Abstract
Background
Glypican 3 (GPC3) is a heparin sulphate proteoglycan whose expression is associated with several malignancies. However, its expression in non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) is limited and ambiguous. This study aimed to comprehensively evaluate the expression of GPC3 in NSCLC and develop a risk-score model for predicting the prognosis of NSCLC.
Methods
The gene expression profiles of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) were downloaded from the UCSC Xena database. Using the limma package, the differentially expressed genes (DEGs) between different comparison groups were analysed and the differential expression of GPC3 was calculated. A functional enrichment analysis was conducted for GPC3-associated genes using the DAVID tool. For the GPC3-associated genes shared by the four comparison groups, a protein–protein interaction network was built using the Cytoscape software. After conducting a survival analysis and a Cox regression analysis, the genes found to be significantly correlated with prognosis were selected to construct a risk-score model. Besides, the gene and protein levels of GPC3 were examined by quantitative reverse transcriptase-PCR (qRT-PCR) and immunohistochemistry (IHC) in LUSC tissues and paracancer tissues.
Results
The differential expression of GPC3 was significant (adjusted P < 0.05) in the NSCLC vs. normal, LUAD vs. normal, LUSC versus normal, and LUAD versus. LUSC comparison groups. GPC3 directly interacted with SERPINA1, MFI2, and FOXM1. Moreover, GPC3 expression was significantly correlated with pathologic N, pathologic T, gender, and tumour stage in LUAD samples. Finally, the risk-score model (involving MFI2, FOXM1, and GPC3) for LUAD and that (involving SERPINA1 and FOXM1) for LUSC were established separately. The qRT-PCR result showed that GPC3 expression was much higher in the LUSC tissues than that in the normal group. The IHC results further showed that GPC3 is highly expressed in LUSC tissues, but low in paracancer tissues.
Conclusion
The three-gene risk-score model for LUAD and the two-gene risk-score model for LUSC might be valuable in improving the prognosis of these carcinomas.
Keywords: Lung adenocarcinoma, Lung squamous cell carcinoma, Glypican 3, Differential expression analysis, Protein–protein interaction network, Risk-score model
Background
Lung cancer, a malignant tumour with the fastest increasing morbidity and mortality rates, is the greatest threat to human health and life [1]. Small-cell lung carcinoma (SCLC) and non-small-cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) are the two main pathological types of lung cancer, with NSCLC accounting for approximately 85% of lung cancers [2]. NSCLC can be categorised into several subtypes, including lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD), lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC), and lung large cell carcinoma (LCLC) [3]. Moreover, the occurrence of LUSC is tightly correlated with smoking, and it has been reported that the rate of exposure to smoking in LUSC patients exceeds 90% [4]. Clinically, only a small proportion of NSCLC patients is diagnosed at the early stages (stage I or II), and surgical resection is the most effective treatment for stage I, II, and IIIA NSCLC [5]. More than 60% of lung cancer patients have locally advanced or metastatic disease (stage III or IV) at the time of diagnosis and have lost the chance of radical treatment [5]. In patients who have undergone surgical treatment, there is a high risk of recurrence despite the possibility of complete remission. Therefore, it is important to understand the pathogenesis of NSCLC to improve treatment outcomes.
The past decades have witnessed rapid development in the pathology of lung cancer, and numerous dysregulated genes involved in NSCLC have been identified. A previous study demonstrated that astrocyte-elevated gene-1 (AEG-1) acts in the formation and deterioration of NSCLC by regulating matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP9), resulting in an unfavourable clinical outcome [6]. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GAPDH) overexpression indicates a poor prognosis in early-stage NSCLC, and the assessment of glucose metabolism has certain prognostic value in this tumour [7]. Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α (HIF-2α) expression is correlated with lymph-node metastasis, tumour size, tumour histology, and tumour stage, making it a potential candidate target for predicting the progression and clinical outcome of LUAD [8, 9]. Decreased N-MYC downstream-regulated gene 2 (NDRG2) is important for the tumorigenesis of lung cancer and may be considered a valuable prognostic marker in lung cancer [10]. Increased Notch homolog 2 (Notch2 expression in LUAD patients can induce a high tumour recurrence rate, and high expression of Notch1 and Notch3 is related to adverse prognosis in LUAD [11]. Claudin-3 (CLDN3) in LUSC tissues is related to tumour progression and represses epithelial–mesenchymal transition (EMT) via activation of the Wnt pathway; therefore, CLDN3 may be a candidate biomarker for the prognosis and treatment of LUSC [12]. However, more genes affecting the prognosis of NSCLC still need to be explored.
Glypican 3 (GPC3) is a membrane-bound heparin sulphate proteoglycan located on chromosome Xq26 [13]. It is highly expressed during foetal life, but its levels decrease after birth [14]. The expression patterns of GPC3 in different cancer types have been reported to be different, and its role is controversial. GPC3 is overexpressed in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), embryonal tumours, melanoma, hepatoblastoma, and testicular germ-cell tumours, and it acts as a tumour oncogene [15–20]. However, mutations or loss of expression have been reported in Simpson-Golabi-Behmel syndrome [21], ovarian carcinoma, breast cancer, and mesothelioma [22–25], suggesting that GPC3 functions as a tumour-suppressor gene. Currently, reports of GPC3 in lung cancer are limited and ambiguous. Kim et al. reported that GPC3 expression was decreased in LUAD compared with that in paired normal tissues [26]. In a study by Sarit et al., GPC3 was found to be overexpressed in LUSC (positive rate of 55%) but not in LUAD (positive rate of 8%), which might be induced by smoking [27].
In this study, the gene expression profiles of NSCLC were obtained. Differential expression and enrichment analyses for different comparison groups were then carried out. After the genes correlated with GPC3 were screened out, a protein–protein interaction (PPI) network analysis, survival analysis, and Cox regression analysis were conducted separately. The present results might help to elucidate the GPC3-correlated prognostic mechanisms of LUAD and LUSC.
Methods
Data source
From the University of California Santa Cruz (UCSC) Xena database (https://xenabrowser.net/datapages/), the gene expression profiles (standardised expression values of log2[fragments per kilobase of transcript per million reads (FPKM) + 1]) of LUAD (including 526 tumour samples and 59 normal samples) and LUSC (including 501 tumour samples and 49 normal samples) were downloaded. Meanwhile, the clinical phenotypes (including smoking and sex) and prognostic information (including survival status and survival time) of these samples were extracted. These samples all contain clinical phenotypes and prognostic information.
Differential expression analysis and enrichment analysis
The samples were divided into seven comparison groups: NSCLC versus normal, LUAD versus normal, LUSC versus normal, LUAD versus LUSC, male versus female, smoker versus non-smoker, LUSC smoker versus LUSC non-smoker. A differential expression analysis was conducted using the R package limma [28] (version 3.10.3, http://www.bioconductor.org/packages/2.9/bioc/html/limma.html), and the P values of the genes were adjusted using the Benjamini & Hochberg method [29]. To screen the differentially expressed genes (DEGs), |logfold change (FC)|> 1 and adjusted P < 0.05 were defined.
For the DEGs of each comparison group, Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopaedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) [30, 31] enrichment analyses were performed separately using the DAVID online tool [32] (version 6.7, https://david-d.ncifcrf.gov/). A false discovery rate (FDR) < 0.05 was the threshold for selecting significantly enriched results.
Construction of PPI network
For each comparison group, the genes involved in the significant GO/KEGG terms correlated with GPC3 were screened. Then, the intersections of these genes in different comparison groups were selected by drawing a Venn diagram [33], and the common genes were considered candidate genes. Using the STRING database [34] (http://www.string-db.org) and Cytoscape software [35] (https://cytoscape.org/), a PPI network was constructed to identify the hub genes and the genes directly correlated with GPC3.
Correlation of GPC3 with clinical phenotypes
There were 585 LUAD and 550 LUSC samples. In addition to GPC3 expression, phenotypes such as age, location, years smoked, pathologic M, pathologic N, pathologic T, radiation therapy, sex, and tumour stage were also investigated. The baseline data of LUAD and LUSC samples are listed in Tables 1 and 2, respectively. GPC3 expression is the standardised expression value of log2(FPKM + 1). The average value of the non-empty samples was calculated for the expression of two characteristics—years smoked and GPC3 expression. The non-empty samples were then compared with the average value and divided into two groups: high and low. Lung cancer was most common between the ages of 45 and 65 years; therefore, the samples were divided into two groups based on age (≥ 65 or < 65 years).
Table 1.
