Abstract
The Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) gp41 membrane proximal external region (MPER) is targeted by broadly neutralizing antibodies (e.g. 2F5, 4E10, Z13e and m66.6), which makes this region a promising target for vaccine design. One strategy to elicit neutralizing antibodies against the MPER epitope is to design peptide immunogens mimicking neutralization structures. To probe 2F5-like neutralizing antibodies, two yeast-displayed antibody libraries from peripheral blood mononuclear cells from a HIV-1 patient were screened against the 2F5 epitope peptide SP62. Two 2F5-like antibodies were identified that specifically recognized SP62. However, these antibodies only weakly neutralized HIV-1 primary isolates. The epitopes recognized by these two 2F5-like antibodies include not only the 2F5 epitope (amino acids (aa) 662–667 in the MPER) but also several other residues (aa 652–655) locating at the N-terminus in SP62. Experimental results suggest that residues of SP62 adjacent to the 2F5 epitope influence the response of broadly neutralizing 2F5-like antibodies in vaccination. Our findings may aid the design of vaccine immunogens and development of therapeutics against HIV-1 infection.
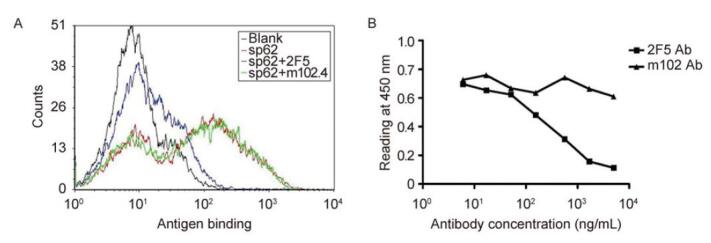
Keywords: HIV-1, membrane proximal external region (MPER), 2F5, neutralizing antibody, yeast display
Footnotes
ORCID: 0000-0002-5969-6407
ORCID: 0000-0003-4308-5799
Contributor Information
Liping Wang, Phone: +86-431-85155348, Email: wanglp@jlu.edu.cn.
Qi Zhao, Phone: +86-755-86585201, Email: zhaoqi@alumni.cuhk.net.
References
- Alam SM, McAdams M, Boren D, Rak M, Scearce RM, Gao F, Camacho ZT, Gewirth D, Kelsoe G, Chen P, Haynes BF. The role of antibody polyspecificity and lipid reactivity in binding of broadly neutralizing anti-HIV-1 envelope human monoclonal antibodies 2F5 and 4E10 to glycoprotein 41 membrane proximal envelope epitopes. J Immunol. 2007;178:4424–4435. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.178.7.4424. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chao G, Lau WL, Hackel BJ, Sazinsky SL, Lippow SM, Wittrup KD. Isolating and engineering human antibodies using yeast surface display. Nat Protoc. 2006;1:755–768. doi: 10.1038/nprot.2006.94. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen WZ, Zhu ZY, Liao HX, Quinnan G, Broder CC, Haynes BF, Dimitrov DS. Cross-Reactive Human IgM-Derived Monoclonal Antibodies that Bind to HIV-1 Envelope Glycoproteins. Viruses. 2010;2:547–565. doi: 10.3390/v2020547. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eroshkin AM, LeBlanc A, Weekes D, Post K, Li Z, Rajput A, Butera ST, Burton DR, Godzik A. bNAber: database of broadly neutralizing HIV antibodies. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014;42:D1133–D1139. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkt1083. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hackel BJ, Kapila A, Wittrup KD. Picomolar affinity fibronectin domains engineered utilizing loop length diversity, recursive mutagenesis, and loop shuffling. J Mol Biol. 2008;381:1238–1252. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2008.06.051. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holl TM, Yang G, Kuraoka M, Verkoczy L, Alam SM, Moody MA, Haynes BF, Kelsoe G. Enhanced antibody responses to an HIV-1 membrane-proximal external region antigen in mice reconstituted with cultured lymphocytes. J Immunol. 2014;192:3269–3279. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1302829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liao HX, Sutherland LL, Xia SM, Brock ME, Scearce RM, Vanleeuwen S, Alam SM, McAdams M, Weaver EA, Camacho Z, Ma BJ, Li Y, Decker JM, Nabel GJ, Montefiori DC, Hahn BH, Korber BT, Gao F, Haynes BF. A group M consensus envelope glycoprotein induces antibodies that neutralize subsets of subtype B and C HIV-1 primary viruses. Virology. 