+-ERK pathway 147. In the field of oncology, there have been several reports showing that TRPV1 activation in cancer cells regulates MMP activity by modulating the expression of TIMP-1 110, 148. However, there were no details of the mechanisms and signaling pathways involved in the TRPV1-regulation of TIMP-1 expression, and these should be investigated in the future. Moreover, whether TRPV1 regulates other ECM proteins is unclear.
TRPV1 and cancer-associated angiogenesis
During angiogenesis, new blood vessels emerge from the existing vasculature via sprouting, which is vital for oxygen and nutrient transportation and is implicated in cancer metastasis. As early as 1995, the first links between the regulation of angiogenesis and calcium signaling were discovered by Kohn et al., who reported that carboxyamidotriazole (CAI), a non-voltage-operated Ca2+-channel inhibitor, inhibited vascular tube formation on Matrigel and angiogenesis in vivo 149. Faehling et al. further suggested that angiogenesis requires Ca2+ influx; vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) induced Ca2+ influx into human umbilical vein endothelial cells (HUVEC), and adding CAI inhibited the VEGF-elicited Ca2+ influx, inhibiting endothelial cell proliferation 150. There are several detailed reviews available covering Ca2+ signaling and angiogenesis, which are not elaborated on here 151-153.
The process of angiogenesis requires the proliferation and motility of endothelial cells, in which several critical proteins, i.e., VEGF, EGFR, and fibroblast growth factor, play important roles 132, 154-156. Among these, VEGF is considered the most potent factor for endothelial cell proliferation and migration. In the context of cancer, VEGF can be released from tumor cells or the tumor-related ECM and binds to VEGFR1/2 to induce the proliferation of vascular endothelial cells 157. As mentioned above, VEGF is able to induce Ca2+ influx into HUVECs 150. Indeed, VEGF has recently been reported to mediate Ca2+ influx by transactivating the channel function of TRPV1. In addition, VEGF secreted by human uveal melanoma cells transactivates TRPV1 function, causing intracellular Ca2+ influx into endothelial cells, which is essential for angiogenesis 158. Interestingly, Su et al. showed Ca2+ influx by simvastatin elicited TRPV1 activation of the AKT signal, which subsequently activated calcium-calmodulin kinase II (CaMKII) and eNOS, leading to angiogenesis 159. VEGF transactivation of TRPV1 might share a similar pathway, although more experimental data is needed to support this hypothesis.
Whether TRPV1 activity regulates the expression and function of VEGF and its receptor is still largely unknown; however, hints have been provided by animal models. Vinuesa et al. showed that Trpv1 -/- mice were more vulnerable to dextran-sodium-sulfate-induced colon cancer 160. Their investigation demonstrated that the NF-kB and STAT3 signal pathways were hyperactivated in Trpv1 -/- mice, resulting in the upregulation of a group of inflammatory factors, including IL-1 and IL-6, and invasion factors such as MMP9, which subsequently enhanced the carcinogenesis 160. NF-kB and STAT3 are known to be regulators of VEGF in several cancers 161-163 and may be involved in the regulation of VEGF expression by TRPV1.
TRPV1 in inflammation and leukocytes
A considerable fraction of TME components is associated with inflammation and leukocyte activities. Cytokines released from tumor cells and TME components attract immune cells and trigger inflammation. Several systematic reviews have pointed out that inflammation contributes to tumorigenesis and helps to shape tumor progression, and modulating immune factors in the TME is a promising therapeutic approach for cancer treatment 164-166. The characteristics of inflammation include heat and pain, and, because TRPV1 functions as a nociceptor, it may be highly relevant to this area of research.
TRPV1 is involved in key immune cell functions, and Ca2+ signaling is important for lymphocyte activation and differentiation 167, 168. The functional expression of TRPV1 in mouse and human CD4+ T-cells was described by Bertin et al., who showed NFAT and NFκB, two key transcription factors of immune cell activation, were less expressed in the nuclear fraction of CD4+ T-cells isolated from Trpv1 knockout mice. This resulted in the reduced production of proinflammatory cytokines and indicated that TRPV1 is necessary for proper downstream T-cell signaling 169. Moreover, TRPV1 was also shown to be expressed in dendritic cells (DCs), which are pivotal in antigen presentation and lymphocyte activation. Notably, the administration of capsaicin induced the maturation of DCs in Trpv1 +/+ mice but not in Trpv1 -/- mice 170.
TRPV1 was also reported to be a modulator for inflammatory cytokines, although the exact regulatory network for TRPV1-inflammation is unclear. Okada et al. showed the expression of several pro-inflammation cytokines, such as MCP-1 and IL-6, was suppressed during the healing of eye injury in Trpv1 -/- mice, and they suggested that TRPV1 may serve a pro-inflammatory role 138. However, the story is completely reversed in cancer. In the AOM/DSS-induced colon cancer mouse model, several pro-inflammation factors, including IL-6 and IL-11, were found to be upregulated 160. Further research demonstrated that Trpv1-deficient mice exhibited hyperactivation of the STAT and NFκB signal pathways; therefore, TRPV1 was believed to exert a protective role in colon cancer 160. The findings of a recent study by Erin were in line with this view, as they showed the activation of TRPV1 by capsaicin downregulated the expression of TNF-a, IL-6, and IL-10 and suppressed lung metastasis in a breast cancer metastasis mouse model 171. However, something that should be brought to the reader's attention is that this study did not rule out the possibility that capsaicin functioned independently of TRPV1. Furthermore, because the above results were based on a TRPV1-deficient animal model, the regulation of inflammatory factors was more likely to be an outcome of systematic changes. Whether TRPV1 regulates the secretion of inflammatory cytokines by cancer cells is not fully understood, and the mechanisms need to be further investigated.
Conclusion
Based on the reviewed evidence, the following conclusions can be drawn. The expression of TRPV1 is elevated in many cancers, and its overexpression suppresses cell proliferation in intestinal, melanoma, and pancreatic cancers and induces apoptosis in melanoma and breast cancers. These findings support the hypothesis that TRPV1 is a tumor-suppressor gene. However, TRPV1 either promotes or inhibits cell death, depending on cancer cell type, implying it has cancer- or tissue-specific functions. Further investigations and experimentations are strongly recommended.
From the current clinical and experimental data, it is likely that TRPV1 serves as a repressor of metastasis, which is in line with its tumor-suppressing role. Whereas the data showing TRPV1 to be a pro-metastasis factor suggest the role of TRPV1 in metastasis may be context-dependent.
As we mentioned, numerous studies have revealed that TRPV1 agonists/antagonists affect cancer proliferation, cell death, and metastasis by activating TRPV1 channels and subsequently increasing the levels of intracellular Ca2+. However, the effects are complex and are determined by the concentration used and treatment duration. Additionally, agonists or antagonists may activate other receptors and, therefore, function in a TRPV1-independent manner. Thus, the effects and mechanisms are unclear, and further studies using combined gene silencing or knockout approaches are needed.