Baseline data of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) samples
| Characteristics | Number | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| ≥ 65 | 310 | 53.0 |
| < 65 | 256 | 43.8 |
| NA | 19 | 3.2 |
| Location | ||
| Central lung | 67 | 11.5 |
| Peripheral lung | 130 | 22.2 |
| NA | 388 | 66.3 |
| Years_smoked | ||
| ≥ 41 | 160 | 27.4 |
| < 41 | 234 | 40.0 |
| NA | 191 | 32.6 |
| pathologic_M | ||
| M0 | 394 | 67.4 |
| M1 | 20 | 3.4 |
| M1a | 2 | 0.3 |
| M1b | 5 | 0.9 |
| MX | 158 | 27.0 |
| NA | 6 | 1.0 |
| pathologic_N | ||
| N0 | 371 | 63.4 |
| N1 | 107 | 18.3 |
| N2 | 87 | 14.9 |
| N3 | 2 | 0.3 |
| NX | 17 | 2.9 |
| NA | 1 | 0.2 |
| pathologic_T | ||
| T1 | 82 | 14.0 |
| T1a | 49 | 8.4 |
| T1b | 60 | 10.3 |
| T2 | 203 | 34.7 |
| T2a | 89 | 15.2 |
| T2b | 29 | 5.0 |
| T3 | 50 | 8.5 |
| T4 | 20 | 3.4 |
| TX | 3 | 0.5 |
| radiation_therapy | ||
| Yes | 69 | 11.8 |
| No | 428 | 73.2 |
| NA | 88 | 15.0 |
| Gender | ||
| Female | 316 | 54.0 |
| Male | 269 | 46.0 |
| tumor_stage | ||
| I | 316 | 54.0 |
| II | 135 | 23.1 |
| III | 97 | 16.6 |
| IV | 28 | 4.8 |
| NA | 9 | 1.5 |
| GPC3 expression | ||
| ≥ 3.19 | 270 | 46.2 |
| < 3.19 | 315 | 53.8 |
NA represents the sample with an empty record
Table 2.
Baseline data of lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) samples
| Characteristics | Number | Percent (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Age | ||
| ≥ 65 | 355 | 54.5 |
| < 65 | 186 | 33.8 |
| NA | 9 | 1.6 |
| Location | ||
| Central Lung | 157 | 28.5 |
| Peripheral Lung | 101 | 18.4 |
| NA | 292 | 53.1 |
| years_smoked | ||
| ≥ 53 | 177 | 32.2 |
| < 53 | 287 | 52.2 |
| NA | 86 | 15.6 |
| pathologic_M | ||
| M0 | 443 | 80.5 |
| M1 | 6 | 1.1 |
| M1a | 1 | 0.2 |
| M1b | 1 | 0.2 |
| MX | 94 | 17.1 |
| NA | 5 | 0.9 |
| pathologic_N | ||
| N0 | 352 | 64.0 |
| N1 | 143 | 26.0 |
| N2 | 43 | 7.8 |
| N3 | 5 | 0.9 |
| NX | 7 | 1.3 |
| pathologic_T | ||
| T1 | 53 | 9.6 |
| T1a | 26 | 4.7 |
| T1b | 44 | 8.0 |
| T2 | 187 | 34.0 |
| T2a | 100 | 18.2 |
| T2b | 40 | 7.3 |
| T3 | 76 | 13.8 |
| T4 | 24 | 4.4 |
| radiation_therapy | ||
| Yes | 51 | 9.3 |
| No | 386 | 70.2 |
| NA | 113 | 20.5 |
| Gender | ||
| Female | 144 | 26.2 |
| Male | 406 | 73.8 |
| tumor_stage | ||
| I | 270 | 49.1 |
| II | 179 | 32.5 |
| III | 89 | 16.2 |
| IV | 8 | 1.5 |
| NA | 4 | 0.7 |
| GPC3 Expression | ||
| ≥ 4.48 | 289 | 52.5 |
| < 4.48 | 261 | 47.5 |
NA represents the sample with an empty record
For each clinical phenotype, GPC3 expression was correlated with the clinical phenotype subgroups of the samples. The Wilcoxon rank sum test [36] was conducted for the phenotypes of the two groups, and the Kruskal–Wallis rank sum test [37] was performed for the phenotypes of multiple groups. A P value < 0.05 was set as the threshold.
Survival analysis
Based on the extracted prognostic information of the samples, the overall survival (OS) and OS status of the corresponding patients were determined. GPC3 and the genes directly correlated with GPC3 were considered as candidate features, and the patients were classified into high-expression and low-expression groups based on the median expression value of GPC3. The median expression value greater than GPC3 was high-expression, and the median expression value less than or equal to GPC3 was low-expression. Combined with the prognostic information of the samples, Kaplan–Meier (KM) survival analysis [38] was carried out. The log-rank test [39] was used to calculate P values. A P value < 0.05 indicated a significant correlation.
Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses
Based on the expression levels of GPC3 and the genes directly correlated with GPC3, along with the prognostic information of the samples, univariate Cox regression analysis [40] was performed using the coxph() function in R [41]. The regression coefficient and P value of each clinical factor, survival time, and state were calculated. Subsequently, a multivariate Cox regression analysis [42] was conducted for the clinical factors with P < 0.05, to obtain the final risk-score model. The samples were divided into high-risk and low-risk groups based on their risk scores, and a KM survival analysis [43] was performed. Furthermore, the 1-year, 3-year, and 5-year survival rates of the samples were predicted based on their risk scores; receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves [44] were drawn, and the corresponding area under the ROC curve (AUC) values were calculated.
cBioPortal analysis
Genome data from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) lung cancer dataset using cBioportal (https://www.cbioportal.org/) have been retrieved in order to identify mutations and copy number alterations (CNAs) of GPC3 [45]. The location and frequency of GPC3 and GPC3-related gene alterations (amplifications, deep deletions and missene mutations) and copy number variance data were evaluated.
Quantitative reverse transcriptase-PCR (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted from LUSC and paracancer tissues using the TRIzol Reagent (Invitrogen, USA). Then, the cDNA was reverse-transcribed using a PrimeScriptTM RT kit with gDNA Eraser (TaKaRa, China). According to the manufacturer’s instructions, qRT-PCR was performed using TB Green® Premix Ex Taq™ II (Takara, Japan) on a CFX96 Real-Time PCR Detection System. GAPDH was used as an internal reference gene. The reaction mixture for qRT-PCR was prepared as follows: 8.5 μL of sterile purified water, 12.5 μL of TB Green Premix Ex Taq II (Tli RNaseH Plus) (2X), 1 μL of PCR forward primer (10 μM), 1 μL of qRT-PCR reverse primer (10 μM), and 2 μL cDNA template (< 100 ng) were mixed. The reaction conditions for qRT-PCR were as follows: initial denaturation at 95 °C for 30 s, followed by 40 cycles of 95 °C for 5 s and 60 °C for 30 s for denaturation and annealing/elongation, respectively. The 2−ΔΔCT method was used to measure relative expression.
Immunohistochemistry (IHC) validation
Cancer tissue specimens and paraffin sections of adjacent tissues were collected from 10 patients undergoing pulmonary malignant tumour surgery at the Liaoning Cancer Hospital and Institute between June 2018 and June 2020. The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of the Liaoning Cancer Hospital and Institute. The paraffin specimens of LUSC patients obtained after surgery were cut into two pieces for IHC staining. The sections were deparaffinized, and antigen retrieval was performed with citrate buffer (pH 6.0) under high temperature and pressure, followed by natural cooling to room temperature and dilution with PBS. After incubation in 3% BSA for 1 h, the cells were incubated with an Anti-GPC3 antibody overnight at 4 °C. Subsequently, the sections were incubated with secondary antibodies (Zsbio, China) and stained with diaminobenzidine (DAB) and haematoxylin.
