Abstract
The cell membrane regulates many physiological processes including cellular communication, homing and metabolism. It is therefore not surprising that the composition of the host cell membrane is manipulated by intracellular pathogens. Among these, the human oncogenic herpesviruses Epstein–Barr virus (EBV) and Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) exploit the host cell membrane to avoid immune surveillance and promote viral replication. Accumulating evidence has shown that both EBV and KSHV directly encode several similar membrane-associated proteins, including receptors and receptor-specific ligands (cytokines and chemokines), to increase virus fitness in spite of host antiviral immune responses. These proteins are expressed individually at different phases of the EBV/KSHV life cycle and employ various mechanisms to manipulate the host cell membrane. In recent decades, much effort has been made to address how these membrane-based signals contribute to viral tumorigenesis. In this review, we summarize and highlight the recent understanding of how EBV and KSHV similarly manipulate host cell membrane signals, particularly how remodeling of the cell membrane allows EBV and KSHV to avoid host antiviral immune responses and favors their latent and lytic infection.
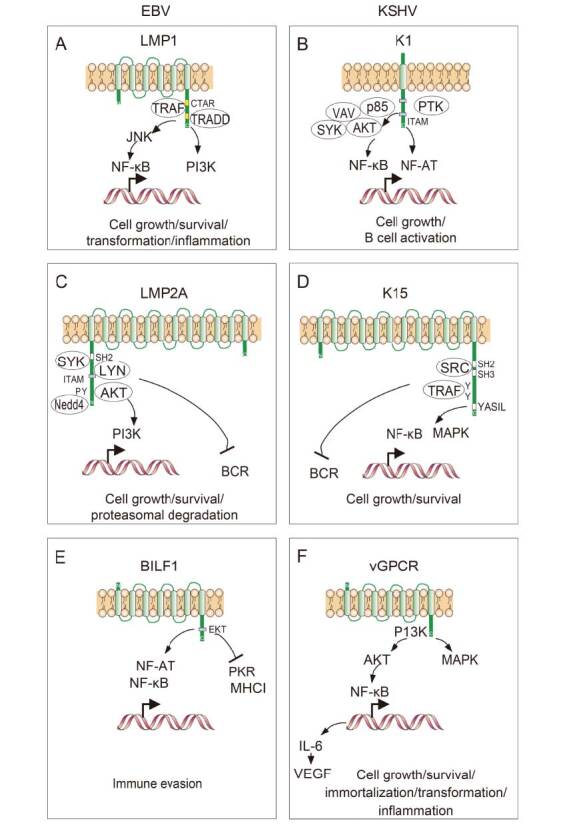
Keywords: cell membrane remodeling, Epstein-Barr virus (EBV), Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV)
Footnotes
These authors contributed equally to this work.
ORCID: 0000-0002-7147-0953
References
- Abend JR, Ramalingam D, Kieffer-Kwon P, Uldrick TS, Yarchoan R, Ziegelbauer JM. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus microRNAs target IRAK1 and MYD88, two components of the toll-like receptor/interleukin-1R signaling cascade, to reduce inflammatory-cytokine expression. J Virol. 2012;86:11663–11674. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01147-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Amort M, Nachbauer B, Tuzlak S, Kieser A, Schepers A, Villunger A, Polacek N. Expression of the vault RNA protects cells from undergoing apoptosis. Nat Commun. 2015;6:7030. doi: 10.1038/ncomms8030. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson LJ, Longnecker R. EBV LMP2A provides a surrogate pre-B cell receptor signal through constitutive activation of the ERK/MAPK pathway. J Gen Virol. 2008;89:1563–1568. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.2008/001461-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arvanitakis L, Geras-Raaka E, Varma A, Gershengorn MC, Cesarman E. Human herpesvirus KSHV encodes a constitutively active G-protein-coupled receptor linked to cell proliferation. Nature. 1997;385:347–350. doi: 10.1038/385347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bais C, Santomasso B, Coso O, Arvanitakis L, Raaka EG, Gutkind JS, Asch AS, Cesarman E, Gershengorn MC, Mesri EA. G-protein-coupled receptor of Kaposi's sarcomaassociated herpesvirus is a viral oncogene and angiogenesis activator. Nature. 1998;391:86–89. doi: 10.1038/34193. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bala K, Bosco R, Gramolelli S, Haas DA, Kati S, Pietrek M, Havemeier A, Yakushko Y, Singh VV, Dittrich-Breiholz O, Kracht M, Schulz TF. Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus K15 protein contributes to virus-induced angiogenesis by recruiting PLCgamma1 and activating NFAT1-dependent RCAN1 expression. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8:e1002927. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beisser PS, Verzijl D, Gruijthuijsen YK, Beuken E, Smit MJ, Leurs R, Bruggeman CA, Vink C. The Epstein-Barr virus BILF1 gene encodes a G protein-coupled receptor that inhibits phosphorylation of RNA-dependent protein kinase. J Virol. 2005;79:441–449. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.1.441-449.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bejarano MT, Masucci MG. Interleukin-10 abrogates the inhibition of Epstein-Barr virus-induced B-cell transformation by memory T-cell responses. Blood. 1998;92:4256–4262. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boshoff C, Endo Y, Collins PD, Takeuchi Y, Reeves JD, Schweickart VL, Siani MA, Sasaki T, Williams TJ, Gray PW, Moore PS, Chang Y, Weiss RA. Angiogenic and HIVinhibitory functions of KSHV-encoded chemokines. Science. 