Abstract
Though efficient vaccines against hepatitis B virus (HBV) and antiviral therapies are available, chronic HBV infection is still a global health problem. The process of HBV infection and HBV life cycle are extensively studied in last decades, however, the mechanisms of HBV-induced alterations of host cell metabolisms and host factors involved in modulating of viral replication are not fully understood. Thus, it is an important issue to examine these specific HBV-host interactions for development of novel strategies for antiviral therapies. Recently, microRNAs (miRNAs), a class of post-transcriptional regulatory small RNA, seem to be the relevant fine tuning factors of various cellular activities and pathways, including cell growth, metabolism, and viral replication. In this review, we summarize the up to date knowledge concerning the virus-host interactions and emphasizing on the role of miRNAs in regulation of HBV replication and host cell metabolism.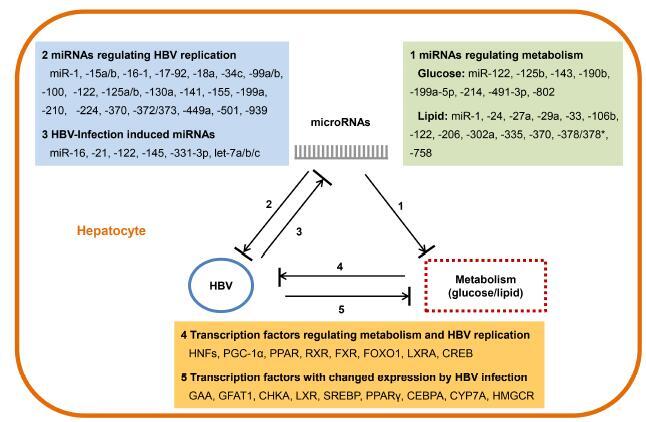
Keywords: microRNA, HBV replication, hepatocytes, cell metabolism, transcription factors
Footnotes
ORCID: 0000-0003-4287-9941
References
- Bar-Yishay I, Shaul Y, Shlomai A. Hepatocyte metabolic signalling pathways and regulation of hepatitis B virus expression. Liver Int. 2011;31:282–290. doi: 10.1111/j.1478-3231.2010.02423.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: Genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. doi: 10.1016/S0092-8674(04)00045-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cao Y, Chen J, Wang D, Peng H, Tan X, Xiong D, Huang A, Tang H. Upregulated in Hepatitis B virus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma cells, miR-331–3p promotes proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells by targeting ING5. Oncotarget. 2015;6:38093–38106. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.5642. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen C, Wu M, Zhang W, Lu W, Zhang M, Zhang Z, Zhang X, Yuan Z. MicroRNA-939 restricts Hepatitis B virus by targeting Jmjd3-mediated and C/EBPalpha-coordinated chromatin remodeling. Sci Rep. 2016;6:35974. doi: 10.1038/srep35974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu R, Mo G, Duan Z, Huang M, Chang J, Li X, Liu P. miRNAs affect the development of hepatocellular carcinoma via dysregulation of their biogenesis and expression. Cell Commun Signal. 2014;12:45. doi: 10.1186/s12964-014-0045-y. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cui M, Wang Y, Sun BD, Xiao ZL, Ye LH, Zhang XD. MiR-205 modulates abnormal lipid metabolism of hepatoma cells via targeting acyl-CoA synthetase long-chain family member 1 (ACSL1) mRNA. Biochem Bioph Res Co. 2014;444:270–275. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.01.051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dai X, Zhang W, Zhang H, Sun S, Yu H, Guo Y, Kou Z, Zhao G, Du L, Jiang S, Zhang J, Li J, Zhou Y. Modulation of HBV replication by microRNA-15b through targeting hepatocyte nuclear factor 1alpha. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:6578–6590. doi: 10.1093/nar/gku260. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Damania P, Sen B, Dar SB, Kumar S, Kumari A, Gupta E, Sarin SK, Venugopal SK. Hepatitis B virus induces cell proliferation via HBx-induced microRNA-21 in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting programmed cell death protein4 (PDCD4) and phosphatase and tensin homologue (PTEN) PLoS One. 2014;9:e91745. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0091745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davalos A, Goedeke L, Smibert P, Ramirez CM, Warrier NP, Andreo U, Cirera-Salinas D, Rayner K, Suresh U, Pastor-Pareja JC, Esplugues E, Fisher EA, Penalva LO, Moore KJ, Suarez Y, Lai EC, Fernandez-Hernando C. miR-33a/b contribute to the regulation of fatty acid metabolism and insulin signaling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108:9232–9237. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1102281108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dluzen DF, Sun D, Salzberg AC, Jones N, Bushey RT, Robertson GP, Lazarus P. Regulation of UDP-glucuronosyltransferase 1A1 expression and activity by microRNA 491–3p. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2014;348:465–477. doi: 10.1124/jpet.113.210658. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esau C, Davis S, Murray SF, Yu XX, Pandey SK, Pear M, Watts L, Booten SL, Graham M, McKay R, Subramaniam A, Propp S, Lollo BA, Freier S, Bennett CF, Bhanot S, Monia BP. miR-122 regulation of lipid metabolism revealed by in vivo antisense targeting. Cell Metab. 2006;3:87–98. doi: 10.1016/j.cmet.2006.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan CG, Wang CM, Tian C, Wang Y, Li L, Sun WS, Li RF, Liu YG. miR-122 inhibits viral replication and cell proliferation in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma and targets NDRG3. Oncol Rep. 2011;26:1281–1286. doi: 10.3892/or.2011.1375. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan H, Lv P, Lv J, Zhao X, Liu M, Zhang G, Tang H. J Med Virol. 2016. miR-370 suppresses HBV gene expression and replication by targeting nuclear factor IA. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gao F, Sun X, Wang L, Tang S, Yan C. Downregulation of MicroRNA-145 Caused by Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Promotes Expression of CUL5 and Contributes to Pathogenesis of Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Cell Physiol Biochem. 2015;37:1547–1559. doi: 10.1159/000438522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerin I, Bommer GT, McCoin CS, Sousa KM, Krishnan V, Mac-Dougald OA. Roles for miRNA-378/378* in adipocyte gene expression and lipogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2010;299:E198–E206. doi: 10.1152/ajpendo.00179.2010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm D, Thimme R, Blum HE. HBV life cycle and novel drug targets. Hepatol Int. 2011;5:644–653. doi: 10.1007/s12072-011-9261-3. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo H, Liu H, Mitchelson K, Rao H, Luo M, Xie L, Sun Y, Zhang L, Lu Y, Liu R, Ren A, Liu S, Zhou S, Zhu J, Zhou Y, Huang A, Wei L, Guo Y, Cheng J. MicroRNAs-372/373 promote the expression of hepatitis B virus through the targeting of nuclear factor I/B. Hepatology. 2011;54:808–819. doi: 10.1002/hep.24441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo W, Qiu Z, Wang Z, Wang Q, Tan N, Chen T, Chen Z, Huang S, Gu J, Li J, Yao M, Zhao Y, He X. MiR-199a-5p is negatively associated with malignancies and regulates glycolysis and lactate production by targeting hexokinase 2 in liver cancer. Hepatology. 2015;62:1132–1144. doi: 10.1002/hep.27929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammond SM. An overview of microRNAs. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2015;87:3–14. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2015.05.001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hao R, He J, Liu X, Gao G, Liu D, Cui L, Yu G, Yu W, Chen Y, Guo D. Inhibition of hepatitis B virus gene expression and replication by hepatocyte nuclear factor 6. J Virol. 2015;89:4345–4355. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03094-14. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoekstra M, van der Sluis RJ, Kuiper J, Van Berkel TJ. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease is associated with an altered hepatocyte microRNA profile in LDL receptor knockout mice. J Nutr Biochem. 2012;23:622–628. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2011.03.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu PP, Sabatini DM. Cancer cell metabolism: Warburg and beyond. Cell. 2008;134:703–707. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2008.08.021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu W, Wang X, Ding X, Li Y, Zhang X, Xie P, Yang J, Wang S. MicroRNA-141 represses HBV replication by targeting PPARA. PLoS One. 2012;7:e34165. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0034165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang JY, Chen HL, Shih C. MicroRNA miR-204 and miR-1236 inhibit hepatitis B virus replication via two different mechanisms. Sci Rep. 2016;6:34740. doi: 10.1038/srep34740. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang JY, Chou SF, Lee JW, Chen HL, Chen CM, Tao MH, Shih C. MicroRNA-130a can inhibit hepatitis B virus replication via targeting PGC1alpha and PPARgamma. RNA. 2015;21:385–400. doi: 10.1261/rna.048744.