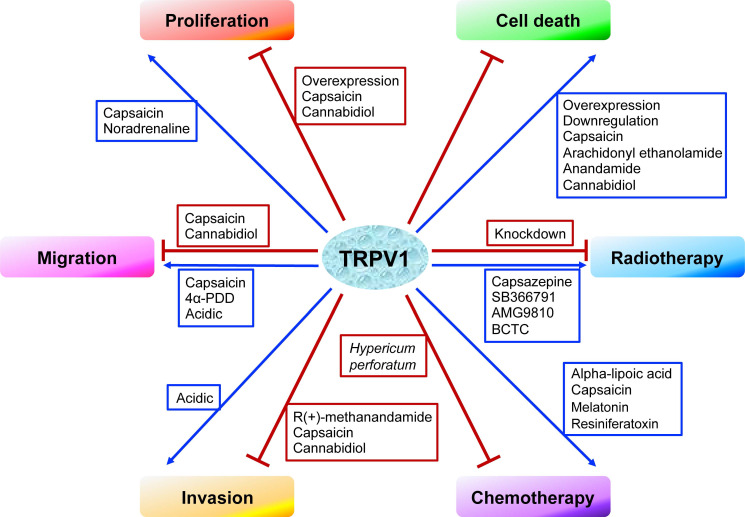
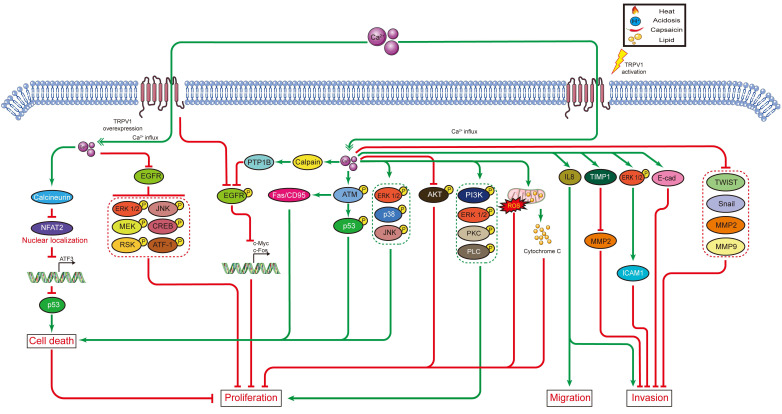
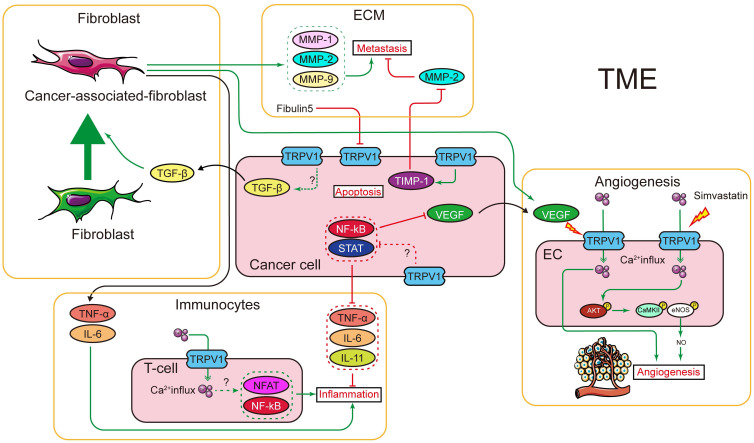
In cancer chemotherapy, the TRPV1 agonist capsaicin has a synergic effect with cisplatin. Nevertheless, capsaicin cannot be systemically administered in large doses, as it induces acute pain and neurological inflammation. In short, current evidence indicates TRPV1 plays certain roles in shaping the TME. However, the signaling networks interacting with TRPV1 have not been fully characterized, and the relationships between TRPV1 and TME need to be further explored. The effects of TRPV1 on cancer cell proliferation, cell death, migration, and invasion, as well as on radiotherapy and chemotherapy, are summarized in Figure 1. Moreover, the TRPV1 signaling pathways in cancer cell proliferation, cell death, migration, and invasion described in this review are summarized in Figure 2. The association between TRPV1 and TME are summarized in Figure 3.
Figure 1.
The effects of TRPV1 on cancer cell proliferation, cell death, migration, invasion, radiotherapy, and chemotherapy.
Figure 2.
TRPV1 signaling pathways in cancer cell proliferation, cell death, migration, and invasion.
Figure 3.
Interaction between TRPV1 and tumor microenvironment. Using transgenic mice, TRPV1 was shown to regulate TGF-β, which is the major factor that activates fibroblasts and transforms the fibroblasts into CAF. The CAF can secret several cytokines and factors, most of which are TME components, e.g., MMPs (regulates collagen in ECM), TNF-α and IL-6 (trigger inflammation), and VEGF (promotes angiogenesis). In cancer cells, TRPV1 was shown to regulate the expression of several inflammation factors, probably through NFκB and STAT signaling pathways. In immunocytes, TRPV1 is important for T-cell signal transduction. Additionally, TRPV1 can regulate the ECM by promoting TIMP-1 expression. In turn, fibulin 5, an ECM component, downregulates TRPV1 expression in cancer cells. Furthermore, TRPV1 was shown to promote angiogenesis by mediating Ca2+ influx and, subsequently, activating the AKT-CaMKII-eNOS signal pathway. The TRPV1 channel function can also be elicited by VEGF, but it is unclear if it shares the same downstream signal.
Finally, a number of important issues need to be considered. Given the fact that TRPV1 also plays several intracellular roles, it remains unclear whether TRPV1 functions independently of its channel activity in cancer progression. Further research with more focus on the role of the TRPV1 gene in tumorigenesis and development using gene overexpression and knockdown (knockout) approaches is therefore suggested.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81802280, 81372149), the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province (2021A1515011046, 2019A1515010210), and the Shenzhen Municipal Government of China (JCYJ20180507182427559, GJHZ20180418190559891). Guangdong Provincial Science and Technology Program (No. 2019B030301009). Shenzhen Key Medical Discipline Construction Fund (No. SZXK060). SZU Top Ranking Project (86000000210).
The authors would like to thank Dr. Jessica Tamanini for editing the manuscript prior to submission. They also thank the members of the Instrumental Analysis Center of Shenzhen University for their support.
Authors' contributions
LL and DZ provided the idea. LL and CC wrote the article. DZ revised the article. CYJ, TX, YCC, and YXZ made suggestions for the article. All authors reviewed the manuscript and approved the final manuscript.