1997;278:290–294. doi: 10.1126/science.278.5336.290. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowser B D, Wire SM, Damania B. Transcriptional regulation of the K1 gene product of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. J Virol. 2002;76:12574–12583. doi: 10.1128/JVI.76.24.12574-12583.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowser BS, Morris S, Song MJ, Sun R, Damania B. Characterization of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) K1 promoter activation by Rta. Virology. 2006;348:309–327. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.02.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann MM, Glenn M, Rainbow L, Kieser A, Henke-Gendo C, Schulz TF. Activation of mitogen-activated protein kinase and NF-kappaB pathways by a Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K15 membrane protein. J Virol. 2003;77:9346–9358. doi: 10.1128/JVI.77.17.9346-9358.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brinkmann MM, Pietrek M, Dittrich-Breiholz O, Kracht M, Schulz TF. Modulation of host gene expression by the K15 protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. J Virol. 2007;81:42–58. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00648-06. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burkhardt AL, Bolen JB, Kieff E, Longnecker R. An Epstein-Barr virus transformation-associated membrane protein interacts with src family tyrosine kinases. J Virol. 1992;66:5161–5167. doi: 10.1128/jvi.66.8.5161-5167.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Calderwood MA, Venkatesan K, Xing L, Chase MR, Vazquez A, Holthaus AM, Ewence AE, Li N, Hirozane-Kishikawa T, Hill DE. Epstein–Barr virus and virus human protein interaction maps. Proc Natl Acad Scie U S A. 2007;104:7606–7611. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0702332104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caldwell RG, Wilson JB, Anderson SJ, Longnecker R. Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A drives B cell development and survival in the absence of normal B cell receptor signals. Immunity. 1998;9:405–411. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(00)80623-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cen O, Longnecker R. Latent Membrane Protein 2 (LMP2) Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 2015;391:151–180. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-22834-1_5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cesarman E, Chang Y, Moore PS, Said JW, Knowles DM. Kaposi's sarcoma–associated herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-related body-cavity–based lymphomas. N Engl J Med. 1995;332:1186–1191. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199505043321802. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chakraborty S, Veettil MV, Chandran B. Kaposi’s sarcoma associated herpesvirus entry into target cells. Front Microbiol. 2012;3:6. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2012.00006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang Y, Cesarman E, Pessin MS, Lee F, Culpepper J, Knowles DM, Moore PS. Identification of herpesvirus-like DNA sequences in AIDS-associated Kaposi's sarcoma. Science. 1994;266:1865–1869. doi: 10.1126/science.7997879. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao Y, Jing Y, Jia Y, Wang Y, Zhao C, Luo B. Conservation and mutation of viral interleukin-10 gene in gastric carcinomas and nasopharyngeal carcinomas. J Med Virol. 2011;83:644–650. doi: 10.1002/jmv.22091. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatterjee M, Osborne J, Bestetti G, Chang Y, Moore PS. Viral IL-6-induced cell proliferation and immune evasion of interferon activity. Science. 2002;298:1432–1435. doi: 10.1126/science.1074883. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chazal N, Gerlier D. Virus entry, assembly, budding, and membrane rafts. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2003;67:226–237. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.67.2.226-237.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Waal Malefyt R, Haanen J, Spits H, Roncarolo M t, Velde A, Figdor C, Johnson K, Kastelein R, Yssel H, de Vries JE. Interleukin 10 (IL-10) and viral IL-10 strongly reduce antigen-specific human T cell proliferation by diminishing the antigen-presenting capacity of monocytes via downregulation of class II major histocompatibility complex expression. J Exp Med. 1991;174:915–924. doi: 10.1084/jem.174.4.915. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Epstein MA, Achong BG, Barr YM. Virus Particles in Cultured Lymphoblasts from Burkitt's Lymphoma. Lancet. 1964;1:702–703. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(64)91524-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fish K, Chen J, Longnecker R. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A enhances MYC-driven cell cycle progression in a mouse model of B lymphoma. Blood. 2014;123:530–540. doi: 10.1182/blood-2013-07-517649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fotheringham JA, Coalson NE, Raab-Traub N. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein-2A induces ITAM/Syk-and Aktdependent epithelial migration through alphav-integrin membrane translocation. J Virol. 2012;86:10308–10320. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00853-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox CP, Haigh TA, Taylor GS, Long HM, Lee SP, Shannon-Lowe C, O'Connor S, Bollard CM, Iqbal J, Chan WC, Rickinson AB, Bell AI, Rowe M. A novel latent membrane 2 transcript expressed in Epstein-Barr virus-positive NK-and T-cell lymphoproliferative disease encodes a target for cellular immunotherapy. Blood. 2010;116:3695–3704. doi: 10.1182/blood-2010-06-292268. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fruehling S, Longnecker R. The immunoreceptor tyrosinebased activation motif of Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A is essential for blocking BCR-mediated signal transduction. Virology. 1997;235:241–251. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8690. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda M, Kawaguchi Y. Role of the immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif of latent membrane protein 2A (LMP2A) in Epstein-Barr virus LMP2A-induced cell transformation. J Virol. 2014;88:5189–5194. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03714-13. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fukuda M, Longnecker R. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) latent membrane protein 2A regulates B-cell receptor-induced apoptosis and EBV reactivation through tyrosine phosphorylation. J Virol. 2005;79:8655–8660. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.13.8655-8660.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn M, Rainbow L, Aurade F, Davison A, Schulz TF. Identification of a spliced gene from Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus encoding a protein with similarities to latent membrane proteins 1 and 2A of Epstein-Barr virus. J Virol. 1999;73:6953–6963. doi: 10.1128/jvi.73.8.6953-6963.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg DM, Riordan JR. Role of membranes in disease. Clin Physiol Biochem. 1986;4:305–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gramolelli S, Weidner-Glunde M, Abere B, Viejo-Borbolla A, Bala K, Ruckert J, Kremmer E, Schulz TF. Inhibiting the Recruitment of PLCgamma1 to Kaposi's Sarcoma Herpesvirus K15 Protein Reduces the Invasiveness and Angiogenesis of Infected Endothelial Cells. PLoS Pathog. 2015;11:e1005105. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1005105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griffin BD, Gram AM, Mulder A V, Leeuwen D, Claas FH, Wang F, Ressing ME, Wiertz E. EBV BILF1 evolved to downregulate cell surface display of a wide range of HLA class I molecules through their cytoplasmic tail. J Immunol. 2013;190:1672–1684. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1102462. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gujer C, Chatterjee B, Landtwing V, Raykova A, McHugh D, Munz C. Animal models of Epstein Barr virus infection. Curr Opin Virol. 2015;13:6–10. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2015.03.014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Han J, Chen JN, Zhang ZG, Li HG, Ding YG, Du H, Shao CK. Sequence variations of latent membrane protein 2A in Epstein-Barr virus-associated gastric carcinomas from Guang-zhou, southern China. PLoS One. 2012;7:e34276. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatzivassiliou E, Miller WE, Raab-Traub N, Kieff E, Mosialos G. A fusion of the EBV latent membrane protein-1 (LMP1) transmembrane domains to the CD40 cytoplasmic domain is similar to LMP1 in constitutive activation of epidermal growth factor receptor expression, nuclear factor-kappa B, and stressactivated protein kinase. J Immunol. 1998;160:1116–1121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heaton NS, Randall G. Multifaceted roles for lipids in viral infection. Trends Microbiol. 2011;19:368–375. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2011.03.007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hensler HR, Rappocciolo G, Rinaldo CR, Jenkins FJ. Cytokine production by human herpesvirus 8-infected dendritic cells. J Gen Virol. 2009;90:79–83. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.006239-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Izumi KM, Kaye KM, Kieff ED. The Epstein-Barr virus LMP1 amino acid sequence that engages tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factors is critical for primary B lymphocyte growth transformation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:1447–1452. doi: 10.1073/pnas.94.4.1447. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jham BC, Montaner S. The Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus G protein-coupled receptor: Lessons on dysregulated angiogenesis from a viral oncogene. J Cell Biochem. 2010;110:1–9. doi: 10.1002/jcb.22524. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jochum S, Moosmann A, Lang S, Hammerschmidt W, Zeidler R. The EBV immunoevasins vIL-10 and BNLF2a protect newly infected B cells from immune recognition and elimination. PLoS Pathog. 2012;8:e1002704. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1002704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones KD, Aoki Y, Chang Y, Moore PS, Yarchoan R, Tosato G. Involvement of interleukin-10 (IL-10) and viral IL-6 in the spontaneous growth of Kaposi's sarcoma herpesvirus-associated infected primary effusion lymphoma cells. Blood. 1999;94:2871–2879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanai K, Satoh Y, Yamanaka H, Kawaguchi A, Horie K, Sugata K, Hoshikawa Y, Sata T, Sairenji T. The vIL-10 gene of the Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) is conserved in a stable manner except for a few point mutations in various EBV isolates. Virus Genes. 2007;35:563–569. doi: 10.1007/s11262-007-0153-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagunoff M, Ganem D. The structure and coding organization of the genomic termini of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Virology. 1997;236:147–154. doi: 10.1006/viro.1997.8713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagunoff M, Majeti R, Weiss A, Ganem D. Deregulated signal transduction by the K1 gene product of Kaposi's sarcomaassociated herpesvirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1999;96:5704–5709. doi: 10.1073/pnas.96.10.5704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H, Guo J, Li M, Choi J D, Maria M, Rosenzweig M, Jung JU. Identification of an immunoreceptor tyrosine-based activation motif of K1 transforming protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Mol Cell Biol. 1998;18:5219–5228. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.9.5219. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee H, Veazey R, Williams K, Li M, Guo J, Neipel F, Fleckenstein B, Lackner A, Desrosiers RC, Jung JU. Deregulation of cell growth by the K1 gene of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Nat Med. 1998;4:435–440. doi: 10.1038/nm0498-435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquester GJ, Greer KA, Stewart JP, Sample JT. Epstein-Barr virus IL-10 gene expression by a recombinant murine gammaherpesvirus in vivo enhances acute pathogenicity but does not affect latency or reactivation. Herpesviridae. 2014;5:1. doi: 10.1186/2042-4280-5-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu J, Lin WH, Chen SY, Longnecker R, Tsai SC, Chen CL, Tsai CH. Syk tyrosine kinase mediates Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A-induced cell migration in epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 2006;281:8806–8814. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M507305200. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyngaa R, Norregaard K, Kristensen M, Kubale V, Rosenkilde MM, Kledal TN. Cell transformation mediated by the Epstein-Barr virus G protein-coupled receptor BILF1 is dependent on constitutive signaling. Oncogene. 2010;29:4388–4398. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.173. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma SD, Xu X, Plowshay J, Ranheim EA, Burlingham WJ, Jensen JL, Asimakopoulos F, Tang W, Gulley ML, Cesarman E, Gumperz JE, Kenney SC. LMP1-deficient Epstein-Barr virus mutant requires T cells for lymphomagenesis. J Clin Invest. 2015;125:304–315. doi: 10.1172/JCI76357. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazzon M, Mercer J. Lipid interactions during virus entry and infection. Cell Microbiol. 2014;16:1493–1502. doi: 10.1111/cmi.12340. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McColl SR, Roberge CJ, Larochelle B, Gosselin J. EBV induces the production and release of IL-8 and macrophage inflammatory protein-1 alpha in human neutrophils. J Immunol. 1997;159:6164–6168. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meckes D Jr, Shair KH, Marquitz AR, Kung CP, Edwards RH, Raab-Traub N. Human tumor virus utilizes exosomes for intercellular communication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010;107:20370–20375. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1014194107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merchant M, Caldwell RG, Longnecker R. The LMP2A ITAM is essential for providing B cells with development and survival signals in vivo. J Virol. 2000;74:9115–9124. doi: 10.1128/JVI.74.19.9115-9124.2000. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mesri EA, Cesarman E, Boshoff C. Kaposi's sarcoma and its associated herpesvirus. Nat Rev Cancer. 2010;10:707–719. doi: 10.1038/nrc2888. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller CL, Burkhardt AL, Lee JH, Stealey B, Longnecker R, Bolen JB, Kieff E. Integral membrane protein 2 of Epstein-Barr virus regulates reactivation from latency through dominant negative effects on protein-tyrosine kinases. Immunity. 1995;2:155–166. doi: 10.1016/S1074-7613(95)80040-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller CL, Lee JH, Kieff E, Longnecker R. An integral membrane protein (LMP2) blocks reactivation of Epstein-Barr virus from latency following surface immunoglobulin crosslinking. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994;91:772–776. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.2.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller CL, Longnecker R, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent membrane protein 2A blocks calcium mobilization in B lymphocytes. J Virol. 1993;67:3087–3094. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.6.3087-3094.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyazaki I, Cheung RK, Dosch HM. Viral interleukin 10 is critical for the induction of B cell growth transformation by Epstein-Barr virus. J Exp Med. 1993;178:439–447. doi: 10.1084/jem.178.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molden J, Chang Y, You Y, Moore PS, Goldsmith MA. A Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded cytokine homolog (vIL-6) activates signaling through the shared gp130 receptor subunit. J Biol Chem. 1997;272:19625–19631. doi: 10.1074/jbc.272.31.19625. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore PS, Boshoff C, Weiss RA, Chang Y. Molecular mimicry of human cytokine and cytokine response pathway genes by KSHV. Science. 1996;274:1739–1744. doi: 10.1126/science.274.5293.1739. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori Y, Nishimoto N, Ohno M, Inagi R, Dhepakson P, Amou K, Yoshizaki K, Yamanishi K. Human herpesvirus 8-encoded interleukin-6 homologue (viral IL-6) induces endogenous human IL-6 secretion. J Med Virol. 2000;61:332–335. doi: 10.1002/1096-9071(200007)61:3<332::AID-JMV8>3.0.CO;2-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Motsch N, Pfuhl T, Mrazek J, Barth S, Grasser FA. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded latent membrane protein 1 (LMP1) induces the expression of the cellular microRNA miR-146a. RNA Biol. 2007;4:131–137. doi: 10.4161/rna.4.3.5206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neipel F, Albrecht JC, Ensser A, Huang YQ, Li JJ, Friedman-Kien AE, Fleckenstein B. Human herpesvirus 8 encodes a homolog of interleukin-6. J Virol. 