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung JH, Yan CW, Su IJ, Wang HC, Lei HY, Lin WC, Chang WT, Huang W, Lu TJ, Lai MD. Hepatitis B virus surface antigen interacts with acid alpha-glucosidase and alters glycogen metabolism. Hepatol Res. 2010;40:633–640. doi: 10.1111/j.1872-034X.2010.00645.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hung TM, Ho CM, Liu YC, Lee JL, Liao YR, Wu YM, Ho MC, Chen CH, Lai HS, Lee PH. Up-regulation of microRNA-190b plays a role for decreased IGF-1 that induces insulin resistance in human hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 2014;9:e89446. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0089446. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iavarone M, Colombo M. HBV infection and hepatocellular carcinoma. Clin Liver Dis. 2013;17:375–397. doi: 10.1016/j.cld.2013.05.002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iliopoulos D, Drosatos K, Hiyama Y, Goldberg IJ, Zannis VI. MicroRNA-370 controls the expression of microRNA-122 and Cpt1alpha and affects lipid metabolism. J Lipid Res. 2010;51:1513–1523. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M004812. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jhuang HJ, Hsu WH, Lin KT, Hsu SL, Wang FS, Chou CK, Lee KH, Tsou AP, Lai JM, Yeh SF, Huang CYF. Gluconeogenesis, lipogenesis, and HBV replication are commonly regulated by PGC-1 alpha-dependent pathway. Oncotarget. 2015;6:7788–7803. doi: 10.18632/oncotarget.3050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jiang JX, Gao S, Pan YZ, Yu C, Sun CY. Overexpression of microRNA-125b sensitizes human hepatocellular carcinoma cells to 5-fluorouracil through inhibition of glycolysis by targeting hexokinase II. Mol Med Rep. 2014;10:995–1002. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2014.2271. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jordan SD, Kruger M, Willmes DM, Redemann N, Wunderlich FT, Bronneke HS, Merkwirth C, Kashkar H, Olkkonen VM, Bottger T, Braun T, Seibler J, Bruning JC. Obesity-induced overexpression of miRNA-143 inhibits insulin-stimulated AKT activation and impairs glucose metabolism. Nat Cell Biol. 2011;13:434–446. doi: 10.1038/ncb2211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khee SG, Yusof YA, Makpol S. Expression of senescenceassociated microRNAs and target genes in cellular aging and modulation by tocotrienol-rich fraction. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2014;2014:725929. doi: 10.1155/2014/725929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim HY, Cho HK, Kim HH, Cheong J. Oxygenated derivatives of cholesterol promote hepatitis B virus gene expression through nuclear receptor LXR alpha activation. Virus Research. 2011;158:55–61. doi: 10.1016/j.virusres.2011.03.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim J, Yoon H, Ramirez CM, Lee SM, Hoe HS, Fernandez-Hernando C. MiR-106b impairs cholesterol efflux and increases Abeta levels by repressing ABCA1 expression. Exp Neurol. 2012;235:476–483. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2011.11.010. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim KH, Shin HJ, Kim K, Choi HM, Rhee SH, Moon HB, Kim HH, Yang US, Yu DY, Cheong J. Hepatitis^B virus X protein induces hepatic steatosis via transcriptional activation of SREBP1 and PPARgamma. Gastroenterology. 2007;132:1955–1967. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2007.03.039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld JW, Baitzel C, Konner AC, Nicholls HT, Vogt MC, Herrmanns K, Scheja L, Haumaitre C, Wolf AM, Knippschild U, Seibler J, Cereghini S, Heeren J, Stoffel M, Bruning JC. Obesity-induced overexpression of miR-802 impairs glucose metabolism through silencing of Hnf1b. Nature. 2013;494:111–115. doi: 10.1038/nature11793. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krutzfeldt J, Rajewsky N, Braich R, Rajeev KG, Tuschl T, Manoharan M, Stoffel M. Silencing of microRNAs in vivo with ‘antagomirs’. Nature. 2005;438:685–689. doi: 10.1038/nature04303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lagos-Quintana M, Rauhut R, Yalcin A, Meyer J, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T. Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr Biol. 2002;12:735–739. doi: 10.1016/S0960-9822(02)00809-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li F, Zhou P, Deng W, Wang J, Mao R, Zhang Y, Li J, Yu J, Yang F, Huang Y, Lu M, Zhang J. Serum microRNA-125b correlates with hepatitis B viral replication and liver necroinflammation. Clin Microbiol Infect. 