Abbreviations
- TRPV1
transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V, member 1
- TRP
transient receptor potential
- VR1
vanilloid receptor 1
- EGFR
epidermal growth factor receptor
- PLC
phospholipase C
- PIP2
phosphatidylinositol-4,5-bisphosphate
- DAG
diacylglycerol
- IP3
inositol triphosphate
- PTP1B
protein tyrosine phosphatase 1B
- AR
androgen receptor
- I-RTX
5-iodo-resiniferatoxin
- ESCC
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma
- ERK
extracellular signal-regulated kinase
- NPC
nasopharyngeal carcinoma
- AEA
anandamide
- FAF1
Fas-associated factor1
- ECM
extracellular matrix
- MA
R(+)-methanandamide
- HGF
hepatocyte growth factor
- UC
urothelial cancer
- ICAM1
intercellular adhesion molecule-1
- BTX
bortezomib
- ALA
alpha-lipoic acid
- TRAIL
tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing ligand
- TME
tumor microenvironment
- MMP
matrix metalloproteinase
- CAF
Cancer associated fibroblasts
- DC
dendritic cell
- CAI
carboxyamidotriazole
- VEGF
vascular endothelial growth factor
- CaMKII
calcium-calmodulin kinase II
- HUVEC
human umbilical vein endothelial cell
- FGF
fibroblast growth factor
References
- 1.Ramsey IS, Delling M, Clapham DE. An introduction to TRP channels. Annu Rev Physiol. 2006;68:619–47. doi: 10.1146/annurev.physiol.68.040204.100431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Nilius B, Owsianik G, Voets T, Peters JA. Transient receptor potential cation channels in disease. Physiol Rev. 2007;87:165–217. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00021.2006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Shapovalov G, Ritaine A, Skryma R, Prevarskaya N. Role of TRP ion channels in cancer and tumorigenesis. Semin Immunopathol. 2016;38:357–69. doi: 10.1007/s00281-015-0525-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Zhai K, Liskova A, Kubatka P, Busselberg D. Calcium Entry through TRPV1: A Potential Target for the Regulation of Proliferation and Apoptosis in Cancerous and Healthy Cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. 21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 5.So CL, Milevskiy MJG, Monteith GR. Transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V and breast cancer. Lab Invest. 2020;100:199–206. doi: 10.1038/s41374-019-0348-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Bevan S, Quallo T, Andersson DA. Trpv1. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2014;222:207–45. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-54215-2_9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Kedei N, Szabo T, Lile JD, Treanor JJ, Olah Z, Iadarola MJ. et al. Analysis of the native quaternary structure of vanilloid receptor 1. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:28613–9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M103272200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Caterina MJ, Schumacher MA, Tominaga M, Rosen TA, Levine JD, Julius D. The capsaicin receptor: a heat-activated ion channel in the pain pathway. Nature. 1997;389:816–24. doi: 10.1038/39807. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Tominaga M, Caterina MJ, Malmberg AB, Rosen TA, Gilbert H, Skinner K. et al. The cloned capsaicin receptor integrates multiple pain-producing stimuli. Neuron. 1998;21:531–43. doi: 10.1016/s0896-6273(00)80564-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Harteneck C, Plant TD, Schultz G. From worm to man: three subfamilies of TRP channels. Trends Neurosci. 2000;23:159–66. doi: 10.1016/s0166-2236(99)01532-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Helliwell RJ, McLatchie LM, Clarke M, Winter J, Bevan S, McIntyre P. Capsaicin sensitivity is associated with the expression of the vanilloid (capsaicin) receptor (VR1) mRNA in adult rat sensory ganglia. Neurosci Lett. 1998;250:177–80. doi: 10.1016/s0304-3940(98)00475-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Patapoutian A, Tate S, Woolf CJ. Transient receptor potential channels: targeting pain at the source. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2009;8:55–68. doi: 10.1038/nrd2757. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Kark T, Bagi Z, Lizanecz E, Pasztor ET, Erdei N, Czikora A. et al. Tissue-specific regulation of microvascular diameter: opposite functional roles of neuronal and smooth muscle located vanilloid receptor-1. Mol Pharmacol. 2008;73:1405–12. doi: 10.1124/mol.107.043323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Cavanaugh DJ, Chesler AT, Jackson AC, Sigal YM, Yamanaka H, Grant R. et al. Trpv1 reporter mice reveal highly restricted brain distribution and functional expression in arteriolar smooth muscle cells. J Neurosci. 2011;31:5067–77. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6451-10.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Birder LA, Nakamura Y, Kiss S, Nealen ML, Barrick S, Kanai AJ. et al. Altered urinary bladder function in mice lacking the vanilloid receptor TRPV1. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:856–60. doi: 10.1038/nn902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Jordt SE, Tominaga M, Julius D. Acid potentiation of the capsaicin receptor determined by a key extracellular site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:8134–9. doi: 10.1073/pnas.100129497. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Olah Z, Szabo T, Karai L, Hough C, Fields RD, Caudle RM. et al. Ligand-induced dynamic membrane changes and cell deletion conferred by vanilloid receptor 1. J Biol Chem. 2001;276:11021–30. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M008392200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Karai L, Brown DC, Mannes AJ, Connelly ST, Brown J, Gandal M. et al. Deletion of vanilloid receptor 1-expressing primary afferent neurons for pain control. J Clin Invest. 2004;113:1344–52. doi: 10.1172/JCI20449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Pecze L, Blum W, Henzi T, Schwaller B. Endogenous TRPV1 stimulation leads to the activation of the inositol phospholipid pathway necessary for sustained Ca(2+) oscillations. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1863:2905–15. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.09.013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Pecze L, Viskolcz B, Olah Z. Molecular Surgery Concept from Bench to Bedside: A Focus on TRPV1+ Pain-Sensing Neurons. Front Physiol. 2017;8:378. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00378. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Brito R, Sheth S, Mukherjea D, Rybak LP, Ramkumar V. TRPV1: A Potential Drug Target for Treating Various Diseases. Cells. 2014;3:517–45. doi: 10.3390/cells3020517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Feketa VV, Marrelli SP. Induction of therapeutic hypothermia by pharmacological modulation of temperature-sensitive TRP channels: theoretical framework and practical considerations. Temperature (Austin) 2015;2:244–57. doi: 10.1080/23328940.2015.1024383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Basith S, Cui M, Hong S, Choi S. Harnessing the Therapeutic Potential of Capsaicin and Its Analogues in Pain and Other Diseases. Molecules. 2016. 21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 24.Garami A, Shimansky YP, Rumbus Z, Vizin RCL, Farkas N, Hegyi J. et al. Hyperthermia induced by transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV1) antagonists in human clinical trials: Insights from mathematical modeling and meta-analysis. Pharmacol Ther. 2020;208:107474. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Zygmunt PM, Petersson J, Andersson DA, Chuang H, Sorgard M, Di Marzo V. et al. Vanilloid receptors on sensory nerves mediate the vasodilator action of anandamide. Nature. 1999;400:452–7. doi: 10.1038/22761. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Huang SM, Bisogno T, Trevisani M, Al-Hayani A, De Petrocellis L, Fezza F. et al. An endogenous capsaicin-like substance with high potency at recombinant and native vanilloid VR1 receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:8400–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.122196999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Chu CJ, Huang SM, De Petrocellis L, Bisogno T, Ewing SA, Miller JD. et al. N-oleoyldopamine, a novel endogenous capsaicin-like lipid that produces hyperalgesia. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:13633–9. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M211231200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Hwang SW, Cho H, Kwak J, Lee SY, Kang CJ, Jung J. et al. Direct activation of capsaicin receptors by products of lipoxygenases: endogenous capsaicin-like substances. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000;97:6155–60. doi: 10.1073/pnas.97.11.6155. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Ahern GP. Activation of TRPV1 by the satiety factor oleoylethanolamide. J Biol Chem. 2003;278:30429–34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M305051200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Ambrosino P, Soldovieri MV, Russo C, Taglialatela M. Activation and desensitization of TRPV1 channels in sensory neurons by the PPARalpha agonist palmitoylethanolamide. Br J Pharmacol. 2013;168:1430–44. doi: 10.1111/bph.12029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Nieto-Posadas A, Jara-Oseguera A, Rosenbaum T. TRP channel gating physiology. Curr Top Med Chem. 2011;11:2131–50. doi: 10.2174/156802611796904870. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Nersesyan Y, Demirkhanyan L, Cabezas-Bratesco D, Oakes V, Kusuda R, Dawson T. et al. Oxytocin Modulates Nociception as an Agonist of Pain-Sensing TRPV1. Cell Rep. 2017;21:1681–91. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2017.10.063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Hu HZ, Gu Q, Wang C, Colton CK, Tang J, Kinoshita-Kawada M. et al. 2-aminoethoxydiphenyl borate is a common activator of TRPV1, TRPV2, and TRPV3. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:35741–8. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M404164200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Martin E, Dahan D, Cardouat G, Gillibert-Duplantier J, Marthan R, Savineau JP. et al. Involvement of TRPV1 and TRPV4 channels in migration of rat pulmonary arterial smooth muscle cells. Pflugers Arch. 2012;464:261–72. doi: 10.1007/s00424-012-1136-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Bohlen CJ, Priel A, Zhou S, King D, Siemens J, Julius D. A bivalent tarantula toxin activates the capsaicin receptor, TRPV1, by targeting the outer pore domain. Cell. 2010;141:834–45. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2010.03.052. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.McNamara FN, Randall A, Gunthorpe MJ. Effects of piperine, the pungent component of black pepper, at the human vanilloid receptor (TRPV1) Br J Pharmacol. 2005;144:781–90. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706040. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Szallasi A, Blumberg PM. Resiniferatoxin, a phorbol-related diterpene, acts as an ultrapotent analog of capsaicin, the irritant constituent in red pepper. Neuroscience. 1989;30:515–20. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(89)90269-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Liu L, Welch JM, Erickson RP, Reinhart PH, Simon SA. Different responses to repeated applications of zingerone in behavioral studies, recordings from intact and cultured TG neurons, and from VR1 receptors. Physiol Behav. 2000;69:177–86. doi: 10.1016/s0031-9384(00)00200-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Pearce LV, Petukhov PA, Szabo T, Kedei N, Bizik F, Kozikowski AP. et al. Evodiamine functions as an agonist for the vanilloid receptor TRPV1. Org Biomol Chem. 2004;2:2281–6. doi: 10.1039/B404506H. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Bisogno T, Hanus L, De Petrocellis L, Tchilibon S, Ponde DE, Brandi I. et al. Molecular targets for cannabidiol and its synthetic analogues: effect on vanilloid VR1 receptors and on the cellular uptake and enzymatic hydrolysis of anandamide. Br J Pharmacol. 2001;134:845–52. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0704327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.De Petrocellis L, Vellani V, Schiano-Moriello A, Marini P, Magherini PC, Orlando P. et al. Plant-derived cannabinoids modulate the activity of transient receptor potential channels of ankyrin type-1 and melastatin type-8. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2008;325:1007–15. doi: 10.1124/jpet.107.134809. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 42.Andre E, Campi B, Trevisani M, Ferreira J, Malheiros A, Yunes RA. et al. Pharmacological characterisation of the plant sesquiterpenes polygodial and drimanial as vanilloid receptor agonists. Biochem Pharmacol. 2006;71:1248–54. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2005.12.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Siemens J, Zhou S, Piskorowski R, Nikai T, Lumpkin EA, Basbaum AI. et al. Spider toxins activate the capsaicin receptor to produce inflammatory pain. Nature. 2006;444:208–12. doi: 10.1038/nature05285. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Ann J, Kim HS, Thorat SA, Kim H, Ha HJ, Choi K. et al. Discovery of Nonpungent Transient Receptor Potential Vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) Agonist as Strong Topical Analgesic. J Med Chem. 2020;63:418–24. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.9b01046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Neacsu C, Babes A. The M-channel blocker linopirdine is an agonist of the capsaicin receptor TRPV1. J Pharmacol Sci. 2010;114:332–40. doi: 10.1254/jphs.10172fp. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 46.Park CK, Xu ZZ, Liu T, Lu N, Serhan CN, Ji RR. Resolvin D2 is a potent endogenous inhibitor for transient receptor potential subtype V1/A1, inflammatory pain, and spinal cord synaptic plasticity in mice: distinct roles of resolvin D1, D2, and E1. J Neurosci. 2011;31:18433–8. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4192-11.2011. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Chakraborty S, Elvezio V, Kaczocha M, Rebecchi M, Puopolo M. Presynaptic inhibition of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) receptors by noradrenaline in nociceptive neurons. J Physiol. 2017;595:2639–60. doi: 10.1113/JP273455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Dickenson AH, Dray A. Selective antagonism of capsaicin by capsazepine: evidence for a spinal receptor site in capsaicin-induced antinociception. Br J Pharmacol. 1991;104:1045–9. doi: 10.1111/j.1476-5381.1991.tb12547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Seabrook GR, Sutton KG, Jarolimek W, Hollingworth GJ, Teague S, Webb J. et al. Functional properties of the high-affinity TRPV1 (VR1) vanilloid receptor antagonist (4-hydroxy-5-iodo-3-methoxyphenylacetate ester) iodo-resiniferatoxin. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2002;303:1052–60. doi: 10.1124/jpet.102.040394. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Uslusoy F, Naziroglu M, Cig B. Inhibition of the TRPM2 and TRPV1 Channels through Hypericum perforatum in Sciatic Nerve Injury-induced Rats Demonstrates their Key Role in Apoptosis and Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress of Sciatic Nerve and Dorsal Root Ganglion. Front Physiol. 2017;8:335. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2017.00335. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Wiskur BJ, Tyler K, Campbell-Dittmeyer K, Chaplan SR, Wickenden AD, Greenwood-Van Meerveld B. A novel TRPV1 receptor antagonist JNJ-17203212 attenuates colonic hypersensitivity in rats. Methods Find Exp Clin Pharmacol. 2010;32:557–64. doi: 10.1358/mf.2010.32.8.1507853. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Valenzano KJ, Grant ER, Wu G, Hachicha M, Schmid L, Tafesse L. et al. N-(4-tertiarybutylphenyl)-4-(3-chloropyridin-2-yl)tetrahydropyrazine -1(2H)-carbox-amide (BCTC), a novel, orally effective vanilloid receptor 1 antagonist with analgesic properties: I. in vitro characterization and pharmacokinetic properties. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2003;306:377–86. doi: 10.1124/jpet.102.045674. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Toth A, Kedei N, Szabo T, Wang Y, Blumberg PM. Thapsigargin binds to and inhibits the cloned vanilloid receptor-1. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002;293:777–82. doi: 10.1016/S0006-291X(02)00293-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Dessaint J, Yu W, Krause JE, Yue L. Yohimbine inhibits firing activities of rat dorsal root ganglion neurons by blocking Na+ channels and vanilloid VR1 receptors. Eur J Pharmacol. 2004;485:11–20. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2003.11.