Abstract
Floral longevity (FL) is an important trait influencing plant reproductive success by affecting the chance of insect pollination. However, it is still unclear which factors affect FL, and whether FL is evolutionarily associated with structural traits. Since construction costs and water loss by transpiration play a role in leaf longevity, we speculated that floral structures may affect the maintenance and loss of water in flowers and, therefore, FL. Here, we investigated the slipper orchid Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium, which are closely related, but strongly differ in their FL. To understand the evolutionary association of floral anatomical traits with FL, we used a phylogenetic independent comparative method to examine the relationships between 30 floral anatomical traits and FL in 18 species of Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium. Compared with Paphiopedilum species, Cypripedium species have lower values for floral traits related to drought tolerance and water retention capacity. Long FL was basically accompanied by the thicker epidermal and endodermal tissues of the floral stem, the thicker adaxial and abaxial epidermis of the flower, and low floral vein and stomatal densities. Vein density of the dorsal sepals and synsepals was negatively correlated with stomatal density. Our results supported the hypothesis that there was a correlation between FL and floral anatomical traits in slipper orchids. The ability to retain water in the flowers was associated with FL. These findings provide a new insight into the evolutionary association of floral traits with transpirational water loss for orchids under natural selection.
Keywords: Cypripedium, floral anatomy, floral longevity, floral water economy, functional traits, Paphiopedilum
Introduction
Floral longevity (FL) is an important floral functional trait that influences the reproductive success of flowering plants by affecting the chance of insects visiting flowers (Primack, 1985; Ashman and Schoen, 1994). Similar to other floral traits, FL shows great diversity in angiosperms. For example, the flowers of Ipomoea and Oenothera species remain open for only a few hours (Kerner von Marilaun, 1895), whereas the flowers of other species, such as orchids, can last for weeks or even several months (Kerner von Marilaun, 1895; Zhang et al., 2017). FL may be affected by biotic and abiotic factors (Yasaka et al., 1998; Arathi et al., 2002; Rathcke, 2003; Harder and Johnson, 2005; Vespirini and Pacini, 2005; Itagaki and Sakai, 2006; Weber and Goodwillie, 2012; Arroyo et al., 2013; Jorgensen and Arathi, 2013). For example, pollination can shorten FL (Giblin, 2005; Weber and Goodwillie, 2012). In addition, the length of FL is closely related to water-use efficiency, altitude, and temperature (Vespirini and Pacini, 2005; Arroyo et al., 2013; Jorgensen and Arathi, 2013). To maintain the normal display and physiological metabolism of flowers, sufficient water and energy are very important. Previous studies have found that water plays an important role for bud expansion, flower opening, and nectar production during the whole stage of flower display (Mohan Ram and Rao, 1984; Patino and Grace, 2002; Tsukaguchi et al., 2003; van Doorn and van Meeteren, 2003; Galen, 2005). In cut flower display, fungicides can be added to the preservative solution to reduce the blockage of microbial breeding on flower vessels to prolong the vase life, and floral stems can be re-cut under water to maintain the continuity of the water column and the water transport in flowers, therefore extending FL (Lu, 2006; Guo, 2013; Li et al., 2020). Although water balance plays an important role in the maintenance of flower life span and turgor pressure, it is still unclear which flower traits affect the water balance and FL.
Flowers contribute only slightly to carbon assimilation of the whole plant and have relatively shorter life span than leaves, but they may still transpire a large amount of water during the flowering period (Lambrecht et al., 2011; Roddy and Dawson, 2012; Lambrecht, 2013; Teixido and Valladares, 2014). However, flowers in water-deficit conditions may wilt, which may affect pollination success. Thus, flowers must keep their turgidity and water balance, maintaining floral functions to attract pollinators (Lambrecht et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2017). Although long-lived flowers may increase the probability of successful pollination, in particular when pollinators are scarce, they may also represent a major drain on the water budget of the plant (Nobel, 1977; Rathcke, 2003; Jorgensen and Arathi, 2013; Zhang et al., 2017).
Previous studies have found that leaf anatomical traits play an important role in maintaining the leaf life span in Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium orchids (Chang et al., 2011; Guan et al., 2011; Yang et al., 2018). For example, a high degree of leaf succulence can contribute to greater water storage capacity, which is beneficial under conditions of drought (Guan et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2012, 2015; Yang et al., 2018). Leaf anatomy plays a key role in maintaining the water balance in Cymbidium species (Zhang et al., 2015). Traits, such as epidermis thickness, stomatal density, and stomatal size, are usually regarded as the adaptations to water-limited conditions, since they contribute to reduce water transpiration rate from leaves (Haworth and McElwain, 2008; Mill and Stark Schilling, 2009; Zhang et al., 2012). Despite this functional link between leaf longevity and morphology has been confirmed, the evolutionary association between the longevity and floral structural traits is unknown.
The Orchidaceae is one of the most diverse families of flowering plants in terms of floral form, size, color, and fragrance, with approximately 28,000 species and 763 genera (Crain and Tremblay, 2014; Christenhusz and Byng, 2016; Zhang S. B. et al., 2018). Most orchids grow on the forest canopies where pollinating insects are relatively rare, but they rely on insects for pollination. In addition, due to the unique floral structure of orchids, many have a special lock–key relationship with pollinating insects (Fay and Chase, 2009; Bernhardt and Edens-Meier, 2010). An orchid often relies on a single insect species for its pollination. Thus, maintaining a long floral life span is of great significance for the reproductive success of orchids. In fact, the FL of most members within the Orchidaceae is longer than those of other angiosperm species (Kerner von Marilaun, 1895), such as Paphiopedilum dianthum, which has an individual FL of 62 days, so that chances of pollination are high (Zhang et al., 2017). The long life spans of orchids are attributed to their floral mass per area (FMA) and the water maintenance characteristics of their flowers and leaves (Fu et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2017). Investigating floral anatomy is crucial to understanding why Orchidaceae species usually have such long FL, because the anatomical traits of organs, such as leaves, may affect plant resource allocation, physiological functions, and adaptations to environmental changes (Holbrook and Putz, 1996; Vendramini et al., 2002; Pandey et al., 2009; Guan et al., 2011; Yang et al., 2018). However, the physiological and anatomical mechanism for long floral life span in orchids remains unclear.
The subfamily Cypripedioideae in Orchidaceae consists of five genera: Paphiopedilum, Cypripedium, Mexipedium, Phragmipedium, and Selenipedium (Cox et al., 1997; Cameron et al., 1999). Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium are closely related in phylogeny (Cox et al., 1997), with their flowers having a pouch-like lip, a shield-like staminode, a synsepal composed of fused lateral sepals, and two fertile stamens (Supplementary Figure 1), and some species of the two genera are pollinated by bees (Lindley, 1840; Cox et al., 1997; Liu et al., 2009; Guo et al., 2012; Chen et al., 2013). However, the life spans of the leaves and flowers of Paphiopedilum are longer than those of Cypripedium (Chang et al., 2011; Guan et al., 2011; Yang et al., 2018). The life span of each flower in Paphiopedilum is 26–62 days, depending on the species (Zhang et al., 2017), whereas that of Cypripedium is only 6–13 days (in this study). There are also other differences between the two genera. Paphiopedilum species are evergreen plants with fleshy leaves and which usually grow in karst limestone areas below an altitude of 2,000 m with a scarcity of soil and low water availability; plants in such areas often suffer from great water deficits, especially in the dry season (Cribb, 1998; Guan et al., 2011; Guo et al., 2012; Zhang et al., 2012; Yang et al., 2018). In contrast, Cypripedium species are deciduous plants with thin leaves that mainly grow in the shade of forests at altitudes above 1,800 m in southwest China (Cribb, 1997; Chen et al., 2005; Guan et al., 2011; Guo et al., 2012). The soil layer in habitats where Cypripedium species grow can store abundant water during the growing and flowering seasons. The differences in FL, morphology, habitat, and physiology between Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium, despite the close relatedness of the two genera, make them ideal candidates for exploring the association between FL and floral structure in orchids.