2016;22:384. doi: 10.1016/j.cmi.2015.12.024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li H, Zhu W, Zhang L, Lei H, Wu X, Guo L, Chen X, Wang Y, Tang H. The metabolic responses to hepatitis B virus infection shed new light on pathogenesis and targets for treatment. Sci Rep. 2015;5:8421. doi: 10.1038/srep08421. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li K, Zhang J, Yu J, Liu B, Guo Y, Deng J, Chen S, Wang C, Guo F. MicroRNA-214 suppresses gluconeogenesis by targeting activating transcriptional factor 4. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:8185–8195. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.633990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y, Deng W, Pang J, Kemper T, Hu J, Yin J, Zhang J, Lu M. Cell Microbiol. 2016. The microRNA-99 family modulates hepatitis B virus replication by promoting IGF-1R/PI3K/Akt/mTOR/ULK1 signaling-induced autophagy. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu AM, Xu Z, Shek FH, Wong KF, Lee NP, Poon RT, Chen J, Luk JM. miR-122 targets pyruvate kinase M2 and affects metabolism of hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One. 2014;9:e86872. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0086872. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu WH, Yeh SH, Lu CC, Yu SL, Chen HY, Lin CY, Chen DS, Chen PJ. MicroRNA-18a prevents estrogen receptoralpha expression, promoting proliferation of hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Gastroenterology. 2009;136:683–693. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2008.10.029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ma XY, Li CC, Sun LC, Huang D, Li TT, He XP, Wu GW, Yang Z, Zhong XY, Song LB, Gao P, Zhang HF. Lin28/let-7 axis regulates aerobic glycolysis and cancer progression via PDK1. Nat Commun. 2014;5:5212. doi: 10.1038/ncomms6212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattis AN, Song G, Hitchner K, Kim RY, Lee AY, Sharma AD, Malato Y, McManus MT, Esau CC, Koller E, Koliwad S, Lim LP, Maher JJ, Raffai RL, Willenbring H. A screen in mice uncovers repression of lipoprotein lipase by microRNA-29a as a mechanism for lipid distribution away from the liver. Hepatology. 2015;61:141–152. doi: 10.1002/hep.27379. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuguchi Y, Takizawa T, Uchida E. Host cellular microRNA involvement in the control of hepatitis B virus gene expression and replication. World J Hepatol. 2015;7:696–702. doi: 10.4254/wjh.v7.i4.696. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Na TY, Shin YK, Roh KJ, Kang SA, Hong I, Oh SJ, Seong JK, Park CK, Choi YL, Lee M-O. Liver^X Receptor Mediates Hepatitis B Virus X Protein-Induced Lipogenesis in Hepatitis B Virus-Associated Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Hepatology. 2009;49:1122–1131. doi: 10.1002/hep.22740. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Najafi-Shoushtari SH, Kristo F, Li Y, Shioda T, Cohen DE, Gerszten RE, Naar AM. MicroRNA-33 and the SREBP host genes cooperate to control cholesterol homeostasis. Science. 2010;328:1566–1569. doi: 10.1126/science.1189123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi N, Nakagawa Y, Tokushige N, Aoki N, Matsuzaka T, Ishii K, Yahagi N, Kobayashi K, Yatoh S, Takahashi A, Suzuki H, Urayama O, Yamada N, Shimano H. The up-regulation of microRNA-335 is associated with lipid metabolism in liver and white adipose tissue of genetically obese mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2009;385:492–496. doi: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2009.05.058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ng R, Wu H, Xiao H, Chen X, Willenbring H, Steer CJ, Song G. Inhibition of microRNA-24 expression in liver prevents hepatic lipid accumulation and hyperlipidemia. Hepatology. 2014;60:554–564. doi: 10.1002/hep.27153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oehler N, Volz T, Bhadra OD, Kah J, Allweiss L, Giersch K, Bierwolf J, Riecken K, Pollok JM, Lohse AW, Fehse B, Petersen J, Urban S, Luetgehetmann M, Heeren J, Dandri M. Binding of Hepatitis B Virus to Its Cellular Receptor Alters the Expression Profile of Genes of Bile Acid Metabolism. Hepatology. 