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 55.Jakab B, Helyes Z, Varga A, Bolcskei K, Szabo A, Sandor K. et al. Pharmacological characterization of the TRPV1 receptor antagonist JYL1421 (SC0030) in vitro and in vivo in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol. 2005;517:35–44. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2005.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 56.Pradhananga S, Shim WS. Caffeic acid exhibits anti-pruritic effects by inhibition of multiple itch transmission pathways in mice. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;762:313–21. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 57.Lee JH, Choi CS, Bae IH, Choi JK, Park YH, Park M. A novel, topical, nonsteroidal, TRPV1 antagonist, PAC-14028 cream improves skin barrier function and exerts anti-inflammatory action through modulating epidermal differentiation markers and suppressing Th2 cytokines in atopic dermatitis. J Dermatol Sci. 2018. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 58.Gunthorpe MJ, Rami HK, Jerman JC, Smart D, Gill CH, Soffin EM. et al. Identification and characterisation of SB-366791, a potent and selective vanilloid receptor (VR1/TRPV1) antagonist. Neuropharmacology. 2004;46:133–49. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(03)00305-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 59.Voight EA, Gomtsyan AR, Daanen JF, Perner RJ, Schmidt RG, Bayburt EK. et al. Discovery of (R)-1-(7-chloro-2,2-bis(fluoromethyl)chroman-4-yl)-3-(3-methylisoquinolin-5-yl)ur ea (A-1165442): a temperature-neutral transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV1) antagonist with analgesic efficacy. J Med Chem. 2014;57:7412–24. doi: 10.1021/jm500916t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 60.Gavva NR, Tamir R, Qu Y, Klionsky L, Zhang TJ, Immke D. et al. AMG 9810 [(E)-3-(4-t-butylphenyl)-N-(2,3-dihydrobenzo[b][1,4] dioxin-6-yl)acrylamide], a novel vanilloid receptor 1 (TRPV1) antagonist with antihyperalgesic properties. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2005;313:474–84. doi: 10.1124/jpet.104.079855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 61.Kitaguchi T, Swartz KJ. An inhibitor of TRPV1 channels isolated from funnel Web spider venom. Biochemistry. 2005;44:15544–9. doi: 10.1021/bi051494l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 62.Moran MM, McAlexander MA, Biro T, Szallasi A. Transient receptor potential channels as therapeutic targets. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2011;10:601–20. doi: 10.1038/nrd3456. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 63.Brederson JD, Kym PR, Szallasi A. Targeting TRP channels for pain relief. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;716:61–76. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 64.Stock K, Kumar J, Synowitz M, Petrosino S, Imperatore R, Smith ES. et al. Neural precursor cells induce cell death of high-grade astrocytomas through stimulation of TRPV1. Nat Med. 2012;18:1232–8. doi: 10.1038/nm.2827. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 65.Hartel M, di Mola FF, Selvaggi F, Mascetta G, Wente MN, Felix K. et al. Vanilloids in pancreatic cancer: potential for chemotherapy and pain management. Gut. 2006;55:519–28. doi: 10.1136/gut.2005.073205. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 66.Marincsak R, Toth BI, Czifra G, Marton I, Redl P, Tar I. et al. Increased expression of TRPV1 in squamous cell carcinoma of the human tongue. Oral Dis. 2009;15:328–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-0825.2009.01526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 67.Czifra G, Varga A, Nyeste K, Marincsak R, Toth BI, Kovacs I. et al. Increased expressions of cannabinoid receptor-1 and transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 in human prostate carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 2009;135:507–14. doi: 10.1007/s00432-008-0482-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 68.Weber LV, Al-Refae K, Wolk G, Bonatz G, Altmuller J, Becker C. et al. Expression and functionality of TRPV1 in breast cancer cells. Breast Cancer (Dove Med Press) 2016;8:243–52. doi: 10.2147/BCTT.S121610. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 69.Roderick HL, Cook SJ. Ca2+ signalling checkpoints in cancer: remodelling Ca2+ for cancer cell proliferation and survival. Nat Rev Cancer. 2008;8:361–75. doi: 10.1038/nrc2374. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 70.de Jong PR, Takahashi N, Harris AR, Lee J, Bertin S, Jeffries J. et al. Ion channel TRPV1-dependent activation of PTP1B suppresses EGFR-associated intestinal tumorigenesis. J Clin Invest. 2014;124:3793–806. doi: 10.1172/JCI72340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 71.Yang Y, Guo W, Ma J, Xu P, Zhang W, Guo S. et al. Downregulated TRPV1 Expression Contributes to Melanoma Growth via the Calcineurin-ATF3-p53 Pathway. J Invest Dermatol. 2018;138:2205–15. doi: 10.1016/j.jid.2018.03.1510. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 72.Huang J, Liu J, Qiu L. Transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 promotes EGFR ubiquitination and modulates EGFR/MAPK signalling in pancreatic cancer cells. Cell Biochem Funct. 2020. [DOI] [PubMed]
- 73.Bode AM, Cho YY, Zheng D, Zhu F, Ericson ME, Ma WY. et al. Transient receptor potential type vanilloid 1 suppresses skin carcinogenesis. Cancer Res. 2009;69:905–13. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-08-3263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 74.Amantini C, Ballarini P, Caprodossi S, Nabissi M, Morelli MB, Lucciarini R. et al. Triggering of transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) by capsaicin induces Fas/CD95-mediated apoptosis of urothelial cancer cells in an ATM-dependent manner. Carcinogenesis. 2009;30:1320–9. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgp138. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 75.Liu T, Wang G, Tao H, Yang Z, Wang Y, Meng Z. et al. Capsaicin mediates caspases activation and induces apoptosis through P38 and JNK MAPK pathways in human renal carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2016;16:790. doi: 10.1186/s12885-016-2831-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 76.Malagarie-Cazenave S, Olea-Herrero N, Vara D, Diaz-Laviada I. Capsaicin, a component of red peppers, induces expression of androgen receptor via PI3K and MAPK pathways in prostate LNCaP cells. FEBS Lett. 2009;583:141–7. doi: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.11.038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 77.Huang R, Wang F, Yang Y, Ma W, Lin Z, Cheng N. et al. Recurrent activations of transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 and vanilloid-4 promote cellular proliferation and migration in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells. FEBS Open Bio. 2019;9:206–25. doi: 10.1002/2211-5463.12570. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 78.Ligresti A, Moriello AS, Starowicz K, Matias I, Pisanti S, De Petrocellis L. et al. Antitumor activity of plant cannabinoids with emphasis on the effect of cannabidiol on human breast carcinoma. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2006;318:1375–87. doi: 10.1124/jpet.106.105247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 79.Aviello G, Romano B, Borrelli F, Capasso R, Gallo L, Piscitelli F. et al. Chemopreventive effect of the non-psychotropic phytocannabinoid cannabidiol on experimental colon cancer. J Mol Med (Berl) 2012;90:925–34. doi: 10.1007/s00109-011-0856-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 80.Morelli MB, Amantini C, Nabissi M, Liberati S, Cardinali C, Farfariello V. et al. Cross-talk between alpha1D-adrenoceptors and transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 triggers prostate cancer cell proliferation. BMC Cancer. 2014;14:921. doi: 10.1186/1471-2407-14-921. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 81.Zhang S-s, Ni Y-h, Zhao C-r, Qiao Z, Yu H-x, Wang L-y. et al. Capsaicin enhances the antitumor activity of sorafenib in hepatocellular carcinoma cells and mouse xenograft tumors through increased ERK signaling. Acta Pharmacologica Sinica. 2017;39:438–48. doi: 10.1038/aps.2017.156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 82.Sanchez AM, Sanchez MG, Malagarie-Cazenave S, Olea N, Diaz-Laviada I. Induction of apoptosis in prostate tumor PC-3 cells and inhibition of xenograft prostate tumor growth by the vanilloid capsaicin. Apoptosis. 