In this present study, we investigated the floral structural traits related to water balance and FL of 13 Paphiopedilum species and 5 Cypripedium species to explore the mechanism that affects the difference in FL between the two genera and test the evolutionary association between FL and floral structural traits related to water balance. We hypothesized that different floral life spans will represent different water-use strategies in the two closely related genera with different floral morphologies. Specifically, the Paphiopedilum species with longer floral life span may have stronger capacity to retain water in flowers to adapt to low-moisture habitats.
Materials and Methods
Plant Materials
We examined the association between FL and floral anatomy using 13 Paphiopedilum species and 5 Cypripedium species. The ecological characteristics, habitats, growth forms, and phenological periods of the 18 species are listed in Supplementary Table 1. The Paphiopedilum species were grown in a greenhouse at the Kunming Botanical Garden (102°410′E, 25°01′N; elevation 1,990 m). The growth conditions included an air temperature of 20–25°C during the day and 10–15°C at night and 60–70% relative air humidity. The Cypripedium species were grown at the Shangrila Alpine Botanical Garden (99°50′E, 27°48′N; elevation 3,260 m). The growth conditions included an air temperature of 15–24°C during the day and approximately 10°C at night and a relative air humidity ranging from 60 to 80% during the growing season.
Floral Longevity
To investigate the FL of a single flower from each species of Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium, we randomly marked 3–20 newly emerged floral buds per species. Their individual flower opening and wilting dates were recorded throughout the flowering period. Each floral bud was sampled from a separate plant. The individual flower was identified as “opening” when the dorsal sepal rose and the visiting insects could enter the lip. The individual flower was regarded as “wilting” when the lip began to discolor, wilt, or was eaten by herbivores, resulting in the individual flower losing its ability to be pollinated (Sugiura et al., 2001; Zhang et al., 2017).
Measurements of Flower Cross-Sectional Anatomy
Six individual flowers from six different plants per species were fixed in a formalin acetic acid–alcohol solution (37% formaldehyde, glacial acetic acid, 95% ethanol, and deionized water in a 10:5:50:35 mixture) for microscopic analysis. The samples (floral stem, petal, lip, dorsal sepal, and synsepal) were cleaned with water before anatomical analysis. Thin transverse cross-sections (20–30 μm) of the samples were made with a Microtome Cryostat (CM3050S; Leica, Germany); the sections were stained with 1% fuchsine for 4–5 s, mounted on glass microscope slides, examined, and photographed with a light microscope (U-CMAD3; Olympus Inc., Tokyo, Japan). Epidermal thickness; exodermal thickness; endodermal thickness of the floral stem; upper epidermal thickness; lower epidermal thickness; mesophyll thickness of the petals, lips, dorsal sepals, and synsepals; and the whole petal, lip, dorsal sepal, and synsepal thickness were determined with the ImageJ program.
Measurements of Vein and Stomatal Densities
Vein density (mm mm–2) and stomatal density (mm2) were quantified from paradermal sections. The entire petals, lips, dorsal sepals, and synsepals were sampled and scanned at 2,400 dpi using a scanner. Vein density was measured as the total length of vascular tissue per mm2 of surface area, and stomatal density as the total number of stomata per mm2 of surface area, using the ImageJ software (National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, United States).
Statistical Analysis
Relationships among variables were analyzed using both pairwise Pearson and phylogenetically independent contrasts (PICs). The evolutionary associations were examined with PIC analysis by employing the “ape” package, utilizing molecular phylogenetic relationships (Cox et al., 1997; Li et al., 2011). A principal component analysis (PCA) was performed with the “prcomp” function of the “vegan” package to characterize the relationships among species or floral traits. Differences in floral traits between species of Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium were determined by the Mann–Whitney U test. All statistical analyses were performed with R software v. 2.15.0 (R Core Team, 2012).
Results
All of the floral traits tested varied significantly across species, and the magnitude of variation differed for each trait (Table 1). The coefficients of variation (CVs) were >50% for endodermal thickness of the floral stem, mesophyll thickness of the petals, and stomatal density of the dorsal sepal and synsepal and <25% for the upper epidermis thickness of the dorsal sepal. Across all traits, stomatal density of the synsepal had the highest variation (93.18%), whereas vein density of the dorsal sepal had the lowest (21.62%).
TABLE 1.
Quantification of floral structural traits for tested species.