2014;60:1483–1493. doi: 10.1002/hep.27159. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peng F, Xiao XQ, Jiang YF, Luo KZ, Tian Y, Peng ML, Zhang M, Xu Y, Gong GZ. HBx Down-Regulated Gld2 Plays a Critical Role in HBV-Related Dysregulation of miR-122. PLoS One. 2014;9:e92998. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0092998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potenza N, Papa U, Mosca N, Zerbini F, Nobile V, Russo A. Human microRNA hsa-miR-125a-5p interferes with expression of hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011;39:5157–5163. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkr067. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez CM, Davalos A, Goedeke L, Salerno AG, Warrier N, Cirera-Salinas D, Suarez Y, Fernandez-Hernando C. MicroRNA-758 regulates cholesterol efflux through posttranscriptional repression of ATP-binding cassette transporter A1. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2011;31:2707–2714. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.111.232066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rayner KJ, Esau CC, Hussain FN, McDaniel AL, Marshall SM, van Gils JM, Ray TD, Sheedy FJ, Goedeke L, Liu X, Khatsenko OG, Kaimal V, Lees CJ, Fernandez-Hernando C, Fisher EA, Temel RE, Moore KJ. Inhibition of miR-33a/b in non-human primates raises plasma HDL and lowers VLDL triglycerides. Nature. 2011;478:404–407. doi: 10.1038/nature10486. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottiers V, Naar AM. MicroRNAs in metabolism and metabolic disorders. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2012;13:239–250. doi: 10.1038/nrm3313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sarkar N, Panigrahi R, Pal A, Biswas A, Singh SP, Kar SK, Bandopadhyay M, Das D, Saha D, Kanda T, Sugiyama M, Chakrabarti S, Banerjee A, Chakravarty R. Expression of microRNA-155 correlates positively with the expression of Tolllike receptor 7 and modulates hepatitis B virus via C/EBP-beta in hepatocytes. J Viral Hepat. 2015;22:817–827. doi: 10.1111/jvh.12390. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schweitzer A, Horn J, Mikolajczyk RT, Krause G, Ott JJ. Estimations of worldwide prevalence of chronic hepatitis B virus infection: a systematic review of data published between 1965 and 2013. Lancet. 2015;386:1546–1555. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(15)61412-X. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shi YX, Huang CJ, Yang ZG. Impact of hepatitis B virus infection on hepatic metabolic signaling pathway. World J Gastroenterol. 2016;22:8161–8167. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i36.8161. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shirasaki T, Honda M, Shimakami T, Horii R, Yamashita T, Sakai Y, Sakai A, Okada H, Watanabe R, Murakami S, Yi M, Lemon SM, Kaneko S. MicroRNA-27a Regulates Lipid Metabolism and Inhibits Hepatitis C Virus Replication in Human Hepatoma Cells. Journal of Virology. 2013;87:5270–5286. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03022-12. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shyh-Chang N, Daley GQ. Lin28: primal regulator of growth and metabolism in stem cells. Cell Stem Cell. 2013;12:395–406. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2013.03.005. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sidhu K, Kapoor NR, Pandey V, Kumar V. The “Macro” World of microRNAs in Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2015;5:68. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2015.00068. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng CF, Hsieh WC, Wu HC, Lin YJ, Tsai HW, Huang W, Su IJ. Hepatitis B Virus Pre-S2 Mutant Induces Aerobic Glycolysis through Mammalian Target of Rapamycin Signal Cascade. PLoS One. 2015;10:e0122373. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0122373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K, Holterman AX. Pathophysiologic role of hepatocyte nuclear factor 6. Cell Signal. 2012;24:9–16. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.08.009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y, Jiang L, Ji X, Yang B, Zhang Y, Fu XD. Hepatitis B Viral RNA Directly Mediates Down-regulation of the Tumor Suppressor MicroRNA miR-15a/miR-16–1 in Hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 2013;288:18484–18493. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.458158. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y, Lu Y, Toh ST, Sung WK, Tan P, Chow P, Chung AY, Jooi LL, Lee CG. Lethal-7 is down-regulated by the hepatitis B virus x protein and targets signal transducer and activator of transcription 3. J Hepatol. 2010;53:57–66. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2009.12.043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y, Wang CM, Jiang ZZ, Yu XJ, Fan CG, Xu FF, Zhang Q, Li LI, Li RF, Sun WS, Zhang ZH, Liu YG. MicroRNA-34c targets TGFB-induced factor homeobox 2, represses cell proliferation and induces apoptosis in hepatitis B virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol Lett. 2015;10:3095–3102. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.3649. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei B, Song Y, Zhang Y, Hu M. microRNA-449a functions as a tumor-suppressor in gastric adenocarcinoma by targeting Bcl-2. Oncol Lett. 2013;6:1713–1718. doi: 10.3892/ol.2013.1609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winther TN, Bang-Berthelsen CH, Heiberg IL, Pociot F, Hogh B. Differential Plasma MicroRNA Profiles in HBeAg Positive and HBeAg Negative Children with Chronic Hepatitis B. PLoS One. 2013;8:e58236. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0058236. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu G, Yu F, Xiao Z, Xu K, Xu J, Tang W, Wang J, Song E. Hepatitis B virus X protein downregulates expression of the miR-16 family in malignant hepatocytes in vitro. Br J Cancer. 2011;105:146–153. doi: 10.1038/bjc.2011.190. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu YL, Peng XE, Zhu YB, Yan XL, Chen WN, Lin X. Hepatitis B Virus X Protein Induces Hepatic Steatosis by Enhancing the Expression of Liver Fatty Acid Binding Protein. J Virol. 2015;90:1729–1740. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02604-15. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Xu Z, Zhai L, Yi T, Gao H, Fan F, Li Y, Wang Y, Li N, Xing X, Su N, Wu F, Chang L, Chen X, Dai E, Zhao C, Yang X, Cui C, Xu P. Oncotarget. 2016. Hepatitis^B virus X induces inflammation and cancer in mice liver through dysregulation of cytoskeletal remodeling and lipid metabolism. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang GL, Li YX, Zheng SQ, Liu M, Li X, Tang H. Suppression of hepatitis B virus replication by microRNA-199a-3p and microRNA-210. Antiviral Res. 2010;88:169–175. doi: 10.1016/j.antiviral.2010.08.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X, Hou J, Lu M. Regulation of hepatitis B virus replication by epigenetic mechanisms and microRNAs. Front Genet. 2013;4:202. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2013.00202. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X, Liu H, Xie Z, Deng W, Wu C, Qin B, Hou J, Lu M. Epigenetically regulated miR-449a enhances hepatitis B virus replication by targeting cAMP-responsive element binding protein 5 and modulating hepatocytes phenotype. Sci Rep. 2016;6:25389. doi: 10.1038/srep25389. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang X, Zhang E, Ma Z, Pei R, Jiang M, Schlaak JF, Roggendorf M, Lu M. Modulation of hepatitis B virus replication and hepatocyte differentiation by MicroRNA-1. Hepatology. 2011;53:1476–1485. doi: 10.1002/hep.24195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong D, Huang G, Zhang Y, Zeng Y, Xu Z, Zhao Y, He X, He F. MicroRNA-1 and microRNA-206 suppress LXRalphainduced lipogenesis in hepatocytes. Cell Signal. 2013;25:1429–1437. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.03.003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhong D, Zhang Y, Zeng YJ, Gao M, Wu GZ, Hu CJ, Huang G, He FT. MicroRNA-613 represses lipogenesis in HepG2 cells by downregulating LXRalpha. Lipids Health Dis. 2013;12:32. doi: 10.1186/1476-511X-12-32. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu H, Shyh-Chang N, Segre AV, Shinoda G, Shah SP, Einhorn WS, Takeuchi A, Engreitz JM, Hagan JP, Kharas MG, Urbach A, Thornton JE, Triboulet R, Gregory RI, Altshuler D, Daley GQ. The Lin28/let-7 axis regulates glucose metabolism. Cell. 2011;147:81–94. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.08.033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