Results
Differential expression and enrichment analyses
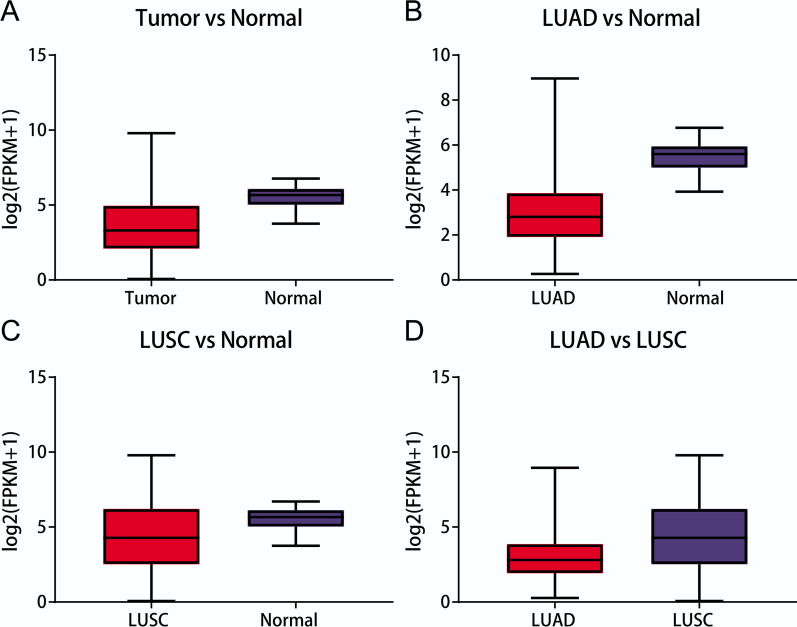
In total, 2478 DEGs (1324 up-regulated and 1154 down-regulated genes) in the NSCLC vs. normal comparison group, 1998 DEGs (904 up-regulated and 1094 down-regulated genes) in the LUAD vs. normal comparison group, 3425 DEGs (1670 up-regulated and 1755 down-regulated genes) in the LUSC vs. normal comparison group, 1072 DEGs (488 up-regulated and 584 down-regulated genes) in the LUAD vs. LUSC comparison group, 63 DEGs (43 up-regulated and 20 down-regulated genes) in the male vs. female comparison group, and 17 DEGs (14 up-regulated and 3 down-regulated genes) in the smoker vs non-smoker comparison group were identified. There was no difference between the LUSC smoker and LUSC non-smoker groups. Among these seven comparison groups, the difference in GPC3 expression only reached a significant level (adjusted P < 0.05) in four comparison groups (Fig. 1). Therefore, the DEGs in these four groups were selected for further analysis.
Fig. 1.
GPC3 is differentially expressed in all of the four comparison groups (P < 0.05 and |logFC|> 1). a Differential expression of GPC3 in the lung cancer vs. normal comparison group; b Differential expression of GPC3 in the lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) vs. normal comparison group; c Differential expression of GPC3 in the lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) versus normal comparison group; d Differential expression of GPC3 in the LUAD versus LUSC comparison group
There were 134 GO/KEGG terms (such as response to wounding, immune response, and cell adhesion, involving 1513 genes) enriched for the DEGs in the NSCLC vs. normal, 105 terms (such as response to wounding, cell adhesion, and biological adhesion, involving 1113 genes) in the LUAD vs. normal, 133 terms (such as response to wounding, mitosis, and nuclear division, involving 1701 genes) in the LUSC vs. normal, and 38 terms (such as ectoderm development, epidermis development, and epithelium development, involving 563 genes) in the LUAD versus LUSC comparison groups. Among these, 19 terms (such as regulation of cell proliferation, tube development, and epithelium development, involving 1015 genes) in the NSCLC versus normal comparison group, 17 terms (such as regulation of cell proliferation, tube development, and branching morphogenesis of a tube, involving 803 genes) in the LUAD versus normal comparison group, 18 terms (such as regulation of cell proliferation, tube development, and epithelium development, involving 1128 genes;) in the LUSC versus normal comparison group, and 12 terms (such as epithelium development, regulation of cell proliferation, and tube morphogenesis, involving 473 genes) in the LUAD versus LUSC comparison group were correlated with GPC3.
Construction of PPI network
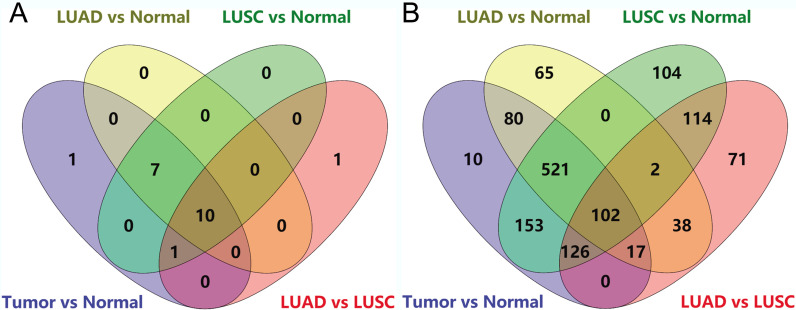
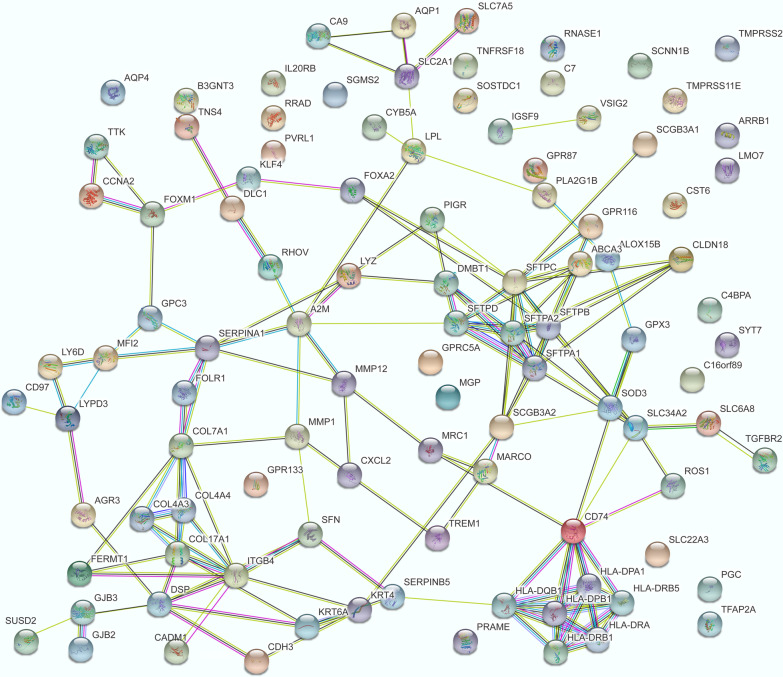
Venn diagrams showed that the 10 GO/KEGG terms (such as regulation of cell proliferation, plasma membrane, and extracellular space) (Fig. 2a) and 102 genes (Fig. 2b) correlated with GPC3 were shared by the four comparison groups. For the 102 common genes (including GPC3), PPI pairs were predicted, and the PPI network (including 148 edges) was visualised (Fig. 3). In the PPI network, GPC3 directly interacted with serpin family A member 1 (SERPINA1), melanin transferrin (MFI2), and forkhead box M1 (FOXM1).
Fig. 2.
Venn diagrams showing GPC3-associated enrichment terms and genes shared by the four comparison groups. a The enrichment terms shared by the four comparison groups; b The genes shared by the four comparison groups
Fig. 3.
Protein–protein interaction network for the 102 common genes
Correlation of GPC3 with clinical phenotypes
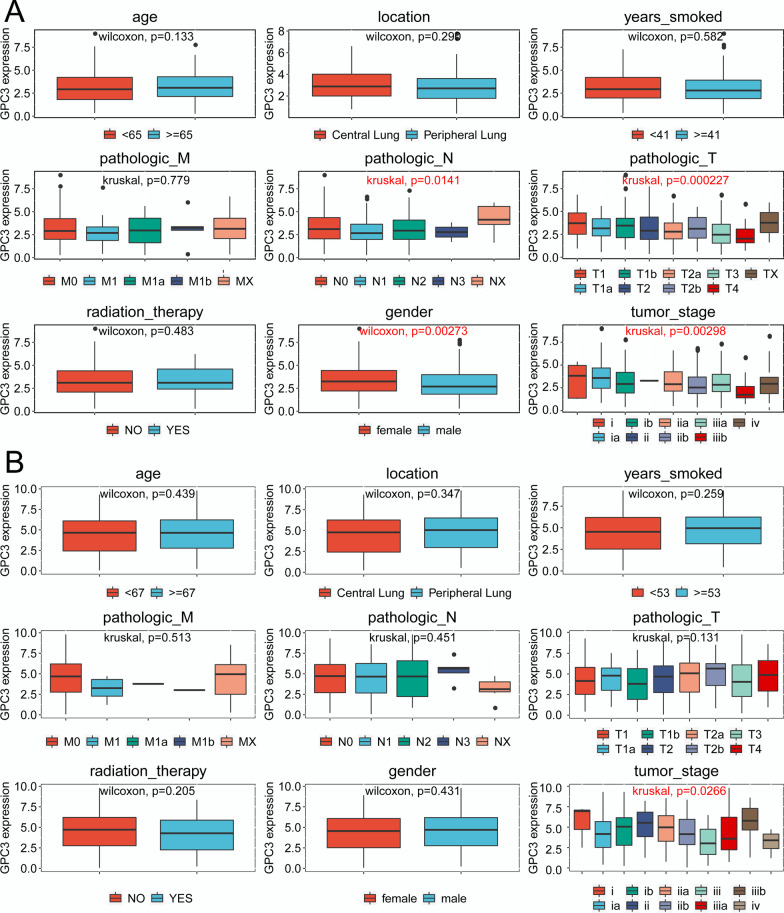
The results showed that GPC3 expression in LUAD samples was significantly correlated with pathologic N (P = 0.01405), pathologic T (P = 0.000227), sex (P = 0.002734), and tumour stage (P = 0.04348), but was not correlated with age, location, years smoked, pathologic M, or radiation therapy (P > 0.05) (Table 3, Fig. 4a). Nevertheless, GPC3 expression in LUSC samples was not significantly correlated with age, location, years smoked, pathologic M, pathologic N, pathologic T, radiation therapy, sex, or tumour stage (P > 0.05) (Table 4, Fig. 4b).