| Traits | Abbreviation | Unit | Functional significance | Mean ± SE | Min | Max | CV (%) |
| Floral stem | |||||||
| Epidermal thickness | SEPT | μm | Water conservation | 45.75 ± 1.18 | 19.32 | 77.67 | 26.71 |
| Exodermal thickness | SEXT | μm | Water transport | 325.76 ± 15.55 | 117.03 | 1,214.46 | 49.62 |
| Endodermal thickness | SENT | μm | Water transport | 136.09 ± 7.36 | 0 | 433.01 | 56.24 |
| Petal | |||||||
| Upper epidermal thickness | PUET | μm | Water conservation | 67.38 ± 2.07 | 27.14 | 123.77 | 31.92 |
| Lower epidermal thickness | PLET | μm | Water conservation | 69.22 ± 2.24 | 26.46 | 128.82 | 33.57 |
| Mesophyll thickness | PM | μm | Water storage | 214.14 ± 10.79 | 55.56 | 483.50 | 52.37 |
| Petal thickness | PT | μm | Water availability | 348.77 ± 13.15 | 146.83 | 683.86 | 39.19 |
| Vein density | PVD | mm mm–2 | Water availability | 1.11 ± 0.05 | 0.47 | 3.29 | 49.55 |
| Lip | |||||||
| Upper epidermal thickness | LUET | μm | Water conservation | 65.87 ± 1.79 | 26.01 | 125.39 | 28.28 |
| Lower epidermal thickness | LLET | μm | Water conservation | 63.29 ± 1.70 | 25.04 | 121.38 | 27.98 |
| Mesophyll thickness | LM | μm | Water storage | 247.58 ± 10.33 | 34.80 | 540.03 | 43.38 |
| Lip thickness | LT | μm | Water availability | 375.53 ± 11.68 | 155.22 | 690.05 | 32.32 |
| Vein density | LVD | mm mm–2 | Water availability | 0.93 ± 0.02 | 0.39 | 1.50 | 27.96 |
| Dorsal sepal | |||||||
| Upper epidermal thickness | DSUET | μm | Water conservation | 64.38 ± 1.50 | 32.24 | 108.75 | 24.23 |
| Lower epidermal thickness | DSLET | μm | Water conservation | 74.81 ± 2.55 | 31.77 | 193.69 | 35.37 |
| Mesophyll thickness | DSM | μm | Water storage | 217.92 ± 8.81 | 16.37 | 478.23 | 42.00 |
| Dorsal sepal thickness | DST | μm | Water availability | 356.40 ± 10.43 | 149.24 | 632.32 | 30.40 |
| Vein density | DSVD | mm mm–2 | Water availability | 1.11 ± 0.03 | 0.59 | 2.05 | 21.62 |
| Stomatal density | DSSD | mm–2 | Water loss | 2.17 ± 0.13 | 0.55 | 6.77 | 61.75 |
| Synsepal | |||||||
| Upper epidermal thickness | SYUET | μm | Water conservation | 61.06 ± 1.52 | 30.17 | 110.60 | 25.79 |
| Lower epidermal thickness | SYLET | μm | Water conservation | 64.75 ± 1.69 | 29.15 | 112.05 | 27.17 |
| Mesophyll thickness | SYM | μm | Water storage | 107.53 ± 4.01 | 17.11 | 238.25 | 38.73 |
| Synsepal thickness | SYT | μm | Water availability | 243.95 ± 5.90 | 130.67 | 452.58 | 25.15 |
| Vein density | SYVD | mm mm–2 | Water availability | 1.22 ± 0.05 | 0.61 | 2.92 | 41.80 |
| Stomatal density | SYSD | mm–2 | Water loss | 3.08 ± 0.28 | 0.56 | 11.29 | 93.18 |
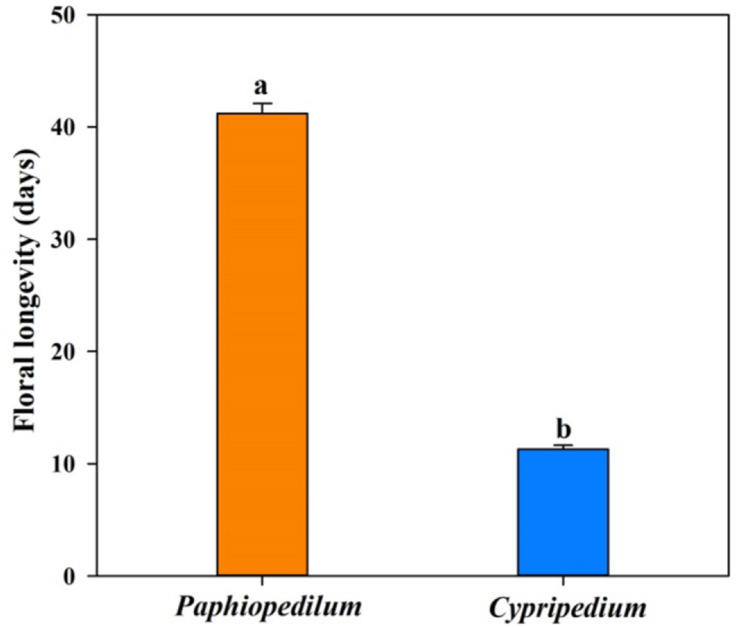
Twenty-four of the 25 floral anatomical traits and FL differed significantly between Paphiopedilum species and Cypripedium species (Figure 1 and Table 2). The former had longer FL and higher values for epidermis thickness (P < 0.001), exodermal (P < 0.001) and endodermal thickness (P < 0.001) of the floral stems, upper (P < 0.001) and lower epidermal thickness (P < 0.001), mesophyll thickness of the petals (P < 0.001) and dorsal sepal (P < 0.001), petal thickness (P < 0.001), lip thickness (P < 0.001), dorsal sepal thickness (P < 0.001), and synsepal thickness (P < 0.001), but lower values for vein (P < 0.001) and stomatal densities (P < 0.001) on the flowers. The values for mesophyll thickness of the lip (P = 0.128) and synsepal (P = 0.480) did not significantly differ between the two genera (Table 2).
FIGURE 1.
The floral longevity in Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium genera. SEs are presented with bars, and different letters signify statistically significant differences.
TABLE 2.
Contrasts in floral anatomical traits between Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium of floral functional traits for tested species.
| Traits | Paphiopedilum (n = 13) Mean ± SE | Cypripedium (n = 5) Mean ± SE | Z | P |
| Floral stem | ||||
| Epidermal thickness | 50.94 ± 1.09 | 32.26 ± 1.23 | –7.31 | <0.001 |
| Exodermal thickness | 371.05 ± 18.91 | 208.02 ± 9.05 | –6.11 | <0.001 |
| Endodermal thickness | 169.94 ± 6.88 | 48.07 ± 4.90 | –7.85 | <0.001 |
| Petal | ||||
| Upper epidermal thickness | 76.99 ± 1.90 | 42.40 ± 1.44 | –7.83 | <0.001 |
| Lower epidermal thickness | 79.28 ± 2.08 | 43.07 ± 1.95 | –7.44 | <0.001 |
| Mesophyll thickness | 252.24 ± 12.39 | 115.08 ± 4.30 | –6.65 | <0.001 |
| Petal thickness | 406.18 ± 13.16 | 199.49 ± 6.15 | –7.83 | <0.001 |
| Vein density | 0.88 ± 0.02 | 1.71 ± 0.13 | –7.01 | <0.001 |
| Lip | ||||
| Upper epidermal thickness | 72.82 ± 1.62 | 47.81 ± 3.00 | –5.84 | <0.001 |
| Lower epidermal thickness | 69.14 ± 1.58 | 48.07 ± 3.22 | –5.29 | <0.001 |
