Figure. Synopsis of the development of single-cell/nucleus RNA sequencing for cardiac applications.
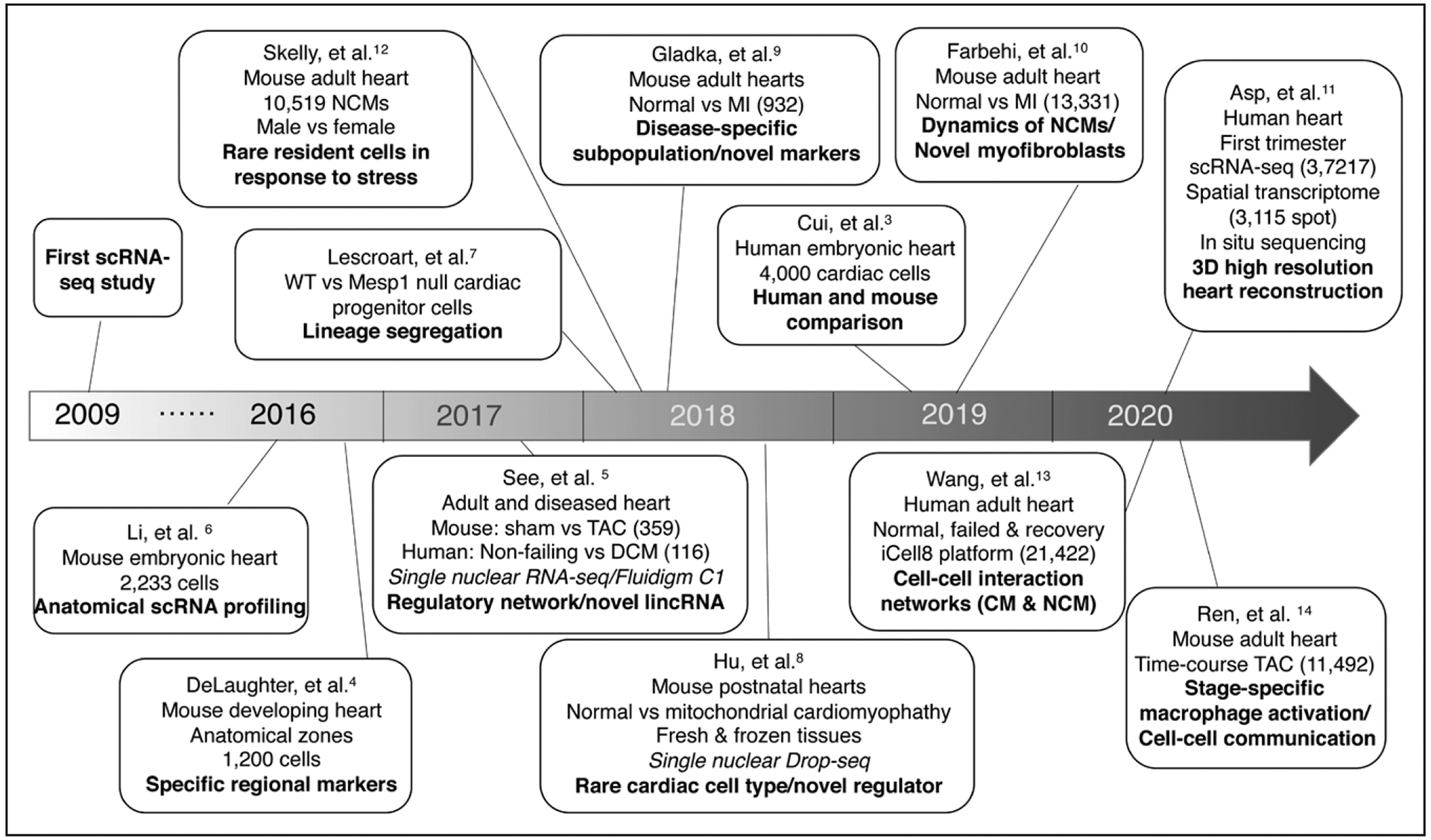
Several landmark studies that incorporated the use of single-cell or single-nucleus RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq or snRNA-seq) for investigations of heart development and disease are presented in a timeline. Seven years after the first reported transcriptome of a single cell, scRNA-seq was conducted in 1000 to 2000 cardiac cells for an investigation of murine heart development. Since then, both the number and types of cells sequenced, and the complexity of the biological processes investigated, as well, have steadily increased. Overall, the findings of these studies have demonstrated the heterogeneous response of cardiac cells to developmental signaling pathways and myocardial disease. 3D indicates 3-dimensional; CM, cardiomyocyte; DCM, dilated cardiomyopathy; Drop-seq, droplet sequencing; lincRNA, long intergenic noncoding RNA; MI, myocardial infarction; NCMs, noncardiomyocytes; TAC, transverse aortic constriction; and WT, wild-type.