Table 3.
Correlation of GPC3 expression with the clinical phenotypes of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) samples
| Characteristics | Variable | Number of patients | GPC3 expression | Test | P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Percent (%) | Low | Percent (%) | |||||
| Age | ≥ 65 | 310 | 146 | 55.9 | 164 | 53.8 | Wilcoxon | 0.1332 |
| < 65 | 256 | 115 | 44.1 | 141 | 46.2 | |||
| Location | Central Lung | 67 | 29 | 39.2 | 38 | 30.9 | Wilcoxon | 0.2896 |
| Peripheral Lung | 130 | 45 | 60.8 | 85 | 69.1 | |||
| years_smoked | ≥ 41 | 160 | 105 | 62.5 | 129 | 57.1 | Wilcoxon | 0.5824 |
| < 41 | 234 | 63 | 37.5 | 97 | 42.9 | |||
| pathologic_M | M0 | 394 | 1 | 0.4 | 1 | 0.3 | Kruskal | 0.7793 |
| M1 | 20 | 3 | 1.1 | 2 | 0.6 | |||
| M1a | 2 | 6 | 2.3 | 14 | 4.4 | |||
| M1b | 5 | 176 | 66.7 | 218 | 69.2 | |||
| MX | 158 | 78 | 29.5 | 80 | 25.4 | |||
| pathologic_N | N0 | 371 | 14 | 5.2 | 3 | 1 | Kruskal | 0.0141 |
| N1 | 107 | 177 | 65.8 | 194 | 61.6 | |||
| N2 | 87 | 38 | 14.1 | 69 | 21.9 | |||
| N3 | 2 | 39 | 14.5 | 48 | 15.2 | |||
| NX | 17 | 1 | 0.4 | 1 | 0.3 | |||
| pathologic_T | T1 | 82 | 24 | 8.9 | 25 | 7.9 | Kruskal | 0.0002 |
| T1a | 49 | 34 | 12.6 | 26 | 8.3 | |||
| T1b | 60 | 34 | 12.6 | 55 | 17.5 | |||
| T2 | 203 | 4 | 1.5 | 16 | 5.1 | |||
| T2a | 89 | 14 | 5.2 | 15 | 4.8 | |||
| T2b | 29 | 91 | 33.7 | 112 | 35.6 | |||
| T3 | 50 | 16 | 5.9 | 34 | 10.8 | |||
| T4 | 20 | 51 | 18.9 | 31 | 9.8 | |||
| TX | 3 | 2 | 0.7 | 1 | 0.3 | |||
| Radiation therapy | Yes | 69 | 33 | 13.9 | 36 | 13.9 | Wilcoxon | 0.4830 |
| No | 428 | 205 | 86.1 | 223 | 86.1 | |||
| Gender | Female | 316 | 110 | 40.7 | 159 | 50.5 | Wilcoxon | 0.0027 |
| Male | 269 | 160 | 59.3 | 156 | 49.5 | |||
| Tumor stage | I | 316 | 163 | 61.5 | 153 | 49.2 | Kruskal | 0.0435 |
| II | 135 | 11 | 4.2 | 17 | 5.5 | |||
| III | 97 | 50 | 18.9 | 85 | 27.3 | |||
| IV | 28 | 41 | 15.5 | 56 | 18 | |||
Fig. 4.
Correlation of GPC3 expression with clinical phenotypes (P < 0.05). a Correlation of GPC3 expression in the LUAD samples with clinical phenotypes; b Correlation of GPC3 expression in the LUSC samples with clinical phenotypes
Table 4.
Correlation of GPC3 expression with the clinical phenotypes of lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) samples
| Characteristics | Variable | Number of patients | GPC3 expression | Test | P value | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| High | Percent (%) | Low | Percent (%) | |||||
| Age | ≥ 65 | 355 | 183 | 64.9 | 172 | 66.4 | Wilcoxon | 0.9002 |
| < 65 | 186 | 99 | 35.1 | 87 | 33.6 | |||
| Location | Central Lung | 157 | 83 | 57.2 | 74 | 65.5 | Wilcoxon | 0.3471 |
| Peripheral Lung | 101 | 62 | 42.8 | 39 | 34.5 | |||
| years_smoked | ≥ 53 | 177 | 146 | 59.1 | 141 | 65 | Wilcoxon | 0.2589 |
| < 53 | 287 | 101 | 40.9 | 76 | 35 | |||
| pathologic_M | M0 | 443 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.4 | Kruskal | 0.5125 |
| M1 | 6 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0.4 | |||
| M1a | 1 | 1 | 0.3 | 5 | 1.9 | |||
| M1b | 1 | 235 | 82.2 | 208 | 80.3 | |||
| MX | 94 | 50 | 17.5 | 44 | 17 | |||
| pathologic_N | N0 | 352 | 1 | 0.3 | 6 | 2.3 | Kruskal | 0.4514 |
| N1 | 143 | 189 | 65.4 | 163 | 62.5 | |||
| N2 | 43 | 73 | 25.3 | 70 | 26.8 | |||
| N3 | 5 | 22 | 7.6 | 21 | 8 | |||
| NX | 7 | 4 | 1.4 | 1 | 0.4 | |||
| pathologic_T | T1 | 53 | 15 | 5.2 | 11 | 4.2 | Kruskal | 0.1308 |
| T1a | 26 | 20 | 6.9 | 24 | 9.2 | |||
| T1b | 44 | 59 | 20.4 | 41 | 15.7 | |||
| T2 | 187 | 14 | 4.8 | 10 | 3.8 | |||
| T2a | 100 | 26 | 9 | 14 | 5.4 | |||
| T2b | 40 | 96 | 33.2 | 91 | 34.9 | |||
| T3 | 76 | 34 | 11.8 | 42 | 16.1 | |||
| T4 | 24 | 25 | 8.7 | 28 | 10.7 | |||
| Radiation therapy | Yes | 51 | 24 | 10.4 | 27 | 13.1 | Wilcoxon | 0.2045 |
| No | 386 | 207 | 89.6 | 179 | 86.9 | |||
| Gender | Female | 144 | 216 | 74.7 | 190 | 72.8 | Wilcoxon | 0.4309 |
| Male | 406 | 73 | 25.3 | 71 | 27.2 | |||
| Tumor stage | I | 270 | 144 | 50.2 | 126 | 48.6 | Kruskal | 0.3464 |
| II | 179 | 1 | 0.3 | 7 | 2.7 | |||
| III | 89 | 94 | 32.8 | 85 | 32.8 | |||
| IV | 8 | 48 | 16.7 | 41 | 15.8 | |||
Survival analysis
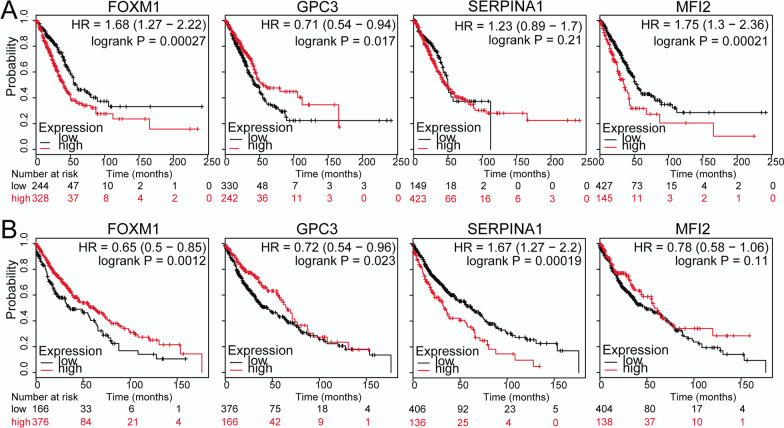
For GPC3 and the genes (including SERPINA1, MFI2, and FOXM1) directly interacting with it, gene expression levels were correlated with the prognostic information of the samples to perform KM survival analysis separately for LUAD and LUSC. The results showed that GPC3, MFI2, and FOXM1 were significantly correlated with the prognosis of LUAD patients (Fig. 5a), and GPC3, SERPINA1, and FOXM1 were significantly correlated with the prognosis of LUSC patients (Fig. 5b).
Fig. 5.