| Mesophyll thickness | 256.68 ± 11.74 | 223.94 ± 21.00 | –2.52 | 0.128 |
| Lip thickness | 397.34 ± 12.68 | 318.84 ± 23.41 | –2.79 | 0.005 |
| Vein density | 0.80 ± 0.02 | 1.26 ± 0.02 | –7.94 | <0.001 |
| Dorsal sepal | ||||
| Upper epidermal thickness | 70.66 ± 1.46 | 48.04 ± 1.56 | –6.93 | <0.001 |
| Lower epidermal thickness | 84.46 ± 2.77 | 49.73 ± 1.77 | –6.94 | <0.001 |
| Mesophyll thickness | 245.34 ± 10.27 | 146.64 ± 7.70 | –5.70 | <0.001 |
| Dorsal sepal thickness | 398.88 ± 10.64 | 245.95 ± 8.93 | –6.79 | <0.001 |
| Vein density | 0.96 ± 0.02 | 1.52 ± 0.06 | –7.26 | <0.001 |
| Stomatal density | 1.50 ± 0.07 | 3.90 ± 0.21 | –7.62 | <0.001 |
| Synsepal | ||||
| Upper epidermal thickness | 67.95 ± 1.40 | 43.14 ± 1.25 | –7.70 | <0.001 |
| Lower epidermal thickness | 72.50 ± 1.56 | 44.60 ± 1.39 | –7.46 | <0.001 |
| Mesophyll thickness | 107.71 ± 5.39 | 107.06 ± 3.62 | –0.71 | 0.480 |
| Synsepal thickness | 262.96 ± 6.86 | 194.52 ± 4.67 | –5.82 | <0.001 |
| Vein density | 1.00 ± 0.02 | 1.79 ± 0.11 | –6.57 | <0.001 |
| Stomatal density | 1.59 ± 0.09 | 6.94 ± 0.50 | –7.54 | <0.001 |
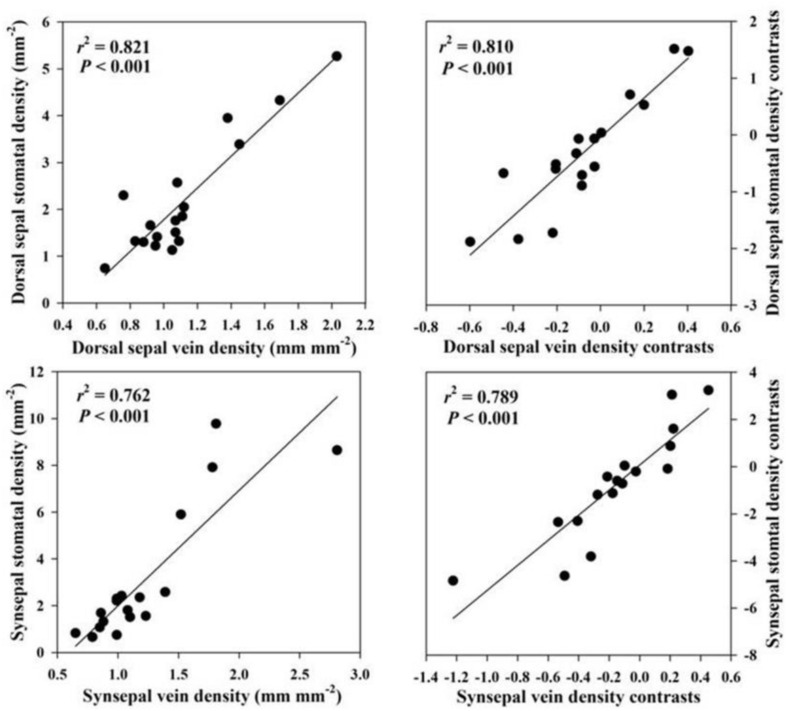
Across species, FL was positively correlated with epidermal thickness (P = 0.001) and endodermal thickness (P = 0.001) of the floral stems, upper (P = 0.007) and lower epidermal thickness (P = 0.006) of the petals, petal thickness (P = 0.036), vein density (P = 0.016) of the petals, upper (P = 0.042) and lower epidermal thickness (P = 0.038) and veins (P = 0.002) of the lips, upper (P = 0.004) and lower epidermal thickness (P = 0.002) of the dorsal sepal, vein (P = 0.001) and stomatal densities (P = 0.001) of the dorsal sepal, upper (P < 0.001) and lower epidermal thickness (P < 0.001), synsepal thickness (P = 0.011), and vein (P = 0.001) and stomatal densities (P < 0.001) of the synsepal. Moreover, these relationships were supported by using PICs (Table 3). No relationship was found between FL and other anatomical floral traits, such as exodermal thickness of the floral stem (P = 0.116), mesophyll thickness of the petals (P = 0.121), mesophyll thickness of the lip (P = 0.411), lip thickness (P = 0.214), and mesophyll thickness of the dorsal sepal (P = 0.06) and synsepal (P = 0.787). Similarly, these relationships were not found whether phylogeny was considered (Table 3). The FL was not correlated with dorsal sepal thickness when phylogeny was not considered (P = 0.161), but a significant correlation was found after phylogenetic correction (P = 0.035) (Table 3). The vein densities of the dorsal sepal (P < 0.001) and synsepal (P < 0.001) were positively correlated with stomatal density when a Pearson regression was used, and that correlation was still significant after correction (Figure 2).
TABLE 3.
Pearson correlations and phylogenetically independent contrast (PIC) correlations for relationships between water-related traits with floral longevity in slipper orchids.
| Correlation with floral longevity |
PIC |
|||
| Variables | r2 | P-value | r2 | P-value |
| Floral stem | ||||
| Epidermal thickness | 0.526 | 0.001 | 0.520 | 0.0011 |
| Exodermal thickness | 0.166 | 0.116 | 0.153 | 0.120 |
| Endodermis thickness | 0.819 | <0.001 | 0.825 | <0.001 |
| Petal | ||||
| Upper epidermal thickness | 0.378 | 0.007 | 0.372 | 0.009 |
| Lower epidermal thickness | 0.382 | 0.006 | 0.401 | 0.006 |
| Mesophyll thickness | 0.144 | 0.121 | 0.226 | 0.054 |
| Petal thickness | 0.247 | 0.036 | 0.322 | 0.017 |
| Vein density | 0.312 | 0.016 | 0.249 | 0.042 |
| Lip | ||||
| Upper epidermal thickness | 0.234 | 0.042 | 0.249 | 0.041 |
| Lower epidermal thickness | 0.242 | 0.038 | 0.217 | 0.040 |
| Mesophyll thickness | 0.042 | 0.411 | 0.004 | 0.799 |
| Lip thickness | 0.094 | 0.214 | 0.037 | 0.457 |
| Vein density | 0.457 | 0.002 | 0.515 | 0.001 |
| Dorsal sepal | ||||
| Upper epidermal thickness | 0.415 | 0.004 | 0.438 | 0.004 |
| Lower epidermal thickness | 0.454 | 0.002 | 0.565 | <0.001 |
| Mesophyll thickness | 0.060 | 0.327 | 0.129 | 0.158 |
| Dorsal sepal thickness | 0.161 | 0.099 | 0.263 | 0.035 |
| Vein density | 0.484 | 0.001 | 0.438 | 0.004 |
| Stomatal density | 0.491 | 0.001 | 0.717 | <0.001 |
| Synsepal | ||||
| Upper epidermal thickness | 0.551 | <0.001 | 0.556 | <0.001 |
| Lower epidermal thickness | 0.635 | <0.001 | 0.659 | <0.001 |
| Mesophyll thickness | 0.005 | 0.787 | 0.073 | 0.295 |
| Synsepal thickness | 0.342 | 0.011 | 0.370 | 0.010 |
| Vein density | 0.506 | 0.001 | 0.536 | <0.001 |
| Stomatal density | 0.610 | <0.001 | 0.612 | <0.001 |
FIGURE 2.
Correlations of vein density with stomatal density in the dorsal sepal and synsepal.