2006;11:89–99. doi: 10.1007/s10495-005-3275-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 83.Skrzypski M, Sassek M, Abdelmessih S, Mergler S, Grotzinger C, Metzke D. et al. Capsaicin induces cytotoxicity in pancreatic neuroendocrine tumor cells via mitochondrial action. Cell Signal. 2014;26:41–8. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.09.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 84.Chiang C, Zhang M, Wang D, Xiao T, Zhu L, Chen K. et al. Therapeutic potential of targeting MKK3-p38 axis with Capsaicin for Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma. Theranostics. 2020;10:7906–20. doi: 10.7150/thno.45191. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 85.Borrelli F, Pagano E, Romano B, Panzera S, Maiello F, Coppola D. et al. Colon carcinogenesis is inhibited by the TRPM8 antagonist cannabigerol, a Cannabis-derived non-psychotropic cannabinoid. Carcinogenesis. 2014;35:2787–97. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgu205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 86.Hamtiaux L, Hansoulle L, Dauguet N, Muccioli GG, Gallez B, Lambert DM. Increasing antiproliferative properties of endocannabinoids in N1E-115 neuroblastoma cells through inhibition of their metabolism. PLoS One. 2011;6:e26823. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0026823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 87.Pecze L, Josvay K, Blum W, Petrovics G, Vizler C, Olah Z. et al. Activation of endogenous TRPV1 fails to induce overstimulation-based cytotoxicity in breast and prostate cancer cells but not in pain-sensing neurons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2016;1863:2054–64. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2016.05.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 88.Chen Y, Li J, Jin L, Lei K, Liu H, Yang Y. Fibulin-5 contributes to colorectal cancer cell apoptosis via the ROS/MAPK and Akt signal pathways by downregulating transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily V member 1. J Cell Biochem. 2019;120:17838–46. doi: 10.1002/jcb.29051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 89.Orrenius S, Zhivotovsky B, Nicotera P. Regulation of cell death: the calcium-apoptosis link. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2003;4:552–65. doi: 10.1038/nrm1150. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 90.Wu TT, Peters AA, Tan PT, Roberts-Thomson SJ, Monteith GR. Consequences of activating the calcium-permeable ion channel TRPV1 in breast cancer cells with regulated TRPV1 expression. Cell Calcium. 2014;56:59–67. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2014.04.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 91.Contassot E, Tenan M, Schnuriger V, Pelte MF, Dietrich PY. Arachidonyl ethanolamide induces apoptosis of uterine cervix cancer cells via aberrantly expressed vanilloid receptor-1. Gynecol Oncol. 2004;93:182–8. doi: 10.1016/j.ygyno.2003.12.040. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 92.Chien CS, Ma KH, Lee HS, Liu PS, Li YH, Huang YS. et al. Dual effect of capsaicin on cell death in human osteosarcoma G292 cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;718:350–60. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.08.011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 93.Naziroglu M, Cig B, Blum W, Vizler C, Buhala A, Marton A. et al. Targeting breast cancer cells by MRS1477, a positive allosteric modulator of TRPV1 channels. PLoS One. 2017;12:e0179950. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0179950. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 94.Fonseca BM, Correia-da-Silva G, Teixeira NA. Cannabinoid-induced cell death in endometrial cancer cells: involvement of TRPV1 receptors in apoptosis. J Physiol Biochem. 2018;74:261–72. doi: 10.1007/s13105-018-0611-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 95.Adinolfi B, Romanini A, Vanni A, Martinotti E, Chicca A, Fogli S. et al. Anticancer activity of anandamide in human cutaneous melanoma cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2013;718:154–9. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2013.08.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 96.Soliman E, Van Dross R. Anandamide-induced endoplasmic reticulum stress and apoptosis are mediated by oxidative stress in non-melanoma skin cancer: Receptor-independent endocannabinoid signaling. Mol Carcinog. 2016;55:1807–21. doi: 10.1002/mc.22429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 97.Ghosh AK, Basu S. Fas-associated factor 1 is a negative regulator in capsaicin induced cancer cell apoptosis. Cancer Lett. 2010;287:142–9. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2009.06.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 98.Lau JK, Brown KC, Dom AM, Witte TR, Thornhill BA, Crabtree CM. et al. Capsaicin induces apoptosis in human small cell lung cancer via the TRPV6 receptor and the calpain pathway. Apoptosis. 2014;19:1190–201. doi: 10.1007/s10495-014-1007-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 99.Chow J, Norng M, Zhang J, Chai J. TRPV6 mediates capsaicin-induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells-Mechanisms behind a possible new "hot" cancer treatment. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007;1773:565–76. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2007.01.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 100.Eichele K, Ramer R, Hinz B. R(+)-methanandamide-induced apoptosis of human cervical carcinoma cells involves a cyclooxygenase-2-dependent pathway. Pharm Res. 2009;26:346–55. doi: 10.1007/s11095-008-9748-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 101.Farfariello V, Liberati S, Morelli MB, Tomassoni D, Santoni M, Nabissi M. et al. Resiniferatoxin induces death of bladder cancer cells associated with mitochondrial dysfunction and reduces tumor growth in a xenograft mouse model. Chem Biol Interact. 2014;224:128–35. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2014.10.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 102.Gonzales CB, Kirma NB, De La Chapa JJ, Chen R, Henry MA, Luo S. et al. Vanilloids induce oral cancer apoptosis independent of TRPV1. Oral Oncol. 2014;50:437–47. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2013.12.023. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 103.Chaffer CL, Weinberg RA. A perspective on cancer cell metastasis. Science. 2011;331:1559–64. doi: 10.1126/science.1203543. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 104.Prevarskaya N, Ouadid-Ahidouch H, Skryma R, Shuba Y. Remodelling of Ca2+ transport in cancer: how it contributes to cancer hallmarks? Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 2014;369:20130097. doi: 10.1098/rstb.2013.0097. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 105.Kadio B, Yaya S, Basak A, Dje K, Gomes J, Mesenge C. Calcium role in human carcinogenesis: a comprehensive analysis and critical review of literature. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2016;35:391–411. doi: 10.1007/s10555-016-9634-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 106.Villalobo A, Berchtold MW. The Role of Calmodulin in Tumor Cell Migration, Invasiveness, and Metastasis. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. 21. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 107.Vriens J, Janssens A, Prenen J, Nilius B, Wondergem R. TRPV channels and modulation by hepatocyte growth factor/scatter factor in human hepatoblastoma (HepG2) cells. Cell Calcium. 2004;36:19–28. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2003.11.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 108.Waning J, Vriens J, Owsianik G, Stuwe L, Mally S, Fabian A. et al. A novel function of capsaicin-sensitive TRPV1 channels: involvement in cell migration. Cell Calcium. 2007;42:17–25. doi: 10.1016/j.ceca.2006.11.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 109.Nakanishi M, Morita Y, Hata K, Muragaki Y. Acidic microenvironments induce lymphangiogenesis and IL-8 production via TRPV1 activation in human lymphatic endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 2016;345:180–9. doi: 10.1016/j.yexcr.2016.06.006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 110.Ramer R, Hinz B. Inhibition of cancer cell invasion by cannabinoids via increased expression of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases-1. J Natl Cancer Inst. 2008;100:59–69. doi: 10.1093/jnci/djm268. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 111.Xu S, Zhang L, Cheng X, Yu H, Bao J, Lu R. Capsaicin inhibits the metastasis of human papillary thyroid carcinoma BCPAP cells through the modulation of the TRPV1 channel. Food Funct. 2018;9:344–54. doi: 10.1039/c7fo01295k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 112.Lazzeri M, Vannucchi MG, Spinelli M, Bizzoco E, Beneforti P, Turini D. et al. Transient receptor potential vanilloid type 1 (TRPV1) expression changes from normal urothelium to transitional cell carcinoma of human bladder. Eur Urol. 2005;48:691–8. doi: 10.1016/j.eururo.2005.05.018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 113.Kalogris C, Caprodossi S, Amantini C, Lambertucci F, Nabissi M, Morelli MB. et al. Expression of transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 (TRPV1) in urothelial cancers of human bladder: relation to clinicopathological and molecular parameters. Histopathology. 2010;57:744–52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2559.2010.03683.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 114.Ramer R, Bublitz K, Freimuth N, Merkord J, Rohde H, Haustein M. et al. Cannabidiol inhibits lung cancer cell invasion and metastasis via intercellular adhesion molecule-1. FASEB J. 2012;26:1535–48. doi: 10.1096/fj.11-198184. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 115.Caprodossi S, Amantini C, Nabissi M, Morelli MB, Farfariello V, Santoni M. et al. Capsaicin promotes a more aggressive gene expression phenotype and invasiveness in null-TRPV1 urothelial cancer cells. Carcinogenesis. 2011;32:686–94. doi: 10.1093/carcin/bgr025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 116.Caballero FJ, Soler-Torronteras R, Lara-Chica M, Garcia V, Fiebich BL, Munoz E. et al. AM404 inhibits NFAT and NF-kappaB signaling pathways and impairs migration and invasiveness of neuroblastoma cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015;746:221–32. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.11.023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 117.Punzo F, Tortora C, Di Pinto D, Pota E, Argenziano M, Di Paola A. et al. Bortezomib and endocannabinoid/endovanilloid system: a synergism in osteosarcoma. Pharmacol Res. 2018;137:25–33. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2018.09.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 118.Nishino K, Tanamachi K, Nakanishi Y, Ide S, Kojima S, Tanuma S. et al. Radiosensitizing Effect of TRPV1 Channel Inhibitors in Cancer Cells. Biol Pharm Bull. 2016;39:1224–30. doi: 10.1248/bpb.b16-00080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 119.Masumoto K, Tsukimoto M, Kojima S. Role of TRPM2 and TRPV1 cation channels in cellular responses to radiation-induced DNA damage. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2013;1830:3382–90. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2013.02.020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 120.Nur G, Naziroglu M, Deveci HA. Synergic prooxidant, apoptotic and TRPV1 channel activator effects of alpha-lipoic acid and cisplatin in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Recept Signal Transduct Res. 2017;37:569–77. doi: 10.1080/10799893.2017.1369121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 121.Zheng L, Chen J, Ma Z, Liu W, Yang F, Yang Z. et al. Capsaicin enhances anti-proliferation efficacy of pirarubicin via activating TRPV1 and inhibiting PCNA nuclear translocation in 5637 cells. Mol Med Rep. 2016;13:881–7. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2015.4623. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 122.Kosar PA, Naziroglu M, Ovey IS, Cig B. Synergic Effects of Doxorubicin and Melatonin on Apoptosis and Mitochondrial Oxidative Stress in MCF-7 Breast Cancer Cells: Involvement of TRPV1 Channels. J Membr Biol. 2016;249:129–40. doi: 10.1007/s00232-015-9855-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 123.Deveci HA, Naziroglu M, Nur G. 5-Fluorouracil-induced mitochondrial oxidative cytotoxicity and apoptosis are increased in MCF-7 human breast cancer cells by TRPV1 channel activation but not Hypericum perforatum treatment. Mol Cell Biochem. 2018;439:189–98. doi: 10.1007/s11010-017-3147-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 124.Keating GM. Sorafenib: A Review in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Target Oncol. 2017;12:243–53. doi: 10.1007/s11523-017-0484-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 125.Sung B, Prasad S, Ravindran J, Yadav VR, Aggarwal BB. Capsazepine, a TRPV1 antagonist, sensitizes colorectal cancer cells to apoptosis by TRAIL through ROS-JNK-CHOP-mediated upregulation of death receptors. Free Radic Biol Med. 2012;53:1977–87. doi: 10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2012.08.012. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 126.Ribeiro Franco PI, Rodrigues AP, de Menezes LB, Pacheco Miguel M. Tumor microenvironment components: Allies of cancer progression. Pathol Res Pract. 2020;216:152729. doi: 10.1016/j.prp.2019.152729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 127.Quail DF, Joyce JA. Microenvironmental regulation of tumor progression and metastasis. Nat Med. 2013;19:1423–37. doi: 10.1038/nm.3394. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 128.Balkwill FR, Capasso M, Hagemann T. The tumor microenvironment at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2012;125:5591–6. doi: 10.1242/jcs.116392. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 129.Stewart TA, Yapa KT, Monteith GR. Altered calcium signaling in cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2015;1848:2502–11. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2014.08.016. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 130.Bong AHL, Monteith GR. Calcium signaling and the therapeutic targeting of cancer cells. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Cell Res. 2018;1865:1786–94. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamcr.2018.05.015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 131.Roberts-Thomson SJ, Chalmers SB, Monteith GR. The Calcium-Signaling Toolkit in Cancer: Remodeling and Targeting. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol. 2019. 11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 132.Kalluri R, Zeisberg M. Fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2006;6:392–401. doi: 10.1038/nrc1877. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 133.Kalluri R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16:582–98. doi: 10.1038/nrc.2016.73. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 134.Ishimoto T, Miyake K, Nandi T, Yashiro M, Onishi N, Huang KK. et al. Activation of Transforming Growth Factor Beta 1 Signaling in Gastric Cancer-associated Fibroblasts Increases Their Motility, via Expression of Rhomboid 5 Homolog 2, and Ability to Induce Invasiveness of Gastric Cancer Cells. Gastroenterology. 2017;153:191–204. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2017.03.046. e16. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 135.Aoyagi Y, Oda T, Kinoshita T, Nakahashi C, Hasebe T, Ohkohchi N. et al. Overexpression of TGF-beta by infiltrated granulocytes correlates with the expression of collagen mRNA in pancreatic cancer. Br J Cancer. 2004;91:1316–26. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjc.6602141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 136.Yoshida GJ. Regulation of heterogeneous cancer-associated fibroblasts: the molecular pathology of activated signaling pathways. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2020;39:112. doi: 10.1186/s13046-020-01611-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 137.Bodo E, Biro T, Telek A, Czifra G, Griger Z, Toth BI. et al. A hot new twist to hair biology: involvement of vanilloid receptor-1 (VR1/TRPV1) signaling in human hair growth control. Am J Pathol. 2005;166:985–98. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)62320-6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 138.Okada Y, Reinach PS, Shirai K, Kitano A, Kao WW, Flanders KC. et al. TRPV1 involvement in inflammatory tissue fibrosis in mice. Am J Pathol. 2011;178:2654–64. doi: 10.1016/j.ajpath.2011.02.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 139.Li HJ, Kanazawa N, Kimura A, Kaminaka C, Yonei N, Yamamoto Y. et al. Severe ulceration with impaired induction of growth factors and cytokines in keratinocytes after trichloroacetic acid application on TRPV1-deficient mice. Eur J Dermatol. 