Kaplan–Meier (KM) survival curves of FOXM1, GPC3, SERPINA1, and MFI2 (P < 0.05). a Survival curves for the four genes in the LUAD samples; b Survival curves for the four genes in the LUSC samples. Black and red curves represent low and high expression, respectively
Univariate and multivariate Cox regression analyses
The results of univariate Cox regression analysis showed that MFI2, FOXM1, and GPC3 had a significant influence on the survival time of LUAD patients (P < 0.05, Table 5). A multivariate Cox regression analysis further suggested that the combination of MFI2, FOXM1, and GPC3 could significantly affect the prognosis (P-values of the likelihood ratio test, Wald test, and score (log rank) test were 2.908e−05, 1.105e−05, and 8.474e−06, respectively). Finally, the following risk-score model was established: Risk score = 0.26187*MFI2 + 0.07721*FOXM1—0.01199*GPC3.
Table 5.
Results of the univariate Cox regression analysis of lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) samples
| Gene | Coef | Exp (coef) | SE (coef) | z | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MFI2 | 0.3160 | 1.3716 | 0.0637 | 4.96 | 7.20E−07 |
| SERPINA1 | 0.0027 | 1.0027 | 0.0399 | 0.07 | 9.50E−01 |
| FOXM1 | 0.1871 | 1.2058 | 0.0538 | 3.48 | 5.00E−04 |
| GPC3 | − 0.0996 | 0.9052 | 0.0459 | − 2.17 | 3.00E−02 |
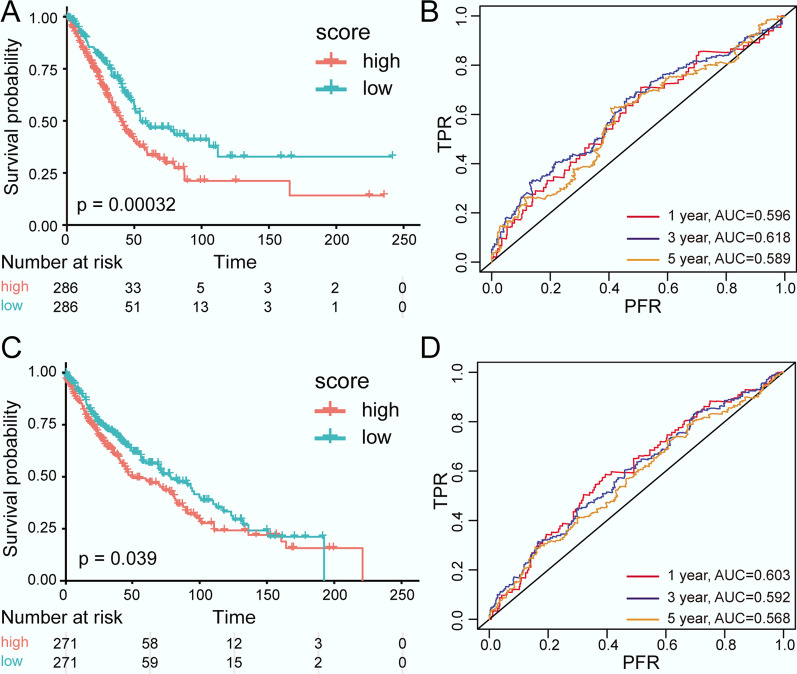
Combined with the risk score model, the samples were classified into high-risk and low-risk groups. A KM survival analysis indicated that the survival time of the low-risk group was significantly higher than that of the high-risk group (P = 0.00032, Fig. 6a). The AUC values of the 1-year, 3-year, and 5-year survival situations predicted by the risk-score model were stabilised at about 0.6 (Fig. 6b).
Fig. 6.
Kaplan–Meier (KM) survival curves and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves (P < 0.05). a KM curves for the LUAD samples; b ROC curves for the LUAD samples; c KM curves for the LUSC samples; d ROC curves for the LUSC samples. In the KM curves, red and green represent high and low risk, respectively. In the ROC curves, red, blue, and orange represent 1-year, 3-year, and 5-year survival situations, respectively
Meanwhile, a univariate Cox regression analysis showed that SERPINA1 and FOXM1 had significant effects on the survival time of LUSC patients (P < 0.05, Table 6). Moreover, SERPINA1 and FOXM1 were included in the multivariate Cox regression analysis, and the P values of the likelihood ratio test, Wald test, and score (log rank) test were 0.002019, 0.002015, and 0.001904, respectively. In addition, the following risk-score model was constructed: Risk score = 0.12417*SERPINA1 + 0.00518*FOXM1.
Table 6.
Results of the univariate Cox regression analysis of lung squamous cell carcinoma (LUSC) samples
| Gene | Coef | Exp (coef) | SE (coef) | z | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MFI2 | −0.0660 | 0.9361 | 0.0505 | −1.31 | 0.1900 |
| SERPINA1 | 0.1219 | 1.1296 | 0.0346 | 3.53 | 0.0004 |
| FOXM1 | −0.0971 | 0.9075 | 0.0474 | −2.05 | 0.0410 |
| GPC3 | −0.0165 | 0.9837 | 0.0301 | −0.55 | 0.5900 |
The LUSC samples were divided into high-risk and low-risk groups based on the risk-score model, and a KM survival analysis showed that the survival time of the low-risk group was significantly higher than that of the high-risk group (P = 0.039, Fig. 6c). Similarly, all AUC values of the 1-year, 3-year, and 5-year survival situations predicted by the risk-score model were approximately 0.6 (Fig. 6d).
Genomic alterations of GPC3 and GPC3-related gene
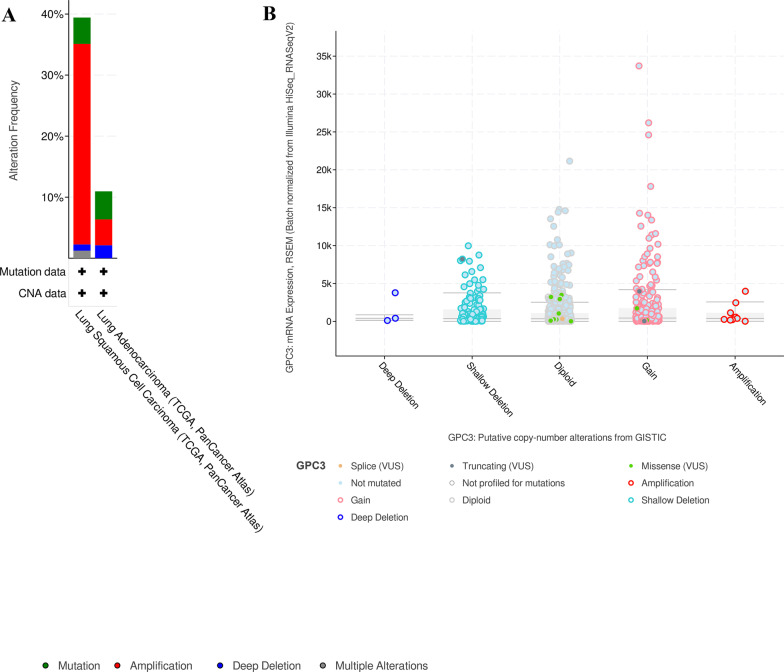
TCGA datasets of all lung cancer samples were chosen to examine mutations and CNAs in the GPC3 and GPC3-related genes. For this analysis, a total of 1053 cases in 2 studies were included (Fig. 7). In LUSC, 4.31% (21 cases) were mutation, 32.85% (160 cases) were amplification, 1.03% (5 cases) were deep deletion, and 1.23% (6 cases) were multiple alteration among 39.43% of 487 cases. However, in LUAD, the overall alteration frequency of GPC3 and GPC3-related genes was 10.95% of 560 cases, the mutation frequency was 4.59% (26 cases), the amplification frequency was 4.06% (23 cases), and the deep deletion frequency was 2.3%. (13 cases). Moreover, mutation analysis revealed the individual alteration frequencies of GPC3 (13 missense and 4 truncating mutations), SERPINA1 (7 missense and 2 truncating mutations), MFI2 (7 missense and 6 truncating mutations), and FOXM1 (15 missense and 1 truncating mutations).
Fig. 7.
GPC3 and GPC3-related genes mutations and CNAs in cBioportal for Cancer Genomics database. a The alteration frequency of GPC3 and GPC3-related genes (SERPINA1, MFI2 and FOXM1) was explored in LUSC and LUAD in 2 studies. b Relative GPC3 expression mRNA level as a function of relative copy number alteration were plotted in one specific LUSC and LUAD database (TCGA, PanCancer Atlas)
GPC3 expression analysis with qRT-PCR
The qRT-PCR was used to determine the expression of GPC3 in LUSC. GPC3 expression was much higher in the LUSC tissues than that in the control group (P < 0.001, Fig. 8). This is consistent with the previous sequencing results.
Fig. 8.
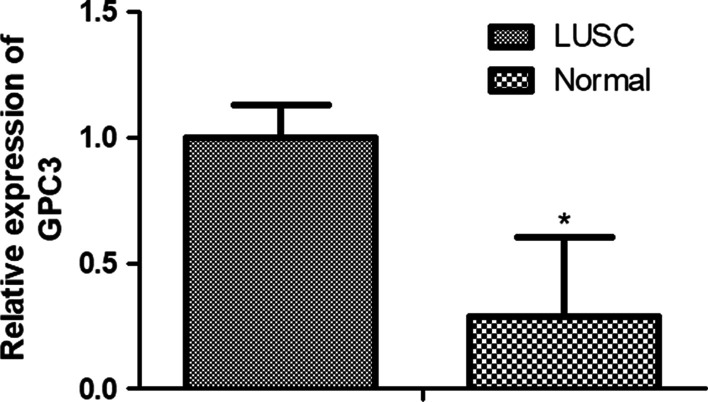
Relative mRNA expression by quantitative real-time PCR of GPC3 in LUSC compared with control group, *P < 0.05
IHC analysis of GPC3 protein expression
IHC analysis revealed positive staining of GPC3 protein in seven of the ten (70%) paraffin-embedded LUSC tissues, while negative staining was observed in the remaining cases (three of ten, 30%) (Fig. 9). This suggests that the high expression of GPC3 may be related to the occurrence of LUSC.
Fig. 9.
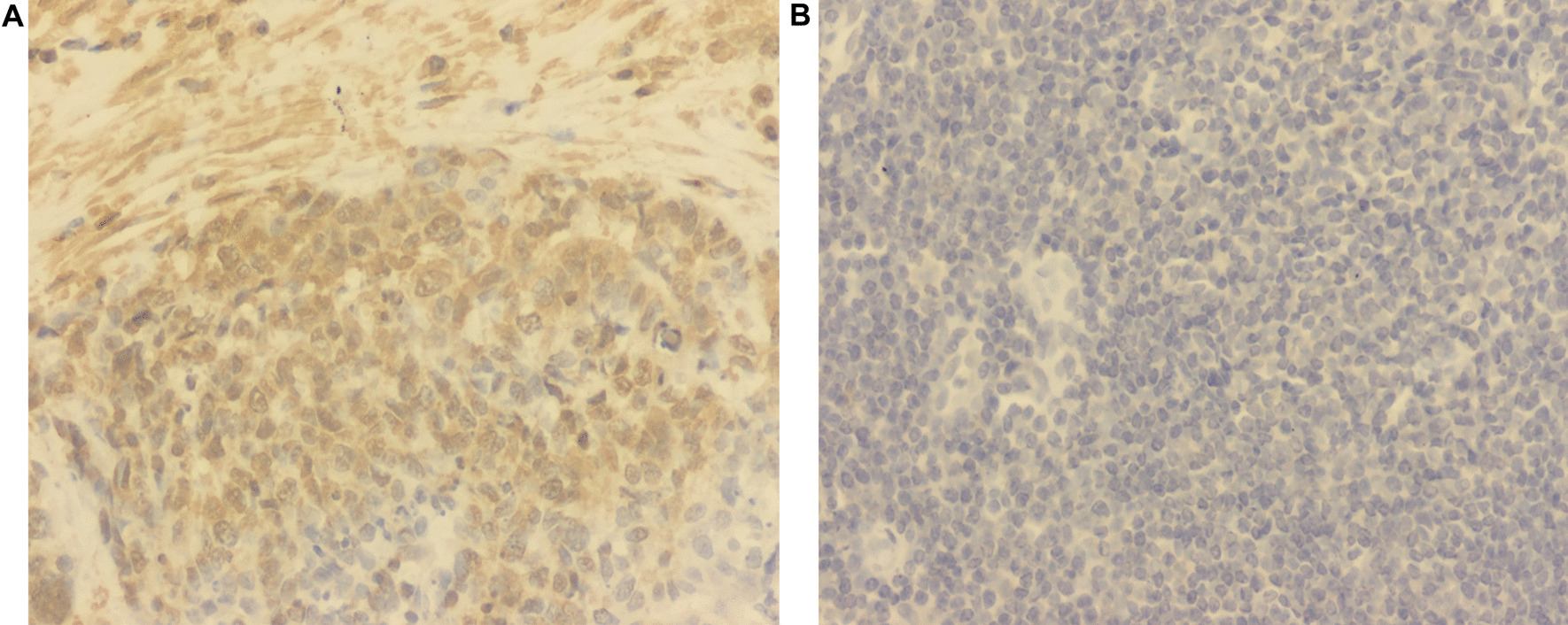
Immunohistochemical evaluation of GPC3 expression in representative luteal phase specimens of a LUSC and b paracancer tissues
Discussion
GPC3 is a heparin sulphate proteoglycan whose expression is associated with several malignancies. However, its expression in lung cancer is limited and remains ambiguous. This study found that GPC3 is significantly downregulated in NSCLC tissues compared with that in paracancer tissues, and its expression in LUAD is significantly lower than that in LUSC. In LUAD samples, GPC3 expression was significantly correlated with pathologic N, pathologic T, gender, and tumour stage. However, GPC3 expression was not significantly associated with these clinical phenotypes in LUSC.
GPC3 overexpression in liver cancer has been frequently reported without debate; however, its expression pattern in NSCLC remains debatable. Kim et al. reported that GPC3 expression was decreased in LUAD compared with that in paired normal tissues [26]. In a study by Sarit et al., GPC3 was found to be overexpressed in LUSC (positive rate of 55%) but not in LUAD (positive rate of 8%), which might be induced by smoking [27]. The present study found that the expression of GPC3 in NSCLC is lower than that in paracancer tissues, which is in line with a study by Kim et al. [26] and in contradiction with a study by Sarit et al. In addition, the present study found that GPC3 was not differentially expressed in the smoker vs. non-smoker group or the LUSC smoker vs. LUSC non-smoker group. This is also different from the study by Sarit et al. It was hypothesised that this is due to the use of different methods to detect GPC3 expression and the sample size. Sarit et al. used immunohistochemistry on tissue microarrays to evaluate the expression of GPC3 in 97 patients. However, the present study was based on high-sequencing data of more than 500 samples in TCGA database.
The molecular mechanism of action of GPC3 in cancer remains unclear. In this study, a PPI network was developed for GPC3-associated genes. In this network, GPC3 exhibited significant correlation with SERPINA1, MFI2, and FOXM1 directly in the PPI network, indicating that GPC3 might also act in NSCLC by interacting with SERPINA1, MFI2, and FOXM1. Germline mutation of MFI2 is significantly greater in LUAD patients among young non-smokers, which may be implicated in the pathogenesis of LUAD [46]. FOXM1 functions in cell cycle progression, and increased FOXM1 expression is related to unfavourable outcomes of NSCLC due to the promotion of cell metastasis [47]. FOXM1 plays a role in EMT induced by TGF-beta1, and miR-134 functions as an EMT suppressor by targeting FOXM1 in NSCLC cells [48]. FOXM1 overexpression contributes to cell invasion and migration in NSCLC, which are responsible for the adverse survival of patients with this disease [49, 50]. FOXM1 can affect gefitinib resistance in NSCLC cells in vitro, making this gene a target for reducing resistance to gefitinib [51]. These results suggest that FOXM1 may be correlated with the prognosis of patients with NSCLC. Combined with Cox regression analysis, a risk-score model consisting of the prognosis-associated genes MFI2, FOXM1, and GPC3 was developed for LUAD prognosis, and the AUC values of the 1-year, 3-year, and 5-year survival situations were stabilised at approximately 0.6, suggesting a relatively higher reliability.
In LUSC, the expression of GPC3 was not significantly related to survival time (P > 0.05). Therefore, a risk-score model consisting of the prognosis-associated genes SERPINA1 and FOXM1 was established for LUSC. α-1 antitrypsin (AAT) is a serine proteinase inhibitor that plays an antiprotease protective role in the human body, and mutations in the gene SERPINA1 can lead to chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases by inducing AAT deficiency [52]. The SERPINA1 PiMZ genotype, combined with smoking, causes lung-function decline by modifying the correlation between longitudinal change and occupational exposure in lung function [53]. Increased SERPINA1 gene expression ameliorates tumour cell migration, apoptosis resistance, and colony formation, and SERPINA1 and its corresponding protein, AAT, influence the mechanisms of lung cancer [54]. Thus, SERPINA1 may influence the outcomes of NSCLC patients.