1997;71:839–842. doi: 10.1128/jvi.71.1.839-842.1997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholas J, Ruvolo VR, Burns WH, Sandford G, Wan X, Ciufo D, Hendrickson SB, Guo HG, Hayward GS, Reitz MS. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated human herpesvirus-8 encodes homologues of macrophage inflammatory protein-1 and interleukin-6. Nat Med. 1997;3:287–292. doi: 10.1038/nm0397-287. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nijmeijer S, Leurs R, Smit MJ, Vischer HF. The Epstein–Barr virus-encoded G protein-coupled receptor BILF1 heterooligomerizes with human CXCR4, scavenges Galphai proteins, and constitutively impairs CXCR4 functioning. J Biol Chem. 2010;285:29632–29641. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.115618. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parravicini C, Chandran B, Corbellino M, Berti E, Paulli M, Moore PS, Chang Y. Differential viral protein expression in Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-infected diseases: Kaposi's sarcoma, primary effusion lymphoma, and multicentric Castleman's disease. Am J Pathol. 2000;156:743–749. doi: 10.1016/S0002-9440(10)64940-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parravicini C, Corbellino M, Paulli M, Magrini U, Lazzarino M, Moore PS, Chang Y. Expression of a virus-derived cytokine, KSHV vIL-6, in HIV-seronegative Castleman's disease. Am J Pathol. 1997;151:1517–1522. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pati S, Cavrois M, Guo HG, Foulke J Jr, Kim J, Feldman RA, Reitz M. Activation of NF-kappaB by the human herpesvirus 8 chemokine receptor ORF74: evidence for a paracrine model of Kaposi's sarcoma pathogenesis. J Virol. 2001;75:8660–8673. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.18.8660-8673.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen SJ, Rosenkilde MM, Eugen-Olsen J, Kledal TN. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded BILF1 is a constitutively active G protein-coupled receptor. J Virol. 2005;79:536–546. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.1.536-546.2005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pietrek M, Brinkmann MM, Glowacka I, Enlund A, Havemeier A, Dittrich-Breiholz O, Kracht M, Lewitzky M, Saksela K, Feller SM, Schulz TF. Role of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K15 SH3 binding site in inflammatory signaling and B-cell activation. J Virol. 2010;84:8231–8240. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01696-09. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Portis T, Longnecker R. Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) LMP2A mediates B-lymphocyte survival through constitutive activation of the Ras/PI3K/Akt pathway. Oncogene. 2004;23:8619–8628. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1207905. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qu L, Green M, Webber S, Reyes J, Ellis D, Rowe D. Epstein-Barr virus gene expression in the peripheral blood of transplant recipients with persistent circulating virus loads. J Infect Dis. 2000;182:1013–1021. doi: 10.1086/315828. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riethmüller J, Riehle A, Grassmé H, Gulbins E. Membrane rafts in host–pathogen interactions. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006;1758:2139–2147. doi: 10.1016/j.bbamem.2006.07.017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbaum DM, Rasmussen SG, Kobilka BK. The structure and function of G-protein-coupled receptors. Nature. 2009;459:356–363. doi: 10.1038/nature08144. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singh UP, Singh S, Ravichandran P, Taub DD, Lillard J Jr. Viral macrophage-inflammatory protein-II: a viral chemokine that differentially affects adaptive mucosal immunity compared with its mammalian counterparts. J Immunol. 2004;173:5509–5516. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.173.9.5509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siouda M, Frecha C, Accardi R, Yue J, Cuenin C, Gruffat H, Manet E, Herceg Z, Sylla BS, Tommasino M. Epstein-Barr virus down-regulates tumor suppressor DOK1 expression. PLoS Pathog. 2014;10:e1004125. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1004125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smit MJ, Verzijl D, Casarosa P, Navis M, Timmerman H, Leurs R. Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus-encoded G protein-coupled receptor ORF74 constitutively activates p44/p42 MAPK and Akt via G(i) and phospholipase C-dependent signaling pathways. J Virol. 2002;76:1744–1752. doi: 10.1128/JVI.76.4.1744-1752.2002. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sozzani S, Luini W, Bianchi G, Allavena P, Wells TN, Napolitano M, Bernardini G, Vecchi A, D'Ambrosio D, Mazzeo D, Sinigaglia F, Santoni A, Maggi E, Romagnani S, Mantovani A. The viral chemokine macrophage inflammatory protein-II is a selective Th2 chemoattractant. Blood. 1998;92:4036–4039. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear PG, Longnecker R. Herpesvirus entry: an update. J Virol. 2003;77:10179–10185. doi: 10.1128/JVI.77.19.10179-10185.2003. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiess K, Fares S, Sparre-Ulrich AH, Hilgenberg E, Jarvis MA, Ehlers B, Rosenkilde MM. Identification and functional comparison of seven-transmembrane G-protein-coupled BILF1 receptors in recently discovered nonhuman primate lymphocryptoviruses. J Virol. 2015;89:2253–2267. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02716-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staskus KA, Sun R, Miller G, Racz P, Jaslowski A, Metroka C, Brett-Smith H, Haase AT. Cellular tropism and viral interleukin-6 expression distinguish human herpesvirus 8 involvement in Kaposi's sarcoma, primary effusion lymphoma, and multicentric Castleman's disease. J Virol. 1999;73:4181–4187. doi: 10.1128/jvi.73.5.4181-4187.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart S, Dawson CW, Takada K, Curnow J, Moody CA, Sixbey JW, Young LS. Epstein-Barr virus-encoded LMP2A regulates viral and cellular gene expression by modulation of the NF-kappaB transcription factor pathway. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2004;101:15730–15735. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0402135101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stine JT, Wood C, Hill M, Epp A, Raport CJ, Schweickart VL, Endo Y, Sasaki T, Simmons G, Boshoff C, Clapham P, Chang Y, Moore P, Gray PW, Chantry D. KSHV-encoded CC chemokine vMIP-is a CCR4 agonist, stimulates angiogenesis, and selectively chemoattracts TH2 cells. Blood. 2000;95:1151–1157. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stuart AD, Stewart JP, Arrand JR, Mackett M. The Epstein-Barr virus encoded cytokine viral interleukin-10 enhances transformation of human B lymphocytes. Oncogene. 1995;11:1711–1719. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki T, Tahara H, Narula S, Moore KW, Robbins PD, Lotze MT. Viral interleukin 10 (IL-10), the human herpes virus 4 cellular IL-10 homologue, induces local anergy to allogeneic and syngeneic tumors. J Exp Med. 1995;182:477–486. doi: 10.1084/jem.182.2.477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swaminathan S, Hesselton R, Sullivan J, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus recombinants with specifically mutated BCRF1 genes. J Virol. 1993;67:7406–7413. doi: 10.1128/jvi.67.12.7406-7413.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorley-Lawson DA, Hawkins JB, Tracy SI, Shapiro M. The pathogenesis of Epstein-Barr virus persistent infection. Curr Opin Virol. 2013;3:227–232. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2013.04.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson CC, Damania B. The K1 protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus activates the Akt signaling pathway. J Virol. 2004;78:1918–1927. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.4.1918-1927.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomlinson CC, Damania B. Critical role for endocytosis in the regulation of signaling by the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus K1 protein. J Virol. 2008;82:6514–6523. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02637-07. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Veettil MV, Bandyopadhyay C, Dutta D, Chandran B. Interaction of KSHV with host cell surface receptors and cell entry. Viruses. 2014;6:4024–4046. doi: 10.3390/v6104024. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D, Liebowitz D, Kieff E. An EBV membrane protein expressed in immortalized lymphocytes transforms established rodent cells. Cell. 1985;43:831–840. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90256-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang D, Liebowitz D, Wang F, Gregory C, Rickinson A, Larson R, Springer T, Kieff E. Epstein-Barr virus latent infection membrane protein alters the human B-lymphocyte phenotype: deletion of the amino terminus abolishes activity. J Virol. 1988;62:4173–4184. doi: 10.1128/jvi.62.11.4173-4184.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L, Brinkmann MM, Pietrek M, Ottinger M, Dittrich-Breiholz O, Kracht M, Schulz TF. Functional characterization of the M-type K15-encoded membrane protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. J Gen Virol. 2007;88:1698–1707. doi: 10.1099/vir.0.82807-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L, Dittmer DP, Tomlinson CC, Fakhari FD, Damania B. Immortalization of primary endothelial cells by the K1 protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus. Cancer Res. 2006;66:3658–3666. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-05-3680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L, Wakisaka N, Tomlinson C D, Wire SM, Krall S, Pagano JS, Damania B. The Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV/HHV-8) K1 protein induces expression of angiogenic and invasion factors. Cancer Res. 2004;64:2774–2781. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-03-3653. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen KW, Damania B. Hsp90 and Hsp40/Erdj3 are required for the expression and anti-apoptotic function of KSHV K1. On-cogene. 2010;29:3532–3544. doi: 10.1038/onc.2010.124. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xiao L, Hu ZY, Dong X, Tan Z, Li W, Tang M, Chen L, Yang L, Tao Y, Jiang Y, Li J, Yi B, Li B, Fan S, You S, Deng X, Hu F, Feng L, Bode AM, Dong Z, Sun LQ, Cao Y. Targeting Epstein-Barr virus oncoprotein LMP1-mediated glycolysis sensitizes nasopharyngeal carcinoma to radiation therapy. Oncogene. 2014;33:4568–4578. doi: 10.1038/onc.2014.32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamin R, Kaynan NS, Glasner A, Vitenshtein A, Tsukerman P, Bauman Y, Ophir Y, Elias S, Bar-On Y, Gur C, Mandelboim O. The viral KSHV chemokine vMIP-II inhibits the migration of Naive and activated human NK cells by antagonizing two distinct chemokine receptors. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9:e1003568. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003568. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeidler R, Eissner G, Meissner P, Uebel S, Tampe R, Lazis S, Hammerschmidt W. Downregulation of TAP1 in B lymphocytes by cellular and Epstein-Barr virus-encoded interleukin-10. Blood. 1997;90:2390–2397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Z, Chen W, Sanders MK, Brulois KF, Dittmer DP, Damania B. J Virol. 2016. The K1 protein of Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV) augments viral lytic replication. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zong JC, Ciufo DM, Alcendor DJ, Wan X, Nicholas J, Browning PJ, Rady PL, Tyring SK, Orenstein JM, Rabkin CS, Su IJ, Powell KF, Croxson M, Foreman KE, Nickoloff BJ, Alkan S, Hayward GS. High-level variability in the ORF-K1 membrane protein gene at the left end of the Kaposi's sarcoma-associated herpesvirus genome defines four major virus subtypes and multiple variants or clades in different human populations. J Virol. 1999;73:4156–4170. doi: 10.1128/jvi.73.5.4156-4170.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuo J, Currin A, Griffin BD, Shannon-Lowe C, Thomas WA, Ressing ME, Wiertz EJ, Rowe M. The Epstein-Barr virus G-protein-coupled receptor contributes to immune evasion by targeting MHC class I molecules for degradation. PLoS Pathog. 2009;5:e1000255. doi: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1000255. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zuo J, Quinn LL, Tamblyn J, Thomas WA, Feederle R, Delecluse HJ, Hislop AD, Rowe M. The Epstein-Barr virus-encoded BILF1 protein modulates immune recognition of endogenously processed antigen by targeting major histocompatibility complex class I molecules trafficking on both the exocytic and endocytic pathways. J Virol. 2011;85:1604–1614. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01608-10. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