2012;22:614–21. doi: 10.1684/ejd.2012.1788. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 140.Nidegawa-Saitoh Y, Sumioka T, Okada Y, Reinach PS, Flanders KC, Liu CY. et al. Impaired healing of cornea incision injury in a TRPV1-deficient mouse. Cell Tissue Res. 2018;374:329–38. doi: 10.1007/s00441-018-2878-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 141.Mouw JK, Ou G, Weaver VM. Extracellular matrix assembly: a multiscale deconstruction. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2014;15:771–85. doi: 10.1038/nrm3902. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 142.Caires R, Luis E, Taberner FJ, Fernandez-Ballester G, Ferrer-Montiel A, Balazs EA. et al. Hyaluronan modulates TRPV1 channel opening, reducing peripheral nociceptor activity and pain. Nat Commun. 2015;6:8095. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9095. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 143.Gonzalez-Avila G, Sommer B, Garcia-Hernandez AA, Ramos C. Matrix Metalloproteinases' Role in Tumor Microenvironment. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1245:97–131. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-40146-7_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 144.Wu T, Dai Y. Tumor microenvironment and therapeutic response. Cancer Lett. 2017;387:61–8. doi: 10.1016/j.canlet.2016.01.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 145.Li WH, Lee YM, Kim JY, Kang S, Kim S, Kim KH. et al. Transient receptor potential vanilloid-1 mediates heat-shock-induced matrix metalloproteinase-1 expression in human epidermal keratinocytes. J Invest Dermatol. 2007;127:2328–35. doi: 10.1038/sj.jid.5700880. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 146.Lee YM, Li WH, Kim YK, Kim KH, Chung JH. Heat-induced MMP-1 expression is mediated by TRPV1 through PKCalpha signaling in HaCaT cells. Exp Dermatol. 2008;17:864–70. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0625.2008.00738.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 147.Huang KF, Ma KH, Chang YJ, Lo LC, Jhap TY, Su YH. et al. Baicalein inhibits matrix metalloproteinase 1 expression via activation of TRPV1-Ca-ERK pathway in ultraviolet B-irradiated human dermal fibroblasts. Exp Dermatol. 2019;28:568–75. doi: 10.1111/exd.13912. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 148.Ramer R, Merkord J, Rohde H, Hinz B. Cannabidiol inhibits cancer cell invasion via upregulation of tissue inhibitor of matrix metalloproteinases-1. Biochem Pharmacol. 2010;79:955–66. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2009.11.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 149.Kohn EC, Alessandro R, Spoonster J, Wersto RP, Liotta LA. Angiogenesis: role of calcium-mediated signal transduction. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995;92:1307–11. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.5.1307. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 150.Faehling M, Kroll J, Fohr KJ, Fellbrich G, Mayr U, Trischler G. et al. Essential role of calcium in vascular endothelial growth factor A-induced signaling: mechanism of the antiangiogenic effect of carboxyamidotriazole. FASEB J. 2002;16:1805–7. doi: 10.1096/fj.01-0938fje. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 151.Moccia F, Negri S, Shekha M, Faris P, Guerra G. Endothelial Ca(2+) Signaling, Angiogenesis and Vasculogenesis: just What It Takes to Make a Blood Vessel. Int J Mol Sci. 2019. 20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 152.Munaron L. Intracellular calcium, endothelial cells and angiogenesis. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2006;1:105–19. doi: 10.2174/157489206775246502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 153.Earley S, Brayden JE. Transient receptor potential channels in the vasculature. Physiol Rev. 2015;95:645–90. doi: 10.1152/physrev.00026.2014. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 154.Nishida N, Yano H, Nishida T, Kamura T, Kojiro M. Angiogenesis in cancer. Vasc Health Risk Manag. 2006;2:213–9. doi: 10.2147/vhrm.2006.2.3.213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 155.Apte RS, Chen DS, Ferrara N. VEGF in Signaling and Disease: Beyond Discovery and Development. Cell. 2019;176:1248–64. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2019.01.021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 156.Winder T, Lenz HJ. Vascular endothelial growth factor and epidermal growth factor signaling pathways as therapeutic targets for colorectal cancer. Gastroenterology. 2010;138:2163–76. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.02.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 157.Ferrara N, Gerber HP, LeCouter J. The biology of VEGF and its receptors. Nat Med. 2003;9:669–76. doi: 10.1038/nm0603-669. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 158.Walcher L, Budde C, Bohm A, Reinach PS, Dhandapani P, Ljubojevic N. et al. TRPM8 Activation via 3-Iodothyronamine Blunts VEGF-Induced Transactivation of TRPV1 in Human Uveal Melanoma Cells. Front Pharmacol. 2018;9:1234. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2018.01234. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 159.Su KH, Lin SJ, Wei J, Lee KI, Zhao JF, Shyue SK. et al. The essential role of transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 in simvastatin-induced activation of endothelial nitric oxide synthase and angiogenesis. Acta Physiol (Oxf) 2014;212:191–204. doi: 10.1111/apha.12378. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 160.Vinuesa AG, Sancho R, Garcia-Limones C, Behrens A, ten Dijke P, Calzado MA. et al. Vanilloid receptor-1 regulates neurogenic inflammation in colon and protects mice from colon cancer. Cancer Res. 2012;72:1705–16. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-11-3693. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 161.Gao P, Niu N, Wei T, Tozawa H, Chen X, Zhang C. et al. The roles of signal transducer and activator of transcription factor 3 in tumor angiogenesis. Oncotarget. 2017;8:69139–61. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.19932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 162.Atsumi T, Singh R, Sabharwal L, Bando H, Meng J, Arima Y. et al. Inflammation amplifier, a new paradigm in cancer biology. Cancer Res. 2014;74:8–14. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-2322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 163.Wang S, Liu Z, Wang L, Zhang X. NF-kappaB signaling pathway, inflammation and colorectal cancer. Cell Mol Immunol. 2009;6:327–34. doi: 10.1038/cmi.2009.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 164.Coussens LM, Werb Z. Inflammation and cancer. Nature. 2002;420:860–7. doi: 10.1038/nature01322. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 165.Ritter B, Greten FR. Modulating inflammation for cancer therapy. J Exp Med. 2019;216:1234–43. doi: 10.1084/jem.20181739. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 166.Greten FR, Grivennikov SI. Inflammation and Cancer: Triggers, Mechanisms, and Consequences. Immunity. 2019;51:27–41. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2019.06.025. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 167.Vig M, Kinet JP. Calcium signaling in immune cells. Nat Immunol. 2009;10:21–7. doi: 10.1038/ni.f.220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 168.Oh-hora M, Rao A. Calcium signaling in lymphocytes. Curr Opin Immunol. 2008;20:250–8. doi: 10.1016/j.coi.2008.04.004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 169.Bertin S, Aoki-Nonaka Y, de Jong PR, Nohara LL, Xu H, Stanwood SR. et al. The ion channel TRPV1 regulates the activation and proinflammatory properties of CD4(+) T cells. Nat Immunol. 2014;15:1055–63. doi: 10.1038/ni.3009. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 170.Basu S, Srivastava P. Immunological role of neuronal receptor vanilloid receptor 1 expressed on dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2005;102:5120–5. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0407780102. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 171.Erin N. Role of sensory neurons, neuroimmune pathways, and transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) channels in a murine model of breast cancer metastasis. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2020;69:307–14. doi: 10.1007/s00262-019-02463-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]