Conclusion
In conclusion, GPC3 was significantly downregulated in NSCLC tissues compared with that in paracancer tissues, and its expression in LUAD was significantly lower than that in LUSC. In LUAD samples, GPC3 expression was significantly correlated with pathologic N, pathologic T, gender, and tumour stage. The PPI network showed that GPC3 can interact with SERPINA1, MFI2, and FOXM1 directly. In addition, the three-gene risk-score model (involving MFI2, FOXM1, and GPC3) for LUAD and the two-gene risk-score model (involving SERPINA1 and FOXM1) for LUSC might be useful in predicting the prognosis of tumour patients. However, the utility values of the risk-score models should be further validated in subsequent experiments.
Acknowledgements
None.
Abbreviations
- GPC3
Glypican 3
- NSCLC
Non-small-cell lung carcinoma
- LUAD
Lung adenocarcinoma
- LUSC
Lung squamous cell carcinoma
- DEGs
Differentially expressed genes
- SCLC
Small-cell lung carcinoma
- LCLC
Lung large cell carcinoma
- AEG-1
Astrocyte-elevated gene-1
- MMP9
Matrix metalloproteinase-9
- GAPDH
Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- HIF-2α
Hypoxia-inducible factor-2α
- NDRG2
N-MYC downstream-regulated gene 2
- Notch2
Notch homolog 2
- CLDN3
Claudin-3
- EMT
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition
- HCC
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- PPI
Protein–protein interaction
- GO
Gene ontology
- KEGG
Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes
- OS
Overall survival
- KM
Kaplan–Meier
- ROC
Receiver operating characteristic
- SERPINA1
Serpin family A member 1
- MFI2
Melanin transferrin
- FOXM1
Forkhead box M1
Authors' contributions
Conception and design of the research: JN; acquisition of data: SJ and YW; analysis and interpretation of data: XD and XL; statistical analysis: ZZ and LH; drafting the manuscript: JN; revision of manuscript for important intellectual content: DW and YJ. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This study was supported by the Key Research and Development Projects of Liaoning Province (No. 2020JH 2/10300064).
Availability of data and materials
The data used for analysis in this study are all from the University of California Santa Cruz (UCSC) Xena database (https://xenabrowser.net/datapages/).
Declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interest.
Footnotes
Jing Ning and Shenyi Jiang contribute equally to the article
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Contributor Information
Jing Ning, Email: jning@cmu.edu.cn.
Shenyi Jiang, Email: jaddison@163.com.
Xiaoxi Li, Email: lixiaoxi@cancerhosp-ln-cmu.com.
Yang Wang, Email: 125029060@qq.com.
Xuhong Deng, Email: 15072752419@163.com.
Zhiqiang Zhang, Email: amao321@163.com.
Lijie He, Email: 17702488896@163.com.
Daqing Wang, Email: 443058216@qq.com.
Youhong Jiang, Email: jiangyouhong2000@aliyun.com.
References
- 1.Travis WD. Lung cancer pathology: current concepts. Clin Chest Med. 2020;41(1):67–85. doi: 10.1016/j.ccm.2019.11.001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 2.Li J, Ran J, Chen L-C, Costa M, Huang Y, Chen X. Tian L: Bituminous coal combustion and Xuan Wei Lung cancer: a review of the epidemiology, intervention, carcinogens, and carcinogenesis. Arch Toxicol. 2019;93(3):573–583. doi: 10.1007/s00204-019-02392-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Herbst RS, Morgensztern D, Boshoff C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature. 2018;553(7689):446–454. doi: 10.1038/nature25183. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Lee W, Jiang Z, Liu J, Haverty PM, Zhang Z. The mutation spectrum revealed by paired genome sequences from a lung cancer patient. Nature. 2010;465(7297):473–477. doi: 10.1038/nature09004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Osmani L, Askin F, Gabrielson E, Li QK. Current WHO guidelines and the critical role of immunohistochemical markers in the subclassification of non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC): Moving from targeted therapy to immunotherapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2018;52(Pt 1):103–109. doi: 10.1016/j.semcancer.2017.11.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Ren F, Ding H, Huang S, Wang H, Wu M, Luo D, Dang Y, Yang L, Chen G. Expression and clinicopathological significance of miR-193a-3p and its potential target astrocyte elevated gene-1 in non-small lung cancer tissues. Cancer Cell Int. 2015;15(1):1–10. doi: 10.1186/s12935-015-0227-8. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Puzone R, Savarino G, Salvi S, Dal Bello MG, Barletta G, Genova C, Rijavec E, Sini C, Esposito AI, Ratto GB, et al. Glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene over expression correlates with poor prognosis in non small cell lung cancer patients. Mol Cancer. 2013;12(1):97. doi: 10.1186/1476-4598-12-97. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Higashi K, Yamagishi T, Ueda Y, Ishigaki Y, Shimasaki M, Nakamura Y, Oguchi M, Takegami T, Sagawa M, Tonami H. Correlation of HIF-1α/HIF-2α expression with FDG uptake in lung adenocarcinoma. Ann Nucl Med. 2016;30(10):708–715. doi: 10.1007/s12149-016-1116-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Liu N, Luo J, Kuang D, Xu S, Duan Y, Xia Y, Wei Z, et al. Lactate inhibits ATP6V0d2 expression in tumor-associated macrophages to promote HIF-2α-mediated tumor progression. J Clin Invest. 2018;129(2):631–646. doi: 10.1172/JCI123027. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Faraji SN, Mojtahedi Z, Ghalamfarsa G, Ta MA. N-myc downstream regulated gene 2 overexpression reduces matrix metalloproteinase-2 and -9 activities and cell invasion of A549 lung cancer cell line in vitro. Iran J Basic Med Sci. 2015;18(8):773–779. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Chen CY, Chen YY, Hsieh MS, Ho CC, Chen KY, Shih JY, Yu CJ. Expression of Notch gene and its impact on survival of patients with resectable non-small cell lung cancer. J Cancer. 2017;8(7):1292–1300. doi: 10.7150/jca.17741. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Che J, Yue D, Zhang B, Hua Z, Huo Y, Gao L, Zhen H, Yan Y, Cao B. Claudin-3 inhibits lung squamous cell carcinoma cell epithelial–mesenchymal transition and invasion via suppression of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Int J Med Sci. 2018;15(4):339–351. doi: 10.7150/ijms.22927. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Aviel-Ronen S, Lau SK, Pintilie M, Lau D, Liu N, Tsao MS, Jothy S. Glypican-3 is overexpressed in lung squamous cell carcinoma, but not in adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol Off J US Can Acad Pathol. 2008;21(7):817–825. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2008.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Xiang YY, Ladeda V, Filmus J. Glypican-3 expression is silenced in human breast cancer. Oncogene. 2001;20(50):7408–7412. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1204925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Toretsky JA, Zitomersky NL, Eskenazi AE, Voigt RW, Strauch ED, Sun CC, Huber R, Meltzer SJ, Schlessinger D. Glypican-3 expression in Wilms tumor and hepatoblastoma. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2001;23(8):496–499. doi: 10.1097/00043426-200111000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Saikali Z, Sinnett D. Expression of glypican 3 (GPC3) in embryonal tumors. Int J Cancer. 2000;89(5):418–422. doi: 10.1002/1097-0215(20000920)89:5<418::AID-IJC4>3.0.CO;2-I. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Guo M, Zhang H, Zheng J, Liu Y. Glypican-3: a new target for diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer. 2020;11(8):2008–2021. doi: 10.7150/jca.39972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Tahon AM, El-Ghanam MZ, Zaky S, Emran TM, Bersy AM, El-Raey F, Elsayed AZ, El Kharsawy AM, Johar D. Significance of Glypican-3 in early detection of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhotic patients. J Gastrointest Cancer. 2019;50(3):434–441. doi: 10.1007/s12029-018-0095-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Kandil D, Leiman G, Allegretta M, Evans M. Glypican-3 protein expression in primary and metastatic melanoma: a combined immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry study. Cancer. 2009;117(4):271–278. doi: 10.1002/cncy.20032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Zynger DL, Dimov ND, Luan C, Teh BT, Yang XJ. Glypican 3: a novel marker in testicular germ cell tumors. Am J Surg Pathol. 2006;30(12):1570–1575. doi: 10.1097/01.pas.0000213322.89670.48. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Pilia G, Hughes-Benzie RM, MacKenzie A, Baybayan P, Chen EY, Huber R, Neri G, Cao A, Forabosco A, Schlessinger D. Mutations in GPC3, a glypican gene, cause the Simpson-Golabi-Behmel overgrowth syndrome. Nat Genet. 1996;12(3):241–247. doi: 10.1038/ng0396-241. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Gonzalez AD, Kaya M, Shi W, Song H, Testa JR, Penn LZ, Filmus J. OCI-5/GPC3, a glypican encoded by a gene that is mutated in the Simpson–Golabi–Behmel overgrowth syndrome, induces apoptosis in a cell line-specific manner. J Cell Biol. 1998;141(6):1407–1414. doi: 10.1083/jcb.141.6.1407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Lin H, Huber R, Schlessinger D, Morin PJ. Frequent silencing of the GPC3 gene in ovarian cancer cell lines. Can Res. 1999;59(4):807–810. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Murthy SS, Shen T, De Rienzo A, Lee WC, Ferriola PC, Jhanwar SC, Mossman BT, Filmus J, Testa JR. Expression of GPC3, an X-linked recessive overgrowth gene, is silenced in malignant mesothelioma. Oncogene. 2000;19(3):410–416. doi: 10.1038/sj.onc.1203322. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Peters MG, Farias E, Colombo L, Filmus J, Puricelli L. Bal de Kier Joffe E: Inhibition of invasion and metastasis by glypican-3 in a syngeneic breast cancer model. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2003;80(2):221–232. doi: 10.1023/A:1024549729256. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Kim H, Xu GL, Borczuk AC, Busch S, Filmus J, Capurro M, Brody JS, Lange J, D'Armiento JM, Rothman PB, et al. The heparan sulfate proteoglycan GPC3 is a potential lung tumor suppressor. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 2003;29(6):694–701. doi: 10.1165/rcmb.2003-0061OC. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Aviel-Ronen S, Lau SK, Pintilie M, Lau D, Liu N, Tsao MS, Jothy S. Glypican-3 is overexpressed in lung squamous cell carcinoma, but not in adenocarcinoma. Mod Pathol. 2008;21(7):817–825. doi: 10.1038/modpathol.2008.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 28.Ritchie ME, Belinda P, Di W, Hu Y, Law CW, Wei S, Smyth GK. limma powers differential expression analyses for RNA-sequencing and microarray studies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2015;43(7):e47. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkv007. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.AaJJG S. Minimally adaptive BH: A tiny but uniform improvement of the procedure of Benjamini and Hochberg. Biometrical Journal Biometrische Zeitschrift. 2017;59(4):776–780. doi: 10.1002/bimj.201500253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Du J, Li M, Yuan Z, Guo M, Song J, Xie X, Chen Y. A decision analysis model for KEGG pathway analysis. BMC Bioinform. 2016;17(1):407. doi: 10.1186/s12859-016-1285-1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Kanehisa M, Furumichi M, Sato Y, Ishiguro-Watanabe M, Tanabe M. KEGG: integrating viruses and cellular organisms. Nucleic Acids Res. 2021;49(D1):D545–D551. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkaa970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 32.Da WH, Sherman BT, Tan Q, Collins JR, et al. The DAVID Gene Functional Classification Tool: a novel biological module-centric algorithm to functionally analyze large gene lists. Genome Biol. 2007;8(9):1–16. doi: 10.1186/gb-2007-8-9-r183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 33.Shade A, Handelsman J. Beyond the Venn diagram: the hunt for a core microbiome. Environ Microbiol. 2012;14(1):4–12. doi: 10.1111/j.1462-2920.2011.02585.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 34.Szklarczyk D, Franceschini A, Kuhn M, Simonovic M, Mering C. The STRING database in 2011: functional interaction networks of proteins, globally integrated and scored. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010;39(Database issue):561–568. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkq973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 35.Kohl M, Wiese S, Warscheid B. Cytoscape: software for visualization and analysis of biological networks. Methods Mol Biol. 2011;696:291–303. doi: 10.1007/978-1-60761-987-1_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 36.Natarajan S, Lipsitz SR, Fitzmaurice GM, Sinha D, Ibrahim JG, Haas J, Gellad W. An extension of the Wilcoxon rank sum test for complex sample survey data. J R Stat Soc. 2012;61(4):653–664. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9876.2011.01028.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 37.Acar EF, Sun L. A Generalized Kruskal-Wallis Test Incorporating Group Uncertainty with Application to Genetic Association Studies. Biometrics. 2013;69(2):427–435. doi: 10.1111/biom.12006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 38.Mezzina N, Campbell Davies SE, Ardizzone S. Nonbiological therapeutic management of ulcerative colitis. Expert Opin Pharmacother. 2018;19(16):1747–1757. doi: 10.1080/14656566.2018.1525361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 39.Gregg ME, Somnath D, Doug L. A log rank test for clustered data with informative within-cluster group size. Stat Med. 2018;37(27):4071–4082. doi: 10.1002/sim.7899. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 40.Vivekanandan T, Narayanan SJ. A Hybrid Risk Assessment Model for Cardiovascular Disease Using Cox Regression Analysis and a 2-means clustering algorithm. Comput Biol Med. 2019;113:103400. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.103400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 41.Team RC R: a language and environment for statistical computing. Computing. 2014;1:12–21. [Google Scholar]
- 42.Provenzano F, D'Arrigo G, Zoccali C, Tripepi G. Cox regression analysis in epidemiological research. Giornale italiano di nefrologia: organo ufficiale della Societa italiana di nefrologia. 2011;28(3):319–322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 43.Stel VS, Dekker FW, Tripepi G, Zoccali C, Jager KJ. Survival analysis i: The Kaplan–Meier method. Nephron Clin Pract. 2011;119(1):c83–c88. doi: 10.1159/000324758. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 44.Gronlund SD, Wixted JT, Mickes L. Evaluating eyewitness identification procedures using receiver operating characteristic analysis. Curr Dir Psychol Sci. 2014;23(1):3–10. doi: 10.1177/0963721413498891. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 45.Arora S, Singh P, Rahmani AH, Almatroodi SA, Dohare R, Syed MA. Unravelling the role of miR-20b-5p, CCNB1, HMGA2 and E2F7 in development and progression of non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Biology (Basel) 2020; 9(8). [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed]
- 46.Luo W, Tian P, Wang Y, Xu H, Chen L, Tang C, Shu Y, Zhang S, Wang Z, Zhang J. Characteristics of genomic alterations of lung adenocarcinoma in young never-smokers. Int J Cancer. 2018;143(7):1696–1705. doi: 10.1002/ijc.31542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 47.Gialmanidis IP, Bravou V, Amanetopoulou SG, Varakis J, Kourea H, Papadaki H. Overexpression of hedgehog pathway molecules and FOXM1 in non-small cell lung carcinomas. Lung Cancer. 2009;66(1):64–74. doi: 10.1016/j.lungcan.2009.01.007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 48.Shen Y, Feng Z, Lin C, Hou X, Wang X, Wang J, Yu Y, Wang L, Sun X. An oligodeoxynucleotide that induces differentiation of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells to osteoblasts in vitro and reduces alveolar bone loss in rats with periodontitis. Int J Mol Sci. 2012;13(3):2877–2892. doi: 10.3390/ijms13032877. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 49.Xu N, Jia D, Chen W, Hao W, Liu F, Ge H, Zhu X, Song Y, Xin Z, Zhang D. FoxM1 is associated with poor prognosis of non-small cell lung cancer patients through promoting tumor metastasis. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(3):59412. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0059412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 50.Kong F-F, Qu Z-Q, Yuan H-H, Wang J-Y, Zhao M, Guo Y-H, Shi J, Gong X-D, Zhu Y-L, Liu F. Overexpression of FOXM1 is associated with EMT and is a predictor of poor prognosis in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncol Rep. 2014;31(6):2660–2668. doi: 10.3892/or.2014.3129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 51.Xu N, Zhang X, Wang X, Ge HY, Wang XY, Garfield D, Yang P, Song YL, Bai CX. FoxM1 mediated resistance to gefitinib in non-smallcell lung cancer cells. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2012;33(5):675–681. doi: 10.1038/aps.2011.188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 52.Geene CM, Hassan T, Molloy K, McElvaney NG. The role of proteases, endoplasmic reticulum stress and SERPINA1heterozygosity in lung disease and α-1 anti-trypsin deficiency. Expert Rev Respir Med. 2011;5(3):395–411. doi: 10.1586/ers.11.20. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 53.Mehta AJ, Thun GA, Imboden M, Ferrarotti I, Team S. Interactions between SERPINA1 PiMZ genotype, occupational exposure and lung function decline. Occup Environ Med. 2013;71(4):234–240. doi: 10.1136/oemed-2013-101592. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 54.Ercetin E, Richtmann S, Delgado BM, Gomez-Mariano G, Schneider MA. Clinical significance of SERPINA1 gene and its encoded Alpha1-antitrypsin protein in NSCLC. Cancers. 2019;11(9):1306. doi: 10.3390/cancers11091306. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Data Availability Statement
The data used for analysis in this study are all from the University of California Santa Cruz (UCSC) Xena database (https://xenabrowser.net/datapages/).