2006;353:268–282. doi: 10.1016/j.virol.2006.04.043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin G, Nara PL. Designing immunogens to elicit broadly neutralizing antibodies to the HIV-1 envelope glycoprotein. Curr HIV Res. 2007;5:514–541. doi: 10.2174/157016207782418489. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehandru S, Wrin T, Galovich J, Stiegler G, Vcelar B, Hurley A, Hogan C, Vasan S, Katinger H, Petropoulos CJ, Markowitz M. Neutralization profiles of newly transmitted human immunodeficiency virus type 1 by monoclonal antibodies 2G12, 2F5, and 4E10. J Virol. 2004;78:14039–14042. doi: 10.1128/JVI.78.24.14039-14042.2004. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montero M, Gulzar N, Klaric KA, Donald JE, Lepik C, Wu S, Tsai S, Julien JP, Hessell AJ, Wang S, Lu S, Burton DR, Pai EF, Degrado WF, Scott JK. Neutralizing epitopes in the membrane-proximal external region of HIV-1 gp41 are influenced by the transmembrane domain and the plasma membrane. J Virol. 2012;86:2930–2941. doi: 10.1128/JVI.06349-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moulard M, Phogat SK, Shu Y, Labrijn AF, Xiao X, Binley JM, Zhang MY, Sidorov IA, Broder CC, Robinson J, Parren PW, Burton DR, Dimitrov DS. Broadly cross-reactive HIV-1- neutralizing human monoclonal Fab selected for binding to gp120-CD4-CCR5 complexes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2002;99:6913–6918. doi: 10.1073/pnas.102562599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phogat S, Wyatt R. Rational modifications of HIV-1 envelope glycoproteins for immunogen design. Curr Pharm Des. 2007;13:213–227. doi: 10.2174/138161207779313632. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prabakaran P, Dimitrov AS, Fouts TR, Dimitrov DS. Structure and function of the HIV envelope glycoprotein as entry mediator, vaccine immunogen, and target for inhibitors. Adv Pharmacol. 2007;55:33–97. doi: 10.1016/S1054-3589(07)55002-7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roben P, Moore JP, Thali M, Sodroski J, Barbas C 3, Burton DR. Recognition properties of a panel of human recombinant Fab fragments to the CD4 binding site of gp120 that show differing abilities to neutralize human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1994;68:4821–4828. doi: 10.1128/jvi.68.8.4821-4828.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shen X, Parks RJ, Montefiori DC, Kirchherr JL, Keele BF, Decker JM, Blattner WA, Gao F, Weinhold KJ, Hicks CB, Greenberg ML, Hahn BH, Shaw GM, Haynes BF, Tomaras GD. In vivo gp41 antibodies targeting the 2F5 monoclonal antibody epitope mediate human immunodeficiency virus type 1 neutralization breadth. J Virol. 2009;83:3617–3625. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02631-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stiegler G, Kunert R, Purtscher M, Wolbank S, Voglauer R, Steindl F, Katinger H. A potent cross-clade neutralizing human monoclonal antibody against a novel epitope on gp41 of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2001;17:1757–1765. doi: 10.1089/08892220152741450. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trkola A, Purtscher M, Muster T, Ballaun C, Buchacher A, Sullivan N, Srinivasan K, Sodroski J, Moore JP, Katinger H. Human monoclonal antibody 2G12 defines a distinctive neutralization epitope on the gp120 glycoprotein of human immunodeficiency virus type 1. J Virol. 1996;70:1100–1108. doi: 10.1128/jvi.70.2.1100-1108.1996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vider-Shalit T, Almani M, Sarid R, Louzoun Y. The HIV hide and seek game: an immunogenomic analysis of the HIV epitope repertoire. AIDS. 2009;23:1311–1318. doi: 10.1097/QAD.0b013e32832c492a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker LM, Bowley DR, Burton DR. Efficient recovery of high-affinity antibodies from a single-chain Fab yeast display library. J Mol Biol. 2009;389:365–375. doi: 10.1016/j.jmb.2009.04.019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeung YA, Wittrup KD. Quantitative screening of yeast surface-displayed polypeptide libraries by magnetic bead capture. Biotechnol Prog. 2002;18:212–220. doi: 10.1021/bp010186l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang MY, Vu BK, Choudhary A, Lu H, Humbert M, Ong H, Alam M, Ruprecht RM, Quinnan G, Jiang S, Montefiori DC, Mascola JR, Broder CC, Haynes BF, Dimitrov DS. Crossreactive human immunodeficiency virus type 1-neutralizing human monoclonal antibody that recognizes a novel conformational epitope on gp41 and lacks reactivity against self-antigens. J Virol. 2008;82:6869–6879. doi: 10.1128/JVI.00033-08. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Q, Ahmed M, Guo H, Cheung IY, Cheung NK. Alteration of electrostatic surface potential enhances affinity and tumor killing properties of anti-GD2 monoclonal antibody hu3F8. J Biol Chem. 2015;290:13017–13027. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M115.650903. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Q, Ahmed M T, Hasan A, Kuo T, Guo H, O’Reilly RJ, Cheung NK. Affinity maturation of T-cell receptorlike antibodies for Wilms tumor 1 peptide greatly enhances therapeutic potential. Leukemia. 2015;29:2238–2247. doi: 10.1038/leu.2015.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Q, Chan YW, Lee SS, Cheung WT. One-step expression and purification of single-chain variable antibody fragment using an improved hexahistidine tag phagemid vector. Protein Expr Purif. 2009;68:190–195. doi: 10.1016/j.pep.2009.08.004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Q, Feng Y, Zhu Z, Dimitrov DS. Human monoclonal antibody fragments binding to insulin-like growth factors I and II with picomolar affinity. Mol Cancer Ther. 2011;10:1677–1685. doi: 10.1158/1535-7163.MCT-11-0281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhao Q, Zhu Z, Dimitrov DS. Yeast display of engineered antibody domains. Methods Mol Biol. 2012;899:73–84. doi: 10.1007/978-1-61779-921-1_5. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Z, Bossart KN, Bishop KA, Crameri G, Dimitrov AS, McEachern JA, Feng Y, Middleton D, Wang LF, Broder CC, Dimitrov DS. Exceptionally potent cross-reactive neutralization of Nipah and Hendra viruses by a human monoclonal antibody. J Infect Dis. 2008;197:846–853. doi: 10.1086/528801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Z, Dimitrov AS, Bossart KN, Crameri G, Bishop KA, Choudhry V, Mungall BA, Feng YR, Choudhary A, Zhang MY, Feng Y, Wang LF, Xiao X, Eaton BT, Broder CC, Dimitrov DS. Potent neutralization of Hendra and Nipah viruses by human monoclonal antibodies. J Virol. 2006;80:891–899. doi: 10.1128/JVI.80.2.891-899.2006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Z, Dimitrov DS. Construction of a large naive human phage-displayed Fab library through one-step cloning. Methods Mol Biol. 2009;525:129–142. doi: 10.1007/978-1-59745-554-1_6. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhu Z, Qin HR, Chen W, Zhao Q, Shen X, Schutte R, Wang Y, Ofek G, Streaker E, Prabakaran P, Fouda GG, Liao HX, Owens J, Louder M, Yang Y, Klaric KA, Moody MA, Mascola JR, Scott JK, Kwong PD, Montefiori D, Haynes BF, Tomaras GD, Dimitrov DS. Cross-reactive HIV-1-neutralizing human monoclonal antibodies identified from a patient with 2F5-like antibodies. J Virol. 2011;85:11401–11408. doi: 10.1128/JVI.05312-11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwick MB, Labrijn AF, Wang M, Spenlehauer C, Saphire EO, Binley JM, Moore JP, Stiegler G, Katinger H, Burton DR, Parren PW. Broadly neutralizing antibodies targeted to the membrane-proximal external region of human immunodeficiency virus type 1 glycoprotein gp41. J Virol. 2001;75:10892–10905. doi: 10.1128/JVI.75.22.10892-10905.2001. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