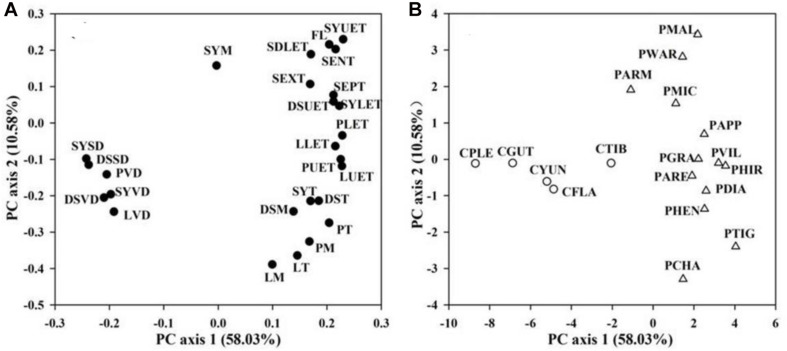
In the PCA of floral traits, the first two PCAs explained 58.03 and 10.58% of the total variation, respectively (Figure 3). The first PCA axis was loaded by FL, floral functional traits of water conservation, transport, and storage (epidermis, exodermis, and endodermis thickness of the floral stems, upper and lower epidermis thickness of the petal, petal mesophyll thickness, petal thickness, upper and lower epidermis thickness of the lip, lip mesophyll thickness, lip thickness, upper and lower epidermis thickness of the dorsal sepals, dorsal sepal mesophyll thickness, dorsal sepal thickness, upper and lower epidermis thickness of the synsepal, synsepal mesophyll thickness, and synsepal thickness) on the positive side, and by floral functional traits of water supply and loss (vein and stomatal densities of the petal, lip, dorsal sepal, and synsepal) on the negative side (Figure 3). The second PCA axis was loaded by FL, the anatomical traits of the floral stem, dorsal sepal, and synsepal on the positive side, and by petal and lip anatomical traits, vein and stomatal densities of the petal, lip, dorsal sepal, and synsepal on the negative side (Figure 3). Species-loadings showed that the two genera, Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium, were well-separated along the first PCA axis. Paphiopedilum species were grouped on the positive side, whereas Cypripedium species clustered on the negative side (Figure 3), indicating that there was a significant difference in flower traits between the two closely related genera.
FIGURE 3.
Principal component analysis (PCA) based on 26 floral traits (A) from 28 slipper orchids. PCA axes are presented in (B). Values in parentheses along each axis indicate percentages of explained variation. Abbreviations for traits and species are shown in Table 1 and Supplementary Table 1, respectively.
Discussion
The present study supported our hypothesis that FL was tightly coupled with water conservation in flowers. The difference in FL between Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium was driven by floral anatomical traits related to reducing water loss, such as endodermal thickness and epidermis thickness of the floral stem and epidermis thickness, vein density, and stomatal density of the flower. Our findings provide new insights into the evolution of flowers in orchid plants.
Our results showed that FL was evolutionarily correlated with floral anatomical traits. The orchid species with longer FL had a thicker epidermis and endodermis of the floral stem and a thicker epidermis of the flowers, but a lower vein and stomatal density than species with shorter FL. This implied that the rate of water loss in flowers played an important role in regulating FL. FL can influence the total number of pollinators visiting a plant, thus affecting plant reproduction. At the same time, FL may reflect the balance between fitness consequences and maintenance costs (Kerner von Marilaun, 1895). Water loss represents a major drain for flowers with longer FL, and water stress can promote the accumulation of senescent-related substances in flowers, thus shortening the life span of flowers (Nobel, 1977; He, 1997; Wu and Zhao, 2001). Leaf life span is linked with leaf water-related traits, and trees with shorter leaf life spans have higher stem hydraulic efficiency and higher photosynthetic capacity and, thus, can achieve greater carbon gain in a shorter time (Fu et al., 2012). Previous research has also reported that stomatal limitations are associated with a long leaf life span (Brooks et al., 1997; Hikosaka et al., 1998). Stomata can rapidly respond to the change in the rate of water supply regulated by xylem conductance, thus reducing water loss and preventing xylem pressure from cavitation (Chaves et al., 2003). Zhang et al. (2017) found that FL is correlated with FMA and water maintenance traits in 11 Paphiopedilum species. This study extended our understanding of the role of floral anatomical traits in maintaining FL of slipper orchids and the critical application of anatomical traits as one of the key functional traits for maintaining FL.
The correlation of FL with anatomy likely reflects co-selection for water supply and loss. Across the species studied, our analyses showed that the strongest driver for the difference in FL was the endodermal thickness of the floral stem. The thicker endodermis was found in the floral stem of the Paphiopedilum species with longer life span, and there was a thinner or even no endodermis in the floral stem of Cypripedium species with shorter life span. The role of the endodermis is efficiently preventing water loss from the interior of the floral stem, allowing internal vascular bundles to transport water (Roppolo et al., 2011; Stasovski and Peterson, 2011; Qi et al., 2020). Moreover, the floral stem acts as a mechanical support (Enstone et al., 2003). The endodermis of plant with long FL tends to have a lower permeability and stronger support capacity than those species with short FL, possibly suggesting the adaptation of species with long FL to the requirements for conserving water, increasing water-use efficiency, and improving mechanical support in flowers during the flowering period in dry environments (Enstone et al., 2003; Roppolo et al., 2011).
We also found that FL was closely associated with epidermis thickness in flowers. This was shown by our Pearson’s and PICs analyses, which demonstrated that longer-lived flowers are more capable of maintaining flower turgor. The epidermis can function as a water conservation layer, and such flowers have a thicker epidermis, implying that they are more tolerant to drought stress (Guan et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2012, 2015; Yang et al., 2018). However, there was no significant correlation between FL and mesophyll thickness (petal: P = 0.121; lip: P = 0.411; dorsal sepal: P = 0.099; synsepal: P = 0.787) (Table 3), indicating that FL might be determined by water conservation rather than water storage. Therefore, the increase in FL was mainly through reducing the water loss of flowers, rather than increasing the water storage capacity.
In leaves, water supply (vein density) is usually coordinated with water loss (stomata density) to keep the water balance (Brodribb and Jordan, 2011; Carins Murphy et al., 2012; Brodribb et al., 2013; Sack and Scoffoni, 2013; Wen et al., 2020). We found that the vein density in the dorsal sepal and synsepal was correlated with stomatal density, showing that this coordination was also mediated by the common dependence of vein and stomatal densities in flowers, and probably suggesting a functional similarity existed between the leaves and sepals in many plant species. The evolutionary correlation between vein density and stomatal density in sepals found in the present study was consistent with the previous study by Zhang F. P. et al. (2018).
Our results showed that there were clear distinctions in FL and floral anatomical traits between Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium species (Table 2). The former had significantly longer FL; thicker epidermis, exodermis, and endodermis of the floral stems; and had much thicker petals, lips, dorsal sepals, and synsepals, but lower vein and stomatal densities. These findings are in accordance with the results reported previously in leaves (Chang et al., 2011; Guan et al., 2011; Yang et al., 2018). The obvious divergences in FL and floral anatomical traits between the closely related genera, Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium, reflect the adaptation to their respective habitats. The natural growth conditions of Cypripedium species usually include nutrient-rich soil with high moisture content during the growing and flowering seasons. In contrast, the natural habitats of Paphiopedilum species in the karst limestone area are characterized by low water availability of leaking rocky substrates.
FL affects successful pollination of plants (Primack, 1985; Ashman and Schoen, 1994). The length of FL is an important mechanism for flowering plants to adapt to the richness of pollinators in specific habitats (Primack, 1985). Species with short-lived flowers are adapted to favorable weather conditions for pollinators to visit, whereas species with long-lived flowers are adapted to environments that are often not suitable for pollinators to visit (Kerner von Marilaun, 1895). In the habitat with rare pollinators and low activity of pollinator, a long FL can compensate for the shortage of pollinators to increase reproductive success (Ashman and Schoen, 1994; Bingham and Orthner, 1998; Fabbro and Körner, 2004; Vespirini and Pacini, 2005; Peng et al., 2012). Orchids often rely on specific pollinators (van der Pijl and Dodson, 1966). A “sit and-wait” strategy to increase FL is likely the only way for the flower to act its reproductive role in orchids (Kerner von Marilaun, 1895; Primack, 1985; Ashman and Schoen, 1994). Fruit set in slipper orchids (Cypripedioideae) with the trap-lip pollination system is highly variable even within the same species or same population in different years (Primack and Stacy, 1998; Zheng et al., 2010; Pemberton, 2013). A previous research showed that fruit set is correlated with FL in five Cypripedium species (Zheng et al., 2010). Fruit set of species in Cypripedioideae is often low, but the longer FL of the plants probably can compensate for rare pollinators (Pemberton, 2013). Thus, the long FL in Paphiopedilum might be explained as the result solely of a need for longer flowering time due to scarcity of pollinators in the habitats, whereas the favorable weather in the flowering period (from May to July) of species in Cypripedium is often suitable for pollinators to visit. Such favorable environments allow greater levels of pollinator visitation. Under such favorable conditions, flowers do not need to open for a long time to be visited by pollinators (Primack, 1985).
Flower represents a drain on the water of the plant as a result of transpiration and respiration (Nobel, 1977). A short FL may reduce the costs of maintaining flowers (Primack, 1985). In contrast, to maintain a long floral life span, flowers need to invest more physiological costs, such as water. Reducing water loss is important for maintaining the water balance of whole plants and flower turgor. Here, we found that Paphiopedilum species were characterized by higher values for floral traits related to water retention capacity. The special floral structures of Paphiopedilum might contribute to the maintenance of longer FL. These floral anatomical traits are important for flowers to be physiologically functional under low water availability conditions, as in leaves (Guan et al., 2011; Zhang et al., 2015; Yang et al., 2018). The differences in FL and floral anatomical traits between Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium indicated adaptations to their natural growing environments. These findings contribute to the conservation and cultivation of species in Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium and also provide a practical basis to predict flower water-stress tolerance for agriculturally important horticultural crops.
Conclusion
In conclusion, our results supported the hypothesis that the cost of maintaining floral function measured by the floral anatomical traits was correlated with FL. The floral anatomical traits related to water conservation rather than water storage capacity contributed to the maintenance of FL in Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium. The divergence in FL and floral anatomical structures between these two closely related genera reflects the adaptations to their growing environments. Our findings provided strong evidence for functional association between FL and water conservation capacity in slipper orchids and highlighted the necessity of considering the water-use strategy of the reproductive organ when predicting global plant models.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.
Author Contributions
F-PZ, S-BZ, J-LH, WH, and HH designed the study. F-PZ, J-QF, and X-WF carried out the experiments. F-PZ analyzed the data. F-PZ and S-BZ wrote and revised the manuscript. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Prof. John Steven for his constructive comments that improved the manuscript. We thank Dr. John A. Meadows for proofreading and editing the manuscript.
Footnotes
Funding. This study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (31960224 and 31970361), the Young Top Talents “Ten Thousands Plan” of Yunnan Province (YNWR-QNBJ-2018-337), the Applied Basic Research Plan of Yunnan Province (2018FA016), the Science Research of Yunnan Provincial Department of Education (2019J1068), the Digital Development and Application of Biological Resources in Yunnan Province (202002AA100007), the Project for Innovation Team of Yunnan Province, and the Project for Construction of International Flower Technology Innovation Center and Achievement Industrialization (2019ZG006).
Supplementary Material
The Supplementary Material for this article can be found online at: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpls.2021.637236/full#supplementary-material
Typical floral structure of Paphiopedilum appletonianum (A) and Cypripedium yunnanense (B).
The floral longevity and ecological traits for slipper orchids, Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium.
References
- Arathi H. S., Rasch A., Cox C., Kelly J. K. (2002). Autogamy and floral longevity in Mimulus guttatus. Int. J. Plant Sci. 163 567–573. 10.1086/340444 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Arroyo M. T. K., Dudley L. S., Jespersen G., Pacheco D. A., Cavieres L. A. (2013). Temperature-driven flower longevity in a high-alpine species of Oxalis influences reproductive assurance. New Phytol. 200 1260–1268. 10.1111/nph.12443 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ashman T. L., Schoen D. J. (1994). How long should flowers live? Nature 371 788–791. 10.1038/371788a0 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardt P., Edens-Meier R. (2010). What we think we know vs. what we need to know about orchid pollination and conservation: Cypripedium L. as a model lineage. Bot. Rev. 76 204–219. 10.1007/s12229-010-9042-z [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Bingham R. A., Orthner A. R. (1998). Efficient pollination of alpine plants. Nature 391 238–239. 10.1038/34564 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Brodribb T. J., Jordan G. J. (2011). Water supply and demand remain balanced during leaf acclimation of Nothofagus cunninghamii trees. New Phytol. 192 437–448. 10.1111/j.1469-8137.2011.03795.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brodribb T. J., Jordan G. J., Carpenter R. J. (2013). Unified changes in cell size permit coordinated leaf evolution. New Phytol. 199 559–570. 10.1111/nph.12300 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks J. R., Flanagan L. B., Buchmann N., Ehleringer J. R. (1997). Carbon isotope composition of boreal plants: functional grouping of life forms. Oecologia 110 301–311. 10.1007/s004420050163 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron K. M., Chase M. W., Whitten W. M., Kores P. J., Jarrell D. C., Albert V. A., et al. (1999). A phylogenetic analysis of the Orchidaceae: evidence from rbcL nucleotide sequences. Am. J. Bot. 86 208–224. 10.2307/2656938 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carins Murphy M. R., Jordan G. J., Brodribb T. J. (2012). Differential leaf expansion can enable hydraulic acclimation to sun and shade. Plant Cell Environ. 35 1407–1418. 10.1111/j.1365-3040.2012.02498.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang W., Zhang S. B., Li S. Y., Hong H. (2011). Ecophysiological significance of leaf traits in Cypripedium and Paphiopedilum. Physiol. Plant. 141 30–39. 10.1111/j.1399-3054.2010.01418.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chaves M. M., Maroco J. P., Pereira J. S. (2003). Understanding plant responses to drought: from genes to the whole plant. Funct. Plant Biol. 30 239–264. 10.1071/FP02076 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen X. C., Zhu G. H., Ji Z. H., Lang K. Y., Luo Y. B., Cribb P. (2005). “Orchidaceae,” in Flora of China, Vol. 25 eds Wu Z. Y., Raven P. H. (St. Louis: Missouri Botanical Garden; ). [Google Scholar]
- Chen X. Q., Liu Z. J., Chen L. J., Li L. Q. (2013). The Genus Cypripedium in China. Beijing: Science Press. [Google Scholar]
- Christenhusz M. J. M., Byng J. W. (2016). The number of known plants species in the world and its annual increase. Phytotaxa 261 201–217. 10.11646/phytotaxa.261.3.1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Cox A. V., Pridgeon A. M., Albert V. A., Chase M. W. (1997). Phylogenetics of the slipper orchids (Cypripedioideae, Orchidaceae): nuclear rDNA ITS sequences. Plant Syst. Evol. 208 197–223. 10.1007/BF00985442 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Crain B. J., Tremblay R. L. (2014). Do richness and rarity hotspots really matter for orchid conservation in light of anticipated habitat loss? Divers. Distrib. 20 652–662. 10.1111/ddi.12179 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Cribb P. (1997). The Genus Cypripedium. Oregon: Timber Press. [Google Scholar]
- Cribb P. (1998). The Genus Paphiopedilum. Kota Kinabalu: Natural History Publications. [Google Scholar]
- Enstone D. E., Peterson C. A., Ma F. S. (2003). Root endodermis and exodermis: structure, function, and responses to the environment. J. Plant Growth Regul. 21 335–351. 10.1007/s00344-003-0002-2 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Fabbro T., Körner C. (2004). Altitudinal differences in flower traits and reproductive allocation. Flora 199 70–81. 10.1078/0367-2530-00128 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Fay M. F., Chase M. W. (2009). Orchid biology: from Linnaeus via Darwin to the 21st century. Ann. Bot. 104 359–364. 10.1093/aob/mcp190 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fu P. L., Jiang Y. J., Wang A. Y., Brodribb T. J., Zhang J. L., Zhu S. D., et al. (2012). Stem hydraulic traits and leaf water-stress tolerance are co-ordinated with the leaf phenology of angiosperm trees in an Asian tropical dry karst fore. Ann. Bot. 110 189–199. 10.1093/aob/mcs092st [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Galen C. (2005). “It never rains but then it pours: the diverse effects of water on flower integrity and function,” in Reproductive Allocation in Plants, eds Reekie E., Bazzaz F. A. (Amsterdam: Elsevier Press; ). [Google Scholar]
- Giblin D. E. (2005). Variation in floral longevity between populations of Campanula rotundifolia (Campanulaceae) in response to fitness accrual rate manipulation. Am. J. Bot. 90 1714–1722. 10.3732/ajb.92.10.1714 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guan Z. J., Zhang S. B., Guan K. Y., Li S. Y., Hong H. (2011). Leaf anatomical structures of Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium and their adaptive significance. J. Plant Res. 124 289–298. 10.1007/s10265-010-0372-z [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guo C. G. (2013). Advancement in fresh-keeping technology of cut flower. Shannxi Forest Sci. Technol. 4 34–37. [Google Scholar]
- Guo Y. Y., Luo Y. B., Liu Z. J., Wang X. Q. (2012). Evolution and Biogeography of the Slipper Orchids: Eocene Vicariance of the Conduplicate Genera in the Old and New World Tropics. PLoS One 7:e38788. 10.1371/journal.pone.0038788 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harder L. D., Johnson S. D. (2005). Adaptive plasticity of floral display size in animal-pollinated plants. P. Roy. Soc. Lond. B Biol. 272 2651–2657. 10.1098/rspb.2005.3268 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haworth M., McElwain J. (2008). Hot, dry, wet, cold or toxic? Revisiting the ecological significance of leaf and cuticular micromorphology. Paleogeogr. Palaeoclimatol. Paleoecol. 262 79–90. 10.1016/j.palaeo.2008.02.009 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- He S. G. (1997). The physiological and biochemical basis of cut flowers. Plant Physiol. Commun. 33 66–70. 10.13592/j.cnki.ppj.1997.01.024 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Hikosaka K., Hanba Y. T., Hirose T., Terashima I. (1998). Photosynthetic nitrogen-use efficiency in leaves of woody herbaceous species. Funct. Ecol. 12 896–905. 10.1046/j.1365-2435.1998.00272.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook N. M., Putz F. E. (1996). From epiphyte to tree: differences in leaf structure and leaf water relations associated with the transition in growth form in eight species of hemiepiphytes. Plant Cell Environ. 19 631–642. 10.1111/j.1365-3040.1996.tb00398.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Itagaki T., Sakai S. (2006). Relationship between floral longevity and sex allocation among flowers within inflorescences in Aquilegia buergeriana var. oxysepala (Ranunculaceae). Am. J. Bot. 93 1320–1327. 10.3732/ajb.93.9.1320 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jorgensen R., Arathi H. S. (2013). Floral longevity and autonomous selfing are altered by pollination and water availability in Collinsia heterophylla. Ann. Bot. 112 821–828. 10.1093/aob/mct146 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerner von Marilaun A. (1895). The Natural History of Plants, Their Forms, Growth, Reproduction and Distribution. New York, NY: Henry Holt. [Google Scholar]
- Lambrecht S. C. (2013). Floral Water Costs and Size Variation in the Highly Selfing Leptosiphon bicolor (Polemoniaceae). Int. J. Plant Sci. 174 74–84. 10.1086/668230 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lambrecht S. C., Santiago L. S., DeVan C. M., Cervera J. C., Stripe C. M., Buckingham L. A., et al. (2011). Plant water status and hydraulic conductance during flowering in the southern California coastal sage shrub Salvia mellifera (Lamiaceae). Am. J. Bot. 98 1286–1292. 10.3732/ajb.1000514 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li J. H., Liu Z. J., Salazar G. A., Bernhardt P., Perner H., Tomohisa Y., et al. (2011). Molecular phylogeny of Cypripedium (Orchidaceae: Cypripedioideae) inferred from multiple nuclear and chloroplast regions. Mol. Phylogenet. Evol. 61 308–320. 10.1016/j.ympev.2011.06.006 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z., Zhuang D. F., Ma C., Xu N. (2020). Effects of fungicides on vase life in cut Dahlia flowers. Hortic. Seed 40 17–18. 10.16530/j.cnki.cn21-1574/s.2020.07.007 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Lindley J. (1840). Genera and Species of Orchidaceous Plants. London: PALL MALL. [Google Scholar]
- Liu Z. J., Chen X. Q., Chen L. J., Lei S. P. (2009). The Genus Paphiopedilum in China. Beijing: Science Press. [Google Scholar]
- Lu L. M. (2006). Effects of harvest treatment and other methods on the vase life of cut Curcuma alismatifolia. Chinese Agri. Sci. Bull. 22 258–262. [Google Scholar]
- Mill R. R., Stark Schilling D. M. (2009). Cuticle micromorphology of Saxegothaea (Podocarpaceae). Bot. J. Linn. Soc. 159 58–67. 10.1111/j.1095-8339.2008.00901.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan Ram H. Y., Rao I. V. (1984). Physiology of flower bud growth and opening. Proc. Ind. Acad. Sci. 93 253–274. 10.1007/BF03053081 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Nobel P. S. (1977). Water Relations of Flowering of Agave deserti. Bot. Gazette 138 1–6. 10.1086/336888 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pandey S. K., Singh H., Singh J. S. (2009). Species and site effects on leaf traits of woody vegetation in a dry tropical environment. Curr. Sci. 96 1109–1114. 10.1371/journal.pone.0005319 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Patino S., Grace J. (2002). The cooling of convolvulaceous flowers in a tropical environment. Plant Cell Environ. 25 41–51. 10.1046/j.0016-8025.2001.00801.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Pemberton R. W. (2013). Pollination of slipper orchids (Cypripedioideae): a review. Lankesteriana 13 65–73. 10.15517/lank.v0i0.11539 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Peng D. L., Zhang Z. Q., Xu B., Li Z. M., Sun H. (2012). Patterns of flower morphology and sexual systems in the subnival belt of the Hengduan Mountains, SW China. Alpine Bot. 122 65–73. 10.1007/s00035-012-0104-1 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Primack R. B. (1985). Longevity of individual of flowers. Annu. Rev. Ecol. Syst. 16 15–37. 10.1146/annurev.ecolsys [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Primack R. B., Stacy E. A. (1998). Cost of reproduction in the slipper orchid (Cypripedium acaule, Orchidaceae): an eleven-year experimental study of three populations. Am. J. Bot. 85 1672–1679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi Y., Huang J. L., Zhang S. B. (2020). Correlated evolution of leaf and root antomic traits in Dendrobium (Orchidaceae). AoB Plants 12 1–13. 10.1093/aobpla/plaa034 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- R Core Team (2012). R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing. Vienna: R Foundation for Statistical Computing. [Google Scholar]
- Rathcke B. J. (2003). Floral longevity and reproductive assurance: seasonal patterns and an experimental test with Kalmia latifolia (Ericaceae). Am. J. Bot. 90 1328–1332. 10.3732/ajb.90.9.1328 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roddy A., Dawson T. (2012). Determining the water dynamics of flowering using miniature sap flow sensors. Acta Hort. 951 47–53. 10.17660/ActaHortic.2012.951.4 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Roppolo D., De-Rybel B., Denervaud-Tendon V., Pfister A., Alassimone J., Vermeer J. E., et al. (2011). A novel protein family mediates Casparian strip formation in the endodermis. Nature 473 380–383. 10.1038/nature10070 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sack L., Scoffoni C. (2013). Leaf venation: structure, function, development, evolution, ecology and applications in the past, present and future. New Phytol. 198 983–1000. 10.1111/nph.12253 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stasovski E., Peterson C. (2011). Effects of drought and subsequent rehydration on the structure, vitality, and permeability of Allium cepa adventitious roots. Can. J. Bot. 71 700–707. 10.1139/b93-080 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Sugiura N., Fujie T., Inoue K., Kitamura K. (2001). Flowering phnolig, pollinations, and fruit set of Cypripedium macranthos var. rebunense, a threatened lady’s slipper (Orchidaceae). J. Plant Res. 114 171–178. 10.1007/PL00013980 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Teixido A., Valladares F. (2014). Disproportionate carbon and water maintenance costs of large corollas in hot Mediterranean ecosystems. Perspect. Plant Ecol. 16 83–92. 10.1016/j.ppees.2014.02.002 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Tsukaguchi T., Kawamitsu Y., Takeda H., Suzuki K., Egawa Y. (2003). Water status of flower buds and leaves as affected by high temperature in heat-tolerant and heat-sensitive cltivars of snap bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Plant Prod. Sci. 6 24–27. 10.1626/pps.6.24 33707419 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- van der Pijl L., Dodson C. H. (1966). Orchid flowers: their pollination and evolution. Coral Gables: University of Miami Press. [Google Scholar]
- van Doorn W. G., van Meeteren U. (2003). Flower opening and closure: a review. J. Exp. Bot. 54 1801–1812. 10.1093/jxb/erg213 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vendramini F., Diaz S., Gurvich D. E., Wilson P. J., Thompson K., Hodgson J. G. (2002). Leaf traits as indicators of resource-use strategy in floras with succulent species. New Phytol. 154 147–157. 10.2307/1513940 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Vespirini J. L., Pacini E. (2005). Temperature-dependent floral longevity in two Helleborous species. Plant Syst. Evol. 252 63–70. 10.1007/s00606-004-0261-9 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. J., Goodwillie C. (2012). Variation in floral longevity in the genus Leptosiphon: mating system consequences. Plant Biol. 15 220–225. 10.1111/j.1438-8677.2012.00595.x [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wen Y., Zhao W. L., Cao K. F. (2020). Global convergence in the balance between leaf water supply and demand across vascular land plants. Funct. Plant Biol. 47 904–911. 10.1071/FP19101 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu H. Z., Zhao Y. (2001). Study advances on physiological and biochemical changes and preservative techniques of postharvest to cut flowers. J.Yunnan Agric. Univer. 16 320–324. 10.16211/j.issn.1004-390x(n).2001.04.020 [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Yang Z. H., Huang W., Yang Q. Y., Chang W., Zhang S. B. (2018). Anatomical and diffusional determinants inside leaves explain the difference in photosynthetic capacity between Cypripedium and Paphiopedilum, Orchidaceae. Photosynth. Res. 136 315–328. 10.1007/s11120-017-0466-8 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasaka M., Nishiwaki Y., Konno Y. (1998). Plasticity of flower longevity in Corydalis ambigua. Ecol. Res. 13 211–216. 10.1046/j.1440-1703.1998.00259.x [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F. P., Carins Murphy M. R., Cardoso A. A., Jordan G. J., Brodribb T. J. (2018). Similar geometric rules govern the distribution of veins and stomata in petals, sepals and leaves. New Phytol. 219 1224–1234. 10.1111/nph.15210 [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang F. P., Yang Y. J., Yang Q. Y., Zhang W., Brodribb T. J., Hao G. Y., et al. (2017). Floral mass per area and water maintenance traits are correlated with floral longevity in Paphiopedilum (Orchidaceae). Front. Plant Sci. 8:501. 10.3389/fpls.2017.00501 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. B., Dai Y., Hao G. Y., Li J. W., Fu X. W., Zhang J. L. (2015). Differentiation of water-related traits in terrestrial and epiphytic Cymbidium species. Front. Plant Sci. 6:260. 10.3389/fpls.2015.00260 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. B., Guan Z. J., Sun M., Zhang J. J., Cao K. F., Hu H. (2012). Evolutionary association of stomatal traits with leaf vein density in Paphiopedilum, Orchidaceae. PLoS One 7:e40080. 10.1371/journal.pone.0040080 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang S. B., Yang Y. G., Li J. W., Qin J., Zhang W., Huang W., et al. (2018). Physiological diversity of orchids. Plant Divers. 40, 196–208. 10.1016/j.pld.2018.06.003 [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zheng G. L., Peng L., Tai Y. D., An D. J., Kou Y., Luo Y. B. (2010). Flowering and fruit set dynamics in Cypripdium. Acta Ecol. Sin. 30 3182–3187. [Google Scholar]
Associated Data
This section collects any data citations, data availability statements, or supplementary materials included in this article.
Supplementary Materials
Typical floral structure of Paphiopedilum appletonianum (A) and Cypripedium yunnanense (B).
The floral longevity and ecological traits for slipper orchids, Paphiopedilum and Cypripedium.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article/Supplementary